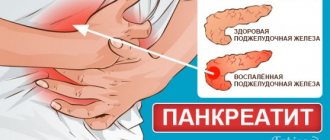
Almost every 5 people experience pancreatitis. Its main symptoms are inflammation, metamorphosis in the pancreas and its soreness. The progression of the pathology will directly depend on the treatment of the disease, nutrition and lifestyle of the patient. However, to overcome chronic pancreatitis, treatment at home is the most important condition for success.
Causes of an attack of pancreatitis
Due to inflammation of the pancreas, its functioning is disrupted, and enzyme deficiency develops in the body. The pathological condition can act as an independent disease or be one of the symptoms of serious problems in the digestive system. Blockage of the common duct is the main cause of pancreatitis, causing acute attacks. Pregnant women and young mothers after childbirth are at risk. In this category of patients, attacks develop due to hormonal changes in the body.
In addition, there are the following reasons for exacerbation of pancreatitis:
- abdominal injury;
- alcohol abuse;
- long-term therapy with hormonal and other potent drugs;
- genetic predisposition;
- cholecystitis;
- allergies;
- poor nutrition (diet deficient in proteins and vitamins);
- chronic infections;
- frequent stress;
- mumps;
- hepatitis;
- hormonal imbalance;
- connective tissue diseases;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- starvation;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract);
- frequent endoscopy sessions;
- inflammation of the duodenal mucosa;
- nervous exhaustion.
Nature and features of the development of pathology
The pancreas becomes inflamed due to congestion. The process is preceded by an increased load on the organ - the need to produce a large number of enzymes. The most common predisposing factor for pancreatitis is overeating and drinking alcohol. The disease does not imply regular violations of the diet and persistent bad habits. Occasional drinking of alcohol with a difficult-to-digest snack can cause an attack.
In addition to bad habits, pancreatitis is provoked by obstructions in the patency of the pancreatic and bile ducts, regular use of medications, and gastrointestinal diseases.
The essence of pancreatitis is premature activation of pancreatic enzymes. The process is accompanied by contact between pancreatic juice and bile; in a healthy person, it occurs in the small intestine. When bile flows into the pancreatic ducts, enzymes are activated ahead of schedule and digest the tissue of the gland itself. Parenchymal cells and vascular endothelium may be damaged. The process is accompanied by acute inflammation and tissue swelling.
Types of pancreatitis
Depending on the characteristics of the inflammatory process, this disease is divided into several types. Treatment is prescribed taking into account the form of the disease and other factors. Experts distinguish 3 main types of pancreatitis:
- Acute is a dangerous type of pathology that can lead to death in the absence of the necessary treatment.
- Chronic pancreatitis accompanies the patient throughout his life. It is characterized by alternating remissions with exacerbations.
- Reactive is a mildly expressed type of disease. This form of pancreatitis can develop into a more serious one if the patient refuses to be monitored by a doctor.
- Diet table number 1
- Can MRI replace colonoscopy?
- Pork knuckle baked in the oven
Diet No. 5
This pathology has one unattractive name - prediabetes. Unfortunately, when it comes to chronic pancreatitis, the chances of developing such a serious disease are high. To avoid the occurrence of diabetes mellitus, patients are prescribed diet No. 5 for pancreatitis. This diet should be followed throughout your life.
The basic nutrition consists of the following products:
- milk, kefir, mild cheese, yogurt, low-sour cottage cheese;
- pasta, cereals (rice, oats, buckwheat);
- vegetables (beets, zucchini, carrots, pumpkin, potatoes);
- white stale bread, wheat crackers;
- lean fish;
- meat (turkey, rabbit, chicken, veal);
- fruit jelly, baked apples, berry sauce;
- oat decoctions, fruit juice, chamomile tea, non-acidic fruit juices;
- puree soups, vegetable broths.
The following should be excluded from the diet:
- fresh cabbage, sour fruits, legumes;
- sorrel, radish, spinach, radish;
- fresh bread, sweets, baked goods;
- spices and hot spices;
- canned food, smoked meats, sausages, eggs;
- fish, meat broths, borscht, cabbage soup;
- sweet sodas, alcohol;
- ice cream, cream, sour cream;
- fried foods.
This diet involves eating about 6 times a day, in small portions. This will avoid the risk of overeating.
Symptoms of an attack of pancreatitis
The disease worsens when the pancreas begins to produce a large amount of enzymatic secretion against the background of obstructed outflow. An acute attack is accompanied by aching pain in the hypochondrium on the left side or the solar plexus. The patient's temperature rises sharply. Also, the attack is often localized on the left side of the sternum from the back. In this case, a sharp pain is felt due to the large number of nerve endings in the pancreatic mucosa.
From the gastrointestinal tract, long-term disorders in the form of vomiting, diarrhea, and nausea are possible. The normal functioning of the cardiovascular system is disrupted. The patient experiences surges in blood pressure, arrhythmia, and severe migraine. In addition, the following signs of an attack are possible: flatulence, belching, hiccups, white coating on the tongue, chills, lack of appetite and change in complexion.
Patient opinions
Surprisingly, with this pathology, all patients recommend one thing: contact a gastroenterologist and do not delay treatment! What do patients diagnosed with pancreatitis indicate? Reviews from patients report a significant improvement in well-being after drug therapy prescribed by the doctor and following the prescribed diet.
Most patients claim that after long-term treatment they were even able to return to their normal diet. And at the same time they no longer experience the characteristic painful symptoms.
First aid for an attack of pancreatitis
If a patient shows signs of acute pancreatitis, it is important to urgently call an ambulance. An attack of the disease must be removed in a hospital setting under the supervision of doctors. Lack of treatment can lead to the development of serious complications. Before the doctors arrive, the patient is advised to fast. This measure will stop the production of enzymes. It is allowed to drink mineral water without gas at room temperature. The fasting period should not last longer than 2-3 days.
Treatment of acute pancreatitis at home should begin with stopping the attack. To do this, you can make a compress of thick fabric with ice on the left hypochondrium. It is not recommended to use anesthetic drugs before doctors arrive, as they will complicate the localization of the attack and diagnosis. To reduce pain, you need to take a sitting position with your knees pulled towards your stomach.
Patients with a low pain threshold can take No-shpu or Drotaverine. It is preferable to use drugs in the form of injections. You can take light enzymatic medications Mezim or Pancreatin. If a single attack develops, home treatment of pancreatitis is prohibited. If the patient often experiences relapses, he can cope with the condition on his own. The lack of a positive effect requires hospital treatment.
- Rassolnik soup: recipes with photos
- Homemade face mask with lifting effect
- How to get rid of fungus in the cellar
Folk remedies
Due to the antispasmodic and antisecretory effects of some medicinal plants, they are used in folk medicine. Care should be taken in choosing recipes, as many of them are not suitable for use in pancreatitis. One of the acceptable options are the schemes presented by E. A. Ladynina and R. S. Morozova. The publications of these authors contain herbal infusions based on herbs:
- motherwort;
- calamus;
- St. John's wort;
- currant;
- linen;
- viburnum;
- plantain;
- valerian;
- fennel;
- sage;
- thyme.
The medicine must be prepared in accordance with the rules. 2-3 teaspoons of crushed raw materials are poured into 200 ml of water and placed on low heat. The mixture is brought to a boil and kept for 10-15 minutes. After the broth is cooled, filtered and taken 1/2 cup twice a day.
Acute pancreatitis is a severe lesion of the pancreas that can lead to the death of the patient. Self-treatment in such cases is unacceptable. At the first signs of pathology, the patient should be given first aid and emergency medical services should be called to assess the condition and subsequent hospitalization. At home, adequate therapy is impossible.
Home treatment
An attack of pancreatitis requires immediate medical attention. If the patient is in a stable condition and there are no complications of the disease, the doctor can give recommendations and send him to be treated at home. The patient must have No-shpa tablets or solution for injection. In addition, to alleviate the condition during an exacerbation, enzymatic preparations are needed.
An important part of successful therapy for pancreatitis is adherence to a special regimen. To quickly relieve an attack and improve your condition, it is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- You should not heat an inflamed pancreas. During acute attacks, ice must be used to alleviate the patient's condition and relieve pain.
- During the first days of treatment, it is important to monitor the enzyme balance. In order not to provoke the release of secretion from the pancreas, the patient is recommended to fast for up to 2-3 days. For the first day, only warm water is allowed. During an attack of pancreatitis, the diet for the following days may include unsweetened tea and crackers.
- Bed rest must be maintained until the attack is completely eliminated and symptoms are alleviated.
Drug therapy
Treatment of pancreatitis with tablets is individual, prescribed by a doctor. Only a specialist can take into account all the nuances (adult or child, weight, concomitant diseases, etc.). Several groups of drugs are prescribed:
- antispasmodics. They are prescribed after an exacerbation and symptomatically;
- enzymes. They are prescribed for a lack of gastric digestive juices, as well as to prevent excessive acid synthesis;
- medications for the treatment of concomitant diseases that can complicate the course of the pathology;
- antibiotics - they are usually prescribed for therapy in a hospital, less often at home.
If the approach is competent and comprehensive, it is possible to alleviate the course of the disease and relieve attacks and acute inflammation of pancreatitis.
Complications
An attack of pancreatitis entails a change in the alkaline balance in the patient's body. Exacerbation of the disease in the absence of proper treatment can cause complications. The condition often leads to infection, cyst formation, and partial necrosis of the gland. The most severe cases require surgery. After the operation, the patient will be forced to constantly maintain a normal state with insulin and enzymes.
Failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner or refusal to undergo diagnostic tests can cause pancreatitis to become chronic. In addition, the disease is fraught with the following complications:
- stagnation of fluid in the pancreas;
- blockage of blood vessels;
- pancreas cancer;
- blockage of the gallbladder or intestinal ducts.
What will happen in the hospital
Pancreatitis must be distinguished from peptic ulcers of the stomach, small intestine, cholecystitis, and intestinal obstruction. The patient will immediately have blood, urine (and possibly stool) taken for analysis. An attack of pancreatitis is accompanied by an increase in ESR and leukocytosis in the CBC. Biochemical analysis reflects excess pancreatic enzymes and high levels of bilirubin. Protein and bilirubin are detected in urine, occult blood and undigested food particles are detected in feces.
The next stage of diagnosis is an in-person examination. The doctor performs a palpation examination of the peritoneum. A sharp pain is detected in the projection area of the pancreas. The anterior abdominal wall is tense, which indicates:
- increased gas formation;
- an increase in the size of the gland;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
If bluish spots are detected on the skin of the abdomen, the patient will be immediately sent to the intensive care unit. This symptom indicates developing pancreatic necrosis.
Hardware diagnostics of acute pancreatitis includes pancreatic imaging methods - ultrasound, MRI and CT. Based on the results, the size and shape of the organ, the presence of seals and liquid inclusions, and the integrity of the capsule are assessed. If necessary, a transdermal biopsy is performed to assess the sterility of necrotic changes or cystic formations. Sometimes diagnosis is made laparoscopically during surgery.
Relapse Prevention
This form of disease is characterized by periodic exacerbations. The patient must do everything to ensure that attacks occur as rarely as possible; the best option is one attack every few years. Prevention consists of:
- Absolute cessation of alcohol and smoking.
- Dieting.
- Small meals 5-6 times a day.
If the cause of the exacerbation is diseases of other organs or systems of the body, it is necessary to treat them in a timely manner.
To reduce the likelihood of relapse of inflammation, the following important points should be adhered to:
- Limit the consumption of fatty, fried and sour foods, avoid marinades and canned food.
- Reduce caloric content of dishes.
- Watch your weight.
- Eat small and frequent meals.
- Avoid alcoholic drinks.
- Do not overeat and make sure you eat on time.
- Take any medications only with the permission of a doctor.
Even if the exacerbation of the disease was quite a long time ago, do not forget about systematically visiting the doctor, doing an ultrasound of the abdominal organs in a timely manner and taking the necessary tests. All these measures make it possible to promptly identify dysfunction of the pancreas in its early stages.
If a person carefully follows all these recommendations, then the prognosis of the disease can be conditionally favorable. With complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages and strict adherence to dietary nutrition, the survival rate in patients with chronic pancreatitis is about 80%.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures are established based on the following parameters:
- History of the disease.
- Analysis of lifestyle features, the presence of bad habits or past diseases. Detecting the disease in other family members.
- General examination of the patient.
- Palpation of the abdomen.
- Determination of the amount of enzymes through biochemical and general blood tests.
- Determination of characteristic tissue changes using abdominal ultrasound.
- MRI and CT (if it is necessary to exclude a tumor process).
- Informative study of the pancreatic ducts - ERCP.
- Laparoscopy is used when conservative therapy is low in effectiveness.
- At a young age, additional consultation with a pediatric gastroenterologist is indicated.
The danger of pancreatitis lies in the fact that the pancreas is not able to restore its own cells. Their death leads to disturbances at the metabolic level and complete depletion of the body.