Gastritis
30.10.2016
Today, all residents, especially of megacities, lead a fairly active lifestyle. We don’t have time to eat normally, so we “snack on the run.” In the evening, we often have meetings with our beloved friends and family, where we give free rein to our “desire to be satiated.”
- What is gastritis?
- Acute form
- Chronic gastritis
- Superficial gastritis
- Symptoms
- How to treat superficial gastritis?
- Diet for superficial gastritis
- Products allowed on the menu
- It is not advisable to use it on the menu for superficial gastritis
- Sample menu for the day
- Conclusion
Recently, people have begun to take more seriously their health, nutrition in particular. They begin to adhere to diets, create easy-to-follow menus for the day, and play sports. But, as a rule, each of these people already has gastritis. Now, probably, only infants are not susceptible to stomach diseases, unless it is a congenital pathology.
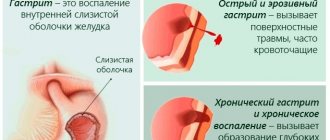
Chronic gastritis
In this case, the opposite is true. The inflammatory process is long-term, sluggish, but leading to persistent pathological morphofunctional changes. This option usually has many reasons.
The disease usually depends both on external factors and on existing changes in the body, including congenital pathologies. Chronic inflammation of the stomach affects 9 out of 10 patients with all gastric diseases. In the vast majority of cases, CG is a Helicobacter-associated disease.
Why do you need a diet?
The most common cause of exacerbation of gastritis is errors in diet. With this disease, the gastrointestinal tract does not work properly. The goal of the diet is to normalize the functioning and condition of the digestive organs. This effect occurs due to the introduction of some products to the menu and the exclusion of others.
The diet for gastritis has the following properties:
- prevention of relapse of the disease;
- elimination of pain in the digestive system;
- regeneration of affected areas of the gastric mucosa;
- preventing attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- restoration of gastric juice acidity;
- normalization of the bowel movement process;
- elimination of heartburn;
- relief from flatulence and bloating.
Superficial gastritis
With superficial (simple) gastritis, as with any other option, there is a combination of various factors, sometimes with the predominance of one.
The causes of this form can be divided into exogenous and endogenous.
External or endogenous factors include:
- The presence of Helicobacter,
- Or other pathological microorganisms,
- Poor nutrition
- Disorder in the autoimmune system,
- Alcohol abuse
- Smoking,
- Drug abuse
- Radiation.
Internal reasons:
- Congenital disorders due to genetics,
- Already existing pathologies of the stomach, duodenum,
- Pathology of other organs and systems with the release of substances affecting the gastric mucosa,
- The source of infection
- Various types of general metabolic disorders,
- Lack of vitamins
- Diseases of the endocrine system
- Ulcer history.
General recommendations
The food diversity that is available to the population of developed countries can hardly be called a factor beneficial for health. Fast food, an abundance of spicy, spicy, fried foods have led to the fact that gastritis is now increasingly being diagnosed from school. And if left untreated, the superficial form of the pathology progresses over time, affecting increasingly deeper layers of the stomach walls, forming foci of erosions, ulcers, and atrophies. Ultimately, this can result in a peptic ulcer or even give rise to the development of cancer.
To prevent deterioration of the condition, patients diagnosed with superficial gastritis must follow the following simple but very effective rules:
- get rid of bad habits as quickly as possible: substances contained in tobacco smoke have a destructive effect on the gastric epithelium; a direct connection between the occurrence of stomach cancer and the abuse of alcohol-containing drinks has also been proven;
- try to avoid situations that provoke stress and other negative nervous conditions, which also lead to additional irritation of the mucous membrane and the spread of inflammatory processes in the gastric epithelium;
- the diet for superficial gastritis of the stomach should include food whose temperature is as close as possible to the human body temperature, since temperature dissonance forms between the walls of the stomach and too cold/hot food, leading to additional irritation of the epithelium;
- you should avoid eating hard-to-digest, rough foods, and if gastritis worsens, all foods must be crushed to a mushy state;
- An important characteristic of proper nutrition for gastritis is adherence to the same food intake regimen, and meals should be fractional - frequent (5-6 times / day) and in small portions.
The main task of the diet for superficial gastritis is to prevent the irritating effects of food on the walls of the stomach, to eat foods that will not worsen the condition of the inflamed mucosa.
Symptoms
Locally, that is, in the stomach area, there are usually the following manifestations of the disease:
- A feeling of heaviness in the stomach (usually above the navel or on the left under the ribs), depending on the time of food consumption;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Heartburn;
- Constipation;
- Diarrhea;
- Bloating.
In addition to local manifestations, there may also be changes in other organs and systems, and manifest themselves as follows:
- Lethargy, weakness;
- There may be weakening or complete absence of sensitivity in the lower and upper extremities.
When visiting a doctor, the first thing the doctor usually does is find out the complaints, concomitant diseases and risk factors, and examine the patient. If a patient is suspected of having a pathology, the following measures are taken:
- Gastroscopy. It is with the help of this method that the endoscopist sees exactly where the pathological process is taking place. Most often, during endoscopy of the stomach, a biopsy of the mucous membrane is also performed to understand the nature of the changes.
- Laboratory tests: CBC, BAM, Blood biochemistry, Feces for the presence of blood in it, Presence of Helicobacter.
- Ph meter.
- Radiation diagnostic methods for the disease of interest to us are not very informative; they can be useful in the presence of ulcers and oncology.
General rules
Diseases of the digestive system occupy third place in the structure of morbidity among adults.
Chronic gastritis develops due to errors in diet (eating poorly chewed, coarse and very spicy food), the presence of Helicobacter pylori, bile acids in gastric contents, prolonged neuropsychic stress, occupational hazards, smoking and alcohol abuse.
Its main forms include superficial (catarrhal) and atrophic. This division means the preservation or loss of glands, which has functional significance. A number of classifications include an intermediate form - subatrophic, meaning beginning atrophy of the glands.
Depending on the prevalence of altered cells and the depth of penetration of inflammation into the thickness of the mucosa, non-atrophic gastritis is divided into mild, moderate and severe gastritis. The inflammatory process can cover the mucous membrane of the entire stomach (pangastritis) or some part of it, then focal gastritis occurs.
Atrophic gastritis is characterized by changes in cells of a dystrophic nature, a decrease in the number of glands and inflammation of the mucous membrane similar to that of severe superficial gastritis. Depending on the decrease in the number of glands, moderate and severe degrees of atrophy are noted. In 50% of cases, this form of gastritis is combined with restructuring of the mucosa (metaplasia of the fundic glands, intestinal metaplasia, and epithelial dysplasia may be observed). A true precancerous change is considered to be epithelial dysplasia, which comes in three degrees.
In addition to the main forms of gastritis, there are also its special forms: hyperplastic (“warty”, polypous), hypertrophic, granulomatous, hypertrophic, collagen and others. Focal mucosal hyperplasia is considered to be the earliest form of polyp. When bile is thrown into the stomach under the influence of bile acids, severe inflammation, metaplasia, gland atrophy and focal hyperplasia develop.
H. pylori infection causes the most severe forms of the disease. Thus, most often the infectious factor is detected in the erosive and hypertrophic form, somewhat less often in subatrophic, atrophic and superficial gastritis. In persons with a long history of the disease (17-20 years), a reduced level of acidity is more often determined, and normal or increased acid formation is observed for a shorter period.
Symptoms and treatment
Symptoms of the disease are nonspecific and varied. Patients are concerned about the appearance of pain and a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium, distension and fullness of the stomach or a feeling of hunger after eating, a burning sensation in the epigastric region and premature satiety, bloating after eating, heartburn, belching, nausea, vomiting, salivation, regurgitation of food, loss of appetite.
Hemorrhagic gastritis is one of the most severe injuries, accompanied by the formation of multiple erosions and manifested by bleeding. Patients experience vomiting in the form of “coffee grounds” and tarry stools. With excessive blood loss, loss of consciousness occurs and anemia develops. The most common cause of this form of gastritis is long-term use of glucocorticoids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment of gastritis is aimed at eliminating all factors that provoke exacerbation of the disease. In the first place are drugs that reduce gastric acidity - H2 blockers, but currently proton pump inhibitors are widely used, since they are 3-10 times more effective than H2 blockers.
When Helicobacter pylori is detected, it is eradicated using a 3-component treatment regimen (De-nol in combination with two antibiotics or proton pump blockers in combination with two antibiotics). If these regimens are ineffective, quadruple therapy is performed (bismuth drug, PPI and two antibiotics).
In parallel, to prevent dysbiotic changes in the intestines, complex probiotics (Bifiform, Linex) are prescribed, containing antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms and populating the intestines at different levels. Antacid drugs (Phosphalugel, Almagel) have a slight effect on the pH level, but are used as coating agents that increase the resistance of the mucous membrane to the effects of hydrochloric acid and pepsin.
For symptoms of gastritis, diet treatment is of great importance, since dry food, irregular and irrational nutrition, consumption of excessively cold or hot food and large amounts of spices cause exacerbation of gastritis. For many decades, this disease has been recommended to follow a diet similar to a peptic ulcer.
Is a strict diet necessary for gastritis? Despite the fact that recently they are moving away from strict restrictions in the diet even with peptic ulcer disease, nevertheless, food, especially during an exacerbation, should not contain irritating substances. A gentle diet is recommended, and the degree of sparing depends on the severity of the exacerbation. In addition, the composition of the diet depends on the condition and acid-forming function of the stomach.
For those who have gastritis with low acidity, Diet number 2 is suitable, which provides for moderate stimulation of the secretory function of the stomach and includes juice products and dishes. Allowed:
- First courses with low-fat meat/fish/mushroom broth, rassolnik with pureed vegetables and cucumber brine.
- Porridge with water or meat broth (excludes millet and pearl barley).
- Boiled and stewed vegetables - potatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini, pumpkin, cauliflower and cabbage.
- Salads from ripe tomatoes, salads from boiled vegetables (excluding fresh onions, sauerkraut and pickles), vegetable caviar, herring and mincemeat.
- Kefir, yogurt, curdled milk and other fermented milk drinks, sliced or grated cheese, omelet with cheese.
- Heat treatment in the form of frying without the formation of a rough crust and stewing, which stimulates the production of gastric juice.
- Ripe, unpureed fruits. Oranges and lemons (in tea), tangerines, watermelon, grapes.
- Sauces based on meat broths, jellied dishes using broths.
- Tea with lemon, vegetable juices, coffee and cocoa, fruit juices (all juices diluted).
For these gastritis, foods and dishes with a choleretic effect are also prescribed: vegetable oils, beets and beet juice, lemons and lemon juice, melons, watermelon, avocado, turmeric, fresh herbs, rose hips, dandelion leaves and root. Restrictions (pea, bean soup, okroshka, millet soup, fatty coarse meat, salted, smoked fish, canned food, hard-boiled eggs, corn, pearl barley porridge, raw vegetables) are necessary only during the period of exacerbation, and as it improves and during the period of remission, nutrition must be complete.
At the same time, the following are excluded: fresh bread, pastries, pastry products, legumes, okroshka, millet soup, fatty meat and poultry, smoked meats, fatty fish, salted and smoked fish, legumes, millet, corn, pearl barley, barley, raw vegetables, pickled vegetables, onions, radishes, radishes, cucumbers, rutabaga, sweet peppers, garlic, mushrooms, very spicy snacks, mustard, pepper, horseradish.
For hyperacid gastritis (high acidity), Table No. 1 and its varieties are recommended. Diet 1A is sequentially prescribed for up to 10 days, then 1B and No. 1 (up to two to three months). The diet includes neutral dishes that have a weak juice effect: milk, eggs, boiled meat and fish, milk porridge, sweet fruit juices.
- Exclusion of foods that increase secretion (spicy, pickled dishes, rich broths, mustard, alcoholic drinks, smoked and fried foods, coffee, tea, carbonated drinks).
- Exclusion of irritating foods (cranberries, tomatoes, garlic, onions, citrus juices, sour fruit juices, peppers, chocolate, turnips, radishes, alcohol, ginger) and foods that increase gas formation (cabbage, legumes, kvass, beer).
- Increasing protein intake and reducing fat in the diet (fatty pork, cream, butter, goose, duck, cakes and other baked goods with cream, animal fats, lamb).
- Reducing the amount of food consumed (no more than 200 g at one time).
- Frequent meals (up to 6 times a day).
- Eating food warm, excluding cold dishes and excessively hot ones that irritate the mucous membranes.
- Using boiling, stewing and baking in cooking.
- Exclusion of foods that do not combine (proteins and carbohydrates) to avoid rotting and fermentation.
- Inclusion in the diet of potato juice, bananas, oat decoction, sweet apples (first baked, later fresh).
In general, dietary nutrition should be followed for 1-3 months. Table No. 1 is complete and physiologically balanced (proteins up to 90-100 g, carbohydrates 300 g, fats 100 g). Gradually, the diet expands to what is familiar to each person, but spices, herbs, spicy foods, pickles, smoked foods, canned food, and fatty foods (meat and fish) are definitely excluded.
Eliminating bad habits and correcting lifestyle is of no small importance. Previously used seasonal therapy is now rarely used. But in the presence of provoking factors (business trips, exams, mental stress), it is advisable to change your usual diet and switch to a dietary diet.
The dietary menu of Table No. 1 has been expanded in terms of products, as well as cooking methods (baking is added). The food is quite varied and complete. Some vegetables are included and the list of cereals is expanded, so you can create a menu that takes into account the daily alternation of protein and cereal dishes.
Diet for superficial gastritis
There are certain rules that are best followed to achieve the desired effect.
- Your stomach should form the habit of receiving food at approximately the same time, this will help avoid hunger and increase the production of juice in the stomach, which in turn will not aggravate the course of existing gastritis, that is, you need to create the right diet (menu).
- You need to eat often, but do not overdo it in the volumes consumed, otherwise the body will not have time to cope with the food received in the allotted period of time and there will be no effect from the treatment.
- Eat slowly; this process should take at least 30 minutes.
- Avoid external irritants (TV, telephone, book, company of friends, no matter how sad it may sound).
- Observe the temperature of the food, it should be warm. In no case hot or cold, as this may cause additional injury to the gastric mucosa.
- For a good start to the stomach, it is useful to drink 200 milliliters of water on an empty stomach (preferably warm).
Products allowed on the menu
Products that “envelop the gastric mucosa” are very useful, helping to protect it from injury.
- Porridge. Oatmeal and rice porridge are very necessary in the diet. There are other varieties, but these are the most useful.
- Soups. Various options are possible here, the main thing is to avoid fatty broths. Soup – puree, a very good option (vegetable, meat).
- Also, all types of lean meat are allowed on the menu, in any form, except fried.
- Fish, preferably lean, for example: pollock, cod.
- Almost all vegetables are allowed on the menu, except cabbage and mushrooms; they are difficult to digest in the stomach. The main thing in consuming vegetables is that they undergo heat treatment, that is, they cannot be eaten raw during an exacerbation of gastritis.
- Fruits are very healthy when baked, but grapes are not allowed on this menu.
- Fermented milk products are welcome, they also coat the gastric mucosa.
- There is special mineral water for the treatment of gastritis. Very helpful. We recommend. Example: “Essentuki - 17”, “Borjomi”. Just buy water without gas
- Olive oil and butter are beneficial.
It is not advisable to use it on the menu for superficial gastritis
- Snacks. This is harmful for both a healthy stomach and a sick one. The body must get used to a precise diet. It is important!
- Floury goodies. It is also advisable to exclude bread, but you can use bran flour.
- Alcoholic drinks.
- Various sodas, except medicinal mineral water.
- Lemon. Acidity begins to change. This interferes with recovery.
- Eliminate external irritants. They have been written about previously.
- Do not overuse coffee drinks.
- Remove spices from your diet.
In fact, all of the above are the basic rules of healthy eating. If you follow them for a week, it will become a habit and then you will not be afraid of any diseases!
Authorized products
It’s worth mentioning right away that foods, drinks, and spices not included in this list are prohibited for gastritis. The range of foods, drinks, and seasonings consumed by modern people, including exotic ones, is so wide that listing them within the scope of the article is not possible.
List of permitted foods and drinks:
- Meat – chicken and turkey breast fillet, rabbit, veal. As digestion improves, lean young lamb and pork are added. You can have low-fat turkey ham, “Doctor’s” sausage.
- By-products - beef tongue, chicken, turkey, beef liver.
- Fish – hake, greenling, pike perch, pollock, trout. Then you can diversify the menu with lightly salted herring soaked in milk.
- Dairy products - low-fat milk, non-sour kefir (ryazhenka, yogurt, bifidok), cottage cheese with fresh, non-fat and non-sour sour cream, cream for tea. Low-fat and mild cheese is allowed - “Russian”, “Poshekhonsky”.
- Chicken, quail eggs, soft-boiled or steamed in an omelet (no more than 1 per day - chicken, no more than 3 per day - quail).
- Oils – unsalted butter, ghee, refined sunflower.
- Cereals, pasta - semolina, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, small vermicelli, boiled pasta.
- Bread, pastries – white bread, dried yesterday, crispbread without yeast. Dry biscuits, biscuits. Pies baked with filling from permitted products, buns that are not tasty.
- Vegetables - pumpkin, zucchini, carrots, beets, potatoes, cauliflower. In summer, in season - sweet, ripe tomatoes, no more than 2 pieces per day, as well as early fresh cucumbers.
- Greens - dill.
- Fruits, berries - pears, apples, apricots - be careful when eaten raw. Boiled, baked, pureed (jelly, mousse, jelly) can be berries and fruits of your climate zone (except citrus fruits).
- Sweets - sugar, jam, marshmallows, marshmallows, meringue, fresh buttercream. As recovery progresses, linden, sweet clover, and flower honey are introduced.
- Sauces – milk, sour cream, without frying flour.
- Drinks – weak warm tea with milk, milk, jelly, dried fruit compote, rosehip infusion.
Most often, with gastritis with high acidity, patients are prescribed table No. 1 according to Pevzner. It provides a balanced diet that meets the body's needs and ensures sustainable recovery. You can eat the following foods:
- Zucchini, pink varieties of potatoes, beets, carrots, celery, white and cauliflower (infrequently), as well as ripe fruits (baked or grated) - apples, bananas, pears, peaches;
- Meat: lean parts and types of meat/fish - rabbit, poultry, veal, cod, hake, pollock. It is advisable to grind until minced;
- Bakery products: dried or “yesterday’s” baked goods, biscuits, homemade crumbly pies;
- Oatmeal, rice, semolina porridge. Prepared to a slimy state or decoction;
- First courses: on the “second” broth. Do not use fatty dressings;
- Pasta: soft varieties, cooked until fully cooked;
- Juices: diluted with boiled or still mineral water, fruit and vegetable mixes, fresh juices;
- Eggs: any boiled (soft-boiled) or as a light omelet (steamed);
- Drinks: weak tea, herbal or berry infusions, jelly, still mineral water (according to acidity);
- Sweets: homemade marshmallows, marshmallows, jams, souffles, mousses;
- Dairy products: kefir, fermented baked milk, curdled milk, sourdough, acidophilus, Greek yogurt (without additives and sugar), cottage cheese, low-fat sour cream, boiled milk (infrequently or in dishes) and soft cheeses.
For superficial gastritis, it is not recommended to consume the following foods:
- Fatty parts or types of meat, fish, as well as rich broths made from them;
- Fresh fruits and vegetables, especially sour or overly sweet ones, as well as juices based on them;
- Whole cow's milk, fatty (hard) cheeses or specific types (with mold, nuts, spices);
- Rough and “junk” foods that increase the load on digestion - fast food (burgers, hot dogs, shawarma/shawarma, pizza, gyros, pies, whites), fatty, fried, smoked foods (ribs, wings, fish, lard ), sausages cooked over an open fire;
- Cakes, sweets, pastries and other confectionery products with a multi-component composition;
- Carbonated water with dyes, sour juices, strong tea/coffee, alcoholic drinks;
- Hard-boiled eggs;
- Freshly baked bread, rolls, loaves, yeast and puff pastry.
Sample menu for the day
| Breakfast | oatmeal porridge with water, coffee, preferably without sugar, a piece of cheese or yogurt |
| Lunch | Omelet or scrambled eggs from two eggs, tea |
| Snack | a piece of cheese or cottage cheese and mineral water (preferably specialized for the treatment of gastritis) |
| Dinner | soup - puree with chicken broth, vinaigrette, turkey baked in the oven with rice |
| Afternoon snack | Apple baked in the oven, mineral water (medicinal), tea |
| Dinner | chicken with vegetables, steamed or baked |
| Two hours before bedtime | a glass of fermented milk products or mineral water |
Basic principles of proper nutrition
The diet for gastritis is prescribed in accordance with the existing form of the disease.
It is possible to establish the specific type of disease and determine its stage only on the basis of a full medical examination. When choosing a nutrition program, an important role is played by the degree of damage to the mucous membranes of the digestive tract, the level of acidity of gastric juice, as well as the presence of additional symptoms.
A general recommendation, regardless of the form of gastritis, is to exclude herbs, spices, hot, fatty, salty and fried foods from the diet. Meals should be balanced and fractional.
Diet principles depending on the type of gastritis:
- with erosive gastritis, it is necessary to reduce the load on the digestive organs (all ingredients in the menu should be crushed as much as possible, and in cooking methods, preference should be given to steam processing);
- gastritis of atrophic form implies compliance with general nutritional rules for this disease, but special attention should be paid to the mandatory use of medicinal mineral water and decoctions based on medicinal herbs (St. John's wort, calendula, mint, rose hips, plantain, chamomile);
- for superficial or catarrhal gastritis, diet is the main and effective method of treatment; it is necessary to exclude from the diet all foods that can irritate the mucous membranes of the digestive organs (spicy, sour, salty and fatty foods are excluded, alcohol and carbonated drinks are prohibited, difficult-to-digest foods are excluded from the menu);
- acute gastritis is accompanied by pain, therefore, in the first days of the diet, food intake must be limited (the diet should be based on diet No. 1, confectionery, baked goods, fermented milk products, alcohol and any types of food with high fat content are excluded from the menu);
- the goal of the diet for gastritis with low acidity is to stimulate the production of acid and special enzymes by the stomach, as well as to accelerate the process of digestion of food (a distinctive feature of the diet is the permission to consume acidic foods and citrus fruits);
- in case of gastritis with high acidity, it is necessary to prevent excessive secretion of gastric juice; any products that irritate the intestinal mucous membranes are excluded from the menu (unlike the diet for acute gastritis, in this case the use of meat balls and cutlets is allowed).
Table 9: diet menu for the week, nutritional rules, list of allowed and prohibited foods.
Find out from this article which Turboslim is the most effective. What types of products are there and how to choose the right one?
Delicious diet recipes
It is wrong to think that switching to a diet will force you to spend hours in the kitchen. Everything is much simpler - you can buy an electric steamer, and the now fashionable multicooker, and save yourself the trouble. We suggest you prepare vegetable stew with a minimum of time.
You will need:
- 1 young zucchini.
- 1 large carrot.
- 1 medium onion.
- 2-3 potatoes.
- 4-5 broccoli florets.
- Salt, vegetable oil, a little milk.
Preparation: wash the vegetables, cut them into large cubes of equal size, put them in a thick-walled pan, add salt. Add a tablespoon of vegetable oil and a little water to the vegetables, so that they cover 1/3 of the vegetables. Cover the pan with a lid and simmer for 15 - 20 minutes. 5 minutes before the end of cooking, you can add 2 - 3 tablespoons of milk - the taste of the stew will be softer.