Suspension in the gallbladder is the first symptom of gallstone pathology. Gradually the particles will bond with each other and form stones. The disease can develop independently or be associated with problems of the digestive tract. Most often, the pathology is diagnosed in women over 40 years of age. In this case, the characteristic symptoms are cramping pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea and vomiting. You should definitely consult a doctor to find out your diagnosis. He will prescribe treatment that will quickly eliminate the pathology that has arisen.
What is a suspension in the gallbladder and what does it look like?
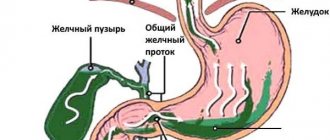
The gallbladder is an organ whose main task is to accumulate, store and release bile in portions. It performs the function of breaking down fats during the digestion of food. Bile itself is a liquid, but with certain health conditions it thickens. Then they talk about the presence of suspension in the bubble.
When an ultrasound examination is performed, the contents of the gallbladder, that is, bile and its components, can be displayed on the screen in different ways:
- Anechoic bile is shown in black. It is clean, homogeneous, and does not contain any inclusions. This is an indicator of health.
- The bile on the screen is gray and dark gray in color, that is, echogenic. This is evidence of the heterogeneity of bile and the fact that flakes have begun to form in the gallbladder. Their density is still quite low, they are able to dissolve and easily reach the intestinal tract without blocking the ducts.
- Hyperechoic suspension, or increased echogenicity. It looks like a white precipitate on the device monitor. This formation has a greater density than just flakes. This condition is called bile sludge (biliary sludge). The clots are already dense. According to some researchers, it is from such formations that, with further progression, sand and then stones can form.
Often, in order for the specialist to see additional inclusions in the organ, the patient has to change his body position several times during the examination. This makes the flakes more noticeable.
The flocculent suspension does not pose any particular health hazard and can be removed from the gallbladder using conservative methods. But its presence significantly worsens the patient’s condition.
Suspension particles consist of various components:
- cholesterol is a component of bile;
- calcium salts;
- bile pigments formed during the work of the liver.
The suspension is usually divided according to the size of the particles that form it:
- fine suspension - particles not exceeding 5 mm in size;
- Sludge is jelly-like clots that move freely in the bile;
- sludged bile - with this condition, both sludge and finely dispersed formations are found in the bladder.
Consequences
In medicine, there are discrepancies regarding the suspension in the gallbladder. Some sources claim that the presence of such particles is an indication for mandatory drug treatment to avoid the formation of stones. Other experts admit the constant presence of suspension without any consequences for the body.
Nevertheless, biliary sludge, in the absence of treatment and diet, can lead to cholelithiasis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, general disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, and deterioration of the liver. Therefore, if flakes and small particles are detected in the bile, you need to give up some habits and rebuild your lifestyle. Refusal of therapy in the initial stages can lead to progression of the disease.
https://youtu.be/QhNjw0qBgw4
Causes and mechanism of suspension formation
Bile suspension can form for various reasons:
- Liver diseases and problems with the biliary tract: treatment of gallstones by destroying them, dyskinesia and blockage of the biliary tract, fatty liver, problems with the pancreas, taking certain medications.
- Poor nutrition. Abuse of fats, sweets, foods with a lot of spices, and alcoholic beverages. High content of cholesterol and calcium salts in food. Non-compliance with the diet - long breaks in meals, and then overeating. A sharp change in weight in one direction or the other.
- Hereditary factor and structural features of the bladder and biliary tract (kinks). These features provoke changes in the structure of bile, since it cannot drain normally from the bladder.
- Features of the human condition - the period of waiting for a child, older age, low physical activity.
In a normal state, bile does not stagnate in the bladder, and is periodically used to digest food eaten. When free outflow is disrupted, it begins to stagnate. This is how clots and other formations form.
What are the dangers of this condition?
If, after clarifying the diagnosis, a person does not follow the doctor’s recommendations, then the violation develops into serious pathologies:
- deterioration of bile outflow and complete blockage of the channels;
- the formation of bile conglomerates, accumulations of salt crystals and stones;
- getting and getting stuck of stones in the ducts;
- inflammation of the bladder and its ducts;
- pancreatitis.
Gallstone disease and cholecystitis are consequences that, in severe conditions, can be solved exclusively by surgery.
What does a person feel?
The sensations directly depend on what reason leads to the formation of unwanted particles. The size of the sand grains also matters.
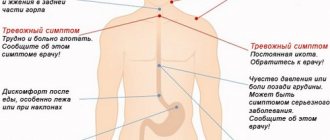
Here are the most common complaints that allow a specialist to determine the condition:
- a painful feeling under the lower right rib that can last from 5 minutes to several hours;
- unpleasant sensations are sharp, pulling, grasping;
- feeling of nausea, vomiting;
- violations of stool and its regularity;
- lack of appetite.
Usually, a suspension in the gallbladder in a child or an adult does not show any signs; the condition is asymptomatic and is detected by chance on an ultrasound.
However, when a person already has diseases, for example, cholecystitis, then the general condition will depend on the amount of suspension in the gall cavity. Biliary colic is likely to occur. If there is pathology of the bile ducts, pain and heaviness will occur after eating fatty foods or after prolonged fasting.
The essence of pathology
The suspension accumulating in the gall cavity is presented in the form of tiny grains of sand. The composition of the suspension is complex - it contains crystallized particles of lipids and cholesterol, protein and calcium salts. As the amount of suspension increases, the particles stick together, forming more voluminous structures - stones. The formation of a solid suspension from bile stagnation in the cavity of the bladder is called sludge syndrome.
The suspension accumulated in the gall cavity may have a different composition:
- microlithiasis, or fine suspension - a fine sediment consisting of potassium and calcium salts, protein particles; microlithiasis is easily detected during ultrasound - the sediment moves inside the bile duct when the patient changes body position;
- sludge - pathological formations in the cavity of the bladder, presented in the form of putty-like clots of bile secretion;
- sludged bile - a combination of fine sediment and bile clots; the formation of sludged bile is considered an early stage of cholelithiasis.
By the nature of its occurrence, the suspension is primary - pathological thickening of bile and sedimentation occurs independently, without the presence of concomitant pathologies of the biliary tract; and secondary - arising from a disorder of the gastrointestinal tract and the influence of other negative factors.
Diagnosis of flakes in the gallbladder
To clarify the diagnosis, a set of research methods is used:
- taking an anamnesis - the doctor finds out when the pain first appeared, where it is localized, and when the condition worsens;
- the presence of chronic and acute diseases, harmful addictions;
- external examination, palpation of the painful area;
- urine and feces analysis, biochemical and clinical blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the digestive organs is the best way to detect gallbladder sludge;
- computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging make it possible not only to evaluate the echo suspension, but also to determine the condition of other organs, problems with which may be the cause of its occurrence (liver and pancreas);
- study of bile from the lumen of the duodenum - duodenal intubation.
Diet
Treatment of sludge syndrome without diet will not bring positive results. For patients with suspension in the gallbladder, diet No. 5 is optimal, with a limitation of fats and foods that increase the concentration of cholesterol in the blood - eggs, mayonnaise, fatty meat and fish, baked goods made from premium flour. All fried and spicy foods, full-fat milk and cream, and alcohol are prohibited.
Despite a number of dietary restrictions, the diet should be complete and balanced. The patients' menu consists of light vegetable soups with the addition of cereals and pasta, lean meat and poultry, fresh vegetables and fruits, low-fat cottage cheese and kefir. Vegetable oil and butter are allowed as fats, but not more than 50 ml per day. Drinks allowed include jelly, compotes, and non-acidic juices from fruits and berries.
General principles of nutrition for patients diagnosed with “suspension in the gallbladder”:
- fractional mode, up to 5 meals per day;
- refusal to overeat;
- eating at the same time;
- proper culinary processing - boiling (including steaming), baking without oil, stewing;
- The optimal drinking regime is at least 2 liters of liquid per day.
How to treat
Therapy prescribed by a specialist and adherence to certain rules will help get rid of flakes in the gallbladder. It is important after the end of the acute period not to stop following a healthy balanced diet and the recommended regimen.
Diet
Since the bladder belongs to the organs of the digestive system, the main recommendations will concern nutrition. Diet No. 5 according to Pevzner will reduce the load on organs and help them recover:
- Sludge in the gallbladder is formed mainly due to stagnation of bile. Therefore, you need to eat food often - from 5 to 7 times a day, portions should be small, comfortable for digestion.
- Avoid foods that irritate the digestive tract - fatty meats, raw vegetables and fruits, salty, sweet and spicy foods.
- It is important to give up alcohol and reduce tobacco use.
- Drinking the required amount of fluid is beneficial for the gall bladder. It is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of water per day. More accurate data should be obtained from your doctor, since for some diseases this volume may change.
Medicines
The drugs will help relieve pain and relax the spasmodic muscles of the bile ducts. It is important that all medications for such conditions are prescribed strictly by a specialist. Self-medication is unacceptable. Here are the recommended medications:
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine) to relax smooth muscles. They help especially quickly with spasms of the bile ducts. Antispasmodic drugs help get rid of suspension in the gallbladder if the cause of its appearance is tension in the smooth muscles of the ducts.
- Medicines with a choleretic effect are necessary for stagnation of bile (Ursosan, Ursohol, Allochol, Holosas, Livodexa).
- Painkillers based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Paracetamol, Nurofen, Nalgesin) will relieve pain and discomfort until the main drugs begin to work. This is very important, because pain with biliary colic can be very painful.
Folk remedies
On the recommendation of a doctor, a person can try treatment with folk remedies.
Pathology can be treated with herbal infusions and decoctions with choleretic and anti-inflammatory effects. But before using such drugs, consultation with your doctor is necessary.
The most commonly used are decoctions of medicinal herbs. Choose plants that relieve inflammation and have a choleretic effect:
- sagebrush;
- chamomile;
- sea buckthorn fruits;
- corn silk.
Usually brew 1 tbsp. selected herb or mixture of herbs in a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour. Strain and drink this entire volume throughout the day. The course of treatment is at least 4 weeks.
Physical exercise
Exercising is not only not prohibited, but is even recommended:
- Cardio training will help burn extra calories, speed up your metabolism, and make all your organs work harder.
- Strength loading is permissible if permitted by the attending physician. It will force the muscles to work and take as many nutrients from the blood as possible. As a result, the digestive system will work more actively.
- Daily walking (at least half an hour) will help if a person cannot engage in more active types of exercise.
Treatment with folk remedies
Problems of the digestive system are a case when treatment with folk remedies can be effective. It involves the use of medicinal herbs in the form of infusions, decoctions, teas, both anti-inflammatory and choleretic:
- chamomile decoction;
- infusions of corn silk, wormwood;
- tea from sea buckthorn, thyme, rose hips;
- berry fruit drinks.
Treatment with folk remedies is usually carried out over a 2-month course, once every six months.