Hydrocele or testicular hydrocele in men is a disease associated with the accumulation of fluid in its membranes. The amount of serous fluid can vary from 20 to 200 ml. But, in rare cases, it can accumulate up to 3 liters. Hydrocele occurs in both adult men and children. Babies may have congenital hydrocele of the testicles, which is normal for most newborns. In adulthood, this pathology is acquired.
What is testicular hydrocele and why does it occur?
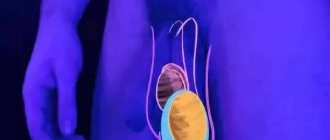
The male gonads are enclosed in 7 dense membranes. With dropsy, fluid accumulates in a saccular formation in the deepest membranes. Hydrocele on the left is manifested by swelling of the left side of the scrotum. It takes on a pear-shaped shape, so the gonads are difficult to palpate. Hydrocele of the right testicle manifests itself with the same symptoms, only on the right.
At an appointment with an andrologist and urologist, men often ask why dropsy of the testicular membranes appears. The causes of hydrocele depend on the form of the disease:
- congenital - caused by abnormal formation of the organs of the reproductive system during intrauterine development;
- acquired - occurs due to an imbalance between the absorption and secretion of serous fluid by the membranes of the testicles.
Dropsy in mature men is provoked by external and internal factors:
- diseases of the gonads;
- inflammation of the epididymis;
- scrotal injuries;
- testicular torsion;
- operations in the perineal area;
- disruption of lymph flow;
- radiation therapy.
In 1/3 of cases, testicular hydrocele occurs against the background of infectious diseases - bacterial prostatitis, gonorrhea, tuberculosis.
Moderate severity of symptoms of testicular hydrocele causes late consultation with a doctor.
In isolated cases, 1-3 liters of fluid accumulate in the scrotum area. Dropsy affects men who suffer from metabolic diseases and heart failure.
Classification of pathology
The following types of hydrocele are distinguished:
- Encapsulated.
- Infected.
- Shingles.
- Unspecified.
Depending on the location, the disease is:
- Communicating hydrocele of the testicle spreads to the entire peritoneal cavity.
- Non-communicating - passes in isolation, and fluid accumulates on the right (dropsy of the right testicle), on the left (dropsy of the left testicle), and less commonly there is a bilateral hydrocele.
- Hydrocele of the spermatic cord.
Based on the causes of testicular hydrocele in a man, the pathology is:
- Symptomatic (associated with another disease).
- Idiopathic (primary hydrocele or the underlying cause cannot be identified).
Signs of hydrocele
The type of disease determines what hydrocele looks like. According to the nature of the course, acute and sluggish forms of hydrocele in men are distinguished. In the first case, the symptoms are pronounced, and in the second they are almost absent or increase very slowly. Typical signs of fluid accumulation in the membranes of the testicles include:
- enlargement of the right or left side of the scrotum;
- no pain;
- a decrease in the amount of fluid is observed after sleep.
In the presence of an inflammatory process in the testicles, complaints arise of redness of the skin in the groin area, chills, fever, acute pain in the perineum.
Chronic dropsy of the testicular membranes is indicated by:
- discomfort in the groin area;
- enlargement of the scrotum;
- difficulty urinating;
- gait disturbance;
- difficulties during sexual intercourse;
- decreased fertility.
To the touch, dropsy is defined as an elastic flowing seal. Visually, it resembles a pear, the base of which faces the anus. Palpation causes discomfort, but the color of the skin in the groin area does not change.
Dropsy is fraught with testicular atrophy and infertility. If the shape or size of the scrotum has changed, consult your doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
Prevention
Hydrocele of the testicle is characterized by an increase in the size of the scrotum due to the inflammatory process occurring in it. The rate of development of pathology directly depends on the functioning of the patient’s immune system and the presence of concomitant diseases, both acute and chronic. To avoid hydrocele, doctors recommend avoiding traumatic injury to the genitals.
It is equally important to streamline your sex life, since among the causes of pathology development is very often an infection that can be sexually transmitted. In addition, it is necessary to prevent parasitic diseases, and if they occur, carry out timely treatment.
In more than half of the cases, testicular hydrocele provokes an inflammatory process in the appendages, the treatment of which is complicated by a high risk of relapse. Therefore, it is important for every man to follow simple preventive rules that will help avoid hydrocele.
Diagnostics
Hydrocele of the testicular membranes manifests itself with characteristic symptoms, therefore it is diagnosed by a urologist at the examination stage. To determine the size of the dropsy and the volume of serous fluid in the membranes of the testicles, they undergo a comprehensive diagnosis:
- Diaphanoscopy is an examination of the scrotum in a darkened room. If there is fluid in the gonads, the skin takes on a pale pink tint.
- Ultrasound of the scrotum is a non-invasive examination of the testicles using ultrasound waves. During the examination, the doctor distinguishes dropsy from benign or malignant neoplasms.
- MRI of the groin area – obtaining a layer-by-layer image of the scrotal organs. Helps distinguish testicular hydrocele from spermatic duct cyst, varicocele, pyocele, inguinoscrotal hernia.
The most informative method of examination for testicular hydrocele is ultrasound. If there are symptoms of inflammation, a general blood and urine test is performed. If the concentration of leukocytes exceeds the norm, PCR diagnostics is required. During the analysis, the causative agent of the infection is determined, which facilitates the selection of appropriate medications.
Causes
In newborn boys, testicular hydrocele is considered physiological and is associated with the developmental characteristics of their body. This pathology goes away on its own over time and does not require treatment. The main causes of testicular hydrocele in an adult man are:
- A traumatic injury that can be caused by a blow to the groin area or during sports training.
- Inflammation of a nonspecific nature (orchitis, epididymitis, etc.).
- Infectious diseases (gonorrhea and other STIs, tuberculosis, etc.).
- Neoplasms in the scrotum.
Immunologist Ermakov Georgy Aleksandrovich will talk about the causes, types and symptoms of the disease:
- Varicocele.
- Severe heart failure.
- Filariasis is a disease that develops when various parasites enter the inguinal lymph nodes.
- Liver failure.
- Hydrocele after surgery (for example, removal of an inguinal hernia, etc.).
Congenital pathology
Approximately 8% of newborns are diagnosed with congenital hydrops. It is associated with the peculiarities of intrauterine development, when the formation of the testicles occurs in the abdominal cavity. By the time of birth, they should descend into the scrotum, and the duct connecting the scrotum to the peritoneum should be overgrown. If this process is disrupted, the boy may develop a hydrocele or inguinal hernia.
How to treat undescended testicles in boys - detailed article.
As a rule, the pathology resolves itself during the first year of the child’s life. Therefore, the baby needs to be regularly shown to a specialist.
Acquired dropsy
Hydrocele of the testicular membranes is diagnosed in approximately 5% of adult men. In most cases, the cause of its occurrence is inflammation in the appendages. The disease can be a consequence of surgery, radiation and chemotherapy, or impaired lymph flow.
Inflammation of the epididymis (epididymitis)
How to treat hydrocele in a man
Hydrocele in men is treated surgically. Drug therapy is indicated for patients whose dropsy is caused by inflammation of the testicles.
Puncture and sclerotherapy
In the absence of complications, hydrocele on the right or left is eliminated by puncture aspiration of viscous secretion:
- the skin in the groin area is disinfected;
- an aspiration needle is inserted into the right or left side of the scrotum;
- Use a syringe to remove the accumulated liquid.
To permanently get rid of testicular hydrocele, sclerosing solutions - carbolic acid, polidocanol - are injected into the pathological cavity. Their action is aimed at gluing the walls of adjacent membranes of the gonads.
Currently, puncture followed by the introduction of sclerosing solutions is almost never used. This is associated with frequent recurrences of testicular hydrocele.
Surgical methods for treating hydrocele
Bilateral hydrocele in men is treated exclusively by surgery. How to cure testicular hydrocele is determined by the doctor. The choice of technique depends on the amount of accumulated fluid:
- Winkelmann operation. The anterior surface of one of the testicular membranes is cut and turned inside out. To make the seam invisible, the edges of the membranes are sewn behind the testicles.
- Operation Lord. To remove the viscous secretion from the cavity of the testicles, the membranes are dissected. During the operation, the gland itself is not separated from the surrounding tissue. This prevents disruption of the blood supply to the gonads.
- Bergman's operation. The inner lining of the testicle is partially excised, after which the edges are sutured. To avoid purulent complications, patients take antibiotics for a week.
Surgical methods for treating dropsy in men do not differ significantly. The most appropriate method for plastic surgery of the tissue membranes is determined during surgery.
Will folk remedies and pharmaceutical medicines help?
Medicinal and traditional methods of treatment are used exclusively to reduce the severity of symptoms. Dropsy disease is often caused by infectious inflammation of the gonads. To destroy pathogenic flora and relieve symptoms, the following are used:
- antibiotics – Moxifloxacin, Azithromycin, Cefixime;
- non-narcotic analgesics – Ketorol, Naproxen, Ibuprofen;
- blood microcirculation correctors – Angionorm, Oksibral, Vasoket.
Antibacterial therapy should be prescribed only by a urologist in the presence of absolute indications - orchitis, appendage abscess, epididymitis.
To reduce swelling in the scrotum area, use the following folk remedies:
- Black radish. The core of the vegetable is cut out. 50 ml of melted honey is poured into the resulting bowl. After 4-5 hours, honey mixed with juice is poured into a glass container. Use 1 tsp. 4 times a day 20 minutes before meals.
- Onion. Grind 2 onions in a blender. Fall asleep 5-7 tbsp. l. sugar and leave for 7-10 hours. Squeeze the juice out of the onion pulp through cheesecloth. Drink 30 ml in the morning on an empty stomach.
Alternative methods of treating dropsy are resorted to on the recommendation of a urologist. It is undesirable to use folk remedies for irritable bowel syndrome.
Nutritional Features
When treating dropsy, it is recommended to follow treatment table No. 5, which was proposed by Pevzner. As part of the dietary program, the consumption of harmful foods is limited - alcohol, eggs, canned food, processed foods, fatty meats. Daily salt intake is reduced to 3-4 g.
The basis of the diet for hydrocele of the testicles should be:
- buckwheat;
- White cabbage;
- fresh cucumbers;
- parsnip;
- dietary meat;
- eggplant;
- soya beans.
Before consumption, the products are boiled, stewed or baked in the oven. The diet is followed until complete recovery.
You should not overuse foods with coarse fiber - rice, bran, corn. They provoke constipation and increased pressure in the pelvic organs.
Treatment
In an adult man, testicular hydrocele cannot go away on its own. It can only be treated surgically.
The exception is acute inflammation. In this case, the patient is prescribed drug therapy to eliminate the inflammatory process (taking antibacterial, decongestant and anti-inflammatory drugs) and wearing a special support bandage.
After the concomitant pathology is cured, the tissue structure, blood circulation and lymph flow in this area are restored, and the amount of fluid gradually decreases to physiological levels.
Puncture
If surgical intervention is not possible, the patient is treated without surgery. For this, hydrocele puncture is used, during which hydrocele fluid is removed from the cavity. But such a procedure carries the risk of various complications.
Treatment of the disease using puncture
Surgical intervention
Direct indications for the patient to undergo surgery are the presence of severe pain and the risk of testicular atrophy. There are several methods for doing this:
- Lord's operation for hydrocele involves cutting the sac in which fluid accumulates and removing it.
- Winkelmann operation - the incision is made to the vaginal membrane. Liquid is pumped out of it through puncture. Next, the testicle is examined after dissecting its membrane. The shell is stitched after first turning it inside out.
- The Bergman operation is considered effective in cases of large hydrocele. During this procedure, the testicular membrane is opened, partially removed, and the remaining tissue is stitched together.
Performing Bergman surgery
The doctor will decide which surgical procedure to choose based on the causes and nature of the pathology. For example, when thickening egg membranes, only the Bergmann method is used. Lord's method is not suitable if the disease has become chronic, since the testicle membranes in this case become hard and their corrugation will spoil the aesthetic appearance of the scrotum.
The operations of Bergmann and Winkelmann are considered more traumatic than the use of the Lord method. This is due to testicular hypotrophy; as a result, the consequences after surgery may be a violation of the synthesis of sperm and the hormone testosterone. In this case, Bergmann's method can only be used in cases where the dropsy is not communicating.
Urologist Kuzma Nikolaevich Milenin talks about modern methods of therapy:
Children are operated on under general anesthesia, while local or general anesthesia is used for adult patients. During the postoperative period after hydrocele, the patient is recommended to wear tight swimming trunks for at least 30 days and use a scrotal jock strap.
As for the cost of the operation, using the Bergman method will cost 15-25 thousand rubles, the Winkelmann method - 11-20 thousand rubles, and the Lord operation - about 25 thousand rubles.
Rehabilitation after surgery
Regardless of what type of operation was performed, during the postoperative period the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy.
Within 10 days after surgery, the sutures dissolve on their own. After this, the man can return to the normal rhythm of life. However, heavy physical activity and sex after surgery should be avoided for at least 1-2 months.
For several months, the patient may experience swelling of the scrotum, which is considered completely normal. But if at this time the patient’s general condition worsens, the temperature rises or there is redness in the area where the operation was performed, then he needs to consult a doctor.
Use of folk remedies
For hydrocele in men, the choice of treatment methods should be individual and prescribed only by the attending physician based on diagnostic data. Self-medicating with such a pathology can be very dangerous due to possible complications. Typically, treatment for hydrocele involves surgery. At home, treatment with folk remedies can sometimes be used, which help to avoid surgical intervention, complications after surgery, and also reduce the period required for recovery. But before using them, you need to consult your doctor.
Judging by patient reviews, traditional therapy can be quite effective. For this use:
- Pea compress. To prepare it, you need to boil the peas for 1 hour. After this, strain the broth and soak a piece of cotton cloth in it, which is applied to the sore spot for 15-20 minutes. It is recommended to carry out the procedure 1-2 times a day. If after 3-4 days the patient does not feel relief and the scrotum continues to enlarge, then treatment should be stopped and a urologist should be consulted.
- Parsley decoction. For its preparation it is allowed to use only fresh, juicy greens. Pour 800 g of parsley into 1 liter of milk and keep in a warm oven for about 3-4 hours. After this, strain the product and drink 50 ml of the medicine every hour. The volume of product obtained from this quantity of ingredients must be used within 24 hours. Afterwards, you need to prepare a new portion.
The photo shows the preparation of a pea compress.
- Infusion of coltsfoot and clover. Dried medicinal herbs are taken in equal quantities, poured with boiling water and infused for 30 minutes. The remedy, which should be taken 3-4 tablespoons 4-5 times a day, effectively eliminates all symptoms of hydrocele. This medicine has an anti-edematous effect and helps remove accumulated fluid from the scrotum.
- Calendula ointment. Calendula decoction and baby cream are mixed in equal quantities. The ointment is applied to the damaged area overnight. You need to put a piece of gauze on top and put on warm underwear. The procedure must be carried out until the signs of hydrocele disappear.
- At the initial stage of the disease, chamomile-based products are effective. It is advisable to take freshly picked flowers. They are twisted through a meat grinder, and the resulting pulp is applied to the diseased testicle. After 20-30 minutes, the paste can be washed off with warm water. You need to apply the product to the sore spot three times a day for 10 days. This paste has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- A decoction of a collection of herbs (sage, chamomile, jaundice and black currant leaves), taken in equal proportions. The herbs are brewed with boiling water, allowed to settle, filtered and taken 100 ml before meals.
- Lotions made from sheep bile mixed with natural honey.
All traditional methods of treatment are safe and effective, but before using them, it is important to consult a doctor.
Nutritional Features
Fatty and spicy foods can provoke the growth of dropsy. During treatment, you should also exclude carbonated and alcoholic drinks, strong coffee and tea from your diet. During this period, you should consume more of these foods:
- Pumpkin juice.
- Onion juice with sugar.
- A decoction of dry watermelon rinds.
- Grape.
- Eggplants, cucumbers and cabbage.
For swelling in the scrotum area, you need to drink half a glass of pumpkin juice every day. Pumpkin perfectly removes excess water from the body
- Black radish juice.
- Grated horseradish root with lemon.
- Apples.
- Citruses.
A small pumpkin seed contains great health benefits for men. If you combine honey and pumpkin seeds, you will get an excellent remedy for prostatitis. Read more here.
Rehabilitation in the postoperative period
After surgical treatment of dropsy, complete rest for 2-3 days is recommended. To avoid complications, men should:
- change the bandage in the operated area once a day;
- limit physical activity;
- wear compression garments;
- take antibiotics prescribed by a urologist;
- monitor body temperature and general well-being;
- give up sports and sex for at least 4-5 weeks.
It is not advisable to lie on your stomach for a week. This is dangerous due to increased pressure in the pelvic organs and suture divergence. Urologists strongly recommend wearing loose cotton underwear. If there is no discomfort in the groin, the sutures are removed on the ninth day after surgery.
Symptoms and signs
Typically, infants do not experience any discomfort. Symptoms of hydrocele in a child are noticed by parents while caring for the baby, or by doctors performing a routine examination.
The first signs of the disease allow you to recognize the disorder:
- Swelling and unnatural size of the scrotum. The substance, getting from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum, causes deformation of the testicles.
- Asymmetry and some swelling. Often 1 testicle is affected. In this case, the right or left side of the scrotum increases.
- Marked mobility of the skin of the scrotum. Excess exudate improves the sliding of epithelial tissues.
- Normal urination. There is no disturbance in the outflow of urine in infants. Babies do not experience pain or discomfort when passing urine.
We recommend additional reading: Preparation of dill water for babies and newborns at home
With the further course of the disease, the following is noted:
- The appearance of intoxication symptoms. The child develops a fever, loss of appetite, and sleep disturbances. He needs emergency medical care in a hospital setting.
- Formation of inguinal hernia. An increase in intra-abdominal pressure leads to the descent of the vaginal duct into the intestine and the formation of a hernial protrusion.
- In advanced conditions, urine excretion is delayed and pain occurs.
Prognosis for hydrocele
With timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable in 90% of cases. Negative consequences and complications arise when 500 ml of serous effusion accumulates around the testicles. In such cases, postoperative complications occur more often:
- seam divergence;
- prolonged swelling of the scrotum;
- keloid scars in the operated area.
Possible long-term consequences include recurrence of dropsy in men. Infertility occurs only when the spermatic cord is damaged during surgery or due to purulent inflammation of the gonads.
General treatments
If the cause is inflammatory and not particularly advanced, testicular hydrocele in men, treatment requires elimination of the infection, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and decongestant therapy is used. The drug option is selected strictly according to individual indicators and it is necessary to complete treatment without interrupting therapy after the disappearance of primary symptoms.
Appointment with a urologist: preparation for examination, diagnosis and treatment measures
It is recommended to wear a jockstrap until the underlying disease is completely healed. As soon as the tissue structure, blood supply, and lymph flow are restored, the volume of serous accumulation between the membranes decreases to a standard level. Such cases are rare, so most often it is necessary to operate on the scrotum area, and you can also try to cope with the problem using traditional methods.
Important! A patient with contraindications to surgery due to age or other reasons is offered testicular puncture with pumping out of serous accumulation. However, it should be remembered that the procedure does not have a therapeutic effect and after a short time the liquid will appear again. Therefore, such treatment of testicular hydrocele without surgery in men is prescribed quite rarely.
Risks and complications
A small dropsy does not cause discomfort. Scrotal asymmetry is often not considered a serious reason to see a doctor. In 30% of cases, several years pass between the first symptoms of hydrocele and examination in the clinic.
Delayed treatment of the disease causes male infertility and sexual dysfunction.
Possible complications of dropsy in men include:
- testicular atrophy;
- decreased potency;
- delayed ejaculation;
- urinary disturbance;
- pyocele (purulent inflammation of the testicles).
In half of the cases, men turn to a urologist for reproductive dysfunction - impotence, decreased fertility. Erectile dysfunction leads to psychological discomfort and depression.
Clinical picture
You should know that testicular hydrocele in men can be one- or two-sided. The first option often develops in the presence of inflammation of the testicles and appendages, the second is a consequence of a chronic form of inflammatory pathologies and a general syndrome of swelling in the body.
Erosion on the penis: causes, symptoms and treatment
Hydrocele most often occurs acutely, but in the absence of adequate treatment it becomes chronic and the symptoms disappear. The acute form of the pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- significant enlargement of the scrotum (up to 10 cm or more);
- sharp pain in the area of the inflamed testicle;
- signs of intoxication: nausea, vomiting;
- weakness, loss of appetite;
- high body temperature.
Among other things, an enlarged scrotum leads to difficulty urinating and a feeling of heaviness. Patients report difficulty walking and having sex. On palpation, the scrotum is dense, sometimes splashing inside the membranes is felt, but without pain. Excessive fluid accumulation does not allow the contours of the testicle to be felt - this is a clear symptom of the acute form of the disease. The chronic form is characterized by a significant increase in the size of the scrotum during the day and a decrease during sleep.
Important! severe infectious pathologies that cause hydrocele cause suppuration of the exudate, which can provoke pyocele. The condition is manifested by a sharp deterioration in health, suppuration of the serous fluid, and the spread of infection to nearby tissues and organs.
If left untreated, dropsy can develop not only into a pyocele, but also cause:
- accumulations of blood - hematocele, which occurs due to traumatic vasoconstriction, hemorrhagic diathesis, or unsuccessful puncture of a hydrocele;
- atrophy, as a result of which the testicle dries out, which occurs due to compression of the vascular blood system supplying the testicle;
- rupture of the testicular membranes;
- scrotal hernia;
- disorders of spermatogenesis and, as a consequence, infertility;
- erectile dysfunction.
Diagnosing the disease is not difficult. You should contact a urologist or surgeon. Based on complaints, the specialist collects anamnesis, draws up an examination plan and prescribes treatment. Palpation of a hydrocele causes pain extremely rarely and only in an acute form - you can notice this on your own and immediately schedule a visit to the doctor.
To exclude varicocele, inguinal-scrotal hernia, and other pathologies, the following may be prescribed:
- diaphanoscopy - examination of the formation in transmitted light;
- Ultrasound is an informative version of the study, which allows you not only to see the fluid in the scrotum, but also the primary and secondary pathology, the reasons that caused the disease.
After diagnosis, the patient is recommended to be treated with one of the prescribed methods.
Prevention of testicular hydrocele in adults
There is no specific prevention of hydrocele in men. To avoid the appearance of dropsy, you need to:
- avoid injuries to the groin area;
- exclude sexual relations with casual partners;
- use barrier contraceptives;
- be examined by a urologist twice a year;
- give up bad habits;
- exercise;
- have regular sex life.
The acquired form of dropsy in most cases occurs against the background of other diseases. To prevent the accumulation of fluid in the testicular area, it is necessary to promptly treat prostatitis, urethritis, cystitis and other urological diseases.
Hydrocele of the testicles in boys: treatment
The method of treating the disease largely depends on what exactly caused it. With physiological hydrocele in a child, treatment is not required, since this form is quite easy to observe at this age. Up to a year, all symptoms and manifestations of hydrocele can go away without any external intervention
Hydrocele of the testicles in boys: treatment of the acquired form
If hydrocele manifests itself in an acquired form, then you first need to cure what led to its appearance. For children, there may even be drug treatment, but it does not always give the desired effect:
- If a hydrocele appears from an injury, then anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs prescribed by a doctor should be used to relieve pain and swelling;
- If it was infectious testicular hydrocele in an infant, treatment involves the use of non-steroidal antiviral antibiotics
Hydrocele of the testicles in boys: surgery
If over time, after a year from birth, the congenital form does not go away on its own, or the drug treatment method turns out to be ineffective, then, as in adults, surgery has to be used. Surgical intervention is much more effective and gives a highly effective result, but for the child it may seem too dangerous, so they try to postpone this moment. It is not recommended to operate on children under two years of age. If surgery is necessary, general anesthesia is used.
If the child is over 12 years old, then the same operations are used for him as for adults:
- Bergman's technique;
- Lord's technique;
- Ross Method;
- Winkelmann technique.
When performing them, you need to make an incision to get to the problem area and pump out the accumulated fluid. After this, the shells are stitched in different ways, which depends on the chosen technique.
For testicular hydrocele, treatment in children using the Winkelmann method involves inverting the membrane of the hydrocele and suturing it. Thanks to this, all surrounding tissues will absorb the emerging fluid. Upon completion of the operation, the wound is sutured in layers.
Bergmann's operation is used when the child's disease progresses sharply and the hydrocele becomes large. As a rule, this is due to the presence of thick shells in this form. After concealment, the vaginal process is simply excised. It is stitched at the base, after which the doctor sutures the wound.
The operation using Lord's method turns out to be the least traumatic. Its main feature is that during it the testicle is not removed into the wound. This reduces the risk of injury to surrounding tissues. The vaginal membrane is only sutured and crimped.
For testicular hydrocele in newborns, treatment using the Ross method involves careful ligation of the processus vaginalis. The ligation is done in the area of the inguinal inner ring, after which it is cut off. Almost all operations require the creation of drainage before suturing the wound. This is a necessary condition that creates temporary restrictions on physical activity. In adults, this is only a month, and since children have higher regeneration, this period can pass noticeably more quickly. However, it is more difficult to keep track of children and ensure that they do everything.
It is worth performing surgery to remove a hydrocele due to injury only six months after receiving this injury. During this entire period, one can only observe the development of the disease. In some cases, in the first months the dropsy decreases in size.
Hydrocele of the testicles in boys: photos, treatment and indications for surgery
They try not to perform surgery until the child is two years old, but there are a number of reasons that cause complications and because of them it is necessary to perform surgery even before the child turns two years old. These reasons include:
- The presence of infection in the hydrocele, which can lead to serious complications;
- An unbearable feeling of discomfort in the groin area that haunts the child;
- The appearance of an inguinal hernia, which creates a high risk of strangulation;
- An abnormally rapid increase in size of the scrotum, which can provoke a number of serious complications.
For hydrocele of the testicles in newborn boys, treatment and photos rarely require mandatory surgery. This happens much less frequently than a simple congenital hydrocele, which goes away without any problems.
Sometimes, if an operation is required, but it cannot be performed at a specific period of time, although you should also not leave opportunities for the development of the disease, then a puncture should be used. It is done as simply as possible, but gives only a temporary effect. This will help buy time without creating a serious surgical impact that could harm your health.
Complications
The fluid inside the scrotum is an ideal environment for bacterial flora to feed.
That is why hydrocele is considered a risk factor for inflammatory diseases. Most often, infections are associated with the migration of the pathogen through the blood from distant organs - carious teeth, tonsils, intestines. The infection is accompanied by general symptoms of intoxication. The child complains of weakness, increased fatigue, nausea and dizziness. There is a rise in body temperature to 38 degrees or higher.
Also, the infectious process is accompanied by external symptoms. The scrotum becomes red and swollen, and becomes painful on palpation. In severe cases, pyocele occurs - an accumulation of pus in the membranes of the organ.
Advanced variants of hydrocele can cause rupture of the membranes. Clinically, the complication is accompanied by acute pain and bleeding. In the absence of competent medical care, the child may experience hypovolemic shock. Its symptoms are increased heart rate, drop in blood pressure, and loss of consciousness.
Prolonged hydrocele in children can cause infertility in the future. The testicles contain special cells that produce sperm. Prolonged compression can lead to their death and disruption of reproductive function.
A previous infection of the testicular membranes increases the chances of infertility in adulthood. The inflammatory process contributes to the death of cells that produce sperm and their replacement with connective tissue.
Acquired dropsy: causes
If we are talking about the formation of testicular swelling in adulthood, then the list of reasons looks completely different:
- testicular torsion;
- disruption of the normal drainage of lymph from the scrotum;
- injuries to the scrotum, genitals and perineal tissue;
- inflammatory diseases of the scrotum, including those caused by sexually transmitted infections (according to statistics, chlamydia is quite often the cause of the development of dropsy in adult patients).
It is also worth noting that during diagnosis it is extremely important to determine not only the presence of edema and its severity, but also the reasons for its appearance - the success of treatment directly depends on this.
Self-healing
What will happen to hydrocele if this disease is not treated?
Do not expect that the hydrocele will leave your body on its own.
Cases of self-healing without any action are very rare, therefore, you should not place high hopes on this.
However, very often a hydrocele is an age-related change in the scrotum, when, due to increased growth, a similar incident occurs in the body. Can hydrocele go away on its own ?
As a rule, hydrocele disappears spontaneously in adolescents aged 15 to 18 years.
But if you are older, or you don’t want to risk your child’s health and wait for the problem to resolve itself, then start acting now.
The main reasons for the development of congenital hydrocele
As already mentioned, quite often this pathology is congenital. The reasons for this may lie in the following:
- during intrauterine development, the testicle descends into the scrotum, but the lumen of the processus vaginalis remains open;
- if the processus vaginalis remains connected to the abdominal cavity, then the fluid continues to circulate through this canal, accumulating between the layers of the testicle;
- disruption of the normal development of the lymphatic system in the groin area can also lead to fluid accumulation.
Conservative treatment
To cure acquired hydrocele, you need to determine the cause of the underlying disease. During this period, maximum rest and wearing a suspensor (a bandage to support the scrotum) is recommended. By puncture, excess fluid is removed and sclerosing drugs are injected into the cavity.
The danger of hydrocele lies in frequent relapses, therefore surgery is considered the most effective method of treating hydrocele. There are different techniques for operating hydrocele: Winkelmann, Lord, Ross, Bergman, as well as laser technology. Surgical treatment is contraindicated in patients under 1-1.5 years of age.
Classification
Dropsy in boys on the testicles has another classification of varieties, in addition to the congenital and secondary forms of the disease. It can occur in a communicating form (when fluid circulates between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum) and an isolated form (when the peritoneal process overgrows and the lymph stagnates in the gonad membrane). The intensity of the pressure of the accumulating fluid determines whether the tense (usually in an isolated form) or non-stressful form of the disease is present, and whether the acute or chronic nature of the course of the disease is observed.
What complications can the disease lead to?
Many men ask questions about whether hydrocele affects reproductive functions. Hydrocele of the testicle has virtually no effect on the quality and quantity of sperm produced. However, the disease can cause dangerous complications. Edema, which constantly increases in size, can lead to compression of blood vessels. Trophic disturbances sometimes lead to testicular atrophy.
Dropsy may be accompanied by a hematocele - in this case, not only fluid, but also blood accumulates between the sheets of the testicular membrane. As a rule, such a complication is associated with direct trauma to the scrotum. Complications include pyocele - an accumulation of purulent masses with further spread of the inflammatory process.
Hydrocele rupture is a complication that is recorded extremely rarely in medical practice. Sometimes, against the background of an inflammatory process, small mineral formations (stones) begin to form between the membranes of the testicle.
Symptoms
The first thing parents may notice is an increase in the size of the scrotum. One or two organs are affected simultaneously. When dropsy is in the acute stage, the following symptoms appear:
- severe pain in the groin;
- fever and chills;
- nausea and vomiting;
- hyperemia of the skin of the scrotum (redness);
- increase in body temperature;
- feeling of weakness;
- decreased activity;
- increased moodiness.
If a hydrocele is detected in infancy, parents notice that the baby constantly pulls his hands towards the groin area.
Results
The pathology discussed in this article has a generally positive prognosis. They consist in the fact that during surgical intervention the chance of complications is only two percent. Moreover, the reliability of the operations can confirm that during the entire period of their implementation there was not a single case that would lead to the death of the patient.
It is possible to cure dropsy - you just need to follow the doctor's instructions
If you follow everything the doctor says, treat yourself correctly and maintain a positive emotional state, then it is quite possible to quickly recover from the disease and have a good prognosis for the future.