The gallbladder is an important organ. His health and performance must be carefully monitored. People can be helped with this by deciphering the results of an ultrasound scan of the gallbladder to determine its function. Thanks to ultrasound, everyone can verify the health of their gallbladder and the ducts that connect to it.
Features of development and main provoking factors
Hydrocele in the gallbladder is a secondary lesion that is prone to long-term progression.
Due to gradual damage to the organ, pronounced symptoms may be completely absent. In most cases, the disease occurs against the background of existing pathologies of the gallbladder or its ducts. The danger of dropsy in this case is that it can lead to stretching of the organ and its subsequent rupture. This threatens with acute peritonitis.
Moreover, the formation of dropsy on the gallbladder impairs the functions of the organ and the digestive process as a whole.
The disease develops for the following reasons:
- Congenital pathologies of the structure of the gallbladder, which can manifest themselves in the form of a bend in the organ. This will interfere with the normal outflow of bile, causing stagnation.
- Mechanical compression of an organ. Can happen in an accident, fall, or blunt blow to the stomach.
- Cicatricial changes in the organ.
- The patient has cholelithiasis, which provokes the formation of stones in the bile ducts. If the pathology is not treated, it will begin to progress and provoke complications in the form of dropsy.
In addition, a previous acute or chronic infectious process (for example, cholecystitis) increases the risk of developing the disease.
As a result of the occurrence of such a lesion, the patient’s process of emptying the gallbladder is disrupted, which is why bile begins to accumulate in the middle of the organ and increases its volume. All this provokes rapid thinning of the walls of the gallbladder, and contributes to the formation of dropsy.
Remember! Those patients who suffer from frequent complications of cholecystitis and do not take any therapeutic measures are most susceptible to dropsy.
Causes of impaired anechoicity of the gallbladder
The organ is almost always filled with bile. Apart from it, there should be no other inclusions in the cavity. If bile is not visualized as an anechoic substance, this means that it also contains foreign formations. Then, lighter shades appear on the ultrasound screen against the background of the black spot.
Depending on the nature of the change in echogenicity, there may be:
- focal - most often it is a cluster of worms or stones;
- diffuse - represented by sediment, blood or pus.
Quite often, parasites settle inside the gallbladder. They are detected mainly in childhood. In addition to impaired anechoicity, the patient has the following symptoms:
- thickening of the walls caused by the inflammatory process;
- stagnation of bile caused by blockage of the excretory ducts by helminths;
- clusters of parasites are defined as bright formations.
In addition to ultrasound signs, the patient also develops a characteristic clinical picture. This is a deterioration in the general condition, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, the appearance of a yellow tint to the skin and mucous membranes.
The next reason for impaired echogenicity of the gallbladder is the formation of stones. They differ not only in chemical composition, size and shape, but also in origin. It is customary to distinguish the following types of stones:
The task of diagnosis is to identify the type of stone depending on the level of echogenicity. Weakly echogenic stones: such stones have a loose structure, which is typical for cholesterol varieties. Formations of this type are easily destroyed with the help of medications.
Symptoms
Hydrocele in the gallbladder can cause the following symptoms:
- sudden attacks of nausea and vomiting containing bile;
- increased body temperature;
- pain and heaviness;
- an increase in the size of the affected organ (may take on the appearance of a tumor);
- pain in the right side upon palpation.
A distinctive feature of this disease is that the above-described symptoms will intensify after the sick person eats fatty foods or exercise.
If you observe at least two of these symptoms, it is important to contact a specialist and conduct a full examination of the gallbladder.
Symptoms of the disease
In order to determine the presence of dropsy yourself, you need to know how this pathology manifests itself symptomatically. The information below will be useful to many:
- hepatic colic;
- aching and severe dull pain in the area of the right side, which radiates to the area of the shoulder blades and shoulder;
- fever, increased temperature;
- discomfort in the right hypochondrium;
- attacks of vomiting, nausea. The masses may be with bile;
- tense stomach.
Intensification of attacks is possible after eating fried, fatty foods, excessive shaking or sudden walking.
The pathology is of increasing symptomatology. It is possible that attacks will occur spontaneously and also pass abruptly.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hydrocele of the gallbladder should be differential, since the disease is easily confused with ordinary acute cholecystitis. In such a condition, the patient should seek examination and consultation with an experienced gastroenterologist.
After collecting anamnesis and examining the patient (palpation of the abdominal cavity), the doctor will prescribe the following mandatory studies to the person:
- Ultrasound examination;
- MRI;
- CT scan (can be performed as an alternative to MRI);
- cholecystography;
- diagnostic laparoscopy (in case of acute disease, the patient may have the affected organ removed during this operation).
Normal ultrasound examination of the gallbladder
The gallbladder looks like a pear. The organ has three parts:
- Bottom. Wide edge, slightly protruding beyond the liver tissue.
- Body. The main part of the bubble, acting as a storage device.
- Neck. The tapering part of the gall bladder through which accumulated bile is discharged.
The gallbladder is a hollow, sac-like organ that collects bile. An ultrasound examination is always performed on an empty stomach. This allows you to maintain the fullness of the organ necessary for a high-quality examination: the specialist gets the opportunity to assess the condition of the walls and liquid contents.
The following indicators are the norm for a healthy organ:
- pear shape;
- length – 8–14 mm, width – 3–5 mm;
- located inside the liver, only the bottom of the gallbladder is located outside;
- clear contours that do not have any violations;
- wall thickness – no more than 3 mm;
- the contents are homogeneous and anechoic.
Any disorder, including anechoicity, is recognized by doctors as a sign of the development of a pathological condition. Thickening of the walls of the organ occurs as a result of inflammation. With the development of cholelithiasis and pathological conditions accompanied by the formation of stones or other formations in the cavity of the gallbladder, it disrupts the anechoicity of bile. It becomes echogenic.
Medical therapy
Treatment of hydrocele in the gallbladder depends on the degree of advanced disease and the presence of complications.
If the patient has small dropsy, conservative drug therapy is used. It is aimed at improving the functions of the gallbladder, getting rid of unpleasant symptoms and normalizing the digestive system as a whole.
If the patient’s dropsy has reached a fairly large size (it is detected in most cases), then the patient is indicated for surgical intervention. This usually involves an operation called cholecystectomy.
It can be done in two ways:
- Open method. This is a traditional operation performed through an incision in the abdomen. Its advantages are a good overview and access to the affected organ. The disadvantages of such an open intervention are high trauma and a long rehabilitation period.
- Laparoscopic method. This is a modern method of surgery, performed through small punctures in the abdominal cavity. In this case, the surgeon sees the organ through a computer screen. The image is transmitted from micro-cameras built into the instruments.
Laparoscopic surgery does not require a long recovery period and heavy blood loss. This is an excellent method of surgical intervention that rarely causes complications.
Worth knowing! After the gallbladder is removed, it must be sent for histological examination.
During laparoscopic organ removal, the patient remains in the hospital for 4-5 days. Surgical punctures heal after 2-3 months.
After surgical treatment, patients are required to be prescribed the following groups of medications:
- antibiotics (taken to prevent infection for 7-10 days);
- probiotics (used to protect microflora);
- analgesics for pain;
- hepatoprotectors;
- drugs to improve bile flow;
- enzymes (prescribed to normalize the digestive system).
If dropsy is detected in an elderly patient with cirrhosis of the liver, he is recommended to refuse surgery and treat the organ by draining the gallbladder.
Remember! To prevent complications after surgery, the patient must be regularly monitored by a doctor and undergo tests. Self-medicating in such a condition is extremely dangerous.
Summing up
At the early stages of development, dropsy in the area of the gallbladder can be treated, and therefore at the first signs of pathology you should not delay a visit to a gastroenterologist.
You can also contact a therapist who will consider the patient’s complaints and refer him to a specialist.
It is possible to avoid the need for cholecystectomy if you follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Remember that it is much better to prevent all pathologies than to then waste your time and energy on their treatment.
You need to be more attentive to your health, not resort to self-medication, but listen to the opinion of a competent doctor.
Diet food
The duration of the postoperative period is 1-3 months. During this time, the patient is advised to adhere to the following dietary rules:
- Avoid fasting.
- Eat 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- Avoid overeating, as this will disrupt the flow of bile and provoke a spasm.
- Dinner should be 2 hours before bedtime.
- Dishes must be served at the optimal temperature (not too cold or hot).
- It is important that food is served crushed or pureed.
- Low-fat fermented milk products should be present on the menu every day.
- Dishes should be prepared without adding salt. In this case, it is allowed to add healthy oils (olive, sunflower) to the porridge.
- Drink at least 2 liters of water per day, not counting medicinal herbal decoctions and soups.
- Reduce the number of calories consumed if you are overweight.
- Dishes need to be steamed, boiled or baked. Any fried foods are strictly controlled.
- You should eat slowly, chewing your food thoroughly.
The basis of the diet in such a state should be vegetable soups, cereals, boiled meat dishes (meatballs). Steamed omelettes, dishes of boiled vegetables, and fermented milk products will also be useful.
For dessert, you can serve diet cookies, jam, preserves or honey.
Prohibited Products
Dietary nutrition includes avoiding the consumption of the following foods:
- fatty meats (morning, pork, lamb) and fish;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- any alcoholic drinks;
- sausages;
- salty fish;
- smoked meats;
- pickled vegetables;
- rich broths;
- coffee;
- fatty dairy products;
- mayonnaise;
- onion and garlic;
- sweets (cakes, candies, chocolate);
- fresh bakery;
- mushrooms;
- legumes;
- juices purchased.
Treatment
In situations where hydrocele of the gallbladder of small volumes has been detected, conservative therapy can be used, which requires regular monitoring of the size of the hydrocele and the condition of the affected organ. But, in the vast majority of situations, surgical intervention is indicated - cholecystectomy. There are several ways to perform this treatment:
- open - through a large incision on the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. This method has recently been used extremely rarely, due to the emergence of other surgical techniques;
- mini-access – the operation is performed through a mini-incision in the abdomen;
- laparoscopic - used most often.
After removal, the gallbladder undergoes histological examination. Culture of the contents is not informative, since it is often sterile. Morphological studies also do not indicate any changes of an inflammatory nature.
The postoperative period lasts from one to three months. At this time, it is necessary to adhere to bed rest and a special diet. Diet treatment involves avoiding:
- spicy and fatty foods;
- carbonated and alcoholic drinks;
- marinades, smoked meats and other irritating products;
- herbs and spices;
- rich broths.
It is best to eat in small portions, six times a day. Food should be boiled or steamed, and the products should be thoroughly chopped. In addition, you should not eat extremely hot or extremely cold foods.
Also, after the operation, you will need to take antibiotics and hepatoprotectors, antispasmodic medications, as well as products containing pancreatic enzymes.
Forecast
The prognosis for hydrocele of the gallbladder is individual for each patient and largely depends on the timely detection of the disease.
If a person begins treatment therapy immediately after diagnosis and follows all medical recommendations, his prognosis will be favorable.
Negative consequences can develop in the following cases:
- failure to see a doctor in a timely manner, which led to organ rupture;
- the patient has additional chronic diseases that complicate his condition;
- long-term asymptomatic course of the pathology, which led to severe damage to the organ;
- internal bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract and peritonitis.
What to do
You don't have to do anything special. At least until a full and detailed diagnosis is carried out with a precise determination of the nature of this content. If it is just a liquid, it may dissolve over time. If this is some kind of neoplasm, it must be checked by a doctor using various manipulations available to him, including invasive ones.
It is not possible to cure anechoic contents on your own - no one has come up with tablets or mixtures for it and no one is going to come up with them.
Anechoic contents can be marked and viewed on a transmission ultrasound image in different organs: gallbladder, uterus, ovaries, etc. There is no pattern.
Prevention
Hydrocele in the gallbladder, the course of treatment of which is selected for each patient individually, is considered an extremely dangerous disease with a high risk of complications.
To reduce the risk of developing this condition, it is important to adhere to the following preventive recommendations:
- Treat cholecystitis in a timely manner, since in most cases it is the main cause of the formation of dropsy. It is extremely dangerous to start such an inflammatory process, since then the disease can become chronic.
- Carefully select food products. It is advisable that the dishes are not too spicy or fatty. It is better to give preference to dietary dishes made from vegetables, lean meat and water-based porridges.
- Regularly consume fermented milk products that are healthy for the digestive system.
- Every six months, undergo a preventive examination by a gastroenterologist and perform an ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. When any abnormality or inflammatory process is identified, it is important to immediately approach its treatment, since damage to one organ of the gastrointestinal tract can spread to a neighboring system through a chain reaction. This is especially true for liver and stomach diseases.
- Stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Lead an active lifestyle, as it significantly reduces the risk of gallstones. It doesn't have to be a professional, grueling sport. Daily walking or cycling will be excellent helpers to keep the body in good shape.
- Eat small meals at the same time every day. It is also important to eliminate the habit of eating at night.
- Avoid stress, unnecessary worries and nervous tension.
- Monitor your weight and avoid obesity. If such a problem already exists, it is important to find an experienced nutritionist who can choose the right diet for the patient. It is important to understand that fasting or following too restrictive diets is irrational, and can only aggravate a person’s condition. Safe weight loss is considered if you lose 0.5 kg per week, no more.
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Causes
During normal functioning of the biliary system, bile from the bladder enters the duct and is excreted into the intestine. However, under the influence of a number of factors, this physiological process is disrupted.
The root cause of the development of dropsy is the fact that the flow of bile from the bladder into the duct ceases. This deviation from the norm can be provoked by the following factors:
- stone migration and obstruction of the bile duct in cholelithiasis;
- formation of scar changes in the lumen that interfere with the normal flow of bile;
- congenital anomalies in the structure of the bile flow (its excessive tortuosity, bends);
- compression of the duct lumen by formations (tumors, adhesions, etc.) from the outside.
The following fact can contribute to the development of the disease discussed in this publication: the bile duct has a peculiar structure - it is located in the thickness of the hepatoduodenal ligament and is shrouded in connective tissue on all sides. The lumen of the duct is very thin and its diameter is no more than 3 mm. The length of this part of the biliary system usually reaches 3-7 cm. Such structural features of the common bile duct indicate the possibility of fairly rapid obstruction of its lumen due to various pathological disorders.
- The theories of researchers suggesting the possibility of developing such a condition with the infectious onset of the disease are very vague. After all, all analyzes of the pathological contents of the affected duct did not end with identifying signs of the presence of infections.
- However, other scientists still question the fact of non-inflammatory damage to the walls of the duct, since in the process of experiments on ligation of the duct they only received the result of atrophy of the organ, and its dropsy did not develop.
- Summarizing all the research data, we can conclude that for now it is impossible to be completely sure that dropsy is provoked only by partial or complete blockage of the bile duct, and a previous infection (for example, cholecystitis) still plays a certain role in the development of this problem. diseases.
Sometimes the process of bile secretion is disrupted immediately after the first attack of colic, and the patient develops hydrocele. The bile remaining after compression of the duct in the organ cavity is absorbed, and the cystic epithelium begins to produce mucus and exudate. These fluids gradually accumulate in the cavity and stretch the bladder walls. Over time, they become thinner, and the bubble itself stretches in length and resembles a cucumber in appearance. Next, the organ expands in the bottom area and becomes like a pear. After repeated biliary colic and cholecystitis, the walls of the hydrocele-affected bladder become thicker, the layers loose, and the folds of the mucous membrane dense.
Diagnosis of hydrocele of the biliary organ
Diagnosis of the disease begins with an initial interview of the patient, collecting anamnesis, studying symptoms, visual examination with palpation of the abdomen and right hypochondrium. Due to the fact that pathological processes involving the accumulation of fluid and mucus in the bladder are not detected by blood and urine tests, laboratory tests are usually not prescribed.
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, various instrumental research methods are used:
- X-rays with contrast agents injected into the abdominal cavity can reveal an increase in the size of the biliary bladder, but the cause cannot be determined. It is also possible to detect a change in the shape of the duodenal intestine - depressions form on it due to compression of the intestinal walls by the enlarged bladder.
- Ultrasound of the liver and bladder indicates the presence of dropsy.
- CT and MRI of the bile-producing and bile-excreting organs make it possible to determine the cause of obstruction of the ducts in the presence of stones, adhesions or tumors, the degree of damage and thinning of the gallbladder.
- The most accurate information about dropsy is provided by laparoscopic examination by inserting a mini-camera (laparoscope) into the peritoneal cavity. At the same time, the full diagnostic picture is clearly visible: the degree of damage to the walls of the gallbladder, the presence of exudate in it, the size of the organ enlargement.
- Narrowing or obstruction of the bile ducts is determined by cholecystography or cholangiopancreatography, when a contrast agent is injected into the bile ducts.
- Stones and other causes of blockage of the ducts are clearly visible during choledochoscopy.
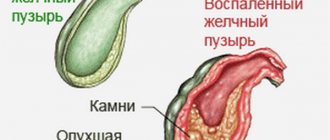
Complications of gallstone disease
The appearance of stones is not always noticed. Gallstone disease is divided into a number of stages, the first being latent. The causes of complications lie in the disruption of bile acid metabolism. There is poor digestibility of fatty foods and indigestion. A number of conditions have been described, identified by doctors into special families.
Acute inflammation of the gallbladder
Cholecystitis in 90% of cases develops against the background of the presence of stones. Elderly seriously ill patients have a high mortality rate. Acute inflammation is divided by type into:
- Gangrenous.
- Phlegmonous.
- Catarrhal.
The process is preceded by an increase in the internal pressure of the organ to 300 mm. Hg Art. The disease is accompanied by a violation of the outflow of bile and the appearance of specific biochemical signs. The process is suppressed by ibuprofen and indomethacin. In two thirds of cases, this is accompanied by bacterial growth, mainly caused by anaerobic strains of microbes. The formed cycle does not allow the patient to get out of the situation on his own.
At the initial stage, colic is pulsating in nature (visceral), then it becomes constant (somatic), the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes (precipitated) in the blood increases. As a result of the symptoms, the temperature often rises, and in some cases a jaundiced skin color is noted. When palpated, the muscles of the right side of the hypochondrium are noticeably tense, the bladder is enlarged. The situation worsens with gaseous cholecystitis, and is more common in males with diabetes.
Clinical symptoms in older people often do not correspond to the actual picture of inflammation. Especially with the development of gangrenous changes in the bladder wall. When the nerves die, a period of temporary well-being begins. Additional tests are prescribed, for example, ultrasound. Ultrasound allows you to determine the presence of gases in the cavity formed by bacteria.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder
Sometimes the gallbladder becomes twisted and the blood supply is disrupted. The pain is constant and radiates to the back. Occurs more often in older, skinny women. The condition is accompanied by dyspepsia, mostly nausea and vomiting. There are cases when, after dissolving stones, it was possible to straighten the walls using electrophoresis with novocaine. Signs often resemble:
- Pancreatitis.
- Appendicitis.
- Ulcer.
- Liver abscess.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Pneumonia on the right side of the lungs.
- Urolithiasis.
- Pleurisy.
Differential diagnosis is required.
Complications of cholecystitis
In addition to the development of cholecystitis against the background of stones, the disease is accompanied by complications. For example, perforation (breakdown) of the wall of the gallbladder with the simultaneous onset of inflammation caused by the contents getting into neighboring organs. Paravesical abscess is more common, accompanied by a number of characteristic clinical signs:
- Chills.
- Temperature.
- Sweat.
- Weakness.
- Cardiopalmus.
- The bladder is enlarged and sharp pain occurs on palpation.
Cholecystitis manifests complications in the form of cholangitis and reactive hepatitis. As a result, bilirubin is practically not excreted, and intestinal bacteria appear in hepatocyte cells. Blood from the portal vein is almost not filtered, poisoning the body. Most often found in bile:
- E. coli.
- Proteus.
- Klebsiella.
- Streptococci.
- Clostridia.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
It turns out, mainly representatives of the facultative flora in full. Many microorganisms move into the liver. In a similar way, gallstones lead to intoxication of the body. Diagnosis of cholangitis is carried out according to the triad of Charcot criteria:
- Fever with chills.
- Slowly growing jaundice.
- Pain in the right side.
Complications of cholecystitis include acute pancreatitis.
Acute pancreatitis
Empyema and dropsy
Complete blockage of the ducts causes dropsy. This happens after an acute attack of cholecystitis. The consistency of the bile changes sharply with inflammatory exudate, the bladder fills with bile, the walls become stretched and sharply thinner. It is typical that at the first manifestation of the disease there are no complaints. In case of relapses, patients complain of dull pain in the right hypochondrium. The swollen bladder is soft to the touch and moves slightly to the sides.
If an infection gets inside, pus accumulates. And dropsy develops into empyema. The symptoms resemble a systemic inflammatory response in form.
Cholangiolithiasis
On average, this complication is observed in 15% of cases in the population; in old age, the percentage increases to one third of the number of patients. The syndrome consists of the appearance of stones in the bile ducts. Cholesterols are formed exclusively in the bladder; the presence of similar ones outside the organ is explained by migrations (caused by any reasons). The condition is dangerous due to the possibility of blocking the duct completely with the development of obstructive jaundice:
- Jaundiced skin.
- Itching.
- Enlarged liver.
- Urine the color of beer.
- Colorless feces.
Older people periodically develop black pigment stones. The formation is accompanied by alcoholism, hemolysis or cirrhosis of the liver. Brown stones are the result of the activity of harmful bacteria.
The process develops in a third of cases of surgical intervention in the extrahepatic ducts. The relapse rate reaches 6.
Scar strictures
When scars heal, the process is disrupted. The causes of the phenomenon lie in the specific action of bile or the presence of infection. When a gallstone passes, the formation is mechanically capable of disrupting normal healing. Defects of this kind are divided into:
- Secondary inflammation.
- Consequence of sclerosing cholangitis.
- Post-traumatic strictures (up to 97% of all cases).
- Defects of biliary anastomoses.
Most accidental injuries relate to gastric surgery. When the gallbladder is removed, a complication develops in approximately 0.2% of cases. The defeat can be strong or weak. Accordingly, the level of stricture is classified as high or low. The degree of narrowing of the duct due to tissue proliferation is:
- Full.
- Incomplete.
Strictures are usually divided by length into:
- Total (full length).
- Subtotal (longer than 3 cm).
- Common.
- Limited (less than 1 cm).
Above the stricture, the walls of the ducts thicken, and below they are replaced by fibrous tissue. The key manifestation is obstructive jaundice (see above).
Secondary cirrhosis caused by bilirubin
The condition is caused by extrahepatic cholestasis, a condition of reduced bile flow into the duodenum that is independent of hepatocyte function. Develops as a consequence of cholecystitis or cicatricial strictures.
As a result of such a course of cholelithiasis, obstructive jaundice may occur. Absorption of fat-soluble vitamins is impaired in the intestines. The liver and spleen are enlarged. The condition develops into liver (or kidney) failure syndrome.
Biliary fistulas
An underlying stone sometimes causes necrotic changes, and cholelithiasis is complicated by perforation of the bladder walls. The clinical picture does not allow us to identify the defect. An indirect sign will be a sharp subsidence of pain (as a result of the release of the contents of the bladder through the resulting hole). Sometimes there is profuse vomiting of bile, along with which stones come out if the formations manage to squeeze through. Ingestion of infection from the intestines leads to inflammation.
Manifestations of dropsy
Often the disease develops after an inflammatory process. The appearance of dropsy is preceded by pain in the liver.
Small-sized dropsy is difficult to detect, since it does not appear in any way. Enlargement of the gallbladder to impressive volumes is expressed by pain in the liver area. The patient is bothered by aching, moderate, dull pain. The pain radiates to the shoulder, shoulder blade, and spreads to the back.
A large bubble can be felt as a dense, elastic formation. It is located along the lower edge of the ribs and is usually motionless. The abdominal wall in this place is tense. In addition to pain, the patient may have other symptoms:
- nausea, vomiting mixed with bile;
- spasms, colic and pain in the intestines;
- constant heaviness in the liver area;
- deterioration of the condition after a diet violation;
- sometimes fever.
Such manifestations are also characteristic of other diseases of the hepatobiliary system. Instrumental studies are required for diagnosis.
Why is mucocele dangerous?
The disorder in question provokes complications that are life-threatening for the patient. Therefore, it is extremely important to identify this condition promptly and begin to treat it correctly. Consequences that can be caused by dropsy:
- Cholecystitis can rupture, and this is very dangerous. This process leads to bleeding, as well as the rapid development of peritonitis.
- Cholecestis may not rupture, but greatly increase in size. As a result, its walls, under the influence of stretch marks, will become covered with microcracks. Then its contents leak into the peritoneum, and acute peritonitis develops.