Procedure in case of pain
The abdominal cavity contains many organs. Some of them are hollow, others have a parenchymal structure. Changes in hollow organs can lead to perforation of their walls. At the same time, the outpouring of their contents into the abdominal cavity is fraught with an extensive inflammatory process (peritonitis, blood poisoning and death).
Determine where it is localized
To facilitate diagnosis, doctors conditionally divide the abdominal area into 4 quadrants. The pain may be localized in the right upper or lower quadrant.
If the pain is concentrated from above, there is reason to suspect pathology of the lungs, diaphragm, liver, gallbladder, pancreas and stomach. If discomfort is localized from below, inflammation of the appendix, kidneys and urinary tract, and organs of the reproductive system is suspected. The cause of pain in the adjacent space is most often the small and large intestines.
What is the nature of the pain
Only the patient himself can describe the nature of the pain; this is of diagnostic importance. When talking with a doctor, it is necessary to describe the unpleasant sensations as accurately as possible.
Periodic weak, nagging or aching pains indicate the initial stages of the development of the disease. Such discomfort often goes unnoticed until the discomfort becomes more intense. The cause of mild pain is inflammatory processes, the onset of functional disorders in the organ, cell degeneration, and the formation and growth of atypical structures.
Intense shooting pains or spasms accompany diseases of the smooth muscle organs. The cause of their occurrence is functional disorders, the development of inflammation, and increased pressure in the organ cavity.
Intense pain of a cutting or stabbing nature appears when nerve endings are damaged or inflamed, when the integrity of the parenchyma or membranes of internal organs is compromised. The cause is often an active inflammatory process. Another option is acute tissue ischemia as a result of circulatory disorders.
Sudden “dagger” or unbearable pain often indicates a perforation of the organ wall. A clear localization of sensations indicates damage in a specific place. Diffuse pain occurs in the later stages of development of pathologies and indicates peritonitis.
additional information
Information about the development of discomfort, the time of its appearance, and its connection with other events is also important for the doctor. In order for a specialist to draw up a complete clinical picture, it is necessary to clarify the following points:
- when the pain appeared (in the morning, immediately after waking up, at night, at another time of day), how long the patient has been experiencing discomfort, whether it hurt in the same place before;
- how it hurts (the sensations appeared suddenly or increased gradually);
- how the discomfort has changed (become weaker, stronger, has the nature of the pain changed);
- additional symptoms (weakness, nausea, chills, heaviness). The doctor must be informed about episodes of vomiting, stool disturbances, fever, as well as the exact body temperature at the time of treatment;
- what the patient did. If you have abdominal pain, taking any medications is not advisable. This may change the clinical picture and make diagnosis difficult. However, in some cases, taking antispasmodics and sorbents is allowed. The doctor must be informed of the name of the drug and the dose taken.
Other information is also important for diagnosis - height, weight, presence of bad habits, diet, chronic diseases, hereditary characteristics of a person.
When to make an appointment with a doctor
Right-sided abdominal pain is a consequence of serious diseases of vital organs. If they are affected, there is a high risk of complications and irreversible changes. Any pain in the abdomen on the right is a reason to visit the clinic and undergo a full examination.
- Weak and aching pains indicate a sluggish course of inflammation. You need to visit a doctor at any convenient time. It should not be delayed, as inflammation can spread to other organs and lead to organic tissue damage.
- Spasms and “lumbago” on the right are the result of intestinal lesions, as well as the accumulation of gases in it. If the discomfort is tolerable and does not tend to increase, the patient can take an antispasmodic and consult a doctor at any convenient time.
- In case of intense pain that occurs suddenly, you should be alert immediately. Unbearable and stabbing pain is a reason to call an ambulance.
If your stomach hurts for more than half an hour, and the discomfort changes in character or its intensity increases, you should go to the clinic or call an ambulance as an emergency.
What is colonic obstruction
This disease is caused by a violation of the movement of contents through the intestines. And the symptoms are cramping pain in the intestines in the lower abdomen, bloating (externally this is expressed by noticeable asymmetry), repeated vomiting, loss of appetite and delayed or absent stool.
But it is pain that is the main symptom in this case. It can occur at any time, suddenly, not related to food intake and without any warning signs. As a rule, painful attacks are repeated every 15 minutes. On the second or third day of the disease, the pain may stop. But this should alert you, because most often it is evidence of a cessation of intestinal motility and the threat of intoxication. Contact your doctor immediately!
Aching pain on the right
You can guess why the pain in the side occurred by the nature of the sensations and accompanying symptoms. However, this is not a reason to self-medicate. Only a doctor of appropriate qualifications can diagnose pathology and prescribe the correct treatment.
Respiratory system diseases
Pain in the hypochondrium on the right may indicate pulmonary pathology - pneumonia, abscess, lung cancer, right-sided pulmonary thromboembolism. The discomfort is aching and constantly present. When blood clots occur, the pain is intense and stabbing. Against the background of lung diseases, the patient experiences fever, difficulty breathing (impaired inhalation-exhalation), dry or wet cough. With the development of cancer pathologies, nonspecific symptoms are present - weakness, apathy, lack of appetite, weight loss.
Another provocateur of hypochondrium pain on the right is pleurisy in the corresponding area. Inflammation of the membranes of the lung is accompanied by fever and signs of intoxication. When you take a deep breath, the pain under the rib sharply intensifies and becomes stabbing.
Stomach pathologies
Inflammation of the stomach walls (gastritis) rarely provokes unilateral pain. Discomfort is felt in the center of the abdomen, just below the sternum. Right-sided pain accompanies ulcerative and erosive lesions of the right wall of the organ, the formation of polyps and malignant tumors. The development of ulcers first provokes spasms. As the pathological process deepens into the wall of the stomach, the pain becomes constant, bordering on cutting. They are directly dependent on food intake. They often appear some time after eating. When an ulcer perforates, the pain is unbearable, “dagger-like.” In oncological pathologies – aching, pulling, constant. Additional symptoms include heaviness, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and increased body temperature.
Pancreas problems
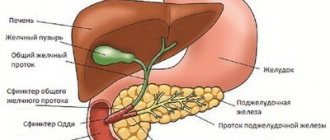
Pancreatitis is the most common disease of the pancreas. It can be acute or chronic. Despite the location of the gland in the center of the abdominal cavity, it can cause right-sided pain. The reason is the anatomical shape of the organ. The pancreas resembles a horizontally unfolded drop. Its largest part (head) is projected into the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. If the inflammatory process during pancreatitis or pancreatic necrosis is concentrated here, right-sided pain occurs. As the disease worsens, the discomfort becomes overwhelming. The pancreas is characterized by sudden intense cutting pain. Damage to the gland is accompanied by digestive disorders (nausea, vomiting, flatulence, stool disorders), and symptoms of intoxication.
Liver pathologies
If the liver is bothering you, the discomfort is localized in the area of the right hypochondrium. Aching, pressing, pulling sensations indicate damage to the parenchyma. An enlarged liver provokes stretching of its capsule, which causes discomfort. Possible diagnoses include hepatitis (of infectious and non-infectious nature), liver cyst, tumor formations, hepatosis and cirrhosis.
Stitching pain in the right hypochondrium after running and fast walking is not related to pathologies. The phenomenon is caused by increased blood supply to the organ and stretching of its capsule.
Paroxysmal stabbing and cutting sensations, spasms and nagging discomfort indicate damage to the gallbladder. The organ signals this when its walls are inflamed (cholecystitis), they are excessively stretched during cholestasis, or the formation and advancement of gallstones. Constant aching and pressing pain indicate a gall cyst, the formation of polyps in it, hypersecretion of bile, or kinks in the bladder.
Hepatic colic syndrome deserves special attention. The condition is accompanied by “dagger” pain in the upper abdomen on the right. Associated symptoms are heartburn, bitterness in the mouth, belching, vomiting with bile.
Other liver diseases are manifested by nonspecific symptoms - weakness and increased fatigue, apathetic mood and deterioration of the skin. As liver pathologies progress, other changes occur in the body. All organs and systems suffer due to increased stress on them, the accumulation of free radicals and the circulation of toxic products in the blood.
Jaundice clearly indicates liver pathology. If the patient's mucous membranes and sclera of the eyes turn yellow, the skin all over the body becomes covered with a hemorrhagic rash, there is every reason to assume congestion in the gallbladder.
Disorders of the small intestine
From the stomach, food enters the duodenum, where it is subject to enzymatic treatment with subsequent absorption of nutrients by the intestinal walls. When the thin section is affected, discomfort most often occurs in the umbilical region. Discomfort migrates to one side in the presence of a pathological process in the folds of the small intestine directly to the right. The causes include duodenitis (inflammation of the walls of the duodenum, ulcer, intestinal obstruction, hernia). All conditions are characterized by a decrease or complete absence of appetite and weakness. Vomiting (often with bile impurities), bloating, and stool disorders may occur. With hernias, the main symptom is protrusion of tissue above the plane of the skin.
Colon diseases
Ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, obstruction, irritable bowel syndrome - all these diseases are accompanied by right-sided painful sensations when the ascending part of the colon is involved in the process.
Right-sided pain may be a sign of appendicitis. Any treatment cannot be prescribed until the absence of inflammation of the appendix is confirmed by tests or diagnostic procedures.
With appendicitis, pain appears in the navel area. As inflammation develops, discomfort is concentrated in the right iliac region and gradually intensifies. In the absence of adequate treatment, the appendix becomes necrotic, which manifests itself as “dagger pain.” Advanced appendicitis almost always leads to peritonitis. The only treatment option is surgery. Associated signs of appendicitis are single vomiting, heaviness, lack of appetite, diarrhea, low-grade body temperature.
Disorders of the urinary system
Diseases and functional disorders of the kidneys often manifest themselves as discomfort in the lower back. Their right-sided localization in the abdominal area is possible, but is extremely rare.
In renal pathologies, this is radiating pain. It occurs against the background of severe discomfort in the area of projection of the kidneys on the back. Pain in the lower quadrant of the abdomen is most often provoked by the ureters (stones that have passed from the kidneys). When released, kidney stones scratch and irritate the sensitive mucous membrane of the urinary tract. As a result, cutting, stabbing, intense painful sensations occur. They weaken some time after urination.
Stones stuck in the ureter provoke dagger pains and renal colic. The patient's body temperature rises, acute disturbances in the outflow of urine occur, and impurities of blood and mucus appear in it. The syndrome is accompanied by severe pain and requires hospitalization of the patient.
Pathologies of the reproductive organs
Due to the anatomical features of the structure of the reproductive system, it rarely provokes abdominal pain in men. Women are more likely to suffer from such symptoms. Aching pain in the iliac region on the right (lower abdomen) appears against the background of polycystic ovary syndrome, cysts, and cancer. The most common cause of right-sided pain is ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy. When an embryo is implanted into the wall of the fallopian tube, the painful sensations are minor (stabbing or cutting), appear periodically, and quickly disappear. With the active division of embryonic cells, the fallopian tube stretches. Lack of adequate assistance leads to pipe rupture. This is manifested by “dagger” pain, impaired consciousness, up to sudden fainting, and vaginal discharge.
Gas-forming products
There are a huge variety of foods that contribute to gas formation in the intestines. These include foods containing carbons, lactose, coarse fiber, and yeast. Consider the list of such products:
- white cabbage causes fermentation in the intestines due to its high content of coarse fiber and sulfur;
- legume products: beans, peas. Such products are poorly processed in the stomach. In the intestines they are susceptible to attack by microorganisms. Before cooking, beans should be soaked in water, this will promote better digestion;
- dairy products. Some people cannot digest lactose at all. But fermented milk products, on the contrary, contribute to good intestinal function;
- raw vegetables and fruits: peaches, apples, pears, grapes, radishes;
- beer, kvass;
- fresh bakery;
- meat dishes;
- sweet carbonated drinks.
An important point in the process of gas formation is the combination of food products. The following products do not combine well with each other: fish and eggs, milk and baked goods, dairy and fermented milk products, multi-ingredient dishes.
How to accurately determine the cause of pain
After collecting anamnesis, the doctor will identify several differential diagnoses. A set of diagnostic measures will help to diagnose the disease. Some of them are represented by laboratory tests of blood, urine and feces. Based on their results, it is possible to determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, functional disorders in the digestive and urinary tracts.
Hardware procedures are selected on an individual basis. To assess the condition of the respiratory system, fluorography is prescribed. To examine the stomach, gastroscopy is used. The condition of the liver and pancreas is assessed using ultrasound. Ultrasound examination is also used for diseases of the urinary and reproductive systems. If the diagnosis is in doubt or there are suspicions of multiple organ disorders, multislice magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal cavity is prescribed. The study provides comprehensive information about all organs at once.
To accurately identify the disorder and make a final diagnosis, additional diagnostic measures may be required. For example, scintigraphy, laparoscopic examination, biopsy.
How to get rid of pain
The ideal way to eliminate discomfort is to begin comprehensive treatment on the recommendation of a doctor after a full diagnosis. If for some reason a trip to the doctor is postponed, you can use special medications to relieve pain. You need to understand that self-medication is fraught with negative consequences for health. The repeated occurrence of pain is a reason to consult a doctor.
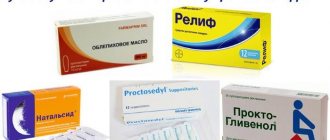
To eliminate spasms and paroxysmal abdominal pain, antispasmodics are used: No-Shpu, Buscopan. If you suspect intestinal diseases, it is advisable to take Spasmomen, Mebsin, Mebeverine. Pain of unknown origin, different from spasms, is relieved with the help of combination drugs (Baralgina, Spasmalgona). Tablets approved for pain relief during the postoperative period (Ketanov, Ketorol) are suitable as an ambulance. For aching and nagging pain, the intensity of which increases, you can take drugs from the NSAID group (Diclofenac, Ibuprofen). However, these drugs have an ulcerogenic effect - they negatively affect the condition of the gastric mucosa. For chronic pathologies of this organ or stomach pain, NSAIDs are prohibited.
Right-sided abdominal pain may indicate diseases of any abdominal organ located on the right. Therefore, a person experiencing pain of any nature and location should seek help from a doctor.
Diagnostics
If a person has abdominal pain on the right side, it is best to seek qualified help from a gastroenterologist, since in most situations the sources of this condition are diseases of the digestive system.
The diagnostic process should always take an integrated approach. The first stage includes several manipulations carried out directly by the clinician:
- studying the medical history - to search for a pathological source;
- collection and analysis of life history - will help to establish the influence of a physiological factor;
- examination by a gynecologist (for women) and a urologist (for men);
- palpating and tapping the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity;
- measurement of temperature, pulse, heart rate and blood pressure;
- assessment of the appearance of the skin, sclera and mucous membranes;
- a detailed interview with the patient will help the doctor create a complete symptomatic picture, which may indicate an etiological factor.
Afterwards laboratory diagnostics begins, which includes the following tests:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- blood biochemistry;
- breath tests for the presence of Helicobacter pylori;
- microscopic examination of stool;
- bacterial tests;
- PCR tests;
- analysis of feces for dysbacteriosis and helminth eggs.
The following instrumental procedures can accurately determine the cause of pain in the lower abdomen on the right side in women or men:
- gastroscopy;
- irrigoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and peritoneum;
- ECG;
- colonoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- endoscopic biopsy;
- CT;
- MRI.
Scheme of sigmoidoscopy
If, after the above diagnostic methods, the clinician was unable to determine the source of pain in the right side of the lower abdomen, the gastroenterologist may refer the patient for additional consultations with the following specialists:
- endocrinologist;
- nephrologist;
- gynecologist;
- urologist;
- neurologist;
- oncologist;
- cardiologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- pediatrician;
- therapist.