What causes the disease?
Many girls and women are susceptible to the development of this disease, but most often varicose veins of the uterine vessels occur precisely in those representatives of the fairer sex of childbearing age, or who are already in a state of pregnancy.
There are a number of causes and risk factors that cause the disease:
- a disruption in the hormonal system, which is inherent in absolutely every pregnant woman, as well as women during menstruation. Due to a sharp increase in the level of the hormone progesterone, the tone of the uterine muscles, along with the tone of the pelvic vessels, decreases;
- varicose veins of the uterine veins are almost always inherited, therefore, in case of problems in the family, there is a high risk of the disease developing in a young girl;
- previous abortions worsen the condition of the uterus and blood vessels;
- chronic diseases that did not have proper treatment at the right time, as well as chronic diseases of the female reproductive system;
- shifts in the menstrual cycle;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- pathologies of the valves in the veins cause an increase in pressure in the vessels of the pelvic organs, as a result of which varicose veins of the uterus appear.
Of course, among the significant risk factors we should also highlight a sedentary lifestyle, congenital pathologies of the female genital organs and blood vessels, and of course pregnancy, which gives a powerful shake-up to all systems of a woman’s body.
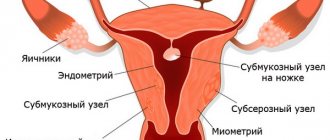
Causes of varicose veins of the uterus
In order to thoroughly understand what this problem of dilated vessels in the uterus is, it is necessary to understand its causes.
- The period of bearing a child. This is due to the fact that during pregnancy, blood flow to the mark increases. Weaker venous vessels begin to stretch, and the functionality of the valves is impaired.
- Symptoms of varicose veins in the pelvis can also appear in professional athletes. Excessive stress on the body contributes to an excessive flow of lymph into the pelvic organs.
- Problems with bowel movements. When a person experiences constipation, the movement of blood in the vessels increases. A constant increase in pressure inside the peritoneum can lead to varicose veins of the uterus.
- Uncontrolled use of hormones as a method of contraception. If there is a constant excess of the hormone estrogen in a woman’s body, then the vascular walls will become less elastic over time.
- Sedentary work and passive lifestyle.
- Anatomically incorrect structure of the pelvic organs. For example, congenital bending of the uterus.
The risk group also includes women who have previously often suffered from inflammatory processes in the pelvis. Patients who have undergone a difficult birth or have had more than 2 abortions should be on their guard.
Clinical symptoms
Due to their non-specificity, the symptoms that appear with this problem are often not detected or are confused with another disease. Thus, varicose veins of the uterus are often manifested by prolonged aching pain in the lower abdomen. In addition to this, there are a number of other signs:
- Abnormal changes in the menstrual cycle.
- The appearance of pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse or sports activities.
- The occurrence of sharp pain or discomfort during urination. In this case, pathology from the kidneys and urinary system should be excluded.
- Less commonly, manifestations of increased sensitivity of the vaginal walls may occur.
The above symptoms occur at later stages, when the process has already started and is developing. The initial stages of the disease, as a rule, occur without clinical manifestations.
In cases where varicose veins in the uterus have a severe course, the clinical picture tends to become more complicated and then an increase in pain intensity, massive bleeding, ruptures of the venous walls, and frequent occurrence of inflammatory diseases in the genital organs may occur. Ultimately, this process risks ending in complete infertility.
Disease detection methods
First of all, when discomfort and pain appear, a woman, based on some nonspecific signs, will be able to suspect a possible problem with the vessels of the uterus and other genital organs.
In such cases, the pain is accompanied by heavy menstrual flow, a larger amount of serous discharge than usual, and the appearance of bloody discharge in the middle of the menstrual cycle.
By contacting a specialized doctor, a full examination should be carried out with questions about complaints. After which the specialist must resort to one of the instrumental diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound diagnostics is the most effective way to detect varicose veins in the uterus;
- Dopplerography;
- computed tomography of the entire pelvis, in order to visualize the pelvic organs and the vessels surrounding them;
- transuterine venography with contrast;
- laparoscopic examination.
Particular attention should be paid to cervical varicose veins, which have some characteristic signs. Varicose veins will pass through the area in which the cervix is located, and other organs of the reproductive system will also be involved in the pathological process: ovaries, vagina, external and internal labia. Rarely, the process tends to move to the legs.
Cervical varicose veins are very typical for pregnant women, which, as already mentioned, occurs due to hormonal dysfunctions, excessive tension in the vascular wall of this organ, genetic predisposition, etc.
Diagnostic principles
A gynecologist can refute or confirm the diagnosis after a thorough examination. If a disease is suspected, the patient is prescribed additional tests. Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the uterus is the most informative method. The examination is carried out using a transvaginal sensor inserted through the vagina. Transabdominal ultrasound examination is also used (insertion of a sensor through the abdominal wall). A blood and urine test and a vaginal smear for microflora will be required.
Attention! Laparoscopy and computed tomography (CT) of the pelvic organs are additional methods that are performed according to indications.
If a pathology is detected, the woman is referred for consultation to a phlebologist. He orders contrast venography (venography), an X-ray examination of deep or superficial veins using a contrast agent that provides an image of the blood vessel. Phlebography determines the patency of the deep veins, the presence of blood clots, valve function and allows for a general assessment of the condition of the deep veins.
How does the disease threaten pregnant women?
Varicose veins of the uterus during pregnancy pose a particular threat to both the health of the fetus and the health of the expectant mother who is carrying it. There are several key factors in the occurrence of illness during pregnancy:
- Every month the fetus inside the uterus grows, which means the uterus also grows, which leads to a greater need for blood supply. The placenta, through which the fetus is nourished, actively requires a significant amount of oxygen and nutrients. The uterus, in turn, increasing in size, puts pressure on nearby organs and vessels, squeezing them. Thus, we have a factor of increased blood flow through the vessels to the uterus and placenta.
- Bearing a fetus is a very costly process that uses absolutely all the forces and resources of the body. There is a massive release of hormonal substances into the bloodstream, namely the female hormone progesterone. Progesterone acts on the vessel wall, relaxing it and reducing the overall tone of the muscle layer. Reduced vascular tone leads to overstretching of the wall, which subsequently affects the state of the valve system of the veins - they are not able to close completely, which causes a disruption in the normal blood flow.
- By combining the increased blood delivery and the hormonal component, it turns out that the outflow of venous blood suffers. Due to the increased inflow and weakened muscle and valve systems of the vessel, the blood simply does not have time to flow. As a result, varicose veins occur in the uterus with the possible development of thrombophlebitis and other complications in the future.
Treatment of varicose veins
First of all, every woman should know: what are varicose veins of the uterus, what threat does it pose and the main question - how to treat such a disease?
First of all, the patient needs a specialized consultation, in which she will be helped by a phlebologist or a gynecologist. They will be able to determine whether the stage of the disease present at the moment is dangerous, and based on this, they will prescribe adequate treatment.
In the initial stages, conservative therapy will be sufficient for treatment. In such cases the following may apply:
- distribution of daily routine and assignment of rational loads;
- eating a diet that should contain many vitamins and minerals;
- strict elimination of bad habits such as smoking and alcoholism, if present;
- physiotherapeutic procedures: physical therapy, Kegel exercises, various water procedures;
- wearing compression garments;
- taking medications that will improve the flow of blood from the veins and the condition of the vascular wall, and will also prevent the formation of blood clots (anticoagulants, thrombolytics, antiplatelet agents, etc.).
Prevention
Prevention of vascular pathology of the uterus consists of following special rules. The main ones:
- Normalization of lifestyle. You need to sleep at least 8 hours a day. You should alternate between rest and work. It is recommended to avoid stress and mental strain.
- Eliminate heavy lifting. Women prone to this disease are advised to avoid excessive pressure in the abdominal area. To do this, you need to minimize lifting objects that weigh more than 4 kg.
- Regular exercise. It is necessary to do light gymnastics, which helps increase blood circulation. Exercises that create reverse outflow are effective, i.e. inverted poses when the legs look at the ceiling.
- Review of diet. To prevent varicose veins in the uterus, it is recommended to include a large amount of vegetables and fruits in your diet. It is necessary to exclude fried and fatty foods, caffeine and soda.
- Rejection of bad habits. Smoking and alcohol abuse, which provoke destructive processes in blood vessels, should be avoided.
- Contrasting douches. Such procedures stimulate venous tone. You need to alternate warm and cool water for 3-5 minutes.
An additional preventive measure is timely treatment of diseases of the female reproductive system.
An additional preventive measure is timely treatment of diseases of the female reproductive system.
What's the prognosis?
Usually, knowing the dangers of such a disease and comparing possible changes in the skin with various photos, women turn to specialists in a timely manner. Otherwise, ignorance of the problem risks leading to a protracted course of the disease and the development of complications.
Most often, the prognosis for diagnosing varicose veins is favorable, but it is still not possible to completely cure it. Therefore, subject to the prescribed regimen, diet and exercise, patients are allowed to maintain the affected vessels in good shape. This tactic significantly improves vital signs and reduces the risk of complications, in particular infertility.
—