The causes of uterine fibroids are directly related to changes in hormonal levels in a woman’s body. Manifestations of pathology may not manifest themselves for a long time, and pathological processes occur covertly and do not make themselves known for some time, which contributes to the neglect of the disease, accompanied by a large number of complications.
Uterine fibroids - what is it?
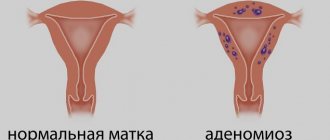
Uterine fibroids are a disease of the female genital area, characterized by the formation and growth of a benign tumor in the myometrium, the muscular layer of the uterus. Most often, women aged 30 to 40 years and older face the problem of uterine fibroids. However, nowadays fibroids have become significantly “younger”, and cases of the disease in young women aged 20-25 are not uncommon.
Uterine fibroids are a tumor (formation, node) located inside the body of the uterus (in 95% of cases, less often in the cervix - 5%). Fibroids can develop from cells of both muscle and connective tissue.
Obstetrician-gynecologists indicate the size of fibroids either in centimeters (the size of the node itself) or in weeks. The phrase “fibroids 12 weeks” means an enlargement of the uterus with a myomatous node to the same size as at 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Based on their location relative to the muscle layer – the myometrium – fibroids are classified as follows:
- Intermuscular (or intramuscular, or interstitial, or intramural) - the node is located inside the myometrium;
- Subperitoneal (or subserous) - the node is located under the mucous membrane of the outer layer of the uterus, near the peritoneum;
- Submucosal (or submucosal) - the node is located under the inner mucous membrane of the uterus, in the cavity of the organ;
- Interligamentous (or intraligamentary) - the node is located between the wide uterine ligaments.
There are pedunculated fibroids, but their localization is exactly the same as we listed above.
Sometimes a diffuse form of fibroid is diagnosed, in which the node as such is absent, but diffuse growth of the myometrium occurs.
What is the difference between fibroids and uterine fibroids?
All types of fibroids are formed from two types of tissue: muscle and connective. The predominant composition of the tumor determines its belonging to the type of fibroid. If muscle fibers predominate in it, then it is a fibroid. If connective fibers predominate, which are mixed with muscle fibers, then this is fibroids. But if the tumor consists entirely of connective tissue, then it is called fibroma.
Classification of myomatous formations
The body of the uterus consists of a muscular layer and a mucous membrane that lines its inside.
Myomatous formations are localized in muscle connective tissue. The source of their growth growth is one defective cell, which undergoes certain changes and begins to divide at a faster rate than neighboring ones.
As a result, a myomatous node appears - a local accumulation of chaotically intertwined smooth muscle fibers. On average, its dimensions range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. However, sometimes very large tumors occur. Some reach a weight of several kilograms.
Myomatous cells practically do not degenerate into malignant ones. This happens in less than 1% of cases.
Attention! Even the rapid growth of fibroids is not a sign of its malignancy
Fibroids of the uterine body can be located in different layers. Based on these characteristics, nodes are divided into the following types:
- Submucosal or submucosal - grows into the uterine cavity. It can protrude inward completely, half or less.
- Intramural or intermuscular - located inside the wall of the organ.
- Subserous or subperitoneal - protrudes outside (into the peritoneum).
Among these types there is fibroid, which grows on a stalk.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids
Symptoms of uterine fibroids depend on how long ago the node appeared, the woman’s age, the size and location of the tumor, the growth rate of the fibroid node and the presence of other chronic diseases. Sometimes fibroids are practically asymptomatic and are detected only during the next medical examination.
The most common and characteristic symptoms of uterine fibroids:
- Pain during the intermenstrual period, varying in duration, arising in the lower abdomen, sometimes radiating to the lumbar region, upper abdomen or legs;
- Menstrual dysfunction. These may be changes in the duration of the cycle towards shortening or increasing, increased pain in menstruation, an increase in the volume of blood loss during menstruation (menstrual uterine bleeding), intermenstrual bleeding;
- Problems in the reproductive sphere (possible development of infertility).
With the rapid growth of uterine fibroids or with a large size of the myomatous node, the volume of the abdomen may increase without gaining body weight, as well as discomfort and constant aching and nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which intensify after physical exertion and emotional and psychological experiences.
When nearby organs are compressed by a myomatous node, persistent constipation occurs, as well as frequent, sometimes painful urination.
When the leg of the myomatous node is torsed, necrosis (death) of the myoma body develops, and then the clinical picture of an “acute abdomen” is observed: sharp pain in the lower part of the peritoneum, rapid heartbeat, cold sticky sweat, fainting. This situation requires emergency surgery.
Other symptoms of uterine fibroids may be expressed in dysfunction of organs indirectly affected by pathogenesis:
- Development of anemia (with frequent bleeding);
- Dizziness;
- Frequent headache;
- Chest pain;
- Neuroses and neurosis-like states due to thoughts about the growth of a tumor, the danger of the disease.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids in the early stages
The first signs of uterine fibroids are usually observed when a woman has a myomatous node measuring 2-6 cm or more:
- The appearance of sharp pain of a cramping nature not associated with menstruation in the lower abdomen;
- Painful menstruation, although this has never happened before;
- Increased menstrual bleeding;
- The appearance of bloody discharge during the intermenstrual period;
- Heavy bleeding between periods;
- Lengthening or shortening the menstrual cycle;
- Inability to conceive a child.
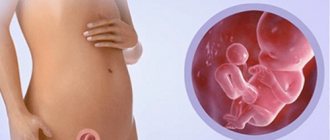
Fibroids and pregnancy
Patients who have a tumor are concerned about the possibility of conception and pregnancy. This problem is very relevant, since the main age category of mothers is women over 30-35 years old, who are at risk.
Conception
The neoplasm is not the cause of infertility, but it does cause some difficulties: it compresses the fallopian tubes, disrupts ovulation, and reduces the permeability of sperm. Therefore, if the patient does not become pregnant and a large fibroid is detected, drug or surgical treatment is recommended. With hypertrophic growth of fibroids and significant enlargement and deformation of the uterus, restoring the ability to bear children is problematic, sometimes impossible.
1st trimester of pregnancy
Problems are fraught with contact of the tumor with the placenta, especially if the fibroids are large. With a small tumor, which occurs in 60% of women during pregnancy, there are no complications or symptoms, but early termination of pregnancy occurs. Causes:
- increase in the number of uterine contractions;
- impaired uterine circulation;
- problems in the functioning of the neuroendocrine system;
- chronic infections;
- proliferation of the uterine mucosa due to polyposis, hyperplasia.
2nd, 3rd trimesters
The risk of miscarriage increases as the space required for the fetus decreases and the intensity of uterine contractions increases. The number, size, location of neoplasms, and their contact with the placenta play an important role. If a miscarriage does not occur, fibroids can negatively affect the development of the fetus, causing deformations of the skull and other parts of the body, and infringement of internal organs.
Childbirth
The neoplasm is often the cause of protracted labor; doctors often decide on a caesarean section. The tumor itself does not affect the birth process, the reason is that due to their presence, there is an anomaly of presentation, the position of the child, when it is impossible to give birth naturally (pelvic, facial, transverse position). Also, during a caesarean section, the surgeon can immediately remove the tumor.
Placental abruption is a particular difficulty, especially if a tumor has formed behind it. During the birth process, doctors must take this into account.
Postpartum period
Myoma causes complications during the postpartum period. They can be early - causing bleeding, placenta accreta, and late. These include involution (the uterus does not return to its original size) and infections.
Causes of uterine fibroids
Medical research allows us to identify several possible causes for the development of uterine fibroids:
- Genetic factor (hereditary predisposition);
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Pathological growths of the endometrium (inner mucous membrane of the uterus);
- Consequences of multiple or frequent abortions and the use of intrauterine devices;
- Infectious and inflammatory processes of the female genital area;
- Chronic stressful conditions;
- Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine diseases, including obesity;
- The presence of chronic diseases of various internal organs and body systems;
- Physical inactivity;
- Lack of regular sex life and sexual satisfaction.
Let's look at some of the reasons in more detail.
Excess estrogen, lack of progesterone. Uterine fibroids are considered a hormone-dependent disease - the tumor forms against the background of an imbalance of female sex hormones. Therefore, the development of fibroids is typical for women of childbearing age. Myoma does not occur in girls before the onset of their first menstruation and in menopausal and postmenopausal women. Studies have shown that the occurrence, growth and development of tumors is influenced by an imbalance in the production of female sex hormones - estrogen and progesterone.
Menstrual irregularities, in which estrogen production is increased, can lead to the development of uterine fibroids. Obesity increases the risk of developing the disease, because... adipose tissue also produces estrogen. An increase in estrogen levels entails a violation of the ratio of the hormones estrogen - progesterone in a woman’s body.
In addition to increased estrogen production, metabolic disturbances in its synthesis and the balance of its fractions (estron and estriol) are often observed in different phases of the menstrual cycle. Therefore, if fibroids are suspected, it is important to conduct a study of hormonal status.
Number of pregnancies, births, abortions. An important factor in the examination is to determine the total number of pregnancies a woman has had, as well as their outcomes - childbirth, miscarriage (abortion). Abortions and miscarriages increase the risk of developing fibroids. Pregnancies ending in childbirth, especially with subsequent breastfeeding, are reduced.
Traumatic, difficult childbirth, diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity, frequent and multiple medical abortions (including “mini-abortions”) can become the root cause of the development of fibroids.
Women's nutrition. Improper nutrition also leads to hormonal imbalance. The predominance of refined foods, trans fats, and insufficient fiber in the diet can cause an increase in the formation of female sex hormones and their imbalance. An unhealthy diet also leads to obesity, which, as we have already indicated, is a risk factor for the development of fibroids (Read more about what you can and cannot eat with uterine fibroids).
If a woman’s diet is balanced, contains a large amount of plant foods, seafood, complex carbohydrates (cereals), low fats and sugars, the risk of developing fibroids is significantly reduced. Outwardly, women who eat right look young and attractive, they are full of health, strength and energy.
Lack of orgasm during sexual intercourse. The occurrence of uterine fibroids is also influenced by the fullness of a woman’s intimate life. Irregular or rare sexual intercourse, lack of orgasms leads to stagnation of venous blood in the pelvis. A chronic state of venous stagnation can provoke hormonal instability and the occurrence of tumors.
Diabetes mellitus and hypertension. The risk of developing fibroids is increased by diseases such as diabetes (impaired production of the hormone insulin) and hypertension. The risk increases if a woman becomes ill at a young age, under 35 years of age.
Other possible causes of uterine fibroids:
- Obesity of the “apple” type;
- Oral contraception with hormonal drugs;
- Injuries and diseases of the female genital area;
- Prolonged exposure to the ultraviolet spectrum of direct sunlight and solariums.
Mechanical factors
Various injuries to the uterus create favorable conditions for the occurrence of fibroids. In places of damage to the myometrium, foci of undifferentiated cells begin to form, which give rise to a myomatous node.
Injury to the uterus is primarily associated with surgery. This may include frequent abortions, cesarean sections, therapeutic and diagnostic curettages.
Hormonal disorders
The main reason for the growth of fibroids is considered to be an increase in the level of sex hormones. Signs of changes in hormonal levels that provoke the onset of the disease are observed during pregnancy and during perimenopause (2 years from the last menstruation). As a rule, in postmenopause, the activity of fibroids and its symptoms are sharply suppressed.
An increase in the level of sex steroids is also observed with:
- Tumors of those areas of the ovaries that are responsible for the production of hormones.
- Diseases of the central nervous system, accompanied by symptoms of hypothalamic-pituitary disorders.
- Disorders of the adrenal glands.
- Using incorrectly selected hormonal contraceptives.
Genetic predisposition
Research into the heritability of a disease such as fibroids has been carried out since the 30s of the 20th century. It has been scientifically established that in women whose mothers and siblings suffered from uterine myomatous tumors, the risk of developing the disease almost doubles.
Quality of intimate life
“Female” chronic inflammatory diseases increase the risk of developing tumor diseases. One of the reasons for the occurrence of uterine fibroids in women is promiscuous intimate relationships without using a condom. Diseases transmitted predominantly sexually may not manifest themselves for a long time, while provoking low-grade inflammation of the uterus and appendages.
Nutrition
Obesity, as a consequence of poor nutrition, may be associated with the occurrence of fibroids. With excess body weight and a high percentage of adipose tissue, the synthesis of estrogen increases, which activates uterine tumors.
Consumption of foods rich in animal fats or fast carbohydrates contributes to the development of obesity.
Diabetes
Insulin resistance that occurs in diabetes mellitus leads to symptoms of metabolic disorders and hormonal imbalance. This provokes the formation of myomatous nodes on the uterus.
Diabetes mellitus also aggravates the course of the disease, and in decompensated forms it is a contraindication for surgical removal of fibroids.
Arterial hypertension
Hypertension is a sign of being overweight or constantly under stress. Both of these factors influence the active growth of myomatous tumor. Arterial hypertension aggravates the symptoms of uterine fibroids.
Why are uterine fibroids dangerous?
Uterine fibroids pose a danger to a woman’s health in terms of the development of complications of the disease. With regular monitoring by a gynecologist and careful attention to her health, a woman can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Therefore, you should be aware of possible potential problems:
- Massive uterine bleeding is dangerous both in itself, a threat to life, and the development of anemia;
- Torsion of a myomatous node on a thin stalk. It is fraught with the development of an “acute abdomen” picture. Requires immediate prompt assistance;
- Necrosis of myomatous node. Necrosis of fibroid tissue. More often it occurs during involution (contraction) of the uterus after childbirth, before the 40th day. Immediate surgical attention is also required;
- Malignancy of a myomatous node is the degeneration of a tumor from benign to malignant. According to research, it occurs in 1.5 - 3% of all cases, which does not detract from the danger of complications;
- The birth of a myomatous node with submucous myoma occurs with inversion of the uterus;
- Violation of a woman’s reproductive activity - development of ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous miscarriages, premature and complicated births, infertility;
- Development of purulent processes in the myomatous node and surrounding tissues. Inflammatory processes without medical attention can lead to severe septic complications.
Women diagnosed with uterine fibroids should be regularly monitored by a gynecologist. At the slightest change in your health, you should seek medical help to avoid all of the listed complications.
On the subject: Uterine fibroids during pregnancy - why are they dangerous? How to treat?
Other
An effective minimally invasive method for treating fibroids is uterine artery embolization (UAE). To carry it out under the control of angiography, a catheter is passed through the femoral artery to the myomatous node. A special embolic drug is released into the uterine arteries, which disrupts the blood supply to the pathological tissues of the uterus. They undergo necrosis, the symptoms of the disease disappear.
This method is distinguished by its speed of execution, a quick period of restoration of the patient’s normal functioning, and the absence of scars on the abdomen. After UAE, pregnancy is possible; the percentage of relapses is significantly lower than after surgical treatment.
How to treat uterine fibroids?
There are two main methods of treating uterine fibroids:
- Conservative treatment – with the help of medications and non-invasive procedures.
- Surgical treatment - through surgery.
The choice of treatment method depends on the severity of the clinical symptoms of uterine fibroids, the size of the fibroid node, the woman’s age, and the intention to have children in the future.
The conservative method is based on the use of hormonal drugs orally and by injection, as well as symptomatic therapy (pain relief, treatment of anemia, reduction of blood loss, etc.).
Conservative therapy is effective only in controlling tumor growth. It is impossible to eliminate uterine fibroids conservatively. Therefore, the non-surgical treatment method is used mainly in women of advanced childbearing age. At the same time, tumor growth is inhibited until the onset of menopause. At this time, there is a high probability of spontaneous resorption of the tumor.
Basic principles of conservative treatment of fibroids
Non-surgical treatment of uterine fibroids is a set of measures, including adherence to an appropriate diet, the use of immunomodulators, herbal medicine, approved physiotherapeutic procedures, and the use of hormonal medications.
The course of treatment consists of the following stages:
- Anti-inflammatory therapy for infectious processes in the gynecological area;
- Activation of the immune system with special drugs;
- Adjustment of diet and diet;
- Normalization of the endocrine system;
- Formation of an even psycho-emotional background;
- Elimination of bleeding;
- Treatment of anemia;
- Bringing the menstrual cycle back to normal.
When is surgery to remove the uterus for fibroids indicated?
Indications for radical surgical treatment of uterine fibroids:
- Tumor size from 12 weeks (a voluminous tumor compresses neighboring organs and blood vessels, interfering with their normal functioning);
- Rapid growth of myomatous node (from 4 weeks per year);
- Myoma causes massive bleeding;
- Severe pain syndrome;
- Torsion of the leg and necrotization of the myomatous node;
- Birth of a submucosal myomatous node;
- Combination of endometriosis and fibroids;
- Suspicion of malignancy of fibroids.
On the subject: Surgery to remove uterine fibroids - is it necessary? Complications and consequences
Uterine artery embolization is a modern unique method of treating fibroids
The essence of the method is to block the blood flow through the arteries feeding the myomatous node. This non-invasive surgery is performed in a cath lab. A catheter is inserted into the femoral artery, through which a special embolizing (artery-clogging) drug is administered. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and control of a radiocontrast agent. For a woman, everything is painless.
Subsequently, without blood supply, the tumor decreases in size and completely disappears. No relapses were observed after this treatment.
FUS ablation
MRI-guided FUS ablation of fibroid nodes is a non-invasive method for treating uterine fibroids. The essence of the method: heating the cells of the myomatous node using a directed ultrasound pulse with the aim of their death.
At the first stage of treatment, the doctor plans the entire process using MRI. At the second stage, while continuing to monitor the process using MRI, the doctor directs ultrasound pulses to the tumor node. The cells of the node heat up to a certain temperature, as a result of which they die. After this, the doctor performs targeted cooling of the tissue. There will be several such short ultrasound sessions, depending on the size of the tumor. MRI allows you to monitor the degree of tissue destruction and adjust the power of the ultrasound beam.
In general, FUS ablation can take up to 4 hours. The third stage of the procedure is a control magnetic resonance scan using a radiocontrast agent.
Advantages of the FUS ablation method:
- Non-invasive;
- No need for anesthesia, postoperative care, intensive infusion therapy;
- No complications or side effects – blood loss, fever, intoxication;
- Preservation of the uterus and reproductive activity, respectively;
- Short rehabilitation periods;
- No relapses in the development of myomatous nodes;
- High efficiency of the method even in the presence of multiple and large nodes;
- Significant reduction in fibroid size immediately after treatment;
- Quick relief from unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
During the procedure, the woman must lie still. Due to a long stay in a prone position, discomfort may occur in the neck, feet, and knees. Any changes in your condition should be reported to the nurse and the doctor providing treatment.
The following symptoms cannot be tolerated:
- Burning or stabbing pain in the lower abdomen;
- Stitching and shooting pains in the back, lower back, sacrum and legs.
On the subject: Treatment of uterine fibroids without surgery - 3 modern methods
Diagnostics
A gynecologist can recognize fibroids even at the stage of a bimanual examination of the patient. During the examination, the doctor also takes smears from the vagina and cervical canal for microflora and cellular composition to determine signs of malignant changes in the epithelium.
The main way to determine fibroids is an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. The size and shape of uterine fibroids, structure and possible signs of malignancy, and the nature of the blood supply are determined.
Hysteroscopy allows you to transvaginally penetrate the uterine cavity and, using a special device, examine everything there and take material for a biopsy. The method is used to study submucosal fibroids, as well as when, in addition to a uterine tumor, symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia (proliferation) are found.
If there are signs of proliferation of the uterine epithelium against the background of fibroids, separate diagnostic curettage is performed. Using a curette, the upper particles of the endometrium are cut off and the tissue is sent for examination to exclude signs of oncology.
Diagnosis of fibroids, in addition to instrumental tests, includes laboratory tests. Blood tests performed:
- General – finding signs of anemia (low hemoglobin, red blood cells, hematocrit).
- Biochemical – detection of metabolic disorders (levels of cholesterol, glucose, enzymes).
- On tumor markers - their appearance in the blood is a sign of malignant tumors of the uterus.
Medicines used in the treatment of fibroids
In conservative therapy, several groups of medications are used. Let's look at each in more detail.
Combined oral contraceptives
Combination of ethinyl estradiol and desogestrel:
- Mercilon;
- Marvelon;
- Novinet.
Combination of ethinyl estradiol with norgestrel:
- Ovidon;
- Rigevidon.
Treatment with contraceptive drugs containing combinations of 2 hormones is effective in reducing the severity of pain and bleeding. Therapy with such drugs can be expected to reduce the size of only those tumors that were initially up to 1.5 cm in size (more details: COCs (combined oral contraceptives)).
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
The action of these drugs is based on creating a temporary “artificial menopause” in a woman’s body. Under the influence of hormones, ovarian function is suppressed. Agonist drugs (analogues) of natural gonadotropin-releasing hormones (AGRH) inhibit the production of sex hormones of the pituitary gland, which affect the functioning of the ovaries.
Drugs in this group:
- Buserelin;
- Triptorelin (Diferelin, Decapeptyl, Decapeptyl-depot);
- Leuprorelin (Lukrin-depot);
- Goserelin (Zoladex).
Under the influence of AHRH, the ovaries “fall asleep”, ovulation does not occur, the uterine mucosa does not change cyclically - menstruation stops. This process is completely reversible; after discontinuation of the drugs, all functions are restored. Treatment lasts no more than 6 months. During this period, the size of the tumor can decrease by up to 50%, and the symptoms of fibroids become less pronounced.
Disadvantages of using drugs:
- Possible complete restoration of tumor size after cessation of treatment;
- Long-term (longer than 6 months) use of drugs is prohibited due to the high risk of osteoporosis and other complications of insufficient estrogen levels.
It is advisable to prescribe AGRH before surgery for uterine fibroids in order to reduce the size of the tumor.
Complete list of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists
Antiprogestogens
Like GnRH agonists, drugs in this group are used before surgery to remove uterine fibroids. The drug commonly used is Mifepristone (RU-486).
Under the influence of hormonal therapy, myomatous nodes decrease in size, and the symptoms of uterine fibroids weaken.
Antigonadotropins
Drugs used:
- Danazol (Danogen, Danoval, Danol, Vero-Danazol).
- Nemestral (active ingredient - gestrinone).
The effect of antigonadotropins is to reduce the intensity of symptoms without reducing the size of the tumor. Often, when using them, undesirable side effects occur (increased hair growth on the face and body, changes in the timbre of the voice, the appearance of rashes).
Antigonadotropins are used to treat uterine fibroids quite rarely, only in the absence of effect from treatment with other hormonal drugs.
Gestagens
Today, the use of gestagens is becoming less and less justified. Some gynecologists consider the use of gestagens to be effective because... With a lack of progesterone, tumor growth occurs. Many doctors, on the contrary, are categorically against the use of any gestagens for the treatment of fibroids. The mechanism of tumor formation is not based on the amount of any hormone, but on the imbalance of the woman’s entire hormonal system.
Currently, the use of gestagens is prescribed for the combination of uterine fibroids and endometrial hyperplasia.
Drugs used:
- Linestrenol (Orgametril, Escluton);
- Nor-ethisterone (Norkolut, Primolut-nor);
- Medroxyprogesterone acetate (Provera, Depo-Provera).
Latest research into drug treatment for fibroids
Scientists at the University of Brussels conducted research at St. Luke's Hospital to understand how the contraceptive drug Esmya acts on uterine fibroids. The main active ingredient in Esmiya tablets is ulipristal acetate. And since in the process of development and growth of fibroids, the level of not only estrogen, but also progesterone, is important, it was decided to study the effect of the drug Esmya and gestagen blockers.
The experiment involved 550 women who were indicated for surgical treatment of uterine fibroids. All subjects were divided into two groups. One group was given a placebo as “treatment” for 3 months, the other was given Esmiya tablets.
At the same time, another study was conducted: a comparison of the effect of the drug Esmya and injections of gestagen hormone blockers.
The results of two experiments revealed the following:
- After using the drug Esmya, the size of uterine fibroids is reduced, the intensity of the symptoms of the disease decreases;
- 90% of the patients studied noted a positive effect from taking Esmiya tablets;
- In 50% of patients taking Esmya, there was no need for surgical treatment (the effect is similar to the use of injections of gestagen blockers);
- After taking Esmiya tablets, there are no such side effects as when using injections of hormone blockers - hot flashes, bone degeneration;
- After treatment for 6 months, no resumption of tumor growth was observed, whereas after stopping injections of hormone blockers, myomatous nodes began to grow again.
It is likely that thanks to the efforts of scientists, the problem of uterine fibroids will soon be solved much faster and easier than at present.
On the subject: Hog uterus and red brush for uterine fibroids / Homeopathic medicines
Complications
The main complications of uterine fibroids that women with unrealized reproductive function face are infertility and miscarriage. They are associated with deformation of the uterine cavity by nodes. This leads to the impossibility of complete attachment of a fertilized egg to its wall. If the embryo manages to gain a foothold, the course of pregnancy and childbirth can be complicated. This is manifested by constant symptoms of threatening miscarriage, signs of fetal hypoxia due to insufficient blood supply to the placenta, and an anomaly of labor occurs - discoordinated contractions and weakness of pushing.
Signs of tumor malignancy are observed only in 0.5-0.7% of cases. This occurs in nodes with active growth and with prolonged exposure to unfavorable factors.
Prevention of uterine fibroids
Since uterine fibroids are an urgent problem, due attention should be paid to the prevention of this disease from a young age. Although there is no single theory for the occurrence of fibroids, it is worth trying to prevent all possible causes of the tumor.
Stress. Cultivating psychological comfort within yourself is what every woman should strive for. Of course, it’s impossible to completely avoid stress. However, you need to learn how to react correctly to conflict situations, not to carry resentments, unspoken claims and many years of experience in your soul.
Healthy lifestyle. A balanced diet, optimal physical activity, sufficient time in the fresh air, hardening procedures, adherence to work and rest schedules - seemingly banal truths can truly help in maintaining women's health.
Controlling your body weight will help you avoid obesity, which, as we have indicated, is a risk factor for the development of uterine fibroids. Every extra 10 kg of weight increases the likelihood of developing the disease by 20%.
The diet should include a sufficient amount of fresh vegetables and fruits, whole grains, and replace simple carbohydrates with complex ones. You should drink plenty of clean water, especially during the hot season.
Regular physical exercise helps improve the functioning of the endocrine system in general and the gonads in particular. Accelerating blood flow improves the supply of oxygen to the pelvic organs, which improves all metabolic processes in the gynecological area.
After physical activity, it is optimal to carry out water hardening measures - contrast showers, douches, rubdowns.
Medical supervision. Every woman should be examined by a gynecologist at least once a year, or better yet, every six months. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe an ultrasound examination of the pelvis. In no case should such an examination be neglected, based on the fact that “nothing is bothering you.” Detection of fibroids in the early stages will allow for non-invasive or conservative treatment.
Contraception, family planning. It is extremely important to organize rational contraception to avoid termination of an unwanted pregnancy. Issues of contraception should be discussed with a gynecologist. Often the best choice is to use oral contraceptives, which is another preventive factor against the occurrence of uterine fibroids. You just need to choose the right drug.
If a young woman has a genetic predisposition to the development of uterine fibroids, it is necessary to continue her first pregnancy.
Childbirth at the optimal age (the first - up to 22 years, the second - up to 25, the subsequent - up to 35 years) followed by breastfeeding reduces the risk of tumor development, and sometimes contributes to the resorption of existing fibroids. The state of motherhood and lactation ensures not only a woman’s harmonious psychological state, but also normalizes the level of sex hormones in the body.
Harmonious intimate life. Regular, full-fledged sex life with the obligatory achievement of orgasm with each sexual intercourse significantly reduces the risk of developing any gynecological tumors, including fibroids. This is due to the acceleration of blood flow throughout the body and in the pelvis in particular, a comfortable psychological state, and increased functioning of the endocrine system.
"Climate control". All women should remember to prevent both general and local (pelvic area, hips, buttocks, feet) hypothermia. You should avoid staying in a wet swimsuit for a long time, as well as sitting on wet ground, stone and other cold surfaces, even on hot days in summer.
The linen must be natural, because... Synthetic fabrics contribute to rapid freezing in the cold, and sweating in the heat. Clothes that are too tight and constrict the body can also disrupt heat transfer.
If symptoms of inflammatory processes occur (pain, discharge, increased body temperature), you must immediately consult a gynecologist to prescribe timely treatment. If you don’t pay attention and wait for “everything to go away on its own,” you can contribute to the development of a focus of chronic inflammation.
Ultra-violet rays. Women should not overexpose themselves to the sun and solariums under direct ultraviolet rays. Before sunbathing, you need to apply a special protective cream to your skin.
Vitamins and microelements. In addition to eating healthy foods, periodic additional intake of vitamin-mineral complex preparations is important for a woman. It is better to discuss this particular step with your doctor, who will prescribe a complex containing iodine, iron, magnesium, copper, selenium, zinc, as well as vitamins A, C, E with antioxidant properties.
Recommendations
Now, knowing everything about fibroids, you need to figure out how you can fully live with this disease and not aggravate its symptoms. To do this, it is recommended to follow some rules:
- Don't overheat. An increase in body temperature increases blood flow in the pelvic vessels, which improves blood supply to the fibroids. It is forbidden to go to the sauna, bathhouse, or use heating pads on the lower abdomen.
- Do not lift heavy objects. This provokes a violation of the trophism of the node, its torsion or separation from the base.
- Do not stay in the sun for a long time, do not go to the solarium. UV irradiation promotes the growth of tumor processes.
- No smoking. Nicotine is one of the most active provocateurs of fibroids.
The diagnosis of fibroids should not cause panic. This gynecological disease responds well to various treatments if you consult a specialist in a timely manner, and following all medical recommendations allows you to live a full life without experiencing any unpleasant symptoms.
Conservative way
It will only be offered in cases where:
- the size of the neoplasms is small;
- symptoms are absent or of little concern;
- no heavy bleeding;
- the fibroid is located in the muscle or under the outer layer of the membranes and “sits” on a wide base, without a “leg” that could twist;
- if a woman wants to preserve her reproductive function at all costs.
The following drugs are usually prescribed:
- if the node is no more than one and a half centimeters - combined contraceptives, which are taken orally;
- androgenic drugs that suppress the production of hormones by the ovaries (used long-term and constantly, more than six months);
- mifepristone or other antiprogestogens that suppress tumor growth (also long-term);
- antigonadotropins, which prevent the node from growing further, but do not contribute to its resorption;
- Mirena hormonal device (contraindicated if nodules grow in the uterine cavity);
- drugs that create “artificial menopause” (have a bad effect on a woman’s body, so they are used extremely rarely);
- anti-inflammatory and anti-anemic therapy;
- medications to stimulate the immune system.
All these medications have a lot of side effects and contraindications and are prescribed only by the attending physician.
No self-medication is acceptable unless you want to upset your hormonal balance and get several ailments in addition to the one you are being treated for.
Folk remedies (extracts of various plants, such as celandine, etc.) and homeopathy are not considered effective enough to be considered as a prospect for getting rid of the disease.
Treatment without surgery with folk remedies
Alternative medicine suggests using medicinal plants containing phytoestrogens, tannins, essential oils, vitamin compounds and beneficial microelements to treat uterine fibroids. Decoctions and tinctures prepared from plants, when taken orally, help eliminate the inflammatory process, stabilize hormonal levels, and stop the growth of pathogenic cells. Many decoctions are used for douching or tampons.
Traditional methods should be used in combination with a conservative course of treatment, after coordinating the process with a doctor, in order to avoid an allergic reaction or hormonal imbalance.
Burdock root
You need to take 5 g of crushed plant root and pour 500 ml of boiling water. Then leave the composition for 12 hours. You need to take 100 ml per day for a month.
Infusion of boron uterus and red brush
The mixture of plants crushed to powder (1 tbsp) is poured with 200 ml of boiling water and the resulting composition is warmed in a water bath for 20 minutes. Filter the tincture and take 1 tbsp 3 times a day an hour before meals. l. within 14 days. Afterwards, take a break for 10 days and, if necessary, repeat the course.
Flax seeds
Contains phytoestrogens and elements of anti-carcinogenic and anti-inflammatory action. You need to pour 30 g of seeds into 500 ml of boiling water and keep in a water bath for 10 minutes. The resulting broth should be filtered and taken 1/2 cup 30 minutes before meals.
Celandine
After taking a decoction of this unique plant, small fibroids can resolve without intervention in 1 month.
1 tbsp. l. Finely chopped plant is poured with 20 g of vodka. The resulting composition is infused in a place protected from natural light for 14 days. Afterwards it is filtered and consumed for a month according to the following scheme: on the first day, take 1 drop of tincture dissolved in 100 ml of water. Gradually the number of drops is increased to a serving of 15 drops, after which you need to decrease 1 drop daily.
Birch chaga
The plant has a strong antitumor effect. The mushroom is poured with boiling water and kept for about 6 hours. Then the water is drained and the mushroom is squeezed through cheesecloth. The already softened chaga is crushed and poured with previously drained water, preheating it to 60 degrees. The resulting composition is infused for 2 days. Take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day for 2 months.
Potato
To treat uterine fibroids, both freshly squeezed juice of the root vegetable and a decoction of its flowers are used.
Potato juice should be taken in an amount of 100 ml per day in the morning on an empty stomach for 3 months.
Potato juice is also used for douching. Fresh root juice is mixed in equal parts (1:1) with freshly squeezed carrot or celery juice. The composition must be prepared each time before the procedure.
The decoction is prepared from blossoming potato flowers, which are collected in the morning, dried and crushed. You need to take 2 tsp. raw materials and pour 400 ml of boiling water, leave the resulting composition for 2 hours. It is recommended to take the tincture 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day before meals.
Motherwort tincture
1 part of dried motherwort flowers and leaves should be poured with 5 parts of alcohol (70%). The composition should be infused in a dark place for 30 days, shaking occasionally. After time, the tincture must be filtered and taken 30-50 drops 4 times a day.
Treatment with propolis
20% propolis tincture is taken orally with water or milk three times a day, 20 drops, before meals for 20 days. Afterwards you should take a break for 10 days and repeat the course.
You can make tampons soaked in an aqueous solution of propolis (you cannot use alcohol tincture for this purpose) or propolis oil. The procedure should be done three times a day for 10 days, then take a break for 5 days and repeat the course if necessary.
Propolis oil is prepared by mixing crushed propolis (20 g), butter (20 g) and vegetable oil (60 g). The composition should be homogeneous.
Uterine fibroids often cause heavy bleeding. To reduce the amount of bleeding, it is recommended to use decoctions or tinctures of barberry, nettle, yarrow, shepherd's purse, cloves, burnet, and burdock.
Symptoms and signs on ultrasound
An ultrasound examination is carried out in two ways: through the abdominal wall and through the vagina. Thanks to the diagnostics, you can get a clear picture of the condition of the tumor and its structural features.
They are:
- roundness and shape of fibroids;
- heterogeneity of structure;
- clarity of boundaries and external contours;
- the presence of a weak signal when approaching the edge of the anomalous area;
- signal enhancement in the center of the tumor.
With a more accurate study using Doppler - a special technique that, unlike the usual gray scale mode, is able to assess the state of blood flow, it is possible to identify blood flows that are not typical for the norm. When studying the structure of fibroids, its heterogeneity is determined in the form of lighter and darker areas. Ultrasound is used to measure the fibroids, which in the case of multiple nodes characterizes the largest of them.
What should you avoid if you have fibroids?
With the development of this disease, certain rules must be observed that will not allow this type of pathology to quickly progress:
- A sick woman should not use procedures that are based on a thermal effect (hot baths, saunas, steam baths).
- When choosing a holiday destination, choose countries with a temperate climate; in summer, avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight. Ultraviolet radiation can lead to sudden exacerbation and progression of the disease
- Allow at least 8 hours of sleep per day.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Follow all instructions prescribed by the doctor.
The effectiveness of therapy for this disease can only be achieved if the rules and regulations are followed before and after surgery.
In the event that the operation has not been performed and treatment is carried out with medication or using traditional medicine recipes, the patient should know that this type of therapy is not effective and does not give much result, and can sometimes cause harm to health (unreasonable and illiterate use of medicinal plants).
What will happen if left untreated?
Experts disagree about the need to treat fibroids. Some people prefer to watch and wait, as there are situations when the hormonal levels return to normal and the tumors resolve. This is especially true for young women of childbearing age and girls going through puberty. Vitamin complexes and proper nutrition are prescribed as aids.
Another category of specialists insists on immediate treatment, including hormonal agents, in order to promptly prevent further tumor growth and preserve the ability to bear children.
The decision is made after a series of analyses:
- blood,
- urine,
- for hormones
- smears for PPIs,
- Ultrasound diagnostics.
The fact is that if fibroids are not treated or folk methods are used, self-medication can lead to serious consequences - disruption of the functioning of other organs of the reproductive system, neighboring organs, and the development of other neoplasms. Considering that in the initial stages the disease occurs without symptoms, women are recommended to be checked annually, twice a year, by a gynecologist.
Popular treatments
Can uterine fibroids be treated? The answer is yes, they are treated with conservative and surgical methods. Conservative treatment is carried out for fibroids up to 10-11 weeks . This includes drug therapy, diet therapy and physical therapy. A set of measures stops tumor growth; such treatment is especially effective during reproductive age, during menopause and postmenopause.
Clinical picture of the disease with the development of complications
In the early stages of the disease, complications do not occur. Negative consequences are observed with long-term existence of the tumor, rapid growth of the node, and refusal of therapy. Symptoms change when the following complications occur:
Compression of the pelvic organs
If the tumor is located on the anterior wall of the uterus and puts pressure on the bladder, the woman complains of frequent urination and urine leakage. Possible urinary incontinence due to disruption of the sphincters. In severe situations, urinary retention is observed. Prolonged compression of the urinary tract leads to the development of hydronephrosis and renal failure.
When the myomatous node puts pressure on the bladder, the woman complains of frequent urination, even to the point of urinary incontinence.
If the tumor is located on the back wall of the uterus and puts pressure on the intestines, constipation occurs. Defecation delay is persistent and not amenable to drug therapy. Constipation is accompanied by increased gas formation and bloating. Intestinal obstruction may develop.
It is also useful to read: The use of hormonal drugs in the treatment of uterine fibroids
Iron-deficiency anemia
Anemia is a natural result of heavy menstruation and uterine bleeding. A general blood test helps to recognize the problem. The examination reveals a decrease in hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells. Low hemoglobin leads to severe weakness, dizziness and even fainting. The patient has pale skin and rapid heartbeat. The woman’s condition deteriorates significantly, her performance decreases, which often becomes the reason for a visit to the doctor.
It is important to know
It is possible to increase hemoglobin in case of anemia with the help of iron supplements, but this will not solve the problem. It is necessary not only to increase hemoglobin, but also to eliminate the cause of this condition - uterine bleeding. When anemia develops due to blood loss, the issue of surgical treatment of uterine fibroids is decided.
Uterine bleeding is often accompanied by anemia. At the same time, the woman feels weak, dizzy, and constantly tired.
Tumor necrosis and infection
Degenerative changes in myomatous nodes are observed when the nutrition of the tumor is disrupted. The cause may be torsion of the legs of the subserous formation, compression of the veins, blood stagnation and other conditions. Tissue edema develops, followed by aseptic inflammation. The main symptoms of the disease are accompanied by additional signs:
- The pain in the lower abdomen becomes acute, strong, cramping;
- Tension of the abdominal wall muscles becomes noticeable;
- Nausea occurs and vomiting is possible.
Necrosis of fibroids leads to the addition of a secondary infection and the development of inflammation in the node. An infected tumor may cause high body temperature, chills and other signs of intoxication. The cause of fever is the breakdown of fibroids. In this condition, urgent hospitalization and surgical treatment are indicated.
With necrosis or infection of the tumor, body temperature rises sharply, which is one of the signs of intoxication in a woman’s body.
Malignant degeneration
Today, gynecologists say that fibroids are not capable of degenerating into a malignant tumor, but they warn that a node in the uterus may turn out to be a sarcoma. This dangerous pathology has no distinctive symptoms and develops in the same way as leiomyoma. The following signs speak in favor of sarcoma:
- Rapid growth of the node - 4 or more weeks per year according to ultrasound;
- Frequent uterine bleeding, difficult to treat;
- The appearance of complications from neighboring organs (possible spread of tumor metastases);
- Enlarged inguinal lymph nodes;
- Unmotivated weight loss, prolonged increase in body temperature are signs of intoxication in a malignant tumor.
All these symptoms should be a reason to immediately consult a doctor. If sarcoma is detected in a timely manner, there is still a chance of saving the uterus. In advanced cases, radical surgery cannot be avoided.
If in the early stages of sarcoma development organ-saving treatment methods are possible, then in the later stages of the disease the only solution is hysterectomy.