The growth and development of the follicle and the subsequent ovulation period of the egg formed in it are the main processes that create the normal functioning of the reproductive systems of the female body. Thanks to them, the body prepares for subsequent conception and gestation. Failure of this mechanism is one of the most common causes of infertility. Only through IVF can the follicle be fully stimulated so that its functions work in natural conditions. To understand the proper functioning of the female body, it is important to know how the follicle grows by day of the cycle.
The condition of the female body greatly depends on the menstrual cycle.
What it is
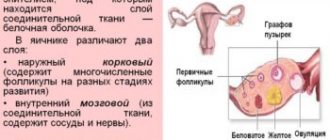
A follicle is a component of the ovaries that is surrounded by tissues of a connective structure and protects the eggs. The component contains the nucleus of the oocyte - a ball for the future embryo. The oocyte is protected by a special membrane made of strong granulosa cells. These cells are surrounded by a thin, cell-free membrane.
The germ cells intended for conception are in the body of any girl even before the moment of her birth, that is, follicles are formed in intrauterine conditions. Their initial number is around 10 thousand, but initially they are not able to perform the function of fertilization, because they still have to go through the processes of division and development. To protect the egg during its formation, the body creates a special layer of epidermis around the egg.
Bottom line
Summarizing all of the above, let's summarize:
- A follicle is a vesicle in which the egg develops and protects it from external factors that may, to one degree or another, interfere with its full development.
- How long does a follicle grow? The beginning of the development of this cell coincides with the first day of the menstrual cycle. That is, the first day of menstruation starts a new cycle and then the development of a group of rudimentary cells begins, one of which subsequently becomes dominant. The growth of follicular tissue continues until ovulation, during which it ruptures and releases an egg ready for fertilization. That is, the duration of the ripening phase is 14-16 days.
- There are standard indicators for the size of a developing DF, deviations from which are most often associated with the development of pathologies of various etiologies.
Have you ever wondered what specific features characterize the development of follicles? Perhaps you or someone you know has already undergone folliculometry? Share interesting facts and personal experiences with us and our readers by leaving your comments at the end of the publication.
https://youtu.be/tWdlaDquM2A
Quantity
You can find out the exact amount in the appendages using ultrasound and a vaginal sensor. So the doctor determines not only the quantity, but also their growth. Their degree of reproduction will allow us to understand the readiness of the egg for fertilization.
Sometimes it is important to know how many follicles are in the ovary
The number is described as follows:
- 16-30 - optimal condition.
- 7-16 is a low amount.
- 4-6 - 50/50 chance of conception.
- less than 4 - the probability of infertility is 90%.
At the time of ultrasound, 4 to 5 units are most often detected. Less commonly, 2-3 follicles are visualized.
In preparation for IVF, a woman must independently stimulate maturation by taking hormonal medications. Therefore, during the examination, 4-6 mature objects may be identified. The mature follicle is determined by day and size; if there is a deviation, then in vitro fertilization is performed.
How to find out about a folliculogenesis disorder?
To see how the process of follicle formation occurs and to assess the likelihood of ovulation, ultrasound monitoring is performed, and folliculometry is done three times during one cycle.
Ultrasound of the ovaries depending on the duration of the menstrual cycle:
- standard, regular cycle of 28 days - examination is carried out on days 10, 15, 20 after the start of ovulation;
- regular long or short cycle - 14, 10, 5 days before the start of menstruation;
- irregular cycle - 5 days after the end of menstruation; based on the results, the doctor draws up an individual plan for further examinations.
During an ultrasound, the specialist determines the presence of a dominant follicular element, its size, assesses the condition and thickness of the endometrium, the degree of wear of the ovaries, and the amount of follicular fluid.
Signs of completion of the ovulation process on ultrasound are the presence of a mature follicle, the gradual destruction of its walls, a decrease in size, and the formation of the corpus luteum.
Important!
Smoking, alcohol abuse, working in hazardous industries, frequent irradiation of the pelvic organs, chronic gynecological inflammatory processes - all these factors accelerate the aging process of the ovaries, leading to a decrease or complete attenuation of reproductive functions.
Main types of folliculogenesis disorders
Various deviations in the development of follicular elements lead to the development of a chronic anovulatory cycle; disturbances in folliculogenesis negatively affect the physical and psycho-emotional state of a woman.
Persistence is a condition when an egg is not formed
Types of violations:
- regression - the growth of the dominant follicle abruptly stops, it is destroyed, does not rupture, ovulation does not occur;
- persistence – due to untimely opening of the follicular element, the egg is not formed;
- cyst - formed due to the accumulation of follicular fluid due to untimely opening of the follicle in the ovaries, the neoplasm is benign, sometimes resolves on its own;
- polycystic disease - a significant excess in the number of follicular compounds along the periphery, which prevents the maturation of the dominant follicle, the onset of ovulation is impossible;
- luteinization - the corpus luteum is formed, but the follicle does not burst; pathology occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance, abnormal structure of the ovaries.
Single follicles cannot fully develop to the required size; pathology occurs against the background of starvation diets, excessive physical activity, menopause, hormonal imbalance, and obesity.
Even with normal growth of follicular elements, ovulation does not always occur; such a pathology normally occurs in women of fertile age no more than 1-2 times a year.
What processes occur inside the cavity
Follicles are laid in the girl’s genitals in utero. Their basis is oogonia - the initial germ cells that migrate into the ovary of the embryo sac at the 6th week of gestation.
Follicles are formed during the maturation of the fetus in the womb
After the transfer of genetic material to the child and the proliferation of connective tissue, the first row of oocytes are formed. These defective and immature germ cells become covered with epithelial tissue and create the so-called resting follicles. They will continue to exist in a dormant state until the girl reaches puberty.
The development of this component of the egg ends with ovulation. In this case, an endocrine yellow organ is formed in place of the follicle.
Menstrual cycle
Early phase
At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, the ovary contains 5-8 follicles less than 10 mm in size. During the process of maturation, one of them (in rare cases two) becomes dominant, reaching a size of 14 mm. On the 10th day of the cycle, it begins to distance itself and increase daily by about 2 mm until it ruptures. The remaining follicles begin to undergo a slow process of involution (atresia), their small fragments can be seen on ultrasound throughout the menstrual cycle.
Follicle maturation time
The blood supply to the ovaries increases significantly during the onset of ovulation under the influence of pituitary hormones - gonadotropins FSH and LH. The formation of new blood vessels leads to the appearance of a follicle shell called theca, which gradually begins to surround it from the outside and inside.
Ovulation period
Two criteria that allow you to determine the maturity of the follicle and impending ovulation using ultrasound examination:
- The size of the dominant follicle should be between 20 and 25 mm
; - the cortical plate of the follicle, under the influence of an increase in internal fluid, slightly deforms one of the walls of the shell.
As ovulation occurs, the follicle stretches in size, protrudes slightly above the surface of the ovary and bursts - ovulation occurs.
Luteal phase
After ovulation, the walls of the empty follicle thicken, and its cavity is filled with blood clots - a red body is formed. If fertilization is unsuccessful, it quickly becomes overgrown with connective tissue and turns into a white body, which disappears after some time. In case of successful fertilization, the red body, under the influence of chorionic hormone, increases slightly in size and turns into the corpus luteum, which begins to produce a hormone called progesterone. It increases endometrial growth and prevents the release of new eggs and the onset of menstruation. The corpus luteum disappears at the 16th week of pregnancy.
What size is normal?
With each menstruation, follicles grow according to the days of the menstrual cycle. Until day 7, their volume reaches 2-6 millimeters. Starting from day 8, there is a vigorous increase in the dominant. Its size varies around 15 mm. The remaining objects gradually lose mass and die. On days 11-14, an increase in the number of follicles is detected. The size of a mature sexual cell often reaches 2.5 cm.
Sizes for different periods of menstruation are shown in the table.
| Cycle day | In millimeters |
| 4-5 | Until 6 |
| 6-7 | Up to 8 |
| At 8 | Up to 9 |
| At 9 | 11-12 |
| 10 | 13,5-14 |
| 11 | 15 |
| 12-13 | 18-19 |
| 14 | 20,5-24 |
| 15 | 22-24 |
Norms of folliculogenesis
Folliculometry is carried out on certain days of the cycle, corresponding to the key stages of folliculogenesis. The data obtained during repeated studies are compared with the average statistical norms. What size follicle should be on different days of the ovarian-menstrual cycle? What fluctuations are considered acceptable?
Normal follicle size on different days of the cycle for a woman aged 30 years with a 28-day cycle, not taking oral contraceptives and not undergoing treatment with hormonal stimulation of ovulation:
- On days 1-4 of the cycle, several antral follicles are detected, each of which does not exceed 4 mm in diameter. They can be located in one or both ovaries. Their number depends on the woman’s age and her available ovarian reserve. It is normal if no more than 9 antral follicles mature simultaneously in both ovaries.
- On the 5th day of the cycle, the antral follicles reach a size of 5-6 mm. Their development is quite uniform, but already at this stage atresia of some vesicles is possible.
- On day 7, the dominant follicle is determined; its size is on average 9-10 mm. It is he who begins to actively develop. The remaining bubbles will gradually be reduced, and they can be detected in the ovaries during ovulation.
- On the 8th day of the cycle, the size of the dominant follicle reaches 12 mm.
- On day 9, the vesicle grows to 14 mm. The follicular cavity is clearly identified in it.
- Day 10 – size reaches 16 mm. The remaining bubbles continue to decrease.
- On day 11, the follicle increases to 18 mm.
- Day 12 – the size continues to increase due to the follicular cavity and reaches 20 mm.
- Day 13 – Graafian vesicle with a diameter of 22 mm (this is the minimum follicle size for ovulation in the natural cycle). At one pole of it, stigma is visible.
- Day 14 – ovulation. Typically, a follicle that reaches 24 mm in diameter bursts.
Deviations from these standard indicators in a downward direction are prognostically unfavorable. But when assessing the results of folliculometry, the duration of a woman’s natural cycle should be taken into account. Sometimes early ovulation occurs. In this case, the follicle reaches the required size on days 8-12 of the cycle.
Follicle size during IVF
With IVF protocols, ovulation is drug-induced and pre-planned.
What are the sizes at ovulation?
The dominant component of the embryonic egg reaches its maximum size before breaking through. In medical practice, a diameter of 18 to 24 millimeters is considered a normal value. With such volumes, the bladder is filled with blood fluid and water from the body.
Maximum size reached at ovulation
If the object in question remains in the minimum volume and does not reach the maximum, then effective ovulation is practically impossible. In this case, the follicle simply becomes depleted and comes out with menstruation.
Unfortunately, even achieving optimal dimensions does not guarantee rupture of the protective film.
How does fertilization occur?
Almost 12 mm is the size of the dominant follicular element on the 8th day of the cycle. The diameter of this vesicle increases to 24 mm on day 12.
This follicle gradually fills with fluid and then bursts in the second week of the menstrual cycle.
The size of this bubble may vary on day 12. When this sac ruptures, follicular fluid enters the peritoneal area.
The ovulation process lasts approximately 2 days. It does not occur if the follicular vesicles do not burst.
When conception occurs, the embryo will appear in the uterine cavity after 10 days.
Fact! If fertilization of a mature egg does not occur, it dies within a day.
Experts have noticed that if ovulation occurs in the right ovary, there is a high probability that a girl will be born.
The concept of folliculometry
To determine the quality of functioning of the female reproductive system and identify discrepancies with the norm, doctors resort to a variety of diagnostic methods. One of the popular and important methods is folliculometry. The procedure is one of the most effective among others, as it helps to find critical defects and increase the chances of a full conception.
The procedure is a safe ultrasound examination to determine the level of follicle growth. The process is carried out at the time of the menstrual cycle, which guarantees a detailed diagnosis and identification of the characteristics of female reproduction.
If it is necessary to calculate the time favorable for fertilization, then it is advisable to begin the examination a week before expected ovulation in order to determine the degree of follicles and find the dominant.
Folliculometry is a way to determine follicle size and ovulation
It is not possible to determine the size yourself. For such purposes, there is a special procedure called folliculometry. This is an ultrasound examination, during which it is possible to determine the size, number and growth dynamics of embryonic cells.
https://youtu.be/4zMy1XFKNnE
Folliculometry is indicated for women who have problems with natural conception and menstrual irregularities. Also during the examination you can determine:
- exact date of ovulation;
- improper functioning of the appendages;
- the effectiveness of the therapy.
Folliculometry makes it possible to identify the presence of pathological diseases:
- follicular cyst - a neoplasm in the appendage, which is an egg that did not come out after the rupture of the epidermal cocoon into the fallopian tube;
- atresia – pathological underdevelopment of the DF;
- persistence – the presence of a virus in the tissues of the appendage, which prevents the full development of the egg;
- luteinization is a violation of the development of the “vesicle”, when the corpus luteum begins to develop into still immature cells.
The specificity of folliculometry is as follows:
- During the first procedure, the doctor identifies the antral follicles, one of which will subsequently become dominant.
- After 3 days, another ultrasound is performed, during which the presence or absence of DF is determined.
- And during the third procedure, the doctor determines the maximum value of DF, which indicates the approach of ovulation.
How does the size change and what does it mean?
The size of follicular units varies depending on the time of development. Only minimal deviations from the norm are allowed.
After watching this video, you will learn about the periods of follicle maturation:
The table shows the characteristics of the days.
| Moment of cycle in days | Diameter in mm | Characteristic |
| 1-4 | 4 | 9 preovular units are formed. The eggs fill with liquid. |
| 5-6 | 5-6 | Release of weak molecules. |
| 6-7 | 9-10 | Development of a dominant. |
| 8 | 12 | Growth continues. |
| 9 | 14 | A cavity is formed. |
| 10 | 16 | Further reduction of “dead” bubbles. |
| 11 | 18 | Bubbles continue to form. |
| 12 | 20 | Enlargement of the cavity. |
| 13 | 22 | The minimum volume for the onset of ovulation. |
| 14 | 24 | The cavity is opened, and the optimal time for fertilization occurs. |
In the therapeutic treatment of female infertility using in vitro fertilization, ovarian stimulation is performed. Specialists perform an injection with human chorionic gonadotropin, then remove the mature germ cells with a needle. The mature components must reach 18–22 mm in order to be able to perform the IVF procedure.
Phases of folliculogenesis
Under the ovarian membrane there are immature, primary, secondary and tertiary follicles - they contain the egg and are necessary for the normal functioning of the endocrine and reproductive systems.
The maturation of follicles in women of fertile age is a continuous process that ends after menopause; during development, the cell goes through several stages.
Primordial stage
The zero stage occurs during pregnancy, the germ cell embryos migrate to the developing ovaries approximately in the middle of 2 months. Before birth, the number of small primordial follicular units reaches 1.5 million; until the onset of puberty they remain dormant.
Initial stage during pregnancy
The size of the follicular elements at this stage is 50 microns, even with the help of ultrasound it is difficult to see them.
Primary (preantral) stage
The transformation of primordial follicular connections into preantral ones occurs, their number decreases to 300 thousand, their size increases to 200 microns, the process starts simultaneously with the onset of puberty.
A shell of 4 types of complex compounds is formed on the surface of the follicular element, an outer film appears, and at the same time there are 10–15 bubbles in this steel.
The reserve determines the duration of reproductive age
Ovarian reserve - the total number of follicular elements capable of further growth, determines the duration of a woman’s reproductive age.
Secondary (antral) stage
There is a sharp growth of follicles, the size reaches 500 microns, the level of estrogen increases, the number of epithelial cells increases, follicular fluid is formed
A cavity with hormonally active cells is formed inside the follicular element, and a shell of epithelium is formed inside the outside of the vesicle.
There is growth of follicles
Usually several antral vesicles are formed, but 1–2 follicles move to the next stage of development.
Tertiary (preovulatory) phase, formation of the Graafian vesicle
The size of the follicular element is 20 mm, the amount of fluid increases, the epithelium and egg shift to the peripheral area, the outer wall of the ovary protrudes, and an ovarian mound is formed.
About 48 hours before ovulation, estrogen levels increase sharply, luteinizing hormone is released, and the process of releasing a mature egg begins.
After the end of the preovulatory stage, the mature follicle ruptures, the egg is released into the uterine cavity, and when connected with sperm, conception can occur. To calculate the time of ovulation, you need to subtract 14 from the number of days in the menstrual cycle, provided that your periods are regular.
The follicle size reaches 2 centimeters
If ovulation does not occur, a cystic follicular formation is formed from the Graafian vesicle - it can come out along with menstrual blood, or remain in the ovary and form into a cyst.
Important!
Violation of folliculogenesis is one of the causes of female infertility; there are no eggs in the body that are ready for fertilization.
Why might it not reach the norm?
In clinical practice, this happens very often: the follicle either exceeds normal size or lags behind. Such conditions require clarification of the causes, since it is almost impossible to conceive or become pregnant with folliculogenesis disorders. In addition, this makes the body vulnerable to inflammatory processes and the growth of pathological tumors.
If the “Graafian bubble” does not reach 18 mm before rupture, then one can suspect:
- Ovarian dysfunction of hormonal origin.
- Early menopause.
- Disorders of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- STI.
- Pelvic diseases (adnexitis, endometriosis, cervicitis).
- Postoperative conditions.
- Stress.
- Malnutrition, strict diets.
In the case of an enlargement of the dominant follicle, the gynecological picture is clearer, since this means the growth of a follicular cyst, which blocks ovulation and the release of the egg. Conception in this case is impossible.
Persistent follicle
As expected, the small bubble develops and grows. It is ready to burst, having reached the required size for a mature egg to be released.
But rupture does not occur if there is an external or internal malfunction, a disruption of the ovarian follicular apparatus.
Such causes of infertility are very common. The egg does not leave the follicle. As a result of such deviations from the norm, ovulation does not occur, and a cyst forms on the ovary.
This growth may grow larger over time.
Failure of the menstrual cycle, pain during menstruation, these are clinical symptoms of the appearance of such a cyst, which can be detected by ultrasound.
Since the follicular elements do not grow, the woman is at risk of infertility if she does not begin the necessary treatment in time.
Important! Pregnancy will not occur, since the follicle does not burst, the mature female cell does not have the opportunity to meet the sperm. A lot of other complications arise.
What changes occur to the follicle during the menstrual cycle?
The egg matures in the ovary inside the follicle. There, all the necessary conditions are created for her: favorable temperature conditions, chemical environment, supply of oxygen, nutrients and hormones.
Thus, the development of the egg can be judged by the increase in the size of the follicle itself.
The menstrual cycle, which begins on the first day of menstruation, is divided into two main periods. In the first half, that is, for about 14 days, folliculogenesis occurs.
Moreover, several follicles can develop at once, but one of them over time outstrips the others in growth and becomes dominant.
It is he who contains the egg, which, at the end of its maturation, leaves its membranes and enters the fallopian tube, from where it will move towards the uterus.
The moment the female reproductive cell leaves the follicle is called ovulation. After this, the egg has the ability to fertilize for some time.
If there was no sexual intercourse and she did not meet the sperm, the female cell dies and is removed from the genital tract along with bloody discharge and the uterine mucosa during the next menstruation.
Normally, during ovulation, only one dominant follicle develops, but sometimes there are two. If for some reason the development of two sex cells starts, a woman has a chance of becoming the mother of fraternal twins.
Interesting! How to get pregnant quickly if you can't?
What parameters do the ovaries and follicles have before ovulation?
As the follicle matures and the corpus luteum grows and fades, the size of the ovaries periodically changes. Within normal limits:
- volume 4-10 cm3;
- length 20-37 mm;
- width 18-37 mm;
- thickness 16-22 mm.
The main influence on ovarian parameters before ovulation is the growth of follicles. At the beginning of each cycle, 7-8 follicles begin to increase, then a dominant one stands out among them (less often - two). It continues to grow, and the rest return to their original state. The approximate size of the dominant follicle at the early stage (5-7 days of the cycle) is 6 mm.
Folliculometry - growth of the dominant follicle on ultrasound
Why do follicular vesicles not mature in pathology?
Women of all ages face the problem of infertility. This is female infertility.
Its common causes are disturbances in the maturation of follicular elements in the female body.
The follicular apparatus is depleted, there are no follicles in the body if the paired sex glands are depleted.
This means that the woman’s follicular reserve has dried up and exhausted ovarian syndrome has occurred.
A manifestation of this pathology is the appearance of single follicles in the ovary. It is necessary to check the condition of the endometrium to assess the functioning of these female organs.
In case of ovarian pathology, treatment is prescribed by a gynecologist. The follicles do not mature, a woman is not able to become pregnant with this pathology, since mature germ cells are not formed.
Maturation of follicular vesicles is a prerequisite for the formation of a full-fledged egg.
Reference! It is rarely possible to identify the exact cause with 100% accuracy if the follicular apparatus is not expressed.
The functional balance of the reproductive system can cause a disruption in the hormonal system. Low levels of progesterone and lutein have a negative impact.
Early menopause or dysfunction of the reproductive organs explains the absence of follicles in both ovaries.
The pathological condition of the endometrium disrupts the process of folliculogenesis.