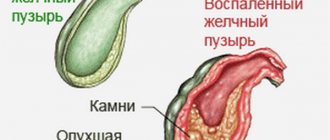
Gallbladder diseases most often arise due to existing pathologies of the liver and pancreas. There may be various symptoms that indicate health problems. If there are alarming signs, a person may be advised to immediately undergo a diagnosis so that the disease can be identified. If the presence of pathology is confirmed, then treatment will have to begin. In this case, patients are recommended to eat a diet for gallbladder disease. Thanks to it, you will be able to quickly restore the body and normalize your health.
Signs of pathology
What symptoms should you be wary of? What clinical signs do the pathologies have? What kind of nutrition is possible if you have gallbladder disease? There are a number of common manifestations that indicate gallbladder disease:
- Prolonged pain or acute spasms concentrated in the hypochondrium on the right side. The intensity of pain corresponds to the specifics of the pathology, in particular, pain is not typical for the formation of polyps, while severe pain is characteristic of cholelithiasis or calculous cholecystitis;
- Functional gastrointestinal disorders, expressed by bloating, defecation disorders, nausea or vomiting;
- The appearance of a bitter taste (this symptom is also a sign of kidney disease, so a thorough examination and differential diagnosis is recommended);
- Change in color of the mucous surface of the tongue or the formation of a pronounced coating;
- Significant darkening of urine (for example, with cholestasis, this sign is caused by an increase in the concentration of urobilinogen);
- Discoloration of feces (due to the absence of stercobilin in feces due to stagnation of bile);
- Jaundice signals the acute phase of cholestasis, when, due to stagnation, bile is absorbed into the blood, increasing the level of bilirubin and bile acids (the acquisition of a yellowish tint begins with the mucous membranes and sclera, spreading further to the surface of the epithelium).
The above conditions are among the most common manifestations of gallbladder diseases, while the range of symptoms is much wider and even includes such common ailments as decreased appetite, increased body temperature, weakness, etc.
To relieve symptoms and further treat gallbladder diseases, it is important not only to take medications, but also to adhere to a diet.
Nutrition for cholestasis in a child
If a child is diagnosed with bile stagnation, then the principles of nutrition remain the same as for an adult, with strict adherence to dietary table number 5. The same foods that are listed are prohibited and permitted. During the therapy period, it is important to explain to the child why some goodies are now prohibited.
The better children follow their diet, the faster they recover. If possible, limit communication with loved ones and relatives who do not understand the importance of dietary nutrition in childhood and try to treat children to prohibited foods. In addition to nutritional correction, the doctor prescribes medications at his discretion.
Therapeutic diet: permitted foods
After examination and diagnosis, medical prescriptions are made in the form of medication or radical therapy, depending on the characteristics and severity of the disease.
To speed up recovery and improve the current condition, it is extremely important to follow a specialized diet, tailored to individual characteristics. For example, acute cholecystitis is a direct indication for eating exclusively liquid foods: chopped vegetable soups, juices diluted with water, herbal infusions.
When the disease passes into the chronic phase, it is possible to expand the diet in accordance with the recommendations of a specialist.
There is a special therapeutic diet “Table No. 5”, which is recommended for patients with pathologies of the pancreas and liver. The diet involves a reduced intake of fats while maintaining the norms of carbohydrates and proteins. If you break this diet down into its chemical components, the diet looks like this:
- 2 liters of liquid;
- 400 grams of carbohydrates;
- 80 grams of proteins;
- 10 grams of salt;
- 80 grams of fat.
Recommendations from nutritionists for people with pathologies of the bile duct include:
- Compliance with a fractional nutrition system (portions should be small, 5-6 meals per day);
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid;
- Reducing the consumption of fats of animal and plant origin;
- When remission occurs, maintaining the therapeutic diet, with a gradual expansion of the diet. Fried, smoked and spicy foods should be included in the diet rarely and in minimal quantities;
- During an exacerbation, refrain from eating and drinking until symptoms subside, then resume eating with minimal portions: 100 ml of fruit juice or tea without sugar, 50 ml of chopped vegetable soup;
- Quitting bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol;
- Exclusion of sweets, including ice cream and sweet soda, fresh bread and baked goods, drinks containing caffeine;
- Drawing up a balanced diet in accordance with personal preferences, which includes dishes such as: chopped vegetable soups, lean meats, various cereals, fruits and berries, low-fat fermented milk products, vegetables in the form of stews or purees.
Diets for the liver and gallbladder
Published 28.08 Author Lyudmila Moroshkina
The liver can rightfully be considered a real chemical factory. It is she who passes through herself and then processes all toxic and harmful substances that enter our body. Not only the liver is important for humans, but also the gall bladder. Both bodies work together
It is very important to follow a diet for the liver and gallbladder
You can often hear complaints that the liver hurts or the gallbladder is bothering you. In fact, with age, metabolic processes in the liver are disrupted, and in some people the gallbladder has to be removed.
The gallbladder is often removed due to stones formed or inflammation of the organ. Diseases of both organs are now quite widespread. So what causes these diseases?
The functioning of the liver is affected by many reasons, such as poor-quality water and food, a large number of preservatives, dyes and flavors in products, rapid environmental deterioration, and medications taken without consultation with specialists. These factors include poor personal hygiene, which often leads to hepatitis. Hepatitis viruses are transmitted through personal contact, through things and blood.
Rare meals, eating dry food, overeating are the main causes of the formation of stones and inflammatory processes in the gallbladder. With age, the liver begins to work worse, even without all the negative factors listed above. Her functions weaken, some liver cells die. Such processes are considered natural. Try to be careful about your liver and gallbladder. Follow a diet for the liver and gallbladder.
Let me tell you what you need to include in your diet.
It is important to follow a diet, nutrition must be correct
Include fermented milk products and cottage cheese in your diet. They should be low-fat. It is useful to eat boiled and raw vegetables without nitrates. Eat watermelons, apricots, and grapes; these fruits contain large amounts of pectin and glucose.
The menu for the diet will be useful: vinaigrette, salads, compotes, dried fruits. He especially loves the liver and gall bladder, dried apricots, raisins and prunes.
Vegetarian soups, chicken, lean beef and fish will not harm the liver. Try to drink enough liquids. Mineral alkaline waters and rosehip decoction are beneficial for the liver diet. Don't forget to take vitamins. The liver and gall bladder respond well to taking vitamins A, C, E, B, and folic acid.
Now let's talk about foods excluded from the diet.
Do not drink alcoholic beverages, it is best to give them up. This is especially true for low-quality alcohol. The liver does not like lard, spicy foods, fatty sausages, marinades, margarine, mayonnaise and sauces.
Sausages, boiled sausages and small sausages are not good for the liver. They cause less harm, but these products should be excluded from the diet. Garlic, horseradish, nuts, mushrooms and legumes are not recommended. Rich meat broths are considered harmful to the liver and gall bladder and should not be included in the diet. Fried foods are excluded.
When using medications, strictly adhere to the dosage. Be sure to read the attached instructions before using a new drug. Some antibiotics have a negative effect on the liver, especially the tetracycline group, paracetamol, and sulfonamides.
Avoid constipation. With constipation, harmful substances that are formed during digestion are not removed from the body, but, on the contrary, are absorbed. Intoxication increases in a person, and this leads to additional stress on the liver.
Pay attention to dysbiosis, in which the composition of the microflora in the intestines is disrupted and harmful substances are formed. You can get a lot of useful information about this problem from here
These substances are also absorbed into the blood, and the liver must process them.
We draw a conclusion. To keep your vital organs healthy, follow a liver and gallbladder diet. Remember your liver and gallbladder as often as possible. Think about what they suffer from and what they love! And I wish you that these organs do not bother you for many years!
Therapeutic diet: prohibited foods
The therapeutic diet for gallbladder disease involves avoiding certain categories of foods (fatty, fried, smoked), quickly digestible carbohydrates (found in chocolate, sugar, bee products, jam) and other foods that can overload the digestive tract.
It is necessary to completely exclude the following products:
- Fatty meat, sausages, canned meat and smoked meats;
- Caviar, canned fish, salted fish;
- Salty cheeses, cream, sour cream, milk with a high proportion of fat;
- Coffee;
- Legumes (with a tendency to flatulence);
- Radishes, garlic, fresh onions and marinades based on them;
- Rich meat and mushroom broths, okroshka, cabbage soup and borscht;
- Seasonings, hot sauces, mayonnaise;
- Fresh flour products, including baked goods, fried pies;
- Yolk of a hard-boiled chicken egg (due to the high content of cholesterol and fats that provoke the formation of stones), scrambled eggs, omelet
Thus, the diet for these pathologies is quite varied; the list of products allows you to prepare various dishes for every taste. Allowed products are rich in vitamins and natural dietary fiber, which has a beneficial effect on the entire body as a whole.
Sizing
In order to determine the size of the organ and its other parameters, the ultrasound diagnostic method (ultrasound) is used. This study shows:
- size (length, width) and volume;
- how thick are the walls of the organ;
- are there stones in the cavity;
- condition of the bile ducts: size, patency;
- disruptions in muscle contractions.
The length of the gallbladder means the distance from the narrowest part of the organ to the base. The width is determined by the largest gap between the walls. These parameters and the thickness of the organ are entered into special formulas with which the volume of the gallbladder is calculated
In addition, during the procedure, the doctor pays attention to the condition of the contours of the walls. An ultrasound is the next step after an external examination of the patient (palpating and tapping)
For diagnostics, a device with a frequency of 2.5−3.5 MHz is used. It is at this frequency that small objects (up to 1 mm) will be visible.
https://youtu.be/yOLadO-jWxE
Menu examples
An example of a daily diet for people with gallbladder pathology:
- Breakfast: low-fat cottage cheese with sour cream, dried bread with butter, soaked herring (no more than 20 grams), vinaigrette, weak tea with milk;
- Second breakfast: boiled or baked meat, crumbly buckwheat, juice diluted with water;
- Lunch: chopped vegetable soup (can be served with sour cream), boiled fish with vegetable stew, white cabbage salad, compote;
- Dinner: baked cabbage cutlets with pasta, jelly;
- Before bed: dried fruit compote, dried bread.
This menu shows that the list of products allows you to eat a variety of healthy and healthy foods.
Recipes
We offer several recipes for dishes that can be served during remission.
Vegetable soup with cheese meatballs
Ingredients:
- vegetable broth – 500 ml;
- carrots, onions, red pepper;
- potatoes – 4 pcs.;
- cheese with a neutral taste – 110 grams;
- egg;
- flour – 90 grams;
- greenery;
- butter;
- salt.
Preparation: grate the cheese, add flour, softened butter, and salt. Mix and put in the refrigerator. Cut the pepper into strips, grate the carrots on a coarse grater, cut the onions and potatoes into cubes. Place in broth and cook for 15 minutes. Roll the cheese mixture into balls and drop them into the soup. Cook for another 15 minutes. When serving, sprinkle with chopped herbs.
Potato cutlets with sausages
Ingredients:
- potatoes - 7 medium-sized tubers;
- bulb;
- greenery;
- hard cheese – 200 grams;
- milk flask – 250 grams;
- eggs – 3 pieces;
- flour – 3 spoons;
- sour cream.
Preparation: boil potatoes, cool. Grind through a grater. Place grated cheese and diced sausage in it. Add flour, eggs, onion and flour. Form cutlets from the well-mixed mixture and cook in a double boiler. Serve with sour cream.
Puff omelette with potatoes in a steamer
Will need:
- boiled potatoes – 210 grams;
- eggs – 4 pieces;
- milk – 100 ml;
- spices to taste and herbs;
- a little bit of cheese.
The patient can be served a dietary omelet cooked in a double boiler.
Preparation: grate the potatoes, beat the eggs with milk, add salt. Cover the steamer bowl with cling film. Place a layer of potatoes, then pour in the omelette mixture and cover with grated cheese on top. Cook for approximately 25 minutes.
Useful tips
- A large number of fruits and vegetables, especially seasonal ones, are irreplaceable sources of nutrients with pronounced choleretic properties. For easy digestibility of the product, it is advisable to consume them in the form of fruit and vegetable juices.
- Vegetables in combination with vegetable oils stimulate the secretion production process well, so the patient’s diet should include vegetable salads and vinaigrettes with vegetable oil.
- High levels of vitamins B and C contained in vegetables and fruits improve the functionality of the gallbladder and liver, and are also an excellent prophylactic for preventing the appearance of stones due to their ability to accelerate the process of removing cholesterol from the body.
- It should be noted that when choosing fruits and berries, preference should be given to ripe fruits of sweet varieties (grapes and apples, citrus fruits (with the exception of lemon and lime with associated disorders in the gastrointestinal tract), pears, cherries and cherries, strawberries and raspberries, watermelons and melons) .
- Vegetables (beets, turnips, carrots, zucchini and pumpkin, fresh cucumbers and tomatoes, lettuce) promote bile secretion and prevent the development of constipation.
- It is allowed to eat legumes, potatoes and cabbage in cases where the patient does not have a tendency to increased gas formation in the intestines.
- You should not eat sour varieties of apples, lemons and limes, gooseberries, cranberries and other sour fruits, since their consumption can have an undesirable effect on the mucous membranes, which can lead to painful spasms.
- Some vegetables can negatively affect liver cells due to the content of essential oils (radish, radish, onion, and citrus zest) and oxalic acid (spinach, sorrel), so they should not be included in the patient’s diet. In addition, oxalic acid promotes the formation of stones.
- Marinades and fried vegetables are prohibited.
- To neutralize the aggressive effects on the digestive tract, it is advisable to consume vegetables and fruits together with other foods.
- As prescribed by a specialist, you can carry out fasting days, during which you need to adhere to a mono-diet: eat only one product of your choice: carrots, apples or another product during the day.
Diagnostics
One of the most reliable ways to detect cholestasis is to perform an ultrasound of the internal organs on an empty stomach. The device allows you to identify bile stagnation; a diagnostic assessment of the functioning of the gallbladder, ducts, and liver is also carried out. Cholestasis can be suspected if there is periodic pain in the right side, regular morning sickness on an empty stomach, and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth. Sometimes a biochemical blood test reveals indirect signs indicating cholestasis. In this situation, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase and liver tests are elevated.
Sample list of dishes for the day
Often patients make up their own diet, combining approved foods. For example, for breakfast they eat a steamed egg white omelette, pureed oatmeal, tea, for lunch - vegetable puree, rosehip infusion, for lunch - potato soup (half a serving), a baked apple, for an afternoon snack - liquid compote, and for dinner - cottage cheese pudding, drink. During the day, it is recommended to eat 200 grams of stale wheat bread and 40 grams of sugar. Doctors advise drinking at least 2 liters of water, rosehip infusion, freshly squeezed fruit juice or jelly. Before going to bed, additionally consume kefir.