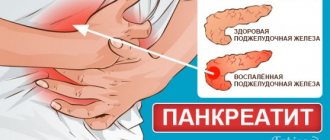
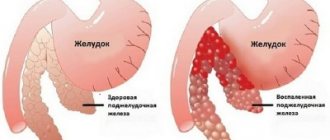
Study of organ structure
Diagnosis of the gland is based on the characteristics of its tissue:
- Unnoticeable during routine x-ray examination;
- The ducts of the gland can be examined using x-rays by injecting a contrast agent inside.
Good access to the gland for diagnostic purposes using ultrasound, Dopplerography helps determine the blood flow inside the vessels. CT helps to visualize its structure in layers; the best option to determine the smallest structures of the gland is magnetic resonance imaging.
X-ray methods:
- Plain radiography makes it possible to visualize pancreatic tissue and large stones in its tracts.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography - a radiopaque substance is injected into the ducts of the gland from the duodenum using an optical device that performs fibrogastroscopy.
- Selective angiography is an X-ray examination of the pancreatic vessels after intravenous administration of contrast agent.
- CT helps to study tumors and inflammation inside the gland.
Ultrasonography
This method is not as accurate as tomography, but due to its accessibility and safety it is considered the main one for the purposes of the initial study of pathological processes of the pancreas.
- Ultrasound makes it possible to visualize acute and chronic inflammation, neoplasms, abscesses, cysts;
- Doppler sonography is of great importance for the initial assessment of blood flow. This method requires preparatory procedures.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI is considered the most informative way to diagnose the pancreas, visualizing its tissue quite accurately in layers. When combining MRI with the introduction of contrast in the pathways or vessels, the most informative diagnosis of the gland is achieved.
Information on tomography of this organ is as follows:
- Neoplasms of a small organ;
- Pathological processes of the liver;
- Pancreatitis;
- Preparation for surgery on the gland;
- Monitoring pancreatic therapy.
Principles of examination of the pancreas:
- When any amount of tissue is damaged, the pancreatic tissue that remains replaces its functioning, and no symptoms of the disease may be observed.
- Sometimes a situation arises when a small area dies or becomes inflamed; this cannot be seen from the structure of the entire organ, but may be accompanied by pronounced interruptions in the functioning of the organ.
- Directly because of this, the diagnosis of this organ must be comprehensive, and fully cover the structure of the gland and its work.
- Therapy should be comprehensive: with the help of medications and treatment of the pancreas with proven folk remedies.
Methods for diagnosing pancreatitis
Everyone knows that it is much more effective to treat diseases in the early stages, before the course becomes chronic. But for this it is necessary to undergo a full medical examination at least once a year, thanks to which deviations from the norm, the development of pathologies and deteriorations can be identified in a timely manner.
How to check the pancreas? First of all, you need to contact a general practitioner. It is he who must carefully examine the patient, palpate the abdomen, determine where the disease is localized, and give directions for tests. Even with palpation, the doctor can determine the etiology of abdominal pain.
If there is a suspicion that the cause of pain syndromes is pancreatitis, then the patient is sent for examination to a gastroenterologist, who prescribes all tests that confirm or refute the preliminary diagnosis.
General blood analysis
They donate blood from a finger prick, after which laboratory workers check the number of leukocytes and ESR in the blood. A general analysis allows you to determine whether inflammatory processes are present in the body. Lack of insulin also indicates the development of swelling of the gland.
Blood chemistry
Venous blood is taken for biochemical analysis. It is tested for increased enzymes. This method is especially effective in the acute stage of pancreatitis.
Urine tests
If amylase enzyme is detected in urine, the presence of pancreatic disease is confirmed almost 100%. These tests make it possible to determine pancreatic problems at a chemical level. But, since many ailments have similar indicators and symptoms, the tests must be confirmed by other examination methods.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is an integral part of diagnosis. Using an ultrasound examination, the size of the glandular tissue and its ducts, its location in relation to other organs, the presence of fluid masses in the abdominal cavity or their absence are determined. Ultrasound makes it possible to visually assess the condition of internal organs and exclude suppuration and peritonitis.
X-ray
Very often, stones in the ducts of glandular tissue lead to pancreatitis. An x-ray makes it possible to visually determine the presence of stones, so-called calcenates.
CT scan
makes it possible to visually determine changes in the size of glandular tissue, narrowing or expansion of ducts. This method is considered expensive, but provides a lot of information, thanks to which a more accurate diagnosis can be made and the correct treatment can be prescribed.
Endoscopy
Using a small probe with a camera, doctors can view the entire situation from the inside in real time. The endoscope is inserted into the duodenum, and the Vater's nipple, through which secretions enter the digestive tract, is carefully examined. Contrast is also injected during endoscopy to make better X-rays and CT scans. But the contrast itself is considered an irritant and can provoke a relapse of pancreatitis.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is considered more of a surgical intervention than a diagnostic method, but it provides important facts about the current state of the disease. Laparoscopy is used more often in acute forms of pathology. This is a minimally invasive method that helps eliminate dead areas of gland tissue
The resulting tests may also indicate the presence of neoplasms and cysts, which is important to recognize in the early development of tumors.
Primary diagnosis
This type of diagnosis consists of collecting a primary medical history when the patient is interviewed by a doctor.
The most common questions relate to the following topics:
- What foods have you consumed in the last 3 days?
- How long does the pain last?
- Do you have problems with bowel movements (constipation or diarrhea) and how long do such problems persist?
- In what part of the abdominal cavity is the source of pain localized and where does it radiate?
- Type of pain on palpation, in which cases does it intensify?
- Do you have chronic diseases of the digestive tract, as well as diabetes?
This is usually enough to identify problems with the pancreas. The presence of these symptoms serves as a reason for conducting a hardware examination that will show the condition of the pancreas.
The only feature of the primary diagnosis is the impossibility of palpation. More precisely, the process itself can be carried out if you know the exact localization, but in most cases it is ineffective.
The fact is that the pancreas is not adjacent to the surface of the abdominal cavity, but is located in its depth. The patient may feel pain when pressing on the area of the left hypochondrium, but this indicator cannot carry any informative load for the doctor. Stomach ulcers and gastritis can be identified with the same success, since the symptoms and primary manifestations are identical.
When is it necessary to be examined?
Any pathological process occurring in the pancreas disrupts its functioning and complicates its functioning.
As a result, the condition of the organ worsens, and a person may experience various unpleasant sensations in the abdominal area. Such symptoms do not always appear suddenly, so in some situations you should check the functioning of the pancreas as planned, without waiting for the disease to worsen.
Signs indicating the need to conduct an examination of the organ:
- Attacks of nausea. This symptom intensifies after drinking alcohol, eating fried and fatty foods. In some cases, nausea leads to vomiting, after which the patient's condition still does not improve.
- Pain. It is felt under the ribs, but can also radiate to other parts of the body (under the shoulder blade or behind the chest area).
- Stool disorders. The symptom manifests itself in the form of constipation or diarrhea. A clear sign of pathology is the presence of food particles in the stool that should not normally be present.
- Flatulence, belching. Symptoms indicate fermentation processes, as well as the accumulation of gases.
- Jaundice. Its appearance may be a consequence of swelling of the organ and pressure exerted on the gallbladder.
- Temperature rise. Its increase signals the development of inflammatory processes.
If all of the above symptoms occur simultaneously, you must immediately call a doctor or go to a clinic in person. A common cause of such unpleasant sensations is various diseases of the gland, so the functioning of the organ must be checked at the first appearance.
What to check first
First you need to assess the general condition of the body.
The first group of tests and examinations of the pancreas includes:
- General clinical blood test and platelet count.
- General urine analysis.
- Biochemical blood test: total protein and its fractions, total and direct bilirubin, glucose, lipid profile, creatinine, urea, ALT, AST, LDH, gamma-GGT, alkaline phosphatase, potassium, calcium, sodium, chlorine, CRP.
- Coagulogram.
- Coprogram.
General blood analysis
Acute pancreatitis is characterized by an increase in leukocytes to 20 thousand with a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left. In chronic cases, this indicator slightly exceeds the reference values. An accelerated ESR will indicate the presence of an inflammatory process.
General urine analysis
This test is not specific for pancreatic disease. But with decreased glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus, the content of sugars and ketone bodies in the urine will be increased.
In the case of tumor formation in the head of the pancreas, the syndrome of biliary obstruction and cholestasis develops. The urine will turn dark brown (“beer-colored urine”), and the sediment will show an increase in urobilinogen and bilirubin.
Blood biochemistry
Blood tests can tell a doctor a lot about how an organ is functioning.
The standard set of indicators that doctors usually prescribe fairly fully reflects the condition of all organs.
If the gland is damaged, the following changes will occur:
- decrease in total protein level below 60 g/l due to albumin;
- increased cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins;
- atherogenic coefficient above 4;
- increased alkaline phosphatase and gamma-GGT with the development of cholestasis;
- there may be an increase in the level of ALT and AST transaminases, indicating the degree of cell destruction;
- increased lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) due to impaired glucose metabolism;
- c-reactive protein increases in the presence of a focus of inflammation.
To obtain reliable examination results, it is necessary to take all tests strictly on an empty stomach.
Coagulogram
There are no blood clotting disorders in chronic pancreatitis, but with the acute development of the disease, due to the release of enzymes into the blood, antithrombin III in the coagulogram will decrease.
Scatology
A stool test is performed to look for the level of damage to the gastrointestinal tract. If the pancreas is diseased, the digestion of proteins, fats and carbohydrates will be impaired. Feces acquire a mushy consistency and a putrid odor; particles of undigested food may be present. The content of muscle fibers and connective tissue, neutral fat, and starch is increased. Additionally, you can study a specific enzyme, elastase-1, which increases in feces during pancreatitis.
It is not at all necessary to take a stool microflora test; this method is not effective for diagnosing pancreatitis.
Self-check of the pancreas
The acute form of this disease is caused by overeating or drinking alcohol:
- The pain during this is girdling , intense, persistent, creating the appearance of tightening near the upper abdomen. It radiates to the back and can get worse when lying down.
- Such attacks of pain are often not relieved with antispasmodics or analgesics.
- Characteristic symptoms are frequent gag reflex, which does not bring relief, bloating of the abdomen, nausea, lethargy, increased temperature, and yellowness of the sclera.
- Blood pressure is reduced during acute pancreatitis.
In the current situation, self-therapy is completely prohibited. When such signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. The situation with the chronic form of pancreatitis is somewhat better. The manifestation occurs slowly and is the result of acute pathologies.
The main role is played by the following symptoms:
- Like weight loss,
- Short-term pain near the hypochondrium on the left side,
- Giving to the lumbar region,
- Changes in stool
- Feeling nauseous
- Sensation of bitterness in the mouth,
- Hunger and thirst increase.
At home, they pay attention to the stool; during pancreatitis it is large in volume, liquid in consistency, and light in color.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
By and large, all patients with this disease undergo instrumental examination only with an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. This is due to the fact that the diagnosis can be easily made after interviewing, examining the patient and obtaining laboratory tests. Ultrasound is a high-quality and reliable first-line study, as it is inexpensive and highly informative. All other studies are of little information and are not highly effective for diagnosis. Their use is justified only when it is not possible to visualize the affected parts using ultrasound examination or when there is a suspicion of the presence of a space-occupying formation in the organ (cancerous tumor, cyst, pseudocyst). In this case, the question arises about the surgical operation and the extent of resection.
Ultrasound examination
"Gold standard" for diagnosis. The doctor will easily see diffuse changes in the tissue of the affected organ, thickening and swelling of the pancreatic capsule. In chronic pancreatitis, calcifications and petrifications, areas of parenchyma destruction, are detected. The advantage of this study is that it makes it possible to assess the condition of other organs (gallbladder, liver and their ducts)
This is important when the outflow of secretions is impaired due to stones and the presence of cholecystitis, since in this case all the conditions for the development of the disease are created.
Important! Currently, new methods of ultrasound diagnostics have been developed. In particular, endoscopic ultrasound and intraductal ultrasound of the pancreas. These studies make it possible to insert sensors into the stomach or into the ducts themselves, and the doctor can study in more detail and give an opinion on the condition of the organ. The disadvantage of these studies is their invasiveness, which exacerbates inflammation and organ destruction.
CT scan
Most often, this study is prescribed when complications occur. X-ray examination allows you to study in detail the structure of an organ (including the circulatory system), assess the degree of destruction, and determine the amount of living and healthy tissue.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
For biliary-dependent pancreatitis, ERCP is performed. A special probe is inserted into the main duct, the opening of which opens on the large duodenal papilla, and a contrast agent is supplied. After this, the patient is given an x-ray. Such an examination allows you to assess the patency of many (even the smallest) ducts, determine the presence or absence of stones and other possible obstacles (strictures, adhesions, kinks). During the examination, small stones can be removed, which will then be removed naturally. This surgical method is minimally invasive, so it is now preferred.
Rarely used instrumental diagnostic methods
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) - allows you to assess the condition of the major papilla of the duodenum, evaluate the final sections of the duct itself, and evaluate the functionality of the sphincter of Oddi.
- Plain radiography of the abdominal cavity is a study used for differential diagnosis. Often, with this disease, there are no changes in the image, except in cases where petrification (areas of calcification) have already formed in the pancreas. This sign allows us to fully guarantee that the patient has chronic pancreatitis.
- Laparoscopy. More of a therapeutic rather than a diagnostic method. It is used in controversial situations when the above studies could not completely visualize the affected organ. During diagnosis, various surgical procedures can be used for therapeutic purposes.
How can exercise therapy help?
When the disease is acute, physical activity is excluded: the pancreas should be completely at rest. In addition to this need, during periods of exacerbation the patient experiences severe pain that limits his physical activity. The patient involuntarily takes the most comfortable position for him to reduce the severity of pain. As a rule, a person is inactive and does not make unnecessary movements due to pain. In this case, bed rest is necessary for several days.
After the pain has reduced, the patient can engage in a special set of exercises designed for the pancreas. Gymnastics plays an important role in the restoration of the organ. It is done at home, on the street. To achieve the effect, it is important to maintain regularity. Classes do not require special equipment.
After discharge from the hospital, simple manipulations are prescribed. Despite their simplicity, they are effective and significantly improve your well-being. These include:
- turns the body left and right,
- belly breathing exercises,
- holding your breath for a few minutes.
It is not recommended to pump up the abs if you have pancreatic pathology, but walks at a calm pace lasting 20-30 minutes are very useful. If you perform breathing exercises at the same time, your metabolism improves and blood circulation is stimulated, including in the pancreas tissues. This normalizes its condition and functions, makes the organ function correctly, and the pathology begins to be cured faster. Strenuous physical activity is prohibited. All exercises and walks should cause slight fatigue and be performed without effort.
Therapeutic exercises in complex therapy are important for strengthening muscles and improving the general condition of the patient. It is prescribed by a doctor, who also teaches individual elements. When performed correctly and regularly, exercise therapy improves the prognosis and relieves unpleasant manifestations of the disease.
The benefits of a healthy lifestyle
When treating at home you need:
- Healthy food,
- increase physical activity,
- take frequent walks in the fresh air,
- quit smoking and alcohol.
A healthy lifestyle is the prevention of any pancreatic pathology.
Preparation for analysis
Before performing tests on the pancreas, you need to know how to do this.
Basically, specialists instruct patients, since errors in the process of collecting biomaterial can lead to significant deviations in the finished data.
General instructions boil down to the following points:
- Diagnosis is carried out on an empty stomach, before noon. 3-5 days before the analysis, it is necessary to exclude the consumption of harmful food products (fried, spicy, fatty, salty, canned products, caffeine-containing and alcoholic beverages). In addition, it is not recommended to eat beans, which can cause intense gas formation.
- Before blood collection, you must stop smoking for at least 2 hours.
- If there are complications such as constipation, care must be taken to ensure that toxic elements remaining inside the intestines do not affect the readings. For these purposes, you need to use some enterosorbents (for example, activated carbon).
- Each container must be sterilized, and hands should be washed thoroughly with soap.
- In the process of collecting urine, females must perform hygiene of the genitourinary organs, then use a tampon in order to maintain the purity of the biomaterial.
- When conducting a urine analysis, you should submit its average portion.
Such simple instructions help to properly take tests and prevent possible deviations.
But it should be taken into account that in some cases even specialists can make mistakes, therefore, with the least doubt, it is necessary to carry out the diagnosis again.
Preparing for research
Some examinations require preliminary preparation, which excludes factors that affect the informativeness of the diagnosis.
What do we have to do:
- follow a diet for a week before examinations;
- exclude dairy products, raw fruits and vegetables from the menu;
- eat in small portions;
- eat meals in small portions so as not to overload the stomach;
- stop taking certain medications for the time recommended by your doctor;
- exclude alcohol and do not smoke;
- give up strong coffee and carbonated drinks.
Ignoring these recommendations may distort test results.
It is important to understand that the choice of method for checking the functioning of internal organs, including the pancreas, should only be made by a doctor. In addition, most methods cannot be covered under compulsory insurance without a referral from a doctor. The price for an ultrasound scan of the pancreas, depending on the tasks set by the specialist, can reach 1500-2000 rubles, depending on the region.
Instrumental methods
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas helps diagnose the inflammatory process in its tissues, as well as tumors, stones, scars and age-related changes.
Instrumental methods are considered an integral part of the verification of diseases affecting the pancreas. They allow you to assess the size and visualize the structure of this organ, detect edema, stones, ulcers, cysts and pseudocysts, narrowing of the ducts, neoplasms, fibrosis, and abnormalities of intrauterine formation. The list of these studies may include:
- fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (endoscopic visual examination can detect changes in the area where the pancreatic duct flows into the duodenum);
- plain radiography of the abdominal cavity (the method can show calcifications in the tissue or in the pancreatic ducts);
- contrast duodenography (as the head of the pancreas enlarges, the shape of the barium-filled duodenum changes);
- ultrasound examination (the most common study studies the size, contour, structure of the pancreas, the state of its ductal system and bile ducts, clarifies the presence of excess fluid in the abdominal cavity, and therefore makes it possible to detect inflammation, age-related changes, stones, cysts, scars, tumors (whose diameter is larger 2 cm), metastatic lesions, some complications);
- endoultrasonography (complements the previous diagnostic procedure, allowing a more detailed determination of structural disorders of pancreatic tissue and changes in the ducts, enlargement of nearby lymph nodes);
- computed tomography (compared to the methods already described, this study is more informative in visualizing pseudocysts, neoplasms, atrophic processes in the pancreas, complications of pancreatitis and lesions of neighboring organs, but has a radiation exposure);
- MRI-cholangiopancreatography (the technique analyzes the patency, shape and size of the ducts of the biliary-pancreatic system, assesses the condition of the pancreatic tissue and gallbladder);
- endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography - ERCP (the most informative study for detecting narrowing of the ducts due to scars, stones, protein plugs or tumors, but sometimes it can provoke an exacerbation of pancreatitis, so it is not performed in all patients);
- biopsy of the pancreas with further microscopic evaluation of the resulting pancreatic tissue sample (the method allows you to most accurately identify inflammation, atrophy, fibrosis of the pancreas, distinguish benign from malignant neoplasms, and determine the type of tumor).
However, doctors can make a final verdict only after a comprehensive analysis of the data from all these diagnostic procedures. With all this, the frankness of patients when drawing up an examination plan, the qualifications of doctors, and the quality of equipment and reagents are not the least important.
How are diagnostic tests performed?
Examination of the pancreas, if necessary, can be supplemented with diagnostic tests to identify non-hormonal functions of the organ (exocrine). All methods are divided into:
- those requiring the use of an intestinal tube;
- non-invasive (probeless).
The advantage of tests (especially probeless ones) is convenience for the patient and low cost.
The disadvantage of the tests is that results appear only with a significant decrease in the secretory capacity of the pancreas, so they are considered insensitive
The following tests are used in practice:
- pancreozymin-secretin;
- Lund test;
- hydrochloric acid;
- elastase.
Pancreozymin-secretin test
For the patient on an empty stomach, a probe is inserted into the duodenum with two holes. Aspiration of gastric and duodenal secretions is carried out step by step. Then secretin and pancreozymin are administered intravenously. After the injection, new samples are taken to study the concentration of bicarbonates and trypsin activity. The rate of secretion is calculated.
Pancreatitis is characterized by a decrease in secretion, a decrease in the level of bicarbonates, and an increase in the concentration of enzymes. It is possible to identify false-positive data in patients with diabetes mellitus, biliary tract dysfunction, hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver.
Lund test
It is distinguished by the use of a standard food mixture as a food irritant to the gland. In the morning, the patient is inserted into the duodenum with a weight attached to the end, through which a food mixture (vegetable oil, milk powder with dextrose) is inserted. Sample aspirates are collected within two hours. Then the level of amylase in them is determined. The option is simpler and cheaper, and does not involve injections.
Hydrochloric acid test
It differs from the previous ones in the type of irritant used - a solution of 0.5% hydrochloric acid in olive oil. Further actions are the same. The disadvantages are general.
Elastase test
Based on the study of elastase in the patient’s stool. Gives a positive result for chronic pancreatitis, liver diseases, gallstones, diabetes.
Treatment of pancreas with folk remedies
An increase in the therapeutic effect can be achieved through the combined use of traditional and traditional medicine. The action of the latter is aimed at cleansing the pancreas of harmful substances that prevent the organ from functioning at full capacity. Treatment with herbs and other folk remedies is often very effective. A common remedy with a bactericidal effect is propolis tincture, which at the same time enriches the microflora of the organ with useful substances. Honey for pancreatitis is used to relieve inflammation.
Herbs
- Herbal mixture for pancreatitis No. 1. Mix St. John's wort, elecampane and burdock roots equally; calendula petals, chamomile; stems of wormwood, horsetail, string, dried grass. Place a spoonful of the mixture in a jar, pour in 250 ml of boiling water, leave for 2 hours and strain. Take the infusion according to Art. three times a day. It is better to take it half an hour before meals.
- Herbal mixture for pancreatitis No. 2. Combine 2 tbsp. motherwort, immortelle and calendula. Brew a liter of boiling water with 3 tbsp. collection, and when the liquid is infused, strain the broth. The product should be taken 5-6 times a day according to Art.
- Herbs. Mix 3 tbsp. sage, ironstone, calendula. Add 2 tbsp. hazel and 1 tbsp. St. John's wort. Take 2 tbsp. mixture, pour 800 ml of barely boiling water. When the decoction for pancreatitis has infused (up to 4 hours), strain it and drink it in a dosage of 50 ml 6 times a day.
Oats
- Oatmeal broth. Place a glass of unrefined grains in a liter of boiling water, place the container on low heat, waiting until it boils. After 15 minutes, pour the broth into a thermos and leave overnight. In the morning, start treating the pancreas by taking a glass of infusion 2 times a day. Continue treatment for at least 3-4 weeks.
- Oat jelly. Pour 1 tbsp. oats with clean water, leave the grain for several days. Then rinse it by draining the liquid and replacing it with new water. Cook the oats by combining 2 tbsp. swollen grains with 2 tbsp. boiling water Eat jelly daily.
Potatoes
Potato juice is especially good for treating pancreatitis. It is prepared and taken as follows:
- Grate several fruits and squeeze out the juice.
- To relieve inflammation of the pancreas, drink 50 ml of potato juice for 2 weeks. After 5 minutes of taking it, wash it down with a glass of kefir.
- The course of treatment is 4 weeks (you need to drink for 14 days, then take a break for 10 days, then repeat the dose).
Self-check of the pancreas
Acute pancreatitis is usually an addition to any holiday and is triggered by overeating or drinking alcohol. The pain is girdling, strong, persistent, and may give the impression of being pulled together by a hoop in the upper abdomen. It radiates to the back and worsens when lying on the back. Moreover, such painful attacks are usually not relieved by antispasmodics or analgesics.
Characteristic symptoms are frequent vomiting that does not bring relief, bloating, nausea, weakness, fever, and yellowing of the sclera may occur. You can measure your blood pressure yourself; in acute pancreatitis it is usually low. In this condition, self-medication is absolutely contraindicated. If such signs appear, you must urgently seek help from the hospital!
Things are a little different with chronic pancreatitis. It manifests itself gradually and may be a consequence of an acute process. Symptoms such as weight loss, periodic pain in the hypochondrium on the left, radiating to the lower back, changes in stool, nausea, bitterness in the mouth, increased hunger and thirst come to the fore.
At home, you can pay attention to the stool; in case of pancreatitis, it is large in volume, smelly, has a liquid or putty-like consistency, and is light in color.
Even if you have a whole bunch of symptoms, remember that the disease can be deceptive, which means you need to start a detailed examination, for this you should know what tests you need to take to check the pancreas.
How is the pancreas checked?
Pancreatic disease is of serious importance to a person. Acute or chronic form of pancreatitis is currently not uncommon and the reason for this is:
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- improper and not entirely healthy consumption of food;
- incorrect dietary patterns for losing excess weight.
Diabetes mellitus and cancer also contribute to the occurrence of pathology. What is dangerous with pancreatitis is the occurrence of side problems during the acute phase of development, which lead to necrosis and death. Therefore, every person must know how to check the pancreas and prevent the development of the disease. After all, preventing the development of organ pathology is much easier than trying to cure it later.
Laboratory stress tests
Sometimes it is necessary to carry out some tests not only on an empty stomach, but also after entering the body of certain substances - a stress test is performed.
Types of load tests:
- Glycoamylasemic test - in this case, the initial concentration of amylase in the blood is determined, and then the person drinks 50 g of glucose. Three hours later, another amylase test is done. In case of illness, the amount of this enzyme will be 25% higher than the initial level.
- Proserin test - the initial level of urine diastase is determined, then the drug Proserin is administered. Then, the diastase content is measured every thirty minutes for two hours. Normally, its amount increases no more than twice, and then returns to its original value. For different pathologies of the gland, the indicators will differ.
- Iodolipol test - upon awakening, the patient must urinate and then drink the drug Iodolipol. Then, the level of iodide in the urine is determined every half hour for 2.5 hours. This diagnosis is based on the activity of lipase secreted by the gland. Normally, iodide in urine begins to be detected within an hour, the degree of its excretion increases and reaches a maximum in a urine sample taken after 2.5 hours.
- Secretin-pancreozymin test - to carry it out, the chemical composition of the contents of the duodenum is changed after secretin (a hormone-like substance) is supplied to it. It enhances the secretion of pancreatic juice into the intestine, which contains a lot of bicarbonates and enzymes.
- , – allows you to determine pathology in the endocrine apparatus of the pancreas. In this case, the glucose level in the blood is first determined on an empty stomach, and then 60 minutes and two hours after ingesting the glucose solution. This test can only be prescribed by an endocrinologist and he should also interpret the results, since there is a high probability of developing complications that occur with increased concentrations of glucose in the blood.
Summarizing
Laboratory testing is a key method for diagnosing pancreatic diseases. The condition of the organ can be checked using blood, urine and stool tests. Laboratory tests are often available to many medical institutions, they allow you to quickly and efficiently clarify the diagnosis. If pancreatitis is suspected, the patient is recommended to undergo a general and biochemical blood test, feces for coprogram, and urine for diastase. If cancer is suspected, hematological tests are performed for tumor markers.
Patients suffering from diabetes need to constantly monitor their blood glucose levels. Recently, the study of glycated hemoglobin has become increasingly popular. The analysis provides information about average glucose levels over the past few months. It is necessary to check the functioning of the pancreas if such alarming symptoms appear as pain in the left hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, weight loss. Laboratory tests can also be taken for preventive purposes, since many pathologies of the endocrine organ are asymptomatic.
Survey principles
Without it, it is impossible to carry out the processes of breaking down food into simpler microelements, which are easily absorbed later into the blood.
The production of a special secretion in the form of enzymes allows food to be fully digested.
If this function is impaired, the body suffers from a lack of nutrients, after which health problems begin: weight loss sharply, problems with the psyche and self-esteem appear.
The main principle that must be observed when examining the pancreas is complexity. It is impossible to make a correct diagnosis based only on the patient’s clinical picture or ultrasound examination. This is catastrophically not enough. Therefore, a comprehensive examination of the organ is carried out in three stages:
- Primary diagnosis is collecting anamnesis and assessing the clinical picture of the disease.
- Refined diagnostics are carried out using special equipment.
- Additional – performed as necessary, when there is no exact certainty in the diagnosis and clarification is required.
The examination depends on the condition in which the patient arrived at the clinic. When the face shows all the signs of acute pancreatitis or cholecystitis, examination is reduced to a minimum
There is no time to clarify; it is important to provide first aid correctly, so palpation and ultrasound results are sufficient.
If the patient himself asked for help and is in satisfactory condition, the examination can last from a day to a week. During this time, specialists will collect all the results of the research, which will help to see the overall picture and make a specific diagnosis, as well as select the most gentle treatment.
Drug therapy at home
Drug treatment can be taken at home only on the recommendation of a doctor after examination. For pancreatitis, complex therapy is used, including several groups of drugs:
- Enzyme agents are prescribed for decreased pancreatic function due to the inflammatory process in the organ tissue and the death of its cells. They eliminate nausea and abdominal discomfort, normalize stools, and reduce flatulence. Pancreatin, Festal, Mezim forte are often used. Creon received the best feedback from experts: it is made using a new, innovative technology; one capsule contains many microspheres that dissolve in the lumen of the duodenum, and not in the stomach, thereby significantly improving the digestive process. The drug is prescribed to both adults and children can take it without any particular risk of side effects.
- Antispasmodics (No-Shpa, Drotaverine, Papaverine) - a tablet of any of them relieves the pain symptom.
- Painkillers are used parenterally in the form of injections or droppers in a hospital setting in cases of acute pancreatitis or severe exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory process. They are not prescribed for use at home, and are not recommended for the patient: if the pain intensifies, they can hide the true picture of the disease or the onset of a complication. NSAIDs (Aspirin, Nise and others) should not be used. They irritate the gastric mucosa and can cause bleeding.
- Antibiotics are necessary to prevent infectious complications. Only a doctor prescribes them: the most effective drug is selected taking into account the patient’s condition, the presence of concomitant diseases, existing contraindications and side effects of the antibiotic. The dosage and duration of administration are calculated.
- PPIs - proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantaprazole) - relieve pain. They block the production of hydrochloric acid, thereby reducing the high secretion of pancreatic juice by the gland. Sometimes H2-blockers of histamine receptors (Ranitidine, Famotidine) are used for the same purpose. Additionally, in some cases, antacids are prescribed. They have an enveloping effect and also soothe pain.
Diabetes mellitus is a pathology associated with damage to the endocrine function of the pancreas. Depending on the condition and laboratory data (glycemia level), glucose-lowering drugs are prescribed. They are taken at home strictly by the hour, in the dosage prescribed by the endocrinologist. In severe cases, the patient is prescribed insulin replacement therapy for a long time (sometimes for life). The patient also monitors sugar independently at home using a glucometer.
Any medicine has side effects and application features. Treatment is always prescribed individually. Therefore, the use of drug therapy should be carried out according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor. Replacing any drug with another on your own, without consulting a specialist, can lead to negative effects.