general information
When normal healthy cells die, the organ begins to replenish them with fatty tissue to maintain integrity and volume. However, fat cells cannot function like normal pancreatic cells. Lipomatosis, therefore, is not the cause of the disease, but its consequence. The pancreas has a high compensatory ability, and therefore fatty degeneration may not appear throughout a person’s life.
Pathologies of this organ do not in all cases result in lipomatosis. Overweight people who already have fatty changes in certain organs are more prone to such changes. Age and heredity also play an important role.
Most often, such changes do not have clinical symptoms, unless accumulations of fat compress the pancreatic tissue and its ducts. Lipomatosis is slow, progressive and always benign in nature. Surgery is very rarely required. What leads to pancreatic lipomatosis?
https://youtu.be/N2CmiRf70RY
Clinical course of the pathology
The clinical picture of the disease directly depends on the extent of organ damage, that is, on the stage of development of the pathology.
| Stages of development | Characteristic symptoms | Possible complications |
| Stage 1, in which no more than 30% of the pancreatic tissue is changed. | The pathology at this stage of development is often asymptomatic; the patient may feel only minor discomfort and heaviness after eating. In most cases, pathology is detected during a comprehensive examination. | In the absence of treatment, the pathological processes of replacement of pancreatic tissue continue, the disease enters the 2nd stage of its development. There are no other complications at this stage. |
| Stage 2, in which 30-60% of the organ tissue is damaged. | There are symptoms such as:
| At this stage of pathology development, various complications may occur. For example, if fatty tissues occupy large areas of the organ, the patient's body may not accept food entering the stomach. This only applies to heavy meals (for example, spicy, fatty, fried foods). As a result, a person experiences a significant deterioration in health, vomiting, and weakness after a meal. |
| Stage 3, characterized by almost complete replacement of organ tissue. | At this stage, the clinical manifestations of the pathology become more and more pronounced, symptoms such as:
| The main and most dangerous complication is the threat of dehydration, which, in the absence of proper treatment, can even lead to death. With the development of stage 3 lipomatosis, not only the digestive system, but also the endocrine system is affected. All this leads to a sharp deterioration in health and well-being. |
Degrees of pathology
Pancreatic lipomatosis is characterized by the following degrees:
- 1st degree – replacement of an organ up to a third. The patient does not feel signs of the disease because any symptoms are absent.
- 2nd degree - half of the cells are replaced by fat, and this is accompanied by belching, flatulence or heaviness in the abdomen.
- 3rd degree - adipose tissue replaces more than 60% of the pancreas, there are pathologies of the digestive tract and the level of glucose in the blood increases.
It is worth noting that diffuse changes in the pancreas such as lipomatosis can develop into malignant tumors.
The mechanism of the disease
It was already noted above that fatty degeneration can develop due to the fact that normal pancreatic cells die off for one reason or another. The body tries to make up for their deficiency and starts this process. The disease progresses very slowly. From its beginning to the second stage, which is characterized by the first signs, several decades may pass. Symptoms most often make themselves felt when more than thirty percent of the cells have already been replaced. Signs of pancreatic lipomatosis are quite unpleasant.
Useful article? Share the link on VKontakte
In later stages, the pathology has a significant impact on the functioning of the endocrine system. Insulin is no longer produced in sufficient quantities by the pancreas, and the body is unable to properly digest fats and proteins. After this, significant health problems begin.
Most patients suffering from pancreatic lipomatosis exhibit carbohydrate metabolism disorders. In addition, their immunity is reduced. If the development scenario is the worst, then the pathology can develop into a cancerous tumor.
Diagnostic methods
It is quite difficult to identify pathology at an early stage, since there are no characteristic symptoms of the disorder. If the disease progresses to stage 2 or 3, to make a diagnosis it is necessary to assess the clinical manifestations, as well as collect an anamnesis (establishing the causes of the disease, assessing the patient’s eating habits, his lifestyle, studying the medical history and heredity).
To obtain a more detailed picture, additional diagnostic methods are used. This:
- Ultrasound of the digestive system to determine the location and size of fat deposits;
- A coprogram for determining the composition of feces (with the development of lipomatosis, fatty elements are found in it, the number of which can be used to judge the degree of damage);
- Blood test for hormone levels to detect damage to the pancreas and endocrine system organs.
Factors provocateurs
Regarding the causes of pancreatic lipomatosis, it can be said that scientists have not yet established them precisely. It was only possible to identify risk factors, which include:
- pancreatitis of a chronic or acute nature;
- diabetes;
- alcoholism;
- obesity;
- heredity;
- organ injuries.
All the factors listed above may not lead to the appearance of lipomatosis. However, when analyzing the medical histories of people suffering from this pathology, it was revealed that replacement most often begins in the presence of one of these signs.
Diagnostics
Lipomatosis is very rarely diagnosed at the first stage of its development. After all, at this time there are no symptoms, so patients do not consult a doctor. But if you experience abdominal discomfort and signs of indigestion, you need to get examined as soon as possible. The sooner treatment is started, the more favorable the prognosis for the patient. The pathology is constantly progressing and can lead to serious consequences.
Lipomatosis can be detected by ultrasound. This study shows increased echogenicity of some areas of the gland, which indicates changes in its structure. In addition, the doctor, based on the results of ultrasound, assesses the size of the gland, the presence of foci of fat cells and their number. It is also very important to determine their location. Indeed, with the accumulation of fat cells around the ducts, the risk of complications increases.
When diagnosing pancreatic lipomatosis, it is very important to differentiate it from other gastrointestinal pathologies. The symptoms of this disease are the same as those of gastritis, peptic ulcer, and are especially reminiscent of pancreatitis.
Clinical symptoms of the disease
Lipomatosis most often does not cause any discomfort to the patient and is detected accidentally during ultrasound in the form of small foci that are diffusely scattered in the pancreatic parenchyma. The specialist will describe them in the conclusion as diffuse changes in the organ. Small lesions do not put pressure on the tissue of the organ and do not interfere with the performance of its functions.
Ultrasound results show the condition of the pancreas as a whole, its size, the presence, size and number of fat accumulations. Enlarged sections of the pancreas may indicate serious pathologies. In this case, the patient needs to undergo treatment to avoid complications such as neoplasms and pancreatic necrosis. Is there pain with pancreatic lipomatosis?
In some cases, focal lipomas, which are located near the excretory ducts of the gland, can severely disrupt its functioning. If the excretory ducts of the pancreas are compressed, then digestion is noticeably impaired. A person feels heaviness in the stomach after eating, pain in the area of the projection of the pancreas, vomiting and nausea appear. Food is not completely digested, which is why fermentation processes develop in the intestines, gas formation increases, and bloating occurs. When the gases go away, the patient feels relief, the pain disappears. There may be bowel disorders in the form of diarrhea. During the survey, general signs are also determined: general health problems, increased fatigue, decreased performance, weakness.
Signs may indicate a number of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, and therefore patients with pancreatitis, ulcers and gastritis attribute them to their main ailment, without attaching much importance. Because of this, the disease progresses.
Degree of development of lipomatosis
The mildest degree of the disease is the first . With it, fat cells are single, which does not affect the functioning of the pancreas or the well-being of the patient. Most often, he learns about his disease by chance, when he undergoes an examination, for example, an echography of the abdominal organs.
The second degree is much more serious. Here, lipomas replace 30 to 60 percent of the total volume of the organ, which, naturally, cannot but affect the pancreas. Due to a decrease in the production of enzymes, the patient begins to have serious digestive problems: dyspepsia, bloating, flatulence, nausea (especially after eating), belching with an unpleasant odor, and abdominal pain.
Troubles, as they say, intensify when the third degree of the disease is noted: overcoming the “threshold” of 60 percent, when wen, like raiders, captures more than two | third of the organ. As the disease progresses, endocrine disorders join dyspeptic symptoms.
Abdominal pain becomes constant, diarrhea becomes more frequent, which can alternate with constipation, vomiting often occurs, appetite increases, and the feeling of thirst increases. As adipose tissue grows, it compresses the organ and nearby tissues, which leads to poor circulation. With a deficiency of insulin, diabetes mellitus develops.
However, before moving on to treatment, it is necessary to make a correct diagnosis, and for this it is necessary to take tests and undergo examinations.
Which doctor should I contact?
The earlier the disease is diagnosed, the more effective the pathology therapy becomes. Since symptoms very rarely manifest themselves at the first stage, to detect them in the initial state requires regular visits to a therapist, as well as undergoing routine medical examinations. For pancreatic lipomatosis, ultrasound is very effective.
If signs appear, it is necessary to contact a gastroenterologist, and he, most likely, will send the person to a surgeon, who will deal directly with the treatment of lipomatosis. In addition, you may need to consult an endocrinologist.
Diagnostics. Specifics of treatment
Lipomatosis can be determined using ultrasound, showing preserved organ size with structural changes, which is evidence of pathology. To confirm the presence of fat cells, a biopsy of gland tissue is used.
Regarding the treatment of fatty degeneration of the pancreas, it should immediately be noted that in the vast majority of cases it will not achieve complete healing. The main goal is to slow down the pathological process. This can be achieved in three main ways.
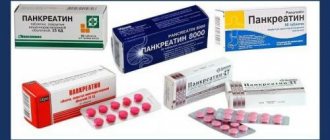
- Treatment with drugs. It is used when the lesions are not total: there are not too many inclusions of fat, they are located throughout the organ, and do not put pressure on the tissue. In this case, drugs are prescribed that normalize digestion (Festal, Mezim, etc.), eliminate hormone imbalance (Insulin), as well as enzyme deficiency (Pancreatin). If there is pain, anti-inflammatory and painkillers (Ibuprofen) are prescribed. How else to treat pancreatic lipomatosis?
- Surgical therapy for fatty degeneration of an organ is required when the lesions take the form of large islands and cover large areas, pressing on the ducts of the organ, pinching the nerve endings. Lipomatous nodes in such cases are removed through surgery. However, this does not make it possible to count on absolute healing, since small lipomas will still remain, and their development can intensify at any time.
- In addition, there are a number of folk remedies for pancreatic lipomatosis aimed at combating the disease. Plants such as nettle, calendula, wormwood, plantain, hemlock, etc. are used. Alcohol tinctures and decoctions are made on their basis for internal use. Such methods are only auxiliary and are quite effective only in the early stages of lipomatosis. In any case, they must be used comprehensively, along with traditional methods.
Treatment
It is impossible to completely cure adipose lipomatosis. Even with surgical removal of fat cells, it is not possible to return the gland to its normal functions. Tissue degeneration is an irreversible process, so the main goal of treatment is to stop it. And the earlier therapy begins, the more favorable the prognosis for the patient. After all, stopping the growth of adipose tissue ensures normalization of digestion and prevents complications.
As symptomatic therapy, medications are prescribed that do not treat the pathology, but simply alleviate the patient’s condition
Most often, treatment of pancreatic lipomatosis is carried out using conservative methods. Typically, patients consult a doctor when their health worsens. Therefore, he is first prescribed drug therapy.
There are no special drugs for the treatment of lipomatosis, so medications are prescribed depending on the symptoms:
How to restore the pancreas
- for pain and inflammation - Ibuprofen and other NSAIDs;
- for spasms and intestinal colic - No-Shpa or Mebeverine;
- to eliminate nausea - Metoclopramide or Cerucal;
- for diarrhea - Loperamide;
- to improve digestion - Pancreatin, Creon or Festal.
In addition to symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating signs of digestive disorders, it is very important to change your lifestyle. First of all, get rid of bad habits. After all, drinking alcohol and smoking can provoke the death of gland cells and their replacement with adipose tissue. It is necessary to increase physical activity, for which physical therapy is prescribed. It is needed not only to reduce fat deposits, but also to improve metabolic processes and blood circulation. In addition, it is very important to change your diet and eating habits.
In the most difficult cases, when conservative therapy does not help eliminate the symptoms of lipomatosis, surgery becomes necessary. This happens if there are a lot of fat cells or they block the pancreatic ducts. In this case, the pathologically altered tissue is removed. But during surgery there is a risk of damaging healthy areas of the pancreas, so this method is used in extreme cases.
You can also improve the patient's condition with conservative or surgical treatment using folk remedies. But first you need to consult your doctor. Most often, decoctions or tinctures of calendula, nettle, wormwood, and plantain are taken orally.
To stop further degeneration of the pancreas, it is necessary to eliminate all the causes of this process. To do this, it is necessary to treat diseases of the liver, gall bladder, stomach and duodenum, which can lead to cell degeneration. Diabetes mellitus requires constant use of special medications. It is necessary to normalize hormonal balance and establish metabolic processes. It is very important to lose weight. Only the integrated use of all these methods can prevent the progression of pathology and the development of complications.
Diet
Since the changes that occur with lipomatosis are irreversible in nature, you need to concentrate on its treatment. The most important thing in it is diet, which helps prevent further proliferation of fat cells in the body. It is based on fractional nutrition, that is, you need to eat in small portions, 5-6 times a day. It is advisable to steam food without adding vegetable oil. You should exclude fried, fatty, spicy, sweet, smoked and alcoholic foods from your diet.
You need to eat lean fish and meat, vegetables, dairy products, various cereals, including oats, rice and buckwheat. The daily calorie requirement should not exceed 2800.
Diagnostic methods
Detection of signs of the development of fatty degeneration often occurs accidentally during an ultrasound examination. The same method is used to establish the final diagnosis of lipomatosis.
In addition to ultrasound, data on previous diseases and test results, including biopsies of pancreatic tissue, are taken into account. A biopsy is prescribed if the size of the organ is within normal limits, but ultrasound shows a change in echogenicity, indicating the appearance of inclusions that are not characteristic of glandular tissue.
If the pancreas regularly fails, measures must be taken. Treatment of the pancreas with folk remedies at home - effective recipes.
What to do if your pancreas hurts, read here.
An example of a proper diet for pancreatic diseases is given here:. And also read diet tips.
Prevention
A pathology such as pancreatic lipomatosis is quite difficult to treat. That is why a healthy person should take measures to reduce the risk of such a disease. To do this you should:
- control your weight;
- reduce alcohol intake;
- eat less fatty foods;
- stop smoking, as it greatly affects the activity of the pancreas;
- reduce stress;
It is equally important to monitor the condition of other digestive organs, especially the biliary tract and liver, since cholelithiasis, cholecystitis and hepatitis increase the risk of pancreatic obesity.
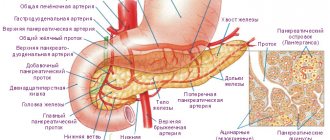
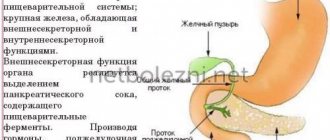
Pancreatic lipomatosis is what is commonly called an irreversible process in which the cells of the pancreas change. They are replaced by fat cells. Therefore, since changes occur in the cells of the pancreas, it can no longer perform its usual functions. This pathology is called pancreatic dystrophy. In general, lipomatosis occurs in cases where cells begin to die due to any inflammation or factors like this. In order to maintain the previous state of the body, the cells begin to transform into fat cells, but this is also not an option - it does not add health to the organ. But it is worth remembering that pancreatic lipomatosis does not always occur with pathologies. It also happens that fat cells grow greatly and entire islands are formed. So, now let's look at the symptoms, treatment and diets of pancreatic lipomatosis.
ethnoscience
Lipomatosis is not considered a life-threatening pathology, but constant monitoring of the condition of the pancreas is required. Traditional medicine suggests treating steatosis with herbal medicine. Infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs will help inhibit the growth of adipose tissue and partially restore the secretory abilities of the pancreas.
It is important to understand that before using traditional recipes you need to consult your doctor. The specialist will take into account the general condition of the patient, weigh the benefits and possible risks of herbal treatment. Additionally, it is necessary to ensure that there are no allergic reactions to the constituent components of herbal infusions.
Popular folk recipes for fatty degeneration of the pancreas:
- a decoction of peeled oats helps to establish metabolic processes in the organ and improve secretory function; They drink the decoction instead of tea, 400 ml per day;
- an infusion of blueberry leaves is useful for lipomatosis in the initial stages, drink 100 ml in the morning and evening before meals;
- Regular consumption of fresh cranberries can prevent further formation of wen in the pancreas;
- A decoction of blackberry leaves is drunk for a long time in case of diffuse damage to the gland; per day take 20–30 ml up to 4 times a day;
- herbal infusion of nettle leaves, valerian root, marigold and St. John's wort is used in courses of 3 weeks with a 7-day break for a long time; You need to drink up to 250 ml per day;
- in addition to herbal medicine, mumiyo is used - a powerful natural stimulant; for uncomplicated steatosis, oral administration of mumiyo 20 mg twice a day for 14 days will help restore pancreatic function.
Symptoms
It often happens that pancreatic lipomatosis occurs without visible symptoms that would help to recognize the disease in time and immediately consult a qualified doctor at the hospital. Typically, the disease occurs without symptoms when fat cells are scattered throughout the pancreas in small islands. If you still go to the doctor, the examination is usually carried out using an ultrasound examination.
Usually, a doctor assesses the condition of the pancreas using an ultrasound examination, only after which can we talk about any pathologies. Some pathologies can be noticed from the fact that part of the organ may be enlarged. The device shows how affected the pancreas is and how large the lesions are. If we talk about pancreatic lipomatosis, then this disease is benign and if you follow a proper diet and consult a doctor on time, then this will not pose a great danger to a person.
Diagnosis of lipomatosis
When conducting diagnostics, examination of the patient reveals the following:
- The seal in the form of a lipoma is located in areas with accumulation of fatty tissue;
- This tumor is painless and mobile when palpated;
- It is soft to the touch, and when the skin above it is stretched, their characteristic retraction occurs.
To carry out an accurate diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is performed, which makes it possible to identify areas with accumulations of fatty tissue. X-rays reveal foci of clearing; in some cases, X-rays with contrast are used. Computed tomography and MRI are widely used in the diagnosis of lipomatosis and related diseases. During the examination, it is possible to identify existing foci atypical for the gland in the form of accumulations of fat and determine the extent of the lesion and its shape.
If there is any doubt about the condition of the pancreas, a biopsy is performed and tissue samples taken are examined. This allows you to confirm existing lipomatosis with an accuracy of one hundred percent by the presence of a large number of fat cells in the analysis.
Degrees of pancreatic lipomatosis
Judging by lipomatosis, it can be divided into three degrees:
- The first is minor liver damage (about thirty percent of the damage to the entire organ)
- Second - up to sixty percent of the liver is affected
- Third - more than sixty percent of the entire organ is affected.
But some researchers have noticed that a lipoma located in a certain place can significantly reduce the functioning of an organ by almost half and may already fall under the first classification.
Treatment of pancreatic lipomatosis
Pancreatic lipomatosis can be treated in the usual way, or if it does not suit you, then you can resort to surgical intervention. The usual way or the conservative way is possible only when the fat cells are small and they are scattered throughout the gland. If fat cells are already forming islands, then surgical intervention is required. Main indicators of conservative therapy:
- weight loss, if you are overweight, this may help remove fats from the pancreas.
- it is necessary to follow a strict diet, which is usually aimed at limiting fat intake.
Drug treatment
Tablets for pancreatic obesity are prescribed only by your doctor. This is a serious enough disease to self-medicate. The following medications are usually prescribed:
- "Ibuprofen." Analgesic, pain reliever. Helps get rid of pain that torments the patient. Replacement drugs - “No-Shpa”, “Platifillin”.
- "Metoclopramide." What are these pills for? The drug can combat the consequences of lipomatosis such as nausea and vomiting.
- "Mebeverine." This medication is designed to relieve intestinal spasms.
- "Pancreatin". It is an enzymatic preparation. It contains biologically active compounds that promote the breakdown of nutrients - proteins, carbohydrates, fats. Thus, it promotes normal digestion. Alternative remedies are Festal or Mezim.
- "Loperamide". With fatty liver, patients often suffer from diarrhea and stool disorders. This medicine allows you to cope with this problem.
- Vitamin complexes. Aimed at strengthening the body's immune forces.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes insulin therapy.
Diet for lipomatosis
Since lipomatosis is irreversible and it is no longer possible to cure the affected areas, you need to focus on its therapy. Diet plays an important role in this, as it helps prevent the proliferation of fat cells. The most important thing in a diet is to eat small meals. This, of course, does not apply to a diet - this is just a nutrition algorithm that will help you in many ways. Food should be taken 4 or up to 5 times a day. You should pay attention to products that are usually taken for diseases of the digestive tract (table No. 5). And, of course, the following must be excluded from the diet: fried foods, all kinds of pickles, smoked foods, spicy, sweet and alcohol.
Table No. 5 is especially good for the body, but prevents the process of obesity, and consists of easily digestible food. In order for food to taste right, you need to steam it. This is what allows you to melt from food all the fats that are not needed for your body. If you want to serve a meat dish. then you should take low-fat food, fish. Also good for such dishes are pumpkin, zucchini, potatoes, broccoli or cauliflower.
Thus, if you suspect pancreatic lipomatosis, you should consult a doctor so that the disease does not develop into a more serious form. Also, you should not self-medicate at home; you will not be able to properly create a diet for yourself. It happens that if you still avoid consuming fats, this does not give positive results. Be healthy!
Pancreatic lipomatosis is an irreversible phenomenon characterized by pathological destruction of the cells of this vital organ. More precisely, healthy cells are replaced with fatty tissue. As a result of this process, the pancreas loses its ability to function healthily. In medical circles, there is another name for this pathology - fatty degeneration or steatosis of the pancreas. How does this disease manifest itself, what do patients complain about, and what are the ways to get rid of pancreatic lipomatosis? Does diet play a role in treatment and what are its basic principles? Let's talk about this...
Folk remedies
Chamomile
For prevention and treatment, take 1 tbsp. chamomile, brew it with boiling water, leave and drink 20 minutes before meals. At the same time, treatment of the pancreas with folk remedies is used not only during exacerbation, but also during the period of attenuation of pain or for preventive purposes.
Collection: yarrow, celandine, calendula.
Plants can be collected and prepared yourself, or purchased at the Pharmacy.
Mix all the necessary ingredients and brew them 30 minutes before meals. Due to individual intolerance, herbal remedies affect the human body with different effects.
Mixtures of several herbs
An excellent way to treat is to use several types of herbs:
- plantain, cucumber, yarrow, St. John's wort, mint and chamomile.
- All this needs to be mixed and brewed 1 tbsp. l. per glass of water. Then let the herbs brew and drink 1/3 cup 3 times a day.
Sage and calendula
Often the pancreas is treated with sage and calendula.
- They are mixed one to one and brewed with boiling water, like tea.
- The resulting infusion must be filtered, after which it can be drunk.
- For the decoction you need to take 3 dessert liters. mixture of herbs per 0.5 l. water.
Hemlock
Many herbalists suggest treating fatty degeneration with hemlock, which has proven to be the best way to get rid of pancreatic problems. Herbal tincture is sold in pharmacy chains. It is accepted as follows. You need to start with 1 drop of tincture per day and gradually increase it to 40. After this, the dose is reduced to a minimum in the same way.
Symptoms of pancreatic lipomatosis
Quite often, the manifestations of lipomatosis are hidden, which negatively affects the development of the disease and the possibilities of early diagnosis of the disease. Most often this happens in those clinical cases where fatty areas form small foci located far from each other. Such diffuse formations do not harm the organ and do not harm its functions.
The most reliable way to detect fatty degeneration is ultrasound. Moreover, the disease is discovered in cases where the patient seeks advice from a doctor on a completely different issue.
Ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to assess the general condition of the pancreas and its visual characteristics. If various bulges are observed, then there are assumptions about possible pathologies. These, in turn, can cause necrosis and severe complications in the form of lipomatosis. This is why it is so important to detect the disease early. If there are fatty patches, the device emits echo signals that are uneven and help the doctor determine the exact location of the damage and its size.
Causes of lipomatosis
The reasons for the development of lipoactosis are not fully understood; only a mutual relationship has been identified between the existing fatty tissues in the subcutaneous layer and in nearby organs and lipomatosis in the pancreas. Not least important in the occurrence of disorders in this organ is genetic predisposition; in those whose close relatives had the same disease, pancreatic steatosis occurs one and a half times more often.
Currently reading: How and with what to relieve a pancreatic attack at home
There are other reasons under the influence of which lipomatosis can develop, namely:
- Having excess weight;
- Existing bad habits such as alcohol abuse and smoking;
- Diseases of the pancreas that are chronic;
- Acute diseases and infections of the pancreas;
- Pathologies of the endocrine system in the form of diabetes or hypothyroidism;
- Hepatitis;
- Oncology affecting the respiratory tract;
- Slow metabolism;
Old age also contributes to the degeneration of liver tissue, this often occurs in people over 70 years of age.
Treatment measures
Fortunately, lipomatosis belongs to the group of benign formations and is not particularly difficult to treat. And the rate of development of the disease does not differ in intensity. Modern medicine knows two ways to treat fatty degeneration: surgical and conservative. Conservative therapy is prescribed when the fatty areas are small in size, do not compress the pancreatic ducts and are scattered throughout the entire perimeter of the organ. In the case of the formation of complete islands from fat cells, compression of the gland ducts and blockage of the outflow of secretions, surgical intervention is indicated, namely the removal of lipomatous nodes. Returning to the issue of conservative treatment, it is worth pointing out a number of procedures carried out within its framework:
- A strict diet, the essence of which is to prohibit the consumption of fats.
- Elimination of excess weight. As a rule, most patients are overweight. This will help remove a certain amount of fat from the pancreas.
general characteristics
With lipomatosis, pancreatic parenchyma cells gradually die and are replaced by fat cells. This process usually happens very slowly, over many years. Therefore, the patient may not be aware of his pathology for a long time. If connective tissue grows along with adipose tissue in place of healthy cells, the patient is diagnosed with fibrolipomatosis. There is no big difference between these pathologies; they equally disrupt the functions of the pancreas.
Lipomatosis is often discovered accidentally during an ultrasound scan. After all, when adipose tissue replaces less than 30% of the area of the gland, this does not affect its functioning in any way and does not cause any symptoms.
But gradually the changes progress and spread throughout the entire organ. There are fewer and fewer normal cells, so the pancreas begins to perform its functions worse. The patient's digestion is disrupted and the production of hormones decreases. First of all, carbohydrate metabolism suffers, and many develop diabetes. In addition, the absorption of proteins and fats is impaired, which seriously affects health. The patient's immunity decreases and there is a lack of essential microelements.
Sometimes diffuse changes are observed when adipose tissue grows evenly over the entire surface of the gland. But most often this happens in certain areas of the parenchyma. If the cells that produce enzymes or hormones are not affected, lipomatosis can be asymptomatic for a long time. Sometimes a patient lives with this pathology for several decades without knowing about it.
It is quite rare for all the fat tissue to accumulate in one place. In this case, the patient is diagnosed with lipoma. This is a benign tumor consisting of fat cells. It grows very slowly and usually does not cause serious problems. But sometimes, as it grows, it can lead to compression of the gland ducts, blood vessels or nerves.
At the initial stage, the pathology does not manifest itself in any way, and it can only be detected by ultrasound
Nutrition and diet for lipomatosis
As mentioned above, fatty degeneration is classified as an irreversible process. Accordingly, it is no longer possible to cure deformed cells. That is why therapy is aimed at preventing further spread of fatty inclusions. A central place in treatment is given to diet and a properly composed daily diet. The diet is a so-called fractional meal. In general, it consists of four or five meals a day. The diet for fatty degeneration is no different from other nutritional indications for diseases of the digestive tract. Basically, a taboo is established on fried delicacies, smoked meats, pickles, fatty and spicy dishes, baked goods, chocolate, sweets and alcoholic drinks.
Mainly, the chosen diet should have lipotropic properties, curb the process of obesity and consist of easily digestible foods that are easily digested by the intestines and stomach.
For food to have a gentle effect, it must be steamed and without adding oil or fat. As for meat products, it is recommended to consume lean poultry and fish. Vegetables – zucchini, pumpkin, potatoes and cauliflower – have a good effect on the patient’s condition. The list of must-use products consists of:
- cereals (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal);
- dairy dishes, especially sour cream and kefir;
- salads, greens;
- baking (for example, cottage cheese casserole).
In general, a person with lipomatosis should consume at least 2800 calories per day.