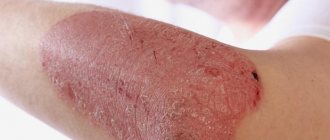
Eczema is a skin disease of an allergic nature, characterized by the presence of an inflammatory process and the ability to frequent relapses.
Mentions of the disease date back to the 2nd century BC. e. Translated from Greek, the term “eczema” means “skin rash” or “boiling.” As a rule, skin lesions affect the surface of the hands, feet or face, but can spread throughout the body.
Both adults and children are at risk of developing the disease. According to statistics, in men and women this disease is diagnosed in approximately 30-35% of cases, and the trend in the spread of the disease is growing every year. Infection in early childhood can quickly lead to death.
Causes of eczema
What are the causes of eczema? Since this skin pathology is idiopathic, the exact cause of its appearance is unclear. But predisposing factors are known. They can be endogenous and exogenous.
Endogenous factors:
- impaired renal function, nephrosis;
- neuroendocrine diseases;
- pathologies of digestion (hepatitis, pancreatitis, flatulence, dysbacteriosis) and evacuation (constipation, diarrhea);
- angiovegetative neurosis;
- heredity.
Exogenous factors:
- allergic reaction to drugs (Benzylpenicillin, Novocaine and others);
- effect on the skin of irritating factors (allergens, chemicals, phenols, alcohols, acids);
- violation of the integrity of the skin and peripheral nerves;
- the effect of high and low temperatures, ultraviolet radiation on the skin.
All these factors lead to increased sensitivity of the epidermis to irritants.
Often, with eczema, pathologies predisposing to it are identified:
- kidney disease;
- pancreatitis, cholecystitis;
- deficiency of polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega-3, omega-6);
- decreased immunity;
- parasitic infestations;
- vitamin B6 deficiency.
Acute eczema occurs seemingly for no reason. But the skin is connected to the internal organs both functionally and metabolically. A huge amount of toxins will enter the body, which are neutralized in the liver and excreted in the feces.
If excretion is impaired and liver pathology is present, the neutralization process is disrupted. Therefore, toxic products begin to come out through the skin. They gradually destroy the epithelium, resulting in eczema on the body.
Dry or asteatotic eczema
Characterized by excessive dryness of the skin and the formation of cracks. The pathological process proceeds very slowly, although seasonality is noted: dry eczema progresses in the winter season, when a person is affected by dry air. When autumn or summer arrives, the symptoms of the disease subside and may even disappear completely.
Causes of dry eczema include:
- prolonged stress;
- helminthic infestation;
- dysfunction of internal organs, in particular the digestive system;
- metabolic disorders;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the body;
- dysfunction of the immune system;
- hereditary (genetic; predisposition
What types of eczema are there?
What is the classification of eczema? Depending on the etiological factor, the following types of eczema are distinguished:
- idiopathic;
- atopic;
- professional;
- microbial;
- dyshidrotic;
- nummular;
- intertriginous;
- seborrheic;
- pruriginous;
- horny;
- varicose;
- mycotic;
- eczema of the nipples and areola;
- children's room
Since the disease occurs sequentially, the following stages of eczema are distinguished:
- Erythematous stage - red, itchy eczema occurs.
- Papulovesicular - rashes and blisters with liquid contents appear.
- Weeping eczema - the opening of blisters, the formation of “serous wells” that secrete fluid.
- Crusty or dry eczema - the appearance of crusts of a yellow-grayish color. At the same time, new eczema may appear on the body, and the process develops from the initial stage, covering more and more areas.
Photo of what eczema on hands looks like
Eczema. Rashes. Photo 1.
Eczema. Redness. Photo 2.
Eczema. Itching and burning. Photo 3.
Eczema. Dryness. Photo 4.
Eczema on hands. Photo 5.
Eczema on hands. Photo 6.
Symptoms of eczema
Acute eczema manifests itself in different ways, depending on its type. But there are also common signs:
- erythema - red skin, the area of which corresponds to the lesion;
- papules - red-pink nodules that rise above the redness;
- vesicles - bubbles filled with serous fluid;
- pustules - blisters with purulent contents;
- erosion - depressions that appear at the site of opened pustules and vesicles;
- crusts in place of eroded surfaces;
- hair loss in areas of erythema;
- exfoliation of crusts, the appearance in their place of pathological skin in the form of patches and dry plates built from the keratinized epithelial layer.
Let's take a closer look at the symptoms of eczema, depending on its type.
Idiopathic
A distinctive feature of this form of the disease is symmetrical eczema on the face, neck and hands. That is, the pathological process is localized in uncovered areas of the skin.
The initial stage of eczema is characterized by small blisters, which over time merge with each other, burst and form point erosions. Later, lichenification (induration, dryness) may form at the site of the lesion.
Atopic
With this type of eczema, the process begins with hyperemia and swelling of the skin, then blisters appear. After their opening, weeping eczema develops. The skin around the lesion peels off, crusts and scales appear. If the disease becomes chronic, patients complain that the eczema itches.
Professional
The process begins with the areas of the skin that were affected by the irritant, gradually spreading to the rest of the skin. The symptoms are similar to idiopathic eczema.
Microbial
Signs of this form of eczema develop due to excessive proliferation of microorganisms around wounds, burns and ulcers. The early stage is characterized by unilateral peeling of scales. Possible accumulation of serous fluid and crust formation. Itching is mild.
Dyshidrotic
The pathology is located on the palmar and plantar surfaces. Characterized by severe itching, burning, slight redness of the skin and dense blisters in its thickness. In case of infection with fungi or bacteria, local lymph nodes become enlarged.
Nummular
This type of eczema is named so because of its resemblance to a coin: the lesion is clearly limited and has the shape of a circle. Vesicles, papules, scales and other elements of the disease form in the area of erythema. Localization may vary. But more often the nummular form is characterized by eczema on the back, chest, and abdomen.
Intertriginous
With intergriginous eczema, lesions form in the area of natural folds: axillary, inguinal, under the mammary glands. The appearance is specific: severe hyperemia and cracks in the area of eczema.
Seborrheic
It forms in areas with sebaceous glands: on the head, face, armpits, and groin. The plaques are small or large, with a yellow tint.
Pruriginous
Typical localization is on the arms and legs, on the inside. Papules and vesicles are small. The rashes itch, but do not break out even when scratched. Lichenification does not occur.
Horny
More typical for women during menopause. Hyperkeratosis, cracks and itching form on the skin of the palms and feet. There are no vesicles or weeping.
Varicose
Develops with varicose veins, ulcers and sclerosis as a result. The process occurs on the lower part of the leg and occurs as a microbial form of the disease.
Mycotic
It forms on the feet and hands and is manifested by severe itching and weeping.
Eczema of the nipples and areola
The causes of this type of disease are injury to the nipple during breastfeeding or scabies. With nipple eczema, hyperemia, cracks, weeping, crusts and scales occur.
Children's
The disease develops at the age of 3-6 months. Manifests itself as a true, seborrheic or microbial form. Lesions on the skin initially appear symmetrically; hyperemia, oozing, crusts, and scales are visualized. The disease spreads from the forehead and cheeks to the head, shoulders, and limbs. Later, eczema forms on the back.
Folk remedies for eczema
Treatment of dry scalp eczema
Wash your hair at least once a week, then rub fine table salt into your scalp. After 20-30 minutes of exposure, rinse your hair with warm water. The course of treatment is 6-7 procedures. To consolidate the positive result, repeat the treatment after thirty days.
Treatment of skin eczema on the legs
Burlap soaked in propolis treats eczema
Ask a beekeeper for canvas soaked in propolis. This burlap is usually placed under the hive cover. Wrap your feet in canvas and go to bed. Repeat the procedure every time before going to bed 4-5 times.
Treatment of eczema in the ear canal
You will need a 30% propolis tincture and a 20% tincture of walnut shell partitions. Mix the tinctures, soak gauze pads in the solution and insert them into your ears. Combine treatment with conservative therapy prescribed by a dermatologist.
Treatment of eczema between fingers
Recipe No. 1
Rub into the skin of the affected areas with a medicinal mixture consisting of natural honey and grease taken in equal parts
Recipe No. 2
Keep your fingers under the steam of boiling milk
Bring a liter of milk to a boil, keep your sore fingers as close to the steam as possible. Just don't scald your hands. Do not wipe off the perspiration that forms on your hands - let the skin dry at room temperature. It is recommended to carry out the procedure before bedtime. You cannot bandage your hands. You will feel relief after 2-3 procedures.
Treatment of allergic eczema
Mix thoroughly 4 s. l. sunflower oil, 2 tsp. l. birch tar, 1 p. l. vinegar essence, 1 tsp. hot sulfur, 1/2 tsp. beeswax and 1 tbsp. natural honey. Apply the ointment in a thin layer until completely cured.
Treatment of weeping eczema
Mix well the beeswax and crushed laundry soap, taken equally (50 g each). Add another 100 g of aloe leaf. Keep the composition in a water bath until a uniform consistency is obtained. Apply a thin layer to problem areas three times a day.
Treatment of dry eczema
Honey and cinnamon treats dry eczema
Twice a day, apply a medicinal mixture of cinnamon and honey, taken in equal parts, to the affected skin. Healing occurs within 10-15 days.
Diagnostics
How to diagnose eczema? The disease is diagnosed based on the presence of the following signs:
- rash of a polymorphic nature;
- itching;
- erythema;
- peeling of the skin and its dryness.
If the diagnosis is questioned, a tissue biopsy is performed and examined. This pathology is characterized by a violation of keratinization, swelling of the papillary and spinous layers of the skin. This picture is observed in the acute form.
In the chronic course, the keratinization process is enhanced, the spinous layer is thickened, and a large number of connective tissue cells and lymphocytes accumulate around the vessels.
Stages
The development cycle of the disease can last 2-3 months. Sometimes the pathology is accompanied by polymorphism of the rash, which manifests itself in the form of symptoms that are characteristic of different stages of the disease. In the classic case, eczema develops in stages, the following stages are distinguished:
- Erythematous stage – itching and redness of the skin.
- Papulovesicular stage - rashes, blisters with liquid form;
- Weeping stage - the bubbles burst, leaving serous wells in their place that secrete fluid;
- Dry or crusty stage - wells and areas next to them are covered with a dry crust of a gray-yellow hue.
Treatment of eczema
To cure eczema forever, you first need to consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease. People often come with an advanced form of the disease, when complications have arisen or the disease has become chronic.
Next, you need to follow a diet. What can you eat if you have eczema? The diet should include plant foods, dairy products, porridge, greens and fruits.
It is necessary to exclude alcohol and coffee, canned food and sausage products, chocolate, fried, smoked, spicy and protein foods. Since constant exposure to the stomach and intestines leads to activation of the trigger mechanisms of the disease. Following such a diet significantly reduces the manifestation of skin eczema.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment for eczema should be prescribed by a doctor, as it is individual and depends on many factors. For therapy use:
- Enterosorbents (Enterosorb, Polysorb, Polyphepan) - bind toxic products in the intestines.
- Hormones - Prednisolone, Corticotropin, Dexamethasone. More often they are prescribed locally. Hormonal treatment is possible only under the supervision of a specialist.
- B vitamins, ascorbic and nicotinic acids, vitamin E, omega-3,6 fatty acids. Vitamin preparations reduce inflammation, accelerate regeneration, and eliminate metabolic disorders.
- Antihistamines are necessary to eliminate any eczema. Chloropyramine, Promethazine, Diphenhydramine, Zodak, Cetrin, Ketotifen are used.
- Immunomodulators - necessary for chronic eczema, in the remission stage. They use Likopid, Polyoxidonium, Timalin, Immunofan.
- To combat dysbiosis and digestive disorders, Pancreatin, Enzistal, Gastenorm, Lactobacterin, Bifiform are prescribed.
Microbial eczema requires special treatment. Before starting treatment, a smear of the contents of the blisters should be made to determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics. Next, the following means are used:
- dyes - brilliant green, methyl violet;
- creams and aerosols: Panthenol, Levovinisol;
- lotions with Resorcinol or Ethacridine lactate;
- lead water;
- Burov's fluid;
- citric acid;
- Diphenhydramine paste;
- Zinc oxide, white clay powder (acute stage);
- Pasta Lessara;
- Naftalan paste;
- hormonal ointments according to indications (Skin-cap, Flucinar, Advantan);
- hormonal ointments with antibiotics and antimycotics in the composition - Travocort, Lorinden S, Kremgen.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures may be prescribed to get rid of eczema:
- aerotherapy;
- ozone therapy;
- reflexology;
- eletroson;
- sunbathing;
- mud baths;
- paraffin applications;
- mineral and radon baths;
- galvanization;
- diadynamic therapy;
- inhalation of Diphenhydramine.
If eczema does not go away for a long time, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause and eliminate it or use other treatment.
Prevention of eczema on hands
To prolong the period of remission and avoid exacerbations, it is recommended:
- follow a diet;
- eliminate stressful situations;
- have a good rest;
- sleep at least 8 hours;
- use gloves when in contact with detergents;
- before going outside, apply creams with ultraviolet filters;
- wear clothes made from natural fabrics;
- do not use cheap cosmetics;
- do not overdry the skin;
- do wet cleaning daily;
- take vitamins;
- promptly treat infectious diseases;
- regularly use non-hormonal ointments and creams.
Find out more: Cream Shampoo Gel
Line of products Losterin
Designed for daily skin care in the complex treatment of chronic skin diseases - psoriasis, eczema, neurodermatitis, atopic dermatitis .
The preparations contain a balanced combination of active ingredients ( resin-free naphthalan, urea, salicylic acid, medicinal herbal extracts, natural oils ) selected for the most effective therapeutic effect on the skin for various skin diseases.
Help from folk recipes - practical advice
Recipes for an unconventional approach to such a problem as treating carpal eczema are often just relieving symptoms, so you shouldn’t rely solely on this method. But it is very useful when eczema on the hands, the causes and treatment of which have already been established, should be cured along with a decrease in the severity of the symptoms. Therefore, traditional medicine will help in the following ways or recipes:
- Hand baths are made with salt or tomatoes and cucumbers in brine.
- Baths for 15 minutes from plant extracts: calendula;
- series;
- coltsfoot;
- chamomile;
- kalanchoe;
- celandine (its fresh juice is very effective).
It should be noted that almost all of these remedies help very much only at the initial stage of the disease. To understand how traditional medicine affects the patient, you can see the condition of the hands in the photo before and after treatment combined with folk remedies.
FOR REFERENCE: Not everyone can tolerate salt baths, because they strongly sting wounds on the skin, so children are usually not allowed to use them. Therefore, baths made from plants will be very good. You just need to check if the child has allergies to a particular plant.
Features and causes of the disease
Acute eczema is characterized by a sudden onset and rapid progression. You should not hope for its complete cure - most often it becomes chronic and can return at any time.
Scientists do not have a consensus on the cause of the disease, so they usually name both external and internal causes.
External reasons include:
- allergens of chemical origin (household chemicals, varnishes, paints, low-quality building materials, pesticides, mineral fertilizers, synthetic fabrics, cosmetics, etc.);
- allergens of a biological or infectious nature (bacteria, viruses, fungi, worms, vaccines, serums);
- allergens of medicinal origin (antibiotics, sulfonamides, vitamins, essential oils, etc.);
- adverse environmental influences (too high or too low temperatures, UV radiation, solar radiation).
Manifestation of an acute form of eczema on various parts of the body
. Internal causes include:
- genetic factor;
- allergic reactivity, when the immune system is always ready to respond in the form of an allergy;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- dysfunction of the nervous system due to stress, mental trauma, etc.);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys;
- metabolic disorders (hypovitaminosis, calcium deficiency in the blood).
The manifestation of acute eczema often resembles dermatitis, so the pressing question is what is the difference between allergic dermatitis and acute eczema?
The difference lies in the cause of development: dermatitis is characterized by an inflammatory process under the influence of external irritants, and the cause of eczema is exposure to allergens.
The peculiarity of this disease is that it can occur suddenly and, if measures are taken promptly, will quickly pass without leaving marks on the skin; however, there is always a danger that it will be accompanied by a microbial or fungal infection, and then the treatment will be delayed for a long time.
Complications and consequences
With proper treatment, eczema on the legs does not leave scars or scars . In the chronic stage, external manifestations of the disease can be severe dryness of the skin, cyanosis and swelling.
Complications that can cause harm to health, as well as be a threat to life, are considered to be fungal, viral and bacterial infections that infect the inflamed area as a result of improper care or scratching.
In this case, purulent weeping formations with an unpleasant odor may appear on the skin surface, deterioration in health, headaches, and an increase in body temperature.
The most dangerous complication that can result from eczema is erythroderma . Requires hospital treatment, can affect large areas of the body and is a generalized process. Another disease that is a likely complication of eczema and requires urgent treatment is Koposi’s eczema herpetiformis.
Features in children
This skin disease often occurs in young children, as well as in infants. Treatment of children over 3 years of age does not differ from the treatment of eczema in adults, but younger children require not only special medications, but also constant supervision by a dermatologist. In infants, eczema can appear as a reaction to complementary feeding, due to care products or due to severe stress. The course of the disease is extremely complex, often accompanied by suppuration and numerous abscesses.
Main article: Eczema in children
Reasons for the formation of pathology
Skin problems on the hands can develop for a number of reasons. However, in most cases, the disease affects people with a tendency to allergies of various kinds. So, the following allergens can trigger the appearance of eczema on the skin of the hands:
- Food products. In particular, excessive consumption of sweets, honey, chocolate, coffee, citrus fruits, red berries, fruits and vegetables, smoked meats or eggs;
- Chemicals of various kinds. Dyes, flavors, volatile components of washing powder and other household chemicals;
- Nickel and other similar alloys. As a rule, they are included in most metal accessories, such as cufflinks, watch bracelets, women's wrist jewelry and costume jewelry;
- Plant and animal components. Such as plant pollen, fluff, feathers, animal hair, etc.;
- Analgesics or vaccines. Especially if uncontrolled intake of the former was noted;
- Rubber components. In particular, contact with rubber gloves, etc.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, treatment of this disease is very difficult, since there are strict restrictions on taking many medications. It is necessary to choose the right medications, in particular ointments and tablets, that are suitable for pregnant women and will not harm the fetus. Since pregnancy directly affects a woman’s hormonal system, eczema often worsens during this period.
The disease does not affect the fetus in any way, but causes considerable discomfort to the mother, so it is necessary to treat eczema efficiently, and most importantly, safely for the fetus. During pregnancy, you can use panthenol-based antipruritic ointments, various lotions and traditional medicine for external use. For very severe exacerbations, zinc paste is often prescribed.
Diet and proper nutrition
Since allergies are one of the factors that provoke acute eczema, it is necessary to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet.
In addition to well-known allergens, such as citrus fruits, chocolate, red fruits and berries (strawberries, apples), eggs, etc., you will have to give up smoked, fatty, sweet, alcohol, coffee, processed foods, whole milk and even tea.
At the same time, a balanced diet is necessary so that the body receives proteins, fats and carbohydrates, as well as vitamins and microelements in the required quantities, which is why doctors often include vitamin-mineral complexes in therapy.
During treatment, the emphasis is on plant foods and fermented milk products. For timely cleansing of the body, the drinking regime is extremely important: you need to drink purified (but not carbonated!) water per day at the rate of 50 ml/kg of body weight.
Nutrition for weeping eczema
A hypoallergenic diet is one of the important components of therapy for skin diseases. By normalizing your diet, you can quickly eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, avoid exacerbations, and prevent complications and chronicity of the pathology.
If signs of weeping eczema appear, it is important to avoid food allergens:
- Strawberries, raspberries, currants and other red berries.
- Citrus and exotic (pineapple, mango, banana) fruits.
- Brightly colored vegetables (tomatoes, bell peppers).
- Sea fish and seafood (shrimp, squid, etc.).
- Eggs, cow's milk.
- Honey, nuts, cocoa, chocolate.
It is important to limit the consumption of fatty, fried foods, smoked foods, pickled foods, spices and sauces. It is recommended to completely exclude sweet carbonated drinks, confectionery, alcohol from the diet, and stop smoking.
The basis of nutrition should be greens, fresh vegetables (cucumbers, cabbage), cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice, wheat), pasta, lean meat (poultry, rabbit, veal). All products should be prepared in a gentle way - boiling, stewing, baking in the oven or steaming.
For sweets, you can eat natural marshmallows, marshmallows, biscuits, crackers without additives, dried bread, baked apples and pears. The list of drinks allowed for weeping eczema includes compote of dried fruits and apples, herbal teas, and rose hip decoction.