Bacteriological examination of vaginal discharge for microflora is an analysis that evaluates the composition of vaginal microorganisms and their ratio. It identifies pathogenic bacteria and is necessary for diagnosing gynecological diseases.
The vaginal microflora in healthy women consists of 95% lactobacilli. Normally, E. coli in the smear should be absent or detected in a minimal amount. By multiplying in the vagina, E. coli disrupts the normal balance of microflora and leads to the development of inflammation. Escherichia coli is often the cause of bacterial vaginosis, colpitis, cervicitis, adnexitis, and endometritis. The infection can subsequently spread to the cervix, ovaries, penetrate the urethra and cause cystitis, affecting not only the bladder, but also the kidneys.
Penetration of E. coli into the vagina occurs in 2 main ways: oral-fecal or genital contact through the anus. Modern medicine knows cases of E. coli penetration through the blood. In children, the bacterium is even found in the lungs. When the entire body is infected, sepsis can occur.
Among the main reasons for the appearance of E. coli in a smear are the following: non-compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene, wearing synthetic, uncomfortable underwear, improper washing procedure, anal-vaginal sexual intercourse.
How to get rid of E. coli
If a significant amount of E. coli is detected in a smear, treatment should be started immediately. It is performed on an outpatient basis by a gynecologist. Antimicrobial therapy is started after determining the sensitivity of the isolated microorganism to antibiotics. This procedure is of fundamental importance because E. coli is resistant to some drugs. The course of antibiotics is on average 7 days.
After antibiotic therapy, they proceed to restoring the normal microflora of the vagina. For this purpose, probiotics and antifungals are used. Immunomodulators will help increase local protection of the vaginal mucosa.
Prevention of infection with E. coli consists of observing the following rules: daily washing from front to back to prevent bacteria from entering the rectum into the vagina, protection during sex, using only cotton, non-pressure underwear.
Normally, E. coli may be present in a smear in women in small quantities.
High values in the analysis results usually indicate the presence of diseases that require treatment. The symptoms of these pathologies and methods of their treatment are discussed in the article.
Escherichia coli, or Escherichia coli, is an opportunistic bacterium whose life activity is possible only in an environment without oxygen. The microorganism lives in the large intestine, in the area closer to the anus.
The bacterium has many subspecies (strains). Many of them are present in the human intestines and do not pose a threat to human health.
On the contrary, these strains are involved in the synthesis of vitamins B1, B2, K; a low bacterial content can lead to the development of dysbiosis.
In addition, E. coli neutralizes many pathogenic bacteria in the human body. The normal content of safe coli strains in the intestines is from 10 6 to 10 8 CFU.
Since some strains of bacteria are toxic to humans, their high levels are harmful to health, for example, impairing the functioning of the digestive system and causing inflammatory processes.
Such microorganisms are especially dangerous for children and women during pregnancy. A large number of E. coli units in a smear during pregnancy indicates the development of an infectious disease that threatens not only the mother, but also the baby.
There are several reasons why harmful subspecies of bacteria enter the vagina:
- violation of personal hygiene standards;
- uncomfortable underwear;
- sexual intercourse without a condom.
If the washing procedure is carried out incorrectly, E. coli is carried from the anus into the vagina. Migration of bacteria is also possible with irregular or infrequent toileting of the genitals.
In addition, wearing tight underwear made of synthetic fabrics often leads to the transfer of pathogenic microorganisms into the vagina. The choice should be given to cotton linen with a loose or loose fit.
Unprotected sexual intercourse is one of the main reasons for the appearance of E. coli in the vagina.
If a man is sick, then a pathogenic bacterium enters the vagina along with the sperm. In men, E. coli usually causes the development of chronic prostatitis.
With combined sexual intercourse (a combination of anal and vaginal types) and the absence of protective equipment, a natural transfer of intestinal microflora into the vagina occurs.
Promiscuous sexual relations with frequent changes of partners and frequent douching upset the balance of bacteria in the female body and often cause the migration of pathogenic E. coli.
Principles of therapeutic interventions
Of course, antibacterial pharmacological agents are used to treat a bacterial infection, but they are not the only ones used.
First of all, an antibiogram is performed, which is used to determine the sensitivity of the microorganism to various classes of medications.
The use of antibiotics negatively affects the metabolic and other systems of the patient's body, so accidental use of antibiotics is unacceptable.
Bacteriophages, which are essentially “bacterial viruses,” are often used. They penetrate the cell of the microorganism, causing its death. These products show high efficiency and are also safe for the patient - their use is allowed even in childhood.
With an intensive course of the disease, symptomatic therapy may be used. In a hospital setting, various agents are infused for detoxification, normalization of metabolic processes and replenishment of lost fluid.
In general, treatment can be carried out at home, but constant supervision by the attending physician is required at all stages of therapy to monitor and correct treatment measures.
All about deciphering urine tests. And all the details about blood sampling are.
It is much easier to prevent the excessive development of microflora than to treat it. It is important to observe the rules of personal and “social” hygiene, which consists of the following principles:
- Carrying out hygiene measures for intimate areas;
- Periodically wash your hands and treat them with disinfectants;
- Refuse to use other people's personal belongings (panties, towels, razors);
- Use mechanical contraceptives for women and men during sexual intercourse;
As you can see, the rules are quite simple and do not affect the quality of your life.
When the first symptoms appear, contact your doctor immediately. It is important to start treatment on time to prevent the condition from worsening.
Remember that self-medication is unacceptable, as the consequences for your health may be much worse than the primary disease.
E. coli is always present in the body of an adult and a child, but it is important to ensure that its indicators do not go beyond the permitted limits
.
As soon as symptoms of a developing disease and damage to the body appear, therapy should be started immediately. This may include the use of traditional medicine, traditional anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics and beneficial bacteria
.
There may be several reasons for infection:
- wearing unsuitable underwear, which may be too tight and made of synthetic materials
; - ignoring the rules of personal hygiene or making mistakes when toileting the external genitalia;
- sexual contact without using a condom and special spermicidal lubricants, suppositories
; - mixed sexual contact, including anal and vaginal sex.
Gynecologists draw the attention of women to the fact that it is especially dangerous to wear tight underwear during pregnancy, this also applies to thongs. This significantly increases the chance of an E. coli infection, but also harms the hemorrhoids and can cause inflammation.
.
https://youtu.be/ZGg_4Oq8JpM
Symptoms and diagnosis of pathology
The presence of E. coli in the body manifests itself through a combination of signs that appear on the first day after infection.
The difficulty of making a diagnosis is that the symptoms of the pathology are also inherent in other more common diseases. In addition, after 2-3 days all signs of the disease may disappear.
The main symptoms of infection with harmful subspecies of E. coli are:
- persistent diarrhea;
- nausea and vomiting;
- hyperthermia;
- decreased appetite;
- general weakness and fatigue.
If there are pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli in a smear in women, treatment should occur as soon as possible, since the pathogenic environment in the vagina leads to the development of inflammation and the appearance of various diseases of the reproductive system: vaginitis, colpitis, endometritis, inflammation of the ovaries.
Often, high levels of hemolyzing bacteria lead to pyelonephritis in pregnant women.
The danger of having harmful bacteria in the vaginal microflora lies in the possibility of developing many serious diseases, which over time can become chronic and lead to infertility.
Sometimes the inflammatory process in a woman’s body passes without pronounced symptoms and remains unnoticed until a planned visit to the doctor.
In this case, inflammation can develop in the shortest possible time and lead to serious diseases of the genital organs.
Any stress or hypothermia can worsen a woman’s condition and stimulate the disease. As a result of increased emotional stress, protective functions slow down, and the body is not able to properly fight the spread of pathogenic bacteria.
When infected with E. coli, a woman often suffers from chronic diseases of the genitourinary organs: cystitis, pyelonephritis, colpitis, etc.
Exacerbation of these diseases is easily provoked by any external influence and even a simple ARVI.
Treatment often takes many years and does not always lead to long-term positive results.
That is why it is important to notice the symptoms of the disease in time and undergo a routine examination by a gynecologist 1-2 times a year.
Since E. coli is common, testing for its presence is part of a woman’s mandatory tests during a routine visit to the gynecologist.
The reason for an unscheduled visit to the gynecologist may be excessive discharge with an unpleasant odor or unusual color, itching and discomfort in the genital area.
At the appointment, the doctor, along with an E. coli test, will conduct other related studies that will allow you to build a complete picture of the disease and select the optimal treatment regimen.
Detection methods
Most women are examined once a year at the antenatal clinic. While examining the genitals, the gynecologist takes material - a smear on a piece of glass. This material is then sent to a laboratory where it is examined in detail.
The vagina is home to a mass of particles that make up the microflora. They protect the woman from pathogens entering this area.
A smear test allows you to determine how healthy the local microflora is. Analysis under a microscope and with chemical reactions makes it possible to identify E. coli in the taken material.
Treatment regimen and prevention
The outcome of the disease and the speed of complete recovery often depend on whether E. coli was detected in the smear on time and how quickly the correct diagnosis was made.
Usually, upon receiving a positive test result, the doctor prescribes antibiotic therapy.
Before taking drugs in this category, you should be tested for bacterial resistance to certain types of antibiotics.
Some strains of E. coli may be resistant to antibacterial drugs. Treatment without an antibiogram can be not only ineffective, but also harmful to the woman’s body.
E. coli in a smear often appears in women during pregnancy. While carrying a child, the range of medications used is limited, so the selection of antibiotics for a pregnant woman should only be performed by the doctor leading her pregnancy, based on test results.
Many antibacterial drugs, if you follow the recommendations of the gynecologist and the established dosage, do not affect the development of the fetus and are safe for women.
A gynecologist may prescribe vaginal probiotics - tablets to restore the vaginal microflora (for example, Gynoflor, Vagilac, Ecofemin).
It is also possible to use suppositories of a similar principle of action - Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin. Taking any medications should be strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Self-medication can have a detrimental effect on a woman’s condition and contribute to the development of chronic diseases.
To maintain the body and intestinal microflora after antibiotic therapy, it is recommended to use probiotics that restore the balance of the microflora.
Changing a woman’s diet would also be a good idea. The menu should include fermented milk products (for example, bio-yogurt) and exclude fatty, fried and smoked foods.
In addition to treating the consequences of E. coli infection, possible re-infection should be excluded.
Since E. coli infection does not always have pronounced symptoms, to exclude the possibility of developing a chronic form, it is recommended to visit a doctor 1-2 times a year and take a smear for E. coli.
The presence of E. coli in a woman’s smear is always an alarming sign.
Even in the absence of complaints and good health, one should not neglect the recommendation to visit a gynecologist for preventive purposes, because a dangerous bacterium may not detect itself for a long time and lead to serious diseases of the genitourinary system.
There are 100 types of E. coli, and most of them are considered pathogenic. Even opportunistic species that inhabit the intestines, when they enter neighboring organs, cause serious disorders. What medications are used to suppress infection in bacterial vaginosis, and how to prevent relapse.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed on a strictly individual basis, based on the results of bacterial culture. Antibiotics are prescribed according to the degree of sensitivity. That is why you cannot self-medicate; the wrong antibiotic will not destroy the infection, but will weaken the defenses of your own microflora. As a result, the infection will penetrate deeper and cause more severe inflammation. Treatment with bacteriophages (literally “devouring bacteria”) will show a good effect.
Proper adherence to personal hygiene measures will enhance the effect of treatment. It is recommended to wash with a decoction of chamomile and calendula. These herbs have pronounced anti-inflammatory and calming effects.
To increase local immunity, vaginal suppositories (Acylat, Vaginorm) and douching with medicinal solutions are used. It would be useful to use drugs that eliminate dysbacteriosis: Linex, Bifiform and others.
During the treatment period you must follow the following diet:
- You should avoid fatty, fried, salty and smoked foods.
- Any baked goods made from yeast dough are also prohibited.
- Pickled foods (cabbage, cucumbers) should be temporarily excluded from the diet.
- Beer, wine and other alcohol are prohibited during treatment.
- It is allowed to eat boiled and steamed food. Use non-fat meat.
- It is necessary to introduce yoghurts (natural) and biokefir into the diet. This will help restore normal intestinal microflora (and therefore improve immunity).
If the general condition is not severely disturbed, then treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. At the end of the treatment cycle, repeat tests must be taken.
Causes of infection
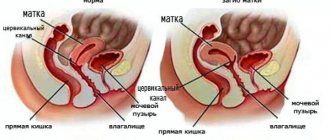
E. coli can penetrate the vaginal cavity and actively multiply in it. If for the intestines the presence of a bacillus is considered a physiological norm, then for the genitals this becomes a prerequisite for the development of bacterial vaginosis, or vaginitis.
Most often, this pathology occurs in women of reproductive age. Infection from the vagina can spread to the bladder, urethra and genital skin. It is quite dangerous, and the chronic course of the disease can cause serious complications that are difficult to treat: endometritis, adnexitis, cervical erosion, cervicitis.
Anatomically, in women, the entrance to the vagina is located close to the anus, and therefore the spread of opportunistic E. coli occurs almost unhindered.
The reasons why infection occurs and the vaginal ecosystem changes:
- Incorrect washing technique, insufficient hygiene of the external genitalia.
- Tight and synthetic underwear.
- Wearing a thong.
- Combined sexual contacts (combination of anal and vaginal).
- Change of sexual partner.
E. coli in the vagina can colonize and actively multiply against the background of weakened immunity and sudden temperature changes (heat or cold), during menopause, from frequent douching, endocrine and metabolic disorders. Provokes the colonization of pathogenic microflora by long-term use of antibacterial drugs, chronic general and sexually transmitted infections.
Symptoms
Initial infection does not manifest itself with pronounced clinical signs.
At the stage of active reproduction, opportunistic E. coli produces abundant clear or white discharge. Their smell is pungent and unpleasant. With the development of the pathological process, vaginal mucus becomes purulent and foul-smelling. A woman complains of itching and burning of the mucous membranes and skin.
Colonization with opportunistic enterococcus is especially dangerous in pregnant women. Bacteria easily penetrate the placenta and can cause meningitis in a newborn.
Therapy
An E. coli infection should be treated by a specialist. Self-medication and traditional methods are completely excluded in the acute stage.
Before undergoing the necessary therapeutic course, the patient undergoes a bacterial culture. The study will accurately determine the strain of the pathogen, and this will determine the intensity and duration of drug therapy.
Comprehensive treatment of E. coli includes antibacterial drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, probiotics, and local procedures.
In gynecology, vaginosis caused by E. coli is treated on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a doctor. Local procedures include washing with chamomile infusion, medicinal douching, and administering vaginal suppositories with nystatin. The doctor prescribes a course of physiotherapy: ultraviolet irradiation on the genitals.
Antibacterial therapy
To suppress pathogenic microflora, a course of antibiotics is prescribed for 7 days. For vaginosis caused by E. coli, the following are indicated:
- Oral preparations based on clindamycin phosphate, metronidazole and tinidazole: Cleocin, Flagyl, Tindamax. Pros of taking: allowed for treatment during pregnancy. Disadvantage: drugs can cause side effects such as a metallic taste in the mouth and dyspepsia.
- Vaginal antibiotics (suppositories, creams, gels): Metro-gel, Kleotsin, Clindess. Advantages of local treatment: symptomatic side effects are excluded, the drug acts directly on pathogenic microflora. Disadvantage: vaginal route of administration is contraindicated during pregnancy.
To suppress pathogenic E. coli, the antiseptic Miramistin is additionally prescribed. The product reduces the resistance of flora, enhances the effect of antibiotics, and stimulates the body's immune response.
Maintenance therapy
In order to restore the vaginal microflora, probiotic and antifungal agents and immunomodulators are prescribed after antibacterial treatment. Medicines for maintenance therapy:
- Probiotics with lactobacilli: Laktogin, Vagilak, Gynoflor. The drugs restore normal pH levels and stimulate the development of healthy microflora.
- Immunomodulators Likopid, Kagocel, Viferon. The tablets prevent and stop purulent-septic processes and strengthen the immune system.
Complex treatment necessarily includes a diet with a sufficient amount of fermented milk products.
Prevention
To prevent infection of the vagina by pathogenic microflora, a woman must follow several important but basic rules. Points that must be observed:
- Toilet the external genitalia at least twice: in the morning and before bed. After washing, wear only fresh underwear.
- Avoid panty liners. Warmth and moisture on it are an ideal environment for the growth of bacteria.
- During menstruation, change pads every 4 hours and wash with the same regularity.
- Carry out hygiene procedures by hand. Washcloths, sponges, and terry gloves cannot be used.
- When washing, only the external genitalia are cleaned. You should not try to wash the vagina.
- For the procedure, use special intimate cleansers. Shower gel and shampoo are not suitable for this purpose.
- The hygienic procedure should take no more than a minute. Prolonged washing destroys the natural vaginal microflora.
To prevent the development of bacterial vaginosis, a woman should undergo regular examinations with a doctor. If the pathogen is identified in the early stages and treatment is started on time, the prognosis for full recovery will certainly be positive.
The human body is inhabited by many different bacteria. Among them there are beneficial bacteria that support the normal functioning of our intestines. These are the well-known lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and E. coli. This is exactly what we will talk about in our article.
Escherichia coli was isolated by the Austrian scientist Escherich back in 1885. Today, numerous varieties of this bacterium are well known: many of them are harmless to the body and are an essential component of the intestinal microflora. In addition, E. coli synthesizes vitamins K, B1, B2, B3, B5.
However, there are more than 100 species of this bacterium, which are pathogenic and can cause the development of serious diseases or poisoning. It is worth noting that even bacteria that are opportunistic (this includes, for example, hemolyzing Escherichia coli), when they enter other organs of the human body from the intestine, can cause serious complications.
Routes of infection
There are several reasons that lead to E. coli entering the vagina or urethra: lack of regular personal hygiene; improper washing; uncomfortable underwear (tight thongs, synthetics); anal-vaginal sex. A newborn baby can receive pathogenic E. coli from the mother through the birth canal.
Manifestations in women
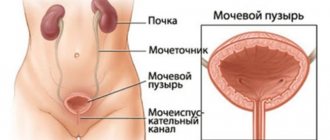
E. coli is present in a smear in women in small quantities, without causing pathogenic reactions. But its reproduction in the vagina inevitably leads to bacterial vaginosis. From the vagina, the microorganism infects the uterus and ovaries. If there is no proper treatment, E. coli in women will penetrate through the urethra into the bladder, and then kidney damage may occur.
Manifestations in men
Basic hand washing helps prevent infection.
First of all, E. coli is detected in a smear in those who neglect the rules of personal hygiene and come into contact with infected partners. Infection occurs through food and liquid. Often, with a smear from the urethra, E. coli in men is detected completely by accident, since there are no signs and symptoms of infection. In this case, the urethra becomes inflamed, gradually causing severe forms of pathology. Possible symptoms of bacterial growth in the urethra:
- severe diarrhea;
- green vomit;
- increased body temperature;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- nausea, poor appetite and weakening of the body.
These symptoms can disappear in men on their own within 2 days, since the intestines tend to cleanse themselves in such a disease. The flora recovers on its own. If they do not go away, you should consult a doctor. The main cause of symptoms is poor hygiene. Promiscuous sexual intercourse and unprotected sexual intercourse can also cause infection.
During pregnancy
E. coli in the vagina during pregnancy is especially dangerous for several reasons. Firstly, during pregnancy a woman’s immune system is weakened, which contributes to the occurrence of various infections. This threatens the fetus, as the infection affects the placenta. Secondly, during the birth process, when the baby passes through the birth canal, he himself can become infected with E. coli from his mother. If, during pregnancy, E. coli causes bacterial vaginosis and disrupts the vaginal flora, this can provoke premature birth. Therefore, if you are planning to give birth, you need to get a smear test in advance and undergo the necessary treatment if necessary to avoid further problems.
Manifestations in infants
If the child is not treated in time, serious consequences are possible.
After birth, a child enters an environment full of dangerous viruses, bacteria and microorganisms. Therefore, harmful bacteria may also be present in the newborn’s body, which causes pathogenic changes in the microflora. When hemolytic E. coli multiplies, even in small quantities, the child’s body begins to function incorrectly. The following symptoms appear:
- skin rashes, diathesis;
- diarrhea;
- bloating, flatulence;
- pain and colic in the abdominal area;
- the stool has a greenish tint or color and a mushy consistency.
These are signs of bacteriosis that need to be treated, otherwise it will become the root cause of frequent ailments and provoke the further development of serious pathologies. The outcome of treatment depends on how quickly treatment begins. If you do not pay attention to infections, pathological irreversible processes in the body will follow. For example, chronic renal failure manifests itself.
The human body is inhabited by many different bacteria. Among them there are beneficial bacteria that support the normal functioning of our intestines. These are the well-known lactobacilli, bifidobacteria and E. coli. This is exactly what we will talk about in our article.
The presence of E. coli in a smear in women: causes, symptoms and treatment
The normal habitat of this microorganism is the area of the colon located closer to the anus. First, you need to understand how E. coli gets into the vagina and how to detect it.
In general, E. coli may be present in the vagina in small quantities, but its proliferation leads to bacterial vaginosis and other diseases.
There are several known reasons for this microorganism entering the vagina:
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, namely improper washing. Due to the close location of the vagina and anus, in order to prevent the introduction of pathogenic microbes, you need to wash from top to bottom, and not vice versa.
- Wrong choice of underwear. Various microbes and bacteria from the anus, including E. coli, may enter the vagina due to wearing thongs and tight underwear. Thongs are certainly beautiful and sexy. But when choosing between beauty and health, it is better to prefer the second. You should also give preference to underwear made from natural cotton fabrics.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse. Here we are talking about combined sexual intercourse, that is, anal-vaginal. So those who like to diversify their sex life should first think about means of protection.
In addition, reasons that contribute to the entry of E. coli into a smear include indiscriminate change of sexual partners, frequent douching, and weak immunity.
Symptoms of pathology
The presence of E. coli in the vagina can cause the development of diseases of the female genital organs, such as:
- adnexitis;
- bacterial vaginosis;
- endometritis, etc.
The development of the above pathological conditions of the female body is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the discharge is copious and has an unpleasant odor;
- suffers from itching and burning in the genital area.
In the absence of proper treatment, E. coli from the vagina easily penetrates the cervical uterus, ovaries, as well as the urethra, bladder and then affects the kidneys.
Treatment methods
If a vaginal smear reveals signs of the presence of E. coli, this is a serious reason to start treatment as soon as possible. After all, the more advanced the disease, the more difficult it will be to fight it and the more strength the body will need to recover.
Of course, only a doctor can describe the treatment in detail. As a rule, the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics. However, some types of E. coli are resistant to certain drugs, and this must also be taken into account.
In addition to drug treatment, specialists usually prescribe the following procedures:
- washing the genitals with herbal decoctions (for example, chamomile);
- in some cases, sessions of UV irradiation of the genital organs are prescribed;
- various therapeutic douchings;
- use of drugs to restore microflora: probiotics, bio-yogurt;
- taking complex vitamins to strengthen the immune system.
After the course of treatment, tests must be taken again.
Symptoms
If E. coli enters the vagina or urethra slightly, there will be no symptoms. The body will suppress the growth of these bacteria. However, if E. colli colonies grow, an inflammatory process develops. Depending on the generalization of the process, the following manifestations of the disease occur:
- Frequent, painful urination (symptoms of cystitis - inflammation of the bladder).
- Copious vaginal discharge. The discharge may be white or yellowish. These are symptoms of vaginitis (colpitis) - inflammation of the vagina.
- Pain during sexual intercourse, loss of sexual desire.
- Lethargy, weakness, headache, fever (symptoms of intoxication).
It is almost impossible to detect the presence of E. coli in a simple microflora smear. The development of the inflammatory process will be indicated by the high level of leukocytes as a result of the analysis.
Therefore, if the level of leukocytes is high, a bacterial culture is always prescribed, which will show E. coli. Simultaneously with the identification of the pathogen, an antibiotic sensitivity analysis will be carried out (this will be necessary to prescribe the most effective treatment).
In cases where a smear of Escherichia coli is detected in the culture up to 104 CFU/ml and the vaginal microflora is good, treatment is not necessary. But if the microflora is weak, or the indicators exceed the norm, then a course of treatment is necessary.
What happens if E. coli is detected in a smear during pregnancy?
Separately, I would like to say about the possible consequences of detecting E. coli in a smear in pregnant women. Since during this period the immune system is greatly weakened, the threat of various types of infections is higher than ever. There is a risk of it penetrating the placenta and infecting the child, and this is fraught with the development of meningitis in the baby, which in itself sounds almost like a death sentence.
In addition, the child can become infected while passing through the mother’s birth canal. Also, a consequence of vaginosis (a disease caused by E. coli) can be premature birth.
Of course, antibiotics will not bring much benefit to the child either. But with timely treatment, the doctor will be able to select the type of medication that will be safe for the further development of the fetus.
In general, in order to avoid problems when planning a pregnancy, it is better to take a vaginal smear for examination in advance and eliminate all possible infections. This will make your life much easier and keep your unborn baby healthy.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent E. coli from entering the vagina, a number of fairly simple rules should be followed:
- wash yourself at least 2 times a day;
- change underwear daily;
- take your choice of underwear seriously: wear only panties made from natural fabrics;
- use condoms during sex.
In men, E. coli lives in the rectum, near the exit from the anus. If hygiene is not observed, it can easily get into other organs.
This bacterium is beneficial if it is present in sufficient quantities to take part in the synthesis of vitamins.
Diseases
When it enters certain organs, it causes various infectious diseases.
- If found in feces, it means it came from the intestines.
- In urine there is a pathology of the urinary system.
- A smear from the urethra shows inflammation of the testicle or its appendages.
- Provokes prostatitis.
To avoid getting infected you need to:
- Keep the groin area clean.
- Avoid unprotected coitus.
- After sex, take a shower.
- Wear neat, comfortable clothes.
Causes
There are also food pathogenic strains of intestinal microbes. Ways of infection are spoiled food, contaminated water. To avoid infection you need to:
- Pay attention to the labeling of the products you buy. Expired ones are a source of infection.
- Wash your hands after using the toilet and going outside, and before eating.
- Drink purified water. Microbes live and multiply in dirty conditions.
- Wash food by pouring boiling water over it.
- After handling your beloved pets or working with the soil, disinfect your hands.
Kinds
The intestinal microbe has more than 100 strains. Conventionally, they can be divided into 4 rows.
Enterohemorrhagic
. When it becomes infected, enterocolitis develops and the urethra is affected. Symptoms:
- Severe pain in the abdominal area, thin bleeding.
- A sharp increase in temperature (up to 39 °C).
- All signs of intoxication appear - nausea, vomiting.
- The infection enters the kidneys through the urethra. Kidney failure and pyelonephritis develop.
- The stick can damage the liver.
At the beginning there are no symptoms; the disease can only be determined by research. A urine test shows the presence of protein. Hemoglobin drops.
Enteropathogenic
is very rare. Sometimes it can penetrate, causing nausea, loss of appetite, insomnia, and abdominal pain.
Enterotoxigenic
– characterized by the fact that the bacterium is located in the rectum. The stool with this infection is very watery, but without blood. I suffer from nausea and vomiting. Found in smears in men.
Interinvasive
similar to dysentery. These include frequent urge to go to the toilet, loose stools with blood, nausea, and vomiting.
What is common to all types of E. coli is that when it enters the body, it multiplies intensively and toxins are released, causing diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. The intestines suffer the most.
The infection affects the genitourinary system, liver, and kidneys. Symptoms appear over several days, the incubation period of infection is about a week.
In a smear
An infectious disease specialist takes bacteriological material during an appointment. The man does not feel any signs of illness, but a smear analysis shows the presence of inflammation.
We need to start treatment urgently. The infection quickly spreads through the genitourinary system and affects the genitals. May cause inflammation of the prostate and kidneys. E. coli can be treated with antibiotics as an inpatient in an infectious diseases hospital.
In a mild form of infection, male thrush occurs. The reason may be unprotected sex and lack of cleanliness. To prevent candidiasis you must:
- Do not neglect personal hygiene.
- Use gels for intimate areas.
- Be sure to shower after sexual intercourse using special antibacterial agents.
In urine
In the bladder, the infection does not manifest itself for a long time. Very rarely the body copes with the problem itself, but in most cases the stick causes cystitis:
Symptoms of the disease:
- Burning in the urethra.
- Fever, chills.
- Urine has an unpleasant odor.
- Drawing pain in the lower back.
If symptoms of infection appear, a course of antibiotics will be required, which will be selected by the doctor. By contacting a specialist in a timely manner, you will get rid of complications.
Men! By following simple rules, protect yourself and your loved ones from E. coli infection. Subscribe to our website. Share useful information with your friends. Be healthy!