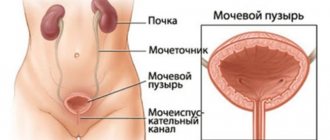
Photo: CITAlliance/depositphotos.com Emergency or post-coital contraception is intended to prevent pregnancy as a result of unprotected intercourse and includes various methods and drugs. Its essence comes down to preventing the fertilized egg from attaching to the wall of the uterus and starting to develop. The effectiveness of this method directly depends on the time of taking the drug - the earlier the drug is used after sex, the higher its effectiveness.
When is emergency contraception needed?
If emergency contraception is taken within 24 hours of sexual intercourse, it is about 95% effective. If the tablet was taken after 25–48 hours, the effectiveness is reduced by 10%. If the product was used after 49–72 hours, the result is 55–60%.
This method can be used very rarely. Under no circumstances should it be used as permanent protection against unwanted pregnancy.
If a woman is breastfeeding, emergency contraception can be used in exceptional cases. To do this, you need to stop breastfeeding for one day until the drug taken is completely eliminated from the body. The use of emergency contraception is justified after physical violence and in cases where pregnancy may threaten the woman's health.
Types of drugs
These products differ in composition and method of application.
Combined oral contraceptives
Taken no later than three days after sexual intercourse. Drugs based on ethinyl estradiol (Marvelon, Miniziston, Microgynon, Femoden, Rigevidon) are usually taken several times. Products based on ethinyl estradiol (Non-ovlon, Bisekurin, Ovulen, Ovidon, Anovlar) should also be taken several times with an interval of 12 hours between doses.
Progestin-only oral contraceptives
The drugs are taken no later than two days after sexual intercourse. Nowadays it is not difficult to purchase escapelle and postinor at the pharmacy. Both medications contain a large dose of the hormone levonorgestrel. The drugs differ in the number of tablets: in escapelle there is one, and in postinor there are two.
Mifepristone
Mifepristone is not hormonal. Its action is aimed at suppressing the female hormone at the level of receptors in the uterus and increasing contraction of its muscles.
Mifepristone is an effective means of emergency contraception. It blocks the egg so that it cannot enter the uterine lining and also stimulates its rejection. It is used to terminate an unwanted pregnancy in the early stages. Mifepristone should only be used after consulting a doctor.
Intrauterine devices
T-shaped copper-containing intrauterine devices are inserted no later than five days after sexual intercourse in the gynecologist's office. If a woman is prescribed an intrauterine device as emergency contraception, then her individual characteristics and contraindications to the use of this method must be taken into account.
Such products are not recommended for women with infectious gynecological diseases and those who are at risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases.
Non-hormonal emergency contraceptives
Many women cannot decide to take a hormonal drug for fear of gaining excess weight or having an adverse reaction. An alternative is tablets that do not contain hormonal components. Gynecologists do not consider non-hormonal drugs against unwanted pregnancy to be effective enough, so they recommend taking additional protective measures.
These contraceptives are used by women over 40 years of age. Drugs in this group are easy to use, safe and inexpensive. Non-hormonal tablets include drugs based on mifepristone.
They have a number of advantages:
- reducing the risk of developing female diseases;
- no side effects other than allergies (rare);
- no age contraindications;
- additional moisturizing effect;
- ease of reception.
Preparations without hormones are not recommended for active sexual women. Non-hormonal EC can be intravaginal; they have a destructive effect on male reproductive cells.
They are made in the form of suppositories or tablets, which dissolve after insertion into the vagina. The effectiveness of non-hormonal drugs is observed during the first three days after sexual intercourse. Later, the effectiveness decreases and disappears completely.
The effect of emergency contraception on the body
Doctors do not advise using this type of contraception all the time, as it has a bad effect on a woman’s reproductive system. In the future, this can lead to dysfunction of the ovaries.
With the constant use of purely progestin or combined contraceptives, the woman’s body receives small doses of the drug, designed for the entire menstrual cycle. Taking a hormonal drug does not disrupt the duration of the cycle, its normal cyclicity, and ovarian function becomes better. Hormonal problems, if any, are also eliminated.
If a woman takes the same drug for emergency contraception, then the body receives a dose of the hormonal drug that is many times higher. As a result of constant use of such contraception, the menstrual cycle will become anovulatory (without the formation of an egg), which threatens infertility.
Violation of normal ovarian function leads to the development of metabolic disorder syndrome. It is expressed in increased blood sugar, increased blood pressure, and the appearance of excess weight.
As for douching with various solutions, this method does not have the desired effect, since sperm penetrate into the cervix within 1 minute after intercourse. In addition, too frequent douching can lead to vaginal dryness and disruption of microflora.
Cons and side effects
Emergency contraception is completely useless while the egg is implanting in the uterus. The effectiveness of combined oral contraceptives can be observed only if the drug is used no later than 72 hours after sexual intercourse.
The first dose of progestin-only oral contraceptives should be taken no later than 48 hours after sex. Intrauterine contraception will be effective if these drugs were introduced into the uterus within 5 days after the act. Mifepristone should only be taken in a clinic setting under the supervision of a physician. Another disadvantage of Mifepristone is its high price.
Emergency contraception should be used only in exceptional cases, if there is simply no other option. It is advisable that it be used no more than three times a year. The less often the better.
The most common side effect of such methods is uterine bleeding, which occurs 2-3 days after administration. And some women, on the contrary, experience delays in menstruation with severe disruption of the menstrual cycle.
Other side effects such as dizziness, headaches, vomiting and diarrhea, and various allergic reactions are uncommon.
You may experience chest pain, rashes on your arms, legs, feet, and shoulders, blurred vision, difficulty breathing, and vomiting 2 hours after taking the tablet. This indicates an incorrect dose of the hormone.
When using Mifepristone, discomfort in the lower abdomen, vomiting, nausea, weakness, dizziness often occurs, and body temperature rises noticeably.
When using intrauterine contraceptives, during the first few days you may experience severe cramping pain in the lower abdomen and an increase in the amount of discharge during menstruation. In addition, there is a high risk of ectopic pregnancy due to disruption of the contraction of the fallopian tubes and the movement of the egg through them. Less commonly, spontaneous prolapse of the intrauterine device and damage to the uterus during its insertion may occur.
Contraindications for emergency contraception:
- intolerance to the components of the drug;
- previous hepatitis;
- diseases of the biliary tract or liver in severe form;
- puberty;
- the onset of pregnancy.
Advice from gynecologists
- The time for taking the dose of the drug should be chosen so that it is convenient to take the next one (for example, 21:00 and 9:00).
- To avoid unpleasant sensations (vomiting, nausea), it is best to take emergency contraceptive pills with low-fat milk.
- In the period before the start of the next menstruation, you need to use additional means of protection (barrier method).
- Emergency contraception is suitable for one-time use. For permanent protection, you need to choose a different method of contraception with your doctor.
- In cases of menstruation occurring a week or more late, you should consult a gynecologist to rule out pregnancy.
Emergency contraceptives during lactation
Breastfeeding is a natural barrier to pregnancy. However, this protective method does not always work. When choosing a contraceptive method, a nursing mother should study the nature of its effect on the child.
For women during lactation, 2 types of EC are used:
- contraceptive IUD;
- hormonal pills.
For protection, an IUD must be installed within 5 days after unprotected sex. In this case, feeding can continue. If a nursing mother decides to take hormonal contraception, breastfeeding is suspended for 36 hours.
This is interesting: Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity: preparation and features of the study
To prevent milk from disappearing during this time, it must be expressed. The baby should be fed with age-appropriate milk formulas. The doctor will advise those medications that are allowed to be taken while breastfeeding the baby. The most suitable drug is Escapelle - tablets based on levonorgestrel. This drug is taken once.
Popular means
Among the most well-known drugs for emergency contraception, the leading places are occupied by postinor and escapelle.
Postinor
Postinor is a popular drug that helps prevent unwanted conception. If this remedy is taken correctly, it is usually possible to avoid unwanted conception. The tablets contain a synthetically created analogue of the hormone levonorgestrel.
This hormone is also included in medications intended for routine contraception. However, its content in Postinor is significantly higher than in planned oral contraceptives.
Postinor should be taken at intervals of 12 hours. The package contains two tablets, one of which is drunk after sexual intercourse, and the second - after 12 hours. This drug can prevent unwanted conception within three days (72 hours). Sometimes two doses are required. This may happen if vomiting occurs after taking at least one of the tablets and the drug is not absorbed. It is advisable to take these tablets after meals. This will reduce the risk of vomiting.
Postinor does not terminate an existing pregnancy; it can only prevent its development. This means that using the drug for abortion will not work. The advantage of postinor is that it does not harm the fetus, and the child can be saved.
Postinor does not prevent sexually transmitted diseases. If you have been physically assaulted or had unprotected sex with an untrusted person, consult a doctor immediately.
The drug, like other emergency contraceptives, may increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. An ultrasound will show the location of the fetus if in doubt.
Escapelle
Unlike postinor, one capsule of escapelle contains 150 mg of the hormone levonorgestrel. Therefore, there is only one tablet in the package. The remedy is most effective if taken on the first day after unprotected sex. The drug may cause nausea and even vomiting. If vomiting occurs earlier than three hours after administration, then you need to re-use the escapelle.
The drug can provoke disruptions in the menstrual cycle, promote the appearance of bloody discharge from the vagina, cause a delay in menstruation, as well as chest pain. If your period is more than five days late, it is recommended to take a test to determine whether you are pregnant.
How do the pills work?
As mentioned above, there are 2 types of emergency contraceptive pills, both of which are hormonal-containing drugs:
- a group of drugs that include levonorgestrel (progestogen)
- tablets containing mifepristone (antigestagen)
Levonorgestrel
The mechanism of action of pills whose active substance is levonorgestrel (the names of birth control pills after the act are Postinor, Escapelle, Eskinor F) consists of three points:
- Delayed or blocked ovulation. By acting on the ovaries, levonorgestrel prevents the release of the egg from the main follicle (when taking the drug on the eve of ovulation), since it suppresses the influence of gonadotropic hormones (FSH and LH).
- The composition of cervical mucus changes. Among other things, levonorgestrel increases the viscosity of cervical mucus. It becomes thick and slows down the process of sperm penetration into the uterus.
- Inadmissibility of implantation of a fertilized egg. There are 2 mechanisms that prevent the egg from implanting into the uterine mucosa. The first is that the structure of the endometrium changes, since levonorgestrel causes a reverse development of proliferative processes in the endometrium, which eliminates the possibility of its transition to the secretory phase, which is so necessary for full ovulation. Thus, Postinor and other drugs containing levonorgestrel have a mild abortifacient effect. In addition, levonorgestrel affects the peristalsis of the fallopian tubes, their contractions decrease, which disrupts the delivery (in time) of the fertilized egg to the uterine cavity for implantation.
1 tablet of Postinor contains a huge dose of the hormone, after taking which a serious hormonal imbalance occurs in a woman’s body. WHO does not recommend the use of such contraceptives at all; the instructions for the drug indicate that even a healthy woman should not take it more than 4 times a year and no more than 1 time per menstrual cycle. However, some women (unknowingly) use levonorgestrel uncontrollably, sometimes even several times per cycle - which is unacceptable and very dangerous.
When taking Postinor, ovarian function is impaired, and even with a one-time dose of the drug, the body needs a certain time to restore their function, and in each case this is individual (see in detail about the harm and side effects of Postinor).
|
|
|
Mifepristone
The effect of drugs from the second group of emergency contraceptive pills (containing mifepristone - Zhenale, Mifegin, Pencrofton, Miropriston) approximately corresponds to that of pills containing levonorgestrel:
- inhibition of ovulation;
- structural changes in the endometrium (mifepristone, the active component of drugs in this group, has antigestagenic activity, it blocks receptors in the uterine mucosa that respond to progesterone, the pregnancy hormone, as a result the endometrium does not undergo changes necessary for implantation);
- increased contractile activity of the uterus, which promotes the expulsion of a fertilized egg that has not attached to the uterine mucosa from its cavity.
|
|
|