The effect of antibiotics on the human body
The effect of antibacterial agents on microorganisms is bactericidal (they kill cells) and bacteriostatic (they stop cells from developing and do not allow them to multiply).
This discovery was made in 1928 and saved millions of lives. Treatment of many injuries, anaerobic infection (gangrene), inflammatory diseases of internal organs (pneumonia, bronchitis, colitis, cystitis, adnexitis and others) is impossible without the use of antibiotics. In patients, fever goes away faster, wounds heal, and organ functions are restored without complications. The unrestricted use of antibiotics for several generations in treatment, their commercial availability, and the illiteracy of the population regarding the need for their use have led to the fact that sometimes the resulting harm outweighs the benefits. Along with the presence of side effects, there are long-term consequences of antibiotic therapy:
- The microbes against which the treatment is directed develop resistance to the antibiotic, which leads to the prescription of courses of new drugs. Such bacteria are dangerous for everyone around them.
- An antibiotic, especially a broad-spectrum antibiotic, kills all bacteria in the body - both harmful and beneficial, with which a person coexists beneficially. This leads to dysbiosis, activation of fungal flora, especially often in children, and requires the administration of probiotics and mycostatic drugs.
- Some antibiotics have a detrimental effect on the liver: instead of neutralizing harmful substances entering the body, it itself begins to produce toxins.
- Cellular respiration of all tissues is disrupted, the body suffers from a lack of oxygen.
- Antibiotics suppress the immune system, preventing the body from fighting off the infection on its own. For the following diseases, their mandatory prescription is required.
- The emergence of microbes resistant to antibiotics leads to the development and production of new, more effective drugs. And they can have a stronger negative impact.
Antibiotics are organic or synthetic substances that can kill, disrupt the structure, and destroy the protein synthesis apparatus of bacteria. Today, these drugs treat pneumonia, colds, tetanus, diphtheria and many other bacterial infections. What is the harm of antibiotics to the human body?
It is due to the fact that these substances have a suppressive effect on microbes. Antibiotics come in two varieties: broad and narrow spectrum. The former inhibit all microbes in the body, but a person also has beneficial microflora in his body, which regulates many processes and acts as a barrier to “bad” bacteria.
The second group of drugs works only with a narrow range of microorganisms or even one, without harming the human microflora.
“Why not use only narrow-spectrum antibiotics?” is a question that will come to mind for many readers. The fact is that it is extremely difficult to obtain such drugs, because to do this you need to find in a certain bacterium some factors that are characteristic only of it and are absent in others. If such features are found, then it is necessary to develop a way to influence them. Because of this, there are very few such drugs and they are more expensive than their “brothers” of a wide spectrum.
Are antibiotics harmful? It is impossible to answer this question unequivocally, because these drugs save lives by fighting the most dangerous bacterial diseases, but with prolonged, irrational or independent treatment, they can be harmful to the body, disrupt the balance of microflora, which is difficult to restore.
Antibiotics negatively affect many vital systems of the body, but they are especially harmful for:
- liver;
- kidney;
- stomach;
- intestinal microflora;
- of cardio-vascular system;
- nervous system.
All areas of impact are discussed in detail below.
Harm to the liver
The first thing antibiotics hit is the liver cells. This universal filter of the body allows blood and everything it contains to pass through it. Any drugs, after ingestion, destroy liver cells, which are very difficult to restore. She tries to remove harmful substances from the body, neutralizes them, but she herself receives the main blow:
- inflammatory processes may occur in the liver;
- gallbladder;
- enzymatic function is weakened;
- pain occurs (especially after prolonged use).
Often, doctors, in order to reduce damage to the liver, together with antibacterial drugs, prescribe special medications that can strengthen the liver. These can be not only tablets, but also teas or decoctions.
Harm to the kidneys
The kidneys are the second to try to cleanse the body of antibiotic breakdown products after taking them. This negatively affects them, because such drugs are aggressive substances, and therefore irritate and destroy the epithelium lining the organs from the inside.
Therefore, after long-term use of antibacterial drugs, cloudy urine, a change in its color or odor, may be observed. The cells are destroyed, and because of this, the absorption and excretory functions of the kidneys are disrupted. They are no easier to restore than the liver. This process occurs independently, and you can help it by drinking plenty of fluids and herbal teas.
Harm to the stomach
Why are antibiotics harmful to the stomach? They increase the acidity inside it, causing increased secretion of gastric juice containing strong chloride acid. This phenomenon is especially dangerous if it was taken not after a meal, but on an empty stomach.
Ulcers can form in the walls of the stomach, and gastritis develops. It is almost impossible to cure such consequences, therefore, before starting treatment, it is necessary to study the features and rules of administration in order to reduce the negative impact on the stomach.
Antibiotics have the most serious effect on the intestinal microflora, especially if they are broad-spectrum. The body is freed not only from harmful microorganisms, but also loses its “protective garrison”. Beneficial bacteria living in the human body create a barrier through which harmful microbes cannot break into cells and tissues. Beneficial organisms also help a person digest and eliminate food and synthesize some necessary substances.
Also, beneficial bacteria protect a person from the penetration of fungal infections that cause fermentation and rotting of food in the gastrointestinal tract, suppress the immune system, and cause allergic reactions. Harmful fungi include yeast, some types of aspergillus and others.
The harm from imbalance of intestinal microflora can be felt within 2-3 weeks after taking antibiotics.
- the functioning of the digestive organs is disrupted;
- bloating develops;
- processes of fermentation and decay;
- allergies or rashes appear;
- the stool becomes upset;
- Dysbacteriosis begins.
Restoring your “protective garrison” is difficult, but possible. To do this, you need to take a course of prebiotics - drugs containing beneficial bacteria, as well as adjusting your diet.
Some types of antibiotics can depress mental activity and disrupt the functioning of the vestibular apparatus and sensory organs. Streptomycin with long-term treatment causes difficulties in perceiving new information, impairs memory, and makes it difficult to concentrate.
There are also safe drugs, so you need to talk about the specifics of the drug with your doctor. Certain types of antibiotics can harm the cardiovascular system, disrupting heart function, irritating the walls of blood vessels, and increasing blood pressure.
In order to avoid unpleasant consequences after a course of treatment, you must first of all follow the advice of the treating specialist.
- You should carefully follow the rules of administration, as well as take auxiliary medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Remember that it is difficult to cleanse the body of antibiotic residues, but the process can be speeded up. Herbal teas and prebiotics will help with this. To cleanse your body, you can drink chamomile, mint, nettle teas, or purchase special herbal teas for the liver, kidneys, and stomach.
- There are also prebiotics in every pharmacy. They contain beneficial bacteria, so they will help restore the intestinal microflora and cleanse the organ cells of drug residues.
- Do not take prebiotics on your own, because each of the many types contains different microorganisms, so only a doctor can prescribe them.
Antibiotics not only treat, but can also cause harm. Take care of your body, do not take medications yourself and follow all doctor’s recommendations - this is the only way to reduce the negative effects of antibacterial drugs.
With the discovery of penicillin in 1928, a new era in people's lives began, the era of antibiotics.
Few people think about the fact that before this discovery, for thousands of years, the main danger to humans was precisely infectious diseases, which periodically took on the scale of epidemics, mowing down entire regions.
But even without epidemics, mortality from infections was extremely high, and the low life expectancy, when a 30-year-old person was considered elderly, was due precisely to this reason.
Antibiotics turned the world upside down and changed life, if not more than the invention of electricity, then certainly no less. Why are we wary of them? The reason is the ambiguous effect of these drugs on the body. Let's try to figure out what this effect is, and what antibiotics have actually become for people, salvation or curse.
“Anti bios” translated from Latin means “against life”, so antibiotics are anti-life drugs. Chilling definition, isn't it? In fact, antibiotics have saved millions of lives.
The scientific name for antibiotics is antibacterial drugs, which more accurately corresponds to their function.
Thus, the action of antibiotics is not directed against a person, but against microorganisms that penetrate his body.
The danger is that most antibiotics affect not just one pathogen of a particular disease, but entire groups of microbes, which contain not only pathogenic bacteria, but also those that are necessary for the normal functioning of the body.
It is known that the human intestine contains about 2 kg of microbes - a huge number of mainly bacteria, without which the normal functioning of the intestine is impossible.
Harmful effects of beneficial drugs
It has long been established that harmless drugs do not exist in nature. Even the most harmless drug, if used incorrectly, causes unwanted effects, let alone such powerful drugs as antibiotics.
It should be understood that side effects are a possible, but not necessary, consequence of taking antibacterial agents. If a drug has been tested and accepted into clinical practice, this means that it has been unequivocally and convincingly proven that its benefits for most people significantly outweigh the possible harm. However, all people have their own characteristics, the reaction of each organism to a drug is determined by hundreds of factors, and there are a number of people whose reaction to the drug, for one reason or another, turned out to be rather negative.
Possible negative reactions are always listed in the list of side effects of any medicine. Antibiotics have a very strong ability to cause side effects, since they have a powerful effect on the body.
Let's look at the main undesirable consequences of taking them:
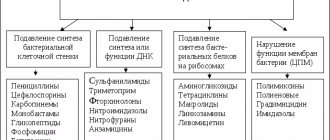
- Allergic reactions. They can manifest themselves in different ways, most often it is a skin rash and itching. Allergies can be caused by any antibiotics, but the most common are cephalosporins, beta-lactans and penicillins;
- Toxic effects. Particularly vulnerable in this regard are the liver, which performs the function of purifying the blood from poisons in the body, and the kidneys, through which toxins are eliminated from the body. In particular, tetracycline antibiotics have a hepatotoxic effect, and aminoglycosides, polymexins and some cephalosporins have a nephrotoxic effect. In addition, aminoglycosides can cause irreversible damage to the auditory nerve, leading to deafness. Fluoroquinolones and antibacterial agents of the nitrofuran series also have an effect on nerve structures. Levomycetin has a toxic effect on the blood and the embryo. Antibiotics of the amphenicol group, cephalosporins and some types of penicillin are known to have a negative effect on the process of hematopoiesis;
- Immune suppression. Immunity is the body’s defenses, its “defense” that protects the body from the invasion of pathogenic agents. Immune suppression weakens the body's natural defenses, which is why antibiotic therapy should not be excessively long. To one degree or another, the immune system is suppressed by most antibacterial drugs, the most negative in this regard is the effect of tetracyclines and the same chloramphenicol.
How do antibiotics work?
Came to the hospital with a fever and immediately received a prescription for antibiotics? Do not rush to the pharmacy, but see another specialist, because to prescribe such serious drugs, you need to take tests to find out the nature of the disease (viral, bacterial, fungal), as well as the strain of the pest.
Antibiotics can only be used to treat bacterial infections, for example: pneumonia, botulism, tetanus, gonorrhea, anthrax, tuberculosis, diphtheria, dysentery and others.
The action of antibiotics begins almost immediately after entering the human body. There are two categories of drugs that differ in their action: narrow and broad profile. Their main difference is selective or general impact on microbes.
Today there are not many such drugs, because from the name it is clear that they act only on a certain type of bacteria (sometimes even a strain). This does not harm the good microflora of the body, does not cause dysbacteriosis and other consequences of such treatment. But developing such drugs is very difficult, because this requires finding a unique characteristic feature of this type of bacteria.
This may be a detail of the structure of the outer membrane, features of the cell wall, substances of the mucous capsule, and more. This is the only way to kill a specific microorganism. Therefore, narrow-profile antibiotics have not been found for all bacterial infections.
After entering the body, the active substance of antibiotics enters the bloodstream. There it finds bacterial pathogens and has a destructive effect on them. This effect can simply kill the bacterium or destroy its cell wall, or inhibit the synthesis of proteins, without which the microbe will not live long.
In addition to these three mechanisms, there are others, for example, ordinary poisoning by the components of the drug, but they are less common. How long the fight process will last depends on the state of your own immunity, the type and strain of the pathogen, and other factors. At the same time, thanks to the narrow range of work, the human microflora is not disturbed and the body functions normally.
The first general medicine was penicillin, which was discovered by Fleming at the end of the 19th century. Since then, many lives have been saved, especially during the war. Today, this “veteran” is practically not used due to toxicity, slow action, and the development of addiction in many types of bacteria. But it has been replaced by many other broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs.
Their mechanism of action is similar to the previous one, but there is one significant difference. After entering the human bloodstream, narrow-spectrum antibiotics use special “signs” (membrane complexes, characteristic substances on the cell wall, outgrowths, secretions) to find their victims and kill only them. With a wide spectrum, everything is not so pleasant.
At the end of treatment, bacterial pathogens can be expelled, but at the same time dysbacteriosis and weakened immunity appear, so prebiotics are prescribed after the course - drugs containing beneficial bacteria that restore flora in the body.
Conditions for effective use of antibiotics
Antibiotics, which suppress growth and reproduction in combination with minor damage to body cells, are used as the basis for medicines.
There is no clear opinion whether antibiotics are harmful or beneficial, so carefully understand this issue before you start taking them.
The benefits of antibiotics
The discovery of antibiotics was a major medical breakthrough. Despite criticism, antibiotics help cure deadly diseases. The effect of antibiotics on the body is constantly being studied, and improved strains are being produced.
Only the attending physician can prescribe antibiotics based on tests.
Pregnancy is a contraindication to the use of antibiotics. Antibiotics have a bad effect on the fetus.
The list of diseases in which the benefits of antibiotics for humans are greater than the harm:
- pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- gastrointestinal infection;
- venereal disease;
- blood poisoning;
- postoperative complications.
Remember that medications are only useful if:
- antibiotics were prescribed by the attending physician;
- the dosage was observed (the liver was not overloaded);
- you drank the full cycle;
- the disease is not viral (viruses cannot be treated with antibiotics).
Thanks to antibiotics, you will be cured of diseases and boost your immunity.
Harm of antibiotics
We are surrounded by bacteria. The use of antibiotics causes a blow to them, but their own body is also under attack. Therefore, the harm of antibiotics has been identified, which sometimes exceeds the benefits.
Before you start taking medications, find out why antibiotics are harmful to you.
Destruction of bacteria
The original antibiotics were close to the microflora of the body, so they destroyed exclusively harmful bacteria. The current generation of antibiotics is synthesized, so they are characterized not by selective, but by total (complete) destruction of bacteria inside the body, including beneficial ones.
Adaptation
Pathogenic bacteria are predisposed to adapt to antibiotics. Therefore, every 2-3 months a new form of medicine is released that can destroy pathogenic flora.
Slow restoration of microflora
Pregnancy
During the 1st and 2nd trimesters, taking antibiotics is contraindicated - toxic effects will provoke defects in the development of the fetus. The only exception is a doctor’s prescription, which takes into account the harm of antibiotics during pregnancy, and strict monitoring.
Impact on children
Infants are exposed to the toxic effects of drugs, so antibiotics are harmful to children during breastfeeding. Uncontrolled use of medications by children leads to weakened immunity, health problems and the likelihood of serious diseases. Therefore, pediatricians can prescribe antibiotics to children if necessary.
Gastrointestinal problems
The harm of taking antibiotics affects the gastrointestinal tract. The mucous membranes of the stomach are irritated, an exacerbation of an ulcer or pre-ulcerative condition is provoked, the balance of microflora in the intestines is disrupted along with the functioning of the liver, kidneys and gall bladder. Monitor your body's reactions - some people are prone to individual intolerance to components.
Allergic reaction
When taking antibiotics, an allergic reaction is possible, sometimes severe, with itching, redness, rashes or swelling.
Effect on the nervous system
Antibiotics have a harmful effect on the human nervous system. This manifests itself in the form of disorders of the vestibular apparatus, disorders with the possibility of visual and auditory hallucinations.
Consult your doctor and take medications strictly according to the schedule - this will ensure minimal harm with maximum benefit.
If the attending physician prescribes antibiotics, then your task is to ensure maximum benefit and minimum harm from taking it.
To reduce the harm from taking antibiotics, follow the rules:
- follow the dosage. When purchasing medicine from a pharmacy, check the dosage and make sure it is correct;
- read the instructions. If you find a disease that you have as a contraindication for use, please consult a physician for advice;
- eat before taking the medicine. A full stomach will reduce the harm from antibiotics without causing irritation of the mucous membranes;
- take the medicine with water;
- Do not take antibiotics and absorbent or blood thinning drugs at the same time;
- take the full course. Even if you feel better, you should not interrupt the course. This will allow incompletely suppressed bacteria to form resistance, ensuring further ineffectiveness of treatment;
- maintain normal intestinal microflora through the simultaneous use of probiotics, lactobacilli, immunomodulators and vitamin complexes with antibiotics.
There was a myth that the combined use of alcohol and antibiotics leads to a worsening of the condition or blocks the effect of the medicine. According to scientists, it is much more dangerous if a patient skips taking an antibiotic because he drank wine beforehand. Each missed tablet causes an increase in the resistance of the pathogenic flora to treatment.
Consult with your doctor first whether it is possible to combine alcohol with tablets, and how long after you can drink alcohol after taking antibiotics (cephalosporin group of antibiotics and nitromidazoles negatively interact with alcohol, so in this case the restriction is reasonable).
After taking antibiotics, you are allowed to drink alcohol. When you carefully study the instructions, find the section “compatibility with alcohol”. Side effects and possible compatibility are described there. But remember that drinking alcohol is harmful.
It has long been known that humans live in a world of bacteria. Many microorganisms have a beneficial effect on human life, but they can also cause harm, especially those. which are capable of penetrating into the body. Antibiotics can cause a strong blow to pathogenic bacteria. These strains of microorganisms were isolated precisely for this purpose and have proven their effectiveness in practice.
With the help of antimicrobial drugs, complex, almost fatal pathologies, including sepsis, pneumonia, and meningococcal infections, are successfully cured. But along with the undeniable benefits, the harm of antibiotics to the body is also obvious and manifests itself in aggressive interference not only in the vital activity of pathogenic microbes, but also in the total elimination of beneficial microflora, primarily the intestines.
Experts consider the following to be particularly difficult consequences:
- irritation of the mucous membranes of the stomach and intestines;
- complex imbalance of gastrointestinal microflora;
- disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys, liver, gall bladder;
- severe allergic reactions;
- disorders of the nervous system, manifested in vestibular disorders.
The widespread popularity of antibacterial drugs and their undeniable effectiveness have led to the fact that many patients began to practice uncontrolled use of antibiotics. Especially often cases of self-medication were recorded among people who are successfully making a career and do not have time for a full examination and correction of the treatment regimen.
Pathological conditions that are caused by viruses cannot be treated with antibacterial drugs, so the decision on antibiotic therapy should be made by the doctor based on the nature of the pathological process. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics in such cases will not only not bring benefit, but can cause irreparable harm to the body.
Antibiotic therapy is considered appropriate for the following diseases:
- Bacterial pathological processes of the nasopharynx: sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, diphtheria.
- Infectious pathologies of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Complex diseases of the respiratory system: deep and prolonged bronchitis, pneumonia.
- Infections of the genitourinary system caused by various pathogens and bacterial agents.
- Renal pathological processes.
- Intestinal dysfunctions of bacterial nature.
When treating viral infections, antibiotics are prescribed only if the disease is complicated by an associated bacterial infection, and the harm of antibiotics is comparable to the benefits for the body as a whole.
In order for treatment with antibacterial drugs to be as effective as possible and not provoke complications, experts have developed a number of recommendations on how to take antibiotics without harm to health:
- When taking an antibacterial drug, you should strictly follow the dosage prescribed by your doctor. The range of drugs in the pharmacy chain is quite wide, so when purchasing an antibiotic, it is worth monitoring its dosage.
- Before taking it, you should additionally carefully study the instructions, since the list of contraindications may include pathologies in your medical history that the treating doctor did not take into account.
- You should not practice taking antibacterial drugs on an empty stomach, since the harm of antibiotics to the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines has long been a proven fact.
- The medicine should be taken with a sufficient amount of water - this will minimize the destructive effect of the agents on the mucous membrane.
In order for therapy with antibacterial drugs to be effective and not cause harm to health, experts recommend taking into account a number of exceptions and additions to treatment.
- Alcohol, sorbents and blood thinning medications are excluded for the period of antibiotic therapy.
- Once your condition improves and the symptoms of the pathology are relieved, you should not stop taking it without permission, since bacteria that are not completely suppressed will quickly develop resistance to the drug, and further treatment will be ineffective.
- The harm of taking antibiotics is minimized by using probiotics and preparations with lactobacilli. Doctors prescribe to their patients a regimen according to which these drugs should be taken throughout the treatment period and for some time after the end of therapy.
- Since antibacterial agents can suppress the immune system, when treating with antibiotics, do not forget about taking immunomodulators and vitamin complexes.
Complications after taking
Often the drug is prescribed when it was possible to do without it. For example, if the doctor decided to play it safe or in the case of self-prescribed medication.
Then serious complications may arise after taking it, including:
- Anaphylaxis – develops within 30 minutes, characterized by laryngeal edema, arrhythmia, and urticaria.
- Serum-like syndrome appears 1-3 weeks after administration, symptoms are accompanied by fever, joint pain, and malaise.
- Drug fever occurs 6-8 days after the start of treatment: it is characterized by bradycardia, elevated temperature, and a high level of leukocytes in the blood.
- Severe dermatitis and inflammation of the mucous membrane appears in men and women after a week of use.
In unjustified cases, doctors advise abandoning antibacterial drugs and replacing them with other active ingredients.
If you take antibiotics correctly and follow the recommendations, there should be no side effects.
Need to know
Let us summarize briefly in which we characterize the main facts presented above.
- Antibiotics do not lower body temperature.
- These drugs do not act on viruses or fungi.
- They can only kill bacterial pathogens.
- There are two types of antibiotics: narrow and broad spectrum (the former is preferred).
- The drugs disrupt the life processes of the microbe, thereby killing it.
- The effect of antibiotics negatively affects the liver, kidneys, immunity, nervous system and heart of a person.
- After treatment with antibiotics, dysbiosis and weakening of the body's protective functions may occur.
Armed with these facts, you can approach your own treatment wisely, and also prevent unscrupulous doctors from prescribing the wrong medications.
Rules for treating babies
Some childhood diseases, indeed, can only be treated with antibacterial treatment. Doctors practice antibiotic therapy in the treatment of childhood diseases in the following cases:
- with sore throat;
- otitis;
- pneumonia and severe bronchitis;
- inflammatory pathologies of the urinary system.
- It is important to strictly adhere to the dosage and frequency of taking the drug prescribed by the doctor.
- The recommended duration of taking the antibiotic should be followed.
- The baby is not given antibiotics at the same time as antihistamines.
- You should strictly follow the diet and principles of feeding the child recommended by the doctor during treatment.
Harm of antibiotics
Adaptation
Pregnancy
Medicines for children with the smallest list of side effects
Every mother worries about the health of her baby, so when a doctor prescribes antibiotics, a woman always double-checks their side effects.
Note! If the baby has a serious illness that can only be treated with antibacterial drugs, they should not be replaced with other options.
The table shows a selection of antibiotics for children with a small number of consequences, since only folk remedies can have no side effects.
Consider:
| Age category | Medicines | When is it prescribed? |
| Newborns | Flemoxin Solutab, Augmentin, Cefuroxime, Cifran | For bronchitis, otitis media, E. coli |
| Up to 1 year | Penicillin antibiotics | ARVI, stomach diseases |
| Over 1 year old | Furagin, Furazolidone, Vilprafen | Urinary tract infection, intestinal infection |