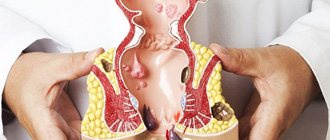
Almost any disease without treatment leads to complications. This statement is also true for hemorrhoidal disease. A common complication of the disease can be thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
thrombosis of the hemorrhoid, photo of external manifestations
Congestion is possible in any blood vessel. The resulting blood clots are also called thrombi. Having discovered them in the patient, the doctor diagnoses “thrombosis” and indicates where exactly the blood clot formed.
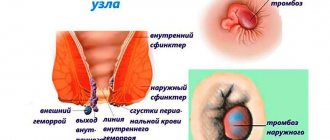
Hemorrhoidal thrombosis is the formation of blood clots in the cavernous formations of the rectum. It can be internal or external.
Thrombosis of the external hemorrhoidal node always manifests itself as inflammation. At the initial stage, anticoagulant drugs help well. Pathology of internal manifestations can be eliminated with special rectal suppositories.
What to do if acute thrombosis occurs
What is thrombosis of hemorrhoids
One form of complications of pathological expansion of hemorrhoidal veins is anorectal thrombosis.
The disease is a thrombosis of existing hemorrhoids and can provoke the development of infectious diseases such as paraproctitis and sepsis. The mechanism of thrombosis formation is based on the activation of the blood clotting process, which occurs in response to damage to the integrity of blood vessels. A blood clot is formed from fibrin and platelets, which enter the area of rupture of the vascular wall. The result of the body’s protective reaction is the blocking of the arterial lumen and blood stagnation. Violation of the outflow of blood from the vein leads to oxygen starvation of cells, swelling and accumulation of metabolic products in the affected tissues, which provokes the development of a local inflammatory process. Hemorrhoidal thrombosis in 80% of cases occurs against the background of exacerbation of chronic hemorrhoids. The likelihood that thrombosis will develop acutely, simultaneously with the formation of lumps, is minimal, but not excluded.
The problem is aggravated by severe pain, which is constant and intensifies during the process of bowel movement. The patient tries to postpone the unpleasant process of defecation, which contributes to increased congestion in the pelvic organs and provokes constipation. When solid stool passes through the rectum, hemorrhoidal nodes, enlarged due to swelling, are damaged, which is accompanied by severe pain and an increased risk of infection.
What is thrombosed hemorrhoids
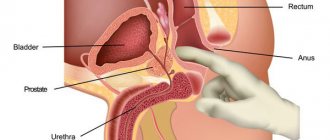
At the exit from the intestines, cavernous (venous) bodies are located around the anus. This area is well supplied with blood, so there are a large number of blood vessels there.
The mechanism of thrombus formation goes through the following stages:
What does the disease look like?
- Under the influence of various unfavorable factors, blood stagnation in this area occurs, the walls of capillaries and veins are deformed.
- An enlarged hemorrhoid is formed.
- Constant trauma to its inner wall from the rectal mucosa leads to infiltration (inflammation) of the damaged area.
- Platelets accumulate in this place and form a loose conglomerate.
- The hemocoagulation mechanism is turned on, and the blood clotting process starts.
- The body responds: a special insoluble protein (fibrin) is produced. It consists of hard fibrous threads and is the main component of a blood clot.
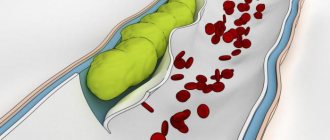
- The resulting clot is located inside the vessel and completely closes its lumen.
As a result of impaired venous outflow, a thrombosed internal hemorrhoid is formed. If it falls out of the anus, strangulation may occur. This is a serious complication requiring surgical intervention.
Causes
The beginning of the development of thrombosis is the formation of blood clots, which occurs under the influence of provoking factors. The risk of thrombosis increases in the later stages of hemorrhoids, but there is a possibility of complications developing in the early stages of the disease, so it is important to promptly minimize the impact of causes predisposing to the formation of blood clots. The main factors contributing to the development of the disease are:
- damage to anal endothelial cells - can occur due to injury to the tissues of the anus and rectum during attempts to independently set a prolapsed node;
- genetic predisposition to hypercoagulation (pathologically increased blood clotting);
- a sharp increase in pressure in the abdominal cavity - occurs with excessive physical effort, heavy lifting, pushing during childbirth, straining during obstipation (loss of nodes during bowel movements during constipation leads to pinching of them by the sphincter);
- stagnation of blood in dilated veins.
Poor circulation in the pelvic organs occurs under the influence of both internal and external factors. If the first group refers to either congenital or acquired diseases and is difficult to correct, then the second group can be influenced with due effort. Exogenous factors that increase the risk of vascular thrombosis include:
- physical inactivity – blood can stagnate in the pelvic organs due to a sedentary lifestyle;
- exposure to low temperatures - frequent hypothermia contributes to difficulty in blood circulation, irreversible narrowing and deformation of blood vessels;
- unbalanced diet - the absence of vital microelements and vitamins in the daily menu leads to disturbances in blood composition;
- adherence to bad habits - abuse of harmful substances (tobacco, alcohol, psychotropic drugs) contributes to worsening blood circulation, disruption of the structure of the walls of blood vessels, and increased fragility;
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs - the lack of timely treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system can lead to the development of chronic ailments in this area and disruption of the functioning of the hematopoietic organs.
Symptoms
A distinctive feature of anorectal thrombosis in relation to other forms of hemorrhoids is the sudden onset of pain. Pain appears unexpectedly and its intensity varies under the influence of various factors, but is not associated with the process of defecation. The pain syndrome that appears does not go away and causes constant discomfort to the patient, due to which he develops a specific “duck gait”.
The size of thrombosed formations does not affect the degree of pain - even small hemorrhoids can provoke unbearable pain. Other symptoms of thrombosis include:
- increased pain when walking or sitting;
- swelling in the rectum and anus;
- inflammation of the endothelium of the perianal zone;
- the appearance of discharge from the rectum, which may look like bloody or mucous masses;
- itching, burning in the anus;
- feeling of fullness in the anus;
- periodic bleeding that occurs after defecation.
Preventive measures
It is better to prevent any disease than to treat it. First of all, it is necessary to prevent the development of hemorrhoids.
The following recommendations should be observed:
eliminate hot and spicy foods from your diet;
- give up alcoholic drinks;
- consume fermented milk products and plant fiber;
- pay attention to the hygiene of the anus after the next act of defecation;
- move more and change positions;
- eliminate hard work;
- avoid hypothermia.
We also have materials on our website that may be of interest to you:
- Do women have a prostate?
- How does cycling affect the prostate gland?
- structure of the prostate gland.
And you can find out about harmful and beneficial products for the male organ here.
Also read about prostate diseases: adenoma, calcifications, stones, fibrosis, abscess, tuberculosis, cyst and why scars form.
Types and stages
Useful article? Share the link on VKontakte
To prescribe adequate treatment for the disease, thrombosis is classified according to several criteria. Depending on the location of the nodes, internal, external (external) and mixed (combined) thrombosis are distinguished. With internal, a blood clot forms in the internal nodes and cones, with external, the thrombotic process develops in the vessels of external nodes, and with combined, the formation of blood clots occurs both inside the rectum and outside it.
Thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid is the most commonly diagnosed type of disease; combined thrombosis is found in very rare cases, but more often leads to complications. Based on the degree of tissue damage, three stages of the disease are distinguished, which successively replace each other in the absence of treatment. The treatment measures taken and the prognosis for recovery will differ at each stage of thrombosis:
| Features | First stage | Second stage | Third stage |
| The presence of an inflammatory process | Absent | Limited | Spreads to tissues adjacent to the hemorrhoid (including fatty tissue) |
| Features of nodes | No visible changes | A sharp increase in size due to the appearance of swelling, compaction, acquisition of a dark red color, bluish tint | High density, localized either inside or inside and outside, necrotic changes in tissues begin |
| Severity of pain syndrome | Sharp, sudden and persistent pain, worsened by mechanical impact | Constant pain, worsens with palpation and compression | It is of a permanent, highly pronounced nature, local anesthesia is required for diagnosis, the anal sphincter is spasmodic |
| Changes in venous tissue | Violation of blood microcirculation in the veins leads to its thickening | A dense thrombus forms, which partially closes the lumen in the vessel | The thrombus almost completely blocks the vessel, preventing the normal outflow of blood |
| Body temperature | Within normal limits | Promoted | High |
| Forecast | Favorable | With timely treatment, favorable, surgical intervention is rarely required | Surgery required |
Complications
The danger of developing thrombotic processes lies in the fact that in the presence of a bacterial infection in the area of thrombosis, the destruction of the thrombus can lead to the spread of infected fragments throughout the circulatory system. Complete blockage of a vessel by a blood clot provokes the development of complete or partial necrosis of adjacent tissues (this condition often occurs when the sphincter spasms or prolapses of deep nodes). Perianal venous thrombosis can lead to life-threatening complications for the patient, such as:
- ulceration - when the necrotic parts of the nodes are rejected, painful and bleeding ulcers form in their place;
- purulent parapractitis - a disease that occurs when the size of ulcers increases and their spread to adjacent tissues; the result of the pathological process is an abscess, when ruptured the infection spreads to the internal organs;
- sepsis is a systemic inflammatory lesion that occurs with an advanced form of parapraktitis; this medically serious condition is accompanied by complex pathological processes throughout the body.
How to treat during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the likelihood of developing hemorrhoids increases for a number of reasons - hormonal imbalance, increased load on the pelvic organs, heaviness due to fetal growth, deformation of internal organs. Thrombosed hemorrhoids are dangerous not only for the life of the mother, but also for the child. It needs to be treated fully, immediately and under the supervision of specialists.
However, not all products can be used during pregnancy. Drugs must be effective and safe. Therapy is prescribed using ointments, creams, suppositories. Tablets are taken in especially severe cases. Approved drugs include Relief, Troxevasin, Gepatrombin G in severe situations.
In addition to drug treatment, it is necessary to adhere to a diet in order to prevent constipation and not burden the intestines. To improve blood flow, move more and do physical therapy. Before going to bed, make baths of medicinal herbs based on calendula, nettle, sea buckthorn, chamomile, nettle, St. John's wort.
Diagnostics
Due to the characteristic symptoms of anorectal thrombosis, diagnosing the disease does not require much effort. During an examination of a patient, a proctologist can visually determine the presence of thrombosed nodes by the presence of dense dark tubercles covered with plaque. When black areas are detected, the presence of necrotic processes is detected. In addition to a visual examination, the doctor prescribes the following types of studies:
- palpation - the density of veins and formations on the rectum is studied, increased muscle tone around the sphincter is detected, examination by palpation in the later stages of the disease is carried out using local anesthetics;
- instrumental - examination of the rectum by inserting a retroscope into the anus, the method helps to visually examine the degree of thrombosis of internal nodes;
- laboratory – the functional state of the blood coagulation system is assessed using a coagulogram by studying venous blood taken from the patient.
Treatment of hemorrhoidal thrombosis
After diagnostic procedures are carried out and the stage of the disease is determined, appropriate treatment is prescribed. Therapeutic methods are selected based on the severity of the disease and the degree of damage to blood vessels and tissues. In the first two stages of acute hemorrhoids, the goal of treatment is to eliminate the inflammatory process, relieve pain and dissolve blood clots. To achieve this goal, conservative methods of therapy using local or systemic drugs are used.
Non-invasive treatment methods are recommended to be combined with physiotherapeutic procedures to achieve quick results. An integrated approach, including oral medication, external treatment of affected areas, adherence to a therapeutic diet, and special exercises will significantly shorten the recovery period.
The last stage of the disease requires radical treatment measures due to the presence of serious tissue damage. The advantages of surgical intervention are immediate relief from thrombosed nodes, the disadvantage is a long rehabilitation period and the presence of postoperative wounds. The method and regimen of treatment must be prescribed by a specialist in the field of proctology; self-medication of acute hemorrhoids is fraught with life-threatening complications.
Medication method
Internal or external acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids in the first two stages responds well to drug treatment. The condition for successfully getting rid of the disease is to follow all the doctor’s recommendations. At the last stage of the disease, medications are also prescribed as part of rehabilitation therapy after surgery. The main groups of drugs prescribed to patients with acute hemorrhoids are:
| Group of drugs | Destination purpose | Drugs |
| Fibrinolytic | Acceleration of the process of lysis (dissolution) of blood clots, restoration of impaired blood flow along the venous bed | Hepatrombin, Heparin ointment, Troxevasin, Hepazolon, Levomekol, Posterizan suppositories, Polidocanol |
| Venotonic | Restoring the tone of veins and blood vessels, improving blood circulation, normalizing lymphatic outflow | Detralex, Phlebodia, Venobene |
| Anti-inflammatory | Suppression of leukocyte activity, inhibition of inflammatory mediators | Diclofenac, Nimesil, Xefocam, Prednisolone |
| Analgesic alcohol-novocaine blockades | Pain relief, spasm relief | Analgin, Baralgin, Nitroglycerin ointment |
| Anticoagulant | Preventing blood clots by reducing the activity of the blood coagulation system | Warfarin, Aspirin |
| Antibacterial | Preventing the development of complications in the presence of an acute inflammatory process | Levosin, Levomekol |
| Laxatives | Softening stool, facilitating bowel movements | Regulax, Lavacol, Bisad, Duphalac |
| Hemostatic | Blocking bleeding of hemorrhoids | Natalsid, Relief, Hemoroidin |
| Biogenic stimulants | Improving the reparative properties of tissues, accelerating the healing process | Solcoseryl, Actovegin, Posterisan |
One of the effective external preparations for acute hemorrhoids is Posterizan ointment. Liniment has a multicomponent composition and provides a comprehensive effect on the problem. Due to its rapid action and absence of side effects, this remedy is popular among patients in proctology departments:
- name: Posterisan;
- characteristics: ointment for the treatment of hemorrhoids with an immunomodulatory effect based on a suspension of bacteria killed by phenol, contains phenol, lanolin and petroleum jelly, due to which it provides an anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and regenerating effect, a contraindication for use is intolerance to phenol;
- method of use: the product should be applied in a thin layer daily in the morning and evening to the affected areas; if hemorrhoids are located internally, the drug is administered rectally using an applicator, the duration of therapy is 2-3 weeks;
- side effect: rare allergic manifestations in the form of redness and itching in the area where the drug is applied;
- advantages: quick effect, minimal side effects;
- disadvantages: none found.
The dual-action drug Detralex has a beneficial effect on blood vessels. The complex of flavonoids included in the tablets helps normalize blood circulation and reduce the negative impact of inflammatory mediators on the venous walls. The maximum therapeutic effect is achieved with the combined use of Detralex and external drugs:
- name: Detralex;
- characteristics: venotonic and angioprotective agent, indicated in the treatment of diseases caused by circulatory disorders, the main active ingredient is diosmin - a plant polyphenol that has the ability to increase the total number of capillaries, after a course of treatment with the drug, hemodynamic parameters improve, tissue regeneration improves, taking tablets is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- dosage: the course of therapy lasts 1 week, during which the first 4 days should be taken 6 tablets per day, dividing the dose into two doses, in the next 3 days the daily dosage is 4 tablets;
- side effects: dyspeptic disorders, dizziness, headache, allergic rashes;
- advantages: systemic multifactorial action;
- Disadvantages: presence of side effects, high price.
Treatment at home
When the first signs of thrombosis of blood vessels in the rectum are detected, proven folk remedies can be used to alleviate the symptoms of the disease and prevent its progression. Self-treatment at home should not be the only measure taken to solve the problem - it is only an auxiliary method, the purpose of which is to prevent the spread of infection or the development of inflammation.
The choice of home treatment method should be agreed with your doctor. The most effective drugs against anorectal thrombosis are:
- Baths with a decoction of medicinal herbs. To prepare the medicinal composition, pour 200 g of dry birch leaves with a glass of boiling water, leave for 1 hour, then pour the mixture into a container for taking sitz baths. In a similar way, you can prepare a chamomile decoction or an infusion of oak bark. The procedure time should not exceed 20 minutes.
- Hirudotherapy. It is worth using the leech treatment method at home only if you have certain skills in this area. The method involves applying medicinal leeches to protruding thrombotic nodes, after which they should fall off on their own. The therapeutic effect lies in the enzyme hirudin secreted by leeches (which is a natural anticoagulant), which promotes the rapid dissolution of blood clots.
- Birch tar. A pharmaceutical product in the form of a liquid substance can be used to prepare an ointment (a mixture of tar and lamb fat in equal proportions) or to soak anal tampons. Tar has numerous healing properties, but can cause an allergic reaction, so before using it you should check your skin's sensitivity to this product.
Operation
Indications for the use of radical therapy for thrombosis are the lack of positive results of conservative treatment and heavy bleeding. At stage 3 of the disease, surgery is prescribed in 90% of cases. If the patient is diagnosed with severe exhaustion, dehydration, sepsis or a dying state, surgery is not performed. A thrombosed hemorrhoid can be removed using the following procedures:
| Type of operation | The essence of the procedure | Possible complications | Advantages | Flaws |
| Thrombectomy | Excision of all formed blood clots on the rectum using surgical instruments. The operation is performed using local anesthesia. The node is removed by making several cuts. The rehabilitation period lasts 5-7 days | Unpleasant sensations for several days after the procedure, rarely - development of sepsis, re-formation of blood clots, bleeding | The result is noticeable immediately after the procedure, the speed of the operation | Frequent complications, helps normalize blood circulation, but does not get rid of the disease |
| Sclerosis | Removal of nodes is carried out by introducing ethoxysklerol (sclerosing drug), the result of manipulation is the development of an inflammatory reaction and fibrotic changes that lead to the destruction of nodular tissue | Bleeding, pain due to the wrong site for drug administration, medication entering the anal veins or prostate gland | Painless, no need for anesthesia, short recovery period | Relapse of the disease after 12-18 months, not suitable for getting rid of large lumps |
| Ligation | Application of latex rings to thrombosed nodes, which leads to compression of the pedicle of the nodule and its death | Presence of pain, rectal bleeding, formation of new blood clots | The presence of scars at the site of fallen nodes; in the presence of multiple formations, several procedures will be required | Not recommended for the treatment of combined hemorrhoids |
| Hemorrhoidectomy | The operation is performed under general anesthesia, excision of the node occurs using a scalpel after suturing the artery approaching the node | Severe pain, external or internal bleeding, wound infection, fecal incontinence, anal fissures | The only method suitable for removing very large nodes | Highly traumatic procedure, difficult rehabilitation period |
| Coagulation | Destructive effects on the mucous membrane of infrared radiation, laser or electric current. The procedure is a minimally invasive treatment method; the principle of action is to coagulate (stick together particles) the affected tissues, which leads to their death | Spasm of the anal sphincter, deformation of the rectum, bleeding | Low tissue trauma | Frequent relapses, postoperative complications, ineffectiveness in treating the disease at stage 3 |
What methods can be used to treat thrombosis?
This is probably the main question for every patient - how will I be treated, is it possible to avoid surgery? It all depends on what stage the disease is at. Based on the diagnosis, the doctor chooses the most appropriate method of therapy. Actually, there are only two of them: medications or surgery.
Drug treatment gives results only at the first or second stage of development of this disease. Medicines are selected to normalize blood circulation and resolve blood clots, as well as to relieve pain.
The most commonly used ointments are Heparin, Levomekol, Gepatrombin, Proctosedyl.
They are used several times a day to lubricate the anus, or compresses are made with them. It is more appropriate to use suppositories for the treatment of internal hemorrhoids. These are Posterizan, Nigepan, Anestezol.
Prevention
A set of preventive measures to prevent the formation of blood clots in hemorrhoids is indicated for patients who have undergone treatment and for those with hemorrhoids in the chronic stage. The main preventive procedure is timely treatment of varicose veins of the rectum and minimizing the negative impact of factors that provoke the transition of the disease to an acute form. Prevention of thrombosis formation involves performing the following steps:
- normalization of the gastrointestinal tract, which is achieved through proper nutrition, eliminating fatty and spicy foods from the diet;
- cessation of addiction to psychostimulants (tobacco, alcohol, narcotic substances);
- increased physical activity;
- periodic completion of a course of physiotherapy;
- the use of traditional medicine to eliminate signs of chronic diseases.
Treatment of the disease
If the first symptoms appear indicating thrombosis of the hemorrhoid, treatment should begin immediately. The first step to success begins with a consultation with a proctologist.
It is important to tell your doctor about all the symptoms and possible causes of hemorrhoids.
If the hemorrhoids are slightly thrombosed, the proctologist may prescribe conservative (medicinal) treatment. Therapy will be aimed at increasing blood flow, eliminating congestion and eliminating blood clots.