What is a stomach ulcer?
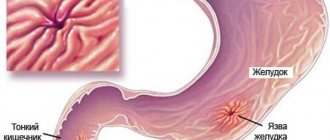
In a narrow sense, a gastric ulcer is understood as a deep defect in its inner lining, penetrating through the entire thickness of the mucous epithelial layer to the smooth muscle layer, often through the entire wall. In a broader and more precise sense, it would be more correct to speak not about an ulcer, but about peptic ulcer disease, because this is a disease of the whole body with a defect localized in the stomach or duodenum.
The logical question is: what is the connection between an ulcer and the body as a whole? The most direct one, because many factors lead to the occurrence of an ulcer:
- disturbance of gastric secretion, which depends on neuroendocrine regulation;
- damage to the mucous membrane by a specific microbe Helicobacter - subject to decreased immunity;
- circulatory disorders, blood circulation - with spasm or sclerosis of the arteries;
- disturbance of nervous trophism – with low resistance to psycho-emotional stress, stress;
- decrease in the reparative (restorative) abilities of mucosal cells - with metabolic disorders in the body, hypovitaminosis, general weakening.
These are just a few simple examples indicating that an ulcer is not a separate disease, but a consequence of trouble in the body, a violation of any function, and most often several at once.
Reasons for appearance
With pain, the body signals that something is going wrong. If an ulcer appears in the stomach, gradual destruction of the mucous membrane occurs. The resulting wound is constantly injured under the influence of aggressive stomach contents, which is why painful sensations occur. The nature and intensity of pain depends on many factors. But the root causes are the provocateurs of the onset of ulceration, more often Helicobacter. Other factors also influence the appearance of painful symptoms of an ulcer:
- abuse of spicy and over-salted foods;
- the predominance of hot or cold dishes on the menu;
- violation of eating habits;
- constant consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking;
- exposure to stress.
Intense, unremitting pain when taking medications prescribed by a doctor requires qualified intervention. It is forbidden to engage in amateur activities even if symptoms increase, fever, or decrease in heart rate.
Why does a stomach ulcer cause pain?
Pain syndrome, in principle, occurs due to irritation of nerve receptors, of which there are a huge number in all organs, including in the wall of the stomach. The signal is transmitted along nerve pathways to the brain, where the feeling of pain that we feel is formed.
What is associated with the symptom of pain during exacerbation of a stomach ulcer? There are many reasons for this. This includes the impact of Helicobacter, its destruction of the mucous membrane, and its irritation by the increased content of acid and pepsin in the gastric juice, and injury from rough, hot food, and alcohol.
The cause is also a violation of the motor function of the stomach, a spasm of smooth muscles, in which, during contraction, excess lactic acid is released, leading to pain. The accompanying inflammatory process also plays an important role during exacerbation of the ulcer. Humoral mechanisms are connected to it - the production of adrenaline, acetylcholine, mediators of pain receptors increases, their susceptibility increases, all this forms a pain syndrome.
The depth of the ulcerative process also plays a role. If the defect grows into the adjacent pancreas, its nerve branches and plexuses are involved in the process, the pain increases sharply. The same thing happens when the ulcer penetrates (germinates) into the biliary tract, and when other complications of the ulcer develop.
However, sometimes there are “silent” or “silent” ulcers that do not cause pain. This happens when the ulcer is located in a place where there are very few pain receptors.
Other types of pain
Migraine with ulcer
If dizziness occurs during a migraine, you should suspect bleeding from an open ulcer.
Pain in the head usually occurs while taking anti-ulcer medications, that is, as a result of side effects. With an advanced ulcer with a severe course, migraines occur due to constant nausea and debilitating vomiting. Due to the appearance of gagging, a sharp contraction of the muscles of the pharynx, neck and head occurs, as a result of which the volume of blood in the subcranial vessels instantly increases. After the vomiting stops, a painful pulsation remains due to the sudden outflow of blood from the head.
If dizziness occurs against the background of an ongoing migraine, you should suspect bleeding from an open ulcer. The condition occurs due to a decrease in blood pressure in the arteries, which causes general weakness. Accompanying signs of bleeding are the presence of blood in vomit and feces. This complication requires urgent hospitalization and assistance, as it threatens the patient’s life.
Back pain
Painful sensations in the back and lower back due to an ulcer occur against the background of impaired gastric motility. Often the symptom occurs earlier than the ulcer is diagnosed, so the cause is not always correctly determined. But as the disease worsens, other (concomitant) signs of progression of the ulcerative process appear in the form of a bitter, sour or rotten aftertaste in the mouth, nausea, dizziness, and vomiting.
Abdominal pain
Physical activity can cause abdominal pain.
Abdominal pain due to an ulcer will be detected in different areas, depending on the location of the problem. More often it hurts in the epigastric region, less often - on the left or right hypochondrium and in the lumbar part, and even less often - in the lower abdomen and sternum. Increased pain is observed during physical activity, when the abdominal muscles come into tension. This provokes stomach spasms and, accordingly, pain. Constant sensations indicate a complication of the course of perigastritis, perivisceritis, penetration of ulcers, requiring urgent treatment.
Abdominal pain is a characteristic sign of an ulcer. Severe painful attacks end in nausea and sour vomiting. The condition is alleviated by lying on your side with your legs pressed to your chest.
What criteria characterize ulcer pain?
Presumably, the nature of the pain that occurs during an exacerbation allows you to create an idea of the characteristics of a stomach ulcer, taking into account the following criteria:
- localization – location;
- intensity and character;
- time of appearance.
Dependence of pain syndrome on the location of the ulcer
Pain with a stomach ulcer is always noted in the upper abdomen - in the epigastrium. If the defect is located in the initial, cardiac region, the pain will be felt in the left epigastric region (hypochondrium), and there may be irradiation to the left half of the chest, the left scapula, as with angina pectoris. An ulcer of the body of the stomach gives pain in the central section, they can radiate to the sternum, and localization in the outlet pyloric section causes pain in the right hypochondrium.
Pain intensity
Most often, with uncomplicated peptic ulcer disease, the severity of pain is moderate. When the disease is complicated by an inflammatory process, the pain is intense, and if neighboring organs are involved in the process, they can be paroxysmal in nature.
A penetrating ulcer is characterized by constant intense pain. If a perforation occurs, the pain is sharp, “dagger-like” in nature, and can even cause painful shock. And if the ulcer has closed, then the pain syndrome is typically reduced due to the blood washing the pain receptors.
Appearance time
The time dependence of pain is associated with food intake. They can be early, late, “hungry” and nocturnal. Early ones occur immediately after a meal, when the ulcerative defect is located in the initial part of the stomach, late ones - 1.5-2 hours after a meal with an ulcer in the area of the body of the stomach. “Hungry” and night pains are characteristic of pyloric ulcers. In fact, the time of their appearance indicates the localization of the ulcer.
Prevention
Prevention of ulcer pain depends on following the recommendations below:
- timely treatment of gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, duodenitis). These pathologies, which develop into a chronic form, significantly increase the risk of developing an ulcer with the appearance of an aggravated syndrome. For control, a test for Helicobacter pylori is required;
- proper nutrition in the presence of a stomach ulcer (exclusion of sour, salty, spicy, smoked foods, alcohol, cigarettes, sour fruits, products containing artificial substitutes);
- adherence to a regimen of fractional meals up to 7 times a day every 2–3 hours;
- prohibition of taking medications that may adversely affect the functioning of the digestive system (aspirin, corticosteroids, non-steroidal analgesics). All medications must be prescribed by qualified specialists if there are clear indications for use;
- undergoing preventive treatment in special sanatorium resorts. These institutions have a course of unique procedures that are aimed at quickly restoring the body and maintaining health;
- eliminating the constant occurrence of stressful situations and nervous disorders with a predisposition to ulcers and the presence of other gastrointestinal diseases.
Types of pain
The range of pain experienced with peptic ulcer disease is very diverse and depends on a number of factors: the nature of gastric secretion, involvement of other organs in the process, and the presence of complications.
Effect of acidity
With reduced and normal secretion, the pain can be aching, pressing in nature; with increased acidity, it is more often of a burning nature; the burning sensation can spread to other parts of the abdomen, accompanied by sour belching. A decrease in such pain is typical after taking soda and other antacids.
Involvement of the abdominal organs in the process
When an ulcerative defect is located in an area with many nerve receptors, pain impulses are transmitted through viscero-visceral reflexes to other organs, and disturbances occur in them - dyskinesia of the bile ducts, pancreatic ducts, and impaired intestinal motility. The inflammatory process can also spread and adhesions form between organs. All this leads to the appearance of cramping pain, often diffuse, and a feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
Impact of complications
An ulcer in the lower third of the stomach can grow into the pancreas. When this happens, the frequency of pain is replaced by its constancy, it becomes more intense, radiates to the lower back, and can have a “drilling” character.
Another complication is pyloric stenosis (narrowing of the outlet of the stomach) manifested by bursting dull pain, which is accompanied by vomiting. Finally, perforation of the ulcer leads to the release of gastric contents into the abdominal cavity, irritation of the peritoneum. In this case, a sharp, intense pain occurs, which patients compare to being stabbed with a knife.
Does pain depend on the location of the ulcer?
The nature of the pain depends on the location and size of the damage to the stomach tissue.
Ulcers of the subcardial and cardiac regions
Placed immediately under the esophageal sphincter or no further than 5–6 cm towards the stomach. Peculiarities:
- “early” pain is felt by patients high in the epigastrium, in the area of the xiphoid process;
- are characterized by frequent irradiation to the heart area, always require differential diagnosis with angina pectoris (you must remember that angina attacks are associated with physical activity, disappear with rest, coronary-dilating Nitroglycerin tablets relieve pain, and “ulcerative” pain follows food intake);
- weakly expressed in intensity;
- often contribute to manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux with belching, heartburn, vomiting, as cardiac sphincter insufficiency develops;
- can be combined with reflux esophagitis, hiatal hernia;
- Perforation rarely occurs; bleeding is typical.
Ulcers on the lesser curvature
They constitute the largest proportion in terms of number. Peculiarities:
- common in old age;
- pain is felt in the epigastrium on the left;
- are classified as “late”, less often “hungry”;
- more often they have a low-intensity aching character, but during exacerbation they are very pronounced;
- accompanied by heartburn, nausea, vomiting is rare;
- a study of gastric secretion in most cases shows a normal level;
- bleeding occurs in 14% of patients, perforation is rare;
- up to 10% of cases transform into a cancerous tumor, this applies to ulcers located in the bend area, the pain becomes constant.
Ulcers on the greater curvature
Characteristics: rarely detected; there are no typical manifestations based on the nature of pain and symptoms. It is important that half of the cases proceed with degeneration into a malignant tumor, so the localization is considered potentially dangerous and requires enhanced monitoring (repeated biopsies of the edges and bottom).
Features of pain in elderly and young people
Pain from a stomach ulcer has age-related characteristics. At a young age, the disease develops rapidly and pain is more pronounced, often accompanied by a burning sensation and abdominal cramps. This is due to the higher reactivity of the body, mobile nervous processes, and high gastric secretion.
As for older people, the picture is completely opposite. Often, peptic ulcer disease remains undiagnosed for a long time and is mistaken for gastritis. The pain is usually moderate, appears after eating and goes away quickly. Characteristic is a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen due to impaired peristalsis and fullness of the stomach. Due to reduced acidity, a burning sensation in the abdomen is not typical, but it appears behind the sternum due to the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus - reflux esophagitis develops.
Main symptoms
At the early stage of development of a stomach ulcer, pain occurs after eating for 2 hours. However, they are temporary and gradually subside. To eliminate unpleasant sensations, it is recommended to take antacid medications (Almagel, Maalox).
The symptoms of a chronic ulcer worsen during the season (autumn, spring) and last for 2–3 months. At the same time, additional factors influence the development of the disease (nervous disorders, excessive physical activity, taking medications, harmful foods).
With a more acute course of the ulcer, unpleasant sensations occur within 6 hours after the last meal. There is belching with a putrid odor and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. This condition can be stabilized with restorative medications (De-nol, Vikalin, Tribimol).
An empty stomach releases hydrochloric acid, which irritates the walls of the stomach and causes pain. In order to eliminate discomfort, it is necessary to establish split meals up to 7 times a day in small portions.
Mild periodic pain indicates the onset of an exacerbation, so if you experience short-term discomfort, you should consult a qualified doctor and start treatment on time.
The appearance of sharp pain at night when the stomach is full also indicates the development of an acute ulcer. In this case, you need a small snack (tea or milk with a piece of dried bread). If the discomfort does not go away, then taking antispasmodics is recommended.
Severe, persistent pain is most often the cause of perforation of the ulcer, since food enters the abdominal cavity and causes severe discomfort and a significant deterioration in the general condition. In this case, immediate treatment to the hospital is necessary.
Pain relief from stomach ulcers
Elimination of pain from a stomach ulcer is necessary, but this is just a relief of the condition. Treatment should be comprehensive, including different groups of medications and folk remedies, including for pain relief.
What medications are used to relieve pain?
Among the drugs prescribed are analgesics - Baralgin , Sedalgin and analogues, antispasmodics - Papaverine , No-shpa , Atropine , antacids and gastroprotectors that reduce the effect of hydrochloric acid on ulcers - Almagel , Rennie , Maalox and analogues. Any medicine must be prescribed by a doctor.
What folk remedies have an analgesic effect?
To relieve ulcerative pain, traditional medicine recommends an infusion of valerian root, motherwort herb, mint leaves, St. John's wort flowers, calendula, and linden. These are tools that will suit everyone. But plantain grass, rose hips and ginger root are not recommended for pain relief; they increase the production of hydrochloric acid.
How to quickly relieve pain
Elimination of pain in acute ulcers is possible only with prior consultation with the attending physician, who will prescribe safe and effective remedies. It is also necessary to follow a diet with a properly selected diet.
Medications
To eliminate all negative symptoms, drugs of the following category are effective:
- anticholinergic drugs (Gastroceptin, Platyfillin);
- antispasmodic tablets (Metacin, Nosh-pa, Spazmolgon);
- gaglioblockers (Dikalin, Kvateron);
- preparations containing bismuth (Bismol, Ventrisol, De-nol, Tribimol);
- antacid medications (Maalox, Vikalin, Phosphalugol).
Before the onset of severe pain, you can drink alkaline water in advance to obtain an analgesic effect. Milk is a natural antacid, so doctors recommend consuming the product before bed.
Elimination of unpleasant sensations is possible by using physiotherapeutic procedures (magnetic therapy, modulated currents), which promote rapid healing and scarring of tissue.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for ulcer pain help eliminate all unpleasant sensations. The advantage of this technique is the naturalness of the ingredients used and relative safety compared to drugs of chemical origin.
The most effective traditional medicine recipes are discussed in the list below:
- propolis tincture, diluted in water in a ratio of 1 tbsp. spoon per glass of water. The resulting remedy is drunk in the evening for 20 days;
- sea buckthorn oil in the amount of 1 tbsp. spoon 30 minutes before meals, as the product envelops incoming food and does not cause unnecessary irritation on the walls of the stomach;
- decoction of herbs (chamomile, calendula, horsetail, rose, dried grass, wormwood, burdock, dill seeds, rose hips, St. John's wort, yarrow, plantain). The finished product is taken 20 minutes before meals in an amount of 20 ml;
- An infusion of dried or fresh blueberries is taken 4 times a day throughout the course of treatment.
One of the effective methods of eliminating pain from ulcers is following a diet with the consumption of certain foods that are prepared using safe methods.
Useful video
What they are and why they arise can be found in this video.
In what cases should you urgently consult a doctor if you have pain?
There are no cases of exacerbation of an ulcer that would not require seeing a doctor. It is imperative to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist at your next appointment, undergo examination and treatment. But there are times when medical help is needed urgently:
- perforation of the ulcer (severe sharp pain in the abdomen);
- stomach bleeding (vomiting like coffee grounds, black stools, pallor, dizziness);
- gastric obstruction (frequent vomiting).
In these cases, you should not take any medications yourself, but call an ambulance.
How do combined and multiple ulcers manifest?
Combined ulcers are the simultaneous detection of ulcerations in the stomach and duodenum (identified in 5–10% of cases), and multiple are non-single ulcers in one organ. It is believed that the duodenum is the first to be affected. Clinical signs express typical symptoms.
When a stomach ulcer occurs, the patient’s condition noticeably worsens:
- the pain syndrome becomes almost constant, “late” pains are supplemented by “early” ones;
- propagation occurs both to the right and to the left;
- heartburn and vomiting become constant;
- worries about the feeling of a full stomach;
- complications occur such as cicatricial pyloric stenosis, perforation, bleeding.
Let's find out how a stomach ulcer hurts depending on its size using the example of signs of giant ulcers. These include identified defects in the stomach wall with a diameter of 20–30 mm. They are more often localized on the lesser curvature, less often in the subcardial zone and on the greater curvature.
The pain syndrome is intense, the sign of periodicity and dependence on food intake disappears. They become permanent, so they must be distinguished from a cancerous tumor. Patients lose weight quickly.
In the clinical course, bleeding, perforation into the pancreas, and degeneration into a malignant neoplasm appear much more often.
Prevention of pain and worsening ulcers
As a rule, outside of an exacerbation, a healed stomach ulcer does not cause pain, so preventing the appearance of pain is nothing more than preventing an exacerbation of the disease; it includes quite accessible measures:
- adherence to a special anti-ulcer diet;
- quitting smoking, alcohol;
- reasonable distribution of work and rest;
- physical activity, therapeutic exercises;
- Regular visits to the doctor, necessarily on the eve of spring and autumn - periods of seasonal exacerbations, undergoing examination and anti-relapse treatment.
Pain in gastric ulcers is an indicative, but not the only symptom. Their elimination should not be an end in itself during an exacerbation of the disease, but only one of the points of a comprehensive treatment program.
Treatment
Treatment of peptic ulcer is combined and is aimed at counteracting the mechanisms of ulcer formation, restoring the gastric mucosa, and combating complications. Pain relief for stomach ulcers is a necessary condition for effective therapy. For this purpose, special medications are used. But the recommendations begin with strict dietary requirements.
It is required to exclude from the menu fatty and fried foods, hot sauces, sour fruits and pickles, smoked meats, legumes, chocolate and coffee.
During an exacerbation, only liquid porridge with water, low-fat broths with white crackers are used, you can drink rosehip decoction. Meals are provided in small portions 5–6 times a day. To find out which painkillers can be used effectively in a particular case, the patient’s gastric acidity and the presence of Helicobacter in the contents are studied.