To be highly effective, first aid for hepatic colic should be carried out as quickly as possible after alarming symptoms are detected in the victim.
Doctors say that colic itself is not as bad as what it indicates. Such deviations are characteristic of chronic severe pathologies of the gallbladder. It is extremely important here not to limit ourselves only to leveling out the dangerous signs of the disease.
To qualitatively improve your health, you need to undergo a detailed examination using ultrasound. This will allow you to understand in detail the cause of the pathology, as well as assess the extent and extent of the lesion.
Causes of hepatic colic in women
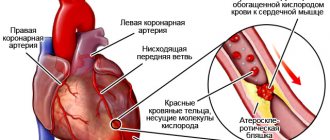
Painful sensations in the right hypochondrium can be caused by diseases of the gallbladder. Due to disruption of the functioning of the organ, stones and mucus plugs can form in it, which can move and block the ducts of the bladder, which entails stagnation of bile and an increase in the pressure of the organ from the inside. This provokes the appearance of severe, unbearable pain.
Symptoms may also occur due to the following reasons:
- The development of tumors and inflammatory processes (inside or outside the organ) can lead to compression of the bile ducts.
- Their patency can be impaired by cholesterol plaques and blood clots.
- Changes in the tone and motor ability of the ducts can lead to their bending.
The following factors can lead to changes in the gallbladder and diseases:
- fatty and spicy foods with lots of spices;
- consumption of low-quality alcohol-containing products in large doses;
- frequent stressful situations and depressed state of the nervous system;
- disruption of the digestive tract;
- abnormalities in the structure of the gallbladder, characterized by nonspecific narrowing of the ducts (in this case, the disease is observed in a woman from early childhood);
- complication after infection in the abdominal cavity;
- lifting heavy objects or staying in a bent position for long periods of time;
- pregnancy with a short interval between them;
- frequent vibrations (may be associated with work), this provokes the displacement of stones;
- liver diseases;
- strict diets;
- being overweight;
- the presence of parasites in the liver or gall bladder. A large number of them can clog the patency of the ducts.
If one of your immediate relatives has gallbladder disease accompanied by hepatic colic, then the woman will have a predisposition to the disease.
How to recognize the symptoms?
It is impossible not to detect biliary colic syndrome in women and the stronger sex. If there is a violation, a lumbago is felt in the right hypochondrium, which sometimes does not allow the person to move. The spasm is sudden and intense, lasting several minutes or up to 6 hours. Mostly with hepatic colic, pain attacks occur at night or in the morning. The pain is localized in the liver area, resulting in difficulty in inhaling. In addition to pain, the patient is concerned about other signs:
Toxic poisoning provokes a constant feeling of nausea.
- severe nausea, which is rarely relieved by medications and provokes a gag reflex;
- pallor of the epidermis, especially in the facial area;
- yellowing of the skin, which is associated with problematic bile output;
- appearance of cold sweat;
- swelling in the abdominal cavity;
- increased muscle tone, which is especially acutely felt when palpating organs;
- change in color of stool and urine.
If colic in the liver area is accompanied by an inflammatory reaction, then the person’s body temperature rises, chills and fever occur.
Symptoms
Hepatic colic (symptoms in women most often occur during sleep or complete rest) sometimes appear after intense physical activity. Before the main symptoms appear, there is discomfort in the right side, and a feeling of bitterness.
Then unbearable pain occurs, which is cramping, sharp and bursting in nature. They do not decrease in any position. They can be localized in the right side, in the stomach area, and also extend to the shoulder, neck, and shoulder blades. Sometimes the pain may involve the heart area.
The painful symptom may be accompanied by bloating with nausea and vomit mixed with bile. After emptying the stomach of food, there is no feeling of relief. If the gallbladder is severely damaged, vomiting may be constant.
Additionally, the number of heart contractions increases (pressure remains normal), the skin becomes pale and may have a yellow tint. A slight increase in temperature is possible. Change in color of stool to a lighter color, and urine, on the contrary, becomes darker.
A woman can stay in this state from 10 minutes to 8 hours. Depends on what triggered the attack. If the pain does not subside for more than a day, it is necessary to call emergency help; emergency surgery may be required.
Prevention
Prevention involves:
- giving up bad eating habits. The diet should be balanced. Ideally, the diet presented above should be followed constantly;
- cessation of smoking, alcohol abuse;
- maintaining an optimal physical activity regime; Moderate physical activity has never harmed anyone. Obesity is the enemy of the liver and gallbladder.
- It is advisable to avoid stressful situations;
- If you have liver and gallbladder diseases, you need to treat them promptly.
Urgent Care. How to quickly stop an attack at home
When symptoms appear for the first time, you should immediately call emergency help. Do not take painkillers or apply heat to your side. Because of the pills, doctors will not be able to fully clarify the picture of the disease. And a heating pad can cause a worsening of the condition if the attack was caused by inflammation or infection.
When a woman knows exactly what caused the pain. Then it is necessary to give injections that relieve spasms and inflammation. Can be used in combination with tablet medications. Medicines are prescribed by a therapist or gastroenterologist. The first available remedies can cause the condition to worsen.
Causes
The pathogenesis of cholelithiasis is directly related to the characteristics of the chemical composition of bile. This is a colloidal solution, which is predominantly composed of bile acids, which act as a natural stabilizer.
When for some reason the balance of bile components is disturbed, the stabilizer ceases to perform its functions and prevent the formation of stones. The bile begins to thicken, forming stones of various types: combined, based on pigments, lime or cholesterol.
A stone formed in the gallbladder can block the ducts and prevent the outflow of bile, which is accompanied by hepatic colic. The attack is also associated with additional traumatization of the mucous walls of the organ by the sharp edges of the stones.
In some cases, biliary colic is not associated with cholelithiasis, but develops on a different pathogenetic basis.
For what reasons does pain occur:
- Impaired tone of the smooth muscles of the gallbladder , the occurrence of periodic spasms and inflammatory processes. This functional disorder is known as biliary dyskinesia.
- Colic can appear against the background of complicated typhoid fever , which affects the intestinal lymphatic system and abdominal organs.
- Giardiasis is an infection caused by single-celled Giardia parasites. They are localized primarily in the duodenum, but can also penetrate the gallbladder. Under the influence of Giardia toxins, the walls of the internal organ are affected, causing spastic pain. Giardiasis causes biliary colic in 90% of children.
- Anomalies of the anatomy of the hepatobiliary system - congenital narrowing of the ducts, functional disorders of the outflow of bile can cause colic even in the absence of stones.
Why is cholelithiasis or dyskinesia accompanied by frequent hepatic colic in some people, while in others it occurs extremely rarely? The reasons lie in concomitant factors that increase the risk of an attack. These include:
- Age characteristics - the older the patient, the more often colic appears.
- Gender – hepatic colic occurs in women several times more often than in men (women who have given birth especially often suffer from attacks).
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Problems with body weight - obesity, a tendency to be overweight, as well as sudden weight loss and fasting increase the likelihood of illness.
- Liver diseases - hepatitis and cirrhosis affect the functioning of the gallbladder and cause its dysfunction.
- Common pathologies – diabetes mellitus, hemolytic anemia – contribute to the rapid formation of stones.
- Hormonal disorders and the use of oral contraceptives negatively affect metabolic processes and the functioning of the hepatobiliary system.
- Tumors - the presence of tumors in neighboring areas leads to compression of the ducts and the occurrence of colic.
- Suppuration in the bladder - the duct may be blocked by clots of pus or dried blood.
- Abuse of junk food and alcohol stimulates the production of bile, which, with a number of additional factors, causes colic.
- Parenteral nutrition through a dropper , when the patient is not able to independently take food by mouth.
Often an attack occurs after increased physical activity, especially in people who are forced to remain in an inclined position for a long time.
Diagnostics
Hepatic colic (symptoms in women are pronounced) require the use of painkillers, as well as a complete diagnosis to prescribe treatment. It is necessary to find out what caused the symptom and what method of treatment the pathology can be treated with.
| Diagnostic method | What is it produced for? | Notes |
| Initial examination and collection of verbal data | The therapist will learn from words when the first symptoms appeared, what preceded it, as well as the duration and characteristics of the pain. With the help of palpation, you can determine an increase in the size of the liver. It is also assessed whether there is yellowness of the skin | If relatives have problems with the gallbladder, this should be discussed during the examination. And also about what measures were taken to eliminate pain. Did the medicine help or not, and for how long? |
| General and biochemical blood test | Using the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, the presence of an inflammatory process in the body is determined. As well as the presence of bile pigments | A blood test does not provide a complete picture of the disease. Inflammation can be detected and is it related to the gallbladder? |
| Urine analysis | Urine may contain bile pigment. What will indicate a malfunction of the organ? | Analysis is not always effective |
| Ultrasound | The condition of the liver and gall bladder is determined. If the latter contains stones, then their location, size and quantity are determined. You can see if there is an inflammatory process, narrowing of the ducts, or tumors. | Ultrasound data is often sufficient to further prescribe treatment. The procedure takes up to 15 minutes and is safe |
| MRI and CT | Most often done before surgery. To more accurately locate stones and determine the condition of the ducts in the gallbladder | During the procedure, the woman must remain motionless, otherwise the results may be distorted. |
| Cholecystography | The procedure is performed using contrast fluid and X-rays. This method allows you to determine the location of the tumor, stones and inflammatory process with the highest accuracy. | For the patient, the procedure is not entirely convenient, since insertion and removal of the fiberscope through the oral cavity causes quite unpleasant sensations |
After collecting all the information, the gastroenterologist can determine whether surgery is required or drug treatment is possible. Medicines and diet therapy are prescribed.
What caused it: reasons
According to ICD-10, hepatic and biliary colic has code R10.4.
Acute pain attacks in the right hypochondrium are associated with the negative impact of many factors. Symptoms of hepatic colic are recorded in men and women for the following reasons:
- problems with the excretion of bile associated with impaired contractile function of the organ;
- formation of stones of various sizes and types in the gallbladder;
- Giardia infection;
- inflammatory reaction in the bile ducts;
- congenital anomalies.
Junk food and an unbalanced diet destroy the organ at the cellular level.
Biliary colic does not occur in all patients for the above reasons. For its appearance, provoking factors are required, which include:
- abnormalities in the liver, in particular, signs of various types of hepatitis;
- problems with excess weight;
- regular fasting or abuse of various diets;
- a sharp decrease in body weight in various pathologies;
- feeding through a catheter due to various surgical interventions;
- abnormalities that cause increased breakdown of red blood cells;
- increased physical stress;
- frequent consumption of junk food, which provokes pain in the liver and gall bladder.
Drugs for hepatic colic
Hepatic colic is always accompanied by severe pain. First of all, it is necessary to relieve the pain symptom and eliminate the cause of its occurrence. After diagnosis, the gastroenterologist prescribes a course of medications:
1. Drugs that help relieve pain:
- ketoprofen;
- metamizole;
- baralgin;
- ketorolac.
2. Remedies for relieving spasms:
- papaverine;
- platiphylline;
- no-shpa;
- mebeverine.
3. Medicines that weaken the body’s sensitivity:
- diphenhydramine;
- morphine
4. Anti-inflammatory drugs:
- voltaren;
- ortofen.
To speed up the removal of bile from the bladder, allochol is prescribed. For severe pain, it is recommended to administer the drug intramuscularly so as not to burden the gallbladder. If drug therapy does not produce results and the pain symptom is not relieved, surgical treatment will be prescribed. Often the gallbladder is removed.
The nature of the pain that occurs
A person who does not have knowledge in the field of medicine, if any exceptionally unpleasant sensations occur in a specific point of the body, can be guided by a few symptomatic manifestations, including the characteristics of the pain syndrome.
So, hepatic colic manifests itself as:
- acute pain;
- localized in the area of the gallbladder (on the right side under the ribs);
- radiating to the area of the right shoulder blade, and sometimes the collarbone, located on the same side.
It is not for nothing that this manifestation is called “colic”, because this is exactly how pain is felt in the case we are interested in: in the form of dagger injections that occur in a specific place, the unpleasant sensations from which spread to the areas we previously indicated.
What causes hepatic colic?
Folk remedies
Hepatic colic can only be treated with medication and under the guidance of a gastroenterologist. When the symptoms are relieved, you can combine medications with the use of traditional recipes.
Among women, the following products are more popular:
- freshly prepared juice from 1 onion with water in a 1:1 ratio. Drink 150 ml (divided into 3 doses) during the day, 25-35 minutes before meals;
- choleretic herbal collection , sold ready-made, prepare according to instructions and add 20-25 ml of holosas syrup to it;
- the infusion from a collection of herbal leaves (rosehip, nettle, celandine) in equal proportions. To prepare, take 40-50 g of the mixture and 400-500 ml of water. Leave for 12 hours. Then boil and consume within 24 hours, in small portions;
- decoction of hay ( grass) and buckthorn bark, 40-50 g required. Boil in 0.45-0.5 liters of water for up to 30 minutes. Next, add 30-50 g of raisins and cook for another 10 minutes. Pour a bubble of holosas into the finished and cooled drink. Before use, dilute 20 ml of decoction with 40-50 ml of water. Drink before eating;
- a drink made from Borjomi mineral water (the gas must be released) with the addition of 10-12 g of sorbitol and xylitol, can be consumed once a month. Drink on an empty stomach in the morning.
Folk remedies are often used to prevent the development of the disease. If they are used during treatment, then the dose and course should first be obtained from a gastroenterologist. Since even herbal decoctions can have a cumulative effect and cause harm to the body over time.
Main signs of colic
Before rushing to help a victim of acute pain syndrome, you first need to make sure that the person has become a victim of an attack of hepatic colic. This will allow for a more productive set of measures.
But, regardless of the severity of the disease, as well as the surrounding organs and tissues involved, the first thing you will need to do is call an ambulance.
The following pronounced symptoms will allow you to recognize the deviation:
- acute pain that is intense;
- nausea, which becomes impossible to tolerate after just a couple of minutes;
- repeated vomiting, which does not bring adequate relief.
Vomiting occurs due to incessant nausea, which becomes impossible to neutralize using traditional methods.
Often the attack begins at night, when the patient remains motionless for a long time. At the beginning of the process, the pain is localized more around the right hypochondrium. And after a few minutes it begins to radiate to the limbs and back.
With the most severe form of damage, even pain in the lower abdomen is possible. Sometimes the pain begins to increase with each breath or even after taking a sitting position.
Separately, doctors in the list of traditional symptoms highlight pallor of the skin, which is explained by general soreness. Against the background of all of the above, profuse sweating is quite common.
Some victims complain of yellowing of the skin after becoming unnaturally pale. The reason lies in the fact that bile ceases to be discharged in normal volumes, accumulating in the wrong place.
Also typical manifestations of colic are:
- bloating;
- pain during palpation of the abdomen;
- muscle strain;
- increased body temperature;
- white feces;
- dark shade of urine.
The average statistical time frame for the duration of a dangerous condition ranges from several minutes to two to three hours. But even if the duration of the attack is insignificant, you should not postpone visiting a specialist or calling an ambulance, since there is a high probability of the clinical picture repeating during the day.
Other methods of pain relief
To eliminate the pain syndrome, but only after examination by a therapist and finding out the cause of the pain, it is allowed, in case of severe pain, to apply heat (a heating pad with warm water) to the liver area. But if there is a fever, the procedure is contraindicated.
An attack can also be relieved with massage. Only an experienced massage therapist can perform the procedure. It is prohibited to do it yourself, as it can disrupt the patency of the ducts. When carried out correctly, patency improves and the attack of pain subsides.
If medications, massages and traditional medicine do not bring changes, then the gastroenterologist prescribes surgery. When the cause of pain is stones and they are large, the gallbladder is removed. When the formations are of medium size, they are surgically crushed to the state of sand (the ducts are first expanded) and they are removed from the organ.
Medicines help relieve pain when it occurs in acute form. If the attacks are mild, then you can relieve the pain with folk recipes. To prevent the onset of symptoms, the gastroenterologist prescribes strict adherence to the diet until complete recovery. When followed properly, pain rarely occurs.
First aid
The first point of the medical care plan should be to call doctors. Next, you will have to try to calm the victim. But you should not use medications for this, as they can distort the clinical picture during subsequent diagnosis. To slightly reduce pain, the person is placed on a flat surface, turning on his right side.
Doctors conduct an initial examination by interviewing the patient or the people around him. This is necessary for drawing up a subsequent detailed treatment program. To reduce discomfort, experts use antispasmodic drugs. To increase effectiveness, injectable medications are used as a basis. They are administered intramuscularly.
You should not try to inject a patient yourself, as there remains a high risk of developing an allergic reaction to the components of the medicine. The ambulance team has in stock funds aimed at neutralizing the onset of anaphylactic shock in case of urgent need.
After providing assistance on the spot, doctors will hospitalize the victim if the severity of the disease is confirmed. In a hospital setting, specialists will conduct detailed diagnostics using ultrasound and other modern instrumental techniques.
Diet
Hepatic colic (symptoms in women more often occur due to poor diet) can be reduced by following a diet prescribed by a doctor. On the first day of the attack, eating is not advisable. Otherwise, the products may cause repeated pain symptoms. Within a day, the digestive tract will have time to recover. Next, it is necessary to follow the treatment menu.
A woman should drink at least 1.5 liters of clean water per day. The amount of salt consumed in dishes should not exceed more than 10 g per day. The menu should contain products that provide a complete supply of all necessary nutrients.
It is also necessary to monitor the amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates consumed. If you are overweight, a low-calorie diet may be prescribed. A large number of fat cells can trigger the recurrence of attacks.
Food should be divided into small portions and kept warm.
If you have liver colic, you should not eat fried, smoked or spicy foods.
If you have hepatic colic, eating fried foods is strictly prohibited!
Vegetables, fruits and meat products can be boiled, baked or steamed. In the first week, it is better to eat liquid foods so as not to overload the digestive tract and additionally use enzymes (but only if they are prescribed by a gastroenterologist). The woman can create the menu herself. During the treatment period, hunger strikes and weight loss diets are prohibited, without consulting a specialist.
Permitted and prohibited products
When drawing up a weekly menu, the patient needs to know which foods are allowed to be included in the diet and which are prohibited. There are also conditionally approved products. That is, they can be consumed in limited quantities and with special preparation.
Products table:
| Allowed | Prohibited | Conditionally permitted |
| Compotes and jelly are cooked with xylitol or sorbitol. Tea can be sweetened only with the same sweeteners | Margarine, fat, lard | Vegetable and animal oils |
| Rye bread or yesterday's white bread | White cabbage, turnip, sorrel, mushrooms | Vegetables only baked and boiled |
| Boiled meat, fish and liver (low-fat) | Citrus fruits, pomegranate, grapes | Apples, bananas, berries |
| Vegetable and chicken broths | Confectionery, jam, chocolate | Honey |
| Porridge, crumbly. Cook with water or low-fat milk | Strong tea, juices, coffee | Juices, only diluted |
| Cereal soups | Fatty meat and fish, sausages | |
| Biscuits and oatmeal cookies | Use spices and pepper | |
| Steamed omelet eggs | Alcohol products | |
| Low fat dairy products |
A more complete list of products should be checked with a gastroenterologist. Since if there are chronic diseases of the digestive tract or other diseases, the list of permitted products will be reduced.
Etiology
Hepatic colic can be triggered by the following etiological factors:
- biliary dyskinesia;
- cholelithiasis;
- giardiasis;
- cholangitis;
- congenital pathologies of the biliary tract.
Predisposing factors for the development of hepatic colic include:
- liver pathologies, including hepatitis of a viral, toxic, alcoholic nature;
- obesity;
- systematic abuse of fatty, “heavy” foods, alcoholic beverages;
- diabetes;
- starvation;
- sudden weight loss due to a strict diet or concomitant diseases;
- parenteral nutrition;
- diseases that lead to massive breakdown of red blood cells;
- excessive physical activity.
Different localization of stones in cholelithiasis
Very rarely, but still occurs, an attack of hepatic colic for no apparent reason.
Complications
Hepatic colic (symptoms in women, this is the main sign to seek medical help) with improper or untimely treatment is dangerous for the development of complications. Treatment, which will take even longer and may lead to the development of chronic diseases.
Common pathologies due to hepatic colic:
- Intestinal obstruction . It may occur due to the release of a stone from the gallbladder into the intestines.
- Mechanical jaundice. It manifests itself as yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. The urine becomes dark and the stool becomes discolored. Caused due to a malfunction of the liver and gallbladder. Accompanied by severe headaches and itching.
- Acute pancreatitis. The end of the gallbladder is intertwined with the head of the pancreas. Inflammation of the former can compress the ducts of the gland, causing increased pressure inside the organ. Bile reflux is also possible. With this complication, death is possible.
- Perforation of the gallbladder. Due to large stones, blood vessels can be compressed, which leads to tissue necrosis. As a result, a gap is formed in the organ, from which bile is released into the abdominal cavity. This can cause suppuration and necrosis of organ tissue.
- Postoperative pain if there was surgery with organ removal. Additionally, this is accompanied by disruption of the digestive tract.
- Cholangitis. This is an inflammatory process that develops due to stagnation of bile in the organ and infection.
- Cholecystitis. This is an inflammation of the bladder walls. The development of the disease is caused by the same factors as cholangitis.
- Purulent cholecystitis. Develops in advanced cholecystitis. Due to long-term blockage of the biliary tract by a stone and the presence of infection, suppuration of the organ begins to develop. Quite a dangerous condition that can result in death.
Treatment
In addition to the main course of treatment, which is prescribed by the doctor after the examination, at home the patient needs to provide first aid for biliary colic to prevent the development of pain shock. Based on this, it becomes clear that the main goal is to relieve pain with the help of antispasmodics or painkillers.
If there is no doubt that these are attacks of biliary colic, the patient can apply a heating pad to the area of the right hypochondrium. If the clinical picture of the attack is ambiguous, it is strictly forbidden to do this, since in some diseases, heating can only do harm.
Patients with this diagnosis must be hospitalized in the surgical department, since in addition to special treatment they require nursing care.
If the cause of such an attack is cholelithiasis, then treatment, in most cases surgical, involves surgical removal of stones from the gallbladder.
The medicinal stage of treatment may include the following drugs:
- Drotaverine;
- Papaverine;
- Spazgan;
- Tramadol;
- Odeston.
The dosage and method of use are strictly prescribed by the attending physician; such drugs cannot be used without permission.
In addition to drug treatment, the patient is prescribed a diet. The specific dietary table is determined individually, but in any case you will need to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Fatty, spicy foods are excluded from the diet. Also prohibited are sour, salty, fried foods;
- the patient’s diet should be light, but at the same time sufficiently high in calories;
- consistency of dishes – liquid, puree, grated;
- food should be consumed only warm;
- The patient’s meals should be frequent, but in small portions, with a time interval of 2-3 hours;
- drinking plenty of fluids. Herbal infusions, weak green tea, and still mineral water are recommended.
The pharmacological group of drugs and the regimen for taking them is determined only by the doctor.
The prognosis will depend on the primary source of the attack of hepatic colic. However, in any case, the sooner treatment is started, the greater the chances of recovery; in addition, the risk of complications is minimized.
Forecast
If you consult a gastroenterologist in a timely manner, take medications and follow a diet, the treatment prognosis is positive. It is important that if the treatment does not bring changes in the condition, you should not adjust the treatment yourself (change medications or increase the dose of medications); all adjustments can only be made by a specialist.
Liver colic, according to statistics of the most common diseases, is in 3rd place. The symptoms of the disease are pronounced; when they first appear, you should immediately go to the hospital; self-treatment is prohibited. In women, the disease can also be provoked by hormonal imbalances caused by pregnancy or taking hormonal medications.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Mila Friedan
How to relieve hepatic colic at home: first aid
If pain occurs, you need to call an ambulance at home. Before the arrival of specialists, the patient is provided with pre-medical care. To alleviate the condition, you should:
- Lay the patient down with a pillow under his head.
- Apply a heating pad or warm compress to your right side.
- Open the windows in the room for fresh air.
- Give painkillers and antiemetics.
Such emergency care is relevant if the cause of the pain is beyond doubt. If the attack is provoked not by colic, but by acute cholecystitis or other inflammatory diseases, you cannot use a heating pad or compresses. To relieve spasms and pain in the side, the following are used:
- Diclofenac is a non-narcotic analgesic that is administered intramuscularly, 1 ampoule no more than 2 times a day;
- Ketorol is an anesthetic solution for intramuscular injection, which is administered in a dosage of 10-30 mg every 8 hours;
- No-Spa is an antispasmodic for relieving spasms in the bladder and hepatic ducts, which is administered 2-4 ml at a time.
If the hepatic or cystic duct is obstructed, the patient experiences severe nausea or vomiting. To eliminate the symptoms, antiemetic drugs are given - Ondansetron, Gravol.
Features and symptoms of biliary colic
- The attack occurs suddenly, more often after fatty, fried, baked, smoked, spicy foods and alcohol. But it may occur due to sudden physical exertion, severe stress, prolonged work in an inclined position, the development of infection, or in a woman - due to the onset of menstruation or after childbirth.
- The culmination of the attack occurs at the end of the second hour from the start and lasts up to 6 hours.
- A long attack with a return to the back signals acute cholecystitis.
- Jaundice disappears 2 days after the attack stops.
- Vomit contains bile.
- If the root cause is not addressed, colic returns. But at the remission stage the patient will feel absolutely healthy.
- If colic is caused by giardiasis with impaired motility of the biliary tract, the main symptoms in a child and an adult are mild and are characterized by:
Biliary colic can occur from eating fried or spicy foods, followed by yellowing of the integument.
- disorders of the digestive system in the form of vomiting, belching, intestinal disorders;
- enlarged lymph nodes (more often in children);
- drooling during an attack;
- increased temperature and weakness if there is stagnation of bile;
- jaundice;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- swollen, painful belly
Emergency care for biliary colic, what treatment to use
If there is a suspicion of cholelithiasis or an attack of colic, the patient needs emergency help. Sometimes the process becomes irreversible. What algorithm of actions will help a patient with biliary colic?
Emergency first aid is as follows:
- Free the patient from tight clothing.
- Ensure position by lying on your right side.
- Administer painkillers, for example, Promedol.
- Make sure that vomiting does not start and the patient does not choke. In case of an emetic effect, the use of antispasmodics in tablets is unacceptable.
- You can apply a warm heating pad to the sore spot if it is firmly established that it is biliary colic.
- If a patient has an attack of acute cholecystitis, something cold should be applied to the right side. This will prevent the development of peritonitis.
The use of cold or a heating pad is possible if the diagnosis of the patient’s disease is known; in any case, urgent hospitalization is required. Antispasmodics are one of the options to relieve pain and provide assistance to a patient with cholelithiasis.
The patient may not need to go to a medical facility; an agent should be administered that relaxes the smooth muscles of the biliary tract. The stone blocking the ducts shifts and gradually moves into the intestines. Small stones pass without surgery, although rarely. Doctors do not approve of the use of antispasmodics. This treatment is considered conservative, but it leads to a dead end; the pathology does not go away. Stones are present in the bile outflow and can suddenly block it again, which will lead to severe inflammation or the development of peritonitis.
The only correct treatment option is surgery (cholecystectomy). During the operation, surgeons remove the bladder, and then the bile enters the intestines. After removal of a diseased organ, you should thoroughly take care of nutrition and proper lifestyle. Eating fatty foods, alcohol and excessive exercise will lead to a relapse of the disease. Stones can reappear and cause the release of bile into the blood. This will end in death for the patient.
It is better to prescribe the operation after biliary colic, when the attack has subsided and the patient’s condition has stabilized. Otherwise, this will lead to tragic consequences. For hepatic colic, a course of antibiotics is prescribed to relieve the inflammatory process. If the bile is thick and stagnant, but there are no stones, doctors prescribe choleretic drugs that remove bile from the body.
Biliary colic is a severe complication of gallstone disease and occurs in men and women. This pathology is life-threatening and should not be started. If colic occurs frequently, seek help from a surgeon; removing the gallbladder may be the only solution. If the patient suffers from biliary colic, hepatic colic is also possible, and attention will need to be paid to nutrition. Do not eat fatty and spicy foods, fried and smoked. The main table is meat and steamed vegetables, following a vegetable diet. You should give up alcohol and tobacco.
How does biliary colic manifest in children?
Medical symptoms of gallbladder pathology in the younger group of the population are more pronounced than in adults. The main symptom is pain. The attack often begins after eating junk food or intense exercise.
With dyskinesia, pain appears in the right abdomen and can lead to vomiting. Often, after it stops, the pain disappears. The disease is characterized by:
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth in the morning;
- bowel dysfunction;
- poor tolerance to fried foods.
If the cause of the spasm is parasites, then the following symptoms are observed:
The main symptom of biliary colic in children is pain
- nausea;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- allergic rash;
- belching;
- weak appetite.
After such an attack, you should immediately seek medical help, otherwise pain shock may develop.
Prevention of development
The best way to prevent pain is to lead a healthy lifestyle and visit your doctor promptly for routine examinations. Proper nutrition and a sufficient level of physical activity prevent congestion in the gallbladder and normalize body weight. Non-obese people are less likely to develop hepatobiliary system disorders.
An annual visit to the doctor for an abdominal ultrasound or blood tests allows you to promptly identify disorders in the body. If there are deviations from the norm, the specialist will prescribe therapy to prevent the occurrence of complications in the future.
What is biliary colic
This is a pathological condition manifested by acute and sharp pain in the right hypochondrium. In most cases, pain signals an exacerbation of gallstone disease or any other disorder of the hepatobiliary system.
When stones form in the gallbladder, blockage of the ducts develops over time, which causes biliary colic. With persistent disruption of bile outflow, biliary pain appears, characterized by compression of the gallbladder. If the stones do not extend beyond the organ cavity, then the clinical picture of the disease does not appear.
If stones or sand begin to move along the bile ducts, acute painful attacks of biliary colic occur. In most cases, a bacterial infection is associated. Depending on the location of the stuck stone, dropsy, peritonitis, wall perforation or empyema may appear. When the ducts are completely blocked, cholangitis develops.
Gallbladder colic occurs mainly at night or in the evening. The pain is sharp, variable or constant. If a bacterial infection occurs, the patient experiences a persistent increase in body temperature.
Causes
The root cause in most cases is cholelithiasis. Exacerbation may occur in the following situations:
- Wrong lifestyle. With frequent abuse of alcohol or alcoholic beverages, increased contraction of the gallbladder occurs, which promotes the movement of already formed stones in the organ cavity to the bile ducts.
- Increased physical activity. Lifting heavy objects, which is more important for men.
- Frequent stress, neuroses, or mental exhaustion can provoke biliary colic.
- Constant overeating, long breaks in meals, over 6 hours.
- Exacerbation of non-calculous cholecystitis.
- Impaired functionality of the sphincter of Oddi.
- Gastric or duodenal ulcer, acute appendicitis.
- Crohn's disease.
According to statistics, the first symptoms of biliary (renal) colic occur when the stones formed 5–10 years ago. In some cases, the first attack may occur after 20 years.
Symptoms
The symptoms of hepatic colic may unknowingly be confused with other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Inexperienced patients confuse malaise with severe poisoning. In some cases, biliary colic resembles a stomach ulcer or an attack of acute cholecystitis.
It is important to pay attention to the localization of the pain syndrome. Pain in the right hypochondrium in most cases indicates problems of the hepatobiliary system.
Are common
Features of biliary colic are as follows:
- The attack begins with a slight tingling sensation in the liver area. Then the pain increases sharply. The typical time of manifestation is during sleep, at night. Spasms can radiate to the shoulder blade, neck and collarbone on the right side. Sometimes the attack resembles signs of angina pectoris.
- Then chills, fever, vomiting, nausea and increased sweating appear.
- Loose stools and headaches may occur.
- Biliary colic affects disorders of the cardiovascular system - the patient experiences tachycardia, increased blood pressure, and increased heart rate.
- The skin and face turns pale, sweat appears.
- The stomach is bloated.
- There is a bitter taste in the mouth.
- When a gallstone completely blocks the flow of bile, jaundice occurs, manifested by yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes.
The pain increases every hour, it becomes difficult to breathe, and when you try to change position or take a sharp breath, it becomes even worse. It is necessary to call an ambulance so that the patient is hospitalized.
How does it manifest in children?
In a child, biliary colic is even more severe than in an adult. A spasm can occur against the background of increased physical activity or after eating fatty foods.
Symptoms of exacerbation in children:
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- nausea;
- incessant vomiting mixed with bile;
- persistent digestive disorders - belching, heartburn and diarrhea;
- fever;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- severe pain in the gallbladder area.
The child needs to be hospitalized urgently.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, this condition is dangerous and severe. Intense pain occurs in the epigastric region, which radiates to the right shoulder, shoulder blade or neck. The remaining signs are the same as in an adult. The situation is dangerous because during pregnancy such attacks are less tolerated and the risk of miscarriage also increases. Biliary colic in the abdomen can provoke uterine hypertonicity, which can lead to spontaneous abortion in women.
How to relieve colic in the liver
Emergency care for biliary colic is aimed at relieving pain in the liver. To relieve colic, folk remedies recommend drinking 1.5 glasses of carrot juice after meals. Taking an infusion of chamomile or immortelle has a positive effect. 15 minutes before meals, you can consume a mixture of grated onion and honey.
For hepatic colic, the patient is injected subcutaneously with No-Shpa solution
In case of hepatic colic, emergency care will be most competently provided by doctors. For this purpose, antispastic and analgesic agents are used. So, solutions of metacin, atropine sulfate, No-Shpa, and papaverine hydrochloride are injected subcutaneously into the patient. Eufillin is used for intramuscular and intravenous injections. For intravenous detoxification therapy, a 5% glucose solution or an isotonic sodium chloride solution is used.
Pathogenesis and causes of biliary colic
Biliary colic is a consequence of blockage of the common bile duct by a stone. Gallstone disease proceeds latently for years, not making itself felt until the first painful attack.
Pain syndrome is formed due to stretching of the walls of the canals and an increase in pressure in them.
Pain of an unbearable nature is observed in men and women against the background of biliary colic from several to six hours. According to statistics, the disease is most often diagnosed in women.
Etiological factors of pain attack
The main cause of pain is the movement of stones through the gallbladder and canals. A more pronounced syndrome develops if the calculus ends up in the cervical area of the organ.
The upper zones of the gallbladder are stretched to the maximum, peristalsis increases, and the flow of bile slows down or stops completely.
The following factors can lead to the development of biliary colic:
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages and fatty foods provoke contraction of the bladder and promote the movement of hard stones into the ductal system.
- Excessive physical activity, heavy lifting.
- Stress, nervous tension, neuroses.
- Constant overeating, prolonged fasting.
- Acute form of acalculous cholecystitis.
- Malfunction of the sphincter of Oddi.
- Ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, acute appendicitis.
- Crohn's disease.
Biliary colic appears 5-10 years after the formation of stones. In some situations, pain syndrome occurs after 15-20 years.
Prevention and diet
An excellent preventive measure is moderate physical activity - walking, morning exercises, cycling, swimming.
Spasms can be prevented by consuming medications, foods or herbs with a choleretic function - corn leaves, birch leaves, agrimony . Prophylactic choleretic substances should be used on an empty stomach. After this, it is recommended to lie down on your right side for a while, applying a warm heating pad to it. But before starting such prophylaxis, it is necessary to consult with a specialist, since such prophylaxis is not suitable for people who have been diagnosed with calcified stones.
To reduce the risk of pathology, dietary ration No. 5 is prescribed. This diet is based on the most optimal composition of nutrients. Biliary colic is not combined with the following products:
- Fried foods.
- Cocoa.
- Coffee.
- Sorrel.
- Tea.
- Spinach.
- Sour vegetables.
It is recommended to consume the following products:
If you have biliary colic, it is good to eat grapefruits.
- Lemons.
- Rhubarb.
- Olives.
- Grapefruits.
- Coriander.
- Olive oil.
Meals are divided into small portions, but it is recommended to eat more often - 5-6 times a day. The temperature of the food should be at room temperature. Deviations from it are not allowed. The diet and products are prescribed by a doctor.
A very important point is the timely treatment of gallstone disease, in which it is necessary to remove stones from the ducts.
Avoiding stressful situations, maintaining a healthy lifestyle , maintaining a healthy diet and getting rid of bad habits will help prevent the risk.
The combination of preventive procedures along with a well-prescribed therapeutic course helps to minimize the risk of spasm formation.
A person must understand that bile spasms are a sign of serious disorders in the body, which without proper medical treatment can lead not only to dangerous complications, but also to death. Experts strongly advise against self-medication. If symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help.
Complications of cholelithiasis
Frequent attacks of biliary colic can occur with cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder. This disease is more serious and requires exclusively surgical treatment. The patient is concerned about the typical symptoms of the inflammatory process: fever, nausea and vomiting.
Injury to the biliary tract will also lead to inflammation - cholangitis. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply. Fever, chills, and sweating appear. Confused consciousness due to severe intoxication. Due to excruciating pain, episodes of loss of consciousness are possible. The most serious complication is the purulent form of cholangitis, which quickly leads to sepsis and death.
Urgent actions
The first step in providing emergency care for hepatic colic is to call an ambulance.
Until the specialists arrive, the patient is provided with first aid at home.
Algorithm of actions to reduce the symptoms of hepatic colic:
- Reassure the patient by explaining that doctors have already been called and he will be provided with qualified assistance;
- Give the patient an analgesic to relieve spasms. Given the presence of severe nausea and incessant vomiting, it is better to administer the anesthetic intramuscularly;
- Place a heating pad under the patient's right side, as heat effectively relieves spasms.
Note!
You can use heat to relieve spasms only if you are completely sure that the patient does not have biliary dysfunction, and there is no movement of stones through the biliary system. In these cases, thermal procedures are prohibited. If preliminary diagnostics have not been carried out on the patient, you cannot take risks: it is better to refuse thermal procedures.
There are a number of actions that are strictly prohibited during emergency care for biliary colic:
- Before the specialists arrive, move the patient or allow him to move independently: you need to provide him with complete rest;
- Any palpating, stroking, or massage at the site of pain is prohibited;
- Give the patient something to eat or drink, as food and liquid will cause a new portion of bile to be produced, which will intensify the symptoms.
Further treatment will be determined by doctors and aimed at eliminating the cause that caused the painful symptoms.
Diagnosis and treatment
After hospitalization, the patient will be prescribed the necessary diagnostic measures to determine the reasons that provoked hepatic colic.
These include the following examinations:
- A blood test will confirm or deny the presence of an inflammatory process;
- A urine test may indicate the presence of jaundice;
- X-rays reveal the presence of gallstones in 15% of cases;
- Ultrasound diagnostics allows not only to detect the presence of stones, but also to determine their size and exact location.
Note!
If the stones have just begun to form and are very small, ultrasound cannot always recognize them. In this case, complex or combined diagnostic methods are used.
Treatment of hepatic colic is carried out by two methods: therapeutic and surgical.
Therapy for the disease is aimed at eliminating pain and relieving spasms. The patient is prescribed a strict diet, which includes a complete abstinence from salty, fatty and smoked foods. In this case, on the first day after hospitalization, a complete refusal to eat is indicated. An important point in dietary treatment is to increase the volume of fluid consumed daily.
Complications that manifest themselves in the inflammatory process of the gallbladder and the movement of stones in it can only be treated surgically.
Help from folk remedies
Many patients, faced with manifestations of hepatic colic, prefer to use traditional medicine recipes in prevention methods. It should be noted right away that they can be used only after preliminary consultation with a doctor and a test to ensure there is no allergic reaction to the components that the formulation contains.
Note!
Any, even the most effective traditional medicine cannot cure the cause of renal colic! Their use is indicated only for complex therapy or preventive purposes.
- Recipe No. 1.
The juice of one onion is diluted in boiled water in proportions of 1 to 1. Take 1 tbsp before meals. l.
- Recipe No. 2.
50 g of senna and the same amount of buckthorn bark are brought to a boil in a pan filled with water (500 ml). Then reduce the heat and simmer for half an hour.
Add some raisins to the resulting broth and boil for another 15 minutes.
After complete cooling, liquid rosehip extract is added to the healing mixture.
Treatment with this remedy should last at least two weeks daily. The medication is taken before meals, 1 tbsp. l.
Prevention methods
If hepatic colic was treated on time and correctly, the prognosis for successful treatment is positive.
However, regardless of the type of treatment, after successful treatment it is important to follow certain preventive rules so that the attack does not recur.
- A balanced diet that excludes the consumption of “harmful” foods. You need to eat small portions 5-6 times a day. It is important to minimize salt intake and increase your daily fluid intake.
- Compensated, properly distributed physical activity, which includes swimming, daily walks in the fresh air, simple gymnastic exercises.
- Limiting psychological stress and stressful situations.
- Completing preventive examinations annually and as indicated.
Causes
Hepatic or biliary colic can occur for a number of reasons:
- Stone formation in the gall bladder. Pain occurs when one of the stones passes from the bladder into its neck or duct. Because of this, the normal flow of bile is disrupted. It accumulates in the gallbladder, which leads to an increase in pressure in the organ cavity. The walls begin to gradually stretch, irritating pain receptors. A spasm develops, accompanied by severe cutting pain.
- Contractile dysfunction of the bile ducts - dyskinesia.
- Excessively thick bile.
- Congenital anomalies of the structure of the bile-producing system and narrowing of its ducts.
- Untreated intestinal infections such as giardiasis.
The syndrome most often appears in patients:
- with obesity or gastrointestinal pathologies;
- elderly;
- females taking oral contraceptives.
There are also complaints of biliary colic from children. This is due to the increasing number of cases of diagnosing abnormal development of the biliary tract system, genetic predisposition, and functional disorders of organ motility.
Clinical manifestations of a pain attack
Symptoms of biliary colic can be provoked by a calculus, the migration of which is caused by other factors. The attack is similar to other pathological conditions, for example, exacerbation of a peptic ulcer or an acute form of cholecystitis.
In 99% of clinical pictures, the pain is unbearable, but in some situations the pain syndrome is moderate. However, even moderate pain is dangerous, as serious complications develop.
In adult patients, the distinctive features of an attack of biliary colic are as follows:
- First, a slight tingling sensation, followed by severe pain in the epigastric region and the liver projection area. In 1/3 of patients, biliary colic occurs at night against the background of complete rest. The pain radiates to the neck, right shoulder blade and collarbone area. The pain is similar to an angina attack.
- Fever, nausea, vomiting, increased sweating, increased temperature.
- Digestive system dysfunction, headache.
- During an attack in adult patients, the heart rate and pulse quicken, and blood pressure readings jump.
- Paleness of the skin and stickiness - cold sweat appears.
- Yellowness of the skin of varying intensity - when a stone clogs the bile duct, preventing the flow of bile.
The pain syndrome only increases after the first hour of the attack. When trying to take a deep breath, it becomes more painful, and the same thing happens if the patient tries to change position - stand up, rise, etc.
For such symptoms, home pain relief is allowed, but you need to call an ambulance for hospitalization and examination. The attack must be differentiated from renal and hepatic colic.
Baby colic clinic
Symptoms in childhood are even more pronounced than in adult patients. Gallbladder spasms in children occur due to physical activity, consumption of fatty foods, or concomitant diseases. The attack begins abruptly.
Main symptoms:
- Rapid increase in body temperature.
- Nausea.
- Indomitable vomiting (the vomit contains an admixture of bile).
- Indigestion - diarrhea, belching, heartburn.
- Feverish condition.
- There is an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Severe pain in the area of the gallbladder projection.
If the cause of spasm of the gallbladder is parasitic diseases, then the clinical picture is complemented by an allergic rash, itching and burning of the skin, and loss of appetite.
Differences from renal colic in symptoms
Many patients have a history of both cholelithiasis and urolithiasis. The development of a painful attack in such a situation requires differential diagnosis, allowing the correct diagnosis to be made.
Biliary and renal colic are characterized by similar symptoms, but there are certain differences:
- With biliary colic, pain radiates to the right upper limb, back and part of the chest. Against the background of renal colic, the pain radiates to the groin, inner thighs, and genitals.
- With GI, additional symptoms are changes in the color of urine and stool, and a yellowish coloration of the skin with a green tint.
- With PC, pain increases with pressure on the lower back.
The treatment of the two attacks is fundamentally different, so it is necessary to correctly determine the nature of the pain syndrome.
Drug therapy
Antispasmodics are used to relieve spasms of the muscular structure of the organ.
The root cause of colic is a spasm of the muscular structure of the organ. It needs to be removed and for this a number of effective antispasmodics are used: “Platifilin”, “Drotaverine”, “Promedol”, “Papaverine”, “Baralgin”, “Atrapin” and “No-shpa”. Moreover, it is necessary to use strong painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs aimed at reducing pain spasms. The most popular are Ketorolac and Metamizole. For acalculous colic, injections of Cholicystokinin and Pancreozemin are prescribed.
Standard procedure for drug administration:
- 1 milliliter of Atropine 0.1% solution with 1 milliliter of Promedol;
- 2 milliliters of No-shpa with 5 milliliters of Baralgin.
For higher effectiveness, injections must be administered intramuscularly. If the spasm does not stop within several hours, the situation worsens and acute cholecystitis occurs. Its therapy requires a different course of treatment using other medications prescribed by the attending physician.
Drug therapy is usually prescribed for a long time (up to three months), after which the patient is examined again. Next, the attending physician either completely cancels the course of drug therapy or prescribes a new one.
Causes and symptoms
Hepatic colic occurs due to blockage of the bile drainage channels. That is, bile cannot leave the body freely. She, trying to resist stones or sand, acts on the muscle tissue of the gallbladder and its ducts, which causes them to spasm, which brings unbearable pain to the patient.
The following factors provoke spasms:
- Complete or partial blocking of bile ducts with stones or sand;
- Cholecystitis and other chronic pathologies of the gallbladder and liver;
- Stress;
- Alcohol addiction;
- Eating fatty or smoked foods in large quantities;
- Excessive physical activity associated with frequent bending of the body.
Note!
The manifestation of pain of this nature in women is associated with cyclical changes in the body. They most often occur in the last trimester of pregnancy, during the postpartum period and during menstruation.
Gallstone disease manifests itself as sharp attacks of pain, the duration of which varies from 30 minutes to 24 hours.
Hepatic colic most often occurs in the evening or at night and manifests itself on the right side of the abdomen in the region of the ribs. The symptoms of pain intensify when a person takes a breath.
If first aid during an attack was not provided on time, serious complications may develop in the form of pancreatitis or intestinal obstruction.
Emergency care for biliary colic is provided if the patient has the following symptoms:
- Intense pain under the right ribs of a stabbing or cutting nature, which gradually spreads to other parts of the body;
- Severe paroxysmal nausea;
- The feces become light, almost white, and the urine darkens;
- During palpation of the liver area, the patient experiences unpleasant sensations, obvious muscle tension is felt;
- Abnormal bowel movements, manifested by constipation or diarrhea;
- Repeated vomiting, after which the patient does not feel relief.
Note!
In case of colic, it is better for the patient to lie on his right side with his knees bent. This pose will help reduce pain.
An immediate call to medical personnel is required when the following manifestations of an attack are added to the main symptoms:
- Increased body temperature;
- The skin becomes jaundiced or pale;
- Increased sweating;
- Bloating.