The internal organs of our body are very sensitive to external influences. Children especially suffer from this. The inflammatory process can be triggered by poor nutrition and aggressive medications. Long-term infections and parasites that penetrate the body also prevent internal organs from functioning normally. The inflammatory process in the gallbladder, called cholecystitis, in children in many cases affects not just one organ, but the entire biliary system.
Classification
Cholecystitis in children has acute and chronic forms, and the symptoms and treatment for each of them are different. The acute form often manifests itself with catarrhal symptoms. Rarely, a purulent form of cholecystitis occurs in a child. a chronic course is observed - calculous (when there is gallstone pathology) and acalculous.
Chronic cholecystitis can be hidden, often recurrent (more than 2 relapses per year) and rarely recurrent (one relapse per year).
Depending on the severity of the disease, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- easy;
- medium-heavy;
- heavy;
- with complications;
- without complications.
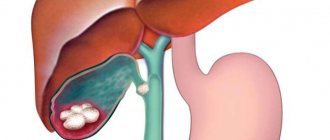
In addition, cholecystitis can lead to biliary dyskinesia, which can be hypomotor, hypermotor, and with shutdown of the gallbladder (this is a variant of calculous pathology, when stones accumulate in the gallbladder or tissue scarring occurs, as a result of which it stops working).
As a rule, inflammation of the gallbladder in a child does not occur in isolation: it is accompanied by inflammation of the bile ducts (cholangitis) and inflammation of the liver cells (hepatitis).
Precautionary measures
Parents can prevent the appearance of some factors that provoke the development of cholecystitis in a child. I bring to your attention recommendations on this issue.
- Monitor your child's well-being closely. Remember that chronic cholecystitis can have a latent form. Therefore, the slightest negative manifestations should be a reason to consult a doctor.
- Carefully ensure that the child has a balanced diet, follows a meal schedule, does not overeat, and has enough proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the diet.
- It is important that the baby maintains an active lifestyle, does not sit all day in front of the TV, but walks in the fresh air.
- It is important in the presence of any diseases affecting the child’s body, especially chronic ones, to be under the supervision of a doctor and follow his recommendations.
Now you know what cholecystitis is and what its main symptoms are. As you can see, there are many reasons that provoke the development of this disease. Parents, knowing what exactly can cause the development of cholecystitis, can prevent these factors by taking preventive measures. At the slightest suspicion of cholecystitis, you should immediately seek specialized help. The sooner therapy is started, the more favorable its outcome will be.
It is possible to cure the disease and prevent its recurrence in a child. To do this, you need to regulate your diet - frequent meals in small portions. Promote an active lifestyle for your child. Be sure to examine your baby for the presence of helminths. Treat infectious diseases in a timely manner and strengthen the immune system.
You can avoid the stage of exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis by leading an active lifestyle, drinking mineral waters of Essentuki, Naftusya, Mirgorodskaya, and limiting nutrition.
The first characteristic manifestations of cholecystitis in a baby should immediately alert parents. Untimely detection of symptoms of the disease, treatment carried out at the wrong time, contribute to the occurrence of severe consequences in which the child’s life can only be saved by removing the gallbladder.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Often, an infectious pathogen penetrates the organ through the bloodstream from any existing infectious foci ( caries, sinusitis, tonsillitis ). In some situations, the disease provokes an acute infection - sore throat, flu, dysentery, salmonella, etc.
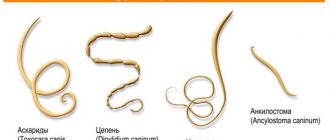
Pathology also occurs as a result of the abnormal structure of the bladder and changes in the composition of bile . Special conditions for inflammatory phenomena are created by parasites (giardia), worms (roundworms, opisthorchid) or inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract - gastroduodenitis, reflux gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.
Factors that provoke inflammation of the gallbladder in children:
- Poor nutrition , especially long gaps between meals, are harmful. This leads to stagnation of bile.
- Poor nutrition: predominance of carbohydrates and fats over vegetables and fruits;
- Low motor activity , abnormal structure of the bile ducts, the organ itself, stagnation of bile.
- Endocrine disorders , including excess weight.
- Constant stress.
- Food allergies.
- Neuropsychic pathological conditions.
- Injuries to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Weak immune system.
30% of the acute phase of the disease turns into chronic if treatment is not started on time or it was carried out illiterately.
Provoking factors
The most common cause of the disease is infection. Most often these are pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic representatives of the bacterial flora:
- coli;
- Klebsiella;
- streptococcus;
- staphylococcus and others.
Viruses, fungi and protozoa infect the gallbladder much less frequently. Microorganisms enter the organ through the intestines or through the bloodstream from distant sources of infection.
Often chronic cholecystitis occurs against the background of:
The precursors of the disease can be intestinal infections, for example, salmonellosis or dysentery. Other causes of gallbladder inflammation include:
- parasitic diseases: opisthorchiasis, ascariasis, enterobiasis;
- congenital anomalies of the organ: kinks, structural changes;
- pathologies of other digestive organs: gastroduodenitis, colitis, Crohn's disease;
- changes in the composition of bile;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- disruption of the blood supply to the organ;
- gallstones.
A common provoking factor is a violation of the diet, namely the abuse of foods containing a lot of “fast” carbohydrates, overeating or too long intervals between meals. Failure to adhere to the diet causes an exacerbation of the disease.
In some patients, pathology develops due to:
- frequent worries;
- autonomic disorders;
- poisoning;
- allergies;
- sedentary lifestyle or excessive physical activity;
- abdominal injuries;
- weak immunity.
Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies lead to metabolic disorders, changes in the composition of bile, the formation of stones and other negative changes in the body that can provoke inflammation of the gallbladder.
Causes of cholecystitis in children
Symptoms of cholecystitis in children
In children, the acute period is rare. Basically, there is a hidden chronic course with exacerbations. At the same time, the signs of cholecystitis in children in the acute and chronic periods are different.
In the latent form, children report headaches, decreased appetite, fatigue, weakness and troubled sleep. During a visual examination, the doctor notices pale skin and dark spots under the eyes. Low-grade fever (a little more than 37.0) may occur; abdominal pain is not always observed. These signs indicate intoxication of the body.
Exacerbation of chronic cholecystitis in children may occur due to the following factors:
- improper eating;
- increased workload in a physical education lesson;
- stress (for example, taking an exam);
- ARVI or exacerbation of any chronic infection.
Symptoms of chronic relapse:
- Painful sensations under the right rib, which intensify while walking or running. The pain can be paroxysmal (from a couple of minutes to several hours) or aching but constant. The pain also intensifies within 1-2 hours after eating fatty or fried foods. The pain radiates to the back, neck, shoulder.
- Dyspepsia. These are belching, bitter taste in the mouth, nausea, flatulence, problems with stool - diarrhea or constipation.
- Restless sleep.
- Low-grade fever.
- Weight loss.
- Ultrasound shows an enlarged liver, sometimes jaundice.
Dyspepsia
Restless baby's sleep
Low-grade fever
Weight loss
The chronic form of inflammation in the organ can continue for many years, and relapses of the disease will be similar to the acute phase.
Calculous cholecystitis can also occur in acute and chronic forms. If the volume of stones is small and they are located in the organ cavity, the symptoms are similar to the course of acalculous pathology. But when the stones increase in size, they can close the lumen of the bile ducts and then an attack of colic occurs. In turn, stagnation of bile leads to liver pathologies and jaundice.
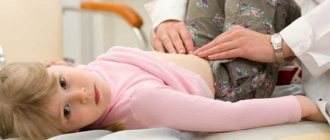
The acute phase begins with severe pain under the right rib, which can radiate to the scapula, arm and shoulder. Body temperature rises to 38 degrees, but it can be higher. There is a bitter taste in the mouth, nausea, vomiting of bile, the tongue becomes dry and covered with a thick coating. The skin turns pale, weakness and dizziness appear. At the same time, the child becomes restless and begins to rush about in order to somehow reduce the pain. When palpating the abdomen, pain and bloating are noted.
This condition may last a couple of days. In addition, inflammatory phenomena can affect nearby organs, and pancreatitis may appear. The course of the disease is aggravated by adhesions that form with neighboring organs.
In the acute phase, a purulent form of cholecystitis may occur, in which inflammation affects all layers of the organ, purulent lesions and ulcers appear. As complications, an abscess occurs under the liver and diaphragm. Possible perforation of the walls , as a result of which fistulas are formed, which is how peritonitis - inflammation of the abdominal cavity, which poses a threat to the life and health of the child.
Prevention
To avoid the occurrence of cholecystitis or reduce the number of relapses, the most important thing is proper nutrition according to age and time.
Also, as prevention is an active lifestyle, timely treatment of any pathologies, including chronic foci of infection, course treatment with physiotherapy (2-3 times a year), choleretic drugs, mineral water (especially Essentuki water).
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder. The disease can manifest itself for various reasons and appears at any age. It occurs in acute or chronic form, with alternating periods of remission and relapses (exacerbations). The degree of its severity depends, among other things, on the cause of development; the same factor determines the treatment method. Thus, cholecystitis in children caused by poor nutrition is treated with basic diet correction. Inflammatory processes in the gallbladder associated with abnormalities in the structure of the organ and other nuances can only be cured surgically.
Diagnostics
The first sign of the disease is rapid weight loss.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor interviews the child’s parents and himself, and examines the patient. The specialist clarifies each complaint in detail, also clarifying the dynamics of the disease. The doctor checks the tongue, skin, palpates the abdomen, listens to the heart and lungs.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a number of additional studies are necessary:
- General blood analysis. An increase in leukocytes and an acceleration of ESR indicates the presence of inflammatory processes. If cholecystitis has been present for a long time, then during the period of remission there may even be a decrease in leukocytes.
- Biochemistry of blood. There is an increase in transaminases (AlAt, AsAt), bilirubin. This indicates inflammation in the bile ducts and liver.
- Analysis of stool for the presence of worms.
- Bile collection using a hardware method. Bile analysis reveals an increase in white blood cells, mucus, and cholesterol crystals. Even in bile, parasites and worms can be found.
- Ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to find out the size of the necessary organs, their deformation, the presence of stones and their sizes, and to assess the contractile function of the bladder.
- X-ray of the gallbladder with the introduction of a contrast agent . It is used extremely rarely in children, only in the most severe cases, when previous diagnostic methods have not given the desired result and the child’s condition is deteriorating. This method allows you to assess the shape and determine the location of the gallbladder, its motility and ability to excrete bile.
General blood analysis
Blood biochemistry
Stool analysis
Bile collection
Ultrasound diagnostics
X-ray of the gallbladder
conclusions
Timely hospitalization of a patient with acute cholecystitis in most cases ends in recovery. The main thing is to follow clinical recommendations and avoid self-medication. Ignoring the signs of the disease is fraught with disruption of the outflow of bile, the formation of stones and the development of chronic inflammation, which takes much longer and more difficult to treat.
Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder that occurs due to an attack by viruses, bacteria or helminths. Recently, cholecystitis is often observed in children, but due to vague symptoms, it is not always detected in time.
Treatment
In case of exacerbation, you need to put the child in a horizontal position and call an ambulance, and also apply ice under the right rib. Just don't use a warm heating pad, it will increase inflammation.
Do not give medications that relieve pain, as they can blur the symptoms of the disease and prevent the pathology from being diagnosed. Such children are subject to hospitalization and further conservative treatment in a hospital.
Surgical intervention is used for the calculous form of the disease and for serious complications.
Methods of conservative treatment of cholecystitis in children:
- diet;
- taking medications;
- physiotherapeutic methods;
- treatment in sanatoriums and resorts;
- mineral water therapy.
Medicines include:
- Antibiotics (penicillins, macrolides, cephalosporins);
- In the presence of helminthic infestation, antiparasitic drugs (Furazolidone, Vermox, etc.);
- Antispasmodics to relieve spasms and pain (Papaverine, Drotaverine);
- Choleretic drugs (Holosas, etc.);
- Hepatoprotective agents for normal liver function (Essentiale, Geparsil, etc.);
- Vitamin complexes;
- Sedatives for troubled sleep.
The dose of medications and the duration of their use are determined by the doctor. In some cases, blind probing is required every day or every other day to ensure timely outflow of bile and prevent its stagnation.
Physiotherapy includes UHF, mud treatment, inductothermy and diathermy, ozokerite and paraffin applications. After the acute phase of inflammation is removed, massage, physical therapy, and ozone therapy are used.
Diet is the main condition of therapy. For the first two days during the acute period, you only need to drink warm drinks (compote, rosehip decoction). It will begin to drive bile and relieve symptoms of intoxication. Next you can eat slimy soup, that is, not with broth, liquid porridge with water (semolina, oatmeal, rice), vegetable purees, jelly. You should also limit salt.
Then the diet expands, you can use diet No. 5. It promotes the discharge of bile and restores the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
What needs to be removed from the menu:
- fried and fatty foods;
- marinades and canned food;
- broths;
- smoked and salted dishes;
- baked goods;
- nuts, mushrooms, sauces, carbonated drinks and any cold food.
Do not eat freshly baked bread; it should be replaced with crackers. Consumption of fermented milk products will have a beneficial effect on the health and general well-being of the child.
You should add boiled meat and fish, cottage cheese, vegetables, fruits, dried fruits, and egg whites to your diet.
Diet
With chronic cholecystitis, children need to eat in small portions, but often. The main emphasis when compiling a diet should be on fresh vegetables, fruits, cereals and dairy products. However, the milk must be skim, that is, skimmed (0.5%). Proteins and healthy carbohydrates are allowed, but fat intake should be limited. Therefore, the meat should be dietary, for example, boiled chicken breast or lean beef. Fats of vegetable origin are allowed, as well as butter. You should avoid sweets and buns.
During an acute attack of the disease, the child completely loses his appetite, which corresponds to the needs of the body at the moment, since fasting is beneficial for cholecystitis. At this time, you need to give your baby a warm drink to help remove pathogenic microbes and their waste products from the body.
Preventive actions
Preventive treatment consists of the following recommendations:
- Diet, formation of an individual diet suitable for the baby. Preference should be given to protein foods rather than carbohydrates. Introduce a large amount of fruits and vegetables, take special vitamin complexes that the patient needs.
- Fractional meals.
- Balanced physical activity. Regular exercise in any kind of sports is encouraged, depending on the baby’s preferences.
- Pay attention to your body mass index. If the indicators are not normal, begin to take appropriate measures.
- Get diagnosed for gastrointestinal diseases. If these diseases appear, begin a treatment course to eliminate them.
- Take choleretic drugs only after consulting with your doctor.
- Practice drinking mineral waters (like Borjomi and Essentuki).