Despite the huge selection of modern contraceptives, abortion is still a means of so-called birth control. Considering the specific nature of medical procedures during abortion, complications after an abortion develop quite often. Even when the abortion procedure is performed technically correctly, there are always negative post-abortion consequences: both psycho-emotional and physiological.
Medical abortion and its consequences
Medical abortion is the artificial termination of pregnancy performed before 22 weeks.
- In case of termination of pregnancy in the first trimester, that is, up to 12 weeks, this is an early abortion.
- In case of a later interruption (13 – 22 weeks), the abortion will be called late.
Removal of the embryo from the uterus during the first 12 weeks in the Russian Federation is performed at the request of the woman, while abortion in the later stages is carried out only by medical advice. indications (if pregnancy poses a threat to the life and health of a woman) and social (of which there are currently only 3 left out of the previously existing 13) and the decision on its implementation is made by a special commission.
There are several methods of artificial termination of pregnancy:
- mini-abortion - when the embryo is removed by vacuum suction up to 21 days of missed menstruation (about 5 weeks);
- medical abortion - carried out by taking medications - Mifegin (Mifepristone), which inhibits the action of progesterone and provokes rejection of the fertilized egg, is carried out until the 49th day of delayed menstruation (approximately 6 - 7 weeks);
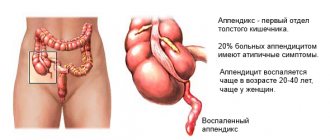
- surgical abortion - scraping of the embryo from the uterine cavity with a special instrument - a curette (it looks like a spoon with a sharp edge and a hole in the center) after preliminary artificial dilation of the cervical canal (performed up to 12 weeks).
Early ones are considered to be those that appeared within 10 to 30 days after the procedure or complications that arose during the abortion process:
- perforation or “puncture” of the uterus;
- bleeding during surgery;
- complications of anesthesia;
- prolonged and/or massive bleeding after the procedure;
- pelvic inflammation, development of sepsis;
- cervical rupture;
- hematometer;
- thrombophlebitis and thrombosis;
- failed abortion attempt.
see the tendency to abortion is inherited.
Early consequences of abortion
The consequences of abortion can be divided into groups depending on the time of their occurrence. Already during the operation or immediately after it, the following consequences may occur:
- damage (injury) to the uterus;
- bleeding;
- complications associated with the administration of anesthesia.
When an artificial abortion is performed to kill and remove the embryo, the cervix, whose canal is normally narrow, expands. Moreover, the longer the pregnancy, the greater the dilation of the cervix is required. This leads to abrasions, cracks and tears of the cervix, and, as a consequence, disruption of normal labor during subsequent “desired” pregnancy. In addition, during curettage, the uterus itself can be injured.
The abortion is performed with a metal instrument, the doctor acts blindly. In this case, damage is possible not only to the mucous membrane of the uterus, but also to the muscle layer. Scars, scars, and polyps may appear, which creates problems with pregnancy, leads to miscarriages, and, ultimately, to infertility. In case of severe damage to the uterus, its rupture poses a danger to the woman’s life, so surgical treatment is required, and sometimes urgent removal.
Any intervention in the uterine cavity can cause severe bleeding, requiring blood transfusion, urgent surgery, and sometimes removal of the uterus. There is also a risk of complications from pain management. The most dangerous consequence of anesthesia is allergic shock. In addition, breathing, heart function, and liver function may be impaired.
Even if problems were avoided during the abortion process, negative consequences such as inflammation and thrombosis may appear soon after the abortion. After an artificial termination of pregnancy, one should be wary of the development of inflammatory processes in the uterus, fallopian tubes, abdominal cavity or periuterine adipose tissue, as well as blood poisoning (sepsis). They can occur as a result of infection during surgery and are accompanied by severe pain, fever, and a general deterioration in health.
In case of blood poisoning, immediate treatment with antibiotics is required. As a consequence of abortion, one can also identify a disorder of blood clotting, and, as a result, the formation of blood clots, which requires urgent treatment.
Complications of abortion. How to avoid serious consequences
Timely diagnosis and adequate treatment of early and late complications of abortion will help avoid such severe consequences of abortion as
, chronic inflammatory diseases of the female genital area,
, pathological course of subsequent pregnancies and childbirth.
Therefore, every woman who decides to have an abortion should be aware of the measures available to her to prevent complications, as well as the pathological symptoms, if they appear, she should immediately seek medical help.
How to reduce the risk of complications after your first abortion?
The risk of complications is reduced if you choose more gentle methods of abortion and perform it up to 5-6 weeks.
Early abortion has less dire consequences, so if this is your first pregnancy, it is advisable to resort to the medication or vacuum method. A surgical first abortion is a very high risk, often depriving a woman of the opportunity to become a mother.
After performing an abortion by any method, subsequent monitoring using ultrasound of the uterus is necessary, as well as strict adherence to medical recommendations on genital hygiene, further sexual activity and methods of contraception.
Perforation of the uterus
Perforation or perforation of the uterus is an iatrogenic complication when the wall of the uterus is “pierced” through during intrauterine manipulation with a surgical instrument. This can be perforation with a probe, dilator, curette or abortion tool (the most dangerous).
Perforation can be uncomplicated when the surgeon feels that the instrument has “gone” too deep, but the internal organs of the abdomen are not damaged, and complicated when a loop of intestine, a section of the omentum, a bladder or another organ is removed through the perforation into the cervical canal.
This complication is accompanied by the occurrence of sharp, very intense pain in the lower abdomen during manipulation, a drop in blood pressure and loss of consciousness are possible. Perforation requires immediate laparotomy or laparoscopy with suturing of the uterus or its removal in severe cases and restoring the integrity of the affected and damaged abdominal organs.
Uterine perforation is the most dangerous complication that can occur during a routine surgical abortion. It is more common during the first abortion in nulliparous women. The risk is especially high in women with congenital uterine anomalies. As pregnancy progresses, the likelihood of this complication increases.
Consequences: scar on the uterus, loss of an organ (often a woman can be saved only by removing the damaged uterus), death.
How to prevent: try in every possible way to avoid a conventional surgical abortion.
What can you console yourself with: this is a fairly rare complication (no more than 1% of cases of conventional surgical abortion); Thanks to modern advances in medicine, some women can be saved even with serious damage to the intestines or bladder.
The very first consequences of a classic abortion at the stage of its implementation
Here are the consequences of an abortion, which will appear almost instantly:
- Injury to internal organs. Sometimes unscrupulous or inexperienced physicians may abort the uterus or its cervix in the process. After all, it is during pregnancy that her soft muscles are tense to the limit, and an instrument inserted into this organ can stretch or tear it. To eliminate such consequences, urgent surgical intervention is required, which usually ends with complete removal of the uterus.
- Heavy bleeding. Blood vessels surround the uterus of a pregnant woman in a dense ring, and the slightest careless movement can lead to them being damaged. This ends with a call to the surgeon and sometimes a blood transfusion; for particularly difficult situations, removal of the uterus.
- Anesthesia and its complications. The local type of anesthesia has fewer consequences than the general one, but it is not always suitable. And the latter can often cause disturbances in heart rhythms, respiratory system and liver function. This most often happens if an abortion at 40 years old has consequences that can last a lifetime. And the most terrible and serious consequence is allergic shock.
Medical abortion and its consequences
Bleeding can develop with any method of termination of pregnancy. But the least risk is posed by vacuum aspiration, and the greatest is medical abortion.
Consequences: posthemorrhagic anemia, death.
How to avoid: seek immediate medical attention in cases where the bleeding becomes alarming (uses 4 or more maxi pads in two hours and/or symptoms of acute blood loss appear, such as increasing weakness, pallor, cold sweats, increased frequency of pulse up to 100 beats per minute, blood pressure drop below 100 mmHg).
As a rule, every woman who decides to have an abortion is interested in whether she will be able to carry and give birth to a healthy child in the future. Unfortunately, no doctor can give a 100% guarantee that an abortion will not affect subsequent pregnancies.
Abortion is an important predisposing factor in the development of the following pregnancy pathologies:
- ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy;
- recurrent miscarriage;
- premature birth;
- bleeding during pregnancy and childbirth (rank first in the structure of maternal mortality);
- placenta previa (incorrect attachment of the placenta);
- premature placental abruption.
. Repeated abortions are especially dangerous, so after termination of pregnancy you should carefully protect yourself. If the desired pregnancy develops, be sure to tell your doctor about the abortion and its complications (if any).
Signs of complications after an abortion are different depending on whether we are talking about early or late symptoms.
As for the early signs, they will be as follows:
- Firstly, such complications arise during the surgical intervention itself or a short period after it. Most often this is bleeding;
- Another sign is pain in the lower abdomen, which is nagging in nature;
- Increased body temperature;
- Weakness and the appearance of bloody discharge mixed with pus from the woman’s genital tract.
Complications that can be observed in a woman in the early period are also inflammation of the peritoneum, which is called peritonitis, uterine perforation, puncture of the uterine wall, inflammation (adnexitis and endometritis).
A puncture of the uterine wall is the most dangerous of the complications, since it can lead to injury to other organs located nearby.
Complications and consequences of late-term abortion include hormonal disorders, infertility, miscarriage of a subsequent pregnancy, endometriosis, aggravation of acute processes in the pelvis, problems with the course of a subsequent pregnancy. Late complications of abortion tend to appear a year after the operation or even later.
- Hyperplasia;
- Uterine fibroids;
- Endometritis.
Complications and consequences of abortion are divided into 2 groups: early and late. Early - deterioration of the condition is called, frolicking during the manipulation or in the first day after it. These include:
- Perforation of the uterine walls
- Bleeding
- Hematometer
- Incomplete abortion
- Traumatization of the cervix
- Infection
Hemorrhages can be caused by damage to blood vessels or pathological neoplasms. This is facilitated by impaired contractility of the uterus, which is a common complication of abortion. The cause of bleeding is also the presence of remnants of the placenta or fertilized egg.
Hematometra is a pathological condition in which the outflow of blood from the uterine cavity is disrupted. This complication can result from:
- Blockage of the cervical canal with part of the fertilized egg, placenta, blood clot, etc.
- Impaired contractile function of the myometrium
- Presence of connective tissue adhesions
Incomplete abortion is the partial removal of the fertilized egg and its membranes from the uterine cavity. In this case, bleeding begins, pain in the lower abdomen increases, and endometritis develops with the addition of infection. In this case, a repeat surgical abortion is indicated.
Rehabilitation helps reduce all possible complications. The duration of the recovery period and effectiveness are influenced by age and general health, the number of births and abortions. The gynecologist selects individually for each person the scope of necessary procedures, studies and medications.
During gestation, the uterus begins to increase in blood vessels, therefore, blood vessels grow in it and blood supply improves. When the embryo is separated during surgery, the vessels are damaged, which leads to bleeding, both during curettage and after surgery.
If large vessels are damaged, the matter may result in removal of the uterus. Bleeding often occurs:
- against the background of uterine fibroids
- improper attachment of the fertilized egg
- after numerous births.
Bleeding also often occurs during medical abortion (“elephant” doses of hormones, in addition to miscarriage, increase bleeding and disrupt the contractile activity of the uterus) and requires surgical hemostasis - curettage of the uterine cavity.
If bleeding continues for a long time (more than 10 days) or significant bleeding with clots periodically occurs, it is possible that parts of the fertilized egg or unremoved pieces of the placenta remain in the uterus, which ends with the need for repeated curettage.
The best abortion is an unmade abortion, so contraception takes first place in the prevention of complications. After the abortion procedure, the patient must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations:
- maintaining sexual rest for a month;
- refusal to take baths, visit saunas, baths, swimming pools and open reservoirs until the menstrual cycle is restored;
- mandatory check-up with a gynecologist after an abortion 7 to 14 days;
- undergoing preventive gynecological examinations every 6 months;
- resolving the issue of contraception (as a rule, it is recommended to start taking oral combination drugs immediately, on the day of the abortion);
- protection from pregnancy for at least 6 months;
- planning the next pregnancy (full examination, rehabilitation of chronic infectious foci, correction of somatic diseases, giving up bad habits and a healthy lifestyle);
- before terminating a pregnancy, a woman must undergo at least the necessary tests (CBC - general blood test, OAM - general urine test, smear for microflora from the vagina) and undergo examination if the smear results are unsatisfactory;
- limit heavy physical labor for 3 weeks after an abortion;
- If any warning symptoms appear, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Late complications
Such complications after an abortion develop after quite a long time from the artificial termination of pregnancy. Sometimes this takes months and years.
Intervention in the normal course of pregnancy with the aim of interrupting it triggers a cascade of negative reactions that affect almost all organs and systems of a woman. Literally from the very first weeks of pregnancy, a restructuring of the work of the endocrine, nervous, immune, cardiovascular and other systems of the female body is carried out. After an abortion, a serious disruption of all these functions occurs.
So, the late consequences of abortion include:
- Inflammatory damage to the structures of the female genital tract.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Formation of adhesions (synechias) in the uterus.
- Infertility.
- Pathology of subsequent desired pregnancy.
- Mastopathy.
- Complicated course of the menopause.
- Cicatricial changes in the cervix.
- Obstruction of the fallopian tubes.
- Psycho-emotional disorders and some others.
Abortions are also risk factors for the future formation of malignant neoplasms of the uterus, ovaries and breast.
Inflammation
According to statistics, inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs are the most common complication of an abortion. The most commonly affected areas are the appendages (fallopian tubes) and the lining of the uterus (endometrium). Inflammation quite often becomes chronic.
Risk factors for inflammatory lesions are:
- Insufficient preparation of the woman for the procedure.
- The presence of foci of infection - both in the genital area (for example, in the vagina) and beyond.
- A decrease in the body's resistance as a result of a malfunction of the immune system.
- An extensive wound surface in the uterus, which serves as a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Violation of the cervical barrier as a result of manipulations on the cervix (dilatation) and penetration of a foreign body (surgical instruments) into the uterine cavity.
Inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs quite often lead to subsequent infertility.
Hormonal disorders
In all women without exception, after termination of pregnancy, the normal balance of female sex hormones is disrupted. The consequences of such an imbalance can manifest themselves in various kinds of menstrual cycle disorders and the appearance of dishormonal diseases of the mammary gland (mastopathy). The risk of developing a benign uterine tumor (leiomyoma) and endometriosis also increases.
Infertility
Female infertility is one of the most important and pressing problems of modern medicine. And the consequences of an abortion constitute one of the leading positions in its structure. The causes of infertility directly related to the abortion procedure are:
- Obstruction of the fallopian tubes as a result of adhesions in the pelvis (as a result of an inflammatory process or endometriosis).
- Structural changes in the endometrium that prevent the normal attachment (implantation) of a fertilized egg. This is caused by inflammatory damage to the endometrium (endometritis), adhesions in the uterine cavity, and cicatricial changes in the uterine mucosa.
- Hormonal imbalance with the subsequent formation of an anovulatory menstrual cycle (normal maturation of the egg does not occur). It may also produce insufficient amounts of hormones necessary to support the further course of pregnancy.
Often such changes are structural and sometimes cannot be treated.
Pathology of subsequent pregnancy
A previous abortion can also be an obstacle to the further normal course of an already desired pregnancy. Even if conception has occurred, there is a high risk for abnormal attachment of the fertilized egg with subsequent development of an ectopic pregnancy.
In case of normal implantation, the following complications may occur:
- Miscarriage, which in most cases is directly related to a previous abortion. There may be several factors for this pathology: hormonal disorders, disruption of the normal structure of the cervix and endometrium, etc.
- Premature birth.
- Abnormal attachment of the placenta as a result of structural disorders of the endometrium or the presence of adhesions in the uterine cavity.
- Bleeding during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period.
- Weakness or incoordination of labor.
- Fetal hypoxia, etc.
According to statistics, after one abortion, the risk of terminating a subsequent pregnancy increases by a quarter, and after three or more, almost half of pregnant women experience spontaneous abortion.
Cervical rupture
Perforation of the uterine wall is possible when performing manipulations with surgical instruments. During pregnancy, the walls of the uterus soften, thin out and become loose, which increases the possibility of damage.
Traumatic injury to the cervix occurs when the cervical canal is dilated with Hegar dilators. This subsequently leads to isthmicocervical insufficiency and recurrent miscarriage. These conditions are diagnosed by a doctor immediately during surgical manipulation. They require medical or surgical treatment. In case of a life-threatening condition, the uterus is removed with or without appendages.
When a pregnancy is terminated surgically, the cervix is often damaged. So that instruments can freely pass through the cervical canal, it is artificially expanded by introducing special Hegar dilators (the last number of the dilator, which means its thickness corresponds to the gestational age).
Tears, abrasions and ruptures of the cervix are more often associated with the consequences of the first abortion, since the cervical canal has not yet gone through the process of opening during childbirth. Sometimes such tears are so significant that they require suturing of the neck.
When performing an abortion, the cervical canal is forcibly expanded, which performs an obturator function and prevents the penetration of infectious agents into the uterine cavity, both before pregnancy and during gestation, and also keeps the fetus inside the uterus. The longer the gestational age at which the abortion is performed, the larger the diameter of the cervical canal.
As a result, the cervical muscles lose their tone and elasticity, the canal remains slightly open throughout pregnancy, and over time the cervix becomes thinner and shortened (that is, incompetence of it and the isthmus is formed), which is called isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This condition significantly increases the risk of miscarriage and intrauterine infection of the fetus.
Also, due to the artificial expansion of the cervical canal, its mucous membrane is easily injured and infected, which predisposes to the development of underlying cervical diseases (cervical erosion, ectropion, cervical dysplasia).
A fairly common complication of conventional surgical abortion. Just as in the case of uterine perforation, primigravidas, women who applied at 9-12 weeks of pregnancy and patients suffering from congenital or acquired deformities of the cervix are at risk.
The consequences depend both on the nature of the damage and on the quality of treatment: cicatricial deformities, cervical inversion, cervicovaginal fistula. Often, in subsequent pregnancies, cervical insufficiency develops, leading to miscarriage.
How to avoid. In cases where conventional surgical abortion has no alternatives, it is best to contact a medical institution for termination of pregnancy, where the WHO regulations on preliminary preparation of the cervix before abortion are observed (the risk of cervical trauma with this technique is much lower).
Abortion - types
Before terminating a pregnancy, doctors talk with the patient about the possible negative consequences of the manipulation. Many people have difficulty conceiving after an abortion. After making the final decision, the girl needs to contact the antenatal clinic, where she can get information about the existing types of abortion operations and the timing of their implementation.
In gynecological practice, several methods of abortion are used. When choosing a specific one, doctors are guided by the duration of pregnancy, the age of the patient, and take into account the presence of pregnancies in the past. Among the existing methods:
- medical termination of pregnancy - involves taking drugs that cause the death of the embryo and its expulsion from the uterine cavity;
- mini-abortion (vacuum aspiration) – carried out using a special tool, the operating principle of which is similar to a vacuum cleaner;
- surgical abortion (curettage) – the uterine cavity is cleaned with special instruments.
Abortion pills
When a medical abortion is performed, the drugs used during manipulation cause the death of the fertilized egg, which then comes out. The procedure is performed exclusively for short periods of time, with small embryo sizes. Talking about how a medical abortion occurs, it must be said that its effectiveness is 98%. It is carried out in medical institutions, under the supervision of doctors. At the first stage, they are offered to take a drug that causes the death of the embryo, after which a drug that expels the embryo (Mifeprestone and Misoprostol).
Mini abortion
Vacuum aspiration, another name for mini-abortion, is a surgical method of terminating gestation. Conducted for short periods of time. The operation lasts no more than 10 minutes. Using a special aspirator with a tip, doctors suction the fertilized egg from the uterine cavity. This is done by creating a vacuum. Due to the lack of a strong connection between the embryo and the uterine wall, detachment occurs easily. The disadvantage of this method is the possibility of incomplete removal of fetal tissue from the uterine cavity. As a result, there is a risk of infection of the uterus.
Medical abortion
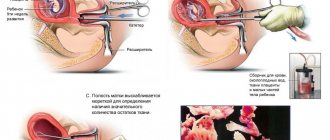
This type of termination of pregnancy is used at later stages, when the embryo cannot leave the uterine cavity on its own (due to its size). The operation is performed using anesthetics. When talking about how this type of abortion occurs, doctors draw patients’ attention to its similarity to conventional surgery on the reproductive system. After installing the gynecological speculum, the cervix is dilated. Having gained access to the uterine cavity, a curette is used to perform a complete curettage - removal of the fertilized egg along with the endometrium.
Termination of pregnancy - artificial birth
Speaking about how late-term abortion occurs, doctors note that it is not possible to carry out the procedure at the sole request of the pregnant woman. To carry out such manipulation, compelling reasons are required. The choice of technique depends on the woman’s condition, the presence or absence of chronic diseases. In the absence of contraindications, a special solution (hypertonic sodium chloride) is injected into the amniotic fluid through the cervix, which causes fetal death. At the next stage, drugs that increase uterine contractility are injected into the pregnant woman’s bloodstream.
Termination of pregnancy using folk remedies
Abortion at home is a dangerous, life-threatening procedure. Methods such as a heated bath with mustard powder, visiting a bathhouse, or lifting weights can negatively affect a woman’s health. These manipulations provoke a rush of blood to the pelvic organs. The pressure inside the pelvic vessels increases, uterine contractions are provoked, as a result of which the embryo is expelled.
It must be taken into account that the abortifacient components used cannot always lead to a 100% result. As a result, there is a risk of infectious infection - the areas of embryonic tissue remaining in the uterine cavity begin to fester. The situation requires medical intervention and cleaning of the uterine cavity. In addition, there is a risk of developing uterine bleeding when using traditional abortifacients and methods. Lack of qualified assistance for bleeding can lead to death.
Hematometer
Hematometra is the stagnation and accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity due to its difficult outflow through the cervical canal. Medical abortion, which is far from rightfully considered safe, often has consequences in the form of the development of hematometra. This complication is characterized by:
- sudden cessation of bleeding or a sharp decrease in it
- nagging or aching pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the lower back
- an increase in temperature, sometimes significant, then the appearance of pain in the form of contractions.
Hematometra occurs as a result of spasm of the cervix, which prevents the outflow of blood and due to a disorder in the contractile activity of the uterus, and stagnation of blood in its cavity leads to infection and the development of inflammation, and in severe cases leads to sepsis.
Therapeutic measures consist of prescribing contractile and antispasmodic drugs. If there is no effect, instrumental expansion of the cervical canal with vacuum aspiration or curettage of the contents from the uterus is performed.
Hematometra is the accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity. This complication can develop with any method of termination of pregnancy. Much depends on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body (the cause of the complication is spasms of the cervix due to post-abortion bleeding).
Consequences. In the absence of timely and adequate assistance, suppuration with the development of septic complications or the formation of adhesions in the uterine cavity is possible.
How to avoid. If symptoms of hematometra appear (increasing pain and heaviness in the lower abdomen against the background of suddenly stopping bleeding), consult a doctor immediately.
How to speed up the body's recovery after an abortion?
Rehabilitation after an abortion begins with restoration of the uterus. During this procedure, the inner layer of the organ is rejected, which after a while begins to recover. Endometrial cells, through division, lead to the gradual restoration of the endometrium. Almost simultaneously, there is a release of old cellular structures that were damaged during the abortion.
To speed up the cleaning process, the uterine muscle layer periodically contracts. In this case, the woman may feel a squeezing pain in the lower abdomen. The attacks are of short duration and stop on their own. Doctors do not recommend using strong analgesics, as this may disrupt the recovery process. It is important to monitor your health and if pain increases or new symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
How quickly hormonal levels are restored after an abortion depends on the type of intervention performed. Thus, minimal consequences associated with cycle disruption are observed with medical termination of pregnancy. In most cases, menstrual flow is observed at the right time, according to the established cycle. The next period comes in 28–35 days.
Recovery after vacuum removal occurs within 3–7 months. According to medical observations, this takes 3–4 months for women who have given birth before. In this case, the first cyclic discharge can be observed as early as a month after the procedure. However, they are not abundant, irregular, often painful and may be absent next month. This phenomenon is a variant of the norm: this is how gradual recovery occurs after a vacuum abortion.
The most unpredictable periods are those after a surgical abortion. Due to severe trauma to the endometrium, a woman may notice light bleeding for 3–4 months. This is due to insufficient thickness of the endometrium. Bloody discharge in the first days after an abortion has no connection with menstrual discharge. Recovery from this type of abortion with the resumption of menstruation occurs within a month.
Recovery of the endometrium after an abortion takes 3–4 weeks. At this time, active cell division processes occur in the uterus. The norm is the presence of nagging pain in the lower abdomen, which is caused by contraction of the muscular structures of the uterus. Throughout this period, a woman may observe light, bloody vaginal discharge.
Complete restoration of the body after an abortion consists of returning to the state of the reproductive system that was observed before the abortion: menstruation acquires the same frequency, they are of the same volume and duration. According to doctors, this process can take from 1–3 months to six months. A longer recovery period requires medical supervision.
Women who have undergone an abortion procedure are often interested in the question of how to quickly recover after an abortion. In order to shorten the recovery period, doctors advise adhering to the following rules:
- Sexual intercourse is allowed after the first menstruation.
- It is not recommended to use gels, ointments, or douching.
- You should use pads instead of tampons.
- Avoid sports for a month.
- Take a shower instead of a bath
At the same time, you can take vitamins to recover after an abortion:
- Complivit-anti-stress;
- Vitrum performance;
- Vitrum-super-stress.
Recovery after medical termination of pregnancy occurs quickly and requires virtually no intervention from doctors. After 2–4 weeks, the uterus returns to its previous state and is ready for a new conception. Therefore, an important point to avoid recurrent pregnancy is the use of contraceptives.
The first days after such an termination of pregnancy, a woman needs to remain calm, completely eliminating physical activity. There is a wound surface in the uterus, so you should refrain from baths, saunas and hot baths. After 7-10 days, you need to see a doctor again to examine the uterine cavity using an ultrasound. Quick recovery after a mini-abortion includes physiotherapeutic procedures:
- mud therapy;
- gynecological massage;
- hirudotherapy.
We suggest you read: Bad mood during pregnancy and changes
Recovery after a surgical abortion requires long-term follow-up with a doctor. A woman should completely exclude:
- physical activity (risk of bleeding);
- sexual intercourse.
The main directions of rehabilitation are:
- antibiotic therapy;
- the use of hormonal drugs to normalize the cycle;
- physiotherapy.
Abortion is a serious stress for the body, so after it the menstrual cycle is almost always disrupted. Normally, in a young and healthy woman, menstruation returns after an abortion in about a month. But it often happens that the duration of the cycle lengthens or shortens, and the nature of the discharge also changes. A scant smudge may appear, and this is explained by incomplete restoration of the endometrium after surgery.
If the restoration of the menstrual cycle after an abortion is accompanied by scanty discharge for quite a long time, it is necessary to be examined. This pathological condition can be caused by the following factors:
- Functional failure in the production of hormones by the pituitary gland, ovaries and hypothalamus. This usually occurs after a medical abortion and is associated with taking a large amount of antiprogestin, and therefore hormonal therapy is necessary.
- Mechanical damage to the endometrium or cervix. Trauma to the endometrium in the uterine cavity leads to the formation of adhesions in the pelvis, which are rejected during menstruation.
You should also be wary if the restoration of the cycle after an abortion is accompanied by heavy discharge. They may indicate that endometrial hyperplasia or adenomyosis is developing.
After an abortion, the uterus suffers the most, and it receives quite serious damage when a pregnancy is terminated at a long term. Particularly severe injuries are caused by scraping with instruments.
After termination of pregnancy, the uterus begins to contract and returns to its normal size. But in the place where the fertilized egg was attached, a large wound appears, which takes time to heal.
If everything proceeds without complications, then restoration of the uterus after an abortion lasts about a month and by the beginning of menstruation it usually has its previous size. But if after 2 weeks, during a mandatory examination, the doctor sees that the uterus has enlarged, softened or become painful and all this is accompanied by dark red discharge with a very unpleasant odor, then its inflammation can be assumed.
This condition occurs for the following reasons:
- a poorly performed abortion, resulting in part of the fertilized egg remaining in the uterus;
- introduction of infection;
- activation of latent infection;
- hematometra formation.
In another way, such termination of pregnancy is called hormonal and is carried out in the early stages (up to 6 weeks) using medications that cause spontaneous miscarriage. Such drugs belong to different pharmacological groups and affect the contractile activity of the uterus and the production of hormones that support the course of pregnancy.
To ensure that recovery after a hormonal abortion goes without complications, there are certain rules:
- you need to try to avoid stress, eat right and rest well;
- to reduce pain after an abortion, women take medications, but only after agreeing with their doctor, as they can weaken the immune system;
- a special diet will help saturate the body with vitamins and microelements;
- it is necessary to abstain from sexual activity for a certain time in order to avoid infection and re-pregnancy;
- it is necessary to monitor the peculiarities of the menstrual cycle and the nature of the discharge, and if after 2 months it does not recover, correction of hormonal levels will be required.
If you follow all these recommendations, you can avoid quite serious complications.
Incomplete or failed abortion
Incomplete abortion is the incomplete extraction of the remains of the fertilized egg. In cases where the fertilized egg is rejected from the wall of the uterus, but remains in its cavity, they speak of a failed abortion. Such complications occur most rarely with vacuum aspiration (about 1% of cases). The highest probability of incomplete abortion is with medical termination of pregnancy. The risk increases with increasing gestational age.
Consequences. In the absence of adequate action (uterine curettage; in case of a failed medical abortion, vacuum aspiration is possible), purulent endometritis develops, fraught with septic complications.
How to avoid. When undergoing a medical abortion, you should strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions so as not to reduce the abortive effect of prostaglandins (do not try to relieve pain with drugs containing non-steroidal inflammatory drugs such as baralgin, spasmalgon, paracetamol, etc.; do not smoke more than 10 cigarettes a day ). After an abortion, undergo a control ultrasound within the prescribed time frame.
Consequences of medical abortion
Termination of pregnancy using the specific action of drugs is a relatively new technique. This method of abortion is an alternative to surgery and, if successful, eliminates the risks of invasive intervention.
The effectiveness of this method of abortion is more than 90%. However, complications from medical abortion can sometimes occur. The most common of them include:
- Further progression of pregnancy. This occurs in approximately 2–3% of cases after this manipulation. Given the negative effects of medical abortion drugs on the fetus, such a pregnancy must then be terminated by other means.
- Incomplete expulsion of the fertilized egg. The most common complication after medical termination of pregnancy, developing in 3–7% of cases. There is a high risk of bleeding or inflammation of the uterus and other organs. Surgery is required to completely empty the uterine cavity.
- Bleeding due to impaired contractility of the uterus.
- There are other complications after medical abortion:
- Intense pain during the expulsion of the fertilized egg. Painkillers are often required.
- Side effects of medications used in the abortion procedure: nausea, vomiting, loose stools, allergic reactions.
- Hormonal disorders (for example, irregular menstrual cycle). It occurs more often than after surgical methods, which is due to the specific effect of drugs for abortion.
- Inflammation. It is formed when infection penetrates from the underlying parts of the genital tract into the uterus and appendages. This is facilitated by the presence of a wound surface in the uterine cavity and a decrease in local immunity.
- Psychogenic disorders. They occur in varying degrees of severity in almost every woman who decides to terminate a pregnancy. The effect of medications used in this method of abortion can aggravate the negative manifestations. They manifest themselves as depression, insomnia, anxiety, mood swings, etc.
In order to early identify complications of medical abortion, it is necessary to strictly adhere to medical instructions for the correct use of medications. In addition, it is necessary to visit your doctor within a week after the expulsion of the fertilized egg with ultrasound monitoring.
Failed abortion attempt
When performing a mini-abortion, a frequent consequence is a progressive pregnancy, which in medical language is called an unsuccessful attempt at abortion. This complication most often occurs when the pregnancy is terminated too early, that is, if the delay in menstruation is less than 14 days.
The fertilized egg is still very small in size and the likelihood of its removal during aspiration is very low. In this case, bloody discharge does not last long, and all early signs of pregnancy (engorgement of the mammary glands, toxicosis, etc.) persist. Repeated termination of pregnancy is performed only surgically - curettage of the uterine cavity.
Planning a pregnancy after a vacuum abortion
Vacuum aspiration is a surgical, but at the same time gentle and safe method of terminating a pregnancy. You can plan a pregnancy after a vacuum abortion no earlier than six months after the procedure. During this period, hormonal levels and the menstrual cycle should be restored, and the female body should return to normal.
Many women are concerned about whether they will be able to have children after an abortion. This is quite likely even before the menstrual cycle returns. After this procedure, the body is able to quickly readjust itself, returning to its normal rhythm. In preparation for a new menstruation, the ovaries begin to produce progesterone and estrogens, promoting ovulation.
You should plan a further pregnancy no earlier than after 6 months, or even after a year. This time will be sufficient for the body to recover, and the likelihood of complications will be significantly reduced.
Infectious complications
Infectious complications, such as endometritis, purulent inflammation of the uterine appendages, peritonitis and blood poisoning, can result from any method of termination of pregnancy. The greatest risk is posed by conventional surgical abortion (the development of endometritis is observed in 5% of cases, purulent inflammation of the appendages - in 3% of cases), with vacuum aspiration such complications are almost half as common.
The least dangerous in this regard is medical abortion (about 1% of cases).
Consequences. Sepsis can lead to extremely severe complications, including death. With purulent inflammation of the uterine appendages, it is often necessary to resort to their removal. Even with successful treatment of acute endometritis, long-term consequences such as chronic inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, infertility, and a high risk of developing ectopic pregnancy are quite common.
How to avoid. If there are indications, before an abortion, especially a surgical one, undergo a course of anti-infective therapy. If symptoms of infectious complications develop (most often develop on the second to fourth day after an abortion), such as nagging pain in the lower abdomen, fever, change in the nature of vaginal discharge (the appearance of pus or an unpleasant odor), immediately seek medical help. After an abortion, undergo a course of treatment for vaginal dysbiosis.
The most dangerous post-abortion consequences
There are many consequences of abortion, but some of them can be identified as the most dangerous.
- Abortion often provokes the development of inflammatory lesions, which cause infertility. Typically, infertility develops against the background of tubal obstruction, although it happens that problems with conception arise against the background of damage to the uterine body with surgical instruments. Moreover, most often infertility is caused by abortions that were performed during the first pregnancy.
- Dangerous post-abortion consequences also include an increased likelihood of developing cancer pathologies. Hormonal imbalance caused by abortion increases the likelihood of developing cancer of the cervix or cervical canal, abdominal cavity or thyroid gland. Proof of this is the fact that girls who experienced an abortion before the age of 18, the likelihood of developing breast cancer increases by 150%.
Particularly dangerous in this regard are criminal interruptions, which, as a rule, are carried out illegally and by people who are far from qualified as an obstetrician-gynecologist. After such abortions, death is quite common.
Causal factors of post-abortion inflammation
An inflammatory process in the uterine cavity after an induced abortion almost always occurs, but in most cases, against the background of preventive treatment, the classic manifestations of the disease can be avoided. The main causative factors of endometritis are:
- traumatic damage to all layers of the endometrium during curettage;
- retention of parts of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity;
- accumulation of blood clots;
- penetration of microbes from the vagina and cervical canal.
The combination of all these factors leads to the formation of inflammation: for microorganisms, the remains of the fertilized egg and blood clots are an excellent nutrient medium on which dangerous microbes quickly grow and multiply, forming a rapidly progressing infectious process.
Contributing factors to post-abortion endometritis include:
- gynecological infections (vulvitis, bartholinitis, colpitis, cervicitis, bacterial vaginosis);
- weakened immune defense;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- blood loss during surgery;
- general diseases (anemia, chronic foci of infection, endocrine pathology).
An extremely negative type of post-abortion complication is the remains of fetal tissue, in which it is necessary to perform repeated curettage of the uterus. Double trauma is the main factor leading to damage to the basal layer of the endometrium and the formation of recurrent chronic endometritis.
The inflammatory process in the uterus after termination of pregnancy can manifest itself as acute symptoms in the first days after surgery or cause a delayed reaction that occurs only a few days later. Depending on the time factor and severity of manifestations, the following are distinguished:
- classic version of post-abortion endometritis;
- abortive form;
- erased type of inflammation.
Vivid classic manifestations occur in cases where there are remnants of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. Most often, a low-symptomatic, erased variant occurs, in which the risk of developing chronic endometritis is maximum.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gTrj5v2L1vA
The most common complication after an abortion is the development of inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs (in 20% of cases of all induced abortions). Due to the destruction of the mucous plug of the cervical canal during manipulation, microorganisms from the vagina (both pathogens and opportunistic pathogens) freely penetrate into the uterine cavity, resulting in the development of:
- endometritis
- metroendometritis
- inflammation of the appendages and periuterine tissue
- in extremely severe cases, inflammation of the peritoneum, rectum, and bladder.
The process is accompanied by:
- temperature rise
- the occurrence of pain in the lower abdomen (their nature varies, it can be nagging or aching pain or very sharp and intense)
- signs of intoxication (weakness, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea and vomiting)
- purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor.
In the absence of timely treatment, sepsis develops, which can cause the patient’s death. Massive antibiotic therapy, intravenous infusions of solutions, and cold application to the abdomen are prescribed. In case of development of peritonitis against the background of uterine pyometra, parametritis or pyosalpinx, surgical removal of the uterus and/or appendages is resorted to.
Recovery period
The rehabilitation period after abortion begins with the prevention of inflammation, for which antibiotic drugs are prescribed. To restore hormonal status, oral contraceptives are prescribed. In general, after an abortion, especially a long-term abortion, drugs like Doxycycline and Metronidazole, Fluconazole, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory drugs, vitamins and oral contraception are used.
After an interruption, the body is especially sensitive to various infections, so experts recommend that mothers pay attention to their diet and proper nutrition. To normalize hormonal imbalance, the patient is prescribed a protein diet with vitamins. Depending on the diet, dishes are selected that help you recover faster.
https://youtu.be/lwLaaIDtJqk
To prevent abortion, the use of contraception is recommended, since today the choice of such means is quite extensive. Comprehensive information is needed about what consequences a girl can expect after abortion, why it is dangerous, and other information and educational work among adolescents.
Abortion and endometriosis
– a severe systemic disease characterized by pathological proliferation of the functioning uterine epithelium beyond its normal location. The greatest risk is posed by conventional surgical abortion, due to increased trauma to the uterus against the background of hormonal imbalance caused by termination of pregnancy. The degree of risk of developing endometriosis in the case of medical termination of pregnancy and vacuum aspiration has not been fully studied (there is no exact data).
Consequences: extremely heavy menstrual bleeding, pain during sexual intercourse, the formation of endometrioid ovarian cysts with the transition of the process to the peritoneum and the development of adhesions, infertility. When the process generalizes, the uterine endothelium can settle in distant organs and tissues.
How to avoid: to prevent endometriosis, it is traditionally recommended to use combined oral contraceptives for 12 months (if there are no contraindications).
Termination of pregnancy causes an exacerbation of the disease in women suffering from endometriosis. The method of termination of pregnancy in this case does not matter much, since the exacerbation is a reaction to hormonal changes in the body, which are inevitable.
The fact is that at one time endometriosis was considered a medical contraindication to continuing pregnancy. The practice of performing abortions in women suffering from this disease has shown that abortion aggravates the course of the disease, and pregnancy, on the contrary, leads to remission.
Consequences. They depend mainly on the form and type of course of the disease. With extragenital forms, pulmonary and gastrointestinal bleeding with a fatal outcome is possible.
What to console yourself with. As a rule, endometriosis heals on its own with the onset of menopause.
Medical indications for abortion
There are situations when doctors do not dissuade their patients from having an abortion, but, on the contrary, insist on having it. Most often they do this when a woman has a disease that is incompatible with bearing a child. Otherwise, the operation could cost her not only her health, but also her life.
When an interruption is necessary and can be done:
- with diabetes mellitus with kidney damage;
- for acute leukemia and severe blood diseases;
- for chronic kidney and liver damage;
- for neuroinfections;
- in severe forms of hypertension and heart failure;
- with organic lesions of the muscles and valves of the heart;
- for drug addiction;
- with severe mental manifestations.
Thrombophlebitis and thrombosis
If a woman has a pathology of the blood coagulation system, then artificial termination of pregnancy, especially in the period of 10–12 weeks, contributes to the excessive formation of blood clots in the uterine vessels, which can break away from the vascular wall, penetrate into the general bloodstream and disrupt the blood supply in any organ and place.
Most often, the blood clot enters the lower extremities, which causes blockage and inflammation of the vein (thrombosis and thrombophlebitis). But if a blood clot enters the pulmonary artery system, an extremely dangerous condition occurs - pulmonary embolism, with an extremely high mortality rate.
With the development of thrombosis and/or thrombophlebitis, bed rest, thrombolytic (streptokinase, etc.) and antithrombotic (heparin, trental, chimes) therapy are prescribed.
Effect on subsequent pregnancies
There are three types of abortion, which occur at different times.
Types of termination of pregnancy:
- Drug. This is the termination of an unwanted pregnancy, the duration of which does not exceed six months. It will not require surgery. This method is the most common.
- General surgery. It is the removal of the fetus from the uterine cavity. It is performed until the 12th week. There are cases of termination due to illness, developmental abnormalities of the unborn baby, as well as pregnancy resulting from rape.
- Vacuum. The safest type of fetal expulsion. It is usually performed at 4-6 weeks of pregnancy. It is also allowed to cleanse from the seventh to 12th week.
During pregnancy, hormonal imbalance occurs. Therefore, after expulsion, a significant restructuring of the entire organism occurs. This can cause quite a lot of problems.
After cleaning, a wound cavity appears in the uterus, which is open to bacteria. Infection can cause inflammation of the appendages. Unfortunately, sometimes women can no longer have children after an abortion.
Effects of various types of abortion on the body:
- One of the threats of medical abortion is often a malfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. Acne may occur, which is quite common. Metabolic diseases such as obesity and cellulite begin.
- Different outcomes may occur after general surgical expulsion. One of them is damage to the cervix. In addition, surgical intervention can cause a rapidly developing infectious disease.
- After vacuum aspiration, there is a threat of convulsive syndrome, and intense changes in body temperature are recorded.
If the abortion proceeds with complications, then this may come back to haunt the woman with an unfavorable course of the subsequent desired pregnancy.
- Firstly, in patients with inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs and adhesions in the pelvis, an ectopic pregnancy may occur after a complicated abortion. This happens because the fallopian tubes, as a result of inflammation, become tortuous, swollen, with kinks due to adjacent adhesions, and the movement of the egg through them is difficult.
- If a fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity with chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane after an abortion, it may not fully attach to the wall of the uterus. This leads to missed abortion or bleeding and pregnancy loss. If the pregnancy takes root and develops further, then the placenta, attached to the defective wall of the uterus, may be thin and not provide nutritional function; ultrasound may describe oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, and the child’s growth retardation.
- If a woman’s abortion was complicated by perforation of the uterine wall, she now has a scar on the uterus. During pregnancy and childbirth, some scars on the uterus are incompetent (this is rare, but uterine rupture due to an incompetent scar does occur in late pregnancy and childbirth).
- If during an abortion the dilatation of the cervix was carried out traumatically, then during the next desired pregnancy, cervical insufficiency (isthmic-cervical insufficiency) may appear. This is clinically manifested by signs of threatened miscarriage, premature dilatation of the cervix, and may result in miscarriage. Sometimes during pregnancy, cervical insufficiency must be corrected by applying a suture or installing a relief pessary.
- If a patient with an Rh-negative blood group has an abortion from an Rh-positive partner, then Rh incompatibility with the unborn child may occur in her body during the next pregnancy. To prevent this complication, it is recommended that Rh-negative women always receive a dose of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin during an abortion.
Problems that arise during subsequent pregnancies
How to avoid. Seek help from a specialist in a timely manner (
, psychiatrist, narcologist).
Abortion is one of the most common surgical operations in gynecology. A woman can terminate an unwanted pregnancy in the 1st trimester (up to 12 weeks) in a medical facility in the following ways:
- medical “velvet” abortion, in which in the early stages (up to 5 weeks) you need to take hormonal pills according to a special regimen prescribed by your doctor;
- vacuum aspiration (use of suction to remove the embryo up to 6 weeks);
- curettage of the uterus to remove pregnancy, used in all cases of termination of pregnancy between 6 and 14 weeks (artificial or spontaneous abortion);
- late termination of pregnancy for medical reasons (congenital pathology of the fetus or diseases of the mother, in which, during pregnancy, a real threat to the woman’s life arises).
Each subsequent abortion increases the chances of developing gestational complications if a woman wishes to carry the pregnancy to term and give birth to a child. If there was 1 abortion in the history, then the threat of termination of pregnancy is observed in 26%, after 2 abortions the risk increases to 32%, and with more than half of the cases there is a threat or spontaneous termination.
In addition, it is extremely undesirable for women who have Rh-negative blood to undergo such manipulation (see Rh-conflict during pregnancy). With each new pregnancy, including those that were artificially terminated, the woman’s immune system begins to produce antibodies against fetal red blood cells in greater and greater quantities, which leads to miscarriage or premature birth, the development of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn in the case of pregnancy.
To prevent the development of Rh conflict, it is necessary to administer human anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin D to the woman before an abortion.
Why are second and subsequent abortions dangerous?
The second abortion is a phenomenon of stupidity and lack of culture in sexual life. Having had her first abortion, a woman must draw conclusions so as to never resort to this harmful operation again. Using contraceptives and monitoring your menstrual cycle are simple rules on how to avoid getting an unwanted pregnancy.
The second abortion, like the first and all subsequent ones, is best performed using medication. As before, this will reduce the risk of complications and adverse effects. A second surgical abortion is even more dangerous than the first abortion. Regardless of the number of abortions, the more there are, the more a woman’s health worsens. Therefore, if you were unable to have a second abortion in the early stages of pregnancy (up to 7 weeks), you should not terminate the pregnancy at all.
In this video, the chief physician of the perinatal center, Lyudmila Nikitina, talks about the possible consequences of an abortion on the female body.
Placental polyp
A placental polyp is a small area of placental tissue that has remained in the uterus either after termination of pregnancy or after childbirth, but has retained nutrition (that is, its blood vessels communicate with the wall of the uterus) and has undergone fibrosis. Over time, more and more blood clots settle on the placental polyp. A polyp appears^
- prolonged spotting
- periodically alternating with uterine bleeding
- if this formation exists for a long time, weakness, lethargy, pale skin, dizziness and other signs of anemia occur.
Treatment for this consequence of abortion involves hysteroscopy and subsequent curettage of the uterine cavity.
Possible complications
Medical termination of pregnancy is considered the safest, but it also carries risks.
- uterine bleeding requiring instrumental evacuation of the uterus in a hospital (vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity) and the use of uterine contractions;
- incomplete abortion (remnants of the fertilized egg are also removed using vacuum aspiration of the uterine cavity in a hospital);
- infectious complications (the risk of their development is less than 1% of cases);
- progression of pregnancy in a situation where rejection of the fertilized egg has not occurred.
Endocrine disorders
Abortion is a forced termination of pregnancy, during which significant hormonal changes in the body occur. Therefore, artificial termination of pregnancy for him is nothing more than a biological trauma. The sudden removal of the fertilized egg leads to a cessation of the production of pregnancy hormones; the ovaries, pituitary gland and adrenal glands do not have time to adjust to a new rhythm of work. As a result:
- failure to resume the normal menstrual cycle
- ovarian dysfunction
- in some cases, hormonal gynecological diseases develop: uterine fibroids, adenomyosis, endometrial hyperplastic processes, polycystic ovaries and others.
- in addition, when curettage of the endometrium during an abortion, its deep layers (basal) may be affected, as a result of which the uterine mucosa grows unevenly by the new menstrual cycle. Therefore, menstruation can become either scanty or heavy (see scanty periods, causes of heavy periods).
- due to injury to the basal layer, the growth of the functional layer (the one that is torn off during menstruation) may be delayed, that is, the menstrual cycle is lengthened.
In connection with the above, the first abortion is especially dangerous. For information on what is and is not possible after an abortion, see rehabilitation after an abortion.
Artificial termination of pregnancy also affects the functioning of the endocrine glands, which can only appear several years after the abortion. It is known that not only the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and ovaries, but also the adrenal glands, thyroid gland and cerebral cortex are involved in the regulation of the menstrual cycle.
- The clinical picture of dysfunction of the central nervous system manifests itself in the form of cerebroasthenia (irritability, fatigue, emotional lability and drowsiness).
- Disorders in the functioning of the endocrine glands also affect sexual life (decreased or loss of sexual desire, anorgasmia).
- They also trigger the development of diseases of the thyroid gland, mammary glands (up to the development of breast cancer), adrenal glands (read about adrenal insufficiency), etc.
Impact on a woman’s body
As soon as a woman decides to terminate her pregnancy for one reason or another, turning points occur in her life that greatly affect the mental subconscious.
If a woman is in an official or civil marriage, then it is a little easier for her. But even here there are pitfalls: not all couples can maintain their relationship at the same level and most of them break up. If the couple remains, then the partners feel latent guilt for what they have done for a long time and can plunge deeply into an emotional crisis.
But the woman who lives alone is most vulnerable. In addition to public criticism (most often silent), she will constantly struggle with her own conscience. And it is especially difficult for those who truly believe in God and reject any violence.
Abortion and Rh negative factor
Abortion reduces the likelihood of having a healthy child in Rh-negative women if they become pregnant with an Rh-positive partner.
Consequences. Hemolytic disease of newborns is an extremely serious disease, often leading to mental and physical disability of the child.
How to avoid. Prophylactic administration of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin within 72 hours after an abortion significantly reduces (although does not completely eliminate) the risk of having a sick child.
What to console yourself with. In order to completely eliminate the risk of having a child suffering from hemolytic disease of the newborn, it is enough to choose an Rh-negative partner (men with a negative Rh factor make up 15% of the male population of the Earth).
General recommendations
In order for recovery after an abortion to be successful and without complications, it is necessary to abstain from sexual activity for 3 weeks.
Sexual incontinence after surgery is very dangerous, as there is a high probability of various complications, such as rejection of the uterine lining or bleeding. This is caused by an infection that enters the body during sexual intercourse. Physical health usually takes 2 weeks to recover after an abortion, and during this period exercise is contraindicated. This is necessary to ensure that the abdominal muscles are at rest. Lifting heavy objects is also prohibited. Successful physical recovery reduces the risk of complications.
https://youtu.be/uFH6oIF2EqY
In order to protect against infection or bacteria entering the body, it is necessary to refrain from swimming in a bathtub, pool or open water for a while.
An important factor after the procedure is proper nutrition. Abortion is a great stress for the body, so you should saturate it with microelements and vitamins, as well as fiber and proteins. It is also necessary to periodically measure body temperature, pulse, and blood pressure. Any deviation of the body from the normal state indicates the beginning of complications, so you should visit a doctor as soon as possible.
Quite often, recovery of the body after an abortion requires taking antibiotics. In this case, you should not drink alcohol.
Asherman's syndrome
Asherman's syndrome is a partial or complete occlusion of the uterine cavity as a result of the formation of intrauterine synechiae (adhesions) in it. Intrauterine synechiae occur due to damage to the basal layer of the uterine mucosa and the development of an inflammatory process in it.
Asherman's syndrome manifests itself as scanty menstruation or its absence for 6 or more months, pain and infertility, and if pregnancy occurs, miscarriage. Treatment consists of hysteroscopic dissection of adhesions followed by the administration of hormones (estrogens and gestagens) according to the phases of the menstrual cycle to restore the cyclic transformation of the endometrium.
More than half of women who voluntarily undergo an abortion procedure develop post-abortion syndrome. Its symptoms may not appear immediately, but may appear years after the operation. Its manifestations include:
- depression and guilt;
- personality changes;
- melancholy and resentment towards oneself, partner, loved ones, doctor, circumstances, etc., which forced the woman to terminate the pregnancy.
A woman who has had an abortion becomes too intolerant of people, aggressive, cannot look at pregnant women and children without tears, or cannot tolerate their presence. In most cases, abortion causes the breakdown of marriage/relationships between partners; not only disharmony in sexual relationships develops, but also distrust and aggression towards one’s partner in particular and towards men in general.
To suppress feelings of guilt, a woman can throw herself into work, actively engage in social affairs, or resort to relief in the form of alcohol and drugs. Constant self-examination and accusations against her turn a former abortion client into an unbalanced and hysterical person, which also affects the woman’s physical health.
Treatment of post-abortion syndrome is a difficult task and consists not only of the help of a psychologist, and sometimes a psychiatrist, but also of turning to the church and God.
Use of contraception
To avoid unwanted pregnancy after an abortion, it is necessary to choose the right means of contraception. The best option is the use of tablets, which, among other things, eliminate the consequences of hormonal imbalance and protect against endocrine disorders. Thanks to birth control pills, the risk of inflammatory processes is sharply reduced. In addition, these contraceptives help:
- reducing the amount of blood released, which can become a source of development of pathogenic microflora;
- reducing the activity of uterine contractions, so that pathogens cannot penetrate from the uterine cavity into the tubes;
- thickening of cervical mucus, which serves as an obstacle to infection.
https://youtu.be/yy9nLRu0_FE
The most effective are considered to be tablets containing a small amount of hormones, since the estrogens included in the drug help increase blood clotting.
Material, psychological and social reasons for abortion
As can be seen from everything written above, there are many medical causes of abortion. However, those parents who dream of a child often continue to fight for his life even at the stage of intrauterine development. And those to whom God gave a healthy and full-fledged child often simply do not want to have one and in any case will find a reason for the abortion and justify it.
It also happens that married couples, where the spouses sincerely love each other, still resort to abortion, explaining this by an unstable financial situation and not wanting their potential baby to have the same penniless and joyless future.
Often, women who have already given birth to one child, soon becoming pregnant, have an abortion because they are not able to bear two children. Unfortunately, in modern realities this is not uncommon. Young mothers strive to finish breastfeeding as quickly as possible and start working somewhere to help their spouse feed their family a little.
Social reasons for abortion include inappropriate age for childbearing, poor financial situation, a woman’s intention to make a career or get an education, the absence of any relationship with the biological father of the unborn child, the presence and number of other children, emotional instability, relationships with parents, religious beliefs.
In modern times, the cause of abortion is often simple ignorance of the rules of contraception. Social reasons for abortion also include pregnancy due to rape or incest.
Basic principles of diagnosis
During a gynecological examination, the doctor will immediately pay attention to the following signs of endometritis:
- increase in the size of the uterus;
- softness and shapelessness of the organ when manually palpated;
- pain on palpation;
- unpleasant-looking bloody-purulent discharge.
To confirm a preliminary diagnosis, the following studies must be performed:
- undergo general clinical tests (there will be signs of inflammation in the blood - high white blood cells, accelerated ESR);
- do an ultrasound (during the scan, a specialist will see the remains of the fertilized egg, blood clots and signs of acute inflammation in the uterine cavity).
https://youtu.be/ht1Mavlmosg
Having made an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will immediately prescribe effective treatment. If indicated, surgical intervention may be required.
Partner pressure
Women in Russia do not make hasty and completely independent decisions regarding their pregnancy - 60% of abortions were discussed with their partner. At the same time, a significant proportion of interruptions were the result of a partner’s contraceptive sabotage, which in some countries is equated to a criminal offense in the category of sexual violence.
Such cases significantly undermine faith in the use of contraception, which is why women in Russia resort to sterilization at will - as soon as they have the opportunity to do it legally. At the moment, this is only allowed if you have at least two children or reach 35 years of age.
Intraoperative problems
Regardless of the chosen method of artificial termination of an unwanted pregnancy, the following complications may occur during surgery:
- injuries and ruptures in the cervical canal area;
- uterine bleeding;
- perforation of the uterine wall with the need for wound suturing.
Some problems can be solved by surgery, but in some situations it is necessary to perform extensive surgical interventions, the purpose of which is to save the woman’s life. Almost always, intraoperative complications affect reproductive function, leading to infertility or the inability to carry future desired pregnancies.
Contraception methods
The most convenient ones after an abortion will be combined oral contraceptives (COCs), or their non-tablet analogues. When using COCs, a woman’s body will maintain a constant hormonal level without fluctuations, so the ovaries and mammary glands will be in a “resting state” (that is, cysts will not appear in them). The uterine lining will also regenerate under protected conditions.
Important! In no case is it recommended to protect yourself with disposable emergency contraception after unprotected sexual intercourse (for example, the drug “postinor” or “escapelle”).
Such drugs contain hormones in large doses; they will also be stressful for the body and can provoke endocrine function disorders. Many women with irregular sex life use emergency contraception several times a year, and then end up with an unbalanced hormonal system, excess weight and menstrual irregularities.
For permanent contraception, it is also possible to use a condom and an intrauterine device. But for reliable results when using condoms, discipline of both partners is needed, in addition, buying high-quality condoms is now more expensive than a package of COCs.
The intrauterine device is a capricious method of contraception; it is not suitable for all women, and is not recommended for use at all in patients at risk of inflammatory diseases. On the other hand, this is a budget-friendly, cheap contraceptive option.
After an abortion, contraception is very important. Regardless of whether the pregnancy was unwanted or the abortion was performed for medical reasons, it is not recommended for a woman to become pregnant for the next six months. Often, post-abortion treatment includes taking combined oral contraceptives (COCs):
- Novinet;
- Yarina;
- Regulon;
- Fewa;
- Femoden.
The pills begin to be taken in the first days after the abortion, but no later than the fifth day. If treatment is started immediately, additional contraception is not needed. If there is a long delay, it is necessary to use a condom during the first 7 days from the start of sexual activity.
Contraceptives effectively prevent the onset of unwanted pregnancy (subject to compliance with the dosage regimen).
Another advantage is the normalization of the menstrual cycle, which may be unstable after an abortion. The danger of irregular and breakthrough bleeding is eliminated, cervical mucus thickens and ovulation temporarily stops. These processes have a beneficial effect on women's health during treatment after an abortion.
Hormones increase blood clotting, which is not always desirable immediately after an abortion. Depending on the patient’s health condition, the doctor will select medications with minimal dosages and a delicate load on the body.
In addition to the main effect, modern COCs also have additional advantages:
- reduction of pain during menstruation;
- reducing the amount of blood loss;
- prevention of edema;
- reduction of skin problems (irritation, acne).
Treatment after an abortion in the form of taking COCs for a healthy woman is carried out for three months. If you do not want another pregnancy, continue taking it.
Typical symptoms of the disease
The classic form of post-abortion endometritis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- high temperature with wave-like chills;
- cardiopalmus;
- abdominal pain (from pressing to cramping);
- purulent-bloody vaginal discharge.
All symptoms occur 1–3 days after the abortion and last for at least 10 days. It is extremely important to consult a doctor promptly when typical symptoms appear in order to begin treatment and prevent the possibility of dangerous complications.
https://youtu.be/nxQiz9Ijv1I
The abortive version of endometritis manifests itself with standard symptoms, but all symptoms subside by 4–5 days of the post-abortion period. This type of complication is rare, but may be a reason to refuse a full course of antibacterial treatment.
The erased form is characterized by the following features:
- the increase in body temperature does not exceed 38 °C;
- pain in the lower abdomen is insignificant;
- bloody-purulent vaginal discharge is scanty.
A woman may ignore scanty or minimal manifestations of the disease without consulting a doctor, which will be the main reason for the development of post-abortion endometritis.
Rehabilitation
After an abortion, many women experience remorse, even if before the operation they were completely confident in their decision. Often, a bad mood and depressed state develops into prolonged depression with attacks of aggression.
The patient suffers from nightmares and sudden mood swings. In part, such changes may be caused by hormonal fluctuations (as with PMS). But they also gradually disappear as a result of proper treatment of the consequences of abortion.
Even if not all loved ones agree with abortion, it is necessary to provide the woman with every support and understanding. Constant reproaches will no longer be able to change the situation, and it is quite easy to irreversibly worsen the quality of life.
If you cannot cope with psychological problems on your own, you can consult a psychologist or attend a group meeting. You shouldn’t blame yourself for what happened for the rest of your life; it’s better to take all possible measures to prevent the situation from happening again.
A change of environment helps restore inner balance. You can go on vacation or sign up for a massage course. Magnetic therapy, acupuncture or spa treatments give good results.
The length of the recovery period is influenced by the woman’s age, her state of health, the number of previous abortions and the presence of children. Abortion is easier for healthy young women who already have children.
Medical rehabilitation involves providing rest to the female reproductive system, which has suffered a hormonal explosion due to artificial termination of pregnancy. Due to changes in hormones, the menstrual cycle may not be restored, and cysts often appear in the ovaries and mammary glands.
For at least six months, there should be no next (wanted or unwanted) pregnancy, and there should be no sharp fluctuations in the woman’s hormonal levels. A woman must understand that the next abortion will worsen the hormonal imbalance in the body. You need to provide yourself with a reliable means of contraception.
If the abortion is complicated by an inflammatory process, then the period of rehabilitation and recovery should additionally include measures to restore normal microflora in the vagina, physiotherapeutic methods of prevention and resorption of adhesions of the internal genital organs.
The woman is prescribed electrophoresis on the lower abdomen with anti-inflammatory drugs, sanatorium treatment, hirudotherapy, laser irradiation and ultraviolet irradiation of the blood, enzyme preparations to reduce the severity of the adhesive process.
Another important component of recovery is psychological rehabilitation. Women may develop depression, feelings of guilt, and impaired sexual function. Therefore, in many cases, the help of psychologists is recommended.
The path to recovery is not only about medications, but also about your inner attitude, which also affects the recovery process. In combination with a balanced diet, this will help you gain strength and return to a full life.
All women need therapy after cleansing, which lasts two weeks. This period is necessary in order to eliminate the likelihood of inflammation or infertility.
To restore the functioning of the immune system, it is necessary to undergo therapy with injections and droppers. In the middle of the second month, rehabilitation occurs at home, in the form of taking medications as prescribed by a doctor.
Not all girls know what to drink after an abortion, so consultation with a specialist is necessary. Doctors prescribe additional pills to improve the overall condition. For the purpose of effective recovery, it is recommended to take vitamin supplements as additional treatment.
To avoid a secondary pregnancy, it is necessary to use oral contraceptives. Novinet and Regulon are the most popular means that provide a 100% guarantee of protection against unplanned pregnancy.
After interruption, pain can be permanent or temporary. To relieve pain, you can take Ibuprofen.
Folk remedies
Not all representatives of the fairer sex trust pharmaceutical drugs, so they choose traditional medicine.
Herbs have healing properties and effectively help to recover after abortion:
- Often women use tincture of boron uterus. It will help regulate the menstrual cycle, eliminate inflammatory processes, and improve the genitourinary system.
- A decoction of red brush is also an excellent remedy after an interruption. It is used for prophylaxis to avoid infections and the development of tumors in the genitals.
- Acacia will help to cope with hormonal imbalances, which greatly affect a girl’s behavior. Infusion and decoction of flowers relieve pain in the lower abdomen.
We suggest you read: Benign tumors of the skin of the eyelids
Consequences of abortion: how to restore hormonal levels
An abortion performed in a medical facility is always accompanied by measures aimed at minimizing the consequences of the intervention. The doctor observes the woman immediately after the procedure, as well as for 1-3 months after.
The most effective method of restoring hormonal levels after an abortion is taking combined oral contraceptives (COCs). Low-dose monophasic drugs are recommended by WHO not only for the prevention of infections and inflammations, but also to prevent new unwanted pregnancies.
In a young healthy woman with a favorable outcome of abortion, the next ovulation occurs 10-11 days after termination of pregnancy. Therefore, progestin analogues (steroidal female sex hormones) should be started on the 1st day after surgery, take a 21-day course, take a week's break and again take the COC for a 21-day course.
Combined contraceptives, in addition to restoring hormonal levels, stop and prevent inflammatory processes in the uterus and ovaries. Medical abortion can cause severe uterine bleeding.
Under the influence of Mefipristone, the tone of the uterus weakens, and the production of cortisol, which is responsible for the contraction of blood vessels, is blocked. This causes severe bleeding, a decrease in the body's defenses, loss of strength, etc.
The uterus contracts poorly, which causes cervical spasm, and blood is retained inside, causing inflammation. Thanks to PDA, the walls of blood vessels are strengthened, the uterine muscle becomes elastic, and the volume of outgoing blood decreases. Due to this, the cervical canal narrows and uterine bleeding is reduced.
We suggest you read: Inflammation of the epididymis in men, treatment
After expulsion of the fertilized egg, even with medical abortion, a wound remains on the inner surface of the uterus, which becomes a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria and microbes. Thanks to the use of low-dose contraceptives, the amount of blood lost is reduced, and, accordingly, bacteria lose the nutrient medium necessary for reproduction.
After a sharp drop in estrogen levels, cervical mucus becomes loose in consistency and easily allows pathogenic microorganisms to pass through. When estrogen is normalized under the influence of PDA, the cervical mucus thickens and prevents infection from entering the uterus.
Contraceptives remove the effect of prostaglandins, causing uterine contractions to lose intensity. This reduces the likelihood of infection spreading to the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
May be observed years after surgery:
- After an abortion, there is always a risk of hormonal shifts, which may disrupt the menstrual cycle and the normal maturation of follicles in the ovaries. This, in turn, increases the risk of endocrine factor infertility.
- The above-described inflammatory processes of the genital organs can lead to the development of adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes (hereinafter referred to as tubal factor infertility). Inflammation of the uterine mucosa is also a common cause of menstrual irregularities.
- Past inflammatory processes and the presence of adhesions in the pelvis can cause chronic pelvic pain syndrome in women, which is very difficult to correct.
- The cervix, injured during an abortion, may not sufficiently perform a locking function during pregnancy. Due to cervical insufficiency, pregnancy losses may occur at various stages or create indications for surgical sutures on the cervix to preserve the pregnancy.
Abortion causes enormous damage to the body. Therefore, it is important to think things through before deciding to terminate a pregnancy.
Discharge
After an abortion, it is important to focus on the discharge and its quantity. Most often they are scarlet in color.
If the pregnancy was stopped at the proper level, bleeding after surgery and medical abortion should stop within 5-10 days. Bleeding gradually takes on a spotting appearance and moves into the standard menstrual cycle.
Vacuum abortion is a more gentle procedure than curettage. For this reason, discharge will be normal.
The discomfort after cleansing is localized in the lower abdomen. In the case of medicinal termination of pregnancy, as a result of the intense work of hormones, a strong contraction of the uterus occurs.
The nature of the pain resembles menstruation. These sensations last for a couple of days during the recovery period during surgical and mini-abortion.
Inflammation
An infectious disease not detected in time can become a prerequisite for prolonged inflammation of the fallopian tubes and uterine cavity. In this case, an ectopic pregnancy may occur, a life-threatening condition.
Once blood clots enter the bloodstream, there is a risk of blood clots forming in the veins. Such deviations require immediate treatment. Sometimes complications arise years later. According to statistics, late complications are observed in 10-20% of women who have had an abortion.
Hormonal background
Despite the difficult rehabilitation, women believe that termination of pregnancy is an acceptable phenomenon in nature. But this is far from true. Various complications slow down the normalization of hormonal levels.
In addition to using contraceptives, the girl resorts to antibiotic therapy. The body functions under stress. After the intervention, it takes a long time for strength and normal functioning of the whole body to be restored.
As a rule, many representatives of the fairer sex experience various psychological difficulties after the procedure.
Most often, after an abortion, a woman begins to:
- depression;
- apathy;
- increased nervousness;
- poor sleep;
- thoughts of suicide.
During this period, the help of relatives becomes important. Be that as it may, the kind words of loved ones are the best medicine. Support will quickly get rid of sad memories and return you to a full life.
Contraceptives
Contraceptives are mechanical, chemical and other means and methods whose purpose is to prevent conception and infection with sexually transmitted diseases.
Types of contraception:
- biological - calendar method, coitus interruptus;
- barrier - condoms, vaginal rings;
- hormonal - drugs prescribed by a doctor;
- surgical - IUD, sterilization;
- chemical - vaginal suppositories and tablets.
Condoms
Protect partners from sexually transmitted infections and unwanted conception. A variety of forms and types can bring piquant variety to the intimate life of a couple, enhance sensations during coitus, and adjust the duration of sexual intercourse. Condoms are recognized as the most common and affordable method of contraception, and are also considered one of the most reliable ways to prevent conception.
Oral contraceptives
Birth control pills are a reliable hormonal method of protection, one of the most effective. They are prescribed exclusively by a gynecologist after the necessary examinations.
Types of oral contraceptives:
- Microdosed - prescribed to nulliparous girls who are starting to take contraceptives for the first time, as well as to women after thirty-five years of age. These tablets contain minimal hormones, which results in an almost complete absence of contraindications. They have some cosmetic effect.
- Low-dose - allowed for use by women who have given birth one and a half months after childbirth. This type of tablet is also prescribed if, when taking a microdosed drug, scanty spotting occurs. They have a positive effect on the condition of the skin and hair, prevent the appearance of rashes, and slow down the growth of unwanted hair.
- High-dose - these drugs contain increased hormone content, which allows them to be taken if you have endometriosis or hormonal disorders.
Vaginal tablets and suppositories
The effectiveness of the drug is 75-80%. The action of this contraceptive is as follows: the active substance penetrates the vagina, reducing the activity of sperm. Available in the form of tablets or suppositories, which must be carefully inserted into the vagina in accordance with the description of the drug. The active substance is benzalkonium chloride or nonaxinalone. The drug is prescribed by a doctor.
IUD (coil)
The principle of operation of the intrauterine device is the disruption of the process of attachment of the embryo in the uterine cavity and the destruction of sperm. Copper, which is part of many intrauterine devices, kills sperm that enter the uterus and has a spermatotoxic effect. In addition, it enhances the action of macrophages, special cells that carry out the process of capturing and processing sperm.
It is installed by a gynecologist after examination and collection of necessary tests.
Vaginal ring
The ring is inserted into the vagina (as close to the cervix as possible) for a long time, prevents ovulation, supplies the body with hormones, and prevents fertilization and the attachment of the egg.
The vaginal ring is similar in effect to birth control pills.
Emergency contraception
Emergency contraception is a list of methods and means used after unprotected intimacy. Conducted no later than on the third day.
There are several types of emergency contraception:
- the Yuzpe method, which is based on taking oral contraceptives in a certain dose;
- the use of drugs containing high dosages of hormones once or twice;
- taking tablets with a small dosage of a progesterone antagonist, which is possible once;
- emergency insertion of an intrauterine device in the clinic.
Other methods
There are also other methods of protection, but their effectiveness and even safety are sometimes extremely questionable.
Here are some of the ways:
- interruption of sexual intercourse;
- douching;
- calendar method;
- temperature method.
What happens after
After an interruption, gradual changes occur in the functioning of the whole organism. After a while, all systems return to normal operation. During this period, you should carefully monitor your health. It is advisable to avoid heavy physical activity, hypothermia and observe sexual rest for 21 days.
The menstrual cycle may be disrupted (it occurs in approximately 12% of women), it becomes irregular, and there is bleeding between periods. The menstrual cycle returns to normal after a few months.
Also, the woman’s psyche becomes more sensitive. And to make it easier to overcome psychological problems, you need the help and support of loved ones - friends, relatives and husband. Kind words from loved ones are the best medicine.
Contraindications for termination of pregnancy
To determine whether an abortion is advisable for a doctor, you must undergo certain laboratory tests and undergo a series of examinations.
Basic tests:
- clinical blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- bacterioscopy of a vaginal smear;
- Wasserman reaction;
- determination of blood group;
- determination of the Rh factor.
After an examination by a gynecologist and mandatory tests, the possibility of getting rid of pregnancy is determined. If the following points are identified, surgical intervention may be refused.
An abortion will not be performed if:
- A woman has been diagnosed with acute genital diseases.
- Presence of purulent infection. Its location does not matter.
- A pregnant woman is currently suffering from an acute infectious disease.
- The period between abortions does not exceed six months.
- In late stages, when an abortion poses a greater danger to the woman’s health and life than pregnancy and subsequent childbirth.
Prevention of complications
Following a few simple rules can significantly reduce the risk of complications after abortion.
- Show up early for an appointment (the shorter the pregnancy, the more gentle the termination method can be used, for example, limiting yourself to a mini-abortion or medication);
- Carry out instrumental abortion only with a sanitized vagina (degree of vaginal cleanliness 1-2);
- Antibacterial prophylaxis of infectious complications once on the day of abortion in all patients;
- A course of antibacterial therapy in patients with chlamydia, other infections and patients at risk of developing an infectious process;
- Carrying out the prevention of Rh immunization and Rh conflict (administration of anti-Rh immunoglobulin to Rh-negative women);
- Prohibition of sex in the first three weeks after an abortion,
- Monitoring discharge that appears after an abortion and, if necessary, consulting a doctor,
- Carrying out an instrumental abortion procedure with an empty bladder and intestines;
- Compliance with hygiene rules, selection of a suitable method of contraception;
- Perform a control ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Visit a gynecologist at least once every six months.
- Clinical recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (treatment protocol) “Medical termination of pregnancy”, Moscow, 2019, team of authors.
- "National Guide to Gynecology", ed. IN AND. Kulakova, G.M. Savelyeva, I.B. Manukhina, 2009.
Important! All materials are for reference purposes only and are in no way an alternative to face-to-face consultation with a specialist.
This site uses cookies to identify site visitors: Google analytics, Yandex metrics, Google Adsense. If this is unacceptable to you, please open this page in anonymous mode.
Reading time: min.
What are the complications after an abortion? What are the consequences after an abortion? Answers to these and similar questions are often sought by women who have undergone abortion.
“Complications after an abortion: forum”, “what are the consequences after an abortion: forum” - these are the types of requests that appear on the Internet in connection with this problem.
Reasons for abortion
The intervention depends not only on the woman’s desire; there are also a number of other factors that force the operation. These include both medical and psychological reasons. Different countries have completely different attitudes towards pregnancy and abortion. But everywhere the illegal business of carrying out these interventions is thriving, sometimes absurd and bordering on elementary mockery of the pregnant woman’s body. Therefore, it is extremely important to know your rights in this matter and the assigned responsibility for your own health in connection with the decision to carry out the procedure.
Medical indications
For medical reasons only, a woman can have an abortion from the twelfth to the twenty-second week of pregnancy.
The main reasons for the operation:
- Infectious diseases of a pregnant woman that can have a detrimental effect on the development of the fetus (for example, rubella).
- Severe heart diseases (chronic hypertension, angina pectoris and others).
- Active tuberculosis.
- Liver disorders.
- Kidney disease, pyelonephritis.
- Ulcer of the duodenum and stomach.
- Oncological diseases.
- Various disorders and pathologies in the functioning of the nervous system.
- Syphilis.
- Having a disability.
To diagnose pregnancy and determine the need to terminate it, the patient must consult a gynecologist. The doctor will be able to objectively assess the patient’s situation, the duration of pregnancy, and possible reasons for its termination. He will give general recommendations for further action if surgical intervention is necessary. And also give directions for the operation itself.
Unwanted pregnancy
Regardless of a woman’s financial situation, social status and personal beliefs, unexpected conception remains quite common.
According to sociological research, in Russia half of pregnancies (officially registered) are unplanned. Every fourth is considered extremely undesirable, which leads to an artificial interruption.
Up to twelve weeks, abortion is allowed at the request of the pregnant woman. During this period, the risks are slightly lower than at later stages, however, even the method of early abortion is fraught with serious consequences for the woman’s body.
The vast majority of unintended conceptions occur during mutually consensual sexual intercourse. Many couples neglect contraception, relying on “maybe it will blow through.” This is an extremely irresponsible attitude towards the health of both partners. Nowadays, the variety of contraceptives is quite wide, so everyone can choose the most suitable method for themselves.
Other preventive measures
It should be remembered that preventing unwanted fertilization is easier and safer than risking your health and having an abortion. Preventing pregnancy using competent and modern methods will help women maintain psychological and physiological health and not cause irreparable damage to the body. It should be remembered that the only 100% reliable method is to abstain from sex.
Why are antibiotics needed?
After cleaning, there remains the possibility of bacterial invasion, which can give rise to various inflammatory processes. There is a risk of developing pelvioperitonitis. In order to avoid such complications, it is recommended to take antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The most common post-abortion drugs are netromycin and gentamicin. Amoxicillin and metronidazole are sometimes prescribed.
The purpose and recommendations should be strictly followed. You cannot extend or cancel medications on your own, because recovery will not be as effective.
How to decide to have an abortion
In some cases, it is difficult for a woman to decide whether to have an abortion or not. All questions and situations should be considered:
- You should visit a doctor and psychologist and hear their opinion.
- Weigh the pros and cons carefully. What problems are worth taking the life of a child?
- Think about the fact that after an abortion there will be no more children. Complications after termination of pregnancy can cause infertility or subsequent miscarriages.
- Accept that if you have an abortion, your own child will not be born.
- Talk to family and friends. Perhaps the expectant mother’s fears are unfounded, and loved ones will be able to help in a difficult situation.
- If you still have doubts, you can contact an organization that helps pregnant women. Psychological help in such a situation is important.
Doctors' advice
Significant interruptions occur in many body systems after expulsion. Changes are observed in the functioning of the endocrine, nervous, immune and cardiovascular systems. From time to time it is necessary to undergo diagnostics to eliminate the risk of cancer.
In addition, abortions are considered to be the cause of the development of malignant neoplasms of the uterus and ovaries. Sharp changes in hormonal levels after an abortion can cause the appearance of nodular tumors in the mammary glands. Therefore, it is also necessary to periodically consult a mammologist.
Doctors advise you to reconsider your diet. Healthy food will help restore the body faster due to the supply of nutrients. It is advisable to include protein-rich foods in your menu.
Sexual rest for two weeks is an important requirement after expulsion. Intimate communication not only activates pain, but also increases the risk of bleeding.
Full hygiene of the genital organs using hypoallergenic cosmetics is also necessary. It is better to do all kinds of hygienic procedures in the shower. The use of a bath is unacceptable due to the risk of infection of the wound cavity.
Douching and the use of sanitary tampons are not recommended.
Uterine diseases
The consequence of induced abortion is often cervical ruptures, perforation of the cervix and uterine walls, i.e. violation of the integrity of the organ by medical instruments, which can occur after repeated curettage of the uterus, as a result of which its walls become defective and thinned.
Depending on the location of the wound, either suturing or even removal of this vital organ is performed. In subsequent births, the uterus may rupture, leading to its removal.
The most damaged organ after an abortion is the uterus. The longer the period at which the abortion was performed, the greater the harm. The uterus begins to contract after the embryo is removed and returns to its original size. But a wound cavity is created in its wall, which takes time to heal.
Most often, the uterus returns to its normal size at the beginning of a new menstrual cycle. If scarlet discharge with an unpleasant odor continues for 12 days, this indicates inflammation, which must be treated immediately.
Endometritis has every chance of appearing if the abortion is performed poorly. For this reason, absolutely all girls after an abortion are prescribed not only a visit to the gynecologist, but also a mandatory examination, during which it is confirmed that the uterus is in order.
Family relationships after abortion
An unborn child appears in the family, the memories of which will accompany the rest of their lives. Most often, after an abortion, conflicts arise in those couples where the woman says: “I don’t want to have an abortion,” and the man insists. The last word remains with the woman, but she can shift the blame onto the man for a long time, sometimes throughout her life.
An aborted child is a rejected child, excluded from the family. If unspoken reproaches remain, then discord sets in in such relationships. A couple stops having sex or experiences a family member's illness. This may lead to separation.
Depression after abortion
More than 20% of women who have an abortion experience depression. The reasons are not only stress for the body, provoked by the interruption of nascent life, but just disrupted hormonal levels.
The triggers for deterioration of the emotional state are:
- social pressure, propaganda of the happiness of motherhood in the media;
- traumatic life situation (birth of children to close relatives, new pregnancy);
- development of anxiety states and disorders (a woman is tormented by nightmares, she talks to an unborn baby);
- intra-family conflicts (if the husband or relatives called for an abortion, there will no longer be a trusting relationship with them, frequent conflicts will arise).
Hormonal treatment largely helps to avoid psychological trauma, which is aggravated by increased activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary zone. Under no circumstances should you be left alone with feelings of guilt or depression. The patient can tell everything to the gynecologist, who will listen and do everything to help the woman recover both physically and mentally.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
What you can and cannot do before the procedure
Before undergoing a medication abortion, it is recommended that you avoid eating heavy food on the day of your clinic visit. You can get by with a snack or come on an empty stomach. It is not recommended to drink alcohol several days in advance, and not to smoke on the day of the procedure. The medicine is better absorbed when at least two hours have passed since the last meal.
The procedure may cause abdominal cramps and heavy discharge, so it is not advisable to undergo physical activity for a while. Just in case, you should buy painkillers at the pharmacy.
Preparations for vacuum aspiration or cleaning of the uterus begin in advance. If a sexually transmitted infection or an acute stage of an infectious disease is detected, the procedure is postponed.
In this situation, treatment is necessary because inflammation in the uterine cavity and other complications may occur.
A few days in advance it is recommended:
- not be sexually active;
- carry out sanitation (treatment with antiseptic agents) of the vagina;
- remove hair in the groin;
- remove jewelry in the intimate area.
Before a surgical abortion, you should eat only light food and avoid drinking alcoholic beverages. If general anesthesia is provided, it is prohibited to take any food or drink. It is important to follow this regime so that everything goes well and safely.
Why is abortion prevention necessary?
In order to similarly understand the essence of the topic of abortion and prevention of unwanted pregnancy, it is necessary to have at least a minimal understanding of the process of conception. This knowledge is extremely important for preventing manipulations that are dangerous to a woman’s body.
So, let's look at how ovulation occurs.
From the moment a girl has her first menstruation, every month one of the eggs matures and is released from the ovary. The egg can survive for up to 24 hours. During this period of time, fusion with the sperm should occur, resulting in pregnancy. If the sperm and egg merge, the fertilized cell descends through the fallopian tube into the uterus. If, on the contrary, fusion does not occur, then menstruation occurs and the egg is excreted from the body.
Thus, women should strictly monitor the periods of ovulation, as it can become both the cause of a very desirable pregnancy and a way to protect against an unplanned one.
The effect of abortion on the body
Prevention of abortions and unwanted pregnancies is extremely important, especially during puberty, when the older generation (parents, guardians, schools) do not yet consider it necessary to inform teenagers about contraceptive methods, and hormones and sexual desire take precedence over common sense. Young girls, for the most part, delay pregnancy so much that later there are no objective reasons to terminate it. Basically, the motivation for hiding is fear. Young ladies are not aware of how radical changes are taking place in their bodies and the extent to which abortion will negatively affect their condition. The same applies to fully mature women, except that they voluntarily and promptly turn to specialists.
What are the main risks of abortion:
- Hormonal disorders. With the onset of pregnancy, a global restructuring of all systems and organs begins, as well as global hormonal changes. Interruption of this process disrupts the hormonal balance and often leads to disastrous health problems.
- When carrying out any type of intervention, the uterine surface is injured, which serves as a favorable environment for the proliferation of microbes.
- Inflammation of the uterus or its cervix, inflammation of the appendages in a chronic form - all these are consequences of infection after an abortion.
- Curettage and subsequent complications often lead to scarring of the uterine cavity and rupture of the cervix, and this already threatens infertility and miscarriages.
- Hormonal surges after intervention have an extremely negative impact on all organs and systems, especially on the reproductive function of women. The result will be the development of oncology, disruption of the menstrual cycle, and infertility.
- With each subsequent abortion, the risk of developing erosions, cysts or fibroids, and mastopathy increases.
A month after any type of abortion, it is extremely important for a woman to undergo a routine examination by a gynecologist in order to immediately detect possible complications and disorders after the manipulations. It is imperative to undergo a colposcopy, ultrasound examination and visit a mammologist (gynecologist, if this specialist is not available in your local clinic).
Psychological trauma
It happens that the result of an abortion is post-abortion syndrome (PAS). Due to the fact that abortion is an unnatural process, it will not always be possible to avoid changes in the psychological state. Moreover, this syndrome can also manifest itself in both a man and a doctor who took one or another part in the abortion. Mental disorder is manifested by the persecution of a person by obsessive thoughts about what he has done; internal subconscious devastation can be reminiscent of an abortion for quite a long time. Also, psychological consequences sometimes appear after a fairly long period of time, when, it would seem, everything went smoothly and in accordance with the woman’s wishes.
Reviews after surgery
“Abortion using vacuum aspiration is also called a mini-abortion. I still don’t understand how long it takes to do it, since different sources say it differently. Some write that there will be a delay of up to five weeks, in others up to seven, and in others up to twenty days. This operation is performed in a antenatal clinic under painkillers. The procedure takes from three to seven minutes.
There are different situations in life. I never thought that I would ever have to have an abortion; I always condemned women for this. But here I am doing a test. There are two stripes on it, which did not please me at all. I have a one-year-old child in my arms, a rented apartment, and a divorce is approaching. There are no assistants to even look after the first child, but what can we say about the second? But what surprised me more was that I became pregnant while taking the contraceptive “Janine”. Moreover, she never missed a single dose and took it strictly on time. The gynecologist suggested that the effect of “Janine” could be reduced by the antibiotic that I was taking at the same time.
I went for an ultrasound examination at my place of residence. The fertilized egg in the uterus is six millimeters. The doctor said it might not be pregnancy. She offered to come again in a week if my period didn’t start. She arrived a week later, the fertilized egg was eight millimeters. Again he says small, it’s too early to make a vacuum. She offered to come back for a vacuum in a week. By my count, seven weeks have passed since the first day of my last period. Is it possible to have a mini-abortion at this time? Or maybe I'm wrong? The doctor warned in advance that vacuum aspiration was done under painkillers.
On the morning of the appointed day of the operation, I had to take two No-Spa tablets and one Xefocam Rapid tablet. I arrived at the clinic and paid. They gave me a painkiller injection and told me to wait. During these forty minutes, I went to the toilet five times out of fear, and I was shaking all over. But I reassured myself that if the vacuum is not done under anesthesia, then it won’t hurt.
I go into the office. There are two women in masks, scary instruments and apparatus. She undressed, put on a robe and lay down on a chair. One of these women put an incomprehensible contraption on my leg and tied it.
Here I became even more scared. Why tie me down? Am I going to run away? Or does it hurt that much?
The manager started: inserted a speculum, inserted some kind of iron tube into the cervix - it was painful. Then she gave an injection into the cervix. It feels like a finger is being pricked when blood is taken, only it is pricked slowly and with a meter-long needle. But these were flowers.
They turned on the device and started suctioning. It feels like a vacuum cleaner has been shoved into you and is being pulled in different directions. At first it didn’t hurt, but then the pain began to increase with great speed.
It didn’t hurt me to give birth as much as the pain I felt! Breathing exercises didn't help me. I wanted to scream in a voice that wasn’t my own! Three minutes seemed like an eternity.
During these three minutes, I regretted a hundred times that I did this. The pain can be compared to when the entire jaw is ripped out without painkillers! I'm not exaggerating!
I almost lost consciousness from the pain. That's why the nurse stood near my head. When it was all over, they moved me onto the couch. The pain gradually subsided. Ten minutes later I felt great, as if nothing had happened.
The doctor asked how I was feeling and allowed me to get dressed.
Before leaving, I asked when I would have another ultrasound. To which they answered that they do not do any repeat ultrasounds.
They explained to me that my period should pass within ten days; if it doesn’t happen, then even without an ultrasound it is clear that the fertilized egg remains. Then I need to come to them for an examination. I was prescribed an anti-inflammatory drug, Aspirin and No-shpu. They told me to take it for five days. My period started the next day. The first week after the abortion there were periodic pains similar to contractions, and a lot of blood came out. Then the temperature even rose. I called an ambulance. The ambulance doctors explained that this was normal and there was no reason for hospitalization.
A month passed, and the blood continued to flow every day. I turned to a gynecologist, and she sent me for an ultrasound. The doctor discovered the remains of the fertilized egg and suggested that I come back for an ultrasound in two weeks. This is despite the fact that I have been bleeding for a month now.
Two weeks later there were no changes on the ultrasound, and I was again asked to come back in two weeks. This is apparently the treatment method used by the head of the gynecology department. I turned to a gynecologist. After all, something needs to be done. The blood had been bleeding for a month and a half and very profusely. I walked around not with pads, but in diapers!
The gynecologist explained that if within the next two weeks a piece of the fertilized egg does not come out with blood on its own, then I will be referred for hysteroscopy (cleaning, in other words). Two months later, a miracle happened. The piece came out on its own. It was about one and a half centimeters long and seven millimeters wide. The bleeding has stopped.
Speaking on the topic of abortion, with my review I want to warn girls not to repeat my mistakes. And if suddenly you have to do this, contact paid clinics. They do it under anesthesia and without consequences. Tested for myself..."
Valentina, 28 years old