Percutaneous transhepatic cholelitholysis is one of the ways to dissolve gallstones.
Yes, indeed, such a method exists.
Scientists, like all people, also think very diversely. This method is called percutaneous transhepatic cholelitholysis. The essence of the method is as follows:
Under the control of ultrasound or X-ray tomography equipment, a catheter is inserted into the gallbladder through a puncture method through the skin and liver tissue. A special drug is injected into the bladder through it, capable of dissolving stones. In the case of cholesterol stones, it is methyl ter-butyl ether. A chemical is injected with a syringe, then the dissolved components of the stones are carefully sucked out, thus achieving the release of the gall bladder from stones.
However, small remnants of stones may remain in the gallbladder, which in the future can serve as a source for the formation of new large ones. Therefore, dissolving stones using chemicals is usually combined with taking ursodeoxycholic acid.
Experimentally, with the help of other chemicals, it was possible to dissolve not only cholesterol stones, but also pigment stones (bilirubin) and even calcareous stones. For inquisitive readers, let's say that in this case palmidrol, methylhexyl ether, and octaglin are used. It is believed that within 3-4 weeks, up to 90% of the stones can be dissolved in this way.
Surgical intervention
Surgical treatment is the only way to solve the problem. Dissolving or crushing stones does not mean curing gallstone disease. According to patients, even after complete cleansing of the gallbladder cavity from stones, after a while they form again. If a pathological process is started, relapses of the disease will be common.
The absolute indication for surgical intervention is attacks of biliary colic, ineffectiveness of conservative treatment. Emergency reasons for removing the affected organ are acute calculous cholecystitis and other complications that threaten the health and life of the patient.
Is surgery necessary if the stones don't bother me?
Today, stone-bearing is found much more often than half a century ago. This is explained by the improvement in the quality of diagnostic studies, as well as the poor nutrition of modern people and a sedentary lifestyle.
The absence of symptoms does not mean the absence of pathology dynamics. According to the observations of diagnosticians, after detecting small stones, a person can live without surgery for another 15–20 years, but in any case, surgical intervention is inevitable.
Doctors agree that elective surgery should be performed to eliminate the risk of dangerous complications. Indications for gallbladder resection are:
- formations 25–30 mm;
- hemolytic anemia;
- If surgery is planned for obesity, the affected organ is removed along with the fat mass.
The operation is offered to patients if the patient's life expectancy is more than 20 years.
When is it better not to touch gallstones?
In asymptomatic cases of cholelithiasis, stone removal is contraindicated in patients with liver cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, or after organ transplantation. Regardless of the form of the disease, surgery is postponed if the following conditions develop:
- pregnancy – first and last trimester;
- Mirizzi syndrome;
- extensive hernias of the abdominal wall;
- advanced acute cholecystitis.
Absolute contraindications are uncorrectable blood clotting disorders, the patient's serious condition, decompensated dysfunction of vital organs.
Types of intervention
In practical medicine, 2 types of surgery are used to get rid of stones:
- Laparoscopy – removal of the gallbladder through 3-4 mini-punctures using endoscopic equipment.
- Mini access - cholecystectomy is performed through a small incision.
In emergency cases, in case of severe complications, abdominal surgery with a large incision of 15–20 cm is prescribed.
Products based on bile acids
Bile acid preparations allow dissolving stones in the gallbladder, the intake of which normalizes the balance between endogenous bile acids and cholesterol. This causes cholesterol to slowly peel off from the loose surface of the stones. As a result, the stone gradually fragments, and the resulting microcrystals leave the body along with bile through the intestines.
Medicines must be taken for a long time (from 6 months to 2 years) before bedtime. Then only prophylactic doses of drugs are prescribed. To monitor the effectiveness of treatment, ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system should be performed twice a year. However, after discontinuation of the drug, stones may appear again.
When are medications prescribed?
Medicines for gallstone disease based on cheno- and ursodeoxycholic acids are prescribed in the following situations:
- The diameter of the stones does not exceed 15 mm;
- There are no conglomerates in the biliary tract;
- Stones occupy less than 50% of the cavity of the digestive organ;
- Body weight does not exceed the age norm;
- In the absence of severe pain;
- Motility of the digestive organ is preserved
- There are no signs of acute cholecystitis or severe liver pathologies.
During periods of exacerbation of diseases of the digestive organs, the use of this group of medications is contraindicated.
Features of application
Medicines based on bile acids should not be prescribed together with oral hormonal contraceptives (Yarina, Diane-35), antacids (Maalox, Almagel), Cholestyramine, which is taken to eliminate excess cholesterol.
The use of drugs to remove stones should be avoided if the following conditions exist:
- Development of acute cholecystitis;
- Liver pathologies;
- Ulcer of the duodenum or stomach;
- The period of gestation and natural feeding of a child.
Contraindications to treatment
Tablets containing bile acids are allowed to be taken to cleanse cholesterol formations only if the patient is fine with the functioning of the gallbladder and there is no exacerbation of it. The bile ducts should be passable, and the stones should fill the bladder less than half. There should be no severe pain. If a person is obese, such cleansing will be less effective for him. Such drugs have a side effect - liver function decreases, because of this creatinine and urea accumulate in the blood. At risk are pregnant women, women during breastfeeding, patients with stomach and duodenal ulcers, patients with inflammation of the liver, gall bladder and tract.
Remember that cleansing stones with such means is not compatible with:
- Hormonal contraceptives that contain estrogen.
- Drugs that remove excess cholesterol from the body (“Cholestyramine”).
- Medicines that provoke a decrease in stomach acidity (Almagel).
There are also warnings for cleansing with Ziflan. It is prohibited for pregnant women, as well as during lactation, people with individual intolerance to immortelle, and children under 12 years of age. For diseases such as jaundice and high blood pressure, this drug is also not used to clear stones. One of the negative effects on the body is the occurrence of allergic reactions. Considering that this is a herbal preparation that tends to accumulate in the tissues of the body, you should not drink it for more than 3 months in a row, even if the pain does not decrease.
General information
Gallstone disease often occurs in economically prosperous countries.
The risk group includes people engaged in intellectual work. Medical statistics state that cholelithiasis is in 3rd place after heart failure and diabetes mellitus.
The gallbladder is a “reservoir” for bile, which is produced by the liver.
The promotion of bile is due to the friendly work of:
- liver;
- duodenum;
- gallbladder;
- pancreas;
- bile duct.
In 92% of cases, stones appear against the background of bile stagnation. The main types of stones are presented in the table.
Table 1. Types of stones.
| Type of stones | % occurrence | Reason for appearance |
| 80-90 | Oversaturation of bile with cholesterol. It precipitates and cholesterol crystals form. |
| 50-70 | Hemolytic anemia, accompanied by increased breakdown of red blood cells. |
| 22-40 | Inflammation of the gallbladder or bile ducts. |
Possible negative consequences of laser crushing of gallstones
In this regard, the risk of recurrent stone formation still remains. Therefore, even after successful removal of stones from the gallbladder, it is necessary to adhere to a special diet called “Treatment Table No. 5” and follow other medical recommendations.
One of the risk factors when carrying out such a procedure is that it requires a highly qualified doctor and high precision of the operation. If the specialist performing the operation deflects the beam from the stone even by a millimeter and touches the mucous membrane of the organ, a severe burn is guaranteed, which can result in a gradually developing ulcer, the treatment of which is only possible through surgery. Therefore, despite the fact that such procedures are performed quite often, the doctor must warn the patient about the possible dangers.
In other words, the main disadvantages of this technique are:
- risk of burns to the mucous membrane of the organ;
- the possibility of injury to its walls by the sharp edges of fragments arising during the crushing process.
The doctor can only recommend one or another treatment method. The decision whether to agree to it or not is made by the patient himself. However, if the doctor prescribes laser lithotripsy, then, despite the presence of some negative aspects, its use in most cases allows you to effectively remove stones from the bladder cavity and at the same time preserve the organ itself.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!
Application of Ziflan supplement
The drug is based on immortelle extract, which stimulates the production of bile with normal rheological properties. This allows you to prevent the formation of new stones and synthesize bile acids using endogenous cholesterol. When reserves of the compound are depleted, cholesterol, which is located on the walls and vessels of the gallbladder, is used for synthesis.
Ziflan should be taken in courses, the duration of which is 1 month, and the interval is 2 weeks. The drug is taken orally, 1 capsule three times a day during meals. To normalize the patient's condition, no more than 2-3 courses are usually required over the course of a year. But with positive dynamics of the disease, the duration of therapy can be 2 years.
The drug should not be prescribed:
- Pregnant women;
- Mothers during lactation;
- Against the background of jaundice;
- If you have hypersensitivity to immortelle;
- In patients with arterial hypertension;
- If the child is under 12 years of age.
Features of drug therapy
The goal of treatment for cholelithiasis is not only to remove stones, but also to reduce the risk of new stones forming. This requires normalizing the digestive process, reducing the amount of cholesterol, and increasing immunity.
To successfully normalize the functioning of the biliary system, the following drugs are prescribed:
- probiotics and prebiotics – restore healthy intestinal microflora;
- choleretic agents - help to avoid stagnation of secretions and sedimentation;
- antispasmodics - used for moderate pain;
- vitamin complexes - allow you to supplement the diet with useful substances in case of disruption of bile production and the process of food absorption.
Simple and effective apitherapy recipes
Before starting self-treatment with bee products, it is recommended to consult with specialists: therapist, gastroenterologist, nutritionist.
Mixture for the treatment of cholelithiasis
Shake equal parts of Provençal (olive) oil with the same amount of honey. The mixture separates, so vigorous shaking is necessary.
On the first day, use ½ tsp. 30 minutes before meals. In the next day, the dose may increase (from 1 tablespoon to ½ cup). The course of treatment takes 3 weeks.
Diet dish
Mix 200 g of low-fat cottage cheese and 30–40 g of natural honey, add a little royal jelly (bee milk). Mix the ingredients well. The resulting honey-curd mass is tasty and useful for moderate pain in the right hypochondrium and the formation of stones.
Honey-pumpkin mixture
A small nutmeg pumpkin is washed, the top is cut off, and the seeds are removed. Honey is poured through the hole and the top is closed. The remaining gap is covered with thick dough. The pumpkin is left in a cool, dark place for 7–10 days.
Then open the “lid” and take out the finished mass with a spoon. Eat 1 tbsp daily half an hour before meals. l. honey-pumpkin dessert. The course of treatment and prophylaxis is 21 days.
Black radish juice
Grind the radish on a grater and squeeze out the juice. The liquid is thoroughly mixed in half with honey. Take ½ cup of solution daily in 1–3 doses. The recipe is most effective if the disease is not advanced.
Herbal medicine and apitherapy
Fruits, berries, vegetables, infusions of medicinal plants are excellent therapeutic and prophylactic agents. For gallbladder diseases, drink apple juice with honey (½ cup).
They are sweetened with decoctions of rose hips, hawthorn, infusions of sandy immortelle, medicinal sage, wormwood, greater celandine, etc.
Recipe with medicinal plants
Prepare a solution from 1 tsp. medicinal plant or mixture of herbs and 250 ml of boiling water. Leave in a thermos for 1 hour, filter. Add 1 tsp. honey per glass of solution.
It is not recommended to heat the sweet product above 50° or boil, otherwise proteins, amino acids and vitamins are destroyed. It is better to sweeten a warm infusion or tea drink with a healing agent. The solution is taken 15–25 minutes before meals.
The proposed apitherapy products improve metabolic processes and increase the amount of bile produced. The likelihood of stone formation and the development of gallbladder inflammation is reduced.
The use of folk remedies
Small stones can be removed using simple folk remedies. Preliminary consultation with the attending physician is strictly mandatory.
| Means | Cooking instructions | How to apply (once/24 hours)? |
| Peel 2-3 beets, cut into small slices, place in a saucepan. The product is boiled until it takes the form of syrup. | 3 |
| The fruits have a healing effect. They can be eaten whole, or pureed and mixed with sugar or honey. The product promotes painless passage of stones. | 3-4, 2 tbsp. |
| 40 grams of dry leaves are crushed and combined with 180 ml of boiled liquid. Place the mixture over low heat and cook until the water is reduced by half. Then the broth is chilled and well filtered. | 3 |
| Its juice has a healing effect. It needs to be squeezed out and, if necessary, diluted with a small amount of warm water. | 3, 100 ml. |
| It is advisable to eat wild strawberries. The fruits can be eaten in their “pure” form, or passed through a blender. | 1-2, 150 grams each. |
| Pass 150 grams through a meat grinder, mix with 600 ml of unpasteurized milk. The mixture is placed on low heat. When the volume of liquid is reduced by half, the broth is chilled and filtered. | 3, 20 ml. |
| The oil is heated before use. | 3-4, ½ tsp-1/2 cup each. |
| The radish is crushed, the squeezed juice is mixed in equal proportions with fresh liquid honey. | 3, 1/3 cup each. |
| 20 grams of leaves are mixed with 160 ml of boiled liquid, infused for half an hour, chilled, and filtered well. | 4-5, 40 ml each. |
Preparations for dissolving gallstones
The method of medicinal dissolution of gallstones is determined by the type of drug used and the patient’s body weight.
Now let’s talk about each group of drugs in order.
I. Preparations containing some of the bile acids act in this way: they restore the imbalance between cholesterol and bile acids, creating such a mixture in the gallbladder, due to which the stones should dissolve.
These are the drugs Ursofalk, Ursohol, Ursosan (the active ingredient is ursodeoxycholic acid) and Henochol, Henofalk, Henosan (contain chenodeoxycholic acid).
Bile acid preparations have been used for over thirty years with some success. It is best to use them together, as they have slightly different points of application. One of them dissolves in bile and “organizes a stone-dissolving bile cocktail,” while the second enters into a chemical reaction with cholesterol, promoting its transition from the stone state to the liquid crystal state.
You can take cheno- and ursodeoxycholic acids to dissolve gallstones only if the following conditions are met:
— diameter of stones from 5 to 15 mm;
- stones fill less than half the volume of the gallbladder;
- no stones in the gallbladder ducts;
- The gallbladder contracts normally.
These medications will need to be taken regularly for a long time (from six months to 2 years), preferably before bedtime. Then a prophylactic dose of medication is prescribed. A control ultrasound is performed twice a year.
The following medications should not be taken while taking these medications:
a) hormonal contraceptives containing estrogen (it itself promotes the formation of stones);
b) medications that reduce stomach acidity, for example, Almagel, Phosphalugel (they interfere with the absorption of bile acid preparations;
c) cholestyramine, which is used to remove excess cholesterol.
In addition, there are contraindications to taking cheno- and ursodeoxycholic acids: Acute inflammation of the gallbladder and bile ducts; liver disease, peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum. Pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
II. Ziflan is a drug containing immortelle extract.
The principle of action of this drug is not to replace bile acids, but to stimulate liver cells to produce bile with a normal composition that is not prone to precipitation, where a sufficient amount of bile acids is present, and they do this using cholesterol (it is a chemical precursor bile acids).
And when the liver cells, after a long rest, begin to use cholesterol from their reserves, gradually its level runs out, and cholesterol is used, which is deposited on the walls of blood vessels, causing atherosclerosis, which is the main cause of coronary and hypertension diseases.
After stopping Ziflan, liver cells are able to work correctly for a long time, only occasionally it is necessary to take it again in a prophylactic dose.
Contraindications to its use include an allergy to immortelle, as well as pregnancy and breastfeeding.
In addition to taking medications, you must not forget to follow a diet with a minimum content of animal fats, fried and smoked foods
Diet after removing stones from the gallbladder is an important link in the fight against the disease. It is important to change your lifestyle: move more, spend time outdoors, attend sports training
It is equally important not to forget to treat foci of infection: treat or remove diseased teeth, carry out prevention and treat sore throats in a timely manner, and so on, so that the treatment you carry out does not come to naught due to an unhealthy lifestyle
Mechanism of stone tablets
Cholelytic agents, when taken orally, have a dissolving effect in the gallbladder. They suppress the process of cholesterol production by the liver, thereby reducing its concentration in bile and, preventing the formation of stones, stimulate the formation of proper bile.
When the cholesterol content in bile decreases, the body strives to replenish its concentration to the original level, as a result of which the structure is loosened and cholesterol stones are destroyed with the further release of microcrystals into the lumen of the duodenum.
Important! The process of drug-induced stone breaking is long. It is necessary to take the medicine, strictly adhering to the dosage prescribed by the doctor, for 1 to 2 years.
Shock wave lithotripsy method
For a small number of small solid formations, shock wave lithotripsy is often used.
This method effectively deals with deposits that consist of cholesterol. This method is based on the impact of a shock wave on the stones, which leads to the destruction (crushing) of the formations. Treatment is carried out in a course of 10 procedures (the number is determined by the doctor). After the stony formations are destroyed, small pieces (3-4 mm) are excreted naturally through the ducts into the duodenum and further into the intestines. This method is always carried out in conjunction with drug therapy.
In addition, the lithotripsy method, in fact, like taking medications, does not guarantee that conglomerates will no longer form.
The method has side effects:
- Damage to the organ mucosa may occur when the fragments vibrate inside under the influence of a destructive wave;
- there is a high risk of formation of foci of inflammation (bacterial infection);
- adhesions often occur;
- Blockage of the ducts may occur, which often causes jaundice.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis to make sure that the stones do not consist of calcium or the percentage of their content is very low.
Otherwise, positive success will not be achieved.
Types of drugs
Means for dissolving gallstones are represented by two types of drugs. We will look at each of them separately.
1) Preparations based on bile acids. With their help, you can restore the balance between the levels of cholesterol and bile acids produced by the liver. An increase in the content of the latter in the gallbladder leads to the dissolution of stones and their transition to a viscous and liquid state. There are two types of choleretic drugs in this group. The former contain ursodeoxycholic acid and are presented in pharmacies under the following names:
- Ursofalk.
- Ursosan.
- Ursohol.
The second group includes choleretic drugs containing chenodeoxycholic acid. Their names are presented below:
- Henofalk.
- Hyeonosan.
- Henochol.
Despite the fact that both choleretic drugs are based on similar bile acids, the effect after taking them is different. Thus, the components of urso preparations are completely dissolved in bile and, by increasing acidity, contribute to the disintegration of stones. Cheno-preparations react with cholesterol, softening its structure and transforming the substance into a liquid state. As a rule, both types of medications are prescribed at the same time, which increases the chances of success of therapy. Their reception is possible only if the following conditions are met:
- the diameter of the stones ranges from 5–15 millimeters;
- there are no stones in the gallbladder ducts;
- stones fill no more than half of the inner space of the bubble;
- the gallbladder has not lost its contractile function.
The patient must be prepared for the fact that treatment with choleretic drugs may take more than one year. Choleretic drugs are prescribed for a period of six months to two years. If the problem does not resolve during this period, the patient is offered other treatment methods. It should be noted that, as is the case with most other drugs, choleretic drugs containing bile acids have a number of contraindications. In particular, they should not be taken simultaneously with the following medications:
- Hormonal agents containing estrogen.
- Cholestyramine.
- Means to reduce the level of stomach acidity (Phosphalugel, Almagel, etc.).
In addition, choleretic drugs based on urso-, chenodeoxycholic acids are not recommended for use in the following cases:
- acute inflammation of the bladder and its ducts;
- stomach ulcers;
- liver diseases;
- inflammation of the duodenum;
- pregnancy and lactation.
2) Dietary supplement Ziflan. Its active ingredient is immortelle extract. With long-term use, it can affect the level of acidity in the gallbladder. Thanks to the dietary supplement, the liver begins to produce balanced bile with a normal content of bile acids. At the same time, cholesterol levels, as a rule, also return to normal. This helps dissolve stones and remove them into the small intestine.
Ziflan is prescribed in several courses for 30 days with breaks of two weeks. The patient should undergo periodic ultrasound examinations to monitor the condition of the gallbladder. If no results are observed within a year, therapy is stopped.
The drug is taken with food. Its effect is long-term and can last for several years after the end of use. If a patient has a history of progressive gallstone disease, doctors recommend taking a course using Ziflan once a year. The dietary supplement has a number of contraindications:
- high pressure;
- jaundice;
- allergy to immortelle extract;
- pregnancy;
- lactation.
Taking the drug can lead to a side effect - an acute allergic reaction. Therefore, before you start using Ziflan, you should consult with an allergist.
When can you be treated conservatively?
Unfortunately, drug treatment for gallstone disease is not always effective. Its result depends on the stage of the disease, the size and location of the stones and, most importantly, on their type.
When metabolic processes are disrupted in the human body, the following types of formations can form:
- cholesterol - the most common;
- pigmented - consist of bilirubin and calcium ions, are insoluble;
- insoluble mixed stones.
Only cholesterol stones can be treated with medication. The treatment regimen for cholelithiasis includes drugs based on bile acids or the drug Ziflan. If other types of formations are detected, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention, and for small stones, crushing.
The type of stones in the bladder can be determined using ultrasound or duodenal intubation. It is not recommended to self-medicate without undergoing these studies and the opinion of a gastroenterologist. If cholelithiasis is caused by bilirubin or mixed formations, therapy will be ineffective.
The symptoms of cholelithiasis, treatment methods and causes are discussed in the following video.
Biological supplement Ziflan
Bile acids are formed in liver cells, the precursor of which is cholesterol. When the ratio of bile acids is disturbed, they can crystallize and form stones. The reason for this may be metabolic disorders, chronic or acute diseases of internal organs, a sedentary lifestyle, or pregnancy.
The drug Ziflan
The drug Ziflan as a herbal dietary supplement contains immortelle extract. This main active ingredient stimulates the production of bile with a normal ratio of bile acids. Such bile does not precipitate and does not form stones. Ziflan stimulates the formation of bile acids from cholesterol from its own reserves. When such reserves run out, cholesterol deposited on the walls of blood vessels and the gallbladder comes into play, promoting the breakdown of stones.
Ziflan is prescribed in courses of 30 days with a break of 10-15 days. Depending on the degree of development of gallstone disease, doctors may recommend 2-3 courses of the drug per year. Sometimes treatment continues for up to two years if, according to ultrasound results, positive dynamics and dissolution of stones are observed. Ziflan is usually recommended to be taken with food, one capsule 3 times a day. Even after discontinuation of the drug, the liver is still able to work in the correct mode for a long period of time, producing the correct bile. Doctors often recommend preventive courses once a year if there is a history of gallstone disease.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
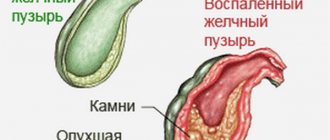
The formation of stones is associated with irreversible changes in the gallbladder that develop after prolonged stagnation of fluid. Delayed outflow is caused by many reasons, from poor nutrition to congenital defects in the development of the liver or gall bladder. Stones form gradually and may not be detected for years. In most cases, the patient learns about the presence of the disease after an attack of biliary colic, when it is necessary to take radical measures.
What is gallstone disease
This is a disease of the hepatobiliary system, the main symptom of which is the presence of stones in the gall bladder. They are formed from bile components, which tend to crystallize. At the initial stage, a suspension of small particles is formed - biliary sludge. Gradually, stones are formed from it; they have different shapes and compositions.
Most often, stones are generated in the gallbladder, but if it is absent, they can also appear in the bile duct. The presence of inclusions leads to disruption of the outflow of bile; stones can partially or completely block the exit from the gallbladder or the lumen of the duct.
Sometimes stones migrate along the biliary tract, causing inflammation and severe pain - biliary colic. This leads to deterioration of the liver and infection of the bile.
Symptoms of gallstones
If the stones are small, cholelithiasis may occur without symptoms. Some patients develop dyspeptic disorders:
- taste of bitterness and metal in the mouth;
- coated tongue;
- heartburn, nausea;
- increased gas formation.
Discomfort and heaviness appear in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. The clinical picture becomes brighter after ingesting fatty foods, alcoholic beverages, and dishes with a spicy taste. The presence of symptoms is due to dysfunction of the bile ducts, sphincter of Oddi, and duodenogastric reflux. This form of cholelithiasis is called dyspeptic.
A characteristic manifestation of the disease is biliary colic. This is an attack of piercing pain of a cutting, tearing nature, which is localized in the right side under the rib and spreads to the right side of the back, involving the neck. Sometimes pain can radiate to the heart area and simulate a heart attack. The pain impulse is present from 10 minutes to several hours, often complicated by repeated vomiting of bile, which does not bring relief. The patient rushes about, tries to change body position to reduce the intensity of the pain syndrome.
Colic is caused by the following factors:
- a rich feast;
- intense physical activity;
- severe stress;
- shaking while running, jumping, or driving.
This leads to the displacement of stones; they can move along the bladder, ducts and obstruct the outflow of fluid. The edges of the formations irritate and damage the walls of the biliary tract, which provokes an inflammatory process and deterioration of the condition.
Causes of stone formation
The formation of stones occurs for 3 main reasons:
- metabolic disease;
- delayed excretion of bile;
- inflammatory process.
As a result of a metabolic failure, changes occur in the composition of bile - the ratio of cholesterol, bilirubin, and bile acids is disrupted. A liquid saturated with cholesterol is called lithogenic. Many small grains of sand appear in it, which gradually merge and form stones. A favorable environment for stone formation is putty-like bile, which thickens when its excretion is impaired.
It is known that the root cause of the formation of gallstones is provoked by the following conditions:
- bile duct dyskinesia;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- infectious damage to the liver and gallbladder;
- helminthic infestations;
- taking toxic medications;
- parenteral nutrition;
- pregnancy;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
Women are at risk; they develop stones more often than men. The likelihood of diagnosing cholelithiasis increases in old age, in people who eat improperly - overeat or starve.
Types of gallstones
Concretions vary in composition:
- Cholesterol - 90% consist of cholesterol. These are the most common formations that can be dissolved and removed non-surgically.
- Pigmented - available in black and brown. Blacks are predominantly calcium-rich and have a hard consistency. Brown ones are soft, formed with the participation of fatty acids.
- Calcareous - includes a large amount of lime salts.
In most cases, formations have a mixed composition. The stones take on bizarre shapes:
- in the form of a barrel;
- hourglass;
- become like an awl;
- smooth, round or with several edges.
The sizes of solid inclusions vary greatly. There are clusters of small grains of sand or one stone, but of impressive size.