Pain in the uterus and the menstrual cycle
Algomenorrhea is what scientific medicine calls pain before the onset of menstruation. Every second out of three women suffers from spasms, accompanied by additional symptoms:
In some cases, this is just a signal about the onset of menstruation, in others it is the first sign of pathologies in the body.
Why does the uterus hurt before menstruation?
Characteristic cramps in the uterus before menstruation occur for one reason: the endometrium, if pregnancy does not occur, is torn away from the walls of the uterus. In this case, a large amount of prostaglandins are released, which are responsible for strong muscle contraction, causing discomfort. It is almost impossible to avoid this feeling. In some women it is strongly expressed, in others it is tolerated.
If the uterus hurts several days before menstruation, most likely this is not a deviation from the norm. This sign will be a characteristic symptom of approaching menstruation.
Several reasons why the uterus hurts before menstruation a week before:
- adhesions of the pelvic organs;
- damage to the digestive tract;
- menstrual irregularities;
- late ovulation;
- pregnancy;
- inflammation of the genital organs.
Why does the uterus hurt during menstruation?
The occurrence of pain directly during menstruation is considered normal: the body tries to remove the rejected endometrium along with the unfertilized egg as quickly as possible.
Most women don't think about it and stock up on painkillers in advance to relieve discomfort. The same thing happens when the uterus hurts a week before menstruation. Naively believing that these are harbingers of discharge, girls block the unpleasant sensations with pills.
The reasons for this phenomenon are:
- Young age - the girl has just entered reproductive age, the menstrual cycle has not yet been established.
- Excessive physical activity causes pain in the uterus during menstruation, as well as the cause of uterine tone before menstruation.
- Sexual contact - when menstruation has already arrived and sexual intercourse has occurred, cramps may also occur.
Why does the uterus hurt after menstruation?
A woman is most alarmed by tingling in the uterus after menstruation, when pain is observed a couple of days after the end of the discharge. If the situation repeats itself every time, gynecologists attribute this to a slight increase in hormones. Besides this, there are several other reasons:
- taking certain medications;
- acute inflammation of appendicitis;
- poisoning;
- cystitis;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- inflammation of other genital organs;
- muscle strain or injury.
All of these problems can cause pain in the uterus, because the discomfort is concentrated in the lower abdomen, which is easily confused with cramps.
Why does the uterus hurt in the middle of the cycle?
Another strange phenomenon that frightens girls is pain in the uterus in the middle of the cycle. The most common reason is the onset of ovulation - it is observed in women of reproductive age. Other prerequisites for the occurrence of pain will be:
- Implantation of the fertilized egg - when conception occurs, the fertilized egg descends into the uterine cavity and attaches to the mucous membrane.
- Gynecological pathologies: inflammation of the appendages, adenomyosis, ovarian cysts, rupture of ovarian cysts.
If the examination shows that pregnancy has not occurred and there has been no ovulation, then it is urgently recommended to consult a doctor. Such a dangerous symptom as tingling in the uterus on the 22nd day of the cycle may indicate serious problems.
Pain during ovulation
The uterus hurts in the middle of the cycle due to ovulation in 20% of women of reproductive age.
The pain that accompanies ovulation can be triggered by several factors.
- It may hurt as a result of the follicle being too large. This causes pathological stretching of the ovarian walls, which is accompanied by pain. Do not forget that the uterus is located in close proximity.
- When a mature egg is released, a small volume of fluid enters the abdominal cavity, which causes irritation of the parietal peritoneum.
- When the capsule of the ovary itself is damaged, involuntary damage to small blood vessels occurs. The small amount of blood pouring out also causes irritation, which is the reason why the uterus hurts (this is how it feels to a woman) in the middle of the cycle.
Another reason why the uterus may hurt in the middle of the cycle is the active contraction of the fallopian tubes, caused by the movement of a mature egg into the uterine cavity.
How to relieve pain
Most women traditionally use antispasmodics to relieve pain when the uterus is in good shape during menstruation. This approach is not considered effective, since the action of the drugs is not directed at the cause of the pain. After some help, the pain returns again.
Instead, gynecologists recommend using anti-inflammatory painkillers. Some girls find regular Ibuprofen helpful, so there is no point in running around pharmacies looking for a medicine with a complex composition. Among nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), you can take Ketanov, Nise, Tempalgin, Nurofen, Dexalgin.
When pain is a symptom of pathology
There are several cases that are worth paying attention to and immediately making an appointment with a gynecologist. To protect yourself from chronic pathologies, you should carefully monitor your health, noting symptoms unusual for the body:
- pulls the uterus in the middle of the cycle, with pronounced pain, accompanied by nausea and vomiting, chills, dizziness and increased body temperature;
- there is bloating and an increase in the amount of gases;
- pulls the uterus before menstruation, a migraine appears, a feeling of heat, loss of consciousness is possible;
- painkillers do not help;
- there is a violation of the cycle, as well as a decrease in body weight;
- pain in the uterus can last about 2 days.
Implantation pain
Pain in the uterus in the middle of the cycle may be a sign of implantation of the fertilized egg. The fastening itself occurs in three stages:
- Joining. The fertilized egg descends into the uterine cavity and clings to the mucous membrane.
- Adhesion. The joining took place. Wall microvilli actively interact with egg cells.
- Invasion and investment. The embryo, partially destroying the mucous membrane, penetrates into it. An embryonic bud is formed. It is at this stage that a woman may feel mild pain.
Signs of implantation include:
- implantation bleeding - scanty, brownish or pinkish discharge;
- slight nagging pain in the lower abdomen (the uterus hurts, but not much);
- an increase in basal temperature, which is explained by a gradual increase in progesterone levels due to the attachment of the embryo;
- slight malaise;
- emotional instability.
Prevention
To eliminate painful periods, it is recommended to carry out preventive measures. For example, avoid a sedentary lifestyle and do not abuse alcohol. You should also give up smoking, drinking strong coffee and tea. An important aspect is the normalization of nutrition. It is recommended to eat foods with unsaturated fatty acids or replace them with ready-made vitamins from the pharmacy. Do not forget about timely hygiene of the genital organs - it should be done twice a day.
Types of pain in the uterus
Depending on the etymology, pain in the uterus differs in location, as well as the nature of the manifestations. They are:
tingling - manifestations of this type may indicate the presence of inflammation of the urinary system, and also develop during the process of ovulation. If tingling is accompanied by a frequent urge to urinate or discharge with a characteristic odor, it is important to visit a gynecologist and get tested for STDs;
sharp, similar to a spasm - in this case, the stomach can get sick completely unexpectedly or after physical exertion. Spasms often accompany diseases such as fibroids, endometriosis, adenomyosis and cervical flexion;
pulling - usually do not cause concern. A distinctive feature of pain in the uterus during dysmenorrhea is cyclicality. They appear in the middle of the cycle and disappear in the first days of regulation. Before menstruation, the mucous layer and cervix of the uterus change their structure and prepare for the rejection of the endometrium, which causes mild pain. If the pulling sensation is accompanied by discharge with a pungent odor, then in this case it is recommended to make sure that there is no inflammation.
Pain occurs both at the beginning of menstruation and every month a week before menstruation. To exclude pathology, it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist and conduct preventive examinations and ultrasounds.
Pain before menstruation
Pain in the uterus can occur for various reasons. If a woman has pain in the uterus before menstruation, it is necessary to undergo a gynecological examination. Perhaps the reason lies in one of the following conditions:
- pregnancy - the first signs of pregnancy may appear in the form of a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen. They occur a few days before the onset of regulation and are very similar to ordinary cyclic pain;
- inflammatory process - in this case the sensations are accompanied by copious discharge with a pungent odor, as well as an increase in temperature and a general deterioration in well-being;
- individual characteristics - painful menstruation can be a manifestation of the individual characteristics of the body. Pain in the uterus before menstruation does not occur in every representative of the fairer sex;
- tumor processes - tumors can be malignant or benign, despite this, they have fairly similar symptoms. The pain in the uterus is pronounced and constant, intensifying before the onset of regulation.
Premenstrual pain causes a lot of inconvenience for women. Regardless of the severity, unpleasant symptoms in the uterus require mandatory monitoring by a gynecologist. In some cases, the patient’s condition can be normalized with the help of medication or surgical treatment.
Physiological causes of pain
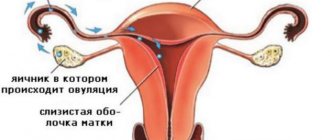
The main cause of pain in the middle of the menstrual cycle is ovulation. The nagging pain in the lower abdomen associated with this process is physiological in nature. Ovulation occurs on the 14th day of the menstrual cycle with its normal duration (28 days). Pain and discomfort occur on the side of the abdominal wall where the ovary with dominant follicles is located.
No matter how severe the pain during ovulation, it in no way harms the woman’s body.
Pain can occur at different stages of ovulation. Before the egg is released from the follicle, it needs to increase in size. The large dimensions of the follicle stretch the surface film of the ovary, which determines the appearance of pain. The follicle leaves the ovary, and its thin membrane, well supplied with blood, ruptures, creating minor bleeding. During rupture of the site of egg maturation, a small amount of fluid and blood is poured into the abdominal cavity, which, in turn, irritates the peritoneum. After this, the discomfort lasts for 1-2 days, after which the fluid and blood are absorbed and the pain goes away. After the release of a mature female reproductive cell, the fallopian tubes begin to contract strongly to capture it and deliver it to the most active sperm. In rare cases, discomfort may be supported by peristaltic movements of the fallopian tubes.
The strength of pain directly depends on several factors, including:
- increased emotional lability of women;
- various diseases in the field of gynecology;
- Increased threshold of pain sensitivity (pain is practically not felt at a high threshold).
During ovulation, simultaneously with the most important symptom – pain – others appear:
- overwork;
- general malaise, deterioration in performance;
- increased libido;
- discharge. Throughout the entire menstrual cycle, the type of discharge changes. During ovulation, they become more fluid, which makes it easier for sperm to penetrate the egg ready for fertilization.
In some women, the ovulation phase occurs with pain in the mammary glands.
In rare cases, after pregnancy, menstrual bleeding does not stop, and the woman is not even aware of her interesting situation. In this case, there is a danger of miscarriage or an abnormal pregnancy - ectopic. If a woman has reasons to suspect pregnancy, she should immediately do a sensitive hCG test and contact a gynecologist for qualified help. This will protect you from the development of unwanted diseases and, perhaps, will be able to save the life of your unborn baby.
Pain syndrome during menstruation
To understand why the uterus and appendages hurt during menstruation, it is necessary to understand what physiological processes occur at this moment in a woman’s body. During regulation, the organ “gets rid” of the endometrium, which comes out along with the blood. At the same time, it contracts, which causes painful symptoms.
In addition to natural causes, pain during menstruation can occur against the background of pathologies. Pain in the lower abdomen sometimes indicates the following problems:
- endometriosis;
- myoma;
- malignant tumors;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- congenital pathologies.
If pain during menstruation affects your usual lifestyle. To eliminate them, you need to undergo an examination and find out the root cause of the problem.
Why does my stomach hurt during menstruation when using an intrauterine device?
Abdominal pain during menstruation is caused only by non-hormonal intrauterine contraceptives (IUDs). The fact is that the very principle of their action is to increase the synthesis of prostaglandins. Non-hormonal IUDs reliably protect against conception, but have unpleasant side effects such as heavy bleeding and pain during menstruation.
Algodysmenorrhea when using non-hormonal IUDs in itself is not an indication for removing the IUD. Abdominal pain during menstruation may completely disappear over time (as a rule, this occurs by the end of the first year of using an IUD).
However, the method of controlling reproduction can be changed at the request of the woman. So, for example, hormonal IUDs do not cause such complications. Moreover, they are recommended for women with heavy and painful menstruation, since the use of a hormonal IUD allows you to get rid of these unpleasant symptoms.
When pain speaks of illness
It is possible to distinguish physiological manifestations of menstruation from pathological ones by the nature of their manifestation, as well as by accompanying symptoms. You should seek urgent medical help if:
- sharp pain occurs suddenly. In this case, it may indicate a bend of the uterus during menstruation;
- there is an increase in body temperature. This condition is typical for purulent and inflammatory processes;
- a woman discovers the presence of purulent discharge;
- bleeding develops.
In the cases listed above, you need to seek specialized help.
Pain due to inflammation of the female organs
Unpleasant manifestations of an inflammatory nature have a number of distinctive features: they are always accompanied by additional symptoms. These include:
- the presence of copious discharge of greenish, brown or yellow color with an unpleasant odor;
- redness of the external genitalia, itching and burning;
- increased body temperature;
- frequent urge to urinate.
Severe pain in the uterine area during menstruation indicates inflammation of the endometrium of the uterus. Also, unpleasant symptoms can be localized in the ovary area. Among the pathologies caused by inflammation are:
- endometritis - affects the mucous membrane of the organ;
- panmetritis - covers the uterus completely;
- endomyometritis - affects the mucous membrane and myometrium.
In the absence of timely treatment, inflammatory processes can develop into both malignant and benign tumors, including uterine fibroids.
Gynecological causes of pain
However, along with physiological reasons, there are also gynecological reasons, which cannot be classified as normal.
Anovulation. This is a pathological condition of a woman’s reproductive system, accompanied by a lack of maturation of the egg and its release from the follicle. Physiological anovulation is observed during pregnancy, premenopausal and menopausal age, as well as while taking hormonal contraceptives. If a woman of childbearing age continues to anovulate for more than two cycles in a row, you should immediately consult a gynecologist, because if there is no ovulation, it means there is no egg and there is no possibility of conceiving a child. According to the practical experience of gynecologists, the main reason for the lack of ovulation is hormonal imbalance. With proper treatment, it can be stopped, which will return the woman a unique opportunity to become pregnant and give birth to a child;
- Pathology of the ovaries (inflammatory process, torsion of the legs, neoplasms (benign or malignant), ovarian ischemia). A feature of the pain syndrome in ovarian diseases is that discomfort occurs in the direction of the affected organ, depending on which ovary is inflamed. In any of the above situations, the severity of the pain increases exponentially along with the development of other symptoms: signs of inflammation of the peritoneum, increased body temperature, etc.;
- Ovarian hyperstimulation. With long-term hormonal treatment for infertility, the normal size of the ovaries increases several times. It is possible that cystic follicular formations and stromal edema are formed on the surface of the ovarian capsule at this time. Subjective sensations at the first stage include a clear increase in total body weight, flatulence, severe pain in the pelvic area;
- Inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. None of the women can be protected from the penetration of pathogenic flora into the uterus or vagina. As a result, an inflammatory process occurs, manifested by diffuse pain, localized in the lower part of the abdominal wall and occurring in the middle of the cycle, together with a large amount of discharge (depending on the nature of the pathogenic bacteria, the discharge changes color and smell). After the inflammatory process, the formation of adhesions is possible, leading to severe discomfort. The rupture of adhesions is accompanied by a severe attack of pain, sometimes shock;
- Malignant formations of the genital organs. To prevent such a terrible diagnosis, you should regularly undergo examinations with a gynecologist. The first and main symptom of ovarian and uterine cancer is increasing pain that occurs in the middle of the cycle.
Read about the causes of pain during menstruation here. Read about what brown discharge means during menstruation here.
Pain in other diseases of the female organs
There are a number of situations when discomfort in the uterus occurs as a result of damage to neighboring organs. Such pain is called radiating pain. Among the most common causes of discomfort in the lower abdomen are:
- gastrointestinal diseases - in this case, a woman feels a slight tingling or sharp stabbing pain during menstruation;
- hemorrhoids - unpleasant sensations occur in the form of spasms;
- lesions of the musculoskeletal system and spine - sensations can be pulling or sharp and radiate to the lumbar region during menstruation;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- congenital or acquired disorders in the pelvis.
Analgesics will help alleviate the condition when such a problem occurs. Taking painkillers is possible only after receiving a doctor’s opinion and making a correct diagnosis.
What to do
If the pain is caused by inflammatory diseases or tumor processes, self-medication will worsen the situation. In the absence of diseases of the pelvic organs, you can use the following tips:
- take painkillers. You can take medications such as No-shpa or Ketorol;
- when the pain during menstruation is very strong, doctors recommend giving up physical activity and try to take a comfortable position;
- take a warm shower or place a warm, but not hot, heating pad on your lower abdomen;
- massage the uterine area. To do this, perform circular movements, being careful not to press your stomach too hard.
Pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation may indicate pathologies affecting both the uterus and abdominal organs. To determine the root cause of discomfort and prescribe effective therapy, it is important to undergo a comprehensive examination and undergo a series of tests.
What is algodismenorrhea
Often, when painful periods come, both a teenage girl and an adult woman begin to really panic and many do not know what to do. Pain in the lower abdomen can be so severe that it leads to decreased ability to work, sleep disturbances, tearfulness, depression, stress, irritability, nausea, vomiting, etc.
Gynecologists remind that menstrual pain is a symptom that in itself cannot lead to complications, but its causes are a signal of possible serious disorders in the female body.
Depending on the time of appearance and characteristics of the course, medicine distinguishes 2 types of algomenorrhea:
✔ Primary algodismenorrhea. It begins with the appearance of severe pain in the lower abdomen during menstruation in girls and nulliparous young girls 1-1.5 years after the arrival of the first menstruation. Primary algodismenorrhea can be congenital with abnormal development of connective tissue, scoliosis, myopia, flat feet, varicose veins, and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms of primary dysmenorrhea appear more often before or with the onset of menarche. Typically, painful sensations are more pronounced in young girls with an asthenic physique. During menstruation, cramping, throbbing pain with distension, colic in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back, anus, and perineal area, appears. Usually, general health worsens at the same time, with nausea, vomiting, weakness, and irritability.
✔ Secondary algodismenorrhea. Occurs during life at an older age. The causes and triggers of menstrual pain can be various gynecological pathologies, surgical interventions on the pelvic organs, appendicitis, hormonal disorders, etc. There is nagging, prolonged pain throughout the menstrual cycle. There may well be an increase in symptoms 3-4 days before the onset of menstruation, when cramping pain appears that cannot be relieved with analgesics, sometimes spotting, “dirty”, vaginal discharge. That is, secondary algomenorrhea is more often caused by organic disorders, such as hormonal imbalance, dysfunction of the nervous system, and impaired prostaglandin production. Our gynecologist will help you get rid of pain during menstruation.
Why does the lower abdomen hurt during menstruation?
When diagnosed with “algodysmenorrhea” in the first days of menstruation, pain is caused by specific biologically active substances produced in the uterus - prostaglandins, which can lead to irritation of the nerve endings of tissues, spasm and increased uterine contractions, and the release of the endometrium with bleeding.
Most girls suffer from abdominal pain during menstruation for physiological reasons , when the genital organs simply do not have time to fully form with the arrival of menarche - primary menstruation. This is facilitated by:
- hormonal instability;
- incomplete formation of the body structure;
- underdevelopment of the uterus (hypoplasia, infantilism);
- irregularity in the location of the genital organs, impeding the free exit of menstrual blood to the outside (bending of the uterus and its displacement to the side or posteriorly, adhesions in the pelvis).
The reason why the stomach may hurt during menstruation may be gynecological diseases:
- endometriosis (with focal growth of the endometrium, extending beyond the uterine cavity);
- chronic inflammation of the uterus and appendages;
- ovarian cysts, polycystic tissue changes;
- polypisis of the endometrium and cervical canal;
- cervical dysplasia, uterine fibroids (severe pain during menstruation that radiates to the lower back).
Very painful menstruation can be caused by:
- hormonal instability;
- deficiency of vitamins, magnesium, calcium in the body;
- decreased vascular permeability and blood clotting;
- weakness of the vaginal muscles;
- excessive contraction of the uterus;
- varicose veins of the pelvis and blood stagnation;
- immaturity of development of the organs of the reproductive system;
- pelvic neuralgia, sciatica;
- bending of the uterus, which obstructs the outflow of blood;
- emotional instability in adolescence;
- lack of regular, safe sex life with orgasm;
- decreased pain threshold.
These are just some of the possible causes of unpleasant phenomena that monthly “turn you off” for several days from your active life. Painful periods can also be caused by a serious illness, so in order to avoid complications and worsening pathology, doctors recommend not ignoring the symptoms of algomenorrhea. If menstrual pain has become unusual - stronger, intrusive and prolonged, then girls should immediately contact a good gynecologist and undergo a detailed examination.
Painful menstruation - video
Many gynecologists ask whether the general condition can change before menstruation? Menstruation accompanied by painful sensations is not uncommon. For women, this process is individual. Therefore, if your uterus hurts before or during your period, you should not panic. It all depends on the intensity of the symptoms that cause discomfort to the woman.
The uterus refers to one of the organs involved in reproductive function. It is necessary to listen to the state of the body so as not to miss alarming signs of any disease. Minor pain in the first days of menstruation is not a pathology. They can radiate to the lower abdomen and lower back, but the woman’s general well-being does not change. Severe, sharp, cramping pain most often indicates a pathology of the organs of the reproductive system. Their development is also accompanied by symptoms of intoxication (fever, chills), deterioration of the general condition in the form of loss of consciousness, dizziness.
The menstrual cycle is cyclical and repeats every 21-36 days. Its development may be accompanied by painful sensations in the lower abdomen, sometimes nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and changes in emotional background. If these signs have a certain periodicity with varying intensity, the doctor determines a condition such as uterine PMS (premenstrual syndrome).
Pain in the middle of the menstrual cycle
Discomfort in the middle of the menstrual cycle may indicate ovulation, when the follicle ruptures and the egg is released. The pain is usually minor and not everyone can feel it. The cause of such sensations in the middle of the menstrual cycle may be ovarian apoplexy. It is more often observed in women 20-35 years old. It has an acute onset: intense pain in the lower abdomen on the side of the ruptured ovary, accompanied by nausea and vomiting, internal bleeding. When examined by a doctor, mild signs of intra-abdominal bleeding are determined, and in case of significant blood loss - hemorrhagic shock and irritation of the peritoneum. Vaginal examination is difficult due to significant blood loss (impossible to palpate), but sometimes an enlarged and painful appendage can be felt.
Pain after sexual intercourse also has several causes. One of them is abnormal development of the genital organs (vagina, uterus, cervix). With this pathology, changes are detected in the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervical canal, which is easily injured with the formation of bedsores.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane inside the cervix, as well as a cervical cyst, can cause postcoital pain. In addition, rawness in the uterus after intercourse can be due to vaginal dryness during menopause, as well as as a result of narrowing or deformation of the genital slit after an episiotomy. Cauterization for cervical erosion can also cause discomfort after intercourse.
Painful sensations can also be caused by adhesions in the pelvis, nonspecific inflammatory or sexually transmitted diseases.
Causes
The development of pain in the uterus or cervix before menstruation occurs for many reasons. These include physiological and pathological. Hormonal disruptions in a woman’s body can occur against the background of psycho-emotional lability, which leads to a decrease in the threshold of pain sensitivity. A decrease in the production of enkephalins and endorphins leads to a woman's greater perception of pain. Prostaglandins play an important role. An increase in their production entails a spastic contraction of the uterine muscles. They also affect the walls of blood vessels, causing them to narrow.
Pain before menstruation
Pain in the uterus of varying intensity before menstruation occurs in all women. This is due to the physiology of the female body. The menstrual cycle involves preparing the body for conception and subsequent gestation. If after the release of the egg it is not fertilized, then processes occur that lead to rejection of the endometrium of the uterus. During this period, menstruation begins. The tone of the uterus increases and contractions occur. They are what women perceive as pain before menstruation. If they occur 1-3 days before the start and in the first few days of menstruation, this is the norm.
But if you have nagging pain in the lower abdomen a week before your period, you should consult a gynecologist. Their causes can be both harmless processes and serious pathology. These include adhesions of the organs of the reproductive system, damage to the digestive tract, menstrual irregularities, chronic inflammatory processes of the genital organs, late ovulation, and pregnancy.
Don't forget about PMS (premenstrual syndrome), which is one of the common causes of pain before menstruation. Its formation can be associated with various symptoms - nausea, vomiting, headaches, sweating, swelling, weakness, emotional disturbances. Depending on the prevailing symptoms, edematous, neuropsychic, cephalgic and crisis forms of PMS are distinguished.
Pain during and after menstruation
The causes of pain in the uterus during menstruation are quite different. The pain itself is called dysmenorrhea and can be primary or secondary. The primary form develops as a result of infantilism or incorrect position of an organ ( An organ is a separate collection of various types of cells and tissues that perform a specific function within a living organism
). The prerequisites for secondary dysmenorrhea are infectious and inflammatory processes of the reproductive system, endometriosis, cystic and tumor formations.
Pain that precedes the onset of menstruation and occurs in the first hours of bleeding is common for primary dysmenorrhea. If the uterus hurts ( in anatomy, this is the middle section of the female reproductive system, serves for the maturation of fertilized eggs, metamorphosis of the embryo and expulsion of the fetus (birth of a baby or laying an egg, larva)
) during all “menstruation”, then this is a symptom of secondary dysmenorrhea.
Uterine pain during menstruation can be a sign of inflammatory diseases. Depending on how the uterus hurts, the symptoms may indicate a certain pathology.
- If vaginitis is a prerequisite, then the pain is accompanied by a feeling of stone in the lower abdomen and pathological vaginal discharge.
- When endocervicitis becomes a prerequisite, the disease is accompanied not only by pain, but also by purulent discharge.
- Sharp pain ( an unpleasant or painful sensation, the experience of physical or emotional suffering
) in the uterus may indicate endometritis. This option also includes fever (sometimes very significant) and symptoms of general intoxication. Blood discharge during menstruation looks like meat slop, with a grayish or brown tint. - If the uterus hurts and hurts intensely, then the prerequisite may be adnexitis - inflammation of the appendages. Severe pain and a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen are common for the disease. The woman's body temperature rises, and she also develops nausea and vomiting.
The reason why the uterus hurts after menstruation may be the following pathologies:
The people were taken aback! Joints will recover in 3 days! Attach...
Few people know, but this is exactly what heals joints in 7 days!
- Benign tumors. These include large cystic and myomatous formations. Pain develops as a result of compression of adjacent organs, as well as dysfunction of defecation and urination. When a cervical cyst forms, pain in the lower abdomen may also develop.
- Endometriosis. The disease is the growth of endometrial tissue in places where it should not be. A common symptom is pain before and after menstruation, as well as a cyclical increase in the affected organs.
- Polypous formation of the cervix. It is diagnosed only after hysteroscopy.
- Inflammation of the organs of the reproductive system. The cause of the pathology is STIs.
- Adhesive processes.
- Long-term wearing of an intrauterine device. From time to time it grows into the endometrial layer, which becomes a prerequisite for pain.
https://youtu.be/nI-WhQnn9UA
Pain during menstruation
So why does the uterus hurt during menstruation? The physiological processes of rejection of the uterine mucosa cause its contractions for the speedy removal of the endometrium and unfertilized egg. These painful sensations are not associated with pathology and do not change the general condition of the woman.
A condition in which the uterus hurts during menstruation is called algodismenorrhea. It can be primary and secondary. Primary algodismenorrhea is functional in nature. The reasons for its development are the following:
- Incorrect position of the uterus, leading to stagnation of blood during menstruation.
- Endocrine pathology, caused by an increase or decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins, leads to hormonal imbalances in the body.
- A woman’s emotional instability leads to a decrease in the threshold of pain sensitivity.
- The constitutional characteristics of a woman play an important role. Thus, with infantilism, due to the small size and insufficient development of the muscles of the uterus, its ability to stretch is impaired. This causes irritation of the nerve endings, which is accompanied by pain.
Pain after menstruation
There is no need to worry if pain in the uterus persists for several days after your period. Slow restoration of hormonal levels leads to their preservation. These phenomena occur especially often in women after 40 years of age. They are associated with excess levels of female sex hormones (estrogens) in the blood or increased release of prostaglandins by the uterus. But if the pain persists for a week or its intensity is high, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Their persistence may indicate a relapse or the occurrence of damage to the reproductive organs.
Pain in the uterus that occurs a few weeks after menstrual bleeding may be associated with ovulation. The release of an egg from the ovary results in a slight defect in its wall, causing minor bleeding. The blood irritates the nerve endings of the peritoneum, so the woman experiences pain in the lower abdomen. Since the maturation of the egg occurs in one of the ovaries, the pain syndrome is felt more on the right or left. It is not intense and does not last long, which does not lead to disruption of the woman’s ability to work.
Possible complications
In addition to discomfort and disruption of the woman’s general condition, failure to identify the cause of pain can lead to various complications. A decrease in hormonal levels disrupts the composition of normal microflora, which causes the development of pathogenic microorganisms, such as fungi of the genus Candida, streptococci, staphylococci, mycoplasma, gardnerella. Untreated pathology leads to the penetration of infection into the urinary tract and the development of genitourinary diseases (cystitis, vulvovaginitis, pyelonephritis).
When myomatous nodes are located in the submucosal layer of the uterus, the outflow of menstrual blood is disrupted. This causes increased contractions and, as a result, increased pain. Uterine fibroids also increase the risk of developing dysfunctional uterine bleeding. The disease may be accompanied by torsion of the pedicle of the node with its necrosis, impaired reproductive function (miscarriage, infertility), transformation of the node into a malignant tumor, and severe forms of anemia. Infertility and ovarian cancer are among the main complications of endometriosis.
Painful periods with synechiae in the uterine cavity
Synechiae (adhesions in the uterine cavity) can obstruct the outflow of menstrual blood, causing abdominal pain during menstruation. The mechanism of development of this pathology is still not fully understood. The overwhelming majority of researchers believe that synechiae occur as a result of trauma and subsequent fusion of the deep basal layer of the epithelium of the uterine cavity.
Often pain in the lower abdomen is the only symptom of this pathology, which in the vast majority of cases leads to infertility or severe complications during pregnancy and childbirth (miscarriages in early pregnancy, premature birth, as well as disturbances of the placenta, leading to severe complications during labor) .
The presence of synechiae can be suspected in cases where there are the following risk factors:
- history of frozen pregnancy or incomplete abortion;
- repeated miscarriages (synechias are found in 5-40% of such patients);
- previous intrauterine manipulations (medical abortions, curettage of the uterine cavity);
- history of surgical operations on the uterus (myomectomy, conization of the cervix);
- postpartum endometritis;
- use of intrauterine contraceptives.