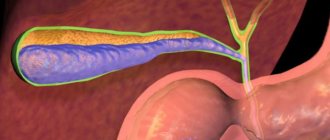
Gallstone disease (abbreviated as cholelithiasis) develops as a result of the formation of stones in the gallbladder. The disease can lead to inflammatory processes in it and the development of chronic cholecystitis. If this disease is diagnosed, surgery is indicated, since the stones need to be removed. But in many cases, treating gallstones without surgery with folk remedies gives a positive result.
Actually, what is cholelithiasis, what symptoms are observed in people with cholelithiasis, and how to cure it at home using exclusively folk recipes and will be discussed in this article.
Causes of the disease
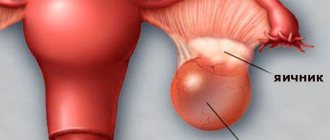
The main cause of the disease is considered to be the presence of stones (calculi) in the gallbladder or bile ducts. They appear as a result of stagnation of bile and high cholesterol. The process of development of cholelithiasis itself is quite long and consists of the appearance of sediment in the bile, then sand, the crystals of which turn into pebbles with sharp edges of different sizes.
Stones can remain in the gallbladder for many years, but the condition is considered especially dangerous when stones enter the bile ducts, injure the mucous membrane, which can cause an acute attack. If not treated at this stage, it can lead to death. In gastroenterology, this disease can often be found under the term “calculous cholecystitis” or “cholelithiasis.”
A variety of factors can trigger the formation of gallstones, mostly related to poor diet and lifestyle. The trigger mechanism is often:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- bending of the gallbladder;
- hormonal disorders;
- obesity;
- unhealthy diet: abuse of fatty and spicy foods;
- taking medications that disrupt metabolic processes;
- heredity;
- constant stress, psycho-emotional disorders;
- concomitant diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Risks for the development of the disease are present during pregnancy, when the amount of progesterone increases and the pressure of the growing uterus on other organs increases. Gallstone disease can manifest itself against the background of diseases of the liver, pancreas or intestines.
To identify the true cause, you need to see a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination. The diagnostic results will become the basis for making a diagnosis and choosing treatment therapy.
Types of stones
It has been proven that the condition for the formation of stones in gallstone disease is the inability of bile to keep cholesterol in a dissolved state. This is facilitated by the entry of large amounts of cholesterol into the body or a decrease in the concentration of bile acids.
An imbalance of active substances responsible for the suppression and formation of cholesterol causes its crystallization and the formation of cholesterol stones in the gallstones. This type is the most common and responds well to conservative treatment methods.
According to the classification of stones, there are 2 more types of gallstones - pigment and calcareous. In pigment formations, cholesterol makes up only the 3rd part, the rest is occupied by various calcium compounds. They are brown in color and are more often found in the common bile duct with a combination of an infectious factor and stagnation of bile; in the gallbladder this type is rare.
Calcareous (black pigment) contains a polymer of black pigment, calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate; cholesterol is not included in their composition. Such stones are more common in elderly patients. Their appearance is associated with changes in blood composition, the presence of artificial heart valves and vascular prostheses, as well as liver cirrhosis (mainly alcoholic).
In addition to their composition, stones can have different shapes and sizes, from a small grain of sand to a solid formation that occupies the entire cavity of the gallbladder. Their number can vary from 1 to hundreds, it all depends on the duration and severity of the disease.
Classification of cholelithiasis
Gallstone disease has several stages, forms and classifications, each of which is characterized by certain changes in the organ and has its own clinical picture.
GSD is divided into three stages:
- Initial (pre-stone). There are changes in the chemical composition of bile, there are no symptoms, the process of stone formation is just beginning. The disease can only be detected through a blood test.
- Formation of stones . Latent stone formation is asymptomatic, but stones can be detected using instrumental examination methods.
- Stage of clinical manifestations . The stones are fully formed, the disease is characterized by the development of acute or chronic calculous cholecystitis.
According to clinical manifestations there are:
- Uncomplicated course.
- Complicated course.
By localization:
- The stones are located at the bottom of the gallbladder body.
- Stones affect the neck of the gallbladder.
According to their chemical composition they are distinguished:
- Cholesterol (pure and mixed):
- Non-calcified.
- Calcified.
- Bilirubin (pigment) black:
- Non-calcified.
In count:
- Single stones (1-2).
- Multiple stones (3 or more).
To size:
- Small (less than 3 cm).
- Large (more than 3 cm).
Considering that the disease has its own varieties and characteristics, treatment can only be carried out after the results of a comprehensive examination.
Chronic and acute cholecystitis as consequences of cholelithiasis
Acute and chronic cholecystitis are the main complications of cholelithiasis, which are accompanied by an inflammatory reaction in the gallbladder due to blockage of the discharge of liver secretions into the duodenum.
The acute form is catarrhal and destructive (purulent). In turn, the authors in the medical literature classify the purulent type of inflammation into phlegmonous, phlegmonous-ulcerative, perforative and gangrenous types.
The main symptom of acute cholecystitis is biliary colic. It manifests itself as unbearable pain in the right side, epigastric region on the right. In certain pictures it radiates to the back, sometimes to the left side of the body. Additional symptoms include nausea and low-grade fever.
Chronic cholecystitis is an inflammation that occurs when the motor function of the gallbladder is impaired. The disease lasts a long time, periods of subsidence are replaced by exacerbations with deterioration of well-being. The dominant symptom is pain.
Treatment of the acute form with medications, the chronic form of the disease requires surgery - the gallbladder, which is the source of the formation of solid compounds, is removed.
Symptoms and signs of gallstone disease
Clinical signs of cholelithiasis depend on its stage. At first, a person may experience heartburn or discomfort in the abdominal area after drinking alcohol or fatty foods. When the stones reach large sizes or have shifted and the stones have entered the bile ducts, the symptoms are pronounced and are accompanied by the development of hepatic colic.
Main symptoms
Its main symptom is acute stabbing or cutting pain, which radiates to the back, shoulder blade, sternum and other parts of the body. An attack of biliary colic can be triggered by:
- fatty, spicy, fried foods;
- severe stress;
- alcohol;
- hard physical labor.
Severe symptoms occur as a result of a sharp contraction of the gallbladder. When stones move along the ducts or obstruction (blocking) of the bile duct occurs. In addition to pain, other symptoms are also noted.
Additional symptoms
Additional symptoms of gallstone disease:
- nausea, repeated vomiting of bile;
- increase in body temperature to high levels;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- liver enlargement;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- urine takes on a dark color;
- light cal.
Against the background of all pathological processes, severe intoxication of the body occurs, which leads to increased fatigue, decreased appetite and other unpleasant symptoms.
Treatment of gallstone disease without surgery
In order to avoid the movement of stones and the appearance of pain, a patient diagnosed with cholelithiasis should be provided with conditions for an optimal regime that excludes physical activity. However, physical inactivity is considered by medical experts as an unfavorable factor contributing to the formation of gallstones. Nutrition for gallstone disease must be strictly regulated.
Tablets for gallstone disease
In case of exacerbation of gallstone disease, hospitalization is indicated for the patient. Myotropic antispasmodics, for example, No-shpa® or Drotaverine®, can reduce pain. For painful attacks caused by spasm of the sphincretus of Oddi, the attending physician prescribes narcotic analgesics. The use of choleretic drugs, so-called choleretics, in the presence of stones in the common bile duct is strictly contraindicated. As a basic therapy, the most effective is the use of medicinal groups that promote the rapid dissolution of cholesterol gallstones with a diameter of up to 10 mm. Ursodeoxycholic acid is prescribed to patients at the rate of 0.01 g/kg body weight per day.
Dissolving gallstones is a long process that requires dedication and patience from the patient and his environment. Often, an unfair attitude towards the treatment process becomes the reason for unsuccessful treatment.
Physiotherapy - paraffin application and magnesium electrophoresis - contributes to improving the outflow of bile and high-quality restoration of the anatomical functions of the liver. Coniferous and fresh baths with a water temperature of 37-37.5 ° C have a tonic effect.
Laparoscopy of the gallbladder
An alternative to conservative treatment is surgery - laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which is not recommended for children under 12 years of age. Removal of the gallbladder corrects the clinical situation, however, it further limits the human body’s functional and compensatory capabilities.
Diagnosis of cholelithiasis
If you suspect cholelithiasis or if you experience an attack of biliary colic, you should consult a gastroenterologist. The specifics of the disease are determined and confirmed after the collected history, examination and examination results.
During the examination, upon palpation of the abdomen, pain intensifies, pronounced bloating and muscle tension are noted. When pressing on the area of the right upper quadrant of the abdomen at the moment of deep inspiration, the pain intensifies, and an enlarged gall bladder and liver are palpated.
To confirm the diagnosis, determine the stage and localization of stones, the doctor prescribes a number of laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods:
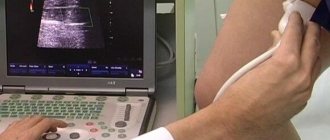
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder and liver;
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
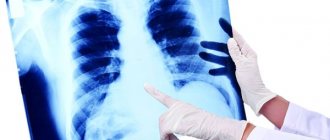
- X-ray examination of the abdominal cavity;
- cholecystography;
- MRI and CT of the bile ducts;
- endoscopic cholangiopancreatography.
The final diagnosis of cholelithiasis is made after receiving a transcript of all the examination results, as well as blood and urine tests.
You can read more about the types of diagnostics in the articles: Ultrasound of the gallbladder and liver CT scan of the liver: indications, contraindications, preparation for MRI examination of the gallbladder and ducts
Causes of stone formation
Stones are formed as a result of changes in the chemical composition of bile. This happens for a number of reasons:
- as a result of rapid increase in body weight,
- when taking foods that contain cholesterol,
- with an infectious disease.
Exorbitant levels of cholesterol in the blood can become a catalyst for disease. Bile saturated with this organic compound changes its composition and becomes more viscous. This condition of bile is called lithogenic and it poses a great threat. Congestion can be caused by kinks in the gallbladder, various infections and pathological formations. In women, hormonal changes during pregnancy can be a provoking factor. Disturbances in the functional state of the biliary tract can be triggered by intestinal disorders or disruption of its microflora.
How to relieve an attack of biliary colic at home
An attack of biliary colic means the appearance of sudden acute pain that intensifies with any movement, coughing or breathing. Appears as a result of spasm of smooth muscles in the walls of the gallbladder against the background of displacement of stones. Stones often get stuck in the neck of the bladder, blocking the outflow of bile, which begins to accumulate and flows directly into the intestines.
In case of severe and acute pain, vomiting of bile, high body temperature, it is recommended to call an ambulance as soon as possible.
Before the ambulance arrives
Before the arrival of specialists, the patient can be given first aid, which will help relieve or reduce the attack:
- take a horizontal position, lie on your back;
- maintain bed rest;
- put an ice pack on the abdominal area, never a heating pad;
- drink plenty of warm water in small portions;
- no food can be taken, complete fasting;
- if the temperature rises, cover the patient with a blanket;
- It is not advisable to take antispasmodics.
After completing all the steps, the patient must be taken to the hospital, even in cases where relief has occurred. Taking antispasmodics can only blur the clinical picture and temporarily improve your well-being. The danger of biliary colic is that there is a risk of rupture of the bile duct, which can lead to the death of the patient.
Help in hospital
Relieve pain with injections of Papaverine or Dibazol. No-Shpu or Eufillin is administered intramuscularly. Analgesics are used as auxiliary painkillers.
If these medications do not help, a potent drug is administered, for example, Tramal, Atropine, etc. If vomiting does not stop, use Cerucal. To replenish fluid losses, a drink based on a solution of Regidron or Citroglucosolan is prescribed.
Main rules of prevention
Prevention of gallstone disease is carried out on the basis of several important rules. For example, a diet that will allow you to normalize your body weight is important. It is necessary to provide the body with a sufficient amount of physical activity. The body must be constantly in motion. It is worth eating frequently, literally every 3 hours, to provoke the gallbladder to empty regularly. Ignoring this point leads to the formation of numerous deposits in this internal organ.
Prevention of gallstone disease necessarily includes compliance with the drinking regime. It is necessary to drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day every day. Tea, coffee, juice do not count, we are talking only about clean water.
Prevention of gallstone disease in children is to reduce the amount of juice in the diet. It must be replaced with water, since juices contain elements that subsequently group into stones.
Some types of work provoke the movement of stones; for example, if a person is in an inclined position for a long time, the stones begin to move.
Female representatives should be concerned about reducing their intake of estrogen - due to its content in the body, gallstones often form in the gall bladder. Anyone who takes oral contraceptives should pay attention to this point.
Treatment of cholelithiasis
Therapy for cholelithiasis directly depends on the size of the stones. If the formation is no more than 5 mm, conservative therapy is prescribed, which consists of taking medications and following a diet. In practice, minimally invasive techniques are often used that affect stones with laser, ultrasound or shock wave pulses. In cases where the stones are large or block the bile ducts, the only treatment option is surgery.
The main goal of treating stones in the gallbladder or ducts is to normalize the composition and physical properties of bile, removing stones from the lumen of the gallbladder and its ducts.
Medicinal method for removing stones
Drug treatment of gallstones consists of the use of several groups of drugs with symptomatic and systemic action. Their use allows you to eliminate symptoms, destroy small stones, remove them naturally, and also normalize the functioning of the digestive system. Among the main groups of drugs, the ones most often used in practice are:
- Antispasmodics - relieve spasms in the gallbladder and ducts, relieve pain: No-shpa, Drotaverine, Papavarine. Prescribed in the acute period for severe pain.
- Medicines based on ursodeoxycholic acid : Ursofalk, Ursosan and Ursoliv. Their use makes it possible to enhance the processes of bile formation, reduce the amount of cholesterol in the liver, and destroy small formations.
- Choleretic - accelerate the secretion of bile, stimulate intestinal function, relieve inflammation, prevent the formation of new stones: Allohol, Flamin, Holosas.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed for relapses of the disease when severe pain symptoms are present: Ibuprofen, Analgin, Nurofen, Nimid and others.
The duration of therapy, dose and frequency of taking medications is prescribed by the doctor individually for each patient. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe other drugs that will relieve acute symptoms and improve the patient’s overall well-being.
Ultrasonic stone removal method
If stones in the gallstones and ducts do not exceed 2 cm, modern medicine offers their removal using ultrasonic waves. Consists of the effect of appropriate equipment on stones. The process uses a shock wave, which allows you to destroy formations and remove them naturally.
Ultrasonic crushing of stones is carried out through the abdominal wall. After the procedure, choleretic drugs are prescribed to help speed up the release of fragments. The disadvantage of the procedure is the risk of damage to the walls of the bile ducts from stone fragments.
Laser stone removal method
An effective method for cholelithiasis is considered to be laser stone breaking or the “lithotripsy” procedure. It is similar to the ultrasonic method. The doctor makes a small puncture over the organ, inserts a special instrument through which the beam penetrates and removes choleliths. This technique is especially effective for cholesterol formations. Treatment consists of 3 to 6 procedures that do not require inpatient observation.
The procedure is not performed on elderly people, those with obesity or stones larger than 3 cm. Crushing stones with a laser is painless and has a good therapeutic effect.
External shock wave lithotripsy (ESWLT)
External shock wave lithotripsy or ESWL - destruction of stones using ultrasonic waves. Under their influence, stones break down into small particles, which are easily removed naturally. Unlike laser fragmentation, with remote lithotripsy, there is no need to insert an endoscopic instrument.
The procedure is carried out under the control of electromagnetic pulses or ultrasound, which affect only the stones, without damaging soft tissues. The procedure can only be performed for stones that are no larger than 2.5 cm in size. Upon completion of the procedure, the crushed stones are excreted naturally through the kidneys.
Surgical method for removing stones
If gallstones are larger than 3 cm, the only method of removing them is surgery (cholecystectomy). There are 3 main methods of surgical treatment:
- Abdominal with open access - removal of the gallbladder along with stones through a large incision on the anterior abdominal wall.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed using special equipment through 3 to 4 small incisions.
- Cholecystolithotomy - consists of removing stones while preserving the organ.
Indications for surgery are conditions when stones in the organ occupy more than 70% of the bladder cavity, there is organ dysfunction, or stones are in the ducts. After the operation, you can completely get rid of the disease, but for this you need to follow a strict diet, take medications prescribed by your doctor, and follow all instructions.
You can read more about everything here: Laparoscopy of the gallbladder Laparoscopy of the gallbladder. Reviews about the operation
Diagnosis of the disease
Initially, the doctor collects data on the course of the disease, complaints, the presence of risk factors for the development of pathology, examines the patient’s abdomen, and palpates it. To clarify the suspected diagnosis, the following is prescribed:
- Ultrasound examination of the liver and biliary system. Safe, affordable, very effective diagnostic method.
- Survey radiography of the abdominal organs. Often allows us to identify other pathological conditions that mimic the clinical manifestations of cholelithiasis (for example, perforation (breakthrough) of an ulcer).
- General blood analysis. Pathological changes (increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, increase in the number of leukocytes) are usually detected with an exacerbation of gallstone disease, as well as with the development of its complications.
- Cholecystography. The study consists of taking an X-ray of the biliary system after first using an X-ray contrast agent orally or administering it intravenously. It is a very informative method for identifying pathology of the gallbladder and ducts.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy. Allows you to detect other pathological conditions of the upper gastrointestinal tract, and sometimes identifies stones at the junction of the bile and pancreatic ducts on the wall of the duodenum.
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography. It is a research method in which the skin and abdominal wall of the patient are pierced with a needle, a radiopaque substance is injected into the lumen of the hepatic ducts, and then an image is taken.
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreaticography. It is carried out using an endoscope, which is placed in the duodenum (as with fibrogastroduodenoscopy), then an X-ray contrast agent is injected into the common bile and pancreatic duct, and pathological changes in them and in the gallbladder are determined.
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. With this method, a conventional MRI study is performed, displaying in detail the condition of the liver, biliary system and pancreas.
- Endoscopic ultrasound examination of the pancreatobiliary zone. As with fibrogastroduodenoscopy, an endoscope is inserted, with an ultrasound sensor at its end. During the study, it is possible to judge the condition of the pancreas, biliary system, including the gallbladder.
- Bilioscintigraphy. Expensive and not the most effective research method, which significantly limits its use. During this procedure, the patient is injected with a drug, which is then secreted by liver cells through the biliary system, revealing its pathological changes, which can be detected using a special camera.
Traditional methods of treating cholelithiasis
As an auxiliary therapy, many use traditional methods of treatment that will reduce the symptoms of the disease and improve the functioning of the digestive system. Herbs are often used as medicinal raw materials, from which decoctions and infusions are prepared.
Recipe No. 1 . To prepare, you need to take equal parts of immortelle flowers, peppermint leaves and coriander fruits. Mix everything, pour boiling water, leave for 2 hours, strain, take 50 ml 2 times a day.
Recipe No. 2 . To prepare the following recipe, you will need wormwood herb, immortelle flowers, dandelion root, madder root. Herbs are taken in equal parts, 10 g is poured with boiling water, left for 1 hour, filtered and taken 50 ml twice a day.
Recipe No. 3 . For preparation, take chamomile flowers, immortelle flowers, peppermint leaves, dandelion root and buckthorn bark. All herbs are poured into 0.5 l. boiling water, put on low heat for 10 minutes. Then infuse, filter and take one glass every day in the morning and before bed.
Various pharmaceutical preparations will be beneficial for cholelithiasis, but they should be taken, like any traditional medicine recipe, after prior consultation with a doctor.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is very common and effective. There are a number of natural products and plants that have beneficial properties in the prevention of gallbladder diseases:
- Dandelion. You can consume both the greens of the flower and make tinctures from it.
- Thistle.
- Mint.
- Pears.
- Lemon.
Apple cider vinegar is also considered very useful; with the help of this remedy it is possible to reduce cholesterol levels in the blood. For daily consumption, fresh vegetable juices are recommended, which you can make yourself.
Gallstone disease in children
In pediatrics, cholelithiasis is much less common than in adults, accounting for only 1% of all diseases of the digestive system, while girls are 2 times more likely to suffer from this disease than boys. The causes of the pathology are often associated with congenital pathologies of the biliary system and poor nutrition.
Clinical signs of the disease are less pronounced. The child often complains of pain in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies after eating, as well as nausea and loss of appetite. All these symptoms should not be left without medical attention.
Treatment tactics depend on several factors: size, age, concomitant diseases. For small formations, the doctor prescribes medications, diet therapy, and only when the stones are large or they block the bile ducts, the doctor prescribes surgery. You can read more about everything here.
What is postcholecystectomy syndrome?
A large percentage of patients after removal of the gallbladder due to cholelithiasis experience many discomforts, such as:
- repeated episodes of pain of varying intensity and duration, localized in the areas of the right and left hypochondrium (sometimes there is girdling pain);
- frequent diarrhea;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increased gas formation in the intestines;
- weight loss, weakness, various signs of vitamin deficiency (arise as a result of impaired absorption in the intestines of substances necessary for the body, micro- and macroelements).
All these symptoms develop as a result of dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi after removal of the gallbladder, since the supply of bile changes, which normally accumulates in the gallbladder and is released only when food enters the duodenum, and after cholecystectomy it flows continuously.
Treatment of the syndrome is usually symptomatic; in addition, it is advised to adhere to dietary recommendations.
Diet and nutrition for cholelithiasis
An important place in the treatment of gallstone disease is given to nutrition. The doctor prescribes treatment table No. 5, which improves the functioning of the liver and biliary tract, stimulates bile secretion, and improves the functioning of the digestive system.
Dietary recommendations
Diet therapy consists of eating the following foods:
- vegetable soups;
- porridge with water;
- vegetables and fruits with non-acidic pulp;
- lean meats and fish;
- crackers, day-old bread;
- low-fat fermented milk products.
Vegetable and animal fats, oxalic acid, salt and coarse fiber should be excluded from the diet. It is recommended to consume sufficient amounts of proteins and carbohydrates. You need to adhere to a strict diet until complete recovery. Patients should be fed in small portions from 5 to 6 times a day. Food should be steamed or served boiled.
What is prohibited
It is strictly forbidden to use:
- fatty meats;
- seasonings;
- smoked meats;
- dairy products;
- sweets;
- pickled products;
- pickles;
- sausages;
- baked goods;
- alcoholic drinks.
Any errors in nutrition or consumption of prohibited foods can cause an attack of biliary colic. If a person takes medications, but at the same time consumes foods that are prohibited, the treatment will have no effect. Only an integrated approach will help reduce the manifestations of the disease and reduce the risk of possible complications.
General nutrition rules
During the period of using folk recipes for getting rid of cholelithiasis and treatment without surgery, the diet and regimen must be strictly observed. Small meals - at least 5-6 times a day. This way the bile will not stagnate.
Daily caloric intake is up to 2500 kC. The menu should include legumes, buckwheat, fruits, and vegetables. We must not forget about mineral water - “Essentuki No. 4”, “Borjomi”.
Foods high in cholesterol and sugar should be limited or eliminated altogether. Drink at least two liters of clean water daily. We also recommend watching a video where nutrition for cholelithiasis is presented.
If you get sick, you need to follow certain rules in eating that will help avoid the development of the disease.
To do this, you must take into account the calorie content of food (should not exceed 2400 Kcal), do not overeat, exclude “harmful” foods from your diet, and eat small meals (5-6 times a day).
| Exclude: |
|
| Give preference: |
|
When there is no exacerbation of the disease, you need to adhere to a diet called “Table No. 5”, which is varied. It contains almost all products. At night with this diet, it is recommended to consume fermented milk products.
Proper nutrition will help normalize a person’s condition: reduce the risk of new pain attacks and the formation of stones.
During an exacerbation - “Table No. 5SH”, it reduces calorie content, limits fats and excludes vegetable oil, all food should be pureed, boiled or steamed, portions are reduced by half, the norm for bread consumption is 200 g / day, meat and fish - 100 g/day.
Complications
In the absence of proper therapy, cholelithiasis can lead to serious complications that can be dangerous to the health and life of the patient:
- Biliary pancreatitis.
- Peritonitis.
- Gangrenous cholecystitis.
- Cholangitis.
- Empyema of the gallbladder.
- Dropsy.
- Secondary cirrhosis.
Self-medication, uncontrolled use of medications, or alternative treatment without prior consultation with a doctor often lead to serious consequences of the disease.
Additional Treatments and Prevention
In addition to traditional methods, both for primary and secondary prevention of cholelithiasis, and for additional therapy, drugs intended to normalize digestion are used. Medicines are used that break down fats and restore the balance of bile composition. Thanks to the crushing and dissolution of stones using shock wave therapy, they begin to leave the body along with feces.
It is important to remember that in all cases, even if we are talking about the prevention of gallstone disease with folk remedies, you need to consult a doctor. After all, independent selection of methods for preventing and treating a disease of this kind sometimes leads to the fact that the bile ducts are simply clogged. And this already creates a danger to life. Complications may begin, and sometimes it is for this reason that an acute form of cholecystitis develops.
Gallstone disease, treatment with folk remedies. How now to get rid of the misfortune?
The most unpleasant property of stones is that if they are present, sooner or later you will still end up on the operating table. It is necessary to fight them at the initial stage, or even better, to prevent them altogether by living actively, without excess weight, cholesterol and the like. And of course, folk recipes will come to the rescue to help get rid of problems.
Our natural doctors will improve the flow of bile, help liquefy it, dissolve small stones, relieve inflammation and spasms. They can help. But God forbid - listen to the advice of grandmothers and aunties on how to remove stones, such as: “after drinking a glass of lemon juice and two glasses of sunflower oil, lie down on a heating pad.”
If you have small sand, it’s not scary, but if the pebbles are larger than a couple of millimeters, you will have severe biliary colic up to the point of rupture of the bladder, an emergency operating table and cholecystectomy are guaranteed for you. It is better to act gradually and gently.
At home, you can make mixtures from mint, chicory, dill seeds, parsley roots and marshmallow. Corn silk is very useful. They stimulate bile secretion, liquefy it and help restore gallbladder motility. They can be bought at a pharmacy, along with instructions for use.
In addition to them, fennel, thyme, lemon balm, yarrow mixtures with chamomile and buckthorn bark will help improve your condition. Tansy flowers should be used with caution. They are not recommended if stones are already present, as they have a strong choleretic effect.
Diet
Only a nutritionist or attending physician can correctly balance the amount of substances that the body needs. However, there are a number of products that interfere with the necessary processes in the bile ducts:
- smoked meat,
- salo,
- hot sauces,
- seasonings and spices.
Recommended for use:
- poultry meat,
- fermented milk products,
- cereal porridges,
- vegetables,
- fruits.
It is best to prepare dishes using a method that is gentle on the body - boiling or steaming. Healthy drinks include natural juices and dried fruit compotes.
Causes of gallbladder disease
- infections - Escherichia coli, streptococcus, staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, cause inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gallbladder and complications in the form of cholecystitis;
- an imbalance in the chemical composition of bile (increased cholesterol, bile acids and minerals) contributes to the formation of stones and the development of cholelithiasis;
- disruption of the innervation of the gallbladder leads to the development of dyskinesia;
- giardiasis;
- the role of hepatitis viruses cannot be excluded;
- hereditary changes in the shape and size of an organ.
Prevention of exacerbation of cholelithiasis
After a course of treatment in a hospital, rehabilitation therapy is prescribed. It includes various drugs that improve liver function, for example, Essentiale and other hepatoprotectors. It is important to prevent a possible attack in the future. A sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes are risk factors.
You should stick to a strict diet for as long as possible; table No. 5 is recommended. It is necessary to refuse semi-finished and instant products. Food should be fresh and balanced towards increasing the proportion of protein and decreasing fat. Sweets are allowed only of natural origin: honey, dried fruits, berries. Physical exercise and quitting smoking, as well as avoiding stress (for example, changing occupations) greatly contribute to recovery.
Latest developments in the treatment of cholelithiasis
Scientists were able to find a direct connection between the composition of bile and the activity of the bladder muscles with the stimulation of androstane receptors in the liver and small intestine. Hence the reduced risk of developing the disease in men and its increase in the event of an imbalance between male and female hormones. These receptors play an essential role in the metabolism of cholesterol and triglycerides. Their activity weakens inflammatory processes in the walls of the bladder.
As part of the research, animals were injected with substances to stimulate these receptors, which reduced the risk of developing cholelithiasis and cholecystitis by 61%. Doctors hope to create a completely new method for the treatment and prevention of cholelithiasis, which will reduce the incidence of complications and the need for surgical treatment.
Preventing stone formation
Due to the serious threat to the pathology of human life and health, the prevention of gallbladder diseases is a necessary precaution even for the healthiest people. Measures to prevent gallbladder diseases will help both avoid their development and strengthen the body. The main components of preventive action are:
- Healthy eating.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Physical activity.
- Stabilization of body weight.
To prevent disruptions in the digestive system, you first need to start eating right. It is necessary to avoid fried, fatty foods, foods containing high cholesterol. Careful control of cholesterol levels will help prevent changes in the composition of bile that result in the formation of gallstones.
It is necessary to pay attention to existing chronic diseases, especially those that can cause blockage of the common bile duct or form a stone in the bile ducts. It is necessary to treat chronic diseases, otherwise they will lead to complications. Accumulated stones in the bile ducts, in combination with other diseases of the digestive system, can cause biliary cirrhosis of the liver, the treatment of which will require significant medical efforts.
Stabilizing body weight will be very beneficial for the gallbladder and will significantly reduce the risk of pathologies. Obesity greatly increases the load on internal organs, especially the heart and those responsible for digestion.
There are a number of medications that can be taken to prevent gallbladder diseases. However, they should only be prescribed by a doctor after conducting research.
Why gallstones form
There are many prerequisites for the development of cholelithiasis. These include congenital and acquired disorders in the structure of the biliary system:
- excesses of the gall;
- adhesions;
- duct contractures;
- tumors;
- scarring;
- fibrous degeneration of fibers.
Metabolic disorders are considered to be the main ones in the mechanism of development of pathology. GSD accompanies fermentopathy, diabetes, lipid metabolism disorders, and hypercholesterolemia. The most common cause is inflammatory changes in the ducts and bladder, provoked by sluggish infectious diseases (hepatitis, cholecystitis). These lead to impaired functioning of hepatocytes with subsequent changes in the ratio of synthesized fatty acids. Metabolism often changes due to hormonal fluctuations. Stagnant processes accompany dyskinesia of the ducts and gallbladder.
Lithogenic bile, oversaturated with cholesterol, is formed when consuming excessive amounts of unsaturated fats and a lack of phospholipids. The root cause of cholelithiasis can be allergic and autoimmune pathologies, chronic diseases of other organs of the digestive tract (stomach, intestines, pancreas).
Provoking factors
Nutritional disorders are considered to be the trigger for the deposition of gallstones. Stagnation can be provoked by fasting and strict diets. Exacerbation of the disease is caused by overeating and consumption of fatty foods. Metabolic disorders are caused by poor nutrition, the predominance of fats and simple carbohydrates in the diet, and obesity.
Provocateurs also include hereditary predisposition, a sedentary lifestyle, and treatment with certain medications. Among females, the likelihood of cholelithiasis is increased by multiple pregnancies, as well as the use of estrogen-type drugs (birth control pills).
Some statistics
According to statistics, cholelithiasis affects approximately 10% of the population. Among people over 70 years of age, the number increases to 30%. In economically developed countries, pathology is more common, and the number of patients doubles every decade, which is associated with the spread of the “Western diet” and a decrease in physical activity of the population. Residents of eastern countries suffer least often from cholelithiasis, which is explained by the consumption of food mainly of plant origin.
In women, cholelithiasis is diagnosed 2-8 times more often than in men. Therefore, being female is considered a risk factor.
In 80-90% of patients with identified stones, the cholesterol nature of the deposits is determined. Drug therapy gives positive results in 40% of cases. Approximately 50% of patients treated with medication experience a relapse of the disease. Surgery is needed in approximately a third of cases of cholelithiasis.
Diagnosis of biliary sludge
Biliary sludge (BS) can be a source of stone formation in the gallbladder, a cause of biliary pancreatitis, a marker of early cancer of the gallbladder, stenosing papillitis (duodenal papilla through which bile enters the intestine).
Biliary sludge (thick bile with microlites) passes through the entire human biliary system, which has a huge number of pain receptors and causes pain.
- Clinical manifestations are similar to those of dyskinesia; they are described in detail here in the paragraph “Biliary dyskinesia - clinical manifestations.” The long-term existence of BS not only causes clinical manifestations and contributes to the development of complications such as: acute cholecystitis, “disabled gallbladder”, cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts), acute pancreatitis. Biliary sludge can also be asymptomatic, but given the prognostic features - the possibility of stone formation, which can subsequently lead to surgical treatment - removal of the gallbladder, examination of the gallbladder and biliary tract should be included in the clinical examination program.
- Biochemical liver tests, pancreatic enzymes of blood, urine, feces.
The main method of examination is ultrasound, which should be carried out after 3 days of preparation for a routine examination or for urgent indications. Ultrasound examination of gallbladder function. More details in the ultrasound section.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (GDS) with mandatory examination of the major duodenal papilla!
- Modern diagnostic methods - hepatobiliscientigraphy with 99mTc, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), bile microscopy are carried out in specialized hospitals.
Diet for gallstone disease
The attending physician gives advice and prescribes a diet, who determines in detail the range of substances allowed and prohibited for use. Provides recommendations for daily balance of proteins and fats. In addition to fatty and spicy foods, it is wise to reduce high-calorie foods containing refined carbohydrates and cholesterol.
Following a proper diet reduces the frequency of spasms of the gallbladder walls, which can provoke the migration of small stones and sand.
With a concomitant acute attack of chronic pancreatitis, it may be recommended to drink water while completely hungry until relief occurs, and then eat frequently only light meals.
If the patient seriously follows the diet, then the periods of remission will become longer and longer. In addition to fractional meals, experts recommend weekly fasting days.
The diet includes:
- Lean meat
- Cheese
- Fish
- Vegetables
- Dairy
- Berries
- Fruits
- Cereals
Eggs are also included in the menu, but not every day, but about one every other day, and it is preferable to cook an omelet. The must-have vegetables are zucchini, cauliflower, carrots, and pumpkin. Watermelon, strawberries, prunes, grapes improve intestinal function and cope with bile stagnation. Low-fat cottage cheese and sour cream provide animal protein and calcium.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptomatic picture of cholelithiasis, or rather its intensity, depends on the degree of development of the disease. So, at the initial stage it practically does not reveal itself. The only thing that may bother the patient is heartburn and heaviness in the hypochondrium after a feast with an abundance of fatty foods.
If there are small stones in the lumen of the gallbladder, when they are in a static state, the patient also does not feel pain or other manifestations of discomfort. This stage of the disease is called hidden or latent.
The following symptoms indicate its occurrence:
- belching and heartburn, accompanied by a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- gas formation;
- diarrhea;
- weak aching pain in the right hypochondrium;
- frequent bouts of irritability and weakness.
Any change in the state of the body, be it eating hot spices, fatty meats or a stressful situation, can cause stones to move through the ducts.
As a rule, colic occurs, which can be identified by a number of symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- a feeling of strong compression under the ribs on the right;
- acute paroxysmal pain;
- sometimes - yellowing of the sclera.
When stones actively move through the bile ducts, there is a risk of spasm and inflammation. That is why it is important to consult a doctor in time for detailed diagnosis and further treatment of the disease.
Diagnosis of pathology
Due to the fact that the disease is quite common, diagnostic methods today make it possible to accurately identify the presence of pathology in the shortest possible time. The most effective method is ultrasound. Using ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible to accurately determine the stage of development of the disease, obtain all the necessary information about the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and other digestive organs, and, based on this data, prescribe the most effective treatment. In addition to ultrasound, in such cases the following is also used:
- cholecystography,
- x-ray,
- MRI.
In order to have a complete picture of the condition of the body, the doctor prescribes additional tests of urine, blood and some other studies.
Sample menu
Breakfast 1. Cheese pudding – 150 g (no sugar). Buckwheat porridge – 150 g (seasoned exclusively with vegetable oil – 10 g). A glass of tea with added milk.
Breakfast 2. Apple – one.
Dinner. Vegetarian borscht – 400 g. Boiled meat combined with milk sauce – 60 g. Stewed carrots – 150 g. Fruit compote.
Afternoon snack. Rosehip decoction.
Dinner. Boiled fish with milk sauce – 80 g. Vegetable stew – 200 g. Tea – a glass.
For the night. One glass of kefir.
You are allowed to allow yourself 300 g of white bread and no more than 30 g of sugar during the day. It is recommended to consume no more than 10 g of butter. It is very important to constantly drink mineral water. Just remember that the liquid must be without gas.
Biliary colic
The stones may not bother you at all for a long time, being in a motionless state. If they move from their place and enter the ducts, they provoke an acute attack. It is called biliary colic. Often such manifestations occur in waves. The patient's normal condition deteriorates sharply. This makes itself felt by cholelithiasis. An attack of colic is localized in the right hypochondrium. It is accompanied by severe pain, stabbing and tearing. The patient experiences extreme pain. The pain is so intense that some even scream. It is worth noting that unpleasant sensations can radiate to the shoulder blade, neck, collarbone, and shoulder. There are cases when the pain spreads to the heart area. Quite often, such manifestations are mistaken for angina pectoris.
Seizures can occur for no reason. But most often their appearance is provoked by spicy fatty foods, alcohol, stress, and physical activity.