Worms are parasites that settle in the body of humans or animals and live off the nutrients of the host’s body, while causing significant damage to it in the form of poisoning with their waste products, mechanical damage and other negative effects. In children, worms occur much more often than in adults, namely, about 80% of worm infestations occur in children.
Symptoms of worm infection are varied, and treatment depends on the type of parasite, so worms in children require medical treatment. Helminthic infestation leads to diseases under the general name helminthiasis.
Types of worms dangerous to humans
Parasites that can settle in the human body are divided into several groups:
- Flat (cestodes). These include pork tapeworm, tapeworm, tapeworm, and echinococcus.
- Round nematodes - pinworms, roundworms, whipworms, trichinella.
- Flukes (trematodes) – cat and liver fluke, schistosome.
Worms can settle in any organ - in the intestines, liver, muscles, heart, lungs. You can cope with a parasitic infection only by knowing well the symptoms and treatment features of each type of helminthiasis.
Treatment
The method of combating helminthiasis varies depending on the complexity and characteristics of the disease. Therapy is always carried out comprehensively, since this is the only way to get rid of parasites quickly and effectively.
Disposal is carried out in several stages. Let's take a closer look at the steps of treatment for roundworms in children:
- Preparatory. At this stage, the little patient’s body is most carefully prepared to remove parasites from the body. Most often, plant-based, organic components are used, such as flaxseed and pumpkin oil, which must be taken internally.
- This stage involves the use of an anti-worm drug (anthelminthic). Both herbal and medicinal preparations are used.
- At this stage, it is typical to use drugs that are aimed at restoring the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, lungs and liver. Immunostimulating supplements are also used.
Infection with pinworms is easier to tolerate than with roundworms. Getting rid of pinworms takes less time, and the drugs used are consumed in smaller quantities.
Folk remedies
Folk products are quite effective in treating helminthiasis. However, before consuming any of these products, we advise you to consult a doctor for advice. Because fighting the disease on your own can lead to complications and poor health for the child. There are several effective remedies that will help get rid of parasites. Let's take a closer look at the most effective folk remedies:
- Garlic is considered one of the most effective products against worms. To perform an enema, you need to boil a few cloves of garlic in milk. Allow the liquid to steep and cool for several hours, then use as directed and leave overnight.
- Wormwood is also a wonderful remedy for helminthiasis. Take a couple of tbsp. wormwood and pour a glass of boiling water. Leave to brew for several hours and take 1 tbsp before meals. spoon.
- Tansy flowers will help you quickly and effectively get rid of parasites. It is necessary to make an infusion and take 2 tbsp several times a day. spoons.
No matter how folk remedies help in the fight against parasites, complex therapy has not been canceled. And in order to get rid of the invasion forever, it is necessary to carry out not only therapeutic measures, but also preventive ones.
Pills
Anti-helminthic drugs for children are selected based on the doctor’s recommendations and only after a diagnosis has been made. The specific drug is selected based on the characteristics of the infection, the age of the patient, as well as the picture contained in the medical history. Typically, the following drugs are used for therapeutic purposes:
- Pirantel. One of the most common drugs for eliminating helminthiasis in pediatric practice. Indicated for use from 6 months. The tablets are intended to eliminate pathogens of enterobiasis, ascariasis, necatoriasis, and hookworm. If a doctor prescribes Pirantel, then one dose of the drug with a repeat dose after two weeks is enough for recovery. The drug is available both in tablet form and in the form of a suspension.
- Mebendazole. An anthelmintic supplement used to treat the disease in children from 2 years of age. The most famous commercial name of the drug is Vermox. A distinctive feature of the product is its wide range of action, which allows you to get rid of the most common helminthic infections. In world practice, the product is recognized as one of the best remedies for eliminating enterobiasis and ascariasis. When eliminating roundworms at an early age, it is recommended to use the drug only in case of severe helminthic infestation. Adverse reactions in the form of dyspeptic disorders or allergic manifestations are possible.
- Piperazine. A medicine for worms with a narrow spectrum of action, used to treat ascariasis or enterobiasis. The principle of action is based on the paralysis of the muscles of helminths and their subsequent removal from the human body through natural means. The drug has low toxicity, due to which it can be used in pediatric practice, however, it has a narrow focus and is low in effectiveness in eliminating severe helminthic infestations. Side effects are rare and occur infrequently in practice.
- Albendazole. The product is also known as Nemozol or Vormil. It has a wide spectrum of action and can be used to get rid of most common helminthic diseases. The tablets have a high intensity of action on both adults and larvae during the migration period. At the same time, the product has a wide range of side effects, including dyspeptic disorders, allergic skin reactions (urticaria, dermatitis), disruption of the autonomic system.
- Levamisole. The greatest effectiveness of the drug was noted in the fight against ascariasis. Has a pronounced immunostimulating effect. Long-term use is not recommended due to the likelihood of kidney and liver damage. Not recommended for use under 3 years of age.
When carrying out anthelminthic treatment, parents should remember that the use of medications entails the death of helminths, as a result of which a large amount of toxic substances is released into an insufficiently strong body. As additional measures to prevent intoxication, it is recommended to use enterosorbents. If the baby shows signs of an allergic reaction, it is necessary to use antihistamines.
Routes of infection
The majority of all cases of worm infection are pinworms and roundworms. This is explained by the method of transmission of infection. Infection occurs mainly through unwashed hands and eating unprocessed foods. It is the insufficiently developed personal hygiene skills in young children that causes the appearance of worms in the child. Parasite eggs are carried into the house on street shoes and enter the child’s body through interaction with animals. Some types of helminthiases are caused by meat and fish that have not undergone the necessary heat treatment.
When infected with pinworms, there is a high probability of reinvasion when, after scratching the anus, helminth eggs remaining on the hands end up on all objects that the child has touched. This causes re-infection of the infection carrier and other children.
Consequences of helminthiasis in children
The consequences caused by infection of a child’s body with worms depend on the scale of the lesion and the severity of the child’s condition, as well as the type of parasite and its location in the body.
The most dangerous for humans, including children, are the larvae of worms, and not sexually mature individuals. After all, their development cycle requires migration from one organ to another, while adult worms settle in one organ and conduct their life activities there. During migration, helminth larvae leave a lot of damage in the tissues and organs of their host, which, in turn, become potential sources of infection. This may interfere with the functioning of certain organs.
What can happen due to worm infection?
Suffering from helminthiasis, the child’s body will experience a constant lack of trophic substances. This is due to the fact that parasites take away part of the nutritional material supplied to the child with food, which manifests itself in the depletion of the child’s body.
- If there are too many worms in a child’s body, they can cause intestinal obstruction, accompanied by severe abdominal pain. This is fraught with intestinal ruptures and peritonitis. Treatment involves surgery.
- If helminths have parasitized other organs, for example, the liver, lungs or even the brain, this also leads to malfunctions in the corresponding systems.
- The emergence of the larvae of some helminths from the cyst state is accompanied by severe poisoning of the body and a sharp increase in temperature. This is fraught with the development of toxic shock.
- Systematic poisoning of a child’s body with toxins is also dangerous.
- An increase in the level of toxins in a child’s body greatly affects the state of his nervous system. The “unreasonable” whims of a baby may not be unreasonable at all.
- Some researchers believe that helminthiasis is one of the factors contributing to the development of cancer.
- In addition, a child infected with worms poses a potential danger to others. Other family members can become infected from it, and animals can also be re-infected.
Thus, symptoms similar to signs of helminthic infestation in a child should be taken seriously. Timely medical care will help avoid many negative consequences of helminthiasis.
General signs of helminthiasis
Some types of parasites live in the human body for years without showing anything. The period of their activation is associated with a weakening of the host’s immunity. The presence of intoxication caused by worms is judged by a number of characteristic signs. In children, the first symptoms of a parasitic infection are observed 2–3 weeks after infection.
The child has:
- Pain in the upper or lower abdomen.
- Nausea.
- Loss of appetite (increase or, conversely, absence).
- Weight loss.
- Manifestation of allergic reactions.
- Frequent infectious and inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
- Headache.
- Growth retardation, developmental delay.
- Chest pain.
- Brittle nails and hair.
- Increased salivation.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Presence of worms in feces.
- Irritability, moodiness, decreased concentration, sleep disturbances associated with intoxication of the body caused by helminths.
If left untreated, worms in children can cause serious problems - hepatitis, pyoderma. Jaundice. Sometimes they cause visual impairment, development of strabismus, pulmonary failure, and intestinal obstruction.
Having discovered the first signs of worms in children, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo the necessary examination, including laboratory tests. After confirming the diagnosis and determining the type of helminthiasis, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Making a diagnosis of helminthiasis
Making a diagnosis of helminthiasis
A general assessment of the symptoms manifested in a child is an indirect method for diagnosing helminthic infestation. Although, an experienced doctor can determine the presence of worms in a child even without laboratory tests, by assessing the list of symptoms.
You can determine the presence of worms in children in the following ways:
- Directly see them in the pot with the child’s feces;
- Take a specific blood test for worms;
- Perform an analysis of duodenal fluid;
- Give a swab taken from the child’s anus;
- Submit a stool test to a laboratory to identify worm eggs under a microscope.
If worms were not found in the child’s stool, but symptoms characteristic of helminthic infestation are present, it is necessary to be tested for worms. The most effective method for identifying helminthiasis in a child is to analyze his stool for worm eggs.
In addition, the specialist can pay attention to the following indicators of the child’s body:
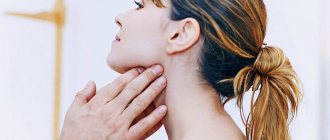
- Condition of the lymph nodes. Helminthic infestation is usually accompanied by their increase.
- Enlargement of internal organs, most often the liver and pancreas. Determined by ultrasound.
- The level of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the child’s blood. Helminthiasis is often accompanied by anemia.
- An increase in the level of leukocytes in the blood (indicates the presence of inflammation in the body).
- Liver tests. Symptoms of helminthic infestation are abnormal levels of bilirubin, immunoglobulin E, and eosinophils.
How to take a stool test for worm eggs
Stool collection for analysis
If parents suspect that their child has pinworms or other intestinal parasites, for an accurate diagnosis it is necessary to analyze the child's stool for worm eggs. To do this, you need to purchase a special container for stool collection from the pharmacy. It consists of a plastic box with a lid. Usually a plastic spoon is also included in the kit. Next, a small part of the child’s stool should be placed into this container using a spoon and the lid should be screwed on tightly, and then the container should be delivered to the laboratory.
If it is not possible to purchase special laboratory glassware for collecting stool, you can use a matchbox or glass flask.
Smear on pinworm eggs
Enterobiasis is also diagnosed by analyzing the contents of the folds near the child's anus. For correct indicators, it is advisable not to visit the toilet and not wash yourself for about 12 hours. Thus, it is optimal to take a smear for worm eggs in the morning.
Enterobiasis
A disease caused by pinworms.
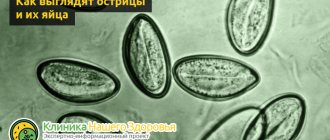
Parasites are small white worms, the size of which does not exceed 2 cm. Their life expectancy is short, however, if hygiene is not observed, there is a risk of re-infection. The eggs of the parasite have high viability. Not all disinfectants have a detrimental effect on them. Penetrating through the mouth into the intestines, they pass into the larval stage, which after 2 weeks become adults. Each of them is capable of laying up to 15 thousand eggs per day. The symptoms of enterobiasis have their own characteristics, so it is not difficult to distinguish the disease from other types of helminthiasis. Fertile females of the parasite tend to lay eggs in the skin folds of the anus, which causes severe itching in this area and inflammation. You can suspect enterobiasis by the child's behavior - the baby scratches the anus, becomes irritable, excitable, and has restless sleep. In girls, irritation of the urethra by pinworms often leads to enuresis. Penetrating into the vagina, parasites can cause inflammatory processes in the internal genital organs.
As a result of the life activity of pinworms, the same symptoms occur as are characteristic of all types of helminthiasis - intoxication, headaches, nausea, weight loss.
How to remove worms from a one-year-old child at home
As a rule, treatment of helminthiases in 12-month-old children is carried out at home and consists of carefully following the pediatrician’s prescriptions. Typically, such treatment is limited to one or two doses of the prescribed drug; in some cases, the course of treatment lasts 3-4 days.
In this case, it is necessary to carefully monitor the child’s condition and behavior, since it is extremely rare, but still there are cases of drug intolerance.
Sometimes the pediatrician prescribes additional medications, in particular, sorbents, since with the massive death of helminths, there is an increased release of toxins from the dying parasites, which can cause a deterioration in the baby’s general condition. Taking sorbents will neutralize the toxic effects on his body.
Treatment of helminthiasis should be accompanied by treatment of all other family members, as well as deworming of pets (this should be carried out twice a year).
Ascariasis
This is one of the most dangerous types of helminthic infestations. Roundworms can infect any organ. Helminths are long worms, sometimes reaching up to 40 cm. If untreated, they can live for a year, but eggs in a favorable environment are preserved for 12 years.
Infection occurs in the absence of hygiene measures. The child comes into contact with sand, where parasite eggs are present, communicates with domestic animals, after which he forgets to wash his hands and puts dirty fingers in his mouth. Often helminthiasis occurs as a result of eating unwashed vegetables and fruits. Within 3 months from the moment of infection, ascaris larvae migrate, penetrating from the small intestine to other internal organs. In this case, the child has a low-grade fever, general weakness, and malaise. One of the symptoms is the presence of a dry cough, sometimes with the production of sputum containing blood.
Helminth damage to the lungs can cause bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy, and asthma. The initial stage of ascariasis is accompanied by enlargement of the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen. The presence of worms in a child’s body is indicated by allergic manifestations in the form of urticaria and dermatosis.
After 3 months, when roundworms migrate back to the intestines, dysfunction of the digestive organs occurs.
The child complains of pain in the abdomen. Abnormal bowel movements, weight loss, and flatulence are observed. Against the background of decreased immunity as a result of helminthiasis, various infectious processes are formed - stomatitis, purulent lesions of the mucous membranes. Intoxication of the body caused by waste products of parasites causes nervous system disorders and insomnia. Possible complications associated with ascariasis pose a serious danger. Often advanced helminthiasis ends in peritonitis, jaundice, and intestinal obstruction.
Anti-worm medications for children from 3 to 6 years old
At an older age, it is much easier to choose effective methods and methods for removing worms from a child’s body.
You can give not only medicines, but also herbs against parasites for children:
- "Pyrantel" . Treatment in children is carried out from the age of 3 for diseases such as ascariasis, hookworm disease, necatoriasis and enterobiasis. Daily dose from 3 to 6 years – 1 tablet, from 6 to 12 years – 2 tablets;
- "Biltricide" . For the treatment of worms in a 4 year old child. Diseases: schistosomiasis, fascioliasis, paragonimiasis, trematodiasis, opisthorchiasis, cestodiasis, cysticercosis. The minimum daily dose is 20 mg per kg of body weight 2 times;
- "Pumpkin seeds" . An effective herbal preparation. For diseases associated with worms in children 3 - 4 years old, a decoction of 75 g is recommended, from 5 years - 100 g;
- "Difezil" . For worms in a child aged 2 years and under 5, the daily intake is up to 3 g of the drug, after 6 years – 3.5 – 4 g.
When getting rid of worms, a diet, eating fruits and vegetables, natural fresh juices, eating garlic and onions is recommended.
After most medications, it is advisable to perform enemas or take a laxative.
It is necessary to maintain cleanliness in the house and observe the rules of personal hygiene, take vitamins and drugs that restore immunity.
Other helminthic infestations
Infections of children with other types of parasites are much less common. However, the consequences can be quite serious. The following types of helminthiasis occur:
- Hymenolepidosis caused by dwarf tapeworm. There are no special symptoms, except those that are characteristic of any helminthic infestation - lack of appetite, drooling, abdominal pain, heartburn, fatigue.
- Trichocephalosis. The causative agent is the whipworm, a parasite whose length is up to 5 cm. The main symptoms of worms in children appear approximately a month and a half after infection. The lifespan of one individual in the human body is on average 5 years. The disease is manifested by periodically occurring dyspeptic disorders. Abnormal bowel movements are accompanied by vomiting and bloating. Sometimes anemia develops. Intoxication can lead to developmental delays.
- Opisthorchiasis. Occurs as a result of infection with the Siberian or cat fluke. The temperature rises to the low-grade level, a blood test shows an increased number of eosinophils, ESR, and anemia. The child complains of pain in the right hypochondrium and in the joints. Severe forms of helminthiasis lead to the development of pneumonia, hepatitis, and gastritis.
- Diphyllobothriasis is an infection with a broad tapeworm. The larvae enter the human body when eating poorly processed fish. Symptoms of worms are abdominal pain, digestive disorders, allergic manifestations.
- Toxocariasis. This type of helminthiasis is transmitted through contact with infected animals. Manifests itself in the form of allergic reactions such as cough, skin rashes. There may be enlarged lymph nodes and signs of swelling on the face. One of the most dangerous complications caused by parasites is toxocariatic ophthalmitis, keratitis, leading to irreversible damage to the organs of vision.
Be careful, worms! From general to specific
Be careful, worms!
The parasites collectively known as worms include a wide variety of worms. There are more than 400 species of worm-like parasites that pose a potential danger to humans.
Types of helminths depending on their biomorphology:
- Tapeworms (tapeworms, tapeworms - these worms have a fleecy covering and literally absorb trophic substances from the host’s body);
- Roundworms (the most famous of them are pinworms and roundworms);
- Flukes (liver, pulmonary flukes - these parasites are equipped with suction cups and hooks to “grab” host tissues).
The most common types of helminthiasis are:
- Enterobiasis (pinworms);
- Giardiasis (giardia);
- Toxocariasis (toxocara);
- Ascariasis (roundworms);
- Opistrichosis (opisthorchids).
Based on localization in the body, the following subspecies of helminths are distinguished:
- Tissue worms - settle inside muscle tissue or functional tissues of certain organs;
- Luminal worms live in the cavities of certain organs.
Most worms are parasitic in the child's intestines. For example, the favorite localization of well-known pinworms is the lower part of the small intestine and the upper part of the large intestine, while roundworms most often settle in the upper part of the small intestine. But it is also characteristic of helminths that they, as a rule, cannot reproduce in the human body and require the removal of their eggs outside of it. However, this does not mean that worms can disappear on their own, because some of these pests (for example, tapeworms) live for decades.
How do worms enter a child’s body?
There are many sources of helminth infection. The eggs of these parasites are found everywhere: in raw water, soil, and on unwashed food. Parasites are often carried by domestic animals, as well as insects - flies, cockroaches, ants.
If the parasite enters the child’s body orally, it is almost always encapsulated in a membrane membrane, which is partially broken down by the action of gastric juice, and completely by the influence of enzymes of the pancreas and bile ducts. After this, the released larva begins to carry out its activities inside the child’s body. Depending on the type of parasite, it settles in the tissues or in the lumen of a certain organ, where it grows to the state of puberty due to the nutrients entering the child’s body. Then the larva begins to actively lay eggs, which are usually released into the external environment with the child’s feces.
Clinical symptoms of helminthic infestation in children
The course of the disease may be asymptomatic. In addition, the presence of a particular symptom of helminthic infestation, as well as its intensity, depend on the type of helminths in the child and the degree of infection. To summarize, worms in a child are manifested by the following three signs:
- General intoxication of the body;
- Allergic reactions;
- Decreased functionality of a particular organ.
Parasites release their metabolic products into the host's body, thereby poisoning it. The child may also be allergic to toxins that enter the bloodstream due to the absorption of helminth secretions. In addition, worms irritate the tissues of the organs in which they settle, thereby reducing their functionality.
For some time after infection with worms, the child does not show any symptoms . But then the signs of helminthic infestation progress. These may include the following indicators:
- Lethargy, drowsiness, lack of mood;
- Decreased appetite after a short period of increased appetite;
- Slightly elevated body temperature;
- General weakness, malaise;
- Nausea, often accompanied by vomiting;
- Specific odor from the mouth;
- Paleness, bruises under the eyes;
- Urticaria, atopic dermatitis and other allergic rashes;
- "Unreasonable" cough;
- Digestive disorders (constipation, diarrhea);
- Bloating, flatulence;
- Irritable bowel syndrome;
- Pain in the abdomen (most often around the navel and in the right side);
- Exhaustion, weight loss;
- Nervousness, moodiness, emotional imbalance;
- Grinding of teeth in sleep (although many doctors attribute bruxism to nervous disorders and do not see any connection between this deviation and helminthic infestation);
- Sleep disturbances, nightmares;
- Anal itching;
- Complaints of pain in the joints and muscles;
- Increased salivation;
- Decreased immunity, which manifests itself, for example, in instability to acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections;
- Symptoms of vitamin deficiency (dry skin, brittle teeth, brittle nails and hair).
More specific symptoms of helminthic infestation can be observed when certain organs are affected. For example, worms in the liver are often accompanied by icteric syndrome. Parasites in the lungs can add shortness of breath, complaints of lack of air, cough with mucus and even blood to the list of symptoms of infection. Infection with pinworms is accompanied by intense anal itching, associated with the peculiarities of the life cycle of these parasites - female pinworms migrate to the anus to lay eggs, thereby provoking severe itching in the child in the perianal area.
In girls, helminthic infestation with pinworms is often accompanied by gynecological abnormalities. For example, this could be inflammation of the vagina, vaginosis, dysbacteriosis, and even cystitis. There are cases where pinworms, migrating, penetrated the genitals and bladder of a child.
The presence of several of the above symptoms in a child is a reason to contact a specialist for laboratory diagnosis of helminthiasis.
Diagnostics
It is possible to detect worms in a child and determine their type after laboratory tests of feces, urine, and blood.
Pinworms are identified by scraping. Tests must be taken 3 times at a certain interval. This will reveal the moment when parasites multiply. A complete blood count helps detect an increased number of eosinophils. Additionally, a test of sputum and bile for the presence of toxins may be prescribed. If echinococcosis is suspected, radiography and ultrasound are performed. To diagnose opisthorchiasis, an examination of the intestinal contents is required. How to be treated for a particular type of helminthiasis is determined only after the necessary diagnostic methods have been carried out.
What folk remedies can help?
In addition to medications, worms can also be treated with folk remedies.
The most popular products that can provide effective treatment for worms in children are:
- Garlic. Successfully destroys roundworms, tapeworms, pinworms and copes with many other types of parasites. Suitable for children from 5 years of age and with a healthy stomach. Give 1 clove before meals once a day. You can drink it with water or milk. Garlic is also an excellent antiviral agent.
- Pumpkin seeds. They should be eaten on an empty stomach and raw. Children usually like this treatment. Otherwise, they can be crushed and mixed with honey if the child is not allergic to honey.
- Sagebrush. Allowed for children over 12 years old. To make it easier to take, mix it with a piece of bread and add salt.
- Fresh carrot juice. Half a glass on an empty stomach once a day for 7-10 days is enough. You can also chew carrots raw.
- Beetroot juice. Given on an empty stomach. It is advisable to alternate it with carrot so as not to provoke bowel dysfunction.
- Walnuts. A few pieces a day will be enough for the child.
- A pineapple. Fresh, not canned fruit is a tasty and effective remedy.
- Citruses. You can add berries and fruits with a sour taste to their “company”.
Anthelmintic therapy
There are many modern medications that can effectively cope with any parasites. The choice of a suitable remedy should be made by the attending physician. It is important to take into account the general condition of the baby, his age, the presence of allergies or dysfunction of internal organs. The mechanism of action of antiparasitic drugs has significant differences. Some agents are effective against adults, others have a wider spectrum of action. In some cases, repeating the course of treatment is required.
Considering the high degree of toxicity of the drugs and the likelihood of side effects, it is necessary to take a very responsible approach to compliance with the dosages recommended by the doctor.
Along with anthelmintics, antihistamines are often prescribed. The safest of them are considered to be Cetrin, Zyrtec, Zodak. For children over 2 years of age, they can be used in the form of drops and suspensions.
Effective drugs included in the course of anthelmintic therapy are:
- Mebendazole.
- Vermox.
- Decaris.
- Pirantel.
- Albendazole.
- Piperazine.
The complex also includes enterosorbents intended to remove waste products of parasites, as well as vitamins C and B.
Treatment of infants at 12 months
Modern medicine makes it quite easy to combat many parasites, but they still need to be detected. Diagnosis of helminthiasis in one-year-old children is carried out on the basis of stool and smear analysis, which is taken directly from the skin around the anus. But there are problems here too.
Analysis of stool for the content of parasite eggs does not always give a reliable result the first time. This is due to the fact that helminths, such as pinworms or roundworms, do not lay eggs every day, so even with careful examination under a microscope they may not be detected. Reliable results can only be obtained by taking daily stool tests for at least three days.
Treatment of one-year-old children is complicated by the fact that the main medications have age restrictions, so the list of drugs for this age group is extremely small.
The following drugs are intended to expel pinworms and roundworms: levomisol, mebendazole, pyrantel. Of course, only a pediatrician prescribes antihelminthic therapy. He chooses the appropriate drug and its dosage for the baby. Do not forget that treatment for worms is carried out simultaneously for all family members.
What can you give from tablets?
For young children, 3 types of medications are most often used: pyrantel; nemocid; piperazine
Pyrantel - used for ascariasis and enterobiasis, whipworm and necator infestations. Dosed at the rate of 10 mg/kg body weight. In order to give a tablet to a small child, it must be crushed, dissolved in the required amount of liquid and given to drink. Course of therapy - 1 dose. In case of necatoriasis, the course is extended to 3 days.
Nemotsid - indications for use are similar. The course is a single dose of the drug for infestation with roundworms or pinworms. Complex mixed infections may require extending the course to 3-4 days.
Piperazine - used only for infection with roundworms or pinworms. For other helminthic diseases the drug is not effective. Take 2 days, twice a day. For children 1 year of age, the dose is 200 mg. Combined use with nemocid and pyrantel is not allowed.
Suspensions and drops
Pyrantel and nemocid are also available in the form of a suspension, which makes it easier for the baby to take the medicine, but at the same time it has a medicinal effect similar to the solid forms of the drug. The suspension itself is a suspension of tiny solid particles of the drug immersed in a liquid base. Suspensions of pyrantel and nemocid have the same indications and course duration as the solid form. For children aged 1-2 years, the drug is given in a dose of 2.5 ml (half a measuring spoon).
Piperazine is also available in the form of drops - a 5% solution of the drug. Course of treatment - 1 dose. The dose for a one-year-old child is 3-5 drops. This dosage form is convenient to use. The drug can be mixed with food, which makes it extremely easy for the baby to swallow the drug.
Traditional methods of treatment
Many of the traditional medicine recipes used in the fight against parasites are known for their effectiveness. However, it is best to use them as a preventive method or as an addition to drug therapy, which cannot be avoided if a child has helminthiasis. Lack of quality treatment can lead to the development of severe complications. The most effective ways to help remove worms from a child are:
- Walnut infusion. Grind the green kernels, add hot water and add a little salt. Leave covered for half an hour, then strain and give the child water throughout the day.
- Pumpkin seeds are one of the most popular remedies for flatworms. It is recommended to eat 100–200 g of seeds daily.
- Carrot juice. Before each breakfast, drink freshly squeezed juice for 3 weeks. The method is contraindicated for disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hemp oil. Take a teaspoon in the morning and evening. You can drip oil onto a piece of bread.
- Camomile tea. Pour boiling water over the dried flowers and leave covered for a while. Before use, dilute with water until translucent. Drink 1 liter of infusion daily.
- Decoction of pomegranate peels. Boil the peel of one pomegranate in a glass of water and strain. Divide the resulting decoction into 3 doses, drink at intervals of half an hour. Give the child a laxative 3 hours after the last dose.
The use of any folk remedy must be agreed with a doctor.
Anti-worm tablets for children 1 year of age and up to 2 years of age
Any medications should be given with caution to children under 2 years of age. Carefully study the instructions and contraindications.
Only after determining the type and class of helminth, a specialist prescribes a medicine against parasites for children from one year of age:
- "Nemocide" . Prescribed for the treatment of helminths in young children from 6 months. Indications: ascariasis, enterobiasis, necatoriasis, hookworm disease, trichuriasis. Daily intake from 6 months to 2 years is 125 mg, for children from 2 to 6 years - 250 mg, age - 6 - 12 years - 500 mg. Taking laxatives is not required;
- "Helmintox" . For worms, it is recommended for children from 6 months of age. An effective remedy for ascariasis, enterobiasis, hookworm, necatoriasis, trichuriasis. Dosage from 6 months to 2 years – 125 mg, from 2 to 6 years – 250 mg, for children over 6 years – 500 mg. Laxatives are not prescribed.
In most cases, it is recommended to supplement treatment with enemas and medications to restore intestinal microflora, and vitamins to strengthen the immune system.
Treatment of worms in children over 2 years of age:
- "Vermox" . From 2 to 10 years, a single dose of 25-50 mg is prescribed for mixed helminthiasis;
- "Mebendazole" . For diseases caused by mixed helminthiasis, a broad-spectrum drug is recommended. Prescribed to a child aged 2 years and up to 10 years in a dosage of 25-50 mg once;
- "Vormin" . Helps treat worms in children from 2 years of age. For mixed helminthic infestations, multiple nematodes. The daily intake ranges from 25-50 mg once.
The doctor can also prescribe suspensions if the baby does not want to take pills. In this case, the dosage will be changed. It is possible to prescribe ointments. Basically, it is a zinc paste for local external use.
Prevention of helminthiases
Despite the fact that worms surround the child everywhere, infection can be avoided. The main preventive measures are:
- Maintaining hygiene. It is necessary to teach your child to wash his hands after using the toilet, returning from a walk, and after each contact with animals.
- Wash berries and fruits thoroughly under running and then hot water.
- Getting rid of the habit of putting fingers and pencils in your mouth.
- Cooking fish and meat dishes requires heat treatment for at least 40–60 minutes.
You can protect your child from helminthiasis with the help of anthelmintic drugs taken for the purpose of prevention in the fall and spring. For children over one and a half years old, the safest of them are recommended - Albendazole, Levamisole, Pyrantel.
Knowing how worm infections occur in children, symptoms and treatment of different types of helminthiasis, you can get rid of the infection and normalize the baby’s condition quite quickly.
How to find out if a newborn baby has worms
Even an experienced qualified specialist during examination will not be able to immediately identify parasites in young children from 1 day of life. For this purpose, a mandatory laboratory study of collected defecation materials is carried out monthly within the children's clinic.
What are the common signs of worms in newborns:
- restless sleep;
- poor appetite;
- sudden weight loss;
- combination of diarrhea and constipation;
- allergic reactions, rashes;
- copious amounts of saliva;
- vomiting, regurgitation of food debris;
- causeless crying and screaming;
- bloating;
- colic;
- temperature rise to 37°C;
- cough.
The baby’s health depends entirely on the parents, whose responsibilities include studying his habits, time spent sleeping and waking, and the amount of food consumed per day.
Manifestations and symptoms of worms in children are screaming, crying for no reason in a newborn, refusal to eat, obvious anxiety and intestinal dysfunction.
Worms are a group of parasitic worms
Of the 256 species of helminths, about 100 have become widespread in Russia. Most often, diseases are caused by pinworms, roundworms, and whipworms. Every year, half of the country's population becomes infected with pathogens of one of the three main helminthiasis (ascariasis, enterobiasis, trichuriasis). The incidence of echinococcosis and toxocariasis is increasing, especially among the younger generation.
The treatment and prevention of the disease largely depends on the belonging of the causative agent of helminthiasis to the biological genus. In addition to worms, there may be other parasites in the body.
Parasitic diseases of children:
- Helminthiases. Pathogens are animals related to nematodes or roundworms, trematodes or flukes, cestodes or tapeworms.
- Protozoonoses. Diseases caused by amoebas, lamblia and trichomonas.
- Mycoses. The causative agents are fungi, for example, candida, penicillium.
Roundworms are roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, pinworms, trichinella, and filaria. The most common flatworms are cat fluke and schistosomes. Tapeworms are most often represented by bovine, pork, dwarf tapeworms, broad tapeworms, and echinococcus. Giardiasis is a protozoan disease caused by a single-celled flagellated protozoan. Giardia is not a worm, but there are medications that relieve both helminthiasis and giardiasis.
Ways of infecting children with helminths:
- Alimentary or food. Ingestion of eggs and larvae with contaminated food, putting them into the mouth with dirt on hands, drinking water containing parasitic larvae.
- Contact and household. From infected people and animals, through household items, personal belongings.
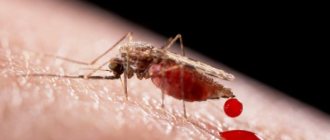
- Transmissible. During the bite of a blood-sucking insect vector.
- Cutaneous. In case of contact of unprotected mucous membranes and/or skin with sand or soil. Through water when swimming in polluted bodies of water.
- Placental (rare).
The risk of infection with worms is highest in long-term and frequently ill children, in large families, in bottle-fed infants, and in children with undeveloped hygienic skills.
Externally, roundworms resemble earthworms, but do not have a ringed structure. These are large worms, spindle-shaped. Ascariasis and trichuriasis in children occur when eating vegetables and berries contaminated with infective eggs or larvae. Pinworms are small, reaching about 1 cm, round helminths that parasitize the intestines. Transmission of the enterobiasis pathogen occurs through direct contact with persons infected with pinworms.
Signs of pinworm infection
It is very easy to become infected with pinworms, as their eggs remain on objects that a person has touched. Not all disinfectants can kill worms.
Symptoms of this disease in a child are the following:
- itching in the anal area (most often it makes itself felt at night, when the female lays eggs in this place);
- restless sleep, also due to itching;
- changes in weight indicators - weight loss or gain;
- fast fatiguability;
- irritability and moodiness;
- enuresis in girls due to the penetration of parasites into the urethra;
- inflammatory processes in the genitals if pinworms enter the vagina;
- grinding teeth at night;
- decreased immunity;
- disturbances of intestinal microflora, constipation or diarrhea;
- abdominal pain in the navel area.
Attention! The accumulation of pinworms in the cecum can cause acute appendicitis in a child.
Due to itching in the anus, the baby begins to itch in his sleep and thousands of eggs fall under the nails, then through the oral route into the intestines, where pinworms appear and grow, ready to lay eggs again after 2 weeks. As you can see, it is impossible to get rid of enterobiasis without treatment.
Who are these uninvited guests and how can they be dangerous?
Worms or helminths are a group of worms that survive by parasitizing in someone else's body. They can exist both in the human body and in animals, fish, and birds.
Once inside, the larvae or eggs immediately begin to develop. They are able to move throughout the body and affect several organs. The longer worms stay in the body, especially children, the more harm they can cause , therefore, the main thing in treatment is efficiency.
Worms can cause an abscess in the digestive system, block the bile ducts, and cause exacerbation of appendicitis, peritonitis, urinary incontinence, or vulvovaginitis in girls.
If symptoms of worms are detected in children, treatment should begin immediately.
Types of helminths
After detecting signs of worms in children, it is determined which specific type of parasite has settled in the body:
- round – nematodes;
- flat (ribbon) - cestodes, capable of receiving nutrition through their entire cover;
- Flukes are trematodes; they have a suction cup-like mouth on their head, with the help of which the parasite clings to the walls of organs and receives nutrition.
I consider the most important prevention against parasites to be instilling in a child the basic rules of cleanliness . Most cases of parasite infection occur precisely because of unwashed hands, especially in the summer. Parents, please pay attention and explain to your child how important this moment is.
The behavior of the parents themselves plays a large role in the treatment of worms. There is no need to cause panic, scare the child , or, conversely, slow down the treatment process. You need to take this as a normal childhood disease and do everything that the doctor prescribes for treatment.
Classification of parasites, signs of infection in children under one year of age and older adults:
- Pinworms are small white worms that live in the human intestines, can be transmitted by contact, and their eggs can be in the air. The larvae are predominantly deposited in the anal area. One individual lives for six months.
- Roundworm is a large round worm that is white and red in color and has something like a hook at the end. The eggs mature outside the human body, after which they enter it and develop rapidly. First of all, roundworms live in the small intestine, from where they can freely move to any organ and infect it, capturing others . In the body, worms form entire balls. The lifespan is up to 2 years.
- Whipworms are small worms that are as thick as hair. Eggs come to humans from the soil. They affect the cecum and appendix. Life expectancy is 3 years.
- Toxocara are medium-sized white worms, infection occurs from street cats and dogs. They travel through the bloodstream to all organs. They live up to 10 years.
- The bovine tapeworm is a tapeworm whose length reaches up to several meters. There are hooks on the head, and the body consists of segments that grow as the worm develops. The tapeworm reaches humans through the meat of an infected animal. Life expectancy is up to 10 years.
- The tapeworm is a long flat worm; infection occurs from fish in which the larvae have developed.
- The Siberian fluke comes to humans from infected fish. The size of the parasite is small, reaching up to 1 cm in length. Located in the intestines, pancreas, bile ducts. Up to a thousand individuals live in one organism, living up to 20 years.
The main signs of worms in a child
Helminthiasis is one of the most common diseases in children. Children under 3 years of age become infected more often due to the immaturity of protective barriers in the gastrointestinal tract, and also due to the fact that they actively explore the world, often tasting everything.
Many parents do not perceive helminthic infestation as a serious disease. After all, its first signs may appear some time after infection; they often resemble symptoms of other diseases. But it is very important to identify the presence of parasites in time to begin treatment. After all, they disrupt the functioning of all internal organs and can lead to the development of allergic reactions and decreased immunity.
Diagnosis of the disease
Very often, parents do not notice that their child is sick with helminthiasis. Many of the symptoms of this disease can be mistaken for a cold or intestinal infection. And it is very important to diagnose the disease on time. To do this, parents need to more closely monitor the child’s condition, and at the first disturbing symptoms, check him for the presence of worms.
Sometimes parasites can be found in a child’s stool, and in babies under one year old they can be felt through the abdominal wall. But most often, helminthic infestations are diagnosed using stool tests. If there is a suspicion of infection with worms, but the analysis did not find eggs, you need to test the feces several more times. Doctors say that a reliable analysis is obtained by following certain rules.
Sometimes an X-ray examination or ultrasound is prescribed, which helps to identify the presence of parasites in the liver, lungs and other organs. You can take a blood test. With helminthic infestation, hemoglobin is reduced, and the number of eosinophils and erythrocyte sedimentation rate are increased.
General symptoms of helminthic infestations
It is believed that almost every person is infected with worms. There is even a theory that parasites cause most diseases.
Important! The danger is that many helminths may not manifest themselves for years. Even with pronounced symptoms, it is very difficult to determine that a child has helminthiasis.
Moreover, for each type of parasite, the manifestations of the disease are different. What are the general signs of a child having worms:
- increased salivation, especially at night, the child wakes up with wet spots on the pillow;
- loss of appetite - the baby refuses to eat, eats poorly, or, conversely, is constantly hungry;
- the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted - the child suffers from constipation or diarrhea, abdominal pain, dysbacteriosis and flatulence appear;
- deficiency of iron, B vitamins and other microelements cause a decrease in hemoglobin and the development of anemia;
- urinary incontinence may occur;
- brittle nails, hair loss and dullness, peeling skin;
- various allergic reactions – a frequent manifestation of helminthic infestations;
- the child often suffers from colds, inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx and genital organs.
Important! The presence of worms can be seen by the fact that the child is pale and gets tired quickly. Such children are weak, lose weight with normal nutrition or do not gain weight at all.
Helminthiases in children under 2 years of age lead to retardation in physical and mental development. It is believed that children grind their teeth in their sleep precisely because of the presence of worms.
Intoxication of the body due to helminthiasis
After infection, after some time, the child’s body begins to be poisoned by the waste products of the parasites. The first signs of this may appear within a couple of weeks if there are a lot of worms. What are the symptoms of body intoxication:
- headaches, dizziness, nausea, fainting;
- sleep disturbance: drowsiness or restless sleep;
- irritability, moodiness, outbursts of anger;
- muscle weakness, fatigue;
- loss of appetite, nausea;
- in children after 7 years of age there is a noticeable decrease in memory, concentration, lack of perseverance and lag in studies;
- If a child infected with worms is vaccinated, he may have a severe allergic reaction to it.
Worms in an infant
Babies also become infected with helminthiasis if the mother does not follow hygiene rules well. Symptoms of the presence of parasites in an infant are the same as in older children. But there are some features:
- the baby eats poorly, loses weight or hardly gains it;
- he becomes capricious, often cries, sleeps restlessly;
- intestinal functions are disrupted, the child experiences either diarrhea or constipation;
- the baby’s skin is pale and there are dark circles under the eyes;
- allergic rashes on the hands and feet;
- the temperature may rise;
- such babies lag behind others not only in weight, but in height and development.
Signs of roundworm infection
According to statistics, most children under 5 years of age have been infected with roundworms at least once. This type of helminthiasis is considered the most dangerous because it occurs very often, and these worms can affect many internal organs and cause intestinal obstruction or asphyxia. This happens because small roundworm larvae that hatch in the small intestine are carried by the blood throughout the body. This is how they penetrate into the lungs, heart, liver, and gall bladder. Signs of this stage of the disease are:
- dry cough, sometimes with blood;
- development of bronchitis, pneumonia or bronchial asthma;
- temperature increase;
- weakness and drowsiness;
- enlarged lymph nodes, liver;
- allergic reactions.
After a few months, roundworms again move into the intestines and parasitize there.
Important! This condition can be asymptomatic for a long time. Only when the child’s immunity is weakened or when there is massive infection, the following signs are noticeable:
- abdominal pain, which may be cramping;
- inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes or skin;
- frequent colds;
- diarrhea or constipation, nausea, vomiting, flatulence;
- sleep disturbances, anxiety, irritability and other neuropsychiatric disorders;
- Sometimes a decrease in blood pressure may occur.
Signs of enterobiasis
This disease is caused by small roundworms called pinworms. They parasitize the human intestine. At night, the female emerges from the anus to lay eggs. This causes severe itching around the baby's anus. It is the main sign of the presence of pinworms. Enterobiasis can be suspected based on other symptoms:
- the child sleeps restlessly, tosses and turns, often screams and jumps up at night;
- redness and irritation in the anus and on the skin around it, inflammation of the skin from scratching;
- girls may experience enuresis due to enterobiasis even after 6 years of age;
- pinworms can crawl into the genitals and cause vulvovaginitis and inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- worms can accumulate in the cecum and cause acute appendicitis;
- these parasites live in the intestines, so disruption of its functioning, dysbiosis, diarrhea or constipation is often observed;
- dry mouth occurs.
Rare types of helminthiases
Other helminthic infestations are rarely found in our country. Most often, a child becomes infected with such worms from cats or by eating poorly cooked fish. How do rare helminthiasis manifest itself in a child:
- whipworm infection is not accompanied by pronounced symptoms; the disease can be suspected by the general signs of helminthic infestations: abdominal pain, moodiness;
- opisthorchiasis causes fever, rash, inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, pain in the liver, joints and disturbances in the functioning of the heart;
- Toxocariasis most often affects young children, and they experience enlarged lymph nodes, joint damage, severe swelling on the face, allergic skin rashes with unbearable itching and inflammatory eye diseases.
- when infected with a broad tapeworm, there may be intestinal disorders, abdominal pain, allergies and signs of mineral deficiency;
- Giardia is also often found in children - not worms, but microscopic parasites that also settle in the intestines and other internal organs. They cause dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract or inflammation of the gallbladder; their presence can also be determined by a yellow coating on the tongue and grinding of teeth.
Every mother should know what symptoms indicate the presence of parasites in the child’s body. This way she can treat him in time and prevent complications.
Are you still sure that it is difficult to cleanse your body of parasitic organisms?
If you are reading these lines, then your fight against parasites apparently was not so successful...
Have you thought about drastic measures to combat the disease? Surely - yes, because parasites are very dangerous - they are capable of multiplying quickly and living for a long time, precisely because of this, the diseases that they provoke often take on a chronic form and occur with constant relapse. Frequent nervousness, lack of appetite, sleep disturbances, problems with the immune system in general, dysbiosis of the intestinal tract... probably all of the above points are familiar to you.
But maybe it would be better to treat not the symptoms, but the cause of the disease? It will be very useful to read the work of Sergei Rykov, who heads the University of Parasitology, on the latest methods of combating parasitic diseases... Read more
We also recommend reading:
netparazitam.ru>
What complications can parasites cause?
Helminths that are detected untimely can lead to serious complications. Parasites cause the development of various diseases. They call:
- Jaundice (mechanical), intestinal obstruction.
- Hepatitis, meningoencephalitis.
- Appendicitis, urinary incontinence.
- Vulvovaginitis.
- Pyoderma.
- Pancreatitis, gastroduodenitis (not only the bile ducts are affected, but also the child’s liver).
- The respiratory tract is affected.
Parasites in a child can cause jaundice
The danger of helminthic infestations for children
The likelihood that a child will become infected with helminths is very high. Therefore, if any negative symptom occurs, you should show your baby to a doctor. Most types of pathology are successfully disguised as various diseases of infectious or non-infectious origin. These signs complicate diagnosis and cause untimely treatment. The particular danger of helminthiases lies in their chronicity and the development of severe consequences:
- hepatitis, jaundice;
- myopia, the appearance of strabismus;
- pyoderma;
- acute pulmonary failure;
- appendicitis;
- dysbacteriosis, candidiasis;
- neurological disorders, meningoencephalitis.
Children diagnosed with chronic helminthiases often suffer from night and daytime urinary incontinence. Before starting treatment for enuresis in a child, laboratory tests of stool are required to check for the presence of eggs of parasitic worms.
Warning: “Doctors state an interesting fact: after infection with worms, the number of antibodies in vaccinated children decreases. This leads to a sharp decrease in specific immunity and the body’s resistance to infectious and fungal pathogens.”
Often a child becomes infected with helminths after interacting with stray and domestic animals.
How to recognize the acute stage of the disease?
Having entered the acute phase, helminthiasis has the following symptoms:
- diarrhea or constipation;
- baby scratches his butt;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea;
- dark circles under the eyes;
- greasy coating on the skin;
- vomit;
- cough;
- acne;
- bad breath (many children do not have this);
- pain in the abdominal cavity (the child needs to be checked for gastrointestinal diseases);
- rashes on the skin (the child scratches them a lot);
- aches in muscles and joints;
- feverish conditions;
- itching (it doesn’t exist after infection, but it appears over time), etc.
If the disease becomes chronic, it may be asymptomatic, so parents need to pay more attention to the health and hygiene of their children and undergo regular medical examinations.
When do people become infected with helminths?
There are many ways for worms to enter the body; for a child, the most common are:
- through dirty hands;
- together with unwashed vegetables, fruits, herbs;
- after contact with pets;
- with unboiled water;
- orally (this is especially true for babies who love to taste everything they can get their hands on);
- with products that have been visited by flies or cockroaches.
Symptoms of the disease in infants
It is much more difficult to detect worm infection in infants than in older children; the following signs can signal it:
- poor sleep and anxiety;
- inflammatory processes in the anus, in girls - inflammation of the labia;
- constipation or diarrhea;
- flatulence, colic;
- decreased appetite;
- skin rashes;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- cough that is not related to respiratory diseases.
Symptoms and treatment of helminthiasis in infants require extreme care.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of the disease is very diverse and depends on the type of helminth, the severity of the lesion, and the presence of concomitant pathology. One can distinguish a number of common syndromes.
Intoxication syndrome in a child is manifested by decreased body weight, increased temperature, night sweats, lack of appetite, weakness, and lethargy. When the gastrointestinal tract is involved in the process, symptoms of dyspepsia develop, which are manifested by unstable stools, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Anemia gradually sets in. Respiratory syndrome is manifested by cough, shortness of breath with little physical exertion, up to eosinophilic pneumonia, obstructive bronchitis.
The phenomena of cholestasis due to impaired bile outflow are characterized by an increase in the amount of liver enzymes and pain under the right costal arch. The liver, spleen, and lymph nodes are enlarged.
Thus, the clinical picture of helminths in children is not very specific. If one of the above symptoms appears, you should always consult a doctor to undergo a proper examination and receive adequate treatment.
Diagnosis of helminthiasis
Diagnosis is usually made by identifying proglottid segments or characteristic eggs in the stool. These diagnostic methods are able to identify the nature of the infection. However, when it is necessary to determine the species (for example, in epidemiological studies), restriction fragment length polymorphisms are used.
PCR can be performed on purified egg samples or native fecal samples after sonication to release individuals from larvae.
Another interesting and effective diagnostic tool is a contrast agent - Gastrografin. It is injected into the duodenum, allowing the parasite to be visualized.
Pinworms are the most common type of worms in children.
Roundworms and pinworms in children are perhaps one of the most common parasites. Pinworms are worms that live in the large intestine and are only one centimeter in length and can cause a serious disease - enterobiasis. As soon as the microscopic eggs of worms enter the baby’s mouth, and from there into the intestines, they begin their development, and after two weeks, a sexually mature female pinworm is ready to lay new eggs. This happens at night when the baby, warmed up under the blanket, relaxes. Then the parasites get out through the anus and lay eggs around it, causing severe itching. In a dream, a child itches, eggs get under his nails, and then, as you understand, on bedding, furniture, toys and clothes, and often directly into the mouth, which causes re-infection.
Ways of worms entering the body
Infection of a child can occur when worm larvae or their eggs enter the body. Routes of penetration may be different:
- when playing with pets;
- while walking down the street or playing in the sandbox;
- when visiting public toilets;
- through unwashed hands;
- through unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- when in contact with dirty objects (for example, toys).
The larvae and eggs of worms are very small. They cannot be seen with the naked eye. Parasites that are not in the human body, but in the environment, can remain viable for a long period. They are activated, begin to grow and multiply when they enter the organs of the child’s digestive system. The most favorable conditions are in the intestines. It is in this organ that worms live. They cannot live in the stomach, because it has an acidic environment.
Is it so easy to detect worm eggs in a child’s stool?
Doctors complain that it is quite difficult to confirm a child’s infection with worms. To do this, it is not enough to take a test for worm eggs once every six months (to be honest, such a one-time test, in principle, does not make much sense)! To detect parasites, the study requires still warm stool, which is collected for three days in a row, or about seven times a month. In addition to this analysis, they will indirectly tell doctors that the baby is infected with helminths, hemoglobin is below normal, increased ESR, as well as a high number of eosinophils in the blood. And pinworm eggs can only be accurately detected by scraping for enterobiasis, since they are deposited only in a fold of skin near the anus and practically do not enter the feces.
Disease prevention
To prevent the spread of helminthic infestation, employees of decreed institutions and children are examined twice a year. When a helminthic infestation is detected, it is necessary to treat members of the entire family of the sick person. Depending on the route of infection and the area of residence, there are special anti-parasitic measures.
The most unfavorable regions are the Far East and the southern part of Russia. Disinfection of water supply sources, cleaning them of shellfish, sanitary treatment of populated areas, places for collecting feces, preschools, school institutions, and public catering associations are carried out.
It is necessary to explain the need to observe personal hygiene measures, wash hands, heat treat fruits, vegetables, meat and fish products. It is prohibited to consume stroganina to people and feed it to domestic animals if the technology for manufacturing the product is violated.
Drugs used to treat childhood helminthiasis
If a child has a severe form of helminthiasis, which is accompanied by the manifestation of myocarditis, arachnoiditis or vasculitis, glucocorticosteroids and dietary supplements are added to the above anthelmintic drugs. When treating a child for helminthiasis, all members of his family should take parasite prevention. It is imperative to maintain personal hygiene, use only your own towel, wash your hands after returning from outside and before each meal.
After successfully treating a child for parasites, he is given mandatory therapy (including dietary supplements) for helminths when he reaches the age of 14.
"Pyrantel" treats ascariasis, enterobiasis