Estradiol in women is the most active female sex hormone.
It can have a significant impact on the proper development of secondary sexual characteristics, the cyclicity of menstruation, a woman’s ability to conceive and bear a child, the health of her cardiovascular and skeletal systems, etc. Despite the fact that estradiol is the most important female hormone, it is also synthesized in men, although in much smaller quantities. Moreover, before the onset of puberty, both girls and boys have approximately the same level of estradiol in the blood. But puberty changes this equality.
The level of estradiol in girls increases significantly synchronously with the development of secondary sexual characteristics, but in boys it remains at the same level.
What does the hormone estradiol do in a woman’s body?
First of all, estradiol is responsible for the fullness of the menstrual cycle and the functioning of the genital organs. The hormone also helps to develop female sexual characteristics. Ovulation occurs only after an increase in estradiol levels.
The hormone estradiol not only helps in reproduction, but is also responsible for primary and secondary sexual characteristics. It regulates the psychophysiological characteristics of a woman’s behavior. During pregnancy, estradiol is responsible for the growth of the uterus. Any interruptions in this hormone affect menstrual function.
Functions of estradiol in the female body:
- proper development of the reproductive system;
- organ formation;
- formation of a female figure type;
- development of the uterus, formation of its endometrium;
- regulation of blood circulation in the uterus;
- strengthening blood vessels in the uterus;
- regulation of cholesterol levels;
- replenishment of energy reserves;
- strengthening the bone structure;
- maintaining tone;
- accumulation of fat on the stomach, thighs and other “female” areas.
The influence of estradiol is dependent on its relationship with testosterone. This is how subcutaneous tissue is formed, blood flow in the uterus improves, and the growth of the endometrium is activated during the period of ovulation. Estradiol increases the synthesis of neurotransmitters that transmit impulses from nerves.
The hormone stimulates protein production, improves blood clotting, promotes bone turnover, and helps bones mature faster. Estradiol retains sodium in the body, which, in turn, transports carbon dioxide, amino acids, and anions. Sodium regulates blood pressure, helps with metabolism, and promotes hydration.
What are the functions of estradiol
The biologically active substance is produced by both female and male bodies, the only difference is in concentration. Therefore, the functions of a substance can be divided into two groups: those that are performed in the body, regardless of gender, and those that are inherent in a purely female body.
Common features for women and men are:
- regulation of the circulatory system;
- bladder activity;
- intestinal motility;
- work of skeletal muscles;
- ensuring skeletal strength;
- relieving nervous tension;
- participation in metabolic processes.
With the onset of puberty in a girl, the female hormone enters the bloodstream , and secondary sexual characteristics begin to appear in her: breast growth, roundness of the figure, high-pitched voice, formation of the uterus, and proper functioning of the gonads. Estradiol in women is involved in the regulation of the menstrual cycle, affects the maturation of the egg, and prepares the uterus for possible pregnancy.
Beauty hormone
Estradiol is rightly called the beauty hormone . In addition to ensuring metabolic processes and performing reproductive functions, it has a strong effect on the nervous system and skin condition.
Under the influence of normal hormonal levels, women's skin becomes soft, velvety, wrinkles are smoothed out, complexion improves, and sparkle appears in the eyes. The female hormone improves mood, increases performance, and helps the female body resist stress.
Indications for testing for estradiol
A gynecologist deals with problems with estradiol. Often the course of treatment is conservative. Sports and moderate physical activity, which lower hormone levels, are also recommended.
Indications for the study:
- pelvic pain;
- periodic vaginal bleeding;
- disruptions in the menstrual cycle;
- infertility;
- accelerated or inhibited development of the genital organs;
- symptoms of menopause (insomnia, sweating, hot flashes);
- problems with conception;
- symptoms of feminization (abnormal growth of mammary glands in men, etc.).
The indicator is above normal
If estradiol is elevated in pregnant women, then the clinical picture is considered completely normal.
Otherwise, excessive dry skin and hair loss occur. She may also suffer from obesity and occasional bleeding.
Other symptoms include breast pain and excessive irritability.
A representative of the fair sex will not be able to get pregnant. If you have these negative manifestations, you should consult a doctor. He is prescribed a blood test, which will allow him to make a diagnosis.
Increased estradiol in the body leads to disturbances in the functioning of the liver and thyroid gland. If a woman eats incorrectly, the situation will further worsen due to weight gain.
Quite often, clinical manifestations occur while taking certain medications.
the risk of developing tumors and cysts in the ovarian area increases
The substance is formed from male hormones, so their excessive amounts can lead to these diseases. This may result in excessive body hair coverage or scalp baldness. The situation is aggravated by the complete absence of menstruation. In this case, infertility further develops.
To regulate the hormone level, you need to find the cause of the negative condition. Hormone therapy is most often prescribed. If necessary, the tumor in the ovarian area will also need to be removed.
Preparing for analysis
The study of estradiol is carried out by chemiluminescence immunoassay. The material for study is venous blood. Results are reported in pg/ml (picograms per milliliter). Determining hormone levels cannot be the only diagnostic method. The analysis is included in the complex.
An estradiol test is performed by drawing blood. For the purity of the study, the test is carried out on days 6-7 of the menstrual cycle (on days 2-4 in a normal cycle). The doctor may choose a different time if the situation requires it. Blood sampling is done on an empty stomach and in the morning. The day before the test, you should not overeat, smoke or drink alcoholic beverages.
Preparing for the study:
- refrain from food (3 hours before the test);
- You can only drink clean water without gas;
- stop steroid and thyroid therapy two days before donating blood;
- refrain from smoking (3 hours before);
- Avoid physical and emotional stress a day before the analysis.
Research objective:
- determine the level of estradiol, which allows you to assess the functioning of the ovaries;
- find the cause of amenorrhea (lack of menstruation);
- diagnose early puberty;
- identify gynecomastia in men (enlarged breast glands);
- track follicle development before IVF.
Factors influencing the result of the study:
- diet (predominance of carbohydrates, lack of fat);
- medications (ampicillin, phenothiazines, glucocorticosteroids, tetracyclines, drugs with estrogen);
- dietary supplements (the herbs in Cascara Sagrada may artificially increase estradiol levels in the test).
The study is carried out only at rest. Strong emotions and experiences can change the results. Strong physical activity and training are also excluded. Alcohol should not be taken two days before, and smoking should not be done at least two hours before blood sampling.
You may have to give up antibiotics and birth control for some period. Drugs used to correct emotional background and treat mental disorders are also removed.
Features of the study
To achieve accurate data, blood is taken to assess estradiol levels on days 4-6 of the cycle. The second study is performed on days 20-21.
To get accurate results, you must follow a number of recommendations:
- 2-3 days before the procedure, it is important to avoid overeating;
- During the day you need to reduce physical and intellectual stress;
- Give up sexual intercourse within 24 hours;
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol one day before.
If you use any medications, you should definitely inform the specialist who recommended the procedure. In some situations, medications should be temporarily discontinued as they may distort the data obtained.
You need to eat no later than 12 hours before the test. Blood must be donated only on an empty stomach. It is best to do this at 8-11 am. To conduct the study, blood must be taken from the cubital vein in a volume of 5-10 ml.
It takes 3-7 days to wait for the results of the study. In urgent situations, you can get the result within 5 hours after donating blood.
Norm of the hormone estradiol for women
The male norm ranges from 7.63 to 42.6 pg/ml. Women's norms depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle. In the first six days, 12.5-166 pg/ml is considered normal. During the follicular phase (3-14 days) the values should not change. During ovulation (days 13-15), estradiol levels increase to 85.8-498 pm/ml. In the luteal phase (from 15 days before the start of menstruation), the values decrease to 43.8-211 pm/ml.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the norm for postmenopause - up to 54.7 pg/ml. In the first trimester of pregnancy, estradiol levels range from 215-4300 pg/ml.
It is not recommended to independently interpret the analysis results. This is justified by the fact that estradiol levels tend to change constantly and dramatically. Having mixed up the phases and seeing a large number, a woman will definitely worry, which will only harm her health. It is better to leave the diagnosis to an experienced doctor.
You cannot consider only individual values. When assessing the results, the doctor relies on the patient’s individual menstrual cycle calendar and takes into account the properties of estradiol. The analysis does not give a clear result, but indicates possible causes of the symptoms.
Estradiol is the norm in women by age
Important. Fluctuations in estrogen levels in women largely depend on age and the phase of the menstrual cycle. Also, the level of the hormone changes during pregnancy.
The hormone estradiol - indicative norms for pregnant women:
Reasons for deviations in analyzes
The amount of hormone in women may increase if:
- dominant follicle (persistence) in the ovary and hyperestrogenism;
- endometrioid cysts or hormone-secreting tumors in the ovaries;
- liver cirrhosis;
- obesity;
- chorionepitheliomas in the uterus (malignant estrogen-secreting neoplasm);
- pregnancy.
Also, taking estrogen-containing contraceptives, anabolic steroids, treatment with nafarelin, carbamazepine, cimetidine, clomiphene, ketoconazole, mifepristone, phenytoin, tamoxifen, troleandomycin, valproic acid leads to an increase in hormone levels.
Estradiol is reduced when:
- excessive physical activity;
- exhaustion, sudden weight loss, strict diets and fasting;
- vegetarian diet;
- long-term or chronic inflammation of the pelvic organs;
- hypogonadism, pituitary dwarfism or hyperprolactinemia;
- adrenogenital syndrome;
- Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome;
- conditions after removal of the ovary (posthysterectomy syndrome);
- insufficiency of LF (luteal phase) of the menstrual cycle;
- hyperandrogenism;
- the threat of spontaneous abortion in pregnant women.
Chemotherapy, treatment with megestrol, moclobemide, nafarelin, mifepristone, nandrolone, pravastatin, cimetidine, cyproterone, danazol, dexamethasone, and oral contraceptives can also lead to a decrease in the amount of estradiol.
Estradiol is low: what to do
Symptoms of a decrease in estradiol include weight loss, abnormal dry skin, and shrinkage of the mammary glands. An alarm signal may be the absence of menstruation for six cycles in a row without pregnancy. Some patients develop osteoporosis (reduction in the mass of bone tissue, disruption of their structure). Osteoporosis causes back pain.
Lack of estradiol can lead to anovulation (lack of ovulation). Pregnancy with this diagnosis is simply impossible, because the egg does not mature or leave the follicle.
The hormone level decreases when:
- anorexia nervosa (can develop against the background of amenorrhea);
- Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome (chromosomal abnormalities causing developmental abnormalities and sexual infantilism);
- Sheen's syndrome or hypopituitarism (low concentration of pituitary circulating hormones, which causes hypofunction, atrophy of the glands);
- Stein-Leventhal syndrome or polycystic ovary syndrome (dysfunction of the ovaries, hypothalamus and pituitary gland, pancreas and adrenal glands);
- hypogonadism (congenital underdevelopment, which leads to poor functioning of the ovaries);
- physical activity;
- postmenopause.
To prevent the development of all these diseases, you should respond to any ailment. Timely consultation with a doctor helps to avoid most dangerous consequences. Abnormalities can even be detected using a blood test.
Options for increasing estradiol levels:
- Hormonal therapy;
- Folk recipes (herbal infusions and decoctions). Sage, linden blossom, and hops are often used. Treatment with folk remedies should only be done on the recommendation of a herbalist.
- Following the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
- Complete cessation of smoking and alcohol.
- Walking outdoors and being active.
- Diet with proteins.
Any deviation from the norm requires study. A large decrease will not cause a serious deterioration in health, but will gradually depress the body.
Reasons for the increase in estradiol
There are many factors that cause an increase in the content of this hormone in the blood. To correct hormonal levels, you need to identify the provoking factor.
Obesity
It is worth considering that adipose tissue is a kind of endocrine organ. It carries out complex transformations of androgens into estrogens. If the layer becomes too large, this process is disrupted.
As a result, the volume of estradiol in the blood increases. This process is often accompanied by the disappearance of ovulation and a decrease in reproductive functions.
Obesity remains a threat after menopause. Excessive amounts of estrogen reduce the symptoms of menopause, helping to cope with excessive vaginal dryness, hot flashes and other symptoms. However, the violation provokes an excessive threat of proliferation of the endometrium, tumor formations, uterus and ovaries.
Hyperandrogenism
This term refers to an increase in the level of androgens in the body. They are estrogen precursors. Therefore, an excess amount of these substances provokes an increase in the content of female hormones.
From a clinical point of view, hyperandrogenism has different symptoms. In simple cases, people have skin problems - seborrhea, acne. Baldness and excessive growth of facial hair are also observed.
A complex degree of pathology provokes the cessation of menstruation and impaired reproductive functions. The female figure changes according to the male type.
The most common disorder that is accompanied by an increase in the level of male hormones in women is polycystic ovary syndrome. In medicine it is called Stein-Leventhal syndrome.
The basis of the disorder is a deviation in the functioning of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, which provokes the active production of androgens in the ovaries. Provoking factors also include obesity, thyroid disease, and increased insulin levels in the blood.
Treatment for the syndrome is selected taking into account the woman’s reproductive plans. If pregnancy is planned, clomiphene is prescribed. In other situations, combined contraceptives are recommended, which contain a small amount of estrogens and have antiandrogenic properties.
Hormone-producing tumors
There are tumors in the ovaries that provoke active synthesis of female hormones. Girls with this diagnosis begin puberty prematurely. In middle age, uterine bleeding is observed. There may also be problems with the menstrual cycle.
With the advent of menopause, spotting is observed, which has varying degrees of intensity. Moreover, the condition of the skin does not correspond to the age category - it is more elastic.
All these processes are provoked by an increased content of estrogen in the body. If a neoplasm is detected with such signs, it should be removed and sent for histology. Therapy is prescribed taking into account the type of tumor - it can be benign or malignant.
Formations that produce hCG
A common factor that causes hormonal imbalance is hydatidiform mole. Choriocarcinoma may also be the cause. These disorders appear when chorionic villi penetrate uncontrollably into the uterus. They grow in the organ. As the pathology progresses, metastases occur that affect other organs.
The cause of the problems is an abnormal set of chromosomes during fertilization. The tumor actively produces hCG, which leads to an increase in the content of progesterone and estrogen.
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor performs an ultrasound examination and prescribes a test to detect the level of hCG. Depending on the severity of the pathology, observation or chemotherapy may be prescribed.
Use of drugs
Sometimes an increase in estradiol levels is observed during the use of certain medications. Provoking factors are anabolic steroids, drugs with estrogen, and ketoconazole. Clomiphene, cimetidine and other substances also cause problems.
Complex liver lesions
The transformation of sex hormones is completed in the liver. It is in this organ that they are metabolized and leave the body. With the development of cirrhosis and other disorders that are accompanied by liver failure, the content of estrogen increases.
Estradiol is increased
High levels of estradiol can be an alarming signal indicating the presence of cancer. Often this is cancer of the uterus and mammary glands. Also, high estradiol indicates hypertension, whose complications can lead to stroke.
Estradiol levels increase when:
- accelerated puberty;
- liver cirrhosis;
- tumors on the ovaries or adrenal glands;
- gynecomastia (hypertrophy of adipose tissue and enlargement of glands in men);
- hyperthyroidism (predominance of estrogens over androgens, increased globulin levels).
Symptoms of elevated estradiol levels are heavy menstrual flow at the wrong time, cycle shifts, severe breast tenderness, bleeding between menstruation. Against this background, the patient becomes irritable, nervous, and suffers from mood swings.
Additional symptoms will be swelling, acne, weak hair, cold extremities, and convulsions. The woman quickly gets tired, feels discomfort in the stomach, pain in the chest.
The role of the hormone
In adolescence, at the time of puberty, this hormone performs the following functions:
- The formation of secondary sexual characteristics in a woman is the breasts and reproductive system and organs, hair growth exclusively according to the female type.
- In his competence is the growth and functioning of the uterus, appendages, plus the formation of the figure of a young body according to the female genotype.
- Formation of a normal menstrual cycle.
- Growth and development of bones and regulation of calcium metabolism.
During reproductive age, this hormone plays an important role - to prepare a woman for conception, bearing and giving birth to a child.
In addition, it performs the following functions:
- In the 1st phase of the cycle, it ensures the growth of the uterine cavity mucosa and its preparation for implantation of an egg fertilized by sperm.
- Under the influence of this hormone, the follicle grows and matures, ensuring its rupture and release of the egg at the appropriate phase of the menstrual cycle.
- When the hormone level decreases at the end of menstruation, it provokes monthly bleeding.
During menopause, this hormone regulates water-salt and lipid metabolism, or more precisely:
- The processes of calcium metabolism in bones and the process of osteosynthesis itself.
- Regulates the exchange of water and sodium in the body.
- Reduces the readings of low-density lipids in the blood and increases the level of high-molecular fats.
Preparations with estradiol
Today, contraceptives based on estradiol or analogues are widely used. They are a good protection against unplanned conception due to their effect on the inner surface of the uterus. The egg cannot attach to the damaged uterine epithelium and begin to develop. But such contraception has a significant disadvantage: over time, the layer of the uterus atrophies, and the chances of pregnancy decrease. The use of drugs with estradiol can be dangerous, so you should not use them without the advice of a doctor.
With prolonged use of drugs with estradiol, the following symptoms may appear:
- intense headaches and dizziness;
- liver dysfunction with all the ensuing consequences;
- mood swings, irritability, nervousness;
- weight gain;
- vaginal bleeding in different phases of the cycle;
- sand and stones in the gall bladder.
Estradiol is widely used to treat underdevelopment of the genital organs and absence of menstruation. The hormone estradiol also helps with osteoporosis and excessive sweating.
Diseases treated with estradiol:
- hypoplasia;
- amenorrhea;
- infections and inflammations of the genital organs with frequent relapses.
Contraindications are:
- liver diseases;
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- sickle cell anemia;
- otosclerosis;
- jaundice;
- herpes;
- gallbladder disease;
- thrombophlebitis;
- hypercalcemia.
Consultation with a doctor is required if the patient suffers from diabetes, epilepsy, heart or kidney failure, endometriosis, migraines, bronchial asthma, porphyria, tumors, mastopathy, connective tissue diseases. Estradiol can reduce glucose tolerance in patients with diabetes.
Signs and consequences of excess estradiol
Symptoms that estradiol is elevated in women may appear with varying intensity. It all depends on how strong the hormone surge is. Often this deviation is accompanied by:
- MC violations;
- the appearance of menstruation during menopause;
- a feeling of extreme fatigue that does not go away even after proper rest;
- sleep problems;
- sudden gain of several extra pounds;
- rapid fatigue;
- coldness of the upper and lower extremities.
In addition, the presence of the following abnormalities may indicate that estradiol is elevated in women:
- causeless irritability, mood swings;
- swelling of the limbs;
- acne that was not previously observed on the skin;
- breast pain, swelling;
- inability to conceive;
- increased dryness of the skin;
- hair loss;
- increased sweating.
Note. One of the signs of increased estradiol in women is a decrease in the reproductive organ. Such changes in the uterus are noted only during a gynecological examination - it is impossible to independently suspect and identify a deviation.
Elevated levels of estradiol in women are fraught with problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, this deviation is characterized by a noticeable decrease in the size of the mammary glands. These are not the most dangerous, but still unpleasant consequences of an excess of this hormone. To avoid more serious complications, you should consult a specialist immediately after the first alarming signs of high estradiol levels in women are noticed.
Prevention
You can avoid problems with estradiol by eliminating all “male” habits from your life: smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages, drug addiction, drug-induced tone enhancement. Most drugs to stimulate sexual function suppress the ovaries.
Leading an incorrect lifestyle, being carried away by bad habits and dubious sexual contacts, a woman actually ceases to be a woman. Estradiol, which makes girls sophisticated and soft, is reduced. As a result, abnormal growth of body hair begins, the voice becomes rougher, and the skin dries out. The woman's gait and movements become abrupt. A severe deficiency of the hormone can even interrupt menstruation.
Causes of elevated estradiol in women and men
Elevated estradiol in women can be caused by the following conditions:
- endometriosis;
- follicle persistence;
- follicular ovarian cyst;
- hormone-producing neoplasms of the ovaries and uterus.
The reasons for the excess of this hormone in individuals of both sexes include:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- thyroid diseases;
- excess body weight (due to increased aromatization of peripheral androgens);
- taking a number of medications (oral contraceptives, which include estrogens, anabolic steroids, etc.).
In addition, estrogen-producing testicular tumors may be the cause of increased estradiol in men.
Treatment
If the hormone level is elevated, the doctor prescribes treatment based on the patient’s age. Therapy also depends on how much the indicator deviates from the norm. If the increase is small, then the woman needs to change her lifestyle to a more active one. It is also important to solve problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Sometimes following a certain diet is enough.
Some herbs help reduce estradiol in the body. Excess amounts of the hormone in the intestines can be removed by consuming fiber of plant origin (for example, wheat bran, cocoa, flax seeds).
Self-medication is unacceptable ! All nuances of therapy should be discussed with your doctor.
Reasons for the high level of content
An increase in this hormone is considered normal only during pregnancy; in all other cases, this phenomenon is accepted as a pathology.
Signs of excess are as follows:
- dry skin and brittle hair;
- irritability and fatigue;
- pain in the chest;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- uterine bleeding;
- excess weight.
In little girls, this pattern leads to early puberty.
Adult women suffer from depressive disorders, anemia, and ovarian and breast tumors.
Sometimes the cause of high levels of the hormone can be excess weight gained as a result of poor nutrition, dysfunction of the liver or thyroid gland. Estrogen-containing medications and their long-term use also cause harm.
The presence of tumors in the body that provoke the production of estradiol and ovarian cysts are also causes of excess. The high content of male sex hormones in the female body, from which estradiol is produced, leads to levels above normal. In this case, the figure becomes masculine, menstruation disappears, hair falls out on the head, but grows throughout the body.
Decreased hormone levels and possible complications
Before engaging in treatment, the doctor is obliged to conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient. First, a clinical blood test is performed to determine the content of estradiol in a woman’s body. It is required for:
- assessment of the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system (in particular, the ovaries);
- finding out the reasons for the long absence of menstruation or shifts in the menstrual cycle;
- preventive monitoring of the follicle development process as part of in vitro fertilization;
- determining the causes of delays in puberty in adolescent girls;
- finding out the reasons for the early onset of menopause.
Only if the reasons why women have elevated estradiol are accurately determined will the doctor be able to give specific recommendations regarding further treatment.
Features of therapy
Hormonal disorders are the responsibility of an endocrinologist. But since in this case we are talking about high estradiol in women, which is a sex hormone and therefore directly affects the reproductive system, you can also turn to a gynecologist for help.
First, the cause of the hormonal imbalance is eliminated, and only then, if necessary, additional treatment is carried out aimed at normalizing the hormone level. So, how to lower estradiol in women? For this purpose, you first need to:
- improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- direct efforts to get rid of extra pounds;
- take a course of vitamin therapy;
- completely cure acute liver diseases, or transfer chronic pathologies into a phase of long-term remission.
There are other, no less effective, ways to reduce estradiol in women. These include:
- following a gentle low-carbohydrate diet with a predominance of Omega-3 fatty acids;
- complete abstinence from drinking beer;
- adequate distribution of time for rest and physical activity;
- sufficient consumption of foods containing macro- and microelements, antioxidants.
Possible consequences of deviation
Hormonal imbalance is dangerous in any case, and it does not matter in which direction the deviation from the norm is observed. If estradiol is higher than normal, this can lead to the following health problems in women:
- serious disturbances in the psycho-emotional state, including prolonged depression;
- intense bleeding that can cause the development of iron deficiency anemia;
- increasing the likelihood of developing oncological processes in ovarian tissues;
- reproductive function disorders up to the development of secondary infertility.
Based on the above complications of hyperestrogenism, we can draw an unambiguous conclusion: such a deviation requires mandatory treatment. It is especially dangerous if it occurs against the background of pathological processes. Ignoring their signs can sometimes be fraught with dangerous consequences not only for a woman’s health, but also for her life!
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LfXObQmUdOA
When to get tested
The doctor sends the woman to the laboratory to clarify the nature of the pathology if there are negative manifestations:
- the patient complains of significant discomfort during menopause or premenstrual syndrome;
- it is necessary to confirm or refute suspicions of the development of infertility;
- during pregnancy, signs appear indicating a high risk of miscarriage;
- monthly bleeding is irregular, too scanty or heavy;
- based on ultrasound results, the doctor identifies negative changes in the tissues of the placenta;
- a tumor process occurs in the uterus or appendages;
- special tests and densitometry confirm the development of osteoporosis;
- outside the period of menstruation, a woman will observe uterine bleeding or minor spotting;
- Puberty began earlier or later than expected.
The gynecologist sends you to the laboratory for analysis of estradiol after ovulation, in the second phase of the cycle.
Preparing for blood collection
Recommendations:
- Do not use oral contraceptives for two weeks before the test. The exact interval is determined by the gynecologist, taking into account the type of drugs and the woman’s condition;
- sexual intercourse is prohibited for two days before the analysis;
- Alcohol consumption and heavy physical activity are not recommended for 24 hours before the test;
- smoking is allowed 6–7 hours before the test;
- It is advisable to exclude nervous overload not only on the day of blood sampling, but also on the previous day;
- in the evening you need to eat lightly; in the morning, eating and drinking liquids is prohibited;
- tablets can also be taken after collecting venous blood;
- A visit to the laboratory is scheduled in the morning, no later than 11 o’clock.
It is useful to know what the hormone estradiol is and what its role is in the female body in order to timely adjust the concentration of an important regulator. If signs appear indicating an excess or deficiency of the most active estrogen, you should contact an endocrinologist and gynecologist
During the period of therapy and to prevent hormonal fluctuations, it is important to eat right, remember the dangers of alcohol and smoking, move more, monitor the body’s signals, and periodically undergo examinations in a high-level clinic.
A specialist will tell you more useful information about what estradiol is, what the role and importance of the steroid hormone is for the female and male body, and about the norm and reasons for deviations in active estrogen levels in the following video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=dt7k41BndIM
After undergoing IVF
The scientific method of IVF determines the rate of estradiol at the end of embryo transfer; their quantity at different periods of time has different values.
To trace estradiol in the dynamics of development, the study must be carried out before the procedure of implanting the embryo into the uterus, however, if the woman was prescribed a course of similar therapeutic agents, then the results obtained will not be of particular significance.
This is interesting: What vitamins should you take after a stroke?
After embryo transfer, estradiol needs constant monitoring; the timing of control studies is prescribed by a specialist, a reproductologist. Together with this indicator, an estrogen analysis must be carried out.
Constant monitoring can promptly show the slightest deviations and adjust further procedures.
Estradiol has the ability to:
- improve metabolic processes in the body;
- ensure the activity of the entire fetoplacental complex in the right direction;
- forms the skeletal system of the fetus;
- increases blood flow to provide the embryo with the necessary amount of nutrients.
It is this estrogen that promotes the growth of uterine tissue and its good stretching as the fetus grows.
Estradiol and progesterone levels after embryo transfer are normal for the first intervention from 75 to 225 units. If everything went well, then estradiol values after embryo transfer will normally increase systemically until the moment of birth.
How does estradiol change during pregnancy?
A very high concentration of the hormone in the blood is observed during pregnancy, but after childbirth the level most often decreases, so treatment is not required.
The importance of estradiol during pregnancy is also great. The hormone is “responsible” for:
- fixation and retention of the placenta;
- improved blood circulation in the pelvic area;
- nutrition of the fetus through the placenta;
- strengthening the pelvic bones;
- preparing the mammary glands for breastfeeding.
Reasons for the decrease in estradiol
- Very low body weight
- Severe stress
- Menopausal syndrome
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Ovarian wasting syndrome and resistant ovarian syndrome
- Hypopituitarism
- Genetic disorders
- Taking medications
Very low body weight
Sudden weight loss (more often with strict diets) affects all organs and systems. The brain is no exception. The pituitary gland stops secreting the necessary gonadotropins, which in turn reduces the production of sex steroids in the ovaries. Estradiol also decreases due to a decrease in the fat layer, because a small amount of it is synthesized in it. As a result, menstruation stops and health worsens. For this effect, it is enough to suddenly lose 10-15% of adipose tissue (or 5-18% of body weight).
There is only one treatment for this condition - returning to the original weight. Sometimes this requires the help of a nutritionist or even a psychotherapist (if anorexia nervosa develops).
Severe stress
Many people know that in difficult times (during war, for example), the birth rate sharply decreases. This is due, among other things, to hormonal imbalances in women: the ovaries stop secreting estrogens, menstruation disappears, and the ability to conceive decreases. Treatment in such cases is not required; after normalization of the psychological state, the ovaries begin to function normally.
Menopausal syndrome
The period of decline of a woman’s reproductive function is called menopause. It begins at the age of 45-55 years and is inevitable. During menopause, the ovaries become smaller, lose hormone receptors, and as a result, the synthesis of all sex steroids, including estrogens, decreases.
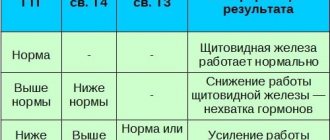
| Symptoms and consequences of menopause | Tests for menopause: | Treatment |
| estradiol is reduced, FSH is increased. | In some cases, with the onset of menopause, a woman’s quality of life sharply decreases. Frequent bone fractures, progressive atherosclerosis, sexual dysfunction are direct indications for estrogen replacement therapy. The same applies to early menopause (before 45 years). |
Hyperprolactinemia
The pituitary hormone prolactin inhibits the production of sex hormones, so its excess affects a woman’s reproductive health. A common cause of this condition is a tumor of the pituitary gland - prolactinoma. As it grows, characteristic symptoms appear:
- galactorrhea (leakage of breast milk outside of pregnancy and lactation)
- interruptions in the menstrual cycle
- headache
- sometimes - hirsutism (appearance of facial hair, acne)
- sometimes – infertility
The above symptoms, combined with increased levels of prolactin and decreased levels of estrogen, are a reason to examine the pituitary gland. If a tumor is detected on CT or MRI, appropriate treatment is prescribed depending on the desire to become pregnant (bromocriptine or surgery).
Ovarian dysfunction
Resistance and exhaustion syndromes (RSS, SES) are one of the reasons for the absence of menstruation and a reduced amount of sex hormones. In SOC, the ovaries are developed normally, they have follicles, but they do not respond to the hormonal influences of the brain. The reasons for this are unknown. Birth defects, autoimmune diseases, and radiation to the pelvic area are thought to play a role. The result is a gradual cessation of menstruation, infertility in the absence of menopause symptoms. The amount of estradiol is significantly reduced.
SIA is a similar condition. But in this case, the follicles are few or absent, and in addition to menstrual dysfunction, hot flashes and other signs of menopause are added. Both of these syndromes develop before the age of 35-38, presenting a major problem. Only unpleasant symptoms can be treated with medication, while infertility can be treated using a donor egg.
Hypopituitarism
Partial or complete loss of pituitary function is called hypopituitarism. This happens for various reasons. Most often, this part of the brain is affected by tumors, infections, and radiation exposure. In women, a special condition is identified - Sheen's syndrome, which occurs after childbirth. This occurs with massive bleeding and a drop in blood pressure, as a result of which the pituitary gland is subject to ischemia (decreased blood flow), which leads to its death.
Complete loss of pituitary function leads to severe symptoms: exhaustion, weakness, bone damage, impaired consciousness and coma. If the syndrome is partial, then individual organs may suffer, including the gonads. The amount of all hormones decreases: estradiol, progestins, androgens. Menstruation stops, mammary glands become smaller, pubic and armpit hair falls out. This condition is diagnosed by symptoms and decreased levels of pituitary hormones. Treatment consists of replacement therapy. If it is chosen correctly, then the prognosis is favorable.
Genetic disorders
A healthy woman has a chromosome set of 46XX, which determines the structure of her genital organs, the ability to bear a child and anatomical features. Sometimes chromosomes group incorrectly, causing various syndromes.
- Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome
In the classic form of the syndrome, the woman’s karyotype is 45X. In such cases, the diagnosis is made in the maternity hospital, as there are characteristic external signs (swelling of the hands and feet, pterygoid folds of the neck). Later, girls have short stature, abnormal structure of the ears and palate, and underdevelopment of the genital organs.
If some of the body's cells have a karyotype of 45X, and some have a normal set of 46XX, then such an erased syndrome often goes unnoticed until adolescence. In this case, the first and only symptom will be the absence of menstruation on time (by the age of 16). The tests will show an increase in FSH (10 times or more) and an extremely low value of estradiol. External signs are somewhat erased: there is underdevelopment of the genital organs and mammary glands. The only treatment for these girls is estrogen replacement therapy. It allows you to make your figure more feminine, cause menstrual-like cyclic bleeding and improve your quality of life.
Taking medications
There are quite a few medications that reduce hormone levels. The main ones are chemotherapy drugs, cimetidine, danazol, dexamethasone, nandrolone, some COCs, mifepristone, pravastatin.
How to bring estradiol levels back to normal
There are only two ways to do this - medication and “natural”. Treatment with medications is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor after studying the results of the analysis and diagnosis of the disease
What is important to know:. Treatment of diseases associated with disturbances in the balance of estradiol is carried out by a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
The treatment of diseases associated with disturbances in the balance of estradiol is carried out by a gynecologist-endocrinologist.
During menopause, treatment is slightly different. In this case, the patient is prescribed drugs based on estradiol, the course of treatment lasts up to three months and is carried out according to the same scheme as when taking OK.
In some cases, estrogen-based drugs may be prescribed. They are available in different forms from ointments and suppositories to tablets. The choice of the form of the drug is at the discretion of the attending physician.
If the ovaries have been removed, medications are prescribed to regulate hormonal levels, in particular the content of estrogens and gestagens.
Reasons for testing for estradiol
In case of delayed sexual development or low estrogen concentrations, a course of estradiol is required, lasting 6 months. The drug is taken for three weeks in a row, then a week break is taken and everything is repeated again.
Surgical intervention is required in extreme cases, when diagnostics showed the presence of oncology. If the deviation from the norm is small and is not caused by specific diseases, you can restore the balance by changing your habits and diet:
- Eat more foods high in phytoestrogens. These are all legumes, nuts, seeds, milk and meat.
- You should not indulge in strict diets or exclude fats and carbohydrates from your diet. This will not only be of no benefit, but will also seriously ruin your health.
- Active sexual life provokes the production of estradiol.
- Sports and moderate physical activity also help increase the amount of estradiol in the blood.
Preparations with Estradiol
If, on the contrary, there is a need for a slight decrease in estradiol levels, you should reconsider your diet and household habits. Quit cigarettes and alcohol, and if necessary, lose weight. It would be a good idea to check the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and, if there are problems, eliminate them.
So, estradiol is a hormone, the norm of which in women regularly changes not only depending on age, but also the menstrual cycle and pregnancy
Maintaining a normal level of this hormone is very important; any significant deviations from the norm can lead to health problems or be symptoms of serious diseases, including oncology. For your own peace of mind, it is recommended to regularly take tests for estradiol and be observed by a gynecologist, this will allow you to notice deviations in time and begin treatment
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fmdKom-85nk
The indicator is normal
In an ideal state, the level of estradiol should be equal to the amount of testosterone.
But there are various factors that cause variations in this indicator. These include:
- woman's age;
- presence of pregnancy;
- period of the menstrual cycle.
High estradiol is characteristic of the female body a few days before ovulation. When this period passes, its level decreases significantly.
Increased estradiol is also observed during puberty in a teenage girl.
The amount of hormone can have the following indicators:
- 210–27000 pg/ml – during pregnancy. The upper limit is characteristic precisely at the moment of childbirth;
- 57–222 pg/ml – on the first day of menstruation. This indicator is satisfactory;
- 127–476 pg/ml – on the eve of ovulation. This amount is also normal;
- 77–227 pg/ml – the final phase of the menstrual cycle;
- 19.7–82 pg/ml – time of menopause.
Video on the topic
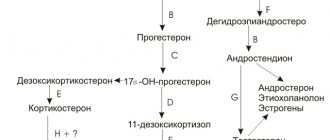
Hormonal changes haunt a woman throughout her life. From puberty to menopause. The participation of the so-called female hormone estradiol in the proper functioning of the reproductive system and its normal functioning is very significant. This estrogenic steroid hormone is produced in the adrenal cortex, placenta and ovaries. It is thanks to him that a woman has an attractive figure, a pleasant voice, velvety skin, healthy hair and other secondary sexual characteristics designed to make a woman truly beautiful and healthy.
Normal levels of estradiol make a woman attractive, healthy, and ready for pregnancy and childbirth.
It also regulates processes associated with conception, metabolism, cholesterol reduction, etc. With a low concentration of estradiol in the body, there is a high probability of failures during pregnancy and lactation, as well as other serious consequences. What a woman can and should do if estradiol is low is described in detail and shown below.
Question Low estradiol levels
The site provides reference information for informational purposes only. Diagnosis and treatment of diseases must be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. All drugs have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required!
Marina asks:
October 29 15:29, 2012
Good afternoon. I am 35 years old. My current chronic diseases are chronic appendicitis and chronic cystitis. The gynecologist diagnosed the first 5 weeks of pregnancy. She sent me to get tested for hormones. As a result: estradiol - 391.70 pg/ml, progesterone - 49.40 nmol/l, beta-hCG - 41094.2 IU/l. I am concerned about the concentration of estradiol, it only corresponds to the norm for 3-4 weeks. Is my concern justified? Is this level of estradiol dangerous for a 5-week pregnancy?
Medical College www.tiensmed.ru replies: October 30 00:33, 2012
For the first trimester of pregnancy, estradiol levels should range from 215 to 4300 pg/ml. Your indicator is completely within these limits. There should be no cause for concern, especially if the ultrasound results show no pathological changes. You can read more about pregnancy, the development of the fetus in each week of pregnancy, and the changes occurring in the body of a pregnant woman in our medical information series: Pregnancy Calendar.
Find out more on this topic:
- Medicines during pregnancy. What is possible and what is not?
- Medicines during pregnancy. Features of application
- Doppler testing during pregnancy is a study of blood flow and blood vessels of the fetus, placenta, uterus and uterine arteries. Normal indicators by week, interpretation of results
- Choosing sex during IVF: so that the stork doesn’t make a mistake
- Gynecologist (antenatal clinic). How is the examination carried out? Diagnosis and treatment
- Gynecologist. What kind of doctor is this and what does he treat? When should you contact an antenatal clinic? The role of the gynecologist in family planning
- Anemia during pregnancy - diagnosis, treatment and prevention
- Anemia during pregnancy. Types, causes, symptoms and signs
New question
Search questions and answers
Find the answer using the question keywords
Our service operates during the day, during business hours. But our capabilities allow us to efficiently process only a limited number of your applications. Please use the search for answers (The database contains more than 60,000 answers). Many questions are already answered.
Similar questions
Pregnancy
- Imudon and pregnancy?
- pregnancy and chickenpox?
- pregnancy?
- Decoding the chlomydia test?
- hepatitis during pregnancy?
- Please help me decipher the analysis on TORCH.?
- Pregnancy of a minor.?
- deciphering a blood test for infections during pregnancy?
Gynecologist
- Itching inside the vagina?
- When should the discharge stop?
- question?
- weakness and anxiety?
- CTG decoding?
- Are leukocytes in the smear elevated?
- is it possible to have an abortion?
- pregnancy?!!?
ATTENTION!
The information posted on our website is for reference or popular information only and is provided only to medical professionals for discussion. Prescription of medications should be carried out only by a qualified specialist, based on the medical history and diagnostic results.
Certificate of registration of mass media IA No. FS 77 - 75685 dated May 23, 2019, issued by the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Communications. Founder and editor-in-chief: R. G. Sorokachuk Editorial office email address Editorial office phone number