Category: Skin formations
Urticaria is a disease of an allergic or toxic nature, manifested in the form of pinpoint red spots - the main symptom of urticaria is unpleasant itching. Diagnosis of the disease is difficult, since such symptoms can be caused by many factors.
To determine the exact cause, the patient must undergo a full examination - the allergic irritant of the body can be of absolutely any nature.
Chronic urticaria in adults photo
Treatment approaches are also varied, but often a specialist (immunologist or allergist) finds the right option that will permanently relieve a person from the painful manifestations of urticaria.
What is urticaria
The content of the article
Urticaria is a broad term that includes a number of diseases that have different causes and similar clinical manifestations in the form of pale pink blisters that resemble a nettle burn. Hives are always accompanied by itchy skin. The reaction can be caused by stress, which is not so dangerous, or toxic substances.
In everyday life, it is believed that urticaria (rash, nettle fever) is a mild allergic reaction that appears on the skin, which is a big misconception.
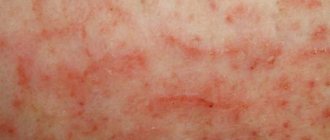
Symptoms of acute urticaria
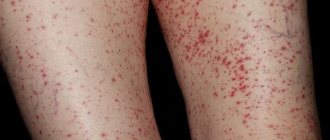
Acute urticaria photo in adults
This type of disease manifests itself as an urticarial rash, as in the photo. In adults, pinkish matte spots with a fuzzy border area appear on the body. Fuzzy edges provoke the possibility of several blisters merging into one, so the affected area does not look at all aesthetically pleasing.
Round (rarely oval or oblong) pink dots are located mainly in areas with delicate sensitive skin: buttocks, arms, sides of the body. It is also possible that blisters may affect the mucous membranes: lips, mouth, palate, pharynx, which causes difficulty breathing.
Symptoms of acute urticaria resemble manifestations of intoxication - the patient’s body temperature rises and slight chills are felt (in common parlance “nettle fever”). Gastrointestinal disorders cannot be excluded: loose stools, nausea, cramping pain and general malaise.
The duration of the rash on the skin in acute form of urticaria can be 1-2 hours or more (up to 3 days). Most often, this type of disease manifests itself after food or injection irritants enter the body.
- An adult may develop a severe rash from taking new medications or undergoing blood transfusions.
Causes of hives: don't be frivolous
It is believed that every person experienced urticaria in childhood. Some got itchy after the first strawberry, some after swimming in cold water, and some had itching all over their bodies before exams. The rash was not treated - it went away quickly, and they remembered about it only when a new strawberry grew up.
Urticaria in adults never appears out of the blue. And if the rash and itching often recur or do not go away at all, dermatologists talk about chronic urticaria.
The chronic stage occurs for the following reasons::
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
caused by Helicobacter pylori (gastroduodenitis, gastritis B (erosive gastritis), helicobacteriosis). To get rid of hives, it is not enough to deal with the pathogen. Helicobacter pylori does not cause the disease, but maintains it in the presence of a source of allergy. - Viral hepatitis
. When the liver is damaged, the amount of bilirubin in the blood increases. Due to disruption of protein metabolism, a rash appears that itches and itches, especially at night. Antihistamines (antiallergic) drugs do not help with this condition. Additional symptoms of hepatitis: with hepatitis A, the temperature rises; with hepatitis B, the rash is accompanied by joint pain and vomiting. - Herpes (type 3 is accompanied by a rash all over the body, type 6 is expressed in red spots like rubella, types 7 and 8 are supplemented by chronic fatigue syndrome).
- ARVI
(infectious diseases cause a rash all over the body). - Infectious lesions of the nasal and pharyngeal mucosa
(sinusitis, tonsillitis, otitis). - Urogenital infections
(cystitis, vaginitis). - Autoimmune thyroiditis
is an inflammation of the thyroid tissue that causes hormonal disorders. - Systemic collagenosis
is atrophy of connective tissue, causing malfunction of internal organs. - Autoimmune diseases
(systemic lupus, vasculitis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis). - Oncological tumors.
Urticaria - photo
Allergic reactions are extremely common among people of any age. Almost everyone at least once in their life has experienced certain symptoms associated with an abnormal reaction of their own immunity to irritants. It is believed that in recent years, allergic manifestations are becoming more common; scientists explain this by an increase in the concentration of potential allergens in the air and a general deterioration of the environmental situation. The most common form of sensitivity is urticaria - it occurs in adults with the same frequency as in children.
How does urticaria manifest itself: symptoms start small
Sometimes the rash appears the day after the trigger, sometimes a week passes before an allergic reaction occurs. The most unpleasant thing is the severe itching caused by red spots on the skin. In the mild phase, if there is no constant factor, the urticaria goes away.
During an exacerbation, the skin becomes dry, covered with a crust, which begins to bleed from constant scratching. Droplets of ichor are visible on its surface. The itching worsens at night. The patient's temperature rises, he cannot sleep normally, he feels hot and uncomfortable. The constant itching is exhausting and there is no escape from it. The acute period lasts several weeks.
Urticaria (urticaria) in an advanced stage is manifested by the following symptoms:
- A person wakes up in the morning and sees swelling on the face and body.
- During the day, the skin becomes covered with tubercles and blisters, which turn red in the evening.
- During the night, the blisters swell so much that they completely merge, forming a crust.
- The body is very itchy, the patient cannot sleep normally, often wakes up and scratches the rash.
The main symptom of urticaria is a skin rash. It is localized on the legs below the knee, arms from wrist to elbow, neck, chest. The itching can be so unbearable that the patient scratches the skin until it bleeds, and ulcers appear in some places.
In severe cases, a person’s lips swell as if they were injected with silicone. Symptoms of a sore throat appear: the neck swells, it hurts to swallow, the voice deepens. If the mucous membranes of the digestive organs swell, diarrhea, bloating, and vomiting occur.
Symptoms
The name of the disease fully corresponds to the main manifestation - the characteristic marks that appear on the skin. However, these red spots, swellings and rashes are not the only manifestation of hives in adults and children. The symptom complex includes the following manifestations:
- pink rashes are an early symptom, later the spots become larger and brighter;
- itching - develops simultaneously with the rash;
- an increase in the size of plaques - they often merge into large tumors;
- rashes cover the limbs, face, are especially painful in the bends of the arms and under the knees;
- the itching is accompanied by a moderately severe pain syndrome;
- an increase in temperature is possible, more often in children, but it can also be a symptom of urticaria in adults;
- weakness, general state of intoxication;
- in severe cases, the tumor affects the larynx - Quincke's edema requires immediate hospitalization.
With adequate treatment, the symptoms disappear as quickly as they appeared. An attack of urticaria can be relieved in three to four hours; more severe ones are treated within three days to a week. It is necessary to immediately call an ambulance only if the face is affected, the lip is swollen and there is a risk of swelling spreading to the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and larynx, which can cause airway obstruction.
Types of urticaria
The type of urticaria depends on the mechanism of triggering the disease.
- Allergic urticaria.
Caused by ingestion of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Commonly prescribed drugs include tetracycline, amoxicillin, flemoxin, aspirin, ibuprofen, and nise. Alcohol consumption can accelerate and intensify the course of the disease. Antibiotics accumulate in the body, so the problem does not manifest itself immediately. The course can be completed, and hives will appear in a couple of weeks. - Food urticaria.
It occurs more often in children after eating certain foods - fruits (citrus fruits and strawberries), fermented milk, fish products, nuts and sweets. This type of urticaria is not dangerous, goes away quickly, and occurs due to the body producing antibodies to a new product. - Contact urticaria
. Side effect during professional activities (reaction to latex in surgeons, allergies to chemicals in cleaners). - Reaction to the sting of a wasp, horsefly, hornet
. The most dangerous manifestation of allergies is angioedema, when the bitten person dies an hour after the bite. - Reaction to the presence of a virus in the body
. Sometimes the rash is provoked by intoxication due to fungal infections (staphylococcus, candidiasis (thrush), tonsillitis, pharyngitis). If the disease is cured, the redness on the skin will disappear. - Nervous urticaria
.
In a state of stress, the functioning of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems diverges, the signaling system fails, and our body incorrectly interprets the impulses sent by the brain. The stress hormone adrenaline is released, blood vessels dilate, their walls stretch and become permeable. Endothelial cells lining the vascular and capillary walls swell, forming red bumps on the surface. This condition is also urticaria.
Classification of urticaria by intensity
According to the intensity of its occurrence, urticaria can be:
- Spicy
. Caused by allergenic foods, medications, chemicals, insect bites. Lasts up to 6 weeks, after which it disappears completely. - Chronic.
Lasts over 6 weeks, after which in 60% the symptoms disappear. In 40% they remain and are observed throughout life.
Atypical urticaria
Atypical forms of urticaria include the following types:
- Cholinergic
. It occurs due to weakened immunity and an increase in the amount of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. - Adrenergic
. It is caused by a sharp release of the hormone adrenaline into the blood. The reason for this is severe stress or mental agitation. The rash, which looks like pale pink blisters, often occurs in people who have to do things they don't like. - Contact
. Occurs due to direct contact with an allergen (pets, metal jewelry). Disappears immediately after contact with the source of the allergic reaction is broken. - Aquagenic
. It can be observed when the patient comes into contact with water. Water is not an allergen, but an activator of allergies to a certain substance. It often occurs during trips abroad, when the local climate promotes the production of histamines (transmitters), and water accelerates its production. - Quincke's edema.
The most acute manifestation of urticaria is Quincke's edema - angioedema with deep skin lesions.
With Quincke's edema, not only the surface of the skin is affected, but also the mucous membranes of internal organs, in particular the lungs, esophagus, and stomach. Antibodies produced by the body affect nerve endings and blood vessels, increasing their permeability and expanding the lumen. Plasma penetrates through the vascular walls to the outside, paralyzed nerve cells reduce vascular tone, provoking the accumulation of membrane fluid in tissue cells. Severe swelling can occur in both the brain and lungs, leading to almost instant death.
Causes
Like any allergy, hives can be triggered by almost anything. Up to 80-90% of cases, especially isolated ones, remain without identification of the allergen. A nonspecific immune response can also occur due to a combination of several factors - for example, if the body is weakened by a viral disease, if a person is stressed. It is impossible to predict the appearance of an acute form of allergy, although the main causes of urticaria are identified:
- Chemical substances. Urticaria occurs as a reaction to medications - antibiotics, anticonvulsants, analgesics. Therefore, doctors in hospitals always conduct tests before prescribing the drug to a patient: they do a small test and see if redness and rash appear.
- Poisonous substances - low-quality paint, cosmetics. Working in hazardous industries can affect the normal functions of the protective system.
- Plants and animals. Poplar fluff, wildflowers, and some herbs are especially dangerous. The fur of cats and dogs can also provoke allergy attacks due to the content of specific proteins, often incompatible with human immunity.
- Ultra-violet rays. Solar radiation can cause a rash that can easily be confused with a second or third degree burn, but hives will be noticeable not only in areas exposed to unwanted influence.
- Some people develop a characteristic rash as a reaction to frosty air. Cold urticaria, as a rule, is accompanied by other allergic manifestations - this is evidence of severe sensitization.
- Food allergies, which are most often provoked by citrus fruits, chocolate, seafood, peanuts, red berries, eggs, honey. An allergy to alcohol is very difficult to tolerate, since ethanol itself is a toxic substance for the body, and with a nonspecific reaction, the manifestations intensify.
- Insect bites, the most dangerous are aspen and bee bites. Sometimes allergies to mosquitoes or ants appear.
- Some diseases that change the immune status are endocrine disorders, oncology.
Urticaria in adults is easily tolerated in 70-75% of cases, provided the person’s general health is satisfactory. Painful manifestations do not spread beyond the skin, and with adequate therapy they disappear within a few hours. A single episode should not cause serious concern, but if the disease recurs, you need to visit an allergist or immunologist.
It is definitely necessary to visit a doctor if allergic reactions become regular and occur in the form of a response to cold, water, or small scratches. This is evidence of abnormally active mastocytes and a chronic excess of histamine. At any moment, the violation can turn into life-threatening forms.
What tests are done for urticaria?
Hives are an allergic reaction, so tests are aimed at identifying the allergen. The dermatologist decides which tests to take. The following tests may be prescribed to the patient:
- Blood analysis. An increased white blood cell count indicates an infection causing a rash on the body. Eosinophils indicate the presence of a foreign protein secreted by the virus. The ESR level shows the state of the immune system.
- Analysis of urine . Toxins in the kidneys occur during genitourinary infections, and because of this, an allergic reaction appears on the skin.
- Biochemistry of blood . Reactive protein indicates inflammation, AST and ALT antibodies indicate the toxic effects of drugs on the body. Bilirubin shows the condition of the liver, creatine – the functioning of the kidneys, urea – the condition of the excretory system, glucose – the functioning of the pancreas. Any indicator outside the normal range helps to understand the nature of urticaria.
- Stool analysis
. Parasites release toxic substances and disrupt digestion, leading to skin rashes. - Smears for genital infections . Sometimes the cause of urticaria is pathogenic microflora, so the patient takes smears from the vagina, urethra, and intestines.
- Allergy tests (blood tests for allergies) are taken if there is a suspicion of a food allergy.
- Antinuclear factor analysis
. Autoimmune diseases cause the body to destroy its own cells, leading to allergies. - A skin biopsy
is taken if cancer is suspected.
Chronic urticaria, features
If there are areas in the body with developing infectious processes, a chronic form of urticaria occurs. Often the causes of the disease are completely harmless inflammations: tonsillitis, adnexitis, caries, minor dysfunctions of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
If chronic urticaria has been diagnosed, symptoms in adults will appear in attacks. The localization of the rash will be less widespread, but it can affect not only the surface of the skin, but also the internal mucous membranes.
Intestinal urticaria provokes disorders of the digestive system. The patient experiences general weakness, headache, and an increase in temperature to the level of low-grade fever. Itching and burning occurs, which negatively affects a person’s sleep and peace of mind.
Papular urticaria
The main symptom of papular urticaria is persistent tissue swelling, but there may be other signs of skin manifestations: hyperpigmentation of the skin in the folds, thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
Papular urticaria looks like red-brown spots of any shape and character. The rash occurs only on the extremities, mainly in the flexure areas. More often, female representatives suffer from persistent edema.
Solar urticaria
This form of the disease must be treated with caution. If urticaria appears in areas of the skin directly exposed to ultraviolet rays in the spring and summer, this is a signal of liver pathology.
Be sure to examine this organ and try to stay out of the open sun until the rash subsides. Sometimes the body reacts to sun blisters with shock, and the patient may need immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Cold urticaria
The cold form of the disease is also dangerous to health, and even cases of death have been recorded in medicine. Due to contact with cold air, water and eating cold foods, a sensitive person may develop hives within 5-15 minutes.
- The wider the area of the rash, the greater the risk to health and life.
It is necessary to urgently eliminate the irritants in order to prevent an anaphylactic reaction in the body. Otherwise, symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness, loss of consciousness, tachycardia, and vascular spasms are possible.
How to treat hives
Urticaria in the acute form lasts about a month, and in the chronic form it continues throughout life, followed by periodic relapses. Treatment of urticaria comes down to eliminating the source of the reaction and restoring the protective barrier of the skin. Only a comprehensive effect on the disease will help you recover faster.
In parallel with the treatment of the underlying disease, the dermatologist selects and prescribes antihistamines (histamine is a mediator of nerve fibers). They soothe the nerve endings that cause itching.
Such drugs include:
- Cetrin
. Refers to second generation drugs. The active component cetirizine acts on receptors selectively, therefore it does not depress the nervous system and does not cause drowsiness. But it does not have such a strong antihistamine effect as first-generation drugs. Relieves itching and swelling. - Tavegil
. First generation drug. The active component clemastine deals a powerful blow to allergies. Relieves itching for 10-12 hours. - Claritin.
Belongs to the third generation. At the same time, it does not cause drowsiness and at the same time has an effective selective effect. Relieves skin irritation for 24 hours.
In addition to tablets, patients are prescribed glucocorticoid ointments. They are made on the basis of steroid hormones that have an anti-stress effect. They lie tightly on the skin and are slowly absorbed, soothing dry skin.
People experiencing urticaria should understand that any medications relieve the symptoms of the disease only temporarily. If the source of the disease is not found and the underlying disease is not treated, urticaria will remain in the body forever. The result of this will be painful itching, scratching on the skin and constant swelling.
If you treat the disease carefully, as a rule, the course of the disease is favorable. With proper treatment, the patient's life is not in danger. lead to death. You can cure urticaria quickly and without relapse at the Diana private clinic.
Treatment
Depending on the form of the disease, therapy is selected.
Allergic urticaria is treated comprehensively:
- local effect on the skin, relieving itching and soothing the skin;
- use of systemic drugs;
- complete exclusion of the patient's contact with the allergen.
Systemic treatment must necessarily include oral antihistamines. They are:
- First generation. They have some side effects - a pronounced sedative effect, a short period of retention of the effect, etc. This group includes, for example, Suprastin and Tavegil.
- Second generation , for example, Loratadine, Xizal. These drugs quickly demonstrate effectiveness, which lasts up to a day. Their sedative effect is insignificant.
In addition to antihistamines, the following drugs may be prescribed if indicated:
- Glucocorticosteroids. Drugs in this group are prescribed only in difficult cases, when urticaria has spread throughout the body, there is difficulty breathing and swelling of the larynx.
- To cleanse the blood - sodium thiosulfate.
- Relieving swelling - Calcium chloride.
- For chronic urticaria - treatment with histoglobulin by subcutaneous administration.
- Adrenaline hydrochloride solution - only for swelling of the nasopharynx and difficulty breathing.
Ointments for urticaria
Preparations in the form of ointments are convenient to apply and distribute over the affected area of the skin. These products are designed to relieve symptoms, including itching.
Zinc ointment. Patients are often prescribed zinc-based ointments, which have the following effect:
- dried;
- act as an antibacterial drug;
- relieve inflammation.
The ointment is applied up to six times a day to areas of the body affected by urticaria.
La Cree. A drug based on herbal ingredients that quickly soothes itching, relieves irritation and swelling. This product contains:
- bisabolol;
- licorice extract;
- panthenol;
- string extract.
Nezulin. Antihistamine cream-gel cools and soothes the skin, relieves swelling and itching, and acts as an antispasmodic.
Fenistil gel. This is a non-hormonal drug that quickly eliminates itching and copes with redness. Despite its effectiveness, use may cause side effects. Because of this, it is not prescribed to children, pregnant or lactating women.
Treatment with tablets
For urticaria, patients are prescribed antihistamines, which have a rapid effect.
Among the most common:
- Erius;
- Loratadine;
- Tazepam;
- Tavegil.
If an acute condition is accompanied by significant swelling, patients are additionally recommended to take diuretics. For example, Furosemide. Calcium supplements - Kalcemin - may also be prescribed.
Treatment of urticaria with folk remedies
Adults understand that such a serious disease cannot be cured using traditional medicine. But it is possible to alleviate the condition before seeing a dermatologist.
Baths of sea salt dissolved in water help relieve itching for a while. It is necessary to wash the areas of redness with the solution without rubbing with a washcloth or towel. It is advisable to let the water dry on the body or simply blot it with a towel. Then you can apply a neutral, odorless and colorless cosmetic oil. It will restore the lipid (fat) barrier and soothe itching. Usually after a bath the skin does not itch for 6-8 hours.
Why is urticaria dangerous?
The most life-threatening is Quincke's edema (giant urticaria). Photos, symptoms and treatment in adults at home must be studied in order to prevent a fatal outcome.
The patient experiences a sudden development of swelling of the mucous membranes on the lips, palate, mouth, larynx and pharynx. The blisters are white or light pink in color and feel like soft thickenings. Subjective sensations of itching or burning are possible, but they are often absent.
Due to swelling, the airways narrow and air cannot enter the lungs normally - the patient experiences asphyxia. Typically, stenosis goes away within 1-1.5 hours, but the patient in any case requires urgent resuscitation.
Further treatment
Treatment of such an ailment and symptoms is possible; for this you need to contact specialists who will conduct an examination and prescribe special treatment methods for everyone. Basically, dermatologists prescribe the following treatment:
- The use of antihistamines (mainly loratadine, diphenhydramine, ebastine, suprastin, acrivastine and pipolfen).
- Injections and injections that are necessary to destroy viruses and bacteria of the disease (if the drugs do not help).
- If it is an allergic type, then medications are prescribed against allergies to any substances.
- It is recommended to exclude certain foods from your diet (sweets, alcoholic drinks and other unhealthy foods).
Such treatment methods are used to relieve inflammation of the skin and discomfort. Hives and rashes are dangerous because they completely disrupt the normal condition of the skin, and at the same time the processes of thermoregulation and metabolism are disrupted. In such cases, experts do not recommend undertaking treatment on their own, especially prescribing medications and dosages that can negatively affect health and affect circulatory processes, in which the level of leukocytes in the blood doubles.
What are the symptoms of the disease?
Symptoms will be different for everyone, depending on the form, stage and other factors that can aggravate the disease and make it more acute.
Basically, common urticaria has the following symptoms:
- Redness, inflammation in the form of blisters on the skin.
- Itching, burning and strange sensation on the skin (it can also burn in the sun and turn even redder).
- Blisters can grow and at the same time allergic reactions of different nature can develop.
- The skin may peel and even peel off, causing severe pain.
- Weakness, nausea and possibly vomiting appear (each individual).
What does hives look like in the photo?
It is best to contact a specialist who will also examine and diagnose the presence of this disease. Symptoms are different for everyone, because such a disease can progress and develop further, causing complications and other unpleasant sensations. This disease is dangerous because it disrupts the normal condition of the skin and thermoregulation processes, and this threatens the development of other diseases and the appearance of annoying itching, burning and other distinctive signs.
The type depends on the classification of urticaria and how and how quickly it begins to progress.
They are classified according to the following classification:
- Slow , in which the skin is pressed downwards, and after this red itchy blisters (mostly small in size) begin to appear.
- Thermal , blisters of which appear as a result of thermoregulation processes.
- Cold , in which the symptoms of the disease progress as a result of cold.
- Solar , in which symptoms depend on exposure to temperature and air.
The doctor checks the appearance and distinctive symptoms during the examination, so you need to contact a dermatologist to understand why the disease is dangerous and what preventive measures should be taken. Each classification type of disease is dangerous in its own way, so its treatment and preventive measures will be necessary. The rash can appear on any part of the body, but most often the disease makes itself felt with blisters on the stomach, arms and legs. Photos of urticaria can be viewed on the Internet to make sure that this disease is not a concern.
Diagnosis of allergic urticaria
Diagnosing allergic urticaria is incredibly difficult and has many pitfalls. In many cases, it is not possible to determine what exactly provokes the development of urticaria, despite numerous examinations.
Sometimes (but very rarely) the causative factor in the development of urticaria can be determined by the appearance of the rash. For example, rashes on exposed areas of the body after contact with cold or sun may indicate the presence of a cold or sun allergy.
A painstaking, detailed history can immediately become a “key” to unraveling the causative factors of allergic urticaria. It is necessary to ask the patient whether there is any connection between medications, foods, all kinds of additives, dyes, flavors, contact with physical factors and the appearance of urticaria symptoms.
If food or drugs are suspected of causing hives, then prick tests are performed with these allergens. This method must be carried out necessarily, because in this way it is possible not only to identify, but also to exclude potential allergens and the possibility of developing anaphylactic shock in the future.
In case of chronic urticaria, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient. In this case, they do a general blood and urine test, liver tests, tests for the activity of the inflammatory process, and examine the feces for the presence of helminths and dysbacteriosis. It is also necessary to conduct fluorography or x-ray of the chest organs, serological tests for the presence of hepatitis B or Epstein-Barr viruses in the blood. All these methods help determine the presence of concomitant diseases that provoke the development of urticaria.
Description of allergic urticaria
Doctors call urticaria of the allergic type urticaria. Most often, the disease manifests itself in young children with symptoms such as redness, itching, burning of the skin due to food allergies or hay fever.
Babies are prone to allergic reactions because they have not yet developed immunity to certain substances and foods, so it is not uncommon to see a doctor due to food allergies. With age, the disease makes itself felt less and less, but the age of thirty is considered a “turning point” - it is during this period that the symptoms of allergic urticaria progress again, and the patients of allergists and dermatologists are predominantly women.
The most intractable type of disease is chronic or idiopathic urticaria, which does not pose a threat to human life, but can be complicated by angioedema or anaphylactic shock, which can be fatal. Therefore, people suffering from a chronic manifestation of the pathology must always have emergency means with them to relieve severe symptoms. A third of the world's population is susceptible to urticaria, but it should be clarified that every year the number of people suffering from rashes of this nature increases.
The rapid development of an allergic reaction is facilitated by the body's increased sensitivity to allergens - this is caused by the deteriorating environmental situation, hereditary, autoimmune diseases and other factors. Nettle rash is a difficult pathology to diagnose. Before being diagnosed with allergic urticaria, the patient must undergo a series of procedures with which an allergist, dermatologist or immunologist will confirm the disease.
Features of the course of urticaria
The basis of the pathogenesis (occurrence) of urticaria is the development of particularly increased sensitivity, due to which the accumulation of chemically active substances corresponding to the type of histamine occurs in the body. Histamine, being a chemical substance, dilates capillaries, simultaneously promoting an increase in the degree of permeability of the vascular walls. This, in turn, contributes to the development of an acute form of edema affecting the papillary dermis, resulting in blistering of the skin. As for the characteristics of the allergen in this case, it can be protein products that have undergone breakdown and have retained their inherent specificity. Such protein substances, once in the blood, cause the production of antibodies against a specific food product.
In addition, toxins found in spoiled foods that are not completely digested can also act as allergens; toxic substances, the accumulation of which occurs in the large intestine with insufficient kidney function, as well as with colitis. A huge role is also given to the presence of foci of chronic infection in the body, acting as a direct source of bacterial allergies provoked by microorganisms (streptococci, staphylococci, etc.).
In the origin of urticaria, a significant role is also played by actual functional disorders of the nervous system (especially the autonomic one). For example, we can consider the situation with nervous excitation that provokes the development of cholinergic urticaria, which, in turn, is caused by the release of acetylcholine by tissues, which occurs due to the influence of the affected cholinergic system. Exposure to acetylcholine provokes the development of a vascular reaction reminiscent of the reaction that occurs when exposed to histamine.
clinical picture (symptoms) of urticaria:
Spontaneous (idiopathic) urticaria is the most common clinical type of urticaria. Clinically, it manifests itself as blisters that do not have a characteristic localization and are accompanied by itching, less often by burning. Blisters may tend to coalesce in areas of greatest friction between clothing or body parts (buttocks, lumbar region, shoulders, thighs). On the face, the elements may practically not protrude above the skin level. In some cases, the rash covers almost the entire skin and may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature. The blisters are first pale pink in color due to local expansion of the superficial network of blood vessels in the dermis (urticaria rubra), and then, as swelling in the connective tissue increases and compression of the network of small vessels, they can acquire a porcelain white color (urticaria alba, seu porcellanea ). As the severity of the swelling decreases, the blisters gradually turn pink and then disappear without a trace.
Thus, the following signs are characteristic of a blister with urticaria:
- central edema of varying sizes, almost always surrounded by erythema;
- itching, sometimes burning sensation;
- reversibility (the blister disappears without a trace within 1–24 hours).
blister
According to the nature of the course, ordinary urticaria is divided into acute and chronic.
Acute urticaria is defined as a sudden, single appearance of blisters (each of which lasts no more than 24 hours) lasting less than 6 weeks, caused by exposure to one of the provoking factors.
Chronic urticaria is a condition that occurs due to known and unknown causes, in which blisters appear daily or almost daily for more than 6 weeks, each of which lasts no more than 24 hours. According to the nature of the course, chronic urticaria is divided into recurrent and persistent, characterized by the constant appearance of urticaria.
chronic urticaria
Acute spontaneous urticaria in most cases remains the only episode in the patient’s life. In 50% of patients with chronic recurrent urticaria, spontaneous remission occurs. Chronic urticaria is characterized by a wave-like course without progressive worsening.
A special case of common urticaria is angioedema (angioedema, Quincke's edema, limited angioedema, giant urticaria). The disease is characterized by rapidly developing, usually limited, deep swelling of the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling can be diffuse, the color of the skin in the affected area is paler, the skin is dense to the touch, in the area of \u200b\u200bthe edema is tense, when pressing with a finger in the area of \u200b\u200bthe edema, an indentation is not formed. Quincke's edema often develops in one area of the skin, and, otherwise, mostly asymmetrically. An important clinical symptom that distinguishes angioedema from ordinary urticaria is the absence of itching. Patients are usually bothered by a feeling of fullness, tightening, and, less often, pain in the affected area. The process involves mainly well-extensible tissues with loose subcutaneous fatty tissue - the area of the eyelids, lips, cheeks, scrotum, foreskin, less often - limbs, abdomen, as well as the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, tongue, larynx, trachea, bronchi, gastrointestinal tract. Damage to the tendon sheaths, joints (intermittent joint swelling), periosteum, meninges, and labyrinth may be observed. In this case, clinical symptoms are determined by the localization of edema. Thus, with the development of giant urticaria on the oral mucosa, an increasing feeling of fullness and paresthesia occurs. Swelling of the nasal mucosa may cause sneezing and difficulty breathing through the nose. When the lips and tongue are affected, there is a sharp asymmetrical increase in their size, and speech is impaired. When edema forms in the larynx, hoarseness occurs, up to aphonia, caused by swelling of the vocal cords, and then difficulty breathing. With the development of giant urticaria in the area of the trachea and bronchi, a cough appears with a large amount of clear sputum, and sudden difficulty breathing. Increasing swelling of the larynx, trachea and bronchi can lead to death from asphyxia. Damage to the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract is usually accompanied by abdominal pain and symptoms of intestinal obstruction; if the mucous membrane of the bladder is involved in the process, dysuric phenomena may occur. In some cases, focal neurological symptoms are noted (loss of consciousness, convulsive seizures, etc.), papilledema is detected, and if the labyrinth is affected, symptoms of Meniere’s disease are detected. Cases have been described in which, due to swelling of the retrobulbar tissue, unilateral exophthalmos developed and visual acuity decreased. Against the background of Quincke's edema, a rise in body temperature, the appearance of a headache, a disturbance in the general condition, a sharp drop in blood pressure, and shock are possible. Angioedema is often accompanied by manifestations of ordinary urticaria.
Quincke's edema
Having developed suddenly, Quincke's edema usually lasts for several hours, less often - up to 72 hours. Manifestations of giant urticaria resolve completely, but this disease can recur. With relapses, the same anatomical locations are often affected.
Thus, angioedema is characterized by the following symptoms:
- rapidly developing swelling of the deep layers of the dermis, subcutaneous tissue and submucosal layer;
- a feeling of fullness and pain more often than itching;
- possible absence of erythema;
- permission within 72 hours.
Physical urticaria is accompanied by the appearance of blisters on the skin as a result of exposure to various physical factors. Depending on the type of irritation of the skin surface, the subtypes indicated above are distinguished.
solar (physical) urticaria
Cholinergic urticaria is a fairly rare type of disease (5% of all cases of urticaria). Provoking factors for its development are exposure to high temperatures (high ambient temperature, taking a hot bath, hot shower), physical activity, emotional arousal, eating spicy and hot food. The disease can recur; most patients note worsening in the winter. Clinically, cholinergic urticaria manifests itself paroxysmally: the patient suddenly develops itching, small (1-3 mm in diameter) urticaria and increased sweating appear. In severe cases, an asthmatic attack may occur. An attack of the disease lasts from several minutes to several hours. The next attack of recurrent urticaria may occur no earlier than 24 hours later. Many patients, knowing this periodicity of the disease, deliberately cause an attack of urticaria before various events that are significant to them in order to avoid an attack in a critical situation. Cases of a combination of cholinergic and chronic recurrent urticaria have been described.
Cholinergic urticaria
Contact urticaria develops 30–60 minutes after skin contact with certain substances. Direct exposure of the skin to these agents may cause localized blistering, generalized urticaria, or urticaria in combination with an anaphylactic reaction. There are non-immune and immune forms of contact urticaria.
Non-immune contact urticaria. The non-immune type of contact urticaria is the most common and is mild in most cases. Histamine-releasing substances are secreted by some plants (nettles) and living organisms (caterpillars, jellyfish). Some chemical compounds have a histamine-releasing effect: dimethyl sulfoxide, cobalt chloride, benzoic acid, cinnamaldehyde and others.
Contact urticaria
Immune contact urticaria. It is an immediate hypersensitivity reaction mediated by IgE. In addition to urticaria, some patients develop allergic rhinitis, laryngeal edema and gastrointestinal disorders. Trigger factors may include latex, bacitracin, potatoes, apples and other factors.
Aquagenic urticaria is caused by skin contact with water of any temperature. Rashes with aquagenic urticaria are similar to those observed with cholinergic urticaria.
Aquagenic urticaria
Treatment in adults and children
How to treat urticaria is determined during diagnosis; usually therapy consists of eliminating exposure to the identified allergen. If it has not been possible to identify what is causing the allergic reaction and there is a clear idiopathic form on the face, then treatment consists of taking antihistamines that quickly suppress external signs on the body and internal symptoms.
During the treatment period, you should avoid certain foods and adhere to the principles of a hypoallergenic diet, which will be discussed below. Adults should not use perfumes and cosmetics; it is important to protect children from the effects of aggressive substances and environments.
Urticaria is treated by an allergist or dermatologist; the main features of therapy are:
- Drugs for treatment are selected based on the severity of external manifestations and the presence of a threat of complications associated with swelling of the respiratory system.
- Chronic urticaria cannot be cured in one day; therapeutic measures extend over many months.
- Often the disease goes away on its own without leaving any traces.
- To effectively suppress the source of the allergic reaction, it is important to check the gastrointestinal tract system for the existence of infectious foci.
Patients with identified allergens are subjected to etiotropic treatment. It is important to protect the adult or child from the substance or other element that causes an acute reaction. To do this, the diet and diet are adjusted, and the premises of permanent residence are thoroughly and regularly cleaned. If the disease is of a medicinal nature, you need to work with your doctor to select analogues that do not cause allergies.
Systemic drug treatment in adults involves taking the following medications:
- Antihistamines - Diphenhydramine, Cetirizine, Loratadine;
- Systemic glucocorticosteroids prescribed for generalized forms of urticaria;
- Reducing sensitivity - Calcium chloride, Unitol;
- If there are threats of death, take adrenaline hydrochloride.
Only a doctor can decide what and how to treat a patient and prescribe medications.
Let us describe the effects of second and third generation agnistamines used in treatment:
- Erius - actively suppresses swelling of the mucous membrane caused by the action of the allergen, due to which the severity subsides and general well-being stabilizes.
- Zyrtec - when treated, quickly relieves the main symptoms, itching and inflammation. After half an hour, allergies, coughing and sneezing attacks decrease.
- Tazepam - has an effect on the central nervous system, eliminating vomiting, headaches and other symptomatic signs.
If an allergic substance is detected:
- A hypersensitization procedure is carried out, due to which the effectiveness of the allergen is noticeably reduced;
- They undergo diagnostics for abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract and their treatment if necessary;
- Relieve skin manifestations and itching with Tavegil or Suprastin;
- If there are infectious foci, they are subject to sanitization in compliance with special prevention;
- If there is a helminthic infestation, then adults and children are subject to mandatory treatment to eliminate helminths and helminthiasis.
First aid for difficulty breathing
If in adults or children urticaria has led to difficulty breathing due to severe swelling of the tongue and larynx, then you must urgently call an ambulance by calling 103. Before the doctors arrive, you should alleviate the patient’s condition as much as possible in order to prevent his death, for this you need :
- Avoid interaction with an allergic substance;
- Make breathing as easy as possible by freeing the neck and chest;
- Ventilate the room, giving an influx of fresh air;
- Take previously prescribed antihistamines;
- Place vasoconstrictor drops into the nose to facilitate nasal breathing;
- Give the patient table mineral water;
- If hives are caused by insect bites, cover the affected area with a cold compress.
Nettle fever: causes
The underlying cause of about half of skin reactions remains unknown. Even laboratory analysis is sometimes unable to determine the source of urticaria, since several irritating factors can play a role in the development of the disease.
Many people mistakenly believe that urticaria is exclusively an allergic disease. This is not true: a nettle rash can also have a toxic origin.
Modern research has identified the following possible causes of urticaria:
- Medical drugs.
Taking antibiotics often causes hives to develop, and the rash can appear days or even weeks after treatment. Most often, an allergic reaction of this kind is caused by drugs from the group of penicillins, sulfonamides, polymyxins, cephalosporins, rifampicins, and tetracyclines. Oral contraceptives, vitamin complexes, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications such as aspirin or indomethacin can trigger the occurrence of urticaria.
- Food.
Known allergens such as seafood, nuts, peanuts, eggs, some types of fruits and berries, cow's milk, and many other foods can cause hives.
- Contact irritants.
There are a number of certain substances that, upon skin contact, can cause a rash (contact urticaria). Such substances include nickel, which is found in some jewelry or on metal belt buckles, components of perfumes, household cleaners and detergents, and latex products.
- Mechanical irritants.
Friction and pressure cause mechanical urticaria. There is dermographic urticaria (dermatographism uticaria), which is also a form of urticaria of mechanical and physical origin.
- Physical factors.
Often there are cases of urticaria due to exposure to low temperatures (cold urticaria); sun exposure (solar urticaria); sweat, fluid or water (cholinergic, aquagenic urticaria); vibrations (vibrational urticaria); physical activity, long-term stay in a stuffy room (cholinergic urticaria).
- Insect bites.
The allergic response to the bites of hymenoptera or blood-sucking insects is due to a number of components in the saliva or insect venom. The most severe type of acute urticaria occurs after the sting of bees, wasps, hornets, tropical ants and bumblebees.
- Concomitant diseases or infections.
It has been established that urticaria, its mostly chronic form, can become a sign of the presence of other disorders in the body. Then the appearance of a nettle rash is associated with various kinds of infections, diseases of the digestive system, diseases of the thyroid or pancreas, benign and malignant tumors, parasitic infestations and some other health disorders.
If urticaria occurs chronically, and the cause of the unpleasant symptoms cannot be found, many experts agree that the autoimmune nature of the disease is at play here.
The factors that cause chronic and acute types of nettle fever are mostly different and have significant differences.
The causes of urticaria, which occurs in acute form, are mainly allergic reactions. Usually here you can easily determine the exact factor that caused the rash.
As for the chronic form of urticaria, it is quite difficult to identify the source of the disease: the main cause is a third-party disease and a nettle rash is only one of its symptoms.
Varieties
Diagnosis of urticaria in children and adults is carried out comprehensively and comprehensively. The doctor is obliged to identify the reasons that provoked the development of such a reaction. Only by eliminating them can good results be achieved during treatment.
There are two forms of this disease:
- Spicy. Develops immediately after the patient comes into contact with an allergen. In just a few minutes, red spots appear on the skin. Such urticaria disappears as quickly as it appears, if human contact with the provoking factor is excluded.
- Chronic. Every day a person is exposed to harmful factors. Symptoms are observed constantly. Moreover, they do not go away immediately after the stimulus is eliminated.
In addition, hives can be physical or a specific type. In the first case, the appearance of characteristic symptoms occurs after exposure to adverse factors on the body:
- Pressure. If any object presses on the skin, spots appear.
- Cold. Appears in the vast majority of people who are exposed to the cold for a long time.
- Vibrating. Appears and goes away quickly.
- Solar. Caused by exposure of the skin to ultraviolet radiation. It may appear as slight redness or blistering.
Treatment of urticaria at home in adults
When treating a disease at home, it is undesirable to make do with folk remedies alone, used without consulting an allergist. Since it will not be possible to overcome the disease with herbs alone, complex treatment is necessary. Traditional medicine can be used as an addition to the main elimination of the disease with pharmaceutical drugs.
Effective folk remedies for urticaria.
In folk medicine, the following remedy for urticaria is widely used: a collection of hop cones, lemon balm leaves, and valerian root, take in equal quantities - 15 grams of each, boil for 10 minutes. You should drink 35 ml of the decoction three times a day.
Celery is effective not only in the fight against allergies, it also improves immunity. The root is squeezed out and drunk four times a day, 15 ml.
Honey (if a person has no contraindications to this product) can be used to treat the disease. It is enough to eat 15 mg of it in the morning on an empty stomach.
Mint will soothe irritation: brew a spoonful of the herb in boiling water and drink 75 ml three times a day.
Urticaria in children
Children's urticaria does not differ significantly from the adult form, and the method of treatment differs mainly in dosage - the doctor prescribes the medicine based on the child's weight.
Good news for parents: chronic urticaria occurs in children much less frequently than in adults, but if the disease does occur, in half of the cases it is completely cured within six months. Infantile urticaria is predominantly an allergic form of reaction.
To relieve itching, the baby’s skin can be lubricated with special products, such as fenestyl - from 1 month of life, Elidel - from 3 months of life; and bathe in nettle decoction.
Parents need to closely monitor the clinical course of urticaria in their child to prevent the acute form from becoming chronic.
What diagnostics is carried out by a doctor if there is suspicion?
The child is recommended to undergo a special allergy examination, including skin tests with allergens and blood tests to identify specific antibodies. An examination for helminthic infestations and a biochemical blood test are required.
As a rule, the true cause of urticaria can be determined only in 50% of cases. This means that the causative allergen can only be found in half of all cases of the disease.
Find out from the material of an allergist-immunologist about when allergic skin rashes occur in children, in addition to urticaria.
Detailed information from a pediatrician on how to distinguish newborn acne from urticaria and other allergic manifestations.
Parents should remember that the rash itself does not pose a danger to the life and health of the child. Edema of the larynx is dangerous, manifested by hoarseness of voice, noisy breathing, and barking cough.
Classification
All forms of allergic urticaria are divided into two types - acute and chronic. The boundary between them is quite arbitrary - it is believed that in the acute form, rashes and itching persist for no more than 6 weeks, while if they bother the patient longer, a diagnosis of chronic allergic urticaria is made.
In addition, it is important to differentiate true allergic urticaria from pseudoallergy, in which activation of mast cells occurs without the participation of immune mechanisms. There are many varieties of this condition - for example, mechanical types of pseudo-allergies include the following:
- Dermographic urticaria (urticarial dermographism) - is provoked by simple physical pressure on the skin (seams of clothing, for example). Non-immune mechanisms of mast cell activation most often play a role in the pathogenesis of dermographic urticaria.
- Cold urticaria - this type of temperature urticaria has become increasingly common in recent years. It was found that in patients with this pathology, during cooling, the level of certain platelet factors increases and the stability of the mast cell membrane decreases. Against the background of increased sensitivity of skin tissue to histamine, this can lead to the development of erythematous rashes and itching, both with local exposure to cold and with the consumption of cold foods and drinks.
- Heat urticaria is a fairly rare variant of urticaria. Just as in the case of urticarial dermographism, the main role in the development of this type of disease is played by non-immune mechanisms of activation of mast cells - their degranulation occurs with increasing temperature.
- Solar urticaria (photoallergy) - the provoking factor in this case is sunlight. Patients with this type of urticaria have an increased sensitivity of the skin to histamine, so the degranulation of even a small number of mast cells leads to noticeable disturbances.
- Vibration urticaria is a fairly rare form and often has signs of an occupational disease (in construction workers, in production). In this case, degranulation of basophils occurs due to mechanical shock of the tissues.
- Aquagenic urticaria - previously did not belong to the mechanical varieties of urticaria, but in recent years there have been indications that the provoking factor in this case is the physical impact of water jets. Activation of skin mast cells occurs through a non-immune mechanism and is quite weak, but with increased tissue sensitivity to histamine, this leads to the development of erythema and itching.
In addition to mechanical factors, an imbalance of the cholinergic autonomic nervous system can provoke the development of urticaria. This causes the development of so-called cholinergic urticaria. In addition to the erythematous rashes and skin itching typical for this pathology, in this case there are also disturbances in sweating and regulation of skin temperature. This type of urticaria is often provoked by a person’s emotional experiences. In addition, urticaria pigmentosa, which is an autoimmune pathology, is close to this skin disease. With it, an increased number of basophils accumulate in the skin tissues, which can be easily activated by various factors.
Types of diseases and their distinctive signs
Experts divide the disease into types, which also have their own distinctive characteristics and forms. It depends on the species what complications will bother you and how best to get rid of them .
The main types of disease are:
- Acute urticaria, in which blisters are accompanied by red swelling and severe pain.
- A chronic form in which the disease occurs frequently and is influenced by many factors and irritants.
- Allergic urticaria, in which symptoms and blisters develop as a result of an allergy to a substance.
Each type has its own distinctive features, by which specialists can easily recognize the disease. The disease is dangerous because the blisters can burst and cause a lot of unpleasant pain, so treatment will be necessary. First of all, when the disease develops, the headache, weakness and even drowsiness begin, which often torments without reason. Also, the main symptom is the skin, which at the initial stage of urticaria begins to flake and even peel, causing irritation and reddish spots.