Polyps in the stomach are single or multiple benign neoplasms that consist of epithelial or glandular tissue, are localized on the inner wall of the affected organ and are attached to it due to a thin stalk or flat base. This disease occurs in both adult men and women (aged 38–50 years) and in children. Moreover, stomach polyps are found 2 times more often in men than in women.
If left untreated for a long time, the pathology is capable of malignancy (degeneration into a cancerous tumor), therefore, at the first signs of tissue nodules in the gastrointestinal system, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Structure of the stomach
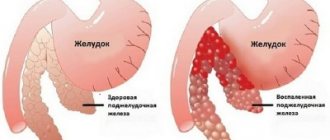
The stomach is a hollow organ of the digestive system, which consists primarily of muscle fibers.
This section of the gastrointestinal tract is located between the esophagus and the duodenum. Due to the fact that the walls of the stomach are made of muscles, it can stretch and contract to almost any size. The maximum volume that this organ can reach is 4 liters. The stomach performs the following functions in the human body:
- Mechanical and chemical processing of food. Thanks to the contractile function of the stomach, food is pushed into the intestines. Chemical treatment involves exposing the food bolus to gastric juice. Gastric juice consists of hydrochloric acid and enzymes. Under the influence of enzymes, complex substances are broken down into simpler ones, which helps prepare food for further digestion.
- Absorption of water, sugar and salts. Alcohol is also actively absorbed by the stomach and leads to degenerative changes in the mucous membrane of the affected organ.
- Disinfection. Due to the hydrochloric acid contained in gastric juice, microorganisms are suppressed and food is treated bactericidally.
- Endocrine. The stomach synthesizes a large number of hormones that stimulate the secretion of gastric juice.
Parts of the stomach in which polyps can be localized:
- the cardiac part (cardia), which is located at the entrance to the organ (at the level of the seventh rib) and prevents the reflux of food into the esophagus. The cardiac glands are also located here;
- organ body;
- the bottom (or fornix), in which the fundic glands are localized;
- pyloric (or pyloric) part. This section is located in the area where the stomach enters the duodenum and contains the pyloric glands.
Experts also distinguish the antrum (or antrum). However, it does not have clear boundaries and makes up a third of the volume of the entire stomach.
The gastrointestinal tract is located in the abdominal cavity. On the peritoneal side, this organ is covered by the left lobe of the liver. The spleen is adjacent to the stomach. Above is the esophagus, and below are the loops of the jejunum.
The walls of the stomach consist of three layers:
- Serous (or external). A large number of blood and lymphatic vessels and nerve fibers are localized here.
- A muscle layer that consists of 3 types of fibers running at different angles. The outlet from the stomach (called the sphincter) is thickened due to the accumulation of these fibers. Thanks to the sphincter, food moves further through the gastrointestinal tract.
- Slimy. The thickness of this layer is from 1 to 2 mm. On the outside, this layer is covered with prismatic epithelial tissue consisting of parietal cells. The serous layer in the stomach forms a large number of folds. Thanks to these folds and gastric fields, the area of the stomach increases, and this facilitates digestion, since the larger the area of contact of food with the mucous membrane, the more efficient the digestion process. This layer contains a large number of glands that produce gastric juice.
Useful video
How to treat polyps is described in this video.
Humanity has been familiar with honey and its health benefits for thousands of years. A product that never spoils is not only an ideal sweetener, but also an effective medicine. When mixed with gastric juice, honey not only does not change its consistency, but also activates anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral and antioxidant properties.
Another bee product, propolis, is more often used to heal erosions and abscesses. But in the absence of allergies, propolis tinctures can be taken to fight infection caused by Helicobacter pliori. When it enters the stomach, bee glue seems to “seal” the polyps and prevent their growth.
Researchers have discovered that caffeic acid phenylethyl ester (the active component of honey propolis) is responsible for antimitogenic and anticancer properties. Propolis has a positive effect on cancer polyps located not only in the stomach, but also in the colon. Regular consumption of propolis prevents metastasis (spread of cancer) by inhibiting abnormal cells.
Causes of polyps in the stomach
Doctors identify the following factors that can cause the development of stomach polyps:
- heredity (if relatives have had similar growths, the risk of developing the disease increases significantly). Most often, due to genetic predisposition, adenomatous polyps of the stomach are formed, which are a precancerous pathology;
- radiation exposure;
- work at a company that produces chemicals;
- unfavorable environment;
- infection of the stomach with Helicobacter pylori bacteria. These microorganisms are able to penetrate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, causing atrophy and neoplasia. Long-term erosive processes can lead to malignancy (malignant degeneration of tissue);
- presence of bad habits (smoking, drinking large amounts of alcohol). These substances irritate the gastric mucosa, and prolonged irritation leads to tissue transformation and the appearance of precancerous polyps;
- gastrointestinal diseases (chronic gastritis, ulcers);
- inflammatory diseases that cause fibrous polyps that are capable of active bleeding, thereby causing serious disruptions throughout the body.
Classification of gastric polyps
Based on their cellular structure, the following types are distinguished:
- Glandular polyps of the fundus (bottom) of the stomach: a. sporadic (non-hereditary) - cystically dilated glands of the gastric mucosa; b. glandular polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis - a hereditary disease, often with dysplasia (structural disorder) of cells, are considered as a precancerous disease.
- Hyperplastic polyps are caused by the growth of an area of the mucous membrane. As a rule, they are associated with Helicobacter pylori, often appearing directly next to erosions and ulcers. They themselves rarely become malignant, but serve as a marker of an increased likelihood of malignancy in nearby areas of the gastric mucosa.
- Adenomatous or glandular polyps. These are true benign tumors that are considered precancerous.
Classification
Experts divide tissue formations depending on their histological and morphological features. The following types of such compactions are distinguished (depending on which type of cells predominates):
- Hyperplastic polyp of the stomach. This is the most common type of neoplasm, which consists of overgrown cells of the epithelial tissue of the stomach. It is not a true tumor. Rarely develop into cancerous tumors.
- Adenomatous (glandular) polyp of the stomach. Benign neoplasms of this type arise from glandular cells. Large adenomatous nodes (more than 2 cm) often degenerate into cancerous tumors, and therefore require special attention. Doctors divide these compactions into tubular, papillary and papillotubular polyps (depending on which structures predominate in the formation - tubular glandular or papillary).
Juvenile polyps are also identified, but this type of formation often resolves on its own. Polyps are oval or spherical in shape, in the form of papillae or mushrooms. The surface of the node can be smooth or villous.
Types of polyps
Gastric polyps are distinguished by histological characteristics. Hyperplastic polyps, due to proliferation (hyperplasia), swelling of the surface epithelium of the stomach, are found in 70-90% of all gastric polyps. Multiple polyps are common. Polyps may have a thin stalk or a broad base. The risk of malignant degeneration is low and amounts to 0.6-4.5%.
Adenomatous polyps are true polyps from the glandular epithelium of the gastric mucosa. They make up 10-20% of diagnosed polyps. The risk of malignancy of adenomatous polyps is high, according to various sources from 5 to 75%, and depends on the size of the polyp. Polyps larger than 2 cm have an extremely high risk of malignant degeneration. Thus, the risk of malignant degeneration of polyps is higher with adenomatous polyps than with hyperplastic ones. The risk increases with age.
Symptoms
There may be no symptoms of small polyps in the stomach. Often the disease is discovered accidentally (when visiting a specialist for another reason). Large polyps may cause the following symptoms:
- heartburn, nausea and vomiting;
- flatulence, constipation, diarrhea;
- pain in the stomach and feeling of fullness;
- gastric bleeding (which is characterized by blood in stool or vomit);
- gastric obstruction;
- weakness, loss of strength;
- anemia (decrease in the content of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood).
Symptoms of stomach polyps
As a rule, polyps are asymptomatic, especially small ones. Large polyps can cause stenosis of the gastric outlet, which is manifested by heaviness in the abdomen, a feeling of rapid satiety, rotten belching, and vomiting of food eaten long ago.
In addition, a large polyp may begin to bleed. With minor but regular bleeding, signs of anemia appear over time: weakness, pallor, palpitations, shortness of breath even with slight exertion, brittle nails, hair loss. With more active bleeding, the stool becomes black due to digested blood (hemoglobin iron is oxidized in the hydrochloric acid of the stomach).
Endoscopy of the stomach is the main method for diagnosing and treating polyps
Massive bleeding causes vomiting of “coffee grounds”, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, even to the point of fainting.
Diagnostics
The main methods for diagnosing polyps in the stomach that specialists use:
Endoscopic (gastroscopy). This research method involves the use of a special device (endoscope), which is a flexible tube with optics. Using an optical system installed in the device, the image is displayed on the monitor so that the specialist can visualize the condition of the mucous membrane and identify polypous growths. A tube is inserted into the stomach through the mouth (this procedure is called gastroscopy). Before inserting the device, the doctor will treat the oral cavity with an anesthetic - lidocaine, which will reduce the discomfort of the procedure. During gastroscopy (if a polyp is detected in the stomach), the doctor will take a piece of tissue for a biopsy. Further histological examination will differentiate the tissue nodule from other neoplasms.
- X-ray. For polyps in the gastrointestinal tract, X-ray examination is used using a contrast agent (barium sulfate). This substance actively absorbs x-rays and allows you to better visualize the condition of the gastric mucosa in the image. In the picture, the location of the polypous growth appears white. Patients need to know that the procedure is performed on an empty stomach. Contraindications for the study are: pregnancy, bleeding in the stomach.
Also, the attending physician may prescribe for diagnostic purposes tests for occult blood in the stool, general blood tests, as well as studies that are aimed at identifying Helicobacter pylori infection.
In the esophagus
The starting material for esophageal polyposis is epithelial cells. Most often, the disease affects middle-aged males. There are several places in the esophagus where outgrowths form especially often - in the area of the gastroesophageal sphincter, in the area of narrowings, on the mucous membrane of the lower part of the esophagus (this area is affected by more damaging factors). They are also characterized by two types of structure, like the others. A pedunculated polyp is dangerous because it can fall into the lumen of the pharynx (if it is close to it) or become pinched in the cardiac region.
Large growths rarely form in the esophagus. As a rule, they are discovered accidentally during research not related to the search for polyps, for example, during fibrogastroscopy. Heredity, concomitant diseases (esophagitis, gastritis, ulcers), and chronic stress predispose to the development of the disease. Injuries from hot and hard foods, alcohol, and cigarette smoke can also affect the formation of outgrowths. The injured area needs healing, and at some point the epithelial cells grow too much.
Symptoms depend on the number of formations, location and size. With large formations, a person feels a lump in the throat, compression in the chest, and heartburn. If the polyp is pinched in any way, pain may occur, especially while eating. As mentioned above, polyps are often discovered by chance - they are usually small in size and grow slowly.
If the formations still go unnoticed and manage to grow, the patient will face complications and serious symptoms, in particular:
- constant painful sensations;
- urge to vomit;
- severe pain when eating;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- irritability.
Diagnosis and treatment
The disease is diagnosed by one of three methods - examination and history taking, endoscopic examination, x-ray.
The results of the examination and survey allow one to suspect the presence of growths and prescribe appropriate diagnostic measures. Endoscopic examination successfully assesses the condition of the mucosa and is highly likely to detect formations. It allows not only to determine the condition of the mucosa, but also to take a biopsy sample for further examination for signs of malignancy.
If endoscopic examination is impossible for some reason, a decision is made to use radiography with contrast. Thanks to the contrast agent, the walls of the organ and all the protrusions and outgrowths on it are visible in detail.
Treatment, as in other cases, is surgical. It is necessary to start it as quickly as possible in order to avoid ulceration, internal bleeding, and pinching of the polyp, which causes pain. Removal is performed endoscopically using a loop, which cuts off the polyp and immediately “seals” the vessels to prevent bleeding. This method is also suitable for removing multiple polyps. It only takes 1-2 weeks to heal.
During the recovery period, you should consume warm, soft foods, steamed or boiled. You should not take sour, peppery, salty foods, hot or cold foods. Foods with fiber, fatty meat, and some cereals are excluded from the diet. A more detailed consultation on diet is provided by a gastroenterologist.
Treatment methods
Treatment methods for polyps in the stomach are chosen by the attending physician based on the diagnostic data obtained and the severity of the symptoms of the disease. To get rid of the pathology, medications, surgical treatment and certain dietary nutrition are used. For small polyps of the body of the stomach, experts recommend adhering to observational tactics, which consists of conducting a fibrogastroscopic examination 2 times a year. If an increase in the size of the node has been diagnosed, there have been more tumors (polyposis has been identified), erosion, bleeding has been diagnosed, or an adenomatous polyp of the stomach has formed, then removal surgery is performed.
What is a stomach polyp and how to treat it?
Polyps in the stomach are benign tumor-like growths that protrude toward the center of the organ cavity. Pathological growths have a glandular structure of dense consistency, with smooth or bumpy edges. There may be multiple or single foci of mucosal proliferation with various symptomatic manifestations.
The main causes of the disease are existing pathologies of the epigastric organs and hereditary factors. Typically, polyps occur in patients over 40 years of age, but there are cases of juvenile (childhood) polyposis. Read more about the reasons for the appearance of polyps in the stomach in adults here.
The disease is usually diagnosed accidentally, during examination of the body for other pathologies.
Adequate treatment is surgery, but if there are contraindications to radical treatment or at the request of the patient, drug therapy can be prescribed.
Drug treatment is justified only when:
- small volumes of polyps;
- absence of obvious disturbances in the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is important ! The adequacy of the prescription can only be determined by a doctor based on:
- data from the patient's clinical history,
- polyp structures,
- the likelihood of a tendency towards malignancy.
Folk remedies for the treatment of polyps in the stomach and medications
Small single polyps of the stomach can be removed without surgery. For this purpose, enveloping medications and a gentle diet are prescribed. Since polypous growths are often a consequence of other gastrointestinal pathologies (gastritis, ulcers), medications are prescribed for these diseases. Apply: Almagel, De Nol, Rennie, Gastal, Klaritsid.
Folk remedies and methods for treating polyps in the stomach must be agreed upon with a doctor. Some herbs can accelerate the growth of the tumor and cause serious complications, so you should be wary of traditional home treatments.
Celandine products
For stomach polyps, celandine, viburnum, and propolis are used. Celandine has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and strengthening effects. This plant contains substances that help destroy polyps.
From this medicinal herb you can prepare:
- an infusion of celandine, for the preparation of which fresh leaves of the plant are used. They are squeezed out and alcohol is added in a proportion of 100 ml per 1 liter of juice. Take 10 drops of the tincture daily, increasing the dosage by 1 drop daily. Having reached 20 drops, the increase in dosage must be stopped. After 20 days of taking the tincture, the dosage begins to be reduced (by 1 drop per day). After this, the drug is taken for another 10 days, after which the course of treatment should be stopped. After 10 days (if necessary), therapy is resumed;
- decoction It is necessary to pour a teaspoon of celandine with a glass of boiling water. This remedy should be taken 1 tablespoon per day for 15 days. After this, a ten-day break is taken, after which the therapy is repeated if necessary;
- collection of herbs. To prepare this tincture, use celandine and agrimony herb. A tablespoon of herbal mixture is poured into a liter of boiled water. The prepared decoction is drunk three times a day before meals. The course lasts 10 days (and the dosage must be increased every day). After this, a break is taken for 10 days and administration is resumed.
Contraindications
Many patients refuse to use medications and prefer to treat polyps in the stomach using traditional medicine, considering them the safest. But this is far from true.
Thus, plants that are used for therapy may not be dried properly. Or the herbs were collected in a non-ecological area, for example, near highways and industrial facilities.
In addition, it can be difficult to choose the right dosage in each specific case. As a result, the body can accumulate many toxic and poisonous substances that can provoke the growth of polyps. Therefore, traditional medicine is not recommended for use by the following categories of people:
- pregnant and lactating women;
- young children;
- elderly people (caution).
But traditional medicine should also be used carefully in patients who have been diagnosed with other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. It is especially worth noting that herbs and additional components (dairy products, alcohol, beekeeping products) that can provoke the development of an allergic reaction are used to prepare folk remedies. Therefore, people predisposed to allergies should carry out this therapy only under the supervision of their attending physician.
Thus, it is quite possible to cure or reduce polyps in the stomach using traditional medicine, but provided that they are small in size and do not have the factor of degeneration into a malignant formation. Therefore, such therapy can be started only after diagnosis and consultation with a specialist.
Treatment of polyps in the stomach is of great importance, since almost every patient who has crossed the age of fifty and suffers from diseases of the digestive system is diagnosed with this difficult pathology.
Most often, a specialist recommends complete removal of such formations. But usually he first observes the general development of the disease for some time, actively trying to stop it using conservative methods. Therefore, the treatment is complex, including a large number of areas.
Removal methods
Whether it is necessary to remove stomach polyps is decided by the attending physician. The operation to remove the node is carried out using the following techniques:
Endoscopy. Endoscopic removal of gastric polyps is performed under local anesthesia. Polypectomy is also performed for multiple polyps (polyposis). After such an intervention, the following complications may occur: bleeding, relapse of the disease, perforation of the organ mucosa. The procedure is contraindicated for patients with pacemakers and impaired blood clotting. Removal of a polyp is carried out using mechanical cutting, electrocoagulation or electroexcision (removal of a node using a special loop and electric current).
- A classic operation to remove polyps, which is performed using a scalpel. This intervention is performed under general anesthesia. Using classical surgery, polypous growths larger than 3 centimeters in size, solitary nodes that are located close to each other, and neoplasms on a wide base are removed. After a classic operation, complications such as thrombosis and wound infection are possible.
- Resection of the affected organ. This method of surgical intervention involves removal of the antral part of the affected organ and is indicated for multiple polyps, large tumors, nodes located in the pyloric part of the stomach (which causes obstruction), formations whose risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor is high. After resection, the following complications are possible: dumping syndrome (sudden onset of weakness with an increase in the number of heartbeats), cancer of the part of the stomach remaining after the removal operation (stump), problems with metabolism.
Read more in our next work about what removal methods surgeons use if polyps occur in the intestines.
Postoperative period
Recovery after surgery to remove stomach polyps is aimed at accelerating tissue regeneration, normalizing the general condition of the body, and preventing relapses of pathology. The duration of rehabilitation directly depends on the method of removal.
During endoscopic removal of polyps, the patient is left under the supervision of a specialist for 1-2 hours in order to timely diagnose and prevent possible internal bleeding. The speed of tissue healing depends on the number of nodes removed and their size. During the first 24 hours after surgery, it is recommended to stop eating. After this, patients must adhere to a special diet, which involves reducing chemical, thermal and mechanical effects on the organ mucosa.
The rehabilitation period after surgery to remove gastric polyps using the classical method or by resection is longer than with polypectomy. In this case, the patient is administered nutrients intravenously within 1-2 days after the intervention. Further, it is allowed to drink weak tea and decoctions that promote tissue healing. After another 4 days, the patient is allowed to consume eggs, soups, and cereals. The late period of rehabilitation involves a gentle diet, which will be prescribed by a doctor.
What to do if polyps are detected
If benign gastric tumors (polyps) are detected, their removal is indicated. Epithelial polyps measuring 3-5 mm are completely removed during biopsy, which becomes both a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure. Pedicled and sessile polyps are removed with a special loop; large polyps are removed surgically. All removed tissues are subjected to histological examination. The final diagnosis of a benign formation in the stomach (polyp) is possible after an endoscopic examination, biopsy and after a morphological examination of the biopsy sample.
Disease prevention
Currently, there are no specialized preventive measures to help prevent the development of gastric polyps. Experts recommend adhering to measures to prevent the development of chronic gastritis, since it is this pathology that often causes the formation of nodes in the stomach. To prevent this disease, it is necessary to adhere to a balanced diet and minimize the use of medications (gastrotoxic drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). If polypous growths are nevertheless diagnosed, then patients should adhere to a certain dietary diet: reduce the consumption of spicy, salty, fried, smoked foods. It is also recommended to give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages), since alcohol irritates the gastric mucosa and leads to erosion. Smoking increases the secretion of hydrochloric acid, which also provokes erosion.
Polyps in the stomach are a disease that can lead to the development of cancer. That is why at the first symptoms you need to contact a qualified specialist. It is dangerous to self-medicate in this case, as this can lead to accelerated growth of nodes, an increase in their number and malignancy.
Risk factors associated with the growth of gastric polyps
There are many risk factors that can increase your risk of developing different types of stomach polyps. The following groups can be roughly distinguished:
- Bacterial infection in the stomach. H. pylori is a bacteria that causes gastritis. Metabolic products of these bacteria contribute to the rapid growth of hyperplastic polyps.
- History of stomach and colon cancer. Overgrowth of polyps is often diagnosed in survivors of stomach or intestinal cancer.
- Age.
Stomach polyps are more common in older people.
It is very important to pay attention to negative symptoms in order to suspect the growth of polyps in time.
Forecast
If polyps are removed in time, the prognosis is favorable. Of course, a person always has a high probability of relapse of the disease. This is why it is so important to undergo regular medical examinations. After surgery, the patient's ability to work is usually completely restored. If you do not get rid of polyps in time, there is a risk of developing cancer.
Polyps in the stomach are a fairly serious disease that can lead to negative consequences. To prevent this from happening, you need to monitor the course of the disease and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
RepostTweet
Causes and risk factors
This pathology is most often acquired; The likelihood of developing a glandular polyp increases with age.
Reasons for the development of adenomatous polyps:
- genetic predisposition;
- neurohormonal pathology, endocrinopathy;
- chronic injury to the mucous membrane of the organ.
It has been scientifically proven that the hereditary factor plays an important role in the development of adenomatous polyp
Currently, a hereditary predisposition to the formation of polyps has been confirmed: about half of all cases of the disease are reflected in the family history. The presence of chromosomal aberration has been proven: changes in the structure of some chromosomes associated with the gene responsible for the formation of polyps have been found.
Polyps of the gastrointestinal tract
The main risk factors for the development of adenomatous polyps of the gastrointestinal tract:
- high content of refined foods that contribute to stagnation of intestinal contents (high-calorie, fatty and protein foods with a small amount of fiber cause a decrease in the efficiency of peristalsis, provoke processes of rotting and fermentation in the intestines, and the development of intoxication);
- imbalance of the gastrointestinal microflora, leading to a decrease in local immunity, changes in the differentiation and regeneration of cells in the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines;
- concomitant diseases of the biliary system and impaired production of bile acids, which have a mutagenic effect on the intestinal mucosa.
What do gastrointestinal polyps look like?
Endometrial polyps
The main risk factors for the development of adenomatous polyps of the inner layer (endometrium) of the uterus:
- infectious and inflammatory diseases during puberty and associated disorders of menstrual and (subsequently) reproductive function;
- menopausal and premenopausal hormonal changes;
- mastopathy;
- surgical interventions (diagnostic or therapeutic curettage of the uterine cavity, probing of the uterine cavity);
- long-term use of an intrauterine device for contraception (endometrial trauma).
What do endometrial polyps look like?
General nonspecific risk factors:
- immunodeficiency states;
- hypovitaminosis (vitamins C and E);
- hereditary burden (uterine fibroids, cancer of the genital organs and breast, gastrointestinal tract);
- active chronic inflammation and dysplasia of the intestinal mucosa or organs of the reproductive system (chronic colitis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, cervical erosion, sexually transmitted diseases);
- some chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, obesity, thyroid pathologies, etc.);
- chronic neuropsychic stress.
Adenomatous polyps are considered a precancerous pathology. The likelihood of malignant degeneration (malignization) of a polyp directly depends on its size.
What do healers advise?
Treatment of gastric polyps with folk remedies includes many recipes. Thus, it is proposed to treat the disease with honey mixed with olive or melted butter, pumpkin seeds, propolis, and golden mustache. But the most common are recipes using celandine and viburnum.
Some herbs may help relieve inflammation of the stomach lining
Application of celandine
Celandine for stomach polyps can be taken according to different recipes, but you just need to remember that the plant is contraindicated during pregnancy, epilepsy, asthma, and angina.
- You need the juice of the plant, squeezed at the beginning of flowering. This juice is diluted with vodka in a ratio of 10 parts juice to 1 part vodka. Drink on an empty stomach starting with 10 drops. Later, add 1 drop per day, bringing the total dose to 20 drops. The maximum dosage is taken for a week, then gradually reduced to 10 drops. Drink the infusion 10 drops for 10 days, take a week break and repeat all over again.
- Dilute the juice with vodka 1:1, pour into a dark glass bottle. The mixture is infused for 24 hours (the bottle must be shaken periodically), then 1 teaspoon of infusion is drunk 3-4 times a day on an empty stomach. The course is no more than 3 months.
- Collect celandine grass, chop, take 1 tsp. it, pour 1 cup of boiling water. Drink 1 tbsp. three times a day, half an hour before meals. In total, you need 2 courses per month with a 10-day break.
- Pour 0.5 teaspoon of herb into 1 glass of boiling water, boil for 2 minutes, drink 3 times.
Advice! Celandine is an extremely toxic plant; it should be used only after consultation with a doctor, while monitoring your condition.
Application of viburnum
Treatment of stomach polyps with viburnum is much safer than using celandine. The recipe for its use is simple: you need to eat 2-3 handfuls of fresh berries throughout the whole of September or October. In winter, take 3-4 tablespoons of fresh or dried berries, pour 500 ml of boiling water, leave for an hour. This volume should be drunk in 3 doses during the day, between meals.
Prevention
As recommendations for prevention, experts advise:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- no smoking;
- do not abuse alcoholic beverages;
- refuse self-medication;
- Healthy food;
- move more;
- promptly contact specialists if alarming symptoms appear.
No special preventive measures are provided. They simply don't exist. Following your doctor's recommendations and paying close attention to your health will help prevent the likelihood of serious complications.
Main symptoms of the disease and methods of differential diagnosis
At an early stage, adenomatous polyp of the stomach does not have any clinical manifestations that allow an unambiguous differential diagnosis. The patient may feel discomfort after eating, suffer from flatulence, experience mild nausea or heartburn. The patient loses his appetite and develops general weakness. If the process has gone far and ulcerations of the mucous membrane have appeared, then the patient begins to experience internal bleeding, which is externally expressed as pallor of the skin. During this period, the patient may experience severe cutting pain in the epigastric region.
Any disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract or changes in well-being are a reason to contact a gastroenterologist. Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis based on certain research methods. An adenomatous polyp of the stomach can be detected on x-rays or during endoscopic examination. The latter method is more reliable, since small polyps are not always detected on x-rays, which makes it difficult to make a correct diagnosis.
Prevention and treatment of the disease
Prevention of all stomach diseases comes down to proper nutrition and diet. People suffering from gastrointestinal diseases should exclude all “aggressive” foods from their diet, namely: fried, salty, smoked, spicy, etc.
Symptoms
A small glandular polyp of any location may not appear at all. However, as the tumor increases in size, more clinical manifestations will occur.
For example, an adenomatous polyp in the intestines or stomach is represented by the following symptoms:
- pain in the epigastrium, umbilical region and anal area;
- stomach bleeding - vomit like “coffee grounds”;
- defecation disorder;
- the appearance of blood and mucus in feces;
- itching in the anus;
- bad breath;
- increased gas formation;
- belching;
- bloating;
- burning in the esophagus;
- the appearance of spots on the skin, the color of which can vary from purple to bluish;
- frequent urge to have bowel movements;
- nausea and profuse vomiting.
An adenomatous endometrial polyp is indicated by:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- spread of pain in the perineum and lower back;
- menstrual irregularities;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- heavy vaginal bleeding that is not associated with menstruation;
- inability to conceive a child.
A gallbladder polyp has the following manifestations:
- obstructive jaundice;
- dull pain, the focus of which is in the right hypochondrium;
- hepatic colic;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- severe skin itching;
- increased heart rate;
- increased blood tone;
- aversion to food;
- nausea, periodic vomiting.
Despite the fact that a polyp can develop in children and adolescents, the clinical picture will be similar.
The essence of the disease
Polyps in the stomach are epithelial tumor formations that are benign in nature and form inside the stomach. This is a fairly common pathology, which usually occurs without any special symptoms and in most situations is discovered by chance during fibrogastroscopy performed to diagnose other disorders.
Typically, polyps occur in middle-aged people - 40-50 years old. However, sometimes the disease is diagnosed in young people and even children. Moreover, such formations are more characteristic of men and are observed twice as often as in women.
Single and multiple polyps
Etiology
The exact reasons why an adenomatous polyp forms remain unknown today. It is well established that education is acquired in nature, and the risks of developing a pathology increase with age.
Among the most likely predisposing factors are:
- genetic predisposition - the presence of polyps in at least one of the closest relatives;
- neurohormonal pathologies;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- chronic inflammation or injury to the mucous membrane of internal organs.
Such provocateurs become sources of all types of polyps, depending on the place of their origin. However, each localization has a list of characteristic individual development factors.
For example, an adenomatous intestinal polyp can develop as a result of such anomalies:
- problematic nutrition - eating a large amount of refined foods and high-calorie foods, lack of fiber and proteins;
- pathological changes in the intestinal microflora - an imbalance leads to a decrease in local immunity and differentiation of organ tissues;
- irrational use of certain medications - the relationship between uncontrolled use of proton pump inhibitors and the appearance of benign tumors in different parts of the intestine has been proven;
- chronic nervous overstrain.
The occurrence of a polyp in the stomach is influenced by the following pathologies:
- gastritis of any etiology;
- familial adenomatous polyposis;
- Peutz-Jigers syndrome;
- duodenitis;
- radiation exposure of the body;
- long-term addiction to bad habits;
- infectious lesion of the stomach.
Polyps of the uterus, vagina and endometrium are common. The following reasons may influence its occurrence:
- hormonal imbalance;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- hypertonic disease;
- dysfunction of the ovaries or adrenal glands;
- incorrect or prolonged use of intrauterine devices or other contraceptives;
- labor activity;
- abortive termination of pregnancy;
- previous intrauterine surgeries;
- the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the uterus or appendages;
- development of sexually transmitted infections;
- incomplete separation of the placenta when the baby is born;
- failure of the body's immune system;
- long-term influence of stressful situations.
Adenomatous polyp of the gallbladder can be caused by:
- inflammatory lesion of the gallbladder;
- deposition of large amounts of cholesterol;
- bile duct dyskinesia;
- diseases of the hepatobiliary system.
Sigmoid colon polyp is provoked by:
- acute infections;
- fecal stagnation due to chronic constipation;
- injury to the mucous membrane from hardened feces;
- consumption of large quantities of foods that cause rotting or fermentation processes.
Damage to the endocervix can be noted with the following anomalies:
In most situations, the development of polyps is simultaneously influenced by several predisposing factors.
Conservative treatment
Since the substrate for the development of gastric polyps is chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa, by stopping the inflammatory process, the appearance of new and growth of existing formations is prevented. There are two ways to reduce the severity of inflammation: drug therapy and adherence to the principles of a therapeutic diet. An alternative method to taking medications is treatment according to traditional recipes.
Drug therapy
Medicines are prescribed depending on the level of acidity in the stomach:
- If you have high acidity, medications are prescribed that lower the pH level by blocking the production of hydrochloric acid. In addition, it is necessary to take agents that envelop the mucous membrane, which will protect it from the aggressive action of stomach acids.
- If the acid-forming function of the stomach is reduced, synthetic analogues of gastric juice and enzymes are prescribed. In this case, enveloping medications are also needed.
- How to treat a polyp in the stomach if the presence of Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium that causes gastritis, is confirmed? To do this, a gastroenterologist prescribes 2 antibiotics and a drug that reduces acid production by organ cells. Therapy lasts a week, after which the test for the presence of bacteria is repeated. If this step is skipped, the operation to remove polyps will have to be repeated several times.
Warning! Medicines can only cure a developing stomach polyp. If the formation is already of sufficient size, then taking medications is indicated as preoperative preparation: this will help reduce swelling of the mucous membrane and reduce the risk of bleeding during surgery.
What diet is indicated
The diet for polyps in the stomach depends on the level of acidity maintained in its cavity:
- If the acid-forming function is reduced, it is necessary to consume foods that stimulate the production of gastric juice: prepare soups and main courses in concentrated meat or mushroom broths, eat pasta, vegetables, cheeses, ham and boiled sausage. Mild seasonings can be added to dishes.
- If a lot of acid is produced in the stomach, you need soups with vegetable or third meat broths, slimy porridges (except pearl barley, wheat and corn), and mashed potatoes.
For both types of gastritis, vegetables should be eaten stewed or baked, as well as with lean fish or meat. Bread – oven-dried, white. In addition, it is prohibited to consume alcoholic beverages, coffee, marinades, smoked and salty foods. More information about the diet for inflammation of the gastric mucosa can be found in the article: What is proper nutrition for gastritis?
Causes
The main cause of the pathology is the inflammatory process occurring in the main digestive organ. This may include chronic pathologies (gastritis, gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcer), as well as infection with the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter Pylori.
A polyp in the stomach can appear as a result of the following reasons:
- long-term (uncontrolled) use of certain groups of medications (for example, NSAIDs, antibiotics);
- living in unfavorable conditions from an environmental point of view, radiation exposure;
- infection of the body with viruses, for example, human papillomavirus;
- exposure to chemicals (nitrates);
- age over 45 years, the older the person, the higher the risk of developing a tumor;
- hereditary predisposition.
The development of the disease in older people is due to the fact that the immune system in this category of people is reduced and is not able to resist cell proliferation. Therefore, the degeneration of an ordinary polyp into cancer occurs rapidly.
But it is also worth noting that polyps often form due to drinking and smoking. Smoking on an empty stomach is especially dangerous. After all, nicotine, when it gets on the gastric mucosa, irritates it, provoking the growth of formations. Alcohol has the same negative effect.
Usually, the appearance of a certain type of polyp involves its own risk factor. The likelihood of cancer of a particular type of formation increases when several provoking causes are combined.
Nutrition for polyps
The diet for polyps in the stomach is essentially based on the principles of a healthy diet: fresh or minimally cooked non-acidic vegetables and fruits; steamed meat, fish; low fat dairy products. Drinks include jelly, non-concentrated juices, weak herbal tea, and green tea. You will have to say goodbye to alcohol and cigarettes forever; polyps do not forgive this.
- The main products of a patient with polyposis are carrots, spinach, onions, garlic and kaline.
- Drink carrot juice regularly, but not store-bought, and prepare it yourself, adding spinach, onion or garlic juice to it.
Nutrition for polyps
- It is recommended to eat cabbage, pumpkin, from which you can cook porridge, and turnip and cress salad.
- Sprouted wheat will help digestion. It also normalizes metabolism in the body.
- Sea cabbage is very healthy. If you don’t like seaweed salads, add it dry to your dishes, using it instead of salt. Just eating a spoonful of seaweed powder is powerful.
- At least during the period of exacerbation, avoid fermented milk, sugar and sugar-containing products. Products and baked goods made from white flour. It is also advisable for you to exclude canned food from your diet. Reduce the amount of protein foods. Or at least consume proteins and carbohydrates separately. Read labels when purchasing products in the store.
- If you see the ingredients, dyes, flavors and substitutes, put them back on the shelf.
- Your food should not be cold, but not hot - about thirty-seven degrees. This is a very important condition that must be strictly observed! It follows that ice cream and drinks from the refrigerator will only harm you.
Causes of polyps
A type of polyp.
Growths can form as a result of pathological processes or other disorders in the mucous membrane. The pathogenesis of polyps may indicate hyperplasia, adenoma, and neoplasms of the fundic glands. The cells of the fundic glands form the inner layer of the stomach; these glands produce hydrochloric acid. They form growths on the walls of the stomach. Middle-aged and older people are susceptible to this disease. The bacterium Helicobacter pylori often provokes the occurrence of adenomatous and hyperplastic neoplasms. The appearance of fundic polyps can be caused by long-term use of certain medications.
Studies have shown that polyposis can be not only acquired, but also congenital. This is evidenced by a polyp found in one of the stomach sections of a 2-month-old baby. Neoplasms and their grouping are diagnosed using gastroscopy. This procedure allows you to take a tissue sample for study - a biopsy. Treatment is determined by the size and classification of tumors. Surgical intervention is necessary if the size of the polyps exceeds 1 cm, or the polyps are adenomatous in nature. Such growths can cause cancer in the future, so they are removed surgically. Hyperplastic polyps may disappear on their own with the treatment of gastritis or Helicobacter pylori infections.
Treatment of gastric polyp
After identifying the disease, the doctor prescribes medication. Take medications strictly following prescriptions and instructions. Small polyps can be cured without surgery using diet. It is important to constantly see a doctor and monitor the dynamics of the disease. Let's consider folk remedies for treating polyps.
Celandine
It is the most effective way to treat polyps in the stomach. The herb celandine will help you get rid of it - a popular method of solving the problem. Many unscientific medical books describe treatment with celandine as the most effective method. Medicines based on celandine have an analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect.
- 1 recipe. Consists of celandine and calendula herbs mixed in equal proportions. Well-mixed herbs are brewed with boiling water. Separate a third of the mixture and leave to steam. Should be taken 2 weeks before meals. Then a break of 5 days and again the course.
- 2 recipe. Chamomile flowers plus celandine are poured with boiling water and infused for 6 hours. The dose is taken 30 minutes before the start of a meal. The treatment period is a month.
- 3 recipe. Pour 400 ml of hot water, add two teaspoons of celandine and pour into a thermos. Steams for 5 hours. Take half a glass before meals 3 times a day. The course of treatment is a week. It is important to follow the dosage of the infusion. The presence of thirst and stomach pain are signs of the beginning of the process of cleansing the body of toxins.
Treatment with viburnum
Viburnum will help in the fight against polyps. Preventive treatment must begin as soon as the viburnum ripens. A tablespoon of berries is taken for a month, chewing thoroughly and swallowing one piece at a time.
Stock up on viburnum before winter. Dry the twigs along with the berries. The decoction is made from 3 glasses of water, a small amount of branches with berries. Within an hour, the amount of water in the broth will decrease, and the amount of beneficial qualities will increase. The decoction is divided into 3 parts, filtered, and taken three times during the day.
Important! Taking viburnum infusion significantly reduces the risk of developing malignant tumors.
Egg and butter mixture
Boil 7 hard-boiled eggs. If you use yolks, you need to separate them. You need 5-6 tablespoons of peeled pumpkin seeds. You need 600 ml of vegetable oil. The mashed yolks are combined with crushed seeds using oil, and the resulting mass is steamed for 30 minutes. Remove, cool, and put in the refrigerator. Take the mixture 3 times a day, a teaspoon. A week of treatment should be followed by a week of rest until the mixture is finished.
Lilac tea
During the year, if desired, they are treated with tea from lilac branches. 1-2 small branches are cut, chopped, and transferred to a warm place. Filled with half a liter of hot boiled water, the branches should steep until the morning. Then you need to strain it, drink half a mug before meals. They are treated with lilac tea every day for a couple of months.
Honey and cream recipe
In a whole enamel pan, 1 kg of honey and butter are heated. After the boil begins, cook for 2 hours, stirring with a spoon so as not to burn. Cool, put in the refrigerator. Take 1 spoon in the morning on an empty stomach.
Honey-herbal recipe
For preparation you need: 2 lemons, half a kilo of honey, vegetable oil. Mix lemon juice, oil and honey. Take daily in 3 divided doses, 1 spoon before meals. Stir the mixture before use.
Tincture of thuja needles
Thuja needles separated from the branch must be filled with water. Leave for a couple of weeks. Stir the contents periodically. When the solution is filtered, it must be drunk before meals, one small spoon at a time, with a small amount of water. You should take it for a month, then you need a break of 30 days, then resume monthly use.
Propolis oil
Attention! This treatment method is not intended for people with liver problems.
10 grams of propolis must be mixed with butter in a ratio of 1:10. Steam for 10 minutes. Once the medicine has cooled down, put it in the refrigerator. Application: for half a glass of warm milk, 1 spoon of the mixture, everything is mixed and consumed. A monthly course of treatment involves taking 3 times a day.
Spruce decoction
The beginning of autumn is the best period for stockpiling. Three times a day, drink steamed spruce branches instead of tea.
Walnut tincture
The shells of 20 nuts are filled with vodka. Place in a dark place. The infusion takes a week to prepare. Take in the morning on an empty stomach, 2 tablespoons at a time.
Tincture with propolis and honey (complex)
You need to prepare: two jars, cedar nut shells, celandine, vodka, propolis, galangal root, aloe leaves with honey.
In the first jar you need to send 30 grams of cedar shells and crushed propolis with galangal root. Then pour 50 ml of medical alcohol into the jar.
Place 30 grams of celandine herb in another jar and fill it completely with vodka. Both jars must be left in a dark place. After 7 days, place several aloe leaves in the refrigerator for a week.
The last stage of drug production. Mix 150 grams of honey and aloe juice. Add the plant mass to the strained tincture and mix thoroughly. Leave for a week in a cool place. Apply a teaspoon 3 times a day. We are undergoing treatment for a month.
Cabbage juice
For any disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to use cabbage juice. Polyposis is no exception. It is recommended to drink juice every day and eat cabbage salads. Seaweed for polyps should be in the patient’s diet.
The use of products with substitutes and food colorings is strictly contraindicated. The temperature of food for problems with the gastrointestinal tract should be optimal - eat neither hot nor cold food. This is an important condition for treatment! Conclusion: ice cream and cold drinks can be harmful.
Treatment
Currently, there are several types of treatment for the disease that help prevent the development of dangerous complications. These include conservative therapy and surgical interventions. In some cases, traditional treatment methods can improve the patient's condition.
Surgical intervention
There are several types of operations when formations appear:
- endoscopy;
- gastric resection;
- excision of polyps with a scalpel;
- organ removal.
The main method of therapy that is currently used is endoscopic removal of polyps in the stomach.
Polyp removal by endoscopy
To treat the disease, a probe approximately 2 cm thick with a camera is inserted into the patient's stomach. The specialist evaluates the appearance of the polyp and decides on the method of its removal:
- a formation up to 3 cm with a pedicle no more than 15 mm is removed with a diathermic loop - it not only removes the tumor, but also cauterizes the vessels;
- formations less than 0.5 cm are removed with a metal loop, after which the vessels are coagulated with current;
- a minor polyp is removed with biopsy forceps, and the vessels are cauterized with an electric current.
This technique is used to treat benign tumors. After the polyps in the stomach are removed, they are sent for histology.
It is important to consider that endoscopy has certain contraindications:
- threat of bleeding;
- serious human condition;
- the presence of a pacemaker in the body.
If the polyp has an atypical appearance, a biopsy is performed. With an impressive size of the formation, the presence of several polyps and poor circulation, there is a need for surgical polypectomy.
In such a situation, under general anesthesia, an incision is made in the abdomen, the stomach cavity is opened and the polyps are excised using a scalpel. The tissue of the formation is urgently subjected to histological analysis. If there are no malignant cells, the organ is sutured. In the presence of malignant cells, it becomes necessary to remove the organ, which can be carried out in whole or in part.
The cost of surgery is influenced by many factors. Removing polyps can cost from 2,500 to 25,000 rubles.
Drug treatment
Medications are selected based on stomach acidity:
- When this indicator increases, it becomes necessary to reduce the pH. This effect is achieved by blocking the synthesis of hydrochloric acid. In addition, you need to use products that help coat the gastric mucosa and protect it from the aggressive effects of acid.
- A decrease in this indicator is the reason for the use of synthetic gastric juice and enzyme preparations. In this case, enveloping agents are also prescribed.
- If there are pathogenic microorganisms in the stomach, the gastroenterologist prescribes antibacterial drugs. You should also use products to reduce acid production. Treatment is continued for a week, after which the bacteria are again analyzed.
It is important to consider that medications help cope with the developing polyp. If the formation has already reached an impressive size, medications are prescribed only as preparation for surgery. This reduces swelling of the mucous membrane and reduces the risk of bleeding during surgery.
Treatment with folk remedies
In some cases, a person’s condition can be improved using folk remedies:
- Celandine decoction. To prepare this product, pour 500 ml of boiling water into a large spoon of raw materials. Leave to infuse and take 1 spoon for a month. This should be done 4 times a day. It is important to be careful, because celandine is considered a poisonous plant. If you violate its use, you can be seriously poisoned.
- Thuja tincture. To do this, grind the needles of the plant and add vodka in a ratio of 1:9. Leave to infuse for 16 days. Take 1 teaspoon of the product, diluting it with water. Drink the tincture for 1 month, and then take a break for the same period and repeat the use.
- Decoction of pine needles . This remedy should be taken in half a cup, replacing tea with it. To obtain the composition, it is necessary to collect raw materials at the end of September. It is poured with boiling water and infused.
- Sea buckthorn oil. To prepare the product you need to take 2 liters of sunflower oil and 2 kg of berries. Place in a saucepan and bring to a boil. Cool the resulting composition and pour into jars. The mixture is injected into the anus. Before use, it is recommended to sit on the herbal decoction for 2 hours.
- Propolis. To do this, 10 g of raw materials are mixed with 100 g of melted butter. Drink the product with milk 1.5 hours before meals. Do this for 3 weeks. Liver disease is a contraindication.