The gallbladder is contracted, what does this mean? The question is asked after undergoing an ultrasound examination. The monitor displays changes in the size and shape of the bile duct. If it is shortened, they speak of hypermotor dyskinesia of the organ. The prefix “hyper” indicates excessiveness. The organ becomes spasmodic due to pathological reasons or due to taking medications or stress. In the latter cases, the phenomenon is temporary and is not considered a disease. If dyskinesia is constant, we are talking about a serious illness. It can appear in anyone, even a newborn child.
Why is the increase dangerous?
An increase in the size of the gallbladder poses a serious danger to the body. If the gallbladder is dilated, this negatively affects the functioning of its ducts, and congestion may occur. The consequence of the bladder stretching is stagnation of bile, and this directly affects the development of cholecystitis and the formation of stones in the organ cavity. The result may be perforation of the organ and the development of peritonitis. Help in this case must be urgent.
Also, with an increase in the volume of the organ, the functions of the digestive system are disrupted . With timely diagnosis and treatment, such consequences can be prevented.
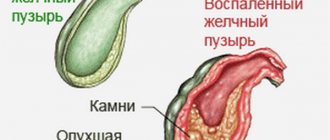
Differences between normal and enlarged gallbladder
The gallbladder is a temporary reservoir for bile.
It is constantly produced by the liver and flows through the bile ducts into the bladder, where it should remain for several hours (before the first meal). As soon as food enters the lumen of the duodenum, the gallbladder contracts and bile is released into the intestine. Average sizes of a healthy gallbladder in an adult:
- Length – 14–15 cm;
- Width – 2.5–4.0 cm;
- Volume – 20–30 ml.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:W5x7nv1ek4Q
An enlarged gallbladder is an excess of the specified normal parameters. This means that he:
- Expanded – the size and volume are larger than expected;
- Full of bile;
- Unable to fully contract;
- Turned off from digestion - accumulated bile stagnates in it;
All these changes can be either a dangerous deviation from the norm or a temporary adaptive reaction of the body.
A normal bladder with a volume of 30-50 ml has a length of up to 10 cm and a width of 2.5-4 cm. The thickness of the walls of the bladder is no more than 4 mm, the organ itself has the shape of a pear and is located in the lower part of the liver.
As the size and volume of the bubble increases, the following are disrupted:
- Contractile functions of organ walls. Because of this, bile accumulates in large volumes and begins to stagnate.
- Ability to store bile. Normally, the bladder accumulates bile, and during digestive processes it releases it into the duodenum. When the bladder is full, bile is released when food has not yet entered the intestines. Because of this, bile enters the stomach and esophagus, corroding their mucous membranes.
- Patency of the bile ducts. The outflow of bile worsens, the amount entering the intestine is not enough for digestion, and the remains stagnate in the bladder.
In most cases, these changes have pathological causes, but sometimes an increase in bile is an adaptive reaction of the body.
Causes of enlargement in adults
In appearance, the liver is pear-shaped and is located directly under the liver. The main function of the organ is the accumulation and gradual release of this secretion. Fluid production occurs in the liver. After which it enters the gallbladder, where it accumulates and is synthesized. In some cases, the function of the internal organ is disrupted, this is caused by the following reasons:
In some cases, gallbladder function is impaired
- Dyskinesia of the bile ducts. In this condition, the gallbladder most often enlarges. The cause of dyskinesia is that the walls of the organ become thinner, resulting in a disruption of the contractile function of the organ and its ducts. Gall disease is manifested by painful sensations in the abdomen on the right, heaviness or discomfort after eating.
- The cause can also often be an increase in the volume of bile, its stagnation in the organ and in the ducts. At the same time, it begins to contract less, and the rate of fluid release into the intestinal cavity decreases.
- The passage of stones from the gallbladder, as a result of which it begins to increase, and its functions are reduced.
- Deposition of a large amount of cholesterol on the walls of the bladder in an adult, due to which it becomes stretched.
- Tumors of the gallbladder and ducts, which become an obstacle to the outflow of fluid.
The reasons for the enlargement of the gallbladder in adults can lie not only in cholelithiasis, but also in other diseases: infectious processes, helminth damage, hepatitis virus, changes in the structure of secretion. This is why the organ enlarges, but the contractile function can decrease significantly. Therefore, timely treatment is very important; with its help, cholestasis can be prevented from removing the gallbladder. The doctor must select a suitable remedy for restoring the gallbladder, with which you can stretch its walls, stimulate the excretion of fluid, and increase the amount of its production in patients with cholecystitis.
Diagnostics
Additional diagnostics are necessary to make a diagnosis and determine the type of functional disorder. The examination protocol includes the following methods, which are reflected in Table 1.
Table 1. Diagnosis of biliary dyskinesia
| Kinds | Indicators |
| General clinical blood test | Detailed leukocyte formula, ESR |
| Biochemical blood test | Level of bilirubin, its fraction, alkaline phosphatase, ALT, cholesterol, y-glutamyl transpeptidase |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder | Reflects the type of dyskinesia and the state of the organ |
| Dynamic cholescintigraphy | Detects initial changes in the biliary tract, impaired contraction of the gallbladder, manifestations of reflux |
| Sphincter of Oddi manometry | Determines the level of pressure in the area of smooth circular muscle on the papilla of Vater |
Reasons for enlargement in children
An enlarged gallbladder in a child can also be observed. If the gall bladder enlarges in a child, regardless of age (in a newborn, infant, 1- or 2-year-old child), the causes most often are concomitant diseases, which include:
Children may also experience an enlarged gallbladder.
- a large bladder in babies is observed with the development of hepatitis or obstructive jaundice, the causes of which are small stones in the ducts;
- in children, the organ is enlarged during the development of scarlet fever;
- in infants and older children, this symptom may accompany pancreatitis or gastroenteritis;
- an infant or older child may suffer from biliary dyskinesia;
- if the bile ducts are twisted;
- when an organ is infected with E. coli or helminths.
Most often, this symptom appears with abnormal development of an organ or with polyps in it. Such factors cause fluid stagnation, organ functions are disrupted, and ducts are blocked. Why can this condition occur in infants? The reason may be improper feeding with artificial formulas, force-feeding of the child, lack of a diet, feeding children with low-quality or excessively fatty foods in large quantities.
Diet and proper nutrition
If the functioning of the gallbladder and liver is impaired, patients are recommended to follow the therapeutic diet No. 5. The main task of this nutritional plan is to provide a gentle regime for the organs, while the body must receive all the necessary microelements and vitamins.
Prohibited products include:
- alcohol, including beer;
- coffee, cocoa, carbonated drinks;
- fatty, salty and smoked foods;
- broths with meat, fish, mushrooms;
- sweets, baked goods;
- some types of cereals: lentils, beans, peas, limited corn, pearl barley, barley;
- conservation;
- sausages;
- fresh berries, some vegetables - onions, garlic, radishes, turnips, radishes, corn, sorrel, spinach, corn;
- any sauces;
- spices, nuts, mushrooms, sesame, sunflower seeds.
Symptoms of pathology
If the bubble increases in size, the liver hurts under the rib in the right hypochondrium, what should you do in this case? With such symptoms, it is important to consult a doctor and receive timely treatment. The key clinical sign of the pathological condition is pain on the right side, which cannot be eliminated with medications. The nature and intensity of pain may vary, but it has been noted that they become more pronounced after eating fried, fatty, or smoked foods.
If there are gastric diseases, the following clinical manifestations additionally appear:
Gallbladder diseases are characterized by attacks of nausea and vomiting
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- hyperthermia, with indicators most often subfebrile;
- a person loses his usual weight;
- there is a bitter taste in the oral cavity, the mucous membrane is dry;
- feces become much lighter, and urine acquires an intense dark color;
- yellowness of the epidermal layer is observed;
- the surface of the tongue becomes crimson.
What examinations need to be completed
At your first visit to a therapist or gastroenterologist, he will order a general blood and urine test. If the results show problems with the gallbladder, you will need to find their cause. To do this, laboratory and instrumental examinations are carried out:
- Stool analysis for suspected parasitic infestation.
- Blood chemistry. It reveals inflammation, injuries to the gall bladder, and confirms problems with the organ due to the presence of bile components in the blood.
- Ultrasound, radiography, MRI, CT - using these methods, doctors will see that the bile ducts are dilated and determine the presence of stones or parasites in them.
- Biopsy. A special needle is used to collect several cells from the bladder for examination. This method is used to examine tumor tissue under a microscope.
- Gastroscopy. The indication is a suspicion of a connection between an increase in bile ducts and a disease of the gastrointestinal tract.
To establish the cause, you will need to visit a general practitioner and a gastroenterologist/hepatologist. When making a diagnosis, you may need to consult a parasitologist, allergist, oncologist, surgeon, or endocrinologist.
Treatment methods
If the organ is enlarged, it is important not to delay with therapeutic measures. If the gallbladder is enlarged, treatment is carried out only after preliminary medical prescriptions. How to treat an enlarged gallbladder:
- taking hepatoprotectors;
- taking medications based on bile acids;
- use of antispasmodics;
- litholic therapy.
It is important to remember that drug treatment will be advisable only if the gallbladder is enlarged for a short time, if the initial stage of the disease develops. No traditional methods should be used in this case. Otherwise, the patient's condition may worsen, and the disease will progress rapidly. In advanced cases, only surgical treatment using laparoscopy, ultrasound, laser or abdominal surgery is indicated.
Possible complications
If left untreated, an enlarged gallbladder can cause dangerous pathologies. Secretions accumulate in the organ, expanding the walls, which gradually become thinner. There is a threat of perforation, as a result of which bile enters the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis. This condition poses a threat to the patient's life.
If the gallbladder is enlarged for a long time, stagnation of the secretion, changes in composition, and the threat of stones appear. Dysfunction of the organ leads to disruption of the housing and communal services. Food is not digested, the body does not receive the necessary nutrients. A person may lose weight and suffer from vitamin deficiency. To avoid dangerous complications, it is necessary to treat an enlarged gallbladder.
How to treat pathology in childhood
If a child is found to have an increase in organ volume, treatment involves hospitalization, the prescription of antispasmodics, hepatoprotectors, bile acids, and proper nutrition. The diet must be followed until the main cause of the pathology is eliminated. After which the child must be observed by a hepatologist or gastroenterologist, children are registered at a dispensary, periodically they need to visit a doctor and undergo prescribed diagnostic measures. If there are stones in an organ or in its canals, even in childhood, a procedure is performed to remove them - laparoscopy (or another option).
To prevent this condition in the future, it is recommended to eat right, lead a healthy lifestyle, give up bad habits, give the body feasible physical activity, and also promptly consult a doctor for treatment of concomitant diseases of the abdominal organs.
Prevention and prognosis
People with a family history and dietary errors should be wary of gallbladder pathology. The following will help you avoid problems:
- Dietary food (table No. 5 - gentle food, excluding fatty, fried foods, spices, smoked meats and baked goods);
- Regular 3 meals a day;
- Annual preventive ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
Following the rules of a healthy diet and lifestyle will help you avoid a pathological increase in gallstones. Compliance with food intake, avoidance of alcohol, and emotional well-being will help you avoid diseases of the digestive system. Regular examination of the gastrointestinal tract will reveal pathological processes in time.
An enlarged gallbladder is a symptom of digestive diseases. In the absence of timely treatment, the pathology causes life-threatening complications.
To prevent the disease, errors in nutrition and consumption of fatty foods should be avoided. Also, if it is necessary to take medications for a long time, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the gallbladder using ultrasound.
Prevent stagnation of bile and moderate physical activity. In order to avoid problems in children, it is necessary to follow the rules for introducing complementary foods in consultation with a pediatrician.
The prognosis of treatment depends on the underlying cause. In most cases, it is possible to normalize the patient's condition. It is important not to start the disease so that peritonitis or sepsis does not develop.