In the article you will find information about the causes, symptoms and methods of treating esophageal spasm.
The main function of the esophagus is to carry food from the mouth to the stomach. During normal operation, the smooth muscles of this organ contract in a wave-like manner for the forward movement of the food bolus.
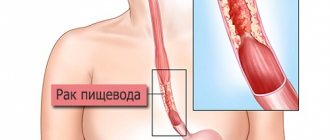
Esophageal spasm is a disease in which there is difficulty in peristalsis, swallowing food and pain of varying severity in the sternum. This condition is associated with pathology of smooth muscle functioning, expressed in involuntary painful contraction of the walls.
Esophageal spasm: symptoms and causes
Among the reasons leading to the occurrence of esophageal spasm (esophagospasm), the main ones are the following:
- Hard, insufficiently chewed, dry, too hot or cold food.
- Microtraumas of the walls, which can be formed as a result of damage from hard food or foreign bodies.
- High-strength alcoholic drinks, which can cause burns to the mucous membranes.
- Food or chemical poisoning.
- Intercostal neuralgia associated with the functioning of the digestive organs.
- Infectious diseases affecting the mucous membrane - acute bronchitis, influenza infections, measles, rubella, scarlet fever.
- Inflammatory processes in the internal organs near the esophagus.
- Stomach or duodenal ulcer, gallstones.
- Gastroesophageal reflux pathology, one of the manifestations of which is the reflux of stomach contents back into the esophageal cavity.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Overwork, psycho-emotional stress and stress.
Spasms are most often recorded at the entrance or exit of the esophageal tube. These areas are supplied with a large number of nerve endings, so they are the first to respond to malfunctions of the nervous system. The function of the esophageal sphincters is to prevent inappropriate food from entering, and therefore there is a sharp reduction in contact with hot, spicy or hard foods.
Signs of pain can be acute - in the form of intense cutting pain or a feeling of “lump”, tightness and heaviness. The duration of the attack ranges from a couple of seconds to one hour.
The main symptom of esophagospasm is chest pain.
The main symptoms of an attack are:
- Acute pain in the chest and area between the shoulder blades, reminiscent of signs of angina pectoris.
- Compressive pain behind the sternum, increasing with exertion.
- Dysphagia is difficulty swallowing food, both solid and liquid.
The appearance of pain symptoms can be associated with the process of eating and active physical activity, and also occur at rest and even sleep.
Recommendations for patients
If esophagospasm occurs, it is advisable to visit a gastroenterologist. He will prescribe the necessary examinations to exclude its secondary nature. Once confirmed, all efforts are directed toward treating the disease that provokes the spastic state. If the reason lies in a malfunction of the nervous system, then measures are taken to normalize it.
How to relieve esophageal spasm at home? The following tips will be useful for both segmental and diffuse spasm:
- Give the individual warm water. This simple method helps in most cases. The attack passes, the pain stops.
- If the cause of the spasm is a stressful situation, then the patient is prescribed herbal sedatives.
It is not recommended to use medications on your own, as they all have contraindications and side effects.
Diffuse spasm of the esophagus: causes and symptoms
It manifests itself as a violation of esophageal motility - uncoordinated contraction of muscles located along the entire length of the esophagus while maintaining normal tone of the lower sphincter.
Symptoms are expressed as:
- Intense pain in the sternum and the area where the esophageal tube connects to the stomach. The pain spreads upward and may involve the lower jaw and shoulder girdle. An attack of sharp pain is not associated with eating.
- Swallowing problems that are more pronounced when trying to swallow pureed foods or drinks than solid foods.
- Regurgitation after the cessation of muscle spasm.
- The attack can last from 2-3 minutes to several hours.
Deformation of the esophagus caused by muscle spasm
TREATMENT OF CARDIA ACHALASIA.
Cardiospasm and achalasia of the esophagus are two different nosologies. Esophageal achalasia is a disease characterized by persistent loss of the LES relaxation reflex in response to the act of swallowing. Motility of the esophagus is sharply reduced. The cardiac sphincter expands only under the influence of the gravity of swallowed food and liquid.
Cardiospasm and achalasia of the esophagus, their differences are that these diseases affect different levels of the parasympathetic ANS.
- In the initial stages of AK you can: Sedatives, Nitroglycerin (before meals) or Long-acting nitrates, Anticholinergics (atropine, metacin).
- Cardiodilation with metal or air dilators, which mechanically rupture the muscle fibers of the narrowed area, is more effective. But in 20-30% of cases, this method does not help, and surgery is necessary.
Segmental spasm of the esophagus
With this type, muscle contractions are observed in some areas of the esophageal cavity with high intensity. With an x-ray, you can see a modification of the esophageal tube like a “rosary” or “nutcracker”.
Main symptoms:
- Difficulty swallowing foods rich in fiber (vegetables, fruits, wholemeal bread) and soft foods (mashed potatoes, porridge, cottage cheese, yogurt).
- The appearance of dysphalgia during fluid intake.
- The pain is characterized as moderate, spreads in the lower segment, begins and subsides gradually.
- The spasm lasts from a few seconds to 2-3 hours.
Prevention
To avoid further development of the disease or prevent the disease, it is important to properly organize your diet. It is necessary to review the diet, exclude rough foods, and do not eat at fast food restaurants. It is not recommended to overeat; meals should be taken in six meals. Seeing a doctor early is a guarantee of complications of the disease.
You should pay attention to the organization of your daily routine. Physical therapy, walks in the fresh air, and swimming will help stop the disease or prevent it.
The prognosis of the disease is favorable with early treatment. Timely diagnosis and compliance with preventive measures is the best way to cope with the disease.
Nervous spasm of the esophagus: symptoms
With a neurospastic spasm, a convulsive contraction of the smooth muscles of the esophageal cavity occurs.
The reasons for this violation are:
- severe nervous tension
- anxiety, fear, sleep disturbance
- stressful situations
- depression
Esophageal spasm when swallowing: symptoms
- The occurrence of a sharp contraction of the muscles of the esophagus during eating.
- Retention of the food bolus in the cavity with subsequent urge to vomit.
- The difference in the appearance of vomit is that vomit contains undigested food that has not had time to enter the stomach.
Difficulty swallowing due to spasm of the esophagus
In pathologies of the nervous system and neurological disorders, an attack can develop regardless of food intake. The main features are:
- The pain spreads to the chest area, reminiscent of heart pain.
- The intensity of the pain varies from a feeling of slight tightness to a sharp burning sensation or severe squeezing.
- Sometimes there are signs of suffocation.
- With neuroses, hysteria, panic attacks, a feeling of “coma” appears in the throat with the inability to even swallow saliva, which indicates a contraction of the initial segments of the esophagus.
- Spasms and gagging can be triggered by fear, anxiety, or sharp sounds.
- Attacks can be short-lived or last up to several hours with varying intensity of pain.
Other types of esophagospasm
In medical practice, there are other types of esophageal spasm:
- Nervous - it is characterized by feverish muscle contraction due to mental disorder (depression), sleep disturbances, stress, increased tendency to anxiety, fear. The attack lasts only a few minutes.
- When swallowing, the following symptoms indicate such a spasm: a feeling of a lump in the throat accompanies a panic attack; during convulsions there is a feeling of suffocation; when there are sharp unexpected sounds, vomiting begins; in a neurosis-like state, a spasm can prevent even saliva from being swallowed; attacks of nausea and vomiting are considered frequent accompaniments of neurosis; in the chest area there are pain sensations similar to cardialgia, and their intensity is not constant and varies from insignificant to severe.
- Cardiospasm can be acute or chronic. Acute – characterized by pain in the chest and epigastric region; feeling that a lump of food is lingering over the stomach. However, drinking water does not bring relief. At the end of the attack, regurgitation or belching occurs. With slight excitement, the pain intensifies. Late therapy is dangerous due to sudden weight loss and esophageal vomiting. The development of pneumonia cannot be ruled out. One of the main causes of esophageal spasm, the symptoms of which are described above, is considered to be a long-term ulcerative lesion. The main provocateurs are smoking, inhaling toxic fumes, and drinking strong alcohol.
- Lower sections - with such a spasm, the organ tube expands along its entire length.
- Non-sphincteric - several of its parts are affected simultaneously along its entire length. Individuals complain of regurgitation of mucus, chest pain, and episodes of dysphagia, lasting from a few seconds to several weeks.
Esophageal spasm also occurs with other anomalies. For example, as a symptom it is observed in tuberculosis, syphilis, scarlet fever, inflammation of the pleura or aorta.
Cardiac spasm of the esophagus: symptoms and causes
Cardiospasm is characterized by signs of expansion of the esophageal tube along its entire length with characteristic changes in its walls and is accompanied by a significant narrowing of the cardiac segment. The causes of this condition can be various factors.
- Internal causes include long-term spasms that occur due to the development of peptic ulcers of the stomach or esophagus, traumatic damage to the mucous membrane, the presence of tumor formations, toxic effects (alcohol, tobacco, vapors of toxic substances). Esophageal stenosis can also be associated with inflammation of the mucous membrane in infectious diseases - typhus, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, syphilis.
- External factors are various kinds of diseases that cause pathological inflammatory processes near the diaphragm (pleurisy, aortic aneurysm, aortitis).
- Cardiospasm can also be caused by disorders of the central nervous system that occur as a result of infectious diseases (poliomyelitis, menigoencephalitis, diphtheria) and intoxication of the body under the influence of certain substances (nicotine, lead, arsenic, carbon monoxide).
Narrowing of the esophagus
Causes
Involuntary contraction of the muscles of the organ is a consequence of many factors. Among them are some diseases that provoke inflammation of the mucous membrane of the organ:
- stenosis or distal esophagitis of the esophagus;
- cholelithiasis;
- reflux of gastric juice into the esophageal tube - gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- ulcers of various etiologies;
- infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes in the muscular tube.
In addition to these serious pathological conditions, the following phenomena can cause the disease:
- insufficiently chewed food;
- rough or scalding food;
- thermal, chemical or mechanical burn of the esophageal tube;
- allergic reactions of various origins;
- presence of a foreign object.
The consumption of strong alcoholic drinks and stress cause great harm to the esophagus.
Esophageal spasms during pregnancy: causes
Esophagospasm during pregnancy is not always associated with pathological damage to the esophageal cavity. The most common causes are physiological and hormonal changes in a woman’s body:
- The gradual increase in fetal size puts pressure on the abdominal organs and sternum. As a result of compression of the digestive organs, stomach contents can be forced back into the esophagus, irritating its walls and causing stenosis.
- During pregnancy, the expectant mother's body sharply increases the production of the hormone progesterone, which leads to muscle relaxation. Thus, the muscle tone of the esophageal sphincters is weakened, which allows gastric juice to enter its cavity.
- Under the influence of hormones, the nervous system of a pregnant woman becomes more excitable, which can provoke spasmodic attacks.
Esophageal spasms are a common occurrence during pregnancy.
Cardiospasm of the esophagus in children
In children, as in adults, the basis of the pathological process is the spastic contraction of the LES and an increase in the diameter of the proximal parts of the organ. This disrupts the tone and motility of the esophagus. In children, organic stenosis and hypertrophy of the muscles of the abdominal esophagus are not detected.
Causes
Histological studies in children with cardiospasm reveal a congenital deficiency of intermuscular neurons, resulting in congenital denervation of the smooth muscle fibers of the esophagus.
Spasm of the esophagus in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine: causes
Spasms of the esophagus can be one of the symptoms of the development of osteochondrosis. This type is called vertebrogenic esophagospasm and is observed in osteochondrosis of the thoracic or cervical spine due to pinched nerve endings (radicular syndrome).
- The digestive organs, like other internal organs, depend on the spinal cord. With the help of autonomic nerves, the functioning of organs is regulated.
- Symptoms caused by esophagospasm in osteochondrosis are sometimes difficult to distinguish from signs of other diseases. Diagnosis of this condition includes a number of examinations.
Osteochondrosis can provoke convulsive contractions of the esophageal muscles
Table of contents
What is cardiospasm of the esophagus and its causes
? Symptoms in adults
Stages of the disease
Diagnostics
Cardiospasm and achalasia of the esophagus: differences
Cardiospasm of the esophagus: treatment
For what types of cardiospasm is surgical treatment indicated?
Balloon dilatation
Surgery
Recovery period after surgery
Diet for cardiospasm
Alternative medicine
Cardiospasm of the esophagus in children
Causes
Cardiospasm of the esophagus: treatment in children
How to treat cardiospasm of the esophagus in children
What to do in case of esophageal spasm, how to remove it?
To help quickly relieve pain, you can do the following:
- During an attack, the patient is usually able to take a few sips of warm liquid - preferably milk, chamomile or mint infusion. This will help the food move forward and relieve acute pain.
- You can perform breathing exercises for 3-5 minutes: take a deep breath using abdominal breathing, mentally count to 5, hold your breath for a couple of seconds and exhale slowly.
- Nitroglycerin has a quick relaxing effect, a tablet of which the patient must dissolve under the tongue.
- An injection of the drug atropine (can be administered intravenously or intramuscularly) will help relieve muscle spasms.
A few sips of warm drink will help relieve an attack
Alternative medicine
How to relieve esophageal spasm at home? This question is often asked to the doctor. It turns out that if the reason that caused this condition is known, then it is quite possible to cope with this problem yourself, using the following effective methods:
- Infusions of flax seeds and anise or mint and plantain. To prepare the drink, take 10 grams of each medicinal plant material and add 500 ml of water. Before use, strain and add honey.
- If the spasm is caused by stressful situations, then it is recommended to drink no more than fifteen drops of motherwort, peony or valerian tincture before meals.
- Baths with the addition of a herbal mixture, which includes lemon balm, motherwort, linden flowers, valerian and one of the oils (tea tree, orange or ylang-ylang), soothe and relieve spasms well. The duration of the procedure is no more than twenty minutes.
- Breathing exercises that are performed slowly. They help prevent further development of muscle contraction.
Now you know how to relieve esophageal spasm at home.
Treatment with folk remedies can be used as an addition to general therapy. They can be used at home during stage I of the disease, and after bougienage or surgery.
To eliminate inflammatory phenomena during esophagospasm, she recommends infusions of alder, quince seeds, oregano or chamomile.
If the symptoms of cardiospasm intensify due to nervousness, then tincture of valerian, peony, and motherwort is recommended.
How to relieve spasm of the esophagus using folk remedies?
For recurring attacks, you can use home recipes:
- Prepare a decoction by adding 1 tbsp to 0.5 liters of water. spoon of flaxseed, 1 teaspoon of anise, 1 tbsp. a spoonful of natural honey. Bring the mixture to a boil, leave to brew for 15 minutes, strain and take warm 2-3 times a day.
- Boil 5 tbsp. spoons of dry plantain leaves and 2 tbsp. spoons of peppermint in 1 liter of water over low heat. Add 3 tbsp. spoons of honey and boil for another 3-5 minutes. Strain the resulting decoction and drink 1 tbsp on an empty stomach. spoon.
- For neurological spasms accompanied by insomnia, increased heart rate, and cardiac dysfunction, tinctures of valerian, motherwort or peony will help. These herbs have a mild sedative and antispasmodic effect. Dilute 15 drops of tincture of valerian roots or motherwort in a glass of warm water and take 100 ml three times a day half an hour before meals. Dilute in 1 tbsp. 10 drops of peony tincture in a spoon of warm water and take 3 times a day before meals.
- A good soothing and relaxing remedy are herbal baths - with a decoction of pine or fir branches or a collection of herbs (motherwort, linden flowers, valerian, lemon balm). Additionally, you can use essential oils of ylang-ylang, tea tree, orange - 5-10 drops each. The optimal duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes at a water temperature of 37-40ºС.
Herbal tinctures to calm the nervous system
Therapeutic measures
After confirming the diagnosis, individuals are interested in the question of how to relieve spasms of the stomach and esophagus. If the exact cause of the disease has not been identified, then doctors do not recommend treating it yourself. Therapy involves the use of:
- medicines;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- diet;
- lifestyle changes;
- medicinal herbs.
If there is an underlying gastrointestinal disease that provokes esophagospasm, then initial treatment should begin with it in order to prevent the occurrence of new attacks. Next, we will consider in more detail how to treat reflex esophageal spasm. For this purpose, drugs of different pharmacological groups are used:
- Antacids, or antacids, protect the mucous membrane of the digestive canal.
- Gastrointestinal motility stimulants - promote the passage of a bolus of food by improving the peristalsis of the muscular tube.
- Antispasmodics – remove spasms.
- Alginates – envelop the mucous membrane, protecting it from aggressive hydrochloric acid.
- Sedatives – a calming effect on the central nervous system.
- Antidepressants, tranquilizers and medications that normalize sleep are prescribed if necessary.
- Analgesics and anesthetics – have a local anesthetic effect.
- B vitamins.
The above medications, doses and treatment regimens are selected by the attending physician individually.
Let's look at how to relieve spasms of the stomach and esophagus with the help of physiotherapeutic treatment. It is aimed at normalizing the functions of the nervous system and includes:
- Electrophoresis with an anesthetic - a direct electric current is applied to the affected organ together with a drug, which helps relieve pain.
- Radon baths - thanks to them, the sensitivity of nerve endings is reduced.
- Galvanization - current is supplied through electrodes with a constant frequency, low strength and low voltage. As a result, the sensitivity of the nerve fibers weakens. This method is especially effective for spasm of the esophagus that occurs against the background of osteochondrosis.
- Warm baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs that have a sedative effect.
- Inductotherapy is the effect of a high-frequency electromagnetic field with a predominance of the magnetic component. The uniqueness of this manipulation is that heat is generated in the muscle layer, which ultimately reduces tone and eliminates spasm of the esophagus. How else can you remove it? Physical activity is especially important, i.e. performing simple exercises aimed at strengthening the spinal column and normalizing the functioning of the central nervous system.
Phytotherapeutic treatment involves the use of medicinal plant materials that have different effects:
- anti-inflammatory – elecampane;
- sedative – peony, valerian, motherwort;
- antispasmodic – chamomile, sage, mint.
Alternative treatments include:
- Acupuncture. The course of treatment is up to ten days, three times a year.
- Medical hypnotherapy.
- Psychotherapeutic methods - sand therapy, autogenic training according to Schultz, art therapy.
Massage of certain points that are located on the midline of the chest is another non-standard way of treating esophageal spasm. How to remove it using this method? The locations of the points are as follows:
- under the cervical fossa;
- between the breasts;
- between the first and second points (at an equal distance from each).
These areas are massaged with the finger bones, making clockwise rotational movements for five minutes. It is noted that when performing this manipulation, the individual experiences severe pain. There is an opinion that this is a normal phenomenon, and after twenty minutes of intense exposure to these points, the pain will completely disappear.
All of the above methods give good results.
Esophageal spasm: treatment
Traditional methods are applicable if attacks are caused by fatigue, overwork or nervous disorder. If the disease is chronic and caused by the presence of any pathology, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of the underlying disease, as well as adhere to a gentle diet.
A proper diet plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of diseases of the digestive tract.
- Food should not irritate the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach - the basis of nutrition should include boiled, stewed or steamed dishes with a semi-liquid consistency. You should eat food in small portions - 4-5 times a day in small portions. The last meal should be no later than 3 hours before bedtime.
- It is necessary to completely eliminate carbonated and alcohol-containing drinks, dark chocolate, strong coffee, fried, hot and spicy foods, salty and sour foods, canned food and smoked foods. Make sure that food and drinks are not too hot or cold, optimally 36-38ºС or room temperature.
Physiotherapy and massage
Physiotherapy methods help stabilize the nervous system and have a relaxing effect on muscle tissue.
For spasmodic attacks, the following procedures are recommended:
- inductotherapy
- microwave therapy
- electrophoresis
- carbon dioxide, radon baths
An important component of treatment therapy is physical activity. If you have a sedentary job, you should take breaks every 2 hours and perform a 5-minute set of exercises to strengthen the spine and stabilize the functions of the central nervous system. In your free time, walking, running, swimming, and moderate strength training are recommended.
A general massage will help restore normal muscle tone, relieve tension, and have an additional relaxing effect on the entire body.
Exercise and breathing exercises will help prevent esophageal spasms
Drug therapy
Drug treatment of esophagospasm is aimed at eliminating all associated symptoms and alleviating the general condition.
- To reduce the acidity level of gastric juice, the following drugs are prescribed: Creon, Famotodin, Omeprazole.
- To relieve spasms, suppress nausea and the urge to vomit: Drotoverin, Cerucal.
- To protect the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach from irritation: Almagel, Rennie, Gastal.
The dosage of drugs is prescribed by a doctor depending on the symptoms and causes of this dysfunction of the esophagus.
The following habits will help reduce the frequency of attacks:
- sleep and relax on a high headboard
- quitting alcohol and smoking
- weight loss
- development of correct posture (to prevent curvature of the esophageal tube)
The basic principles of treating a patient for esophageal spasms should include making the correct diagnosis and combining a set of procedures for successful therapy.
Diagnostics
To diagnose esophageal spasm, methods such as:
- Gastroesophagoscopy. To do this, a flexible endoscope is inserted into the esophagus.
- Biopsy (examination of a tissue fragment).
- Radiography. It is done using a special X-ray contrast agent.
- Manometry. In this case, the pressure of the esophageal wall is measured while the patient swallows water.
- Measuring the alkaline index of gastric juice.
Laboratory tests do not play a significant role in the diagnosis.
Basically, the diagnosis of the disease is based on x-ray, endoscopic studies and manometry.
- X-ray with contrast of the esophagus. The main radiological sign is a cone-shaped narrowing of the esophagus with the apex in the region of the cardia, the overlying parts of the organ are dilated, sometimes significantly, the peristalsis of the organ is impaired, and there is no gas bubble in the stomach.
- An endoscopic examination allows one to determine how dilated the upper parts of the esophagus are and the severity of inflammatory and metaplastic changes. Although the cardiac sphincter is closed, in case of cardiospasm it is usually possible to enter the stomach during endoscopy; if the fiberscope does not pass into the stomach, then it is necessary to exclude oncological pathology.
- Manometry can confirm the diagnosis. The main manometric syndrome is the absence or decreased relaxation of the LES during swallowing. The study reveals an increase in pressure in the area of the lower sphincter and impaired peristalsis.
If these symptoms occur, you should immediately go to a medical facility for diagnosis. A plan of diagnostic measures is drawn up by a gastroenterologist after an initial examination and interview. The most informative methods include radiography using a contrast agent, as well as endoscopic examination of the esophagus and stomach.
Treatment of the pathological condition consists of three stages:
- preparing a diet. You should take any food at least 4 times a day, but in small portions. This will help reduce the load on the esophageal tube;
- conservative therapy. Some pharmaceuticals are prescribed, in particular anesthetics, anticholinergics, tranquilizers;
- invasive treatment. If conservative therapy does not bring any effect, then in this case they resort to surgical manipulations - chemical denervation, bougienage of the esophagus, myotomy and others.
If the cause of spasms is psycho-emotional stress, stress, depression, then psychotherapy is included in the treatment plan.