Treatment of diseases of the pancreas and liver involves not only taking medications, but also following a diet that excludes foods that negatively affect organs with impaired functioning. Despite the strictness, a special diet promotes good absorption of nutrients and prevents exhaustion of the body.
Diet for the pancreas and liver
When is a diet necessary?
You need to start following a diet after you suspect a disease of the pancreas or liver, without waiting for a specialist diagnosis. Correcting your diet, which involves switching to proper nutrition, excluding the consumption of hard-to-digest and harmful foods, will in any case have a beneficial effect on the body.
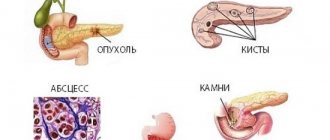
Diseases of the liver and pancreas can be recognized by a number of symptoms:
- bowel problems (frequent constipation or diarrhea);
- bloating;
- distortion of taste;
- changes in appetite;
- pain in liver diseases - in the right abdomen, in diseases of the pancreas (on the left or surrounding);
- general deterioration in health (lethargy, fatigue, etc.).
Liver and pancreas
Attention! In most cases, jaundice is observed in cases of liver dysfunction. It is not a separate disease, but a symptom consisting of yellowing of the sclera and skin.
Who is prescribed dietary nutrition?
Healthy foods for the liver and pancreas will smooth out the activity of organs, reduce blood pressure, and eliminate painful discomfort and a feeling of heaviness.
Table No. 5 is required for patients with such diseases of the digestive organs.
- Pancreatitis.
- Hepatitis of various types.
- Cholecystitis.
- Gastritis.
- Cirrhosis of the liver.
A therapeutic diet can have a beneficial effect in the presence of pyelonephritis.
Such diseases of the liver and pancreas develop due to various factors:
- infection of the body;
- intake of harmful foods;
- independent therapy;
- frequent drinking of alcohol;
- smoking;
- heredity;
- other.
smoking causes liver and pancreas diseases
The pancreas and liver are considered the largest digestive glands, which ensure the normal functioning of the body.
In the case of poor nutrition and an unfavorable lifestyle, their performance is impaired and will begin the formation of pathologies of acute and chronic manifestations.
To avoid the occurrence of problems in an already affected organ, you need to follow a therapeutic diet for liver and pancreas diseases; it is not difficult to prescribe a menu for the week.
Such a measure is necessary, because when the activity of the pancreas and liver changes, the consumption of medications exerts auxiliary pressure, and, in general, does not bring the desired outcome. The functionality of the organs is closely related, and following a therapeutic diet will be reflected in a beneficial way on both organs.
A diet for problems with the liver and pancreas can be prescribed both for treatment and as a prevention of exacerbations. Eating foods that are healthy for the liver and pancreas normalizes the function of these organs. The diet perfectly relieves the feeling of heaviness in the hypochondrium and pain.
Nutrition for diseases of the liver and pancreas requires compliance with food restrictions in accordance with dietary table No. 5, which is indicated for:
- hepatitis of various etiologies;
- pancreatitis;
- inflammation of the gallbladder;
- gastritis;
- liver cirrhosis;
The main factors influencing the development of liver and pancreas diseases are:
- genetic predisposition;
- poor nutrition;
- infection of the body;
- self-medication and, as a result, uncontrolled use of medications;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking.
Symptoms at the initial stage are mild and can occur both with a diseased liver and with inflammation of the pancreas. They appear:
- discomfort in the hypochondrium;
- stabbing and/or aching pain localized in the hypochondrium;
- skin rash;
- periodic nausea;
- increased gas formation;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- general weakness.
The symptoms of liver and pancreas diseases in women require a separate comment. It is closely related to hormonal metabolism. As a rule, the pain syndrome in women is more severe than in men: the pain radiates to the back, hypochondrium, upper abdomen and has a girdling character. It is also accompanied by such characteristic symptoms as a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, and vomiting.
The onset of diseases of the liver and pancreas often occurs during pregnancy, when the organs are under increased stress associated with the development of the fetus. At the initial stage of the disease, a woman feels:
- drowsiness;
- loss of appetite;
- pain in the hypochondrium;
- nausea with a bitter taste in the mouth;
- chills;
- temperature rise to subfebrile (from 37.1o to 38o), indicating inflammation.
Treatment methods for diseases of the liver and pancreas may be different, but the diet, regardless of the nature of the therapy, must be prescribed by a doctor.
https://youtu.be/VpFxLyEFojw
Basic principles of the diet
A special diet followed for diseases of the pancreas and liver has several effects:
- Reducing the load on the digestive system. The effect is achieved by eliminating “heavy” foods from the diet.
- Removing toxins and preventing them from entering the body. When following a diet, it is necessary to consume large amounts of liquid foods and drinks that help cleanse the organs, and avoid foods with carcinogens and other harmful substances.
Diet for diseases of the pancreas and liver
Important! With the help of a special diet you can speed up your metabolism. Activation of the process is achieved through the consumption of predominantly natural plant and fermented milk foods, which are easily digested and do not cause stomach upsets.
Principles of diet for organ dysfunction
Diseases of the liver, such as hepatitis and cirrhosis, or of the pancreas, such as pancreatitis, can change how the body absorbs nutrients from food. A special diet should provide a person with the amount of calories, vitamins, minerals and fluid necessary to eliminate the symptoms of the disease. It is recommended to prepare the diet together with a nutritionist, depending on the type of disease. To do this you need:
- Before you start following a diet, you should consult a specialist. Recommendations may vary depending on test results, the condition of the organ, and the presence of underlying health problems (for example, obesity).
- Increase your intake of carbohydrates and proteins. Liver disease is a general term for a range of dysfunctions of this organ. The liver is responsible for protein synthesis and the production and storage of cholesterol from carbohydrates. It is recommended to consume about 1 g of protein per 1 kg of body weight. In this case, you should limit the amount of sodium (salt) in your food and take vitamin supplements, in particular, a B complex.
- Add foods containing folic acid, lycopene and healthy fats to your diet. Diseases contribute to the deterioration of the pancreas, which produces insulin. This hormone plays an important role in the process of digestion and metabolism. Substances such as folic acid, found in leafy greens, pasta, beans, and lycopene, available in tomatoes, as well as fats obtained from olive oil, can help the pancreas do its job.
Forbidden food
Some foods that are familiar to the body cause disruptions in the digestion process, as they put a serious burden on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to the high content of chemicals, fats and hard-to-digest carbohydrates in them.
Do's and don'ts for pancreatic and liver diseases
For diseases of the liver and pancreas, you should avoid:
- Any fatty food. The group includes not only dishes made from lamb, pork, mackerel, halibut, etc., but also sweets made from cooking fats (cakes, cakes, biscuits). It is also recommended to exclude fatty dairy products (fat milk, soft cheeses, cream).
- Any kind of baking. This includes confectionery and soft white baked goods.
- Fast food. “Fast food” is full of flavor enhancers, harmful additives of synthetic origin and fats.
- Strongly salted foods. Eating chips, crackers, homemade pickles, etc. is fraught with a violation of the water balance in the body.
- Products saturated with synthetic additives. Coloring substances, flavor enhancers and other components of chemical origin are poorly absorbed and harm the digestive system.
- Smoked meats. Also, you should not eat marinades or any preserved food.
- Vegetables that stimulate the production of bile. Tomatoes, sorrel, rhubarb, green onions and celery should be avoided.
- Gribov. They cannot be eaten even after heat treatment.
- Bobov. You should not eat either fresh legumes (corn, etc.) or cereal dishes (pea porridge, etc.).
- Seasoning When preparing dishes, you can only use salt in small quantities.
- Sauces and vinegars. Mayonnaise, ketchup, mustard - all this must be excluded from the diet.
- Alcohol. Alcohol-containing drinks of any strength are strictly prohibited.
- Carbonated drinks. In addition to them, you should not drink coffee, strong tea, packaged juices and compotes.
Prohibited Products
Egg yolks should not be consumed either. Proteins are acceptable, but no more than two servings maximum twice a week.
Important! It is necessary to limit the consumption of sour fruits and berries, as they irritate the mucous membranes of the digestive organs. If you have increased stomach acidity, you need to avoid them.
What diet is prescribed for diseases of the pancreas and liver
In order to restore the impaired functions of the bile ducts and liver, a therapeutic diet No. 5 is prescribed. Depending on the pathology of the hepatobiliary system and its stage, modifications of the dietary table are prescribed, which differ in the chemical composition of the diet and energy value.
Small changes in the basic diet N o 5 can speed up or slow down bile secretion. All diet options involve mechanical sparing of the digestive tract, which means that products with coarse fiber are excluded from the menu. Some diet options require chemical sparing, so a number of foods that can enhance the production of hydrochloric acid and enzymes are excluded.
If you have a disease of the liver and pancreas, you need to eat often, but in small portions, so that the receptors responsible for the production and secretion of bile are irritated. Basic diet No. 5 will be prescribed for chronic inflammation of the liver and gallbladder, cholelithiasis, and also after relapse of hepatitis.
The diet not only removes the functional load from the gland and helps improve bile secretion, but also provides mechanical sparing of the digestive tract, which is often involved in the pathological process. The calorie content of the daily diet should be no more than 3100 kcal.
The patient’s body should receive 100 g of proteins, 100 g of fats and 450 g of carbohydrates, the amount of table salt should not exceed 10 g. When drawing up the menu, daily doses of necessary microelements and vitamins (carotene 10.5 mg, thiamine 2 mg, riboflavin) should be taken into account 4 mg, vitamin PP 20 mg, ascorbic acid 200 mg, calcium 0.8 g, magnesium 0.5 g, phosphorus 1.6 g, iron 15 mg).
In case of acute hepatitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, angiocholitis, as well as during their relapse, diet No. 5A is prescribed. It minimizes the load on the hepatobiliary system so that the functional state of the glands, gallbladder and ducts, intestines and stomach is normalized. It implies not only mechanical sparing of the gastrointestinal tract, but also chemical.
Diet N o 5A reduces the recommended intake of fats to 70–80 grams and carbohydrates to 350–400 grams, the protein content in the daily diet remains within 80–100 grams. The calorie content of the diet should be 2300–2500 kcal. Despite the reduction in the amount of food consumed, the content of vitamins and minerals remains the same as in diet No. 5.
After removal of the gallbladder, an even stricter diet of N o 5Sh is prescribed. It should ensure complete liver sparing and reduce bile production. Vegetable fats are completely excluded from the patient’s diet, and the consumption of simple carbohydrates is also limited to 30–50 grams per day.
The chemical composition of food is approximately the following: proteins 90–100 g, fats 50–60 g, carbohydrates 300–350 g. In the postoperative period, the daily intake of minerals and vitamins decreases, with the only exceptions being iron and ascorbic acid. Thus, the patient should receive daily retinol 0.3 mg, carotene 6.7 mg, thiamine 1 mg, riboflavin 1.5 mg, nicotinic acid 13 mg, vitamin C 200 mg, sodium 3.7 g, calcium 0.3 g, potassium 2.8 g, phosphorus 1.2 g, iron 50 mg.
If, after cholecystectomy, bile stagnation syndrome with reduced motility of the biliary tract has developed, then diet No. 5F is indicated. It promotes bile secretion and has a lipotropic effect (burns fat), since it introduces complete proteins and polyunsaturated acids into the diet.
The chemical composition of food in diet N o 5Zh is the same as in diet N o 5, only the amount of fat is increased by 20–30 grams, half of which should be of plant origin. The calorie content of foods should not exceed 3400 kcal per day.
When the inflammatory process in the pancreas worsens, the N o 5P diet is prescribed, which has two options. First, it is recommended to eat a diet that helps relieve pain and reduce the load on the pancreas, as well as reducing reflex excitation of the gallbladder. This diet involves chemical and mechanical sparing of the tract and for the first day calls for abstaining from food altogether.
You can adhere to therapeutic nutrition according to this diet for no more than a week. The patient should limit the intake of proteins (up to 40–80 g), fats (up to 40–70 g) and easily digestible carbohydrates (total carbohydrates 200 g), as well as salt (no more than 8 g). Unlike other diet options, it requires eating only pureed dishes and foods. The total daily caloric intake is 1300–1800 kcal.
The second option of the N o 5P diet is prescribed after acute pancreatitis has subsided and when the inflammatory process is not very pronounced. In addition to boiled food, fried foods are allowed, but all of them must be pureed. The chemical composition of food should be as follows: proteins 120 g, carbohydrates 300–350 g (simple ones are limited), fats 70 g. The calorie content of the diet is up to 2500 kcal.
Healthy food
When choosing foods that have a beneficial effect on the digestive organs, you need to choose proteins and easily digestible carbohydrates. When following a diet prescribed for the treatment of diseases of the liver and pancreas, it is recommended to consume:
- Vegetables. It is advisable to steam them, bake them or make soups from them.
- Fruits. It is recommended to eat them raw or steamed.
- Low-fat dairy products. Fermented milk products are especially beneficial for the microflora of the digestive organs. You need to include kefir, yogurt and Varenets in your diet.
- Cereals. The longer you cook buckwheat, millet or oatmeal, the better it will be digested.
- Dietary fish and meat. Perch, navaga, turkey, young veal - these products fill the body with the necessary amount of fat, but do not cause an excess of it.
- Bakery products of the second or third grade. You can eat black or dry white bread. Baking from dough without yeast is acceptable.
- Healthy drinks. These include jelly, green tea, still mineral water and natural juices without various additives. It is advisable to drink plain water after boiling.
Liver Pancreas Diet
Attention! Oils can be added to food only in small quantities. When preparing dishes, it is better to use butter than sunflower oil.
Diet for acute diseases
A healthy diet for acute pathological processes in the digestive organs is aimed at restoring damaged tissues, cleansing the liver of toxins, its goal is to relieve the diseased organ. In case of acute hepatitis and pancreatitis, diet No. 5A is prescribed, which both adults and children must adhere to. It means:
- exclusion of all fried, smoked, salted products,
- active use of low-calorie cottage cheese, boiled lean, finely chopped meat (chicken, turkey, rabbit, beef), as well as the inclusion in the diet of meat souffle, steamed cutlets, meatballs,
- vegetables, steamed or boiled,
- dried wheat bread, biscuits,
- viscous semi-liquid porridges made from rice, buckwheat, oatmeal,
- fresh grated fruit.
The following dietary requirements must be observed:
- Vegetables and cereals should be boiled until pureed.
- The diet allows no more than 6-8 g of salt per day, from fats - vegetable, they make up 20%, proteins - 60%, the rest - carbohydrates. Margarine and mayonnaise are excluded.
- The amount of liquid required is 2.5 liters.
A week of such restrictions will lead to a relative improvement in the condition.
Useful tips
Before drawing up the menu, you need to take into account a number of recommendations from experts:
- Cook until a crust appears. This applies to baking meat, fish and vegetables. You can only simmer in a frying pan; fried foods should be avoided. Steaming and boiling are suitable cooking techniques.
- Consume food immediately after preparation. The fresher the product, the less likely it is to cause digestive disorders.
- Consume food warm. Avoid cold and too hot foods.
- Try to eat small meals as often as possible. The optimal number of meals per day is 5-6.
- Keep an eye on your water balance. Drink as much as your body requires and stay hydrated.
- Don't overeat. If you have problems with excess weight, you need to reduce your usual portion size.
- Consume maximum food before hours of peak physical activity and do not overeat before rest. Eat most of your daily food intake at breakfast and lunch. Have dinner lightly and no later than 4 hours before bedtime.
- Make your diet varied and balanced. Giving up the usual tasty but unhealthy food is stressful for the body. To make it easier for him to tolerate it, it is necessary to prepare dishes from different fruits, vegetables, seafood and meat. It is important to maintain a balance, that is, to consume foods of both plant and animal origin.
Prohibited foods for pancreatitis
Attention! It is necessary to take into account not only the beneficial properties of products, but their tolerance to the body. If the recommended food causes an allergic reaction, stomach upset, etc., it must be excluded from the diet.
Products useful for cleansing the liver
What is good for the liver if there are already problems? With proper nutrition, the development of liver diseases can be avoided if you know which foods help cleanse the liver. Let’s pay attention to them and include them in our diet more often.
Apples
Apples have a slight choleretic property, so they are very useful for the gallbladder, preventing stagnation of bile, the development of cholelithiasis and cholecystitis. For the liver, it is best to eat sweet apples, raw or baked, two apples a day.
Green tea
Green tea is extremely beneficial for the liver; it contains antioxidants that help the liver neutralize harmful substances and remove toxins from the body. Green tea is preferable to black tea, as it also has an antitumor effect.
Grapefruit
Grapefruits, like green tea, contain a large amount of antioxidants, which means that this sunny fruit also helps the liver with its cleansing properties. Grapefruits reduce cholesterol levels, improve appetite and digestion.
Quote: Grapefruits do not combine with medications, so they should never be eaten if you are taking medications.
Flax seeds
Flax seeds contain a large amount of fiber, which helps remove harmful substances from the human body. Flaxseed is also rich in minerals and omega-3 fatty acids, which are very important for the prevention of vascular and heart diseases, and cancer.
Cabbage
Any cabbage is good for the liver - white cabbage, Peking cabbage, cauliflower or broccoli. Cabbage is high in vitamin C and antioxidants, making it good for the liver. But if your liver problems are serious, then consult your doctor about sauerkraut, as it may be too heavy a food for a diseased liver.
Pumpkin
Levocarnitine, a substance similar to a vitamin, is found in pumpkin pulp, which improves the absorption of fats, thereby relieving the liver, and also participates in protein and lipid metabolism.
Beet
Beets are extremely beneficial for the liver; be sure to include them in your diet, prepare borscht, vinaigrettes, and add to salads. Beets enhance the secretion of bile, improve fat metabolism, and remove excess fluid and heavy metal salts from the body.
Garlic
Garlic activates liver enzymes and cleanses the body of toxins. The compounds allicin and selenium in garlic support the cleansing process and protect the liver from toxic damage. Regular consumption of garlic reduces cholesterol and triglyceride levels, which can interfere with the liver's functioning.
Walnuts
Walnuts contain a lot of unsaturated fatty acids, which do not contain cholesterol and even help the body remove its excess, which serves as a good prevention of atherosclerosis. 3 to 5 walnut kernels per day are enough to improve liver function, strengthen the immune system and become more resilient.
Greenery
Leafy greens are extremely beneficial for the liver, it cleanses it of toxins and promotes its proper functioning. Leaf and head lettuces, parsley, celery, dill should be included in your diet all year round; this is beneficial not only for the liver, but also for the whole body. And we can grow greens on our windowsill all year round.
What else is good for the liver? I suggest watching the video “12 products that cleanse the liver themselves.”
Sample menu
The table shows an approximate diet menu that is useful for diseases of the liver and pancreas. These products can be replaced with analogues.
| Day | First breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| 1 day | Rice porridge with banana, green tea | Sandwich with cheese, kefir | Broccoli soup, buckwheat porridge with baked turkey, bread, apple juice | Cottage cheese with raisins, yogurt | Baked vegetables with cod, bread, still mineral water |
| Day 2 | Steamed egg whites, bread, varenets | Apple | Fish soup, mashed potatoes with steamed chicken wings, bread, peach juice | Oatmeal cookies, green tea | Rice with boiled squid, bread, carrot and apple salad, rose hip broth |
| Day 3 | Oatmeal with apricot, green tea | Kefir | Vegetable soup, buckwheat porridge with stewed veal, bread, carrot juice | Savory pear pie | Barley porridge with boiled turkey, beetroot and apple salad, bread, green tea |
Attention! Before creating a menu, you should consult your doctor. The specialist will take into account the peculiarities of the course of the disease and, if necessary, make adjustments to the selected diet.
Video - Super food for the liver
Simple and healthy recipes
During the absence of symptoms of the disease, you can use simple but safe recipes that will not worsen the condition or aggravate the inflammatory process.
Pumpkin and oatmeal soup
- 100 g pumpkin,
- 2 tablespoons oatmeal,
- 0.5 teaspoon butter.
Boil pumpkin, cut into cubes, until half cooked, transfer to a frying pan, mix with oatmeal, butter and pumpkin broth. Under a closed lid, simmer over low heat for 30 minutes, then add more pumpkin broth and sugar to taste.
Egg white sponge cake
- 6 egg whites whipped with sugar (1/3 cup),
- add 1 cup of crushed white bread croutons to the resulting mass,
- half of the resulting mass is poured into a greased form, sprinkled with poppy seeds, then the second half is added,
- baked until ready at +180 in the oven.