Stones in the human body occur not only in the bladder, kidneys and gall bladder. The pancreas can also become a target for calcifications. Are stones in the pancreas spontaneous, or is this a pattern due to poor nutrition?
Calcifications in the pancreas occur both directly in the ducts of the pancreas and in its tissue. Due to the formation of stones, the organ stops performing its work, which affects both the exocrine and intrasecretory activity of the gland. The disease manifests itself with characteristic signs that cannot be missed at the first stage of development of the disease, so diagnosing the pathology is not difficult. Calcific pancreatitis can be cured comprehensively, combining both conservative and surgical techniques. Importance is given to the rehabilitation and restoration of organ function.
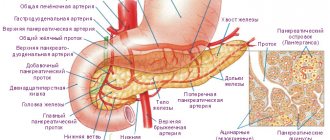
What are stones in the pancreas?
The composition of the formations includes chemical components: calcium salts - calcium orthophosphate and calcium carbonate, admixtures of aluminum and magnesium salts. They contain organic substances - cholesterol, protein elements, particles of epithelial membranes and leukocytes. The color of pancreatic calcifications is white or with a yellowish tint.
Stones in the pancreatic ducts vary in size and shape, and can be single or multiple. Large single stones are often located in the head of the pancreas, small multiple ones - in the tail and small ducts. The parenchyma of the pancreas also undergoes calcification.
Diseases of the pancreas are directly related to pathologies in the biliary system and gall bladder. The composition of gallstones and the mechanism of formation differ from pancreatic calcifications. Gallstones are formed as a result of dysfunction of the liver and gallbladder, excess cholesterol in the body and lack of bile acids.
The composition of gallstones and the structure of formations depend on the causes of their appearance, conditions of growth and development.
The mechanism and causes of the appearance of calcifications in the pancreas
The beginning of pancreolithiasis is stagnation and changes in the composition of pancreatic juice as a result of tumors and cysts, the entry of stones from the gallbladder into the common duct, and blockage of the sphincter of Oddi by stones.
How stones form in the pancreatic ducts
As a result of stagnation, a process of thickening of the pancreatic secretion occurs, changing the chemical composition, turning into an insoluble protein mass that settles inside the ducts. Calcium salts gradually permeate the sediment, turning it into calcification.
Stones in the pancreatic ducts
Inflammatory processes occurring in the intestines, gall bladder and ducts, in the pancreas, accelerate the process of stone formation. The pressure in the pancreatic ducts increases as a result of the openings being blocked by calcifications; pancreatic cells begin to die, forming necrosis. The islets of Langerhans, responsible for the production of hormones, are damaged. The pancreas largely loses its secretory and enzymatic functions.
How is pancreolithiasis related to diseases of the biliary system?
A close connection has been established between inflammatory processes in the pancreas and cholelithiasis. Under certain conditions, gallstones lead to the development of acute pancreatitis.
The pancreatic and bile ducts empty into the duodenum in the area of the Vater's nipple. If a stone from the gallbladder gets stuck in the indicated place, further flow of pancreatic juice and bile into the intestine becomes impossible. The pressure in the ducts increases, the inflammatory process begins, pancreatic enzymes develop activity not in the intestine, but in the gland. Due to the increasing pressure, the ducts rupture, the contents enter the pancreatic tissue, triggering the development of acute pancreatitis or pancreatic necrosis, the gland undergoes negative changes. Pancreatitis becomes a trigger for the formation of stones in the pancreas.
Causes and risk factors for the formation of calcifications
Stones in the pancreas are formed under the influence of many factors; the inflammatory process is the basis of the phenomenon.
The reasons for the appearance of stones are:
- Disease of the pancreas – pancreatitis.
- Inflammatory bowel disease – duodenitis.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder – cholecystitis.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- The presence of tumors, cysts, edema and inflammation in the abdominal organs.
- Hormonal disorders – disorder of the parathyroid glands.
- Violation of phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the body.
- Infectious diseases.
- Poor nutrition.
- Bad habits – smoking, alcohol abuse.
According to statistics, men are more likely than women to be affected by the disease. As a rule, pathology develops between the ages of 30 and 50 years.
Diagnostic methods
Symptoms of pancreolithiasis are difficult to distinguish from signs characteristic of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other abdominal organs. Therefore, in addition to a visual examination of the patient and analysis of his complaints, the following activities are mandatory:
- radiography, which allows to identify the presence of calcitis, determining their number, size and location;
- Ultrasound using a probe and sensor;
- CT and MRI, which help assess the condition of the gland itself.
Also required are blood and urine tests, and examination of stool for fatty inclusions and calculi in the form of calcium salts.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of stones in the pancreas are varied and depend on the underlying disease and the severity of inflammation, the location of calcifications, and their quantity. Often the symptoms of pancreathiasis are similar to the symptoms of other diseases of the internal organs; a specific diagnosis can be made only after diagnostics.
- First of all, the patient complains of pain, which can be sharp or aching, periodically subside and return with renewed vigor. Pain occurs in the upper abdomen, radiates to the back or to the area under the shoulder blade, and can be girdling in nature.
- Nausea and vomiting with bile impurities are accompanied by pain, which is similar to attacks of biliary colic.
- When a stone enters the common duct, signs of obstructive jaundice sometimes appear - yellowing of the sclera and skin.
- As a result of disruption of the endocrine function of the pancreas, an increase in blood glucose levels is observed.
Many of the symptoms described are characteristic of third-party diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary system. Before making a final diagnosis, diagnostics and differential diagnosis are carried out.
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms depends on the stage of development and localization of the stones - they can be located in the ducts or the parenchymatous layer of the gland. In all cases, the main sign of stone formation is pain. Pain from pancreolithiasis can last from several minutes to several hours. The nature of the pain is burning, in the form of colic, covering the abdomen and lower back, radiating to the shoulder blade. Attacks can be daily or occur rarely, several times a month or even a year.
Other symptoms of stone formation:
- increased pain during eating and palpation;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting of bile;
- lightening of the stool and the presence of undigested fat in it (steatorrhea - fatty stool);
- excessive salivation;
- the stomach looks bloated;
- general malaise, sweating.
With a long course of pancreolithiasis, against the background of a decrease in pancreatic secretory function, insulin production decreases. Along with the typical signs, symptoms of diabetes mellitus appear - dry skin, irresistible thirst, polyuria, the smell of acetone from the mouth. Migration of stone from the pancreas to the bile duct causes the development of obstructive jaundice.
Complications of pancreolithiasis are dangerous. If a stone clogs the ducts for a long period, acute pancreatitis develops with infection of the gland tissue. Often, purulent abscesses and cysts appear against the background of stones. In the presence of large stones, there is a high risk of hemorrhage into the duct or parenchyma of the gland with subsequent tissue death.
Diagnosis and treatment of pancreolithiasis
Treatment of stones in the pancreas is absolutely required, due to the danger of possible complications. The presence of stones is accompanied by a constant inflammatory process, leading to the fading of the functions of the pancreas.
In addition to the patient’s complaints, the attending physician looks closely at telling signs: increased salivation, the presence of calcium compounds in the stool, increased levels of the enzyme diastase in the blood and urine.
It is impossible to diagnose stones in the pancreas based on symptoms, due to the similarity of the clinical picture with other diseases. Therefore, during the examination, instrumental and hardware methods are used:
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity in several projections.
- Ultrasonography.
- CT scan.
- MRI.
The symptoms and treatment of pancreolithiasis are similar to pancreatitis; pathological processes deeply affect the pancreas. The algorithm and methods of treatment depend on the complexity of the lesions, the location of concentration and size of calcifications, and the severity of the patient’s condition.
Conservative method of therapy
The goal is to stop the inflammatory process, eliminate the cause that caused the process, and relieve swelling of the pancreatic tissue. Conservative treatment includes:
- Painkillers that relieve spasms - "No-shpa", "Papaverine", "Buscopan", analgesics - "Baralgin", "Acetamifen". Reduces spasms by taking alkaline mineral waters.
- Drug treatment using drugs that relieve inflammation in the ducts and tissues of the pancreas, restoring metabolic processes.
- Replacement therapy. Pancreatic enzymes are prescribed: “Pancreatin”, “Creon”, which facilitate the digestion of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
- In the initial stages, stones are removed using popular drugs: Ursosan, Henodiol, Ursodiol. Treatment takes a long time, but the use of the drugs helps reduce cholesterol levels in the blood. The drugs cause the dissolution of stones. However, they cannot be used to remove large formations and in the case of calcification of gallstones that cannot be dissolved by drugs.
- Diet assignment. Nutrition in diseases of the pancreas becomes crucial. Diet helps enhance the effect of treatment and prevents new attacks. The basic rules are fractional meals, the exclusion of fatty and fried foods, an emphasis on pureed vegetable soups and purees and porridges - buckwheat and oatmeal. The doctor recommends that the patient drink plenty of water during the day. It is useful to acidify the liquid with lemon juice.
- Treatment using traditional medicine methods using medicinal plants. Healing decoctions of linden, chamomile, mint, and St. John's wort gradually remove sand and help relieve inflammation of the pancreatic ducts and pancreas.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking, active lifestyle.
Conservative treatment methods significantly alleviate the patient’s condition, however, not every stone in the pancreas can dissolve under the influence of medications. Then the calcifications must be removed through surgery or an alternative method.
Non-surgical treatment using modern technologies
Non-surgical modern methods for removing small stones are known:
- endoscopic stone extraction – removal of formations using a fiber-optic endoscope;
- remote shock wave lithotripsy - crushing stones using ultrasound, the remaining fragments are removed from the body.
These methods are easier to tolerate by patients than traditional surgery, however, large stones located in the head or body of the pancreas cannot be removed using these methods.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is used in cases of severe disease accompanied by:
- severe pain that cannot be relieved with painkillers;
- frequent and prolonged attacks;
- weight loss and general exhaustion;
- rapid growth of pathological processes in the pancreas.
The operation helps relieve the patient of large formations and create the possibility of free outflow of pancreatic secretions.
Pancreatotomy - used to remove stones through an incision in the duct. If the stone is single, the pancreatic tissue is dissected over the stone, and the surgeon removes the formation. If there are a lot of stones, the duct is opened along the length of the gland body, gradually removing the stones. In order to prevent subsequent relapses and complications, careful probing and cleaning of the sinuses and recesses from the smallest particles and sand are performed.
The operation to remove stones is complex, and in some cases it is impossible to do without the procedure. When stones are found in the pancreas, inflammatory processes develop and sclerotic changes in the organ occur, leading to atrophy.
Phytotherapy
Since malfunction of the pancreas is a serious symptom, before starting treatment it is worth establishing whether there are stones, their location and size. This will help make a correct diagnosis. Treatment with traditional methods should be agreed with your doctor
Grind the chicory root. Boil it for about 5 minutes in 250 ml of water. Filter after cooling. The entire decoction should be drunk in small portions throughout the day. This remedy is recommended for use not only for pancreolithiasis, but also for chronic pancreatitis.
A decoction of barberry bark helps with pancreolithiasis. Need 1 tbsp. l. Brew 250 ml of boiling water with crushed bark. Boil for 10-15 minutes, then cool and filter. Take 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day.
For the treatment of pancreolithiasis, an infusion of burdock root is an effective folk remedy. You need to grind the root of the plant to a powder. 2 tbsp. l. raw materials, brew 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for 3 hours, then filter. Take 30 minutes before meals. The resulting infusion should be drunk throughout the day in several doses.
To improve the functionality of the organ, mix herbs in equal parts: St. John's wort, linden blossom, chamomile, tricolor violet, mint. Pour 1 tbsp. l. herbal mixture 250 ml of boiling water, filter after 30 minutes. Drink 120 ml 2 times a day.
To reduce pain, you need to brew 1 tsp. crushed blueberry leaves 250 ml boiling water. Leave to infuse for 45 minutes. This drink should be sipped throughout the day. The daily dose of infusion is 250 ml. Treatment should be carried out for 2 weeks, then take a break for a week. If necessary, repeat the course.
If exacerbation of pancreolithiasis occurs frequently, it is recommended to treat with an infusion of medicinal herbs: mint, cudweed, chamomile, plantain, St. John's wort, yarrow. The herbs taken in equal parts must be crushed and mixed. 1 tbsp. l. pour boiling water over the collection and leave for 2 hours. The finished medicine should be drunk 80 ml three times a day before meals.
Icelandic moss helps dissolve formed stones. You will need 20 g of raw materials and 250 ml of apple cider vinegar. The medicine needs to be infused for 2 days. For 2 weeks you need to take 1 tsp before bed. product diluted in 250 ml of water.
To remove stones, it is recommended to take a decoction of dandelion roots with mint for 5 weeks. You need to grind the dandelion root. 1 tsp. mix it with 3 tsp. mint leaves. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water, boil for 7 minutes, leave to steep for half an hour. The strained decoction should be drunk before each meal, 50 ml.
An infusion of immortelle and chamomile helps destroy stones, relieves pain and inflammation, and prevents the formation of cysts. Take 1 tsp. each herb and pour 250 ml of boiling water over the raw material. Strain after cooling. Take 70-80 ml of medication 30 minutes before meals.
Prevention of pancreolithiasis
Stones in the pancreas are in most cases a consequence of the inflammatory process caused by other diseases. Treatment of pancreatiasis often involves eliminating the cause that caused the disease.
Prevention of diseases of the biliary system, timely treatment will help prevent dangerous inflammatory diseases in the pancreas, including pancreathiasis. Herbal medicine for cholelithiasis becomes a means of troubleshooting the biliary system, a lever for the prevention of dangerous diseases of internal organs.
Following a diet, giving up alcohol and smoking will help restore health and prevent the occurrence of diseases, primarily of the pancreas.
An active lifestyle is an essential condition for health and longevity. Breathing exercises are extremely useful for preventing relapses of chronic pancreatitis. Walking is a mandatory attribute of a healthy lifestyle. This is a wonderful form of physical activity that replaces working out in the gym. An important advantage of walking is the healing effect of movement, fresh air and emotional release. It’s easy and effective to combine walking and breathing exercises.
Forecast
In most cases, with stones in the pancreas, the prognosis is quite favorable. If the disease is not complicated and is not accompanied by other ailments, it can be easily cured through the use of conservative therapy.
Surgical intervention also gives a positive result: more than 80% of patients recover completely and can lead a normal, “pre-operative” lifestyle (except perhaps follow a not too strict diet). Only 2% of operations end in death, and then only due to the extremely advanced condition of the patient.
Have you been diagnosed with pancreatic stones? Be sure to contact a gastroenterologist! Timely removal of stones will help prevent the development of various complications: abscess, bleeding, chronic pancreatitis, inflammation of fatty tissue and cystic growths.