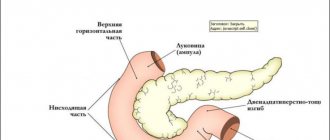
In all cases, treatment of esophagitis is complex. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the esophageal mucosa. Esophagitis is manifested by burning pain in the chest, increased salivation, dysphagia, and belching.
Its occurrence is possible against the background of poor nutrition, smoking, alcoholism, increased stomach acidity, reflux disease and incompetence of the lower sphincter.
Characteristics of the disease
Peptic esophagitis (ICD code 10 - K20) is a condition of the epithelial lining of the esophagus that occurs as a result of prolonged aggressive acid exposure. Contents with such characteristics end up in the cavity of the esophagus as a result of reflux, that is, the process of reverse reflux. During regurgitation (rapid movement in the opposite direction from the point of view of physiology) of the stomach contents, inflammation of a chemical nature is formed.
The normal pH value of the contents of the esophagus should be at least 7.0, that is, indicate an alkaline environment. When food debris is released back from the gastric cavity, acidic juice with an aggressive effect penetrates into the esophagus, and therefore this indicator decreases to 4.0 or less. Inflammatory changes in the epithelial lining occur.
Gastroesophageal reflux is the sudden ejection or leakage of stomach contents back into the esophagus, not accompanied by preliminary nausea and subsequent vomiting. In some cases, duodenogastric reflux can be combined with gastroesophageal reflux, as a result of which not only bile, but also pancreatic secretions affect the esophageal mucosa.
https://youtu.be/hFhP4aC71oQ
Reflux in certain cases may not be an abnormal phenomenon. The stomach component is thrown back into the esophagus even in a practically healthy person, primarily in children. However, the maximum duration of one oxidation of the esophagus should be five minutes, and the total duration of these processes within 24 hours should not exceed 2% of the total amount of time in an upright position, 0.3% of the hours spent by a person lying down.
Gastroesophageal reflux of a physiological nature in most cases is observed during the process of eating, much less often - after the end. At night, this phenomenon is practically absent in normal conditions.
Pathogenesis
Gastroesophageal reflux is based on relative or absolute insufficiency of the obturator sphincter of the cardia. This disruption in its activity leads to motor-evacuation disorder in the stomach.
Intense contractions of the antrum will give rise to gastroesophageal reflux even in individuals with a satisfactorily functioning distal esophageal sphincter. Relative cardiac failure is typical for 9–15% of patients with peptic esophagitis.
Much more often the absolute form of this disorder is diagnosed. The main role in its formation is played by a significant weakening of the tone of the lower obturator sphincter. For example, due to taking certain medications, or food addictions - chocolate, citrus fruits, tomatoes.
No less important in the pathogenesis of the disease are antiperistalsis, as well as a decrease in the evacuation capacity of the stomach. It is because of them that acidic contents are thrown into the area of the esophageal tube. The result of all three components of reflux is the appearance of a focus of inflammation in the mucosa - hyperemia, swelling, pain.
The contents of the duodenum, which contains bile components, are much more aggressive. With existing duodenogastric reflux and its combination with gastroesophageal disorder, the mucous membrane of the esophageal tube is much more injured. Unpleasant sensations arise faster and last much longer.
Types and categories
The contents of the stomach in most cases affect the lower part of the esophagus, located right at the junction with the stomach. This process, called distal peptic esophagitis, is the most common type of disease.
Peptic reflux esophagitis is divided into several categories depending on the course of the disease.
- The acute form occurs due to a combination of external irritant influence and the action of gastric contents, most often hydrochloric acid, less often bile.
- Subacute peptic esophagitis is a disease that lasts from 3 to 6 months. Over time, the disease may progress to a protracted stage.
- The chronic form of peptic esophagitis is diagnosed in the case of long-term development of the disease, when its course is accompanied by temporary exacerbations and further remission.
From the point of view of the characteristics and severity of inflammation, the following categories are distinguished. Catarrhal and edematous forms are the most common types of peptic esophagitis in practice, accompanied by hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane. Erosive peptic esophagitis is the formation of erosions of the mucous membrane during infectious processes, as well as thermal and chemical burns. Necrotic form - occurs in case of severe infection. Hemorrhagic peptic esophagitis - characterized by hemorrhages in the walls of the esophagus. Pseudomembranous form, in which there is no fusion of fibrinous exudate with the submucosal layer. Exfoliative esophagitis is the reverse of pseudomembranous esophagitis in terms of the presence of fusion.
Phlegmonous peptic esophagitis usually occurs when the wall of the esophagus is damaged by a foreign object.
Stages of the disease
In terms of the degree of damage, acute peptic esophagitis is classified as follows.
- Superficial, in which there are no ulcerations or erosions.
- A disease affecting the entire thickness of the mucous membrane and is accompanied by ulcers and necrosis.
- Severe damage, involving also the layers located under the mucosa. Accompanied by deep tissue erosion, up to perforation of the walls of the esophagus and bleeding. As a result of successful treatment of peptic esophagitis, the lesions may become scarred.
Chronic esophagitis in terms of the level of wall damage is divided into four categories (Savary and Miller classification):
- hyperemia, in which there are no erosions in the distal sections;
- the appearance of individual small lesions affecting the mucous membrane;
- merging of adjacent erosive lesions of the mucosa with each other;
- the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane, as well as the development of stenosis.
https://youtu.be/dWTrjcyz0FY
Peptic esophagitis is divided into several degrees in accordance with changes in the mucous membrane detected during endoscopic examination.
0th degree. Visually detectable pathologies on the walls of the esophagus are practically absent; defects on the pink mucous membrane are not detected. A more thorough examination allows the patient to be diagnosed with sphincter dysfunction. At this stage, peptic esophagitis for the most part manifests itself only by clinical signs.
1st degree. On the walls of the esophagus, one or several separate foci of inflammation can be identified, having a bright red color. In addition, there is thickening and hyperemic changes in the mucosa with a large amount of mucus. Considering the changed shade and density of tissues, this stage is called “catarrhal peptic esophagitis.”
2nd degree. Foci of inflammation begin to merge with each other, erosions appear on the surface of the esophagus - areas with damage to the mucous membrane.
3rd degree. Spread of changes on the walls of the esophagus: hyperemia and erosion are located in a circle, the affected area is constantly growing.
4th degree. As a result of regular chronic damage to the mucous membrane, various complications arise. This may include bleeding, a decrease in the diameter of the esophagus, the formation of ulcerative lesions, Barrett's esophagus syndrome, etc.
The specific stage of peptic esophagitis has a significant impact on the treatment of the disease prescribed by a specialist.
Therapy
Treatment of erosive esophagitis is carried out using medications. It directly depends on the cause of the disease. If the patient has a peptic ulcer or GERD, then it is necessary to take proton pump blockers or inhibitors. In this case, it is recommended to treat the disease with alginates, antacids, and D-nol.
If the patient experiences severe pain, treatment should be carried out using antispasmodic traditional medications. The most effective drug is No-shpa. If there are contraindications to the pharmaceutical drug, patients are prescribed Spasmomen. Esophagitis is characterized by the presence of erosions on the walls of the esophagus. To eliminate them, you need to take a pharmaceutical medicine such as Solncoseryl.
During the development of the disease, many patients are prescribed prokinetics - Motilium, Domperidone. With the help of these medications, the process of hydrochloric acid entering the intestines is normalized. Patients are recommended to take medications four times a day. For the treatment of the disease, it is recommended to use inhibitors in the form of Pariet, Rabeprozole. The patient's condition with esophagitis is significantly improved by taking enveloping and anti-inflammatory drugs - Venter, Bismuth Subcitrate.
Stressful situations are not recommended during the treatment of the disease. That is why it is recommended to use sedative medications and folk remedies. During the development of complications of the pathological condition, treatment is carried out by surgical intervention.
Drug treatment of esophagitis is quite effective if the patient strictly adheres to the dosage of traditional medications.
Reasons for development
In most cases, retrograde ejection of stomach contents back into the esophagus is a consequence of certain diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract. The causes of the development of an acute form of peptic esophagitis are usually short-term damaging effects.
Clinical picture of esophagitis
These can be acute inflammatory processes that occur during infectious diseases (influenza, diphtheria, fungal infection, etc.). Physical damage to the esophageal tissue is possible as a result of a burn, trauma during insertion of the probe, or exposure to other foreign bodies. A burn that is of a chemical nature and occurs as a result of contact of any caustic substances with the mucous membrane. An allergic reaction to certain foods is most often accompanied by other allergy symptoms. The most severe injuries are those sustained by the esophagus as a result of burns.
Chronic peptic esophagitis can develop for a variety of reasons:
- consumption of too spicy and hot food, as well as strong alcoholic drinks;
- professional activity in which a person inhales caustic vapors of chemicals;
- irritation of the mucous membrane with food debris accumulating as a result of certain difficulties in the evacuation function of the esophagus;
- food allergies;
- metabolic disorders, such as hypovitaminosis, deficiency of certain microelements, tissue hypoxia, prolonged intoxication, etc.;
- a special form in which the etymology of chronic inflammation of the esophagus is unknown, from a morphological point of view it is similar to ulcerative colitis and granulomatosis of the esophagus.
In general, the development of peptic esophagitis is provoked by gastroesophageal reflux, resulting from a reduction in the length of the esophagus, insufficiency of the lower sphincter or hiatal hernia.
Characteristic signs
Peptic esophagitis is usually accompanied by a number of specific symptoms. The most common is heartburn. The patient experiences a strong burning sensation behind the sternum and in the upper abdomen. This indicator is the leading one, due to the presence of inflammation and burns of the esophagus.
Chest pain is the second most common symptom of peptic esophagitis. The pain is provoked by both inflammatory changes occurring in the walls of the esophagus and reflex muscle spasms as a result of irritation caused by aggressive substances coming from the stomach. Muscle spasm is a reflex response of the esophagus directly to pain, the intensity of which varies. Pain can be transmitted to the area of the shoulder blades, left side of the chest, neck and lower jaw. In certain cases, a specialist has to differentiate pain from heart disease and peptic esophagitis.
A fairly common manifestation of the disease is belching, the severity of which can vary. When regurgitating, the patient feels a bitter or sour taste in the mouth. This symptom is a rather unpleasant manifestation of peptic esophagitis, causing social discomfort when in crowded places. Also, such regurgitation is especially dangerous at night: when the esophagus of a sleeping person is located horizontally, the risk of reflux contents entering the respiratory system increases, which can lead to pneumonia and aspiration.
In addition to the indicated symptoms, patients with peptic esophagitis often complain of manifestations caused directly by underlying diseases and pathologies of the digestive system, such as stomach ulcers, diaphragmatic hernia, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, etc.
Sometimes patients with peptic esophagitis experience aerophagia - special painful and unpleasant sensations in the area of the stomach and esophagus. This is caused by the fact that during conversation or eating, a certain amount of air enters the stomach. To get rid of pain, belching is required, which can be either spontaneous or forced.
Symptoms
Symptoms at the first stage of the disease are not noticeable. Peptic esophagitis is initially confused with hiatal hernia syndrome. Refluxes occur rarely, so patients are in no hurry to see a doctor. Only vivid symptoms and discomfort make one think about treatment.
Symptoms of peptic esophagitis:
- Pain in the lower third of the esophagus after eating food. Esophagitis differs from other gastric diseases by the symptom of “tilts”. When tying shoelaces, bending over, as a result of which the stomach is compressed and the pain intensifies.
- Lump in throat, heartburn.
- Dry cough due to gastric composition entering the respiratory branch.
- Symptoms of ulcers and gastritis are possible if distal esophagitis does not develop for the first time.
The listed symptoms do not clearly indicate that this is esophagitis, but there is a reason to consult a doctor.
Diagnostic methods
In the process of determining peptic esophagitis, a detailed collection of the available medical history, including interviewing the patient, plays an important role. In particular, some patients experience pain and heartburn only when directly adopting a particular position. Manifestations of the disease may decrease by drinking water, milk, and drinking soda. Such nuances make it possible to diagnose the specific nature of peptic esophagitis. In particular, to relieve the manifestations of the “alkaline” form, it is recommended to drink fruit or lemon juice.
In the process of diagnosing peptic esophagitis, scintigraphic examination of the esophagus and other instrumental methods are used.
| Surveys | Efficiency |
| Esophageal manometry. | Evaluates changes in pressure in the area of the sphincter and lumen of the esophagus. |
| FEGDS (gastroscopy). | It is performed simultaneously with a biopsy. |
| X-ray examination using the contrast method. | Detects the presence of barium ejection from the stomach back into the esophagus, and also determines changes in the outline of the walls of the esophagus. |
| Carrying out pH-metry of the esophagus | Allows you to directly detect the presence and characteristics of reflux. |
During the diagnostic process, it is very important to identify the primary pathologies that cause esophageal reflux.
Potato juice
It is considered one of the most effective traditional medicines. Used for acute and chronic esophagitis. Among all the beneficial properties of this familiar vegetable, its wound-healing and anti-ulcer effect should be noted. Juice drunk on an empty stomach coats the walls of the esophagus, reduces acidity, promotes scarring of ulcers, and weakens the intestines. Potato juice improves liver function, has a mild diuretic effect, and relieves swelling and heartburn. The first remedy for esophagitis during pregnancy. Moreover, potato juice removes toxins, radionuclides, and waste. Improves overall well-being.
Therapeutic measures and recommended medications
The specific treatment of peptic esophagitis is determined according to the severity and extent of the disease. The most relevant methods of therapy in this case are conservative and surgical treatment. In general, therapy is aimed at solving the following problems.
- Treatment until complete elimination or compensation of the disease causing peptic esophagitis.
- Reducing the acidity of the stomach contents using medications aimed at reducing the production of hydrochloric acid, as well as reducing the level of acidity already present. In this case, antacids and drugs that block H2-histamine receptors are used.
- The use of medications that have an anti-inflammatory effect and help restore damaged mucous membranes.
- Optimization of gastrointestinal motility.
When treating peptic esophagitis, antacid drugs are usually prescribed to reduce the degree of negative effects of gastric juice on the mucous membranes. Such remedies are used in the form of a course of therapy. In addition, certain emulsions are prescribed to reduce acidity levels.
Depending on the specific clinical picture of peptic esophagitis, the specialist may also prescribe the patient antisecretory drugs aimed at reducing secretion. The most popular among these medications are Famotidine and Omeprazole, therapy for which involves a five-week course of administration.
Also, pyrokinetics play a fairly important role in the treatment of peptic esophagitis - drugs designed to increase the tone of the lower part of the stomach. As a result, the rate of absorption of products that are eliminated from the stomach in the normal way and without long delays increases. The most widespread among such drugs are Motilak and Motilium. These medications are taken before meals and before going to bed.
During the treatment process, it is recommended to completely prevent the risk of increased intra-abdominal pressure as a result of overeating, lifting heavy objects, bending the body forward, doing abdominal exercises, and wearing tight belts.
Medicines used for treatment
Therapy for inflammation of the esophagus involves the use of several groups of drugs. At different stages of the disease, medications are used comprehensively in different combinations and dosages.
Prokinetics
The active substance affects the muscular activity of the digestive organs and normalizes the tone of the esophageal sphincter. Restoring the normal functioning of the esophagus promotes the rapid movement of food and helps cleanse the mucous membrane. This group includes Itopride, Domperidone, Motilium. The latter is prescribed in the presence of vomiting and nausea. Ganaton helps relieve symptoms in a week, heals in three weeks and has no side effects.
Proton pump inhibitors
Drugs that help reduce the production of hydrochloric acid by mucosal cells. They are used to relieve severe symptoms of inflammation and relieve pain. Fast-acting substances with minimal side effects.
The course of therapy is prescribed by a specialist, since long-term use can lead to bone fragility and affect kidney function. The main drugs included in the group: Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Pantoprazole.
N-2 blockers
They have a similar effect to PPIs, the action occurs due to the blocking of histamine receptors. The production of hydrochloric acid is suspended, which makes it possible to alleviate the condition of the esophagus and stomach.
The fifth generation of such medicines has been developed. The most effective are Ranitidine and Famotidine. Abrupt cessation of use can lead to a short-term increase in symptoms of the disease.
Alginates and antacids
For esophagitis, for successful treatment, medications are prescribed that neutralize the effect of acid on the esophagus. Antacids are recommended to be taken in liquid form. The duration of the medicine is 10-15 minutes. The course of therapy is a maximum of two weeks, since the products contain magnesium and aluminum. This group includes Phosphalugel, Almagel, Maalox.
Alginates have a milder effect, so they are prescribed during pregnancy. The composition includes alginic acid, which after administration forms a protective layer on the surface of the mucosa.
Cytoprotectors
Increases the degree of protection of the mucous layer of the esophagus and stomach during reflux esophagitis. The tablets help improve blood flow, increase the secretion of protective mucus, lower the level of acidity, and in case of erosive esophagitis, promote the healing of erosion lesions. The most well-known drugs are Misoprostol and Dalargin.
Use of antibiotics for esophagitis
For the phlegmous type of esophagitis, antibiotics are prescribed to relieve inflammation in adult patients and relieve pain. With prolonged therapy, candidal esophagitis can develop, so concomitant use of antifungal agents is recommended.
Folk remedies
Home methods for treating peptic esophagitis can be used both in combination with drug therapy prescribed by a specialist, and in the form of an independent fight against the pathology. In the case of acute forms of peptic esophagitis, traditional methods are ineffective.
The medicinal mixture used in the treatment of peptic esophagitis involves mixing in equal parts the following plants: snake knotweed (roots), anise fruits, fireweed, lemon balm, oregano, calendula flowers. Two tablespoons of the mixture of these herbs are poured into 500 ml of boiling water, covered with a lid, wrapped warmly and left to infuse for three hours, after which the decoction is filtered. The finished infusion is taken throughout the day, every 2 hours, two spoons at a time.
Treatment of peptic esophagitis with dandelion. Collect a liter jar of flowers and fill it with a glass of granulated sugar. The resulting mixture is crushed or pounded in a mortar until the juice is released. A solution of a teaspoon of this juice in half a glass of water is taken before meals.
Also, traditional methods of treating peptic esophagitis involve the use of potatoes. Take several potatoes, pour boiling water in a ratio of 1:2 and cook for 60 minutes, regularly adding boiling water. The resulting decoction, in which the potatoes were boiled, is used as a remedy: it is taken before meals, half a glass at a time.
It is recommended to drink two tablespoons of freshly squeezed potato juice three times a day before each meal.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment of peptic esophagitis is resorted to in the following situations:
- ineffectiveness of drug therapy;
- recurrence of bleeding;
- increased incidence of aspiration pneumonia;
- the presence of a diaphragmatic hernia of the esophagus.
In this case, the surgical intervention is aimed at rehabilitating the closing function of the sphincter by changing the level of pressure in the lower part of the esophagus, which should be 3 times higher than the same value inside the stomach. The main technique for surgical treatment of peptic esophagitis, which most often gives a positive result, is Nissen fundoplication, that is, attaching the gastric vault to the right diaphragmatic leg and the left pericardial dome. Also used, but much less frequently, are surgical methods such as hiatoplasty, gastropexy, fundopexy and the production of a silicone prosthesis to prevent reflux.
Causes of peptic esophagitis of the esophagus
Provoking factors influencing the development of reflux disease in a healthy person:
- Regular overeating. When the volume of food increases, the stomach stretches and pressure increases, which provokes reflux.
- Sudden forward bending of the body or excessive physical activity immediately after a meal.
- Excessive passion for carbonated drinks, alcohol, sweets.
- Constantly wearing thick, tight clothes, underwear and belts, which provokes an increase in pressure inside the abdominal cavity.
If reflux develops as a reaction to other pathologies in the human body, the root causes lie in the underlying disease. It can be called:
- gastritis with high acidity;
- stomach and/or duodenal ulcers;
- diaphragmatic hernia of the esophagus, when the closing function of the sphincter is disrupted.
https://youtu.be/KriFixTTaj0
A possible cause of the development of distal esophagitis is a hereditary factor.
Nutrition rules and diet options
In the process of treating peptic esophagitis, the diet also plays an important role. Food intake is carried out 5-6 times a day in small portions, the last meal is completed 3-4 hours before bedtime. You should adhere to a special menu, formed in accordance with the type of primary pathology.
As part of your diet, you must exclude all foods that cause increased gas formation, such as dried apricots, mushrooms or legumes. In addition, for peptic esophagitis, it is recommended to remove tomatoes and citrus fruits that are harmful to the body from the diet. And, of course, alcoholic drinks, as well as carbonated drinks and coffee.
To increase tone during peptic esophagitis, you should eat foods that are high in protein. You should include various fermented milk drinks in your diet, eat porridge in the morning, and fruit on an empty stomach. There are also a number of recommendations that should be followed in the process of following a diet. So, before each meal, a patient with peptic esophagitis is recommended to drink a glass of warm water, and at night - to refuse food completely.
A separate condition is the prohibition of taking a supine position for an hour after eating, so that the eaten foods have time to penetrate the small intestine, thereby preventing the risk of them being thrown back into the esophagus.
Possible complications
Esophageal ulcer
Treatment of peptic esophagitis in superficial zero and mild grade 1 usually proceeds without difficulty. At these stages of the disease, the patient is able to eliminate the pathology by adjusting the diet and normalizing the acid levels of the gastric environment. At the same time, you need to understand that with any subsequent violations of the established regime, peptic esophagitis can remind itself with renewed vigor.
In the case of prolonged reflux and chronic inflammatory process, the risk of certain complications of peptic esophagitis increases.
- Ulcers on the surface of the esophagus, which often result in bleeding into the esophagus. In such situations, an endoscopic operation is provided, in which a special coagulator is inserted into the esophagus using a medical tube, cauterizing the bleeding vessels.
- Esophageal stenosis, when due to an increase in the thickness of the walls of the organ caused by chronic inflammation, the lumen of the esophagus noticeably narrows. As a result, the patient faces problems swallowing food and a constant feeling of a foreign object in the throat. In case of stenosis, only surgical therapy is used.
- Barrett's esophagus is a complication of peptic esophagitis in which the natural epithelium of the esophagus is replaced by gastric tissue. As a result of this abnormal process, there is a risk of developing cancer of the esophagus.
Considering the seriousness and complexity of treating complications of peptic esophagitis, it is very important not to allow the disease to become chronic by providing appropriate therapy in the initial stages.
Treatment methods for reflux esophagitis
The following treatment methods for reflux esophagitis are possible:
- physiotherapy;
- operation;
- radiofrequency therapy;
- use of folk remedies.
In acute infectious forms of inflammation, complete abstinence from food is often required. If necessary, infusion therapy is performed.
In the chronic form of esophagitis, physiotherapy helps well. The most commonly performed are amplipulse therapy and electrophoresis. Complex treatment of patients includes balneotherapy.
Physiotherapy is not performed for severe esophagitis.
The most commonly used types of radical treatment are:
- fundoplication;
- radiofrequency ablation;
- endoscopic plication;
- bougienage;
- dissection of strictures;
- plastic surgery of the esophagus;
- resection.
For complicated reflux or candidal esophagitis, treatment often involves expanding the lumen of the organ.
Otherwise, eating will be difficult or completely impossible.
Modern methods of surgical treatment include endoluminal gastroplasty.
During this operation, suture material is used to reduce the size of the opening of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Preventive measures
In the absence of complications, such as stenosis, perforation of the esophagus, bleeding, inflammatory processes in the mediastinum, etc., the prognosis for treatment of peptic esophagitis is favorable. An important criterion for the possibility of curing a disease is the obligatory adherence to food intake, proper lifestyle and requirements for a therapeutic diet.
Preventive measures to prevent peptic esophagitis are aimed at combating the very causes of the disease and preventing them: burns from hot food and chemicals, tissue damage from foreign objects, etc. As part of the prevention of the chronic form of peptic esophagitis, regular gastroenterological examinations are provided in a dispensary. , according to the results of which, if necessary, you should immediately undergo treatment. Therapy aimed at preventing relapses is carried out twice a year. In the presence of erosive changes on the surface of the mucous membrane, this amount is doubled: up to four courses per year.
Measures to prevent peptic esophagitis include stopping any activity that threatens to increase internal pressure in the abdominal cavity; compliance with the most gentle diet and diet; complete cessation of any bad habits; strict adherence to the specialist’s instructions. In the case of a chronic form of peptic esophagitis, to prevent exacerbations, patients are recommended to be treated in a sanatorium-resort setting. When diagnosing a severe form of peptic esophagitis, the patient receives a second disability group.
A failure in the functioning of certain body systems goes unnoticed or can cause very unpleasant processes that over time become chronic. This type of disease is peptic esophagitis, which occurs due to the fact that the esophagus is exposed to increased exposure to hydrochloric acid released from the stomach. To correct this disorder and its consequences, it is necessary to undergo appropriate treatment at the first sign of discomfort and follow all recommendations prescribed by a specialist.
Drugs for esophagitis: groups of drugs used
What should be the treatment for a diagnosis of esophagitis? The drugs that are used can be divided into several main groups. These are antacids and alginates, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2-histamine blockers, conventional and gastrointestinal prokinetics, cytoprotectors. Here is a brief functional description of each type:
Each group of drugs has its own purpose. The action of some of them is similar, but it is impossible to completely replace any group with another.