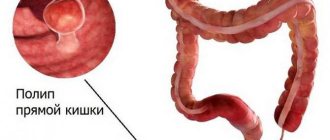
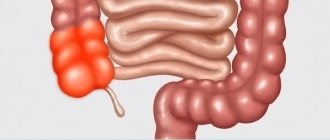
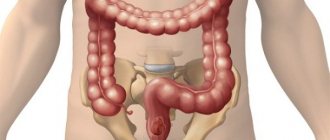
Polyps in the large intestine are benign neoplasms formed from glandular epithelial cells. Normally, tissues from this type of cells line the inside of the intestine, but under the influence of certain factors they begin to grow uncontrollably, forming single or multiple mushroom-shaped, spherical or branched outgrowths directed into the intestinal lumen. In the international classification of diseases ICD-10, colon polyps are designated by code K63.5. (colon polyps).
Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in men and women of the older age category. The greatest surge in incidence is observed after overcoming the 60-year mark. In childhood, polyps are found more often in boys aged 3 to 6 years (in 80% of cases), and most often neoplasms are localized in the distal intestine.
The main danger of polyps in the large intestine is the high risk of malignancy (degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one). That is why, regardless of what polyps (type, shape and size) are detected, they are considered precancerous neoplasms with varying degrees of malignancy.
Types and sizes of colon polyps
In medicine, a branched classification of polyps of the large intestine has been formulated depending on the cellular structure, appearance, nature and number of tumors. The size of the polyps also plays a role in diagnosis, since this parameter is directly related to the risk of intestinal cancer.
Polyps are divided into 4 types (forms) depending on their structure:
- Adenomatous is the most common and dangerous form of polyps, which can differ in appearance. There are tubular (tubular), tubular-villous and villous. The neoplasms are penetrated by many tiny vessels and often bleed. Regardless of appearance, they have a high level of malignancy (malignancy). It is diagnosed mainly in older people.
- Hyperplastic - a small glandular polyp, slightly rising above the surface of the intestinal mucosa, has a color natural to the surrounding epithelium. It is quite rare to transform into a malignant tumor. Often diagnosed in patients over 40 years of age.
- Hamartomatous - white-pink neoplasms that consist of several types of cells that develop disproportionately. Rarely reaches large sizes, as they grow evenly and very slowly. Such a neoplasm often bleeds and has a low risk of malignancy.
- Inflammatory - a glandular polyp that forms against the background of an acute inflammatory process in the intestine.
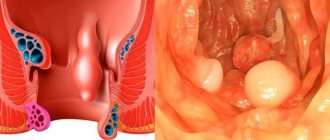
Based on the number of neoplasms in the intestine, single, multiple and diffuse (hundreds of rapidly growing and spreading neoplasms) polyps of the large intestine are distinguished. Diffuse and multiple polyps have the greatest tendency to transform into cancerous tumors.
Good to know! Affects the rate of malignancy and the size of polyps. Thus, small formations with a diameter of up to 1 cm have a degree of malignancy from 3 to 9%, while large polyps with a diameter of more than 3 cm transform into a cancerous tumor in 30% of cases.
Classification
The division into classes of polyps in the rectum, including the colon region, took a long time, and different characteristics of the processes were considered.
As a result, the following divisions were adopted, divided into groups:
- Group I – the presence of single or group polyps (hyperplastic, fibrous tumors of the anal canal, glandular-villous, glandular, non-epithelial).
- Group II – implies villous adenomas.
- Group III – diffuse, it includes secondary pseudopolyposis, familial.
Learn more about some of the most common types:
- Hyperplastic - has a size of 2-4 mm, is based in a cone-shaped shape, appears in large quantities.
- Villous - modified in 30% of cases. The neoplasm has a villous structure, and its symptoms are characterized by the presence of blood, mucus in the stool, transformation of diarrhea into constipation, and abdominal pain.
- The lobular form is considered the largest in terms of the level of degeneration into malignant and spread. Located in the rectum and sigmoid colon. It differs from others in its increased secretion of mucus (can reach up to one and a half liters). There is always blood in the feces.
- Adenomatous - occurs more often than others, looks like a smooth tumor, created from glands that differ in structure; in some you can see a cyst. Degeneration occurs in 50% of cases when the polyp is 2 cm in size.
But diffuse colon tumors grow in large numbers, which increases the risk of progression to oncology. The disease manifests itself as swelling, skin rash, and anemia. Sometimes with diffuse polyposis, baldness and changes in the nail plates occur.
https://youtu.be/8Wm5dJfvXic
%0D
Causes of colon polyps
Doctors cannot name the exact reasons for the formation of benign tumors in the large intestine. Previously, it was believed that their formation occurs under the influence of bad habits - alcoholism, smoking. However, a considerable number of patients diagnosed with colon polyposis follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle, which raised some doubts about the validity of such judgments.
Recent studies have found that bad habits as such are not the main risk factor. They play the role of a trigger, but in most cases the disease occurs in those whose close relatives suffered or suffer from polyps in various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, colon polyps threaten people with acute and chronic diseases of the digestive system, excess weight, and chronic stool disorders due to non-compliance with norms and diet.
According to statistics, approximately 50% of men and women over 60 years old have polyps in the large intestine. This indicates that age-related changes are the most common cause of the disease.
Important! Certain types of polyps are formed due to inflammation of the intestinal mucosa.
Symptoms and signs of colon polyps
At the initial stages of development, polyps do not appear in any way, and therefore they are discovered by chance when examining the intestines for other diseases. Clinical manifestations of polyposis appear if there are several benign formations or they are more than 1 cm in diameter. In this case, the symptoms can be very diverse and nonspecific. Most often, patients complain of the following phenomena:
- unstable stool with frequent alternation of diarrhea and constipation, sometimes within one day;
- irritation of the mucous membrane of the anus and the skin of the perianal area, which occurs against the background of abundant mucus secretion from the rectum (a symptom characteristic of polyps located in the lower part of the colon);
- scant rectal bleeding that is not accompanied by acute pain in the anus (a symptom characteristic of villous polyps located in the lower part of the large intestine);
If you have these problems, you should urgently contact a gastroenterologist or coloproctologist, since they are the ones who diagnose and treat the disease.
How to prevent disease
Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle.
Because there may be a link between diet and the development of intestinal polyps, a balanced diet that is low in fat and fiber is recommended. You should limit your alcohol consumption and avoid nicotine. Regular exercise and losing weight also help reduce the risk of developing a hyperplastic polyp.
Timely consultation with a doctor.
In addition, it is important to identify and remove possible polyps at an early stage to prevent the development of colon cancer. Therefore, it makes sense to undergo the recommended examinations. Intestinal complaints such as irregular bowel movements such as diarrhea or constipation, or blood in the stool should be investigated in any case.
Diagnostics
Very often, the symptomatic manifestations of colon polyps are similar to other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. When making a diagnosis, differential diagnosis is used, during which the doctor excludes other pathologies.
First of all, the doctor collects anamnesis and conducts a survey of the patient, during which he establishes the characteristics of the patient’s symptoms, diet and gastronomic habits.
Important! To make a correct diagnosis, a specialist will need information about previous diseases and diseases of the colon that immediate relatives have suffered.
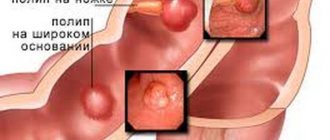
Next, the coloproctologist conducts a digital examination of the rectum, during which it is possible to determine the presence of polyps in the area of the rectum remote from the anus, their size, method of attachment to the mucous membrane (pedunculated or wide base), shape, consistency and degree of displacement.
In addition to the listed studies, patients with suspected colon polyposis will have to undergo a number of laboratory tests:
- general blood test (in some situations, low hemoglobin levels indicate polyposis);
- stool occult blood test (often replaced by the Colon-View occult blood screening test).
To establish the exact location, size, number and shape of polyps in the colon, instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
- sigmoidoscopy - a visual examination using endoscopic equipment equipped with a fiber optic system, a light source and forceps for taking a biopsy;
- colonoscopy is a method of visual examination of the intestines using a flexible probe (colonoscope) equipped with a camera, a lighting device, an air injection tube and forceps for taking a biopsy;
- irrigoscopy - x-ray examination of the colon using a contrast agent;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
After colonoscopy and sigmoidoscopy, a study of biological materials (parts of the mucous membrane of the colon or the polyp itself) is carried out to determine their cellular structure and the risk of malignancy.
Treatment methods for colon polyps
Conservative methods of therapy for colon polyps are not used, as they are not effective. Doctors call surgical removal of tumors the only way to eliminate them. Depending on which polyps are detected during diagnosis, the following methods are used:
Surgical colonoscopy is used to remove single and multiple polyps. It is performed using a colonoscope equipped with a loop electrode. During the procedure, a loop is placed on the stalk of the polyp and tightened until it fits as tightly as possible. Then high-frequency currents are passed through the loop, as a result of which the head is cut off and the leg is charred. The resulting wound is cauterized.
If the polyp is located on the mucous membrane of the colon on a broad basis, an endoscopic operation is performed, the so-called endoscopic resection of the mucosa, with coagulation of the base of the wound. The operation is performed using a special electric knife, which is used to resect a section of the mucous membrane along with the polyp. Surgeries for resection of colon polyps can be quite lengthy, the duration depends on the size of the polyp, but they are minimally traumatic and do not require long-term hospitalization. Typically, the hospitalization period is from 1 to 3 days.
Radio wave and laser coagulation. Used to remove one or more polyps. The tumor is exposed to a narrow beam, causing its tissue to die. To prevent bleeding, coagulation of blood vessels is performed. The procedure, like the previous one, is low-traumatic, does not cause side effects and does not require long-term rehabilitation and recovery.
Abdominal surgery. For diffuse familial polyposis, a subtotal or total colectomy is performed, i.e. resection of the colon with the affected area, subsequently an anastomosis is formed.
Immediately after surgery, a gentle diet with limited salt, sour, and spicy foods is recommended. Do not eat too hot or cold foods, mushrooms, fatty meat and fish, fried and smoked foods, alcohol and strong coffee. You will have to stick to the diet for at least 4 weeks.
After removal of types of polyps prone to malignancy (villous, multiple and large), a year after treatment, the patient is shown an endoscopic examination of the intestine to monitor the condition of the mucous membrane. Medical supervision is recommended for two years.
If there are no symptoms of polyposis, colonoscopy is subsequently performed every three years.
Complications of the disease
In patients who ignore the signs of the disease, colon polyps can provoke various complications:
- intestinal bleeding;
- intestinal obstruction;
- severe forms of anemia.
The most dangerous complication of colon polyposis is colorectal cancer. This disease poses a serious threat to the patient’s life and requires complex combined treatment - surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
About the risks of colorectal cancer and the importance of timely diagnosis of colon polyps, watch the video:
The only complication that threatens patients who have undergone the procedure for removing polyps in the large intestine is intestinal perforation, when a hole forms in the intestinal wall at the site of polyp removal. As a result of the effusion of intestinal contents into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis may develop. Fortunately, such complications occur extremely rarely.
Surgery
Large adenomas that the examiner cannot remove during a colonoscopy must be removed surgically. If the polyp is cancerous (colon cancer), treatment depends on the location and type. It may be necessary to remove part of the intestine. If the tumor has only spread superficially, it may also be sufficient to remove only the polyp itself and subsequently carry out regular examinations. Intestinal surgery is also necessary if high-risk cancer cells are found in a distant mass. The risk that previous polyp removal may have left cancer cells in the intestine is so great that the affected part of the intestine must be removed in a subsequent operation. In the hands of an experienced physician, polypectomy is a low-risk treatment. However, complications may occur, especially due to bleeding. Damage to the intestinal wall is also possible when removing large polyps.