Pharmacodynamics
A medicine is a remedy in the hands of a doctor.Read
Pharmacokinetics
Studies the peculiarities of the drug entering the body.Read
Vitamins
Vitamins have been known to us for more than 100 years. Read
Massage
The term massage came to us from the French language. Read
Exocrine pancreas
After evacuation from the stomach to the small intestine, food undergoes intensive digestion, and the secretion of the pancreas, gall bladder and the small intestine itself plays a decisive role in this process. The most important components of pancreatic juice are bicarbonate, which neutralizes acidic chyme, and digestive enzymes, which break down the basic substances in food. The secretion of pancreatic juice is mainly regulated by the hormones secretin and cholecystokinin (CCK), as well as the vagus nerve.
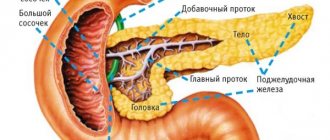
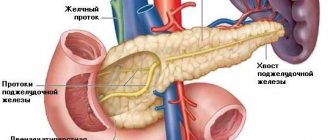
The pancreas is capable of secreting 1.5 liters of secretion per day. The main duct of the pancreas (Wirzungian duct) passes through the entire gland and opens into the duodenum behind the common bile duct, and in 30-40% of people along with it at the apex of the major duodenal (Vater's) papilla.
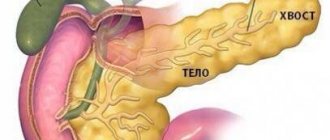
The pancreas (pancreas) is the second largest gland of the digestive system, is an unpaired glandular organ, its weight is 60-100 g, length is 15-22 cm.
The gland is grayish-red in color, lobulated, located in the retroperitoneal space at the level of 1-2 lumbar vertebrae. It distinguishes 3 anatomical sections of the organ: head, body, tail.
The head of the pancreas is adjacent to the duodenum, and the tail is located at the gate of the spleen.
Anterior to the pancreas is the stomach and the initial part of the duodenum. Her wide head is located inside the horseshoe. The gland is covered with a thin connective tissue capsule. The main pancreatic (Wirsung) duct runs along the entire length of the pancreas from tail to head.
The pancreatic duct merges with the common bile duct to form the ampulla of the papilla of Vater (large duodenal nipple). The sections of the common gastric duct and pancreatic duct, as well as the ampulla of the papilla of Vater, are surrounded by smooth muscle fibers that form the sphincter. Some have a complex structure, are not common to both ducts, but regulate the portioned flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
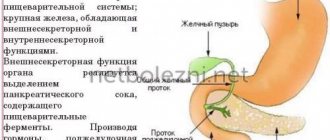
The pancreas consists of 2 glands: exocrine (exocrine) and intrasecretory (endocrine) functions.
The exocrine part of the pancreas is a complex alviolar-tubular gland. It is covered with a thin connective capsule, from which layers of connective tissue extend, dividing the pancreatic parenchyma into separate lobules. Most of the lobules are represented by terminal secretory sections - acini, the cells of which secrete pancreatic juice. The excretory ducts of the lobules merge into the excretory ducts of the gland.
The exocrine part of the pancreas consists of 4 types of cells:
- acinar, producing glycolytic and lipolytic enzymes;
- endopeptidases (trypsin and chymotrypsin), capable of cleaving peptide bonds at any point in the polypeptide chain;
— exopeptidases (acrboxypeptidases) and aminopeptidases, which cleave C- and N-terminal amino acids from peptides, respectively;
All of them are secreted in the form of inactive precursors - proenzymes. Enterokinase, an enzyme produced by the cells of the duodenal mucosa, converts trypsinogen into trypsin and breaks down the bond between leucine and isoleucine. Trypsin, in turn, activates other proteases (also itself).
Specific prevention Nowadays there is no longer any doubt that effective fight against influenza is possible only through mass immunoprophylaxis. Vaccination or active immunization is the main method of the pros.
Features of the structure of the gland
This organ, which has a body, a head and a tail, is located in the peritoneal space. Its weight in an adult varies from 70 to 80 grams. The length ranges from 16 to 22 cm. The head is located in the horseshoe of the duodenum.
The pancreas consists of parenchyma and excretory ducts. They carry out the outflow of pancreatic juice. It contains numerous food enzymes.
Endocrine part of the organ
In the tail zone between the lobules there are specific tissue formations - the islets of Langerhans. They are the functional and structural unit of the endocrine part of the organ. Their cells secrete glucagon and insulin into the blood.
The islands have a complex structure. They include the following cells:
Glucagon is produced by alpha cells. It provides an increase in glucose levels. The synthesis of ameline and insulin is carried out by Beta cells.
Somatostatin is produced by delta cells. It is responsible for inhibiting the secretion of other glands. The production of pancreatic polypeptide is carried out by PP cells. It suppresses pancreatic functions. Ghrelin, which is responsible for the feeling of hunger, is secreted by epsilon cells.
The main function of the structural and functional unit of the pancreas is to maintain carbohydrate balance and normalize other endocrine organs.
Exocrine part of the organ
Zymogenic tissue represents the exocrine part of the pancreas. This is a complex tubular-alveolar area, divided into segments by thin partitions.
The structural and functional unit of this section is the acinus. It includes intercalary and secretory parts. The acini is the initial section of the excretory ducts. It has a round shape, parameters vary from 100 to 150 microns.
The exocrine part of the pancreas produces from 500 to 2.0 thousand ml over 24 hours. watery pancreatic juice. It is responsible for the digestion of nucleic acids, fats, and carbohydrates.
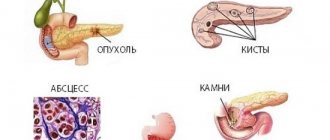
Pathologies of pancreas development
Pathologies of the development of the pancreas often occur. The main provoking factor should be considered hereditary defects. The most common defects include:
- accessory pancreas;
- cystic fibrosis;
- duct abnormalities;
- ring-shaped pancreas.
The accessory organ is located in the gastrointestinal tract. He is inactive and does not manifest himself in any way. Often its presence is detected against the background of a gastrofibroscopic examination of the gastrointestinal tract. It is difficult to distinguish a small gland from ulcers and polyps. To clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy is prescribed.
An annular pancreas is a rather dangerous defect. The defect has a bad effect on the passage of food. A dull pain syndrome appears on the right side of the abdomen. A person complains of malaise, a feeling of heaviness, and nausea. A defect is detected when diagnosing pancreatitis or peptic ulcer.
Cystic fibrosis occurs in cystic fibrosis. This pathology is characterized by thickening of almost all biological fluids. This negatively affects the condition of all systems and organs. Condensed pancreatic juice causes stagnation. The gland gradually degenerates.
What is digestion?
Our body consists of almost 40 trillion cells. Each of them needs energy to function. Cells die, building materials are needed to form new ones. Food serves as a source of energy and building material. It enters the digestive tract, is broken down (digested) into individual molecules, which are absorbed in the intestines into the blood and distributed throughout the body, to every cell.
Digestion, that is, the breakdown of complex food substances - proteins, fats and carbohydrates, into small molecules (amino acids), higher fatty acids and glucose, respectively, occurs under the action of enzymes. They are contained in digestive juices - saliva, gastric, pancreatic and intestinal juices.
Carbohydrates begin to be digested in the mouth, proteins begin to be digested in the stomach. Yet most of the reactions of the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins and all reactions of lipid breakdown occur in the small intestine under the influence of pancreatic and intestinal enzymes.
Undigested parts of food are eliminated from the body.
Danger of exocrine insufficiency
Dysfunction of the pancreas is called exocrine insufficiency. There is a shortage of produced juices. They are not enough for normal digestion of food. There is constant discomfort. The patient complains of nausea and diarrhea. Nutrients supplied with food are not fully absorbed. Sometimes they are not delivered to the body at all. A weakened patient loses a lot of weight.
Exocrine insufficiency is provoked by pathologies:
- duodenum.
- Stomach.
- Gallbladder.
Specific symptoms appear when there are irreversible changes in the tissues of the organ. Symptoms also occur against the background of partial resection of the pancreas.
Another cause of exocrine insufficiency is long-term alcohol consumption. The disease is diagnosed in people who practice diets inconsistent with a doctor, fasting, and malnutrition.
Diagnosis is possible only on the basis of laboratory tests. Next, the doctor undertakes to ensure control of blood sugar concentrations. This helps prevent diabetes, which often develops against the background of exocrine insufficiency.
Metabolic liver function
This internal organ is involved in the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
- Carbohydrate metabolism. Ensures constant blood glucose levels. After eating, when a large amount of glucose enters the blood, its reserves are created in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen. In between meals, the body receives glucose through the hydrolysis of glycogen.
- Protein metabolism. Amino acids that have just entered the body from the intestines are sent through the portal vein to the liver. Here, proteins of the coagulation system (prothrombin, fibrinogen) and blood plasma (all albumins, α- and β-globulins) are built from amino acids. Here, amino acids enter into deamination and transamination reactions necessary for the interconversion of amino acids, the synthesis of glucose and ketone bodies from amino acids. The liver neutralizes toxic products of protein metabolism, mainly ammonia, which turns into urea.
- Fat metabolism. After eating, the liver synthesizes fats and phospholipids from fatty acids coming from the intestines; Some fatty acids are oxidized to form ketone bodies and release energy. Between meals, fatty acids are transported from adipose tissue to the liver, where they undergo β-oxidation to release energy. The liver synthesizes ¾ of all cholesterol in the body. Only ¼ of it comes from food.
Restoring organ function
The patient undertakes to take medications prescribed by the doctor that restore beta cells. Often you have to drink them for several months. The patient must also adhere to a strict diet.
Resuscitation of organ functions after an attack begins with cleansing the stomach. The doctor mechanically induces vomiting. Then the patient drinks 1 liter. non-carbonated mineral water. Then the specialist induces vomiting again.
The procedure can be carried out several times in a row. This is necessary to completely cleanse the body of harmful elements. The doctor then gives the patient an enema. This allows you to cleanse your intestines.
Then the patient is prescribed therapeutic fasting. Its duration is 2-3 days. The patient is allowed only non-carbonated mineral water. The first day after an attack you can drink 2 glasses.
Taking medications after an attack is prohibited. This can trigger spasms. If a person complains of pain, medications are administered intravenously.
What is pancreatitis and how is it treated?
In diseases of the liver and pancreas, the digestion of food components is impaired. The most common pathology of the pancreas is pancreatitis. The disease develops in case of obstruction of the pancreatic duct. Enzymes produced in the gland and capable of digesting proteins, fats and carbohydrates do not enter the intestines. This leads to:
- enzymes begin to digest the organ itself, this is accompanied by severe abdominal pain;
- food is not digested, this leads to upset stool and severe weight loss.
Pancreatitis is treated with drugs that suppress the production of enzymes by the gland. Proper nutrition for pancreatitis is critical. At the beginning of treatment, complete fasting is required for several days. The main rule of nutrition for pancreatitis of the pancreas is to choose foods and a diet that do not stimulate the production of enzymes by the gland. To do this, prescribe fractional meals of warm food in small portions. Dishes are chosen first with carbohydrates, in semi-liquid form. Then, as the pain subsides, the diet is expanded, excluding fatty foods. It is known that the pancreas, if all recommendations are followed, is completely restored a year after the start of treatment.
The functions of the liver and pancreas in the body are diverse. These two organs are of exceptional importance in digestion, as they ensure the digestion of proteins, fats and carbohydrates of food.