Fibroadenoma
Many people are interested in the size of breast fibroadenoma for surgery.
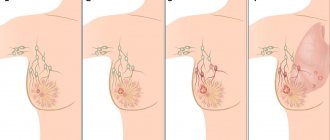
Let's look at this issue in more detail. Fibroadenoma is a nodular formation of the mammary gland with unclear contours. This is a type of nodular mastopathy that usually affects one of the mammary glands. Often the development of this disease is a consequence of a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. Fibroadenoma reaches up to 7 cm in diameter.
In this case, the formation is not associated with subcutaneous tissue and skin and is benign. If a lump is detected in the mammary glands, women should undergo a high-quality diagnosis, consult a mammologist and undergo tests. A diagnostic method such as histology helps to find out whether a given tumor is malignant. A piece of pathological tissue is taken for examination and a biopsy is performed.
https://youtu.be/IlVkNXXZCRk
Mammary cancer
In the early stages, the oncological process does not manifest itself in any way.
At later stages, the following manifestations are possible:
- changes in the shape of the breast, its contour, the occurrence of asymmetry;
- peeling of the skin, psoriasis-type spots, itching, burning;
- the appearance of areas with reddish, bluish or yellowish skin color;
- the appearance of wrinkled, dense, finely cellular areas of the “lemon peel” type;
- lumps or depressions on the breast;
- nipple retraction;
- sores and abrasions in the nipple area;
- discharge from the nipple not associated with pregnancy and lactation;
- hardening or swelling in the axillary or supraclavicular area;
- chest pain.
At an early stage, a small malignant tumor can be detected by palpation, ultrasound or mammography. Therefore, oncologists and mammologists never tire of convincing women of the importance of regular breast self-examination and preventive medical examinations.
Breast cancer treatment
A malignant tumor of any stage requires immediate surgical removal. The use of radiation, chemical, hormonal or targeted therapy is mandatory, but the choice of technique will depend on the nature of the tumor and the type of surgery chosen - radical or organ-preserving.
The radicality of the surgical intervention is dictated by the stage of the process, the type of tumor and the age of the patient.
At stages I–II, organ-preserving surgery is usually performed. Only the affected area is removed. In this case, radiation therapy is mandatory.
In III, a radical mastectomy is performed along with the removal of nearby lymph nodes.
IV is considered inoperable. Chemo-antihormonal and targeted therapy are used. Operations are performed to provide quick symptomatic relief to the patient's condition.
Cystic mastopathy
In the first stages of development, nodular mastopathy is usually very similar in symptoms:
- small formations have clear boundaries and are mobile under the skin;
- before menstruation, acute painful sensations occur in the affected gland;
- Before menstruation, the breasts become very tight and swell, but after this period they almost completely disappear;
- small nodes can be detected by chance during self-examination - most often the cystic form of mastopathy is diagnosed in this way;
- in a supine position it is very difficult to detect nodules - this is called the absence of Koenig’s sign;
- lymph nodes do not enlarge in benign mastopathy;
- Various discharges are possible from the nipples, both when pressed and in the form of involuntary leaks.
This neoplasm is a capsule filled with liquid. Cysts can be single or multiple. This neoplasm provokes frequent stress and hormonal imbalances, which are characterized by an increase in estrogen levels in the body. Pain most often worries a woman before the onset of menstruation, due to an increase in progesterone levels and the resulting fluid retention.
In this case, a fluid similar to colostrum, mixed with pus or blood, may be released from the nipples. The disease in most cases develops after menopause, but nulliparous and smokers, patients with a genetic predisposition and a history of numerous abortions are also at risk. The disease can also occur due to improper treatment with hormonal drugs, pathologies of the endocrine glands and liver.
If the breast cyst is small in size, it is usually treated without surgery. The patient is prescribed vitamin and iodine-containing medications, diet, and some hormonal therapy.
Treatment is carried out for a long time, under the supervision of a doctor. If after its completion no positive result is observed, the specialist may recommend surgical removal of the tumor.
General characteristics of the disease
Benign tumor or dysplasia occurs in 70% of women. A benign breast tumor is a compaction formed from epithelial and connective fiber cells. A foreign formation in the breast appears in different forms - it can be a cyst, a node, a small lump, etc.
A benign breast tumor in women is considered not a dangerous disease, but requires careful monitoring by a doctor. Some species have the ability to degenerate into an oncological node with severe health complications. A malignant process is observed in 30-33% of patients. But this happens in the absence of medical care or refusal to follow the recommendations of the attending physician.
The ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) code for pathology is N60 “Benign mammary dysplasia.”
Dimensions of the tumor
Let's talk about the size of breast fibroadenoma for surgery. If the tumor is no more than 8 mm, then treatment begins with traditional methods: taking hormonal medications, using folk remedies. Conservative methods of therapy are used for 6 months with constant monitoring of the condition of the formation using ultrasound.
If the doctor notices that the nodular formation of the mammary glands has increased in size, an operation may be prescribed, which involves removing the pathological focus. The absolute indication for intervention is the rapid growth of the tumor, the likelihood of transformation into an oncological tumor and pregnancy planning. Large fibroadenomas are considered to be nodes exceeding 2 cm in diameter. Most often they lead to a change in the shape of the gland.
Fibroadenoma is classified into several types:
- leaf-shaped;
- pericanalicular;
- intracanalicular;
- involutive.
Prevention
The development of benign breast formations cannot be prevented. The fact is that the health of the mammary glands is most influenced by heredity. However, you can reduce your exposure to certain risk factors. For example, if benign breast formations in your case are caused by excess weight, you need to lose weight. If the cause is hormonal or oral contraceptive use, talk to your doctor about effective methods to reduce your risk. However, in some cases you may need to take oral contraceptives to prevent certain types of growths.
Types of nodal diseases and their features
Fibroadenoma is the most common type of mastopathy, manifests itself as small dense balls and often causes pain. At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, such nodes do not disappear. In most cases, surgical removal is required.
Breast cysts almost always occur against the background of hormonal imbalance due to tumors, endocrine disorders, and stress. There are retention cysts of the mammary gland that appear during breastfeeding. Requires surgical removal.
Mastitis is an inflammatory disease of the gland that occurs against the background of bacterial infection. The chest turns red, hurts, and the temperature rises. If left untreated with medications and herbs, mastitis develops into an abscess.
There are other types of benign tumors, which can only be determined after tests and instrumental diagnostics.
Lipoma
Lipoma is a benign tumor arising from adipose tissue. It can develop in various parts of the body, including the mammary gland. The neoplasm has a characteristic soft elastic consistency and a spherical, smooth surface. Usually these are harmless formations that do not cause complaints from patients or concerns from doctors. In most cases, when they are relatively small in size, they do not require treatment. However, to differentiate a lipoma from other, more serious changes in the mammary glands, a consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Causes of lipoma
This is a benign neoplasm in the mammary gland, formed due to excessive growth of adipose tissue. This compaction looks like a capsule. It is not painful, but is soft and mobile. The lipoma reaches 2 cm in size, but in some cases it can increase to 10 cm in diameter. Such a large formation in the mammary gland begins to compress the surrounding tissues and cause pain.
The causes of lipoma formation are:
- violation of metabolic processes;
- hereditary predisposition;
- blockage of the sebaceous gland duct;
- accumulation of toxins in the body.
Cases of such a node degenerating into a malignant tumor are quite rare, but it probably still exists. Surgical intervention in this case is necessary if the formation has greatly increased in size and deformed the breast, as well as if pain develops. The operation is also performed in cases where the lipoma affects other tissues and organs. Typically, small lipomas are removed under local anesthesia. For large nodular formations of the mammary glands, general anesthesia is used.
Formations in the mammary glands can be provoked by physiological or pathological factors. During breastfeeding, a problem may arise due to blockage of the ducts when the breast is not completely emptied of milk. If at the same time a woman’s temperature rises, skin hyperemia and pain appear, there is a very high probability that mastitis will develop.
In pregnant women, the appearance of dense formations in the breast is associated with increased synthesis of estrogens, progesterone and prolactin. The breasts become enlarged and lumps appear in them. After the birth of a child, hormonal levels should normalize.
Pathological changes that cause seals to appear:
- cyst,
- lipoma,
- fibroma,
- atheroma,
- fibroadenoma,
- lymphoma,
- mastopathy,
- thrombophlebitis.
Predisposing factors for the formation of lumps in the breast can be:
- injuries,
- wearing a bra that compresses the breasts,
- abortions,
- stressful situations.
The formation of cysts in most cases is associated with hormonal disorders. When connective tissue grows in the breasts, sacs appear, inside of which there is a clear liquid. Overgrowth of fibrous tissue causes fibroids.
Fibroadenoma is a benign formation that can be nodular or leaf-shaped. The nodular form of fibroadenoma has a single node and a sheet-like layered structure.
Malignant tumors include:
- Breast cancer is the appearance of cancer cells in the epithelium and glandular tissues, which can be localized in any part of the organ.
- Sarcoma is a distinct, lumpy lump that tends to grow and ulcerate rapidly.
- Lymphoma formation of a rounded compaction.
When a vein passing through the area of the axillary fossa is damaged, thrombophlebitis develops. The appearance of blood clots causes lumps in the chest.
Galactorrhea
Galactorrhea is the release of milk or colostrum outside of breastfeeding. Small discharge may remain for a long period (up to several years) after the child has stopped breastfeeding or after an abortion. This discharge usually goes away over time without any treatment. But doctor's supervision is necessary. In some cases, a cytological examination of nipple discharge is necessary (taking smears on a glass slide and examining them under a microscope). For heavy and long-lasting discharge, certain drug therapy is indicated to suppress the hypersecretion of prolactin, a hormone that stimulates secretion in the mammary glands.
Reasons for the formation of lumps in the female breast
Mastopathy
Most tumors and lumps are benign. There is a general term for all diseases of this type - mastopathy. They appear when hormonal levels change - before menstruation or during menopause, during breastfeeding, untimely pumping, after injuries or wearing tight underwear.
The lump in the chest can be diffuse, which indicates extensive damage to the gland, or nodular, with a limited area of damage.
Stages of breast mastopathy
Hormonal changes occur in the female body throughout life. In addition to the sex hormones - estrogen and progesterone - the hormones of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands can affect the condition of the breast.
Mastopathy sometimes occurs in teenage girls with high estrogen levels, especially with the early onset of menstruation - before the age of 12. Further, temporary compactions appear in the corpus luteum phase before menstruation. This is not dangerous and goes away on its own after menstruation.
During the reproductive period, when using hormonal drugs for contraception, estrogen levels can dangerously increase, so the slightest lumps in the mammary gland in women should be diagnosed using ultrasound or MRI.
The most common type of tumor. Occurs at the site of tissue damage or after inflammatory processes in the gland. The secretion accumulates, but is difficult to remove, resulting in the formation of a dense area. Cysts with fluid cannot always be felt due to their small size. Surgical treatment is not required, since this form is well treated conservatively.
Fibroadenoma
Occurs in adolescence and premenopausal age, as well as after an abortion or a course of contraceptive drugs. It is an elastic, round, movable ball, painless on palpation. Ovarian hyperfunction is a predisposing factor. It has several types: in older women, calcium salts may be deposited around the ducts. Sometimes the connective tissue grows and affects the ducts.
Leaf-shaped tumor
The most dangerous form of fibroadenoma. Characterized by accelerated growth. The tumor grows to 20–30 cm in diameter in 5–6 months. This is approximately 4 – 5 kg. This type of benign tumor more often than others degenerates into sarcoma. Removal surgery and checking for the presence of affected lymph nodes and metastases are necessary.
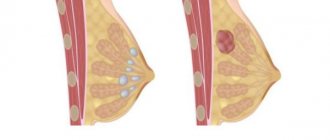
Breast cyst
A cavity inside the mammary gland filled with fluid. The reason is frequent hormonal imbalances, endocrine disorders, excess weight. Symptoms of a cyst include:
- menstruation disorders;
- breast enlargement;
- soreness when touched, redness;
- presence of a seal inside.
Lipoma
A tumor of adipose tissue that sometimes develops into liposarcoma. It occurs in women after 40 years of age and grows slowly. It is diagnosed randomly during a routine examination by a gynecologist. When large, it causes a feeling of fullness. It is treated with a gentle surgical method.
Intraductal papilloma
A benign tumor of the papillary type is more common in women during menopause, although it also occurs in girls. In this case, a greenish or brown liquid is released from the nipple. The papilloma is easily damaged, so mechanical impact causes blood to appear from the nipple. The main reason is hormone imbalance.
Mastopathy can manifest itself on a large scale - diffusely or locally - in a nodular form. In this case, patients experience breast enlargement, tenderness, and bloating, which intensify before menstruation. It can be one-sided or two-sided.
Atheroma
Atheroma is a cyst that appears in the sebaceous gland
Appears due to blockage of the sebaceous gland. If a woman has hair growing on her areola, there is a risk of atheroma. Endocrine disorders can provoke excessive activity of the sebaceous glands. With atheroma, a cystic capsule with a thick substance forms inside the mammary gland. In severe cases, the breasts may become swollen and painful. If an infection occurs, an abscess forms, the temperature rises and urgent medical attention is required.
Hemangioma
A benign tumor growing from vascular tissue. Most often it is congenital and is diagnosed in girls. Premature babies are considered at risk due to the characteristics of the endocrine system. The reason for the appearance of this pathology has not been fully studied, but it is believed that its occurrence is influenced by viral diseases of the mother during pregnancy.
Lactostasis
During breastfeeding, women often develop lumps in their breasts. This is due to inadequate milk sucking or improper breastfeeding technique. The result is stagnation and obstruction of the duct, followed by inflammation and mastitis.
Lactostasis
Milk is synthesized in acini; there are about 15–20 of them in one mammary gland. They are connected to the nipple by ducts. If milk is not renewed in one acini for several days in a row, a plug forms in it. Lactostasis ends with mastitis - uninfected or infected. Massage is a way to free the acini from milk and improve its outflow.
The main reason for the development of mastopathy is hormonal imbalance
The mammary gland is a hormone-dependent organ, which is why hormonal imbalance is considered the main cause of mastopathy. It can occur during the following periods:
- pregnancy or breastfeeding;
- hormonal disorders, when the level of certain substances in the body increases or decreases;
- puberty and menopause.
In some cases, a single nodule in the mammary gland may disappear on its own after these periods, while other diseases remain and develop.
Additionally, we can identify provoking factors that affect the hormonal and reproductive systems and disrupt hormonal levels:
- mental fatigue and frequent stress;
- constant feeling of fatigue;
- excessive physical activity;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- gynecological disorders;
- chronic inflammatory process in any organ;
- parasitic diseases.
Benign breast tumors
Benign changes in the mammary gland include all types of mastopathy, including cysts, intraductal papilloma, fibroadenoma.
Mastopathy is fibrocystic structural changes in the breast tissue. With this disease, inadequate growth of connective tissue occurs, the appearance of compactions, cysts in the structure of the gland. This is a hormone-dependent disease.
Mastopathy is divided into diffuse and nodular (localized). Diffuse changes do not have a clearly defined boundary. This is the most common form of mastopathy, which accounts for more than half of all benign diseases. The diffuse form is considered a borderline state between normal and pathological in young women, but is regarded as a disease in patients over 40 years of age.
Nodular mastopathy is characterized by the local location of the changed area and its clear boundaries. They can be considered breast tumors, and have a greater tendency to malignant degeneration compared to diffuse ones.
Local mastopathy is divided into the following types:
- Nodal.
- Cyst.
- Intraductal papilloma.
- Fibroadenoma.
Symptoms of mastopathy:
- Soreness and tension of the mammary glands. Typically depends on the monthly cycle. The pain can be transmitted to the arm, armpit, shoulder blade.
- Swelling of the mammary gland, feeling of fullness.
- Discharge from the nipple.
- Depressive state.
Nodular mastopathy
It is a flat granular compaction that does not disappear during the intermenstrual period. It may increase slightly before menstruation.
Cystic formations
A breast cyst is a hollow, mobile formation in tissues or ducts filled with liquid contents.
Small cysts, less than 1 cm in diameter, are usually painless. They can be detected by a doctor during a routine examination or by the woman herself during a self-examination.
The appearance of pain or discomfort indicates a complicated course of the disease - the development of an inflammatory or purulent-inflammatory process, rupture or malignancy of the cyst.
Intraductal papilloma
It is also called Mintz disease or "bleeding nipple." It occurs as a result of cystic dilatation of the milk duct and the proliferation of epithelium inside it. Placed in a large duct under the nipple or areola. On palpation, it is sometimes determined in the form of a spherical soft elastic formation or an oblong cord.
A characteristic manifestation is discharge from the nipple area.
Pain may also occur, especially when pressing on the chest.
This pathology has a high level of oncogenicity and is considered precancer.
Fibroadenoma
This is an elastic, round neoplasm made of glandular and fibrous tissue, which has a more dense structure compared to other tissues. The formation is not enclosed in a capsule, is mobile and painless even with pressure. Usually located in the upper outer quarter of the chest. Diameter from a few millimeters to five centimeters.
Treatment of benign tumors
Diffuse mastopathy is treated conservatively - mainly with hormonal drugs, and focal mastopathy is removed surgically. Only small cysts are subject to hormonal therapy, but if it is ineffective, they are also removed. In case of rapid growth, any neoplasms are removed urgently.
In the vast majority of cases, organ-preserving operations are performed. Hormonal therapy can be used auxiliary - to equalize hormonal levels and alleviate the patient’s condition.
Diagnostic methods
Ultrasound diagnostics of mammary glands
To begin adequate treatment of nodes in the mammary gland in a woman, you need to undergo diagnostics:
- general examination in a lying and standing state;
- studying the symptoms that a woman should describe;
- palpation of the mammary gland;
- biopsy and obtaining material from the tumor for further identification of atypical cells;
- laboratory analysis of human fluids and secretions;
- mammography, ultrasound or x-ray.
Methods such as CT and MRI are mainly used when the formation is confirmed, but its structure needs to be studied layer by layer.
Diagnostics
The doctor performs a visual examination of the breast and palpates it. If a tumor is detected, mammography or ultrasound is prescribed. The choice of technique depends on the indications and age of the woman. For patients under 40 years of age, ultrasound is more informative. For older people – x-ray, which is associated with the density of the glandular tissue structure. The reliability of mammography is about 90%, ultrasound is 70–80%.
Reference! Mammography - X-ray of the breast. It allows you to detect a tumor with a diameter of 2 mm, which is impossible with palpation (even professional). Therefore, it is so important to perform it preventively.
X-ray and ultrasound methods can confirm or refute the presence of a neoplasm, indicate its size and location.
Important! The diagnosis of breast cancer, its type and stage, can only be established based on the results of histological analysis of a tumor sample.
The material can be taken by puncture (puncture in the gland) or by surgical removal of the pathological area.
If indicated, cytological analysis of nipple discharge can be performed.
Reference! Cytological analysis is the study of cell structure under a microscope. Histological - microscopic study of tissue structure.
If the presence of a malignant process has been confirmed, additional x-ray and ultrasound examinations are prescribed.
To clarify the shape and depth of tumor spread, CT and MRI of the breast may be prescribed. Chest X-ray and abdominal ultrasound are used to detect metastases.
How often is preventive diagnostics needed?
Every woman should undergo preventive examinations with a gynecologist or mammologist once a year. This is especially important to do after 40 years of age, when the risk of developing breast cancer increases sharply.
Between the ages of 40 and 50, mammograms should be done every two years. After 50, and also if you are at risk - once a year. Women under 40 years of age need to undergo a breast ultrasound every two years.
Intraductal papilloma
These breast nodules are also called papillary cystadenomas or cystadenopapillomas. They are papillary benign outgrowths developing from the epithelium of the gland ducts. Pathology can occur at any age. Macroscopically, such neoplasms resemble cystic balls with papillary growths.
The papilloma is easily injured, and the bloody fluid released from it penetrates the excretory ducts and begins to flow out. Necrosis and hemorrhage are possible in the area of this tumor. Multiple breast formations of this type most often undergo malignancy.
The factor leading to the appearance of intraductal papillomas is hormonal imbalance. The development of papilloma can be provoked by any changes in hormone levels: oophoritis, ovarian dysfunction, adnexitis, obesity, abortion, stress, etc. Smoking and nulliparous women are at risk. Patients who were breastfeeding, having children, and using hormonal contraception are less susceptible to the development of such neoplasms.
Papillary cystadenomas occur against the background of fibrocystic (diffuse or nodular) mastopathy. As a result of the development of this disease, local expansion of the gland ducts occurs, in which papillary growths develop. The first clinical symptoms of intraductal papilloma include the appearance of discharge from the nipple. They can be white, transparent, greenish, brown and contain blood impurities.
You can palpate the papilloma only when it is located in the main duct. In this case, upon palpation in the area of the areola, a round node of soft consistency is felt, painful when pressed.
Surgery for intraductal papilloma of the mammary gland is considered the most effective method of therapy.
Causes of formations in the mammary gland
The most basic reasons for the development of neoplasms are:
- hormonal imbalance, which is caused by dysfunction of the ovaries, thyroid gland or constant exposure to stressful situations;
- inflammatory process in the female genital organs;
— hormonal imbalance due to taking hormonal contraceptives.
These factors mainly lead to the formation of fibroadenoma and cysts. These pathologies are most often caused by increased production of estrogen.
If we are talking about mastopathy, then the risk group includes women who started menstruation early, menopause occurred late, had frequent miscarriages or abortions, had a late pregnancy, or had a short period of breastfeeding. In addition, the development of mastopathy is facilitated by prolonged stress, which has a detrimental effect on the condition of the endocrine glands.
Prevention of nodular neoplasm
To prevent diseases, it is recommended to eat well
To prevent nodular mastopathy from developing, it is necessary to constantly adhere to the rules of a healthy lifestyle:
- alternate between work and rest, never work excessively, to the detriment of sleep and nutrition;
- provide yourself with nutritious and healthy nutrition;
- create a favorable psychological environment that does not lead to depression, stress and nervous breakdowns;
- have regular sex life;
- when using hormonal contraceptives, consultation with a doctor is required;
- after every menstruation, you need to examine your breasts in a standing and lying position;
- You should not wear tight synthetic underwear that puts pressure on the mammary glands;
- It is not recommended to have abortions on a regular basis;
- You should not be in direct sunlight for more than 20-30 minutes a day;
- To detect pathologies in the first stages, you need to regularly visit a mammologist.
Various vitamins and supplements, which can be included in the diet after consultation with a doctor, help fight pathological tumors in the breast.
Causes of the disease
Several unfavorable environmental factors or internal disorders in the body can provoke the formation of a benign node in the chest. The cause of the disease may be the following:
- diseases of a gynecological nature of the pelvic organs;
- hereditary predisposition;
- artificial termination of pregnancy;
- first pregnancy at a late age - after 35 years;
- endocrine system disease - diabetes mellitus;
- inflammatory processes in the uterus and breasts;
- established diagnosis - infertility;
- the impact of carcinogenic substances and chemical compounds on a woman’s body;
- refusal to breastfeed a newborn baby;
- taking oral contraceptives for a long time;
- the onset of menopause after 55 years;
- early puberty in teenage girls;
- frequent exposure to direct sunlight or tanning in a solarium;
- abuse of alcoholic beverages and nicotine;
- unbalanced diet - lack of plant fiber.
Pathology can be caused by a number of factors simultaneously or by adverse environmental influences. The area where a woman lives is of great importance. Air pollution with various radioactive substances or chemical compounds can be the main cause of the disease.
Breast mastitis in non-lactating women
Non-lactation mastitis is an inflammatory pathology of the mammary gland that occurs in women outside the lactation process. The causes of this disease are injuries, infections, chronic diseases of other systems and organs. This disease is not classified as a nodular disease, however, during its course, focal changes resembling nodules may be observed in the mammary gland.
Mastitis in non-breastfeeding women occurs for several reasons:
- menopause, during which hormonal imbalance occurs;
- chest injuries;
- complications after operations;
- decreased immunity;
- avitaminosis;
- metabolic disorders;
- infectious lesion.
Most often, non-lactational mastitis occurs in women after 35 years of age. At risk are patients with endocrine disorders, as well as those who abuse alcohol and smoking.
An advanced form of mastitis leads to serious consequences: the transition of the pathology to the chronic stage, the formation of an abscess, sepsis.
With this disease, women notice the following symptoms:
- breast pain;
- inflammation of the cervical and axillary lymph nodes;
- aching joints, muscle pain;
- fever, febrile syndrome.
What to do if you suspect a breast nodule?
Cyclic mastodynia
Cyclic mastodynia . As already mentioned, a healthy woman may experience minor pain in the mammary glands in the middle of the menstrual cycle or a few days before the onset of menstruation. However, such cyclical pain in the mammary glands can intensify and disturb no longer 1-3 days, but for 1-2 weeks or longer. Such symptoms are caused by certain disturbances in hormonal and water metabolism in the body, swelling of the breast tissue and, of course, require medical advice. In some cases, it is possible to relieve or reduce pain in the mammary glands simply by limiting the daily intake of salt and liquid in the premenstrual period (salt - no more than 3 g and liquid - no more than 1 liter). In addition, adherence to such a water-salt regime in the last week before menstruation is a preventive measure for a number of pathological changes not only in the mammary glands, but also in the uterus and appendages.
In the treatment of cyclic mastodynia, various types of vitamin and hormonal therapy are also effectively used, aimed at normalizing hormonal metabolism in a woman’s body.
Surgery
Surgery to remove nodular tumors can be performed in three ways:
- Resection, the task of which is to remove the tumor and the tissues surrounding it. It is prescribed in the presence of large nodular formations in the gland, as well as if there is a risk of malignancy.
- Enucleation is a more gentle method of surgical treatment of breast nodules. It is used when tumor lumps are small in size.
- Mastectomy. During this manipulation, the affected mammary gland is completely removed. This method is used by specialists only in cases of extremely severe development of the pathological process, when, in addition to nodules, cancer cells are detected in the gland cavity. After breast removal, a woman is prescribed radiation or chemotherapy.
Cancer factors
Breast cancer occupies a leading position worldwide. Based on the statistics provided by WHO, doctors identify about 1 million cases of this particular disease every day.
Doctors name a number of factors that provoke the occurrence of this health problem. This may include:
- smoking cigarettes;
- inability to become pregnant and give birth;
- being overweight;
- diabetes mellitus of any type;
- menopause, which began at a later age;
- hereditary predisposition;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Reasons for the development of breast tumors
According to medical sources, during reproductive age, from 30 to 50% of women have signs of mastopathy, and in the postmenopausal period, about 25%.
Breast cancer ranks first among cancer diseases among women, and second after lung cancer among both sexes. The risk of developing this type of cancer increases sharply as menopause approaches.
Fact! Men also get breast cancer. According to statistics, for every 99 sick women there is 1 man.
The surge in breast diseases is a kind of payment for civilization. A woman’s body is designed to give birth and breastfeed throughout the entire reproductive period. This means that the mammary gland will “work”, and the number of menstruation will be much less.
Each menstruation means strong fluctuations in hormonal levels, which means a surge in estrogen levels. Under their influence, the mammary gland becomes thicker, the diameter of the ducts increases, and the tissues retain more fluid. When estrogen levels drop, everything returns to normal. Gradually, the mammary gland itself becomes coarser and denser, fibrous tissue grows, small milk ducts turn into cysts. This is how mastopathy develops. And over time, it can develop into cancer.
Symptoms of a breast tumor, their therapy and prognosis depend on the type of tumor, the stage of the process and the form of its course.
Malignant neoplasms
More than 15 types of breast cancer have been identified in medicine. Most often it affects the ducts and individual lobes of the breast.
In total, there are 4 degrees of cancer development, and there is also one preliminary one.
- A precancerous condition, that is, a lump appears, but it does not yet spread to nearby organs. If the doctor identified the presence of a problem, then it means that the patient had a predisposition to the disease.
- Stage 1 is represented by an invasive form, that is, the disease gradually spreads to nearby tissue. Typically, the affected cells quickly spread beyond the main focus. It is important to carefully monitor your health and not neglect routine examinations with a doctor. If cancer can be detected at this stage, appropriate measures will be taken. During this period, the formation can grow up to 2 centimeters.
- At the 2nd stage, the size increases to 5 centimeters and damage to the lymph nodes located in the armpits is noted. When adhesions with healthy tissues appear, another stage of the disease begins.
- From the 3rd stage, you can visually notice the first symptoms, that is, the mammary gland changes its shape, and red spots appear on the skin.
- At stage 4, there is practically no point in carrying out treatment, since during this period most of the organs are already affected by cancer cells.
One of the reasons for the appearance of a lump in the sternum in women may be a cancerous tumor. At the initial stage, the ball in the chest is very dense and motionless. Women often underestimate the degree of danger due to the fact that a cancerous tumor is rarely painful. Malignant tumors are divided into three types.
Adenocarcinoma
Breast carcinoma
The most common disease, the age range of which is from 20 to 90 years. There are two types: lobular cancer and ductal cancer. There are 5 species in total, the most dangerous of which is undifferentiated; the identity of the cells in this case is difficult to determine. Doctors give a favorable prognosis if the tumor is detected early and its size does not reach 2 cm in diameter.
Sarcoma
Refers to rare types of breast tumors. The number of cases is less than 2% of the total number. Most often it is a degeneration of a leaf-shaped benign tumor. The course of the disease is aggressive - it grows rapidly and has an unfavorable prognosis.
Treatment is complex: radical mastectomy with lymph nodes, as well as chemotherapy. Relapses are possible, so the patient is registered and the condition is monitored every 3 months.
Lymphoma
Grows from lymphatic tissue. It is highly malignant, but is relatively rare. Breast lymphoma tends to grow into adjacent tissues; after treatment, it often recurs and metastasizes.
This is a secondary tumor, the cells of which enter the organs of the human body and form a secondary focus. With lymphoma, a person quickly loses weight and anemia is diagnosed. Along with the appearance of a lump in the chest, lesions can be diagnosed in the kidneys, lungs, and liver.
Cancerophobia
Cancerophobia . It should be said about another, not so rare, pathological condition when, in the absence of objective changes in the mammary glands, a woman is worried about the presence or possible occurrence of a tumor. This state of prolonged, irresistible fear of developing cancer, called cancerophobia, belongs to the category of mental disorders of the obsessive-compulsive type. At the same time, as a rule, a person is physically and mentally healthy. However, obsessive thoughts about the possibility of developing a terrible cancer disease, or even the belief that a tumor has already appeared in the body, only doctors cannot recognize it, poison the entire existence of such persons, disrupt their normal functioning and can even lead to pathological changes for the second time. Cancer, of course, will not develop from self-hypnosis, but such persons may actually experience a deterioration in their health, loss of appetite and body weight, and possible pain. Such symptoms, caused by self-hypnosis, further strengthen the belief in the presence of cancer and increase fear.
The changes and diseases of the mammary glands listed above are the most common, although they do not cover the entire variety of possible abnormalities and pathological processes in the mammary glands. It should also be noted that often different diseases have the same symptoms and a similar picture of external manifestations. On the other hand, each individual case of the same disease occurs in different patients to a certain extent differently. Doctors even have a postulate that no two patients are alike. All this often complicates an objective assessment and final diagnosis of changes in the mammary glands, requiring qualified specialist consultation and the use of instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods. An accurate and timely diagnosis allows you to determine the correct tactics in the behavior of the patient and the doctor and carry out effective treatment. The wait-and-see attitude is especially dangerous: “I’ll see what happens next,” “If it doesn’t go away on its own, then I’ll go to the doctor.” This position often leads to the fact that time for easy and simple therapeutic measures is missed, and severe complications develop that require complex, sometimes traumatic, treatment methods.