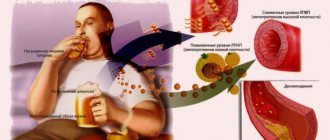
Cholesterol is a substance, most of which is produced by the human body; it is from it that plaques are formed on the walls of blood vessels during the development of atherosclerosis, a dangerous pathology that can lead to death. Translated from ancient Greek, “cholesterol” means “solid bile,” and just by the name it’s easy to imagine what this compound is.
Cholesterol belongs to the class of lipids; only 15-20% of the total enters the body with food. This substance is found in animal fats, meat, and egg yolks. Cholesterol is involved in vital processes; it is a building material for membrane cells. In addition, without it, the production of certain sex hormones is impossible. Chl is part of lipoproteins; they can have low density (this is the so-called “bad” cholesterol) or high density (this is “good” cholesterol).
Standards have been established for general, good and bad Chl. If they are violated, a person begins to develop a variety of pathologies.
Important! The level of cholesterol in the body of high and low density, as well as total cholesterol in the blood of a person by age and in the elderly, as a rule, should always be normal. People are accustomed to maintaining normal cholesterol levels by age with various medications and diets. The normal level of cholesterol in the blood according to age should be four or five mmol/liter.
Blood cholesterol levels in women by age (table)
In medicine, a whole range of tests for cholesterol levels in the blood is used. First of all, in order to determine the total cholesterol level, a biochemical blood test from a vein is used, which is carried out on an empty stomach. In case of atherosclerosis, it is necessary to conduct a more detailed blood test for cholesterol (lipidogram) to determine the following indicators:
- total cholesterol includes free and bound forms (HDL, LDL, VLDL);
- high density lipoproteins;
- low density lipoproteins.
| Age, years | Total cholesterol, mol/liter | HDL, mol/liter | LDL, mol/liter |
| Up to 19 | 3,1-5,9 | 0,13-1,3 | 1,55-3,89 |
| 20-39 | 3,1-7,0 | 0,78-1,85 | 1,55-4,1 |
| 40-59 | 3,9-8,5 | 0,78-2,07 | 2,07-5,7 |
| Over 60 | 4,1-8,5 | 0,78-2,20 | 2,59-5,57 |
After 25 years, women are recommended to check the concentration of cholesterol in their blood every 5 years, and after 40 years – every two to three years, since hormonal changes during the period of preparation for menopause, menopause and the postmenopausal period can significantly affect lipid metabolism in a woman’s body.
One of the significant factors in increasing cholesterol above normal in women after 50 years of age is a decrease in the sex hormones estrogen, as a result of which metabolic processes associated with triglycerides, lipoproteins and cholesterol slow down.
The normal level of cholesterol indicates the proper functioning of the heart and blood vessels, therefore, with a significant increase in indicators, hormone replacement therapy with estrogen can be carried out in order to reduce the level of lipoproteins in the blood.
Atherogenic coefficient
The atherogenicity coefficient is a special formula for measuring the likelihood of developing atherosclerosis with high blood cholesterol.
The atherogenic coefficient is often used when examining overweight women and men, with high LDL levels, or with a hereditary predisposition and is calculated using the formula (total cholesterol - HDL) / HDL.
The norms for the atherogenic coefficient are as follows:
- newborn children – 1;
- men 20-80 years old – 2.6;
- women 20-80 years old - 2.2.
The higher the coefficient, the greater the likelihood of atherosclerosis and the occurrence of pathologies of the heart and vascular system.
"Bad" and "good" cholesterol
An organic fat-like compound plays a vital function in the body, promoting the renewal of the epithelium of the skin and organs.
- It, like cement, supports the cellular framework;
- Being integrated into the membrane, it increases the density and makes it rigid;
- Progesterone, androgens, estrogen, testosterone and other hormones are synthesized on a cholesterol basis;
- For its development, the baby receives cholesterol from breast milk;
- Cholesterol is an important component of bile, which helps digest fats and, therefore, cholesterol;
- The dietary compound helps maintain a healthy intestinal lining;
- Vitamin D, used for growth, immune support, insulin synthesis, and steroid hormones, is produced from cholesterol with the help of sunlight.
80% of cholesterol is formed in the kidneys, liver, adrenal glands, and intestines. The body receives another 20% from food. The substance does not dissolve in water, so it is delivered through the blood along with proteins that form a soluble form. This substance is called lipoproteins.
There are several classes of lipoproteins: low density, very low, high, triglycerides, chylomicrons.
Each variety performs its own function. LDL is insoluble, so it often precipitates and forms seals in blood vessels, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis. In everyday life they are called “bad” cholesterol. HDL transports cholesterol to the liver, from where excess is excreted from the body.
This class of lipoproteins does not have an atherogenic effect, which is why they are called “good” cholesterol. Labeling does not mean that the first type only brings harm to the body, while the other works for benefit.
Low density of lipoproteins is dangerous because they do not always reach their goal (transporting cholesterol into the cell) and settle in the vascular bed in the form of dense plaques. High density guarantees not only proper transportation, but also the ability to remove some of the accumulated cholesterol plaques.
If LDL can be considered as a supplier, then HDL plays the role of regulators, controlling excess cholesterol. If a disorder occurs and the first type of lipoprotein dominates, suppressing the activity of the second, a biochemical analysis shows increased cholesterol.
Not only the doctor should know these features - it is the patients who have to take emergency measures.
Causes of high cholesterol
An increased level of “good” cholesterol is not dangerous, but indicates proper fat metabolism and reduces the possibility of developing cardiovascular diseases.
An increase in cholesterol in the body causes pathological processes associated with disruption of blood vessels and capillaries. A significant increase in low-density lipoproteins can be caused by the following reasons:
- Poor nutrition is the main cause of increased cholesterol if the diet includes large amounts (more than 40% of daily calories) of foods with saturated fats (palm oil, fatty pork) and trans fats (margarine, confectionery fat).
- Physical inactivity is a sedentary lifestyle, which leads to weakening muscles, weight gain and the occurrence of cardiovascular diseases.
- Bad habits - smoking and alcohol - increase the likelihood of angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, stroke, etc.
- Diabetes mellitus causes liver dysfunction and weight gain.
- Hypothyroidism is a deficiency of thyroid hormones, as a result of which the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) increases significantly. The TSH level directly affects the production of cholesterol, increasing the level of low-density lipoproteins.
- Hepatitis C. In the chronic course of hepatitis, active production of fatty acids occurs in liver cells, as a result of which cholesterol levels in the blood increase.
- Cholestasis is a pathological condition associated with improper flow of bile into the duodenum, which occurs with alcoholic cirrhosis, heart failure, and hepatitis. With cholestasis, lipid metabolism is disrupted, resulting in a discrepancy in cholesterol levels, which leads to the appearance of vascular plaques and changes in the structure of red blood cells.
- Chronic kidney diseases cause the development of lipid metabolism disorders, while the functional state of the kidneys further deteriorates due to the deposition of fat in the membranes of the kidney cells.
- Genetic predisposition to lipid metabolism disorders.
It is believed that in men and women after 50 years of age, the likelihood of an increase in “bad” cholesterol increases as a result of a combination of several reasons: decreased physical activity, a slowdown in overall metabolism, the presence of chronic diseases of internal organs, overeating and excess weight.
Triglycerides
These substances refer to fats contained in the blood plasma of every person. This is one of the most common types of fat cells; they are the main supplier of energy. But, like cholesterol, triglycerides should not exceed certain standards - then everything will be fine with a person’s health. Their level can be determined with a detailed blood test.
Typically, an increase in these substances is observed if a person receives more calories from food than he burns. If there are too many of them, metabolic syndrome develops. In this case, the following symptoms occur:
- a sharp rise in blood pressure;
- increased blood glucose levels;
- decrease in the concentration of beneficial chol.
Outwardly, this manifests itself as fat deposits, first on the stomach and around the waist, then on the hips, etc. A consistently high triglyceride content leads to the development of pathologies such as heart attack, stroke, other heart diseases, and diabetes.
The normal triglyceride level is considered to be no more than 150 mg/dL for both sexes. If the readings exceed 200 mg/dL, you should consult a doctor and begin taking measures. The condition is considered critical if triglycerides rise to 400-1000 mg/dL.
But too low a triglyceride concentration is also a reason to consult a doctor. This happens with hyperthyroidism, excessive consumption of vitamin C, certain heart and lung diseases, myasthenia gravis, and cerebral infarction.
Main symptoms
An increased level of cholesterol in the blood is manifested by pathological deposits of fat-containing cells and disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Typically, symptoms of high cholesterol appear as follows:
- xanthomas are fatty tumors that occur locally or throughout the body (under the skin and in internal organs) and have a flat, nodular or tendon shape;
- xanthelasmas are yellow fatty tumors that appear on the upper eyelid, mainly in women;
- lipoid arcus cornea - a gray line at the edge of the cornea caused by cholesterol deposits;
- lipid infiltration of the retina - deposition of fat molecules in the retina of the eyes;
- impaired glucose tolerance - hidden, latent diabetes mellitus, determined by tests;
- pancreatitis;
- pain in the sternum resulting from narrowing of the coronary arteries of the heart muscle;
- dull pain in legs, varicose veins.
The high-risk group includes women with so-called abdominal obesity, when excess fat deposits are concentrated in the “apple”-shaped abdomen. At the same time, as the waist size increases, the possibility of developing atherosclerosis increases (more than 88 centimeters).
High level reasons
The main reasons why cholesterol may increase:
- smoking;
- insufficient physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- pregnancy;
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- diabetes;
- hereditary predisposition;
- obesity;
- kidney diseases;
- hypertension;
- pancreatic diseases;
- chronic increase in blood pressure (hypertension);
- liver pathologies.
This condition is considered the most favorable for increased cholesterol deposition in blood vessels. Often the symptoms of pathology go unnoticed.
The reason for this is the woman’s poor health , which is associated with the onset of menopause.
The same can happen during pregnancy. The expectant mother, due to changes in the body, accompanied by general malaise, may not notice the main problem with cholesterol deposition.
Since during pregnancy a woman's production of progesterone , the hormone responsible for fat deposition, increases, the doctor may recommend that the pregnant woman undergo blood tests several times to rule out an increase in cholesterol levels.
And what is the normal level of general indicator in the blood of women:
- at 20 years old - 3.16-5.6 mmol/l;
- at 30 years old - 3.36-5.95 mmol/l;
- at 40 years old - 3.81-6.52 mmol/l;
- at 50 years old - 4.0-7.3 mmol/l;
- at 60 years old - 4.2-7.5 mmol/l;
- at 70 years old - 4.48-7.42 mmol/l.
Read about what tests are done during menopause in our publication.
You can learn how to correctly determine your facial skin type from this article.
Recipes for masks for hair growth that are easy to make at home are in this material.
Cholesterol standards during pregnancy
During pregnancy, cholesterol levels in women change due to hormonal processes in the body. Since fats are involved in many aspects of metabolism, as well as in building the child’s nervous system, an increase in indicators is not a pathology, provided that there are no additional negative symptoms.
| Age, years | Maximum permissible cholesterol level, mol/liter |
| Up to 20 | 10,4 |
| 20-25 | 11,2 |
| 25-30 | 11,6 |
| 30-35 | 12 |
| 35-40 | 12,6 |
If cholesterol levels are elevated during pregnancy, it is necessary to carry out analysis regularly to monitor the dynamics of changes. In the absence of pathologies, lipid levels will remain stable or change slightly.
If the cholesterol concentration drops or rises sharply, and also exceeds the maximum permissible level by several points, it is necessary to conduct an additional examination, since rapid changes in tests may indicate the development of the following diseases:
- kidney and liver diseases;
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- metabolic disorders.
The cholesterol level in the body should be stable until the end of pregnancy. After childbirth, indicators decrease to normal over 2-3 months, provided there is normal nutrition and the absence of a genetic predisposition to lipid metabolism disorders.
Who's at risk
It is advisable for all adults to undergo blood tests on a regular basis, but there is a so-called risk group.
This category includes patients with the following problems:
- Obesity;
- Cardiovascular diseases;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Thyroid dysfunction;
- Pregnant women.
They must constantly monitor the level of biochemical indicators, taking tests every 1-3 months. This is the only way to notice a significant increase in cholesterol levels and respond to it in a timely manner.
How to lower blood cholesterol
Normalization of high cholesterol is carried out using complex therapy. To improve fat metabolism, women should adhere to the following recommendations:
- proper nutrition with limited fat and fast carbohydrates;
- combating physical inactivity – a sedentary lifestyle;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- drug prevention of cardiovascular diseases;
- treatment of diseases that increase cholesterol levels (diabetes mellitus, kidney failure, liver disease).
An integrated approach to reducing cholesterol will normalize your lipid profile even without the use of medications.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment for high cholesterol levels is aimed at improving the functioning of the vascular system and preventing the formation of plaques and blood clots in blood vessels and capillaries. The main drugs used for this purpose:
- Fibrates are medications that reduce triglyceride (fat) levels and increase con (gemfibrozil, clobifrate, phenobirate). Fibrates are prescribed to prevent heart attack and pancreatitis.
- Nicotinic acid is a B vitamin that helps reduce the amount of “bad cholesterol” (niacin).
- Statins are drugs that reduce the amount of low-density lipoproteins. The action of statins is aimed at the liver, as a result of which the formation of cholesterol is significantly reduced (fluvastatin sodium, simvastatin, atrovatin calcium, etc.).
- Absorption inhibitors are drugs that promote the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines rather than in the liver, resulting in a decrease in the level of LDL in the blood (ezetimibe).
Medications are prescribed when cholesterol levels are significantly elevated, as well as when there is a high risk of developing atherosclerosis and heart disease. In milder cases, to normalize fat metabolism, it is enough for women to adhere to a diet, lose weight and exercise.
What is it and what functions does it perform?
Cholesterol, cholesterol is an organic component, a natural fat-soluble compound that is part of the cell wall.
Types of cholesterol:
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is “bad.”
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is “good.”
Its main task is to transport substances into the cell and back.
It takes part in the production of female hormones , in the metabolism of fat-soluble vitamins, in the production of vitamin D, protects cell membranes, insulates nerve fibers, and is an additional element in the formation of bile products.
30% of cholesterol comes from food, and the rest is produced by the body itself.
Cholesterol analysis - important numbers from the “Live Healthy!” program:
Diet
The 10-table diet is an important condition for lowering cholesterol and is prescribed for high plasma lipid concentrations (6.5 mmol/liter and above). At the same time, all fatty foods of animal origin are excluded from the diet, since this is the main source of harmful fats.
It is prohibited to consume foods that increase low-density cholesterol, namely:
- lard, fatty meat;
- meat by-products;
- meat broths;
- sausages (sausage, sausages, ham, etc.);
- smoked, salty foods high in fat;
- hot sauces, ketchup, mayonnaise;
- butter, fatty cheeses;
- full fat whole milk, fatty fermented milk products;
- white bread, butter pastries, desserts with butter cream;
- products containing sugar (sweets, chocolate, jam, etc.);
- carbonated drinks;
- foods high in fat, salt and chemical flavor enhancers (chips, crackers, noodles, bouillon cubes, etc.);
- strong tea, coffee, alcoholic drinks;
- fried foods.
It is allowed to consume the following foods that reduce low-density cholesterol levels, namely:
- low-fat sea fish (tuna, hake, pollock, cod);
- lean poultry (chicken breast, turkey);
- wholemeal or wholemeal bread;
- durum wheat pasta;
- vegetables (cabbage, carrots, onions, tomatoes, cucumbers, pumpkin, beets, limited potatoes);
- vegetable broths;
- cereals (buckwheat, oatmeal, rice, etc.), legumes;
- vegetable fats (except palm oil);
- low-fat fermented milk dishes (cottage cheese, sour cream, yogurt, fermented baked milk, kefir);
- fruits and berries, nuts;
- fruit compotes, rosehip infusion, green tea.
If the norm of cholesterol in the blood is exceeded by several points, it is necessary to adhere to fractional meals and monitor the caloric content of the diet.
Nutritional correction to reduce cholesterol 7 mmol/l
The first thing you will have to do on the path to health is to adjust your diet using simple but effective techniques. You shouldn’t completely give up food of animal origin, but you will have to reduce the amount of fat you consume.
It is necessary to completely avoid the following products:
- High fat butter;
- Pork;
- Salo;
- Whole and condensed milk, cream;
- Fatty types of cheese;
- Fatty fish.
It is advisable to give up fast food - sandwiches, hamburgers, french fries. It is necessary to reduce the amount of sweets and flour products consumed. In addition to animal fats, you will have to give up fast carbohydrates, which, when entering the body, are converted into fat.
To correct the level of natural fatty alcohol, it is necessary not only to exclude its entry into the body from the outside, but also to deal with existing internal reserves. To do this, increase your consumption of fiber-rich foods.
This category includes:
- Unrefined cereals;
- Fresh vegetables;
- Unsweetened fruits;
- Legumes.
Folk remedies
Along with lifestyle changes and nutritional correction, you can use folk remedies that can lower blood cholesterol. Herbal decoctions have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the liver, kidneys and gastrointestinal tract, improve fat metabolism and increase the metabolic rate.
Dandelion roots
. The roots of the plant contain many useful substances, including inulin, flavonoids and organic acids. An infusion of dandelion roots improves metabolism, liver function, fat metabolism and increases the amount of bile acids.
Preparation: pour a teaspoon of roots with a glass of boiling water and let it brew. After the infusion has cooled, strain and drink in the morning after meals. The decoction must be consumed daily for two months.
Lemon-garlic cocktail
. Eating lemon is very useful in cases where cholesterol is higher than normal, since lemon contains acids, essential oils, phytoncides and flavonoids, as well as macro- and microelements.
Garlic is also a very useful product that is used to lower cholesterol, as it contains enzymes, minerals, glycosides and organic acids.
To prepare the cocktail, you need to extract the juice from one kilogram of lemons and grind the garlic into a puree so that its quantity is 200 grams. Garlic and lemon juice should be mixed and stored in the refrigerator for three days.
The cocktail should be consumed daily in the morning before breakfast, diluting one tablespoon of the mixture in a glass of water. The course of treatment is 3 months.
Who is at risk
Doctors believe that the pathology can be caused by a sedentary lifestyle, uncontrolled consumption of fatty and high-calorie foods, and overeating.
The age of the woman is also important in this case. Over time, cholesterol levels in the female half of humanity may change.
This process depends on the presence of diseases and pathologies. Uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages, smoking, and junk food leads to exhaustion of the body.
As a result, metabolic disorders, various diseases and a sharp jump in cholesterol in the blood.
The role of cholesterol for the male body
There is an opinion that most often men suffer from problems associated with high cholesterol.
They are the ones at risk and are required to carefully monitor their health. This organic substance takes a huge part in the natural production of corticosteroid hormones and vitamin D. Regulates the functioning of bile acids and the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Cholesterol is especially important for representatives of the stronger sex due to the production of sex hormones, which allow men to be them in all respects.
Cholesterol itself is not harmful and is responsible for a number of functions in the body. First of all, it is needed to ensure the stability of the cell membrane layer. Cholesterol provides a protective effect that makes cells denser, ready to withstand temperature changes.
This essential fat-like substance has a huge impact on brain and heart activity, any mention of it causes an association with a stroke or heart attack. Since cholesterol is transported by blood vessels, it is there that the excess substance settles. Cholesterol plaques accumulate on the walls of blood vessels, thereby narrowing them. After deformation of the vessels, the blood flow changes its rhythm. As a result, due to insufficient blood supply and supply of substances necessary for the body, the performance of various organs dependent on the hematopoietic system decreases. The vessels become flabby and vulnerable. This state of affairs causes acute cerebrovascular accident with a fatal outcome.
With every quarter of a century (give or take), signs of high cholesterol in men are being diagnosed at an earlier age. Half a century ago, complaints came from people over 50 years old. At the beginning of this century, there were already cases of people turning to medical institutions at the age of 40. Today, everything is going to the point that problems can arise in men as early as 35 years of age.
The production of “bad” cholesterol is not a purely male problem. Lately, women have been consuming an equally large amount of not very healthy food and are addicted to bad habits. Diseases such as stroke, heart attack, obesity, thrombosis, have begun to occur among the fairer sex.
Reasons for changes in indicators
With constant exercise, the body gets used to constantly burning cholesterol levels
The reasons for the occurrence of abnormal cholesterol levels in the body can be different. At a high level, the main reasons may be as follows:
- Hereditary disease. It is especially important to consider this case if there are relatives in the family who have previously suffered from atherosclerosis or other diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- Excessive physical activity. With constant exercise, the body gets used to constantly burning cholesterol levels. After stopping an active lifestyle, cholesterol also continues to be produced in large quantities;
- Constant overeating or the presence of foods high in cholesterol in the diet;
- Constant psychological impact on the body. Excessive smoking or constant drinking of alcohol, all this, along with stressful situations, affects the central nervous system, which causes the liver to produce more cholesterol to support nerve endings;
- Sensitivity to high blood pressure;
- Kidney and liver disease;
- The presence of cancer directly or indirectly related to the production of cholesterol;
- Taking medications that affect the liver. Which drugs can be treated as diuretics, steroids and hormonal drugs;
- Belonging to a certain age group.
On a note! It is believed that the presence of cholesterol in the body has a bad effect on the general condition. However, low cholesterol also has a detrimental effect on the body as a whole.
The causes of low cholesterol in the body can be the presence of the following diseases:
- Anemia;
- Consequences of an infectious disease;
- Cholesterol low-calorie diet;
- Tuberculosis;
- Various diseases of the blood and vascular system;
- Liver pathologies that interfere with the production of normal cholesterol levels;
- Thyroid diseases.
The listed higher causes of high and low cholesterol are just the main reasons. Even in the absence of these symptoms or diseases, the cause of an incorrect level can be a changed lifestyle.
What not to do when promoted
To reduce high blood cholesterol levels in women, you need to avoid the following foods :
- salo;
- lamb, pork;
- yolks;
- offal;
- beef, veal;
- margarine;
- coffee;
- canned food;
- mayonnaise;
- duck meat;
- sausages, sausages;
- easily digestible carbohydrates (sweets, pastries, cakes);
- fast food;
- fermented milk and high-fat dairy products.
Fatty, fried, hot and spicy foods should be excluded from the diet
Alcoholic drinks and cholesterol levels
If a biochemical blood test shows a cholesterol level above 7, the patient should seriously think about giving up alcohol completely. Nutritionists call the calories that come into the body from alcohol “empty”, and alcoholic drinks as “food waste”. Alcohol takes a heavy toll on the liver, which undoubtedly leads to increased cholesterol levels.
If you take a biochemical blood test and drink even a small amount of alcohol the day before, then almost all the indicators when deciphering the analysis will be extremely disappointing.
Is total cholesterol level 7.0-7.9 normal or too much?
Despite general reference values of around 3 units, there are several factors that are considered normal.
- The boundaries lie within the range of “cholesterol 7.1-7.2 mmol/l” if the patient is over 50 years old.
- For older women, the norm is when cholesterol is 7.3-7.85 due to decreased reproductive functions and the effects of estrogen.
- During pregnancy, levels reach 9-13 mmol/l. against the background of hormonal changes.
If an excess of 7.9 mmol/l is detected by doctors under the age of 45, then this level is critical and requires additional research and preventive measures.
If cholesterol is higher than 7.0 -7.9, then screening tests are prescribed. The patient must undergo tests every six months.
Why is high cholesterol dangerous?
Elevated cholesterol levels (hypercholesterolemia) are a risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis and a laboratory symptom of some diseases. If the content of blood sterol is high, it begins to settle on the walls of damaged blood vessels. This starts the formation of cholesterol plaques.
Initially, they look like fatty spots, stripes, and do not interfere with the functioning of the circulatory system. However, the growth of plaques is accompanied by a narrowing of the lumen of the artery, ending in blockage of the vessel. The organ to which the artery supplied blood ceases to receive an adequate amount of oxygen and nutrients. Atherosclerotic plaques can break off, clogging the vessel.
The vascular network of our heart is very unreliable. Each heart muscle cell is supplied by only one vessel. When the lumen of such an artery narrows, the cardiomyocyte experiences oxygen deficiency. This condition is called coronary heart disease. But if the lumen of the coronary artery is completely blocked, some of the cells are deprived of nutrition and die - a myocardial infarction develops.
Brain cells are fed by several vessels. However, they are very demanding on the quality of blood supply. Lack of oxygen provokes the development of ischemic brain disease, the most terrible complication of which is stroke.
When large vessels of the legs are affected by atherosclerosis, the nutrition of the tissues of the extremities is disrupted. The skin becomes dull, wounds heal poorly. Patients experience severe pain when walking. The most terrible complication is gangrene of the feet, requiring amputation of the limb. Most often, the advanced form of the disease is observed in patients with diabetes.
Symptoms
High cholesterol in the blood causes the patient to develop the following clinical manifestations, which is most often associated with atherosclerotic vascular damage:
In men, the pathology can manifest itself as problems with erection.
- chest pain that worsens with physical or psycho-emotional stress;
- attacks of cerebral ischemia;
- strokes;
- heart attacks;
- erectile dysfunction in men;
- thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities due to rupture of atherosclerotic plaques;
- pain in the legs and arms in case of damage to the peripheral arteries.
In addition, there are a number of external manifestations of elevated cholesterol. Most often, in such patients, xanthelasma forms on the surface of the skin of the eyelids. It looks like yellow stripes and nodules located under the upper layer of the epithelium, and with prolonged absence of treatment and changes in lifestyle, they reach significant sizes, covering the entire upper and lower eyelid. This effect is only cosmetic and does not cause any other problems. It is possible to form xanthoma or nodules of cholesterol over the tendons. High cholesterol is dangerous for the development of life-threatening complications caused by necrosis of brain and myocardial tissue.
Cholesterol test - how to prepare correctly?
The accuracy and reliability of the results obtained depend not only on the correct implementation of the standard analysis technique, but also on the preparation of the patient himself. The biomaterial for the study is serum from venous blood, which is taken from the cubital vein on the elbow. The turnaround time may vary depending on the workload of the laboratory, but, as a rule, does not exceed 1 day from the moment the biomaterial is taken.
Preparing to donate blood for cholesterol:
- per day, the diet is adjusted towards reducing fatty and fried foods, since its excess can lead to falsely increased results;
- the last meal should be at least 8 hours before;
- half an hour before taking biomaterial, smoking is prohibited;
- in an hour it is necessary to reduce emotional and physical stress, since stress affects the condition of all cells in the human body.
To carry out diagnostics, the colorimetric photometric method is used. In order to minimize instrument errors, if a repeated examination is necessary, the patient is recommended to take the test in the same laboratory.
How to be treated
Medications
An increased content of the cholesterol component in the blood will become a source of fatty deposits in the blood vessels.
These deposits will be the source of a decrease in blood flow dynamics, due to which the brain and heart cease to receive the required amount of oxygen-enriched blood for normal functioning.
Treatment of the disease is based on taking lipid-lowering drugs .
More often, a doctor for hypercholesterolemia (increased cholesterol levels in a woman’s blood) prescribes the following medications:
- Gemfibrozil (Lopid, Hypolixan, Normolil, Gevilon), Fenofibrate, Clofibrate. Available in the form of tablets and capsules. Prescribed 2 times a day, one capsule (tablet). The drug is contraindicated for pregnant women and people with gallbladder diseases.
- Vitamin B3, PP and niacin can reduce cholesterol levels. Take 2-6 grams. per day, dividing the dose into 3 doses. To prevent fatty liver degeneration, methionine is prescribed at the same time.
- High cholesterol can be treated with drugs belonging to the group of bile acid sequestrants. These are Cholestyramine, Questran, Cholestan. Medicines are available in powder form. They are usually prescribed in doses of 4 grams. 2 times a day.
- Medicines belonging to the statin group are also capable of reducing the production of lipoprotein: Fluvastatin, Simvastatin, Pravastatin, Rosuvastatin. Drugs are prescribed at 5-10 mg per day.
ethnoscience
Traditional methods of therapy can also reduce cholesterol levels.
Herbalists often recommend consuming periwinkle . Just half a teaspoon of the herb, poured into a glass of milk or water, will get rid of pathology.
Take the medicine once a day before meals. Hawthorn blossom can also reduce cholesterol levels. 2 tbsp. l. The dried plant is poured with a glass of boiling water.
The future medicine should infuse for 20 minutes. You should take it one tablespoon 3 times a day. Caucasian Dioscorea is good .
Grind the rhizome of the plant and mix in the same amount with honey. Take half a teaspoon 2 to 4 times a day.
The duration of therapy is 10 days. Walnut leaves are also effective against pathology.
Chop 5 leaves and pour 500 ml of boiling water. The decoction is infused for 1 hour. Take half a glass 3 times a day before meals.
How to lower blood cholesterol levels:
We'll tell you how to do a mustard wrap for weight loss. Find out more now!
How to choose a hairstyle according to a woman’s face shape? Useful recommendations are in our article.
Reviews of keratin eyelash lamination are presented in this publication.
At-risk groups
There are also predisposing factors that contribute to increased production of “bad” cholesterol. These include:
- heredity;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- chronic liver and kidney diseases;
- uncontrolled use of certain drugs, especially hormonal ones;
- early menopause in women.
If at least one of these factors is present, it is necessary to carefully observe preventive measures so that blood counts are normal. By themselves, they are the causes of high cholesterol, but in combination with each other or an incorrect lifestyle, they can serve as an impetus for the development of problems.
Normal indicators
There is an average cholesterol indicator that applies to everyone - 5 mmol/l, which is considered normal. A cholesterol concentration above 7 mmol/l is considered dangerous. The results of the analysis can be assessed as follows:
- optimal – up to 4–5 mmol/l;
- slightly elevated – 5–6.4 mmol/l;
- high – 6.5–7.8 mmol/l;
- very high – 7.9 and above.
However, in practice it is dangerous to use such average values. With age, the concentration of cholesterol in the blood increases in any person. This process is inevitable, therefore it is not considered a deviation from the norm. And also female and male organisms have their own characteristics of lipid metabolism, which also affects the results of blood tests.
Norm for men
The table below shows the acceptable levels of total cholesterol in the blood for men of different ages.
| Age | Total cholesterol (mmol/l) |
| Up to 10 years | 2,95–5,25 |
| 10–20 | 3,08–5,10 |
| 20–30 | 3,16–6,32 |
| 30–40 | 3,57–6,99 |
| 40–50 | 3,91–7,15 |
| 50–60 | 4,09–7,15 |
| 60–70 | 4,12–7,1 |
| Over 70 years old | 3,73–6,86 |
Although the cholesterol level gradually increases until the age of 60, after this age it begins to decrease slightly. At the age of over 70 years, an indicator of 7.0 is already dangerous.
If the analysis indicator does not exceed the norm by much, a retake is required. For example, in a man aged 60 years, the results showed 7.3–7.4 mmol/l, and normally should not exceed 7.15. The doctor may consider it necessary to prescribe a retake of the test after a while.
Determination of the atherogenic coefficient
In order to correctly explain and evaluate the results of individual analyzes taking into account summary data, the concept of coefficient, or index, of atherogenicity (CA, IA) was introduced in medicine.
Definition of the concept
CA in a biochemical blood test is an established ratio, a connection between good and bad cholesterol, thanks to which it is possible to recognize cardiovascular diseases at the initial stage, as well as the degree of their risk.
Cholesterol cannot move throughout the body on its own because it does not dissolve in liquid. Therefore, it is transported as part of lipoproteins - chemical compounds that are proteins containing lipids (fats).
Lipoproteins vary in density and functional purpose. Thus, complex high-density proteins (HDL, or good cholesterol), clearing the walls of blood vessels of excess cholesterol, send it to the liver for further processing.
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL, bad cholesterol), on the other hand, move cholesterol from the liver to peripheral tissues, creating plaques on the inner walls of blood vessels. With a high concentration of deposits in the vessels, obstruction may occur with a dangerous consequence - stroke or heart attack.
Very low density is characterized by large particles of lipoproteins (VLDL, very bad cholesterol), which deliver contents to the tissues of the peripheral systems of the body. If lipid metabolism fails, it is important to monitor the level of VLDL, an overestimated value of which indicates serious diseases of the kidneys, liver, endocrine system, heart and blood vessels.
How to calculate CA
To calculate this value it is necessary to have correct data, initially depending on the patient's discipline. There are rules for preparing the body that will help you get real, not conditional, indicators. In this regard, you need:
- follow the diet prescribed by your doctor for 10-14 days before donating blood;
- do not overload yourself with physical and mental work;
- do not smoke 30 minutes before the test;
- do not eat for 12 hours;
- do not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours.
The doctor should know whether the patient is taking specific medications and prescribe recommendations before the analysis, since some drugs (especially antifungal and hormonal) can distort the indicators. Also, the CA value will be biased when donating blood during the menstrual period or during pregnancy.
If the patient has suffered a serious illness or surgery, then a lipid profile (blood lipid test) should be postponed for 1.5 months.
If these rules are followed, the patient will not have to re-donate blood for biochemical analysis, but will purposefully move forward to establish a diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
CA is found using a special calculation formula:
KA = (total cholesterol - HDL) / HDL
The numerator indicates the value of LDL and VLDL, which is obtained by subtracting the HDL value from the total cholesterol level.
By substituting the obtained values of the analysis results into the formula, you can easily obtain the CA. For example, if a patient has a cholesterol level of 6.19 mmol/l and HDL cholesterol of 1.06 mmol/l, the atherogenic coefficient will be 4.8.
In order to accurately determine KA, it is necessary to conduct a thorough study not only of the components of this indicator, but also of other values that affect the actual diagnosis: low and very low density lipoproteins, triglycerides (neutral fats). Thus, you can see a complete picture of the composition of the blood and the exact amount of all components.
Norm of indicators
The normal atherogenicity coefficient is 2-3 units, which takes into account the error of laboratory equipment. In other words, the amount of LDL should be 2-3 times higher than the value of HDL.
If the KA level has exceeded 3 units, this indicates moderate vascular damage, which can be corrected by diet. An index value approaching 4 indicates a risk of developing atherosclerosis.
When the coefficient crosses the border of 4 units, it is necessary to begin emergency treatment with drug therapy, diet and control of coronary artery disease in the blood.
A significant increase in KA to 7 or more requires surgical treatment to prevent cardiac failure.
A reduced index of 2 units or less is not a threat to health and shows no risk of developing atherosclerosis.
With age, metabolic processes in the body slow down, and the atherogenicity coefficient may increase. However, an AI value above 3.5 in patients of both sexes over 60 years of age requires close medical attention.
In young people under 30 years of age, KA is normally no higher than 2.5. From 30 to 40 years old, the acceptable male norm for the atherogenic coefficient is 2.07-4.92. With satisfactory heart function in representatives of the stronger sex 40-60 years old, AI should be within 3-3.5 units. If the index in the blood of men increases, additional examinations are prescribed, the causes are studied and eliminated.
For women 20-30 years old, the AI norm is up to 2.2; from 30 to 40 years – 1.88-4.4; after 40 years, the coefficient is considered normal to 3.2 or less. With the onset of menopause in women over 50 years of age, there is a risk of vascular damage by atherosclerosis. Taking this into account, the KA for older women is calculated as for men: 3-3.5 units.
A reduced atherogenicity coefficient in young women indicates clean blood vessels and is not a health hazard. If a middle-aged woman has a lower KA than normal due to a decrease in HDL (good cholesterol), then in this case there is a suspicion of problems in the body that need to be identified and eliminated.
Increased CA
A cholesterol coefficient of atherogenicity exceeding 4 units indicates the presence of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels, which impede the passage of blood to the organs and increase the risk of heart and vascular disease. With the active development of this process, the CA can be several times higher than 4.
The composition of total cholesterol plays an important role. With the same value in two patients, a patient with a predominance of high-density lipoproteins has a normal index. If there is more LDL in the blood, then KA will be elevated and treatment is necessary to reduce this indicator. Two elevated indicators - the atherogenic index and cholesterol - indicate a high risk of cardiovascular problems.
The absence of expressive symptoms of increased KA for a long time can one day result in a serious complication and even death. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly take a biochemical blood test to determine KA.
Reasons for deviations
There are factors influencing the increase in the atherogenicity coefficient:
- regular smoking and drinking alcohol, which lead to damage to the internal walls of blood vessels and the formation of plaques that disrupt normal blood supply;
- lack of active movements, against the background of which rapid formation of fat occurs;
- excess weight that occurs due to excess caloric nutrition and metabolic disorders;
- insufficient liver function;
- hypertension, which negatively affects the strength of the walls of blood vessels;
- diabetes mellitus, in which glucose molecules, passing through blood vessels, damage the walls, on the defects of which atherosclerotic plaques are firmly established;
- heredity as one of the most common causes;
- nervous stress, which affects the condition of blood vessels.
Treatment of the disease
To normalize the atherogenic coefficient, you need to change your attitude towards bad habits, pay attention to physical activity, and eat foods that do not contain large amounts of animal fat.
Gradual cessation of smoking and self-restraint in alcohol will improve health and help reduce coronary artery disease.
As for physical exercises, in the absence of additional diseases, you can exercise 4 times a week for 30-40 minutes a day. If the patient has illnesses, the doctor adjusts the activities in a more gentle direction, taking into account the characteristics of the pathological process. Hiking and cycling, tennis, and swimming are very useful.
The diet should strictly limit fatty meat, lard, sausages, fatty dairy products, and confectionery products. In this case, it is necessary to include in the menu boiled fish and lean meat, almonds, walnuts, fruits, fresh and stewed vegetables, honey, green tea, herbal infusions, garlic, cereals; sunflower, cottonseed, corn, rapeseed, olive, peanut and flaxseed oil.
To strengthen the result or if the CA value is critical, it is necessary to take medications recommended by the attending physician, in compliance with the course and dose. Medicines that reduce the atherogenic index have many contraindications, which only professionals can properly take into account. Therefore, taking them on your own is prohibited. To reduce KA, statins, fibrates, and bile acid sequestrants are prescribed.
Low atherogenicity
An underestimated AI indicator is considered to be favorable, since it indicates the correct ratio of good and bad cholesterol in the blood and the presence of healthy blood vessels. As already mentioned, a low index value occurs in young women (less than 1.9), which is the norm considering age. In addition, a decrease in AI is possible if:
- the patient is on a long-term cholesterol-lowering diet;
- Treatment is carried out with drugs of the statin group;
- there is increased physical activity (professional sports activities).
Low KA occurs in people who maintain a balanced diet and physical activity, which has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the body.
For preventive purposes, you need to regularly (every 3-5 years) donate blood for the atherogenic index and, if necessary, adjust your lifestyle: eat right, move a lot. In this case, all paths to atherosclerosis are cut off.
Controlling IA will ensure cleanliness of blood vessels, health of the body and an optimistic mood in the soul.
How to downgrade
Considering the fact that cholesterol norms change in women as they age, in most cases due to improper lifestyle, it can be adjusted. So, at 60 years old, women should have a healthy diet. If at a younger age you could still experiment with food, now it’s better to refrain from doing so. Cholesterol levels can be significantly reduced by minimizing fried and fatty foods. The diet should be based on poultry (lean, without skin) and fish. As much as possible, butter in dishes should be replaced with vegetable oil, ideally olive oil. Unprocessed, coarsely ground porridge will also be beneficial.
Your diet should also include vegetables and fruits rich in fiber every day. By the way, these products will not only help ensure that the norm is easily restored after 65 years, but will also saturate the body with all the necessary vitamins. And this is also important for an elderly person, and for his health in general.
When calculating what cholesterol should be normal after 60, you should also remember not only about proper nutrition, but also about a healthy lifestyle. Smoking and alcohol are the first harbingers of an increase in the accumulation of “bad” cholesterol.
If a woman leads an active lifestyle, monitors her weight, and eats right, then the problem of what the norm should be will not be relevant.
Cholesterol 7 in a woman, what threatens
High cholesterol levels are a potential danger to the body. It is the cause of sudden death, atherosclerosis of the cardiovascular system, cerebral circulation. As a result, strokes and acute heart attacks occur, and the likelihood of death in sleep is high. Therefore, the indicator “cholesterol 7 mmol/l.” is a worrying sign.
Increased cholesterol is based on a physiological mechanism. The main element is cholesterol. It is a fatty alcohol that is used for:
- Productive metabolism of steroid hormones;
- The natural synthesis of cholecalciferol (under the influence of sunlight) and ergocalciferol (supplied with food) are vitamins of group D;
- Construction of cell membranes.
Normally (cholesterol 7.0 mmol/l) is produced by the cells of the largest human gland - the liver. Stereol synthesis is supported by the work of the adrenal glands, intestinal tract, and skin. These are additional functions of lipid metabolism that are associated with the formation of cholesterol plaques.
A newborn's cholesterol level is low, equal to 1-2 mmol/l. Unlike men, cholesterol levels are maintained as long as the production of the typical female hormone is normal. Only after menopause in the fair sex does the risk increase. In men it is present, but in lower concentrations, so they are more often at risk of detecting “cholesterol 7 mmol/l.” in their blood.
Due to physiological characteristics, males are most at risk. Due to disruption of hormonal systems in women, the risk zone expands significantly, especially in adulthood. All problems can begin earlier if you do not pay attention to indicators.
Medical experts believe the following categories are at risk.
- Passive, inactive with signs of physical inactivity. Blood must constantly circulate, and this can only be ensured by physical activity.
- Alcohol abusers, when the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and liver is disrupted.
- People who allow themselves to break their diet or not follow the basics of proper nutrition are at risk when the cholesterol value is 7 mmol/l. and above is discovered by chance.
- Obese, sedentary people.
- Women with hormonal system failure.
- Elderly and senile age, regardless of gender, when estrogen production decreases or stops. It is he who is responsible for the regulation of cholesterol.
A special risk zone is childhood, especially adolescence, when hormonal levels increase. Diagnostics allows us to identify the onset of the disease.
Excessive formation of cholesterol plaques at the initial stage occurs unnoticed. There are no obvious symptoms, complaints, or poor health.
The first signs of a malfunction in the body are expressed in later, delayed periods, when not only prevention is necessary.
High cholesterol is accompanied by:
- From the musculoskeletal system: a feeling of stiffness, heaviness, tremor in the limbs; varicose veins of the knees, legs, feet; redness and blueness;
- Cardiac pathology: shortness of breath, tachycardia or bradycardia, chest pain;
- In reproductive function: early menopause, decreased fertility, potency, loss of interest in sex (frigidity);
- Decreased visual acuity, identification of a gray rim around the cornea;
- Violation of brain functions: memory, thinking, attention, concentration.
A specific symptom is the formation of xanthomas. These are fatty plaques on the surface of the skin, filled with a white mass, concentrated around the eyes, on the palms, soles, fingers, and buttocks.
In a biochemical analysis of a person, one of the vital indicators that determine the general condition of the body is cholesterol in the blood. Modern laboratories are equipped with special equipment that eliminates errors in data calculations.
Therefore, 30 years ago it was not possible to accurately determine the amount of cholesterol. On this basis, most patients consider the fact far-fetched and not dangerous. As a result, they do not listen to recommendations on dieting, exercise and treatment.
To determine cholesterol, no more than 5 ml of venous blood is taken with a special vacuum syringe. The tube is marked with the name, age of the patient, date and time of collection.
Another method is a portable biochemical device for determining cholesterol in the blood. It is a small box that looks like a glucometer. Using a test strip and lancet, the patient can determine the levels of: uric acid; cholesterol; triglycerides; glucose. The device can do analysis at home. Most often used for express diagnosis of acute conditions during pre-medical appointments.
Only a comprehensive examination of the body will make it possible to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment under medical supervision.
The accuracy of the indicators will increase strict adherence to the rules of blood sampling:
- The test is taken on an empty stomach (more than 8-10 hours have passed before the last meal) in the morning;
- You cannot drink alcohol 1 day before going to the laboratory, it disrupts lipid metabolism;
- In case of thirst, plain water without additives or gas is allowed;
- Smoking is not allowed an hour before the test;
- Physical activity and psycho-emotional disorders are completely excluded.
Find out from your doctor exactly which pills you should not take so that the analysis is as “clean” as possible.
A high level of indicators is an alarming sign of the development of serious pathologies. Physiology “works” so that excess sterol settles on the walls of blood vessels, and plaque formation begins. The process looks like this:
- In the initial stage, they look like stripes, fatty spots that do not interfere with blood circulation.
- As they grow, they narrow the openings in the arteries.
- Vessels are clogged.
As a result, the organs do not receive enough nutrients and oxygen. Cholesterol plaques can break off, accumulate and completely block blood access to the heart.
A similar situation occurs with the brain and limbs. A cerebrovascular accident causes a cholesterol level of 7.9 mmol/l. and higher,” a stroke occurs with complications including paralysis of vital functions and death.
Atherosclerosis disrupts trophism in the lower extremities, swelling, dry skin. Any injury becomes a threat of severe pathologies (gangrene, venous stagnation). The only way out is amputation.
Despite general reference values of around 3 units, there are several factors that are considered normal.
- The boundaries lie within the range of “cholesterol 7.1-7.2 mmol/l” if the patient is over 50 years old.
- For older women, the norm is when cholesterol is 7.3-7.85 due to decreased reproductive functions and the effects of estrogen.
- During pregnancy, levels reach 9-13 mmol/l. against the background of hormonal changes.
If an excess of 7.9 mmol/l is detected by doctors under the age of 45, then this level is critical and requires additional research and preventive measures.
If cholesterol is higher than 7.0 -7.9, then screening tests are prescribed. The patient must undergo tests every six months.
If a cholesterol level exceeds 7 mmol/l, the therapist prescribes several therapeutic measures that can not only reduce, but also maintain normal levels.
The first thing you need to do is adjust your diet. A “cholesterol-free diet” is prescribed. It is based on the following principles.
- All dairy products with a high fat content are excluded: cheeses, sour cream, cream.
- You cannot eat smoked meats and lard: sausages, brisket, boiled pork, ham, sausages, grilled wings and the like.
- Fresh baked goods will be prohibited. They are replaced with crackers, dried slices of bread. No vanilla buns with jam, pies or buns.
- Forget about snacks (chips, dried fish, etc.).
- A dangerous product for cholesterol is alcohol. It disrupts the functioning of the liver and pancreas.
- Carbonated waters, especially sweet types, harm lipid metabolism.
It is better to make all food products yourself.
Since the formation of cholestorol and its regulation directly depend on the general blood supply and metabolism system, moderate physical activity is prescribed. This is a means of not only prevention, but also treatment.
- Easy calm jogging;
- Walking at a moderate pace;
- Morning exercises, fitness in the gym under the guidance of a trainer;
- Walking in the morning or before bed.
Do physical activity while working. Take a walk, walk, stretch.
Among the recommendations when it is necessary to reduce cholesterol, there are often non-drug treatment methods. It is suitable for the initial stage of the disease and is only being developed. Effectiveness assessment is carried out 1-3 months after the start.
- Laser therapy, when plaques are removed using a targeted method. Complications are possible due to the formation of microparticles and thromboembolism.
- Ultrasound cavitation method. Under the influence of high frequencies, cholesterol plaques are removed, stagnation is destroyed, passages in the vascular beds become freer. Tested on the lower extremities when the patient faces amputation.
The effect of such procedures brings results, but so far this has not been implemented everywhere, since lipid metabolism, its features, and the formation of cholesterol are all associated with other pathologies.
The general practitioner prescribes statin drugs, which prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques and are mood stabilizers for lipid metabolism. Active ingredients: lavostatin, fluvastafin, simvastatin, pravastatin. The most effective for severe pathologies are:
- Choletar, Cardiostanitis (the main substance is lovastatin), reducing the levels to 6-4 mmol/l;
- Mertinil, Roxera, Crestor with rosuvastin;
- Lexol Forte based on fluvastatin, effectively affecting high values (from 9 mmol/l. and above);
- Owencor, Simvastol, Vasilip with fluvastine, allowing to achieve stable results with long-term use for more than 4 months.
Taking into account that increased cholesterol is associated with pathological processes of other diseases, therapy should be comprehensive, depending on the pathology.
Elevated cholesterol levels are a high risk of sudden death and disability due to strokes, myocardial infarction, obesity, and decreased reproductive functions. If its indicators exceed the norm of 7.9 mmol/l, then you will need:
- Review of daily routine and nutrition;
- Elimination of potentially dangerous risk factors, normalization of the cardiovascular system, digestion;
- Constant monitoring of the level of indicators of disturbances in lipid metabolism and cholesterol.
The older you get, the higher your risk of developing cholesterol plaques.
Watch your diet, don’t break your routine and diet, live an active life! We will defeat cholesterol only if we strictly follow the recommendations.
source
High cholesterol levels - 7.0-7.9 mmol/l - are a consequence of lipid metabolism disorders.
The total amount of natural fatty alcohol formed in the liver and supplied with food from the outside significantly exceeds the body's needs and ability to process it.
This imbalance can be determined and its consequences assessed by testing the blood for quantitative indicators of some of its fractions: total cholesterol, high- and low-density lipoproteins.
Each of the indicators allows us to assess the state of a certain process during the physiological breakdown of cholesterol with its subsequent utilization.
The level of total cholesterol characterizes the degree of risk of atherosclerosis in general. By itself, this indicator is not informative enough: additional studies are carried out to get a complete picture of the state of lipid metabolism.
LDL takes up cholesterol in the liver and carries it to the cells and tissues of all organs. This is “bad” cholesterol, which has a pronounced atherogenic effect - the ability to attach to the walls of blood vessels, narrow their lumen, and form atherosclerotic plaques.
LDL indicators are used to judge the risks and stage of development of the pathological process:
- from 2.5 to 3.3 mmol/l – physiological norm, in the absence of provoking risk factors there is no risk;
- from 3.4 to 4.1 – high probability of developing atherosclerosis;
- from 4.1 to 4.9 – corresponds to the initial manifestations of the disease;
- above 4.9 means that the disease is progressing and the risk of complications is increasing.
When the cells of organs and tissues have disassembled the amount of free cholesterol necessary for their own needs, HDL captures the remaining amount and transfers it back to the liver for further utilization. High-density lipoproteins are “good” cholesterol; they prevent the growth of atherosclerotic plaques.
Difference between LDL and HDL.
Average physiological indicators of HDL are 1.0-2.0 mmol/l, if they:
- Higher is a favorable sign; the risk of developing atherosclerosis tends to zero.
- Lower than 0.8 mmol/l means the disease is progressing and complications are possible.
A medical report based on the research results is drawn up taking into account all three indicators:
- the risk prognosis will be extremely unfavorable with a combination of high levels of total cholesterol and low-density lipoproteins with low HDL content;
- while a large overall indicator against the background of an increased level of high-density lipoproteins and low LDL content will not pose a significant threat.
When interpreting test results, it is also taken into account that cholesterol and lipoprotein levels are individual and depend on age, gender differences, existing diseases, lifestyle and nutrition.
About 70-75% of cholesterol is produced by the liver and about 25% comes from food.
Based on numerous studies, experts have determined the average physiological values for the content of this natural fatty alcohol in the blood plasma.
What is this substance
Everyone has heard this word more than once: commercials talk about it, in the hospital from doctors, but most have no idea what it means. However, many believe that the substance is extremely harmful and also dangerous to human health. Essentially, cholesterol, or cholesterol as it is also called, is a fatty alcohol. Its role for the body is enormous.
It occupies a special place for the synthesis of cell membranes:
- blood - red blood cells, this is about 24%;
- an important organ for humans - the liver, 17% is concentrated here;
- gray matter of the brain, the amount varies from 5 to 7 percent.
Results
- a one-time deviation from standard values may be caused by improper patient preparation or other physiological reasons;
- Consistently elevated results (with two or three repetitions) are a reason to conduct a lipid profile and prescribe diagnostic methods to identify the causes;
- It is important to monitor LDL levels. Its excess content leads to the formation of fatty plaques inside blood vessels, which significantly increases the risk of heart attack or stroke.
Yulia Martynovich (Peshkova)
Certified specialist, in 2019 she graduated with honors from the Orenburg State University with a degree in microbiologist. Graduate of the graduate school of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Orenburg State Agrarian University.
In 2019 At the Institute of Cellular and Intracellular Symbiosis of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, she completed advanced training in the additional professional program “Bacteriology”.
Laureate of the All-Russian competition for the best scientific work in the category “Biological Sciences” 2019.
Cholesterol is a very important component of many life support processes in our body. In recent years, the problem with an imbalance of cholesterol compounds has taken a leading position, because due to poor nutrition and an inactive lifestyle, it can affect everyone. Let's look at how cholesterol works in the body in women and its normal levels in the blood depending on age.
What to do?
Changing your lifestyle, playing sports and giving up bad habits will help reduce cholesterol. It is important to bring into a state of compensation major somatic diseases, such as diabetes and hypertension. When there is a significant increase in cholesterol, medications are used to reduce their synthesis by the liver and kidneys, as well as to reduce the absorption of fats from the intestines. Vitamin complexes and supplements will be useful. Traditional treatment is used in combination with traditional methods of therapy.
Medicines
In case of a pronounced pathological process, the patient may be prescribed Lovastatin.
Drug therapy is carried out if there is severe atherosclerotic damage to the vascular bed and includes various drugs to normalize the level of lipoproteins in the body. The main ones are statins, such as Mevacor, Baykol and Lovastatin, which block the synthesis of specific enzymes involved in the formation of cholesterol by the liver. This allows you to reduce the level of blood lipoproteins by half. To eliminate the imbalance between different fractions of lipoproteins, Niacin is used. Bile acid sequestrants will help reduce the absorption of fats from the intestines. In addition, Omega-3, vitamins and minerals will be useful.
Folk recipes
With cholesterol 7 units. and above, the use of the following methods of alternative medicine is recommended:
- Dandelion root powder, take 1 teaspoon before meals.
- Alfalfa leaves are eaten raw.
- Blue cyanosis roots in the form of a decoction are taken 20 mg every day for 2 weeks.
- Propolis tincture - 20 drops before meals.
- Garlic juice and oat infusion take 1 tablespoon each in the morning on an empty stomach.
Diet features
Such people should prepare their own food by boiling.
If cholesterol is 7 or higher, it is harmful to eat foods high in fat, fried, spicy and salty foods. You need to choose fresh vegetables and fruits that are rich in vitamins and fiber. Steamed and boiled food will be beneficial. You should avoid drinking alcohol, strong coffee and tea.
In men, the normal level of blood lipoproteins is slightly higher than in women, which is explained by their lifestyle.
What does the indicator 7-7.9 mean?
If cholesterol levels are above 7, a stroke is possible
Blood cholesterol readings above 6 are considered high and require immediate reduction. Indications at level 7 are the first stage of the formation of atherosclerosis. At levels from 7 to 7.9 millimoles, the following list of diseases develops:
- Atherosclerosis in various places. Most often, the limbs and places where a large amount of blood accumulates are affected by blockage of blood vessels;
- Cardiac ischemia. As a result of the formation of blockages in the coronary arteries, the risk of heart attack and coronary heart disease increases;
- Stroke. Stroke often results from abnormal cholesterol levels. This happens especially often where the risk of becoming overweight is increased.
- Often, due to excess cholesterol, coronary intestinal disease occurs and intestinal death begins. As a result, digestion suffers.
- Poor blood supply to the lower extremities. This disease occurs as a result of atherosclerosis of the dividing channel of the vessel.
If one or more symptoms occur, it is necessary to reduce cholesterol from 7 to 5 as soon as possible.
The risk group for the disease includes all obese people. This factor is considered the most important. It is the high fat content in the body that creates ideal conditions for the formation of atherosclerosis.
People suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system are no less at risk. When blood vessels and the heart are weakened, the risk of other diseases is high. This is also due to the fact that the human immune system is greatly undermined.
Pregnant women should be especially vigilant. Cholesterol levels during pregnancy can be unpredictable. A woman must constantly monitor the biochemical processes of her body.
Since it is impossible to notice the presence of high cholesterol, it is recommended to do the analysis at least 1-2 times a month. Thus, even a slight change in cholesterol can be noticed, and measures will be taken to eliminate the disease.
Treatment of high cholesterol
If a cholesterol level exceeds 7 mmol/l, the therapist prescribes several therapeutic measures that can not only reduce, but also maintain normal levels.
Nutritional correction to reduce cholesterol 7 mmol/l
The first thing you need to do is adjust your diet. A “cholesterol-free diet” is prescribed. It is based on the following principles.
- All dairy products with a high fat content are excluded: cheeses, sour cream, cream.
- You cannot eat smoked meats and lard: sausages, brisket, boiled pork, ham, sausages, grilled wings and the like.
- Fresh baked goods will be prohibited. They are replaced with crackers, dried slices of bread. No vanilla buns with jam, pies or buns.
- Forget about snacks (chips, dried fish, etc.).
- A dangerous product for cholesterol is alcohol. It disrupts the functioning of the liver and pancreas.
- Carbonated waters, especially sweet types, harm lipid metabolism.
It is better to make all food products yourself.
Physical activity as a method of combating high cholesterol
Since the formation of cholestorol and its regulation directly depend on the general blood supply and metabolism system, moderate physical activity is prescribed. This is a means of not only prevention, but also treatment.
- Easy calm jogging;
- Walking at a moderate pace;
- Morning exercises, fitness in the gym under the guidance of a trainer;
- Walking in the morning or before bed.
Do physical activity while working. Take a walk, walk, stretch.
Non-drug treatment
Among the recommendations when it is necessary to reduce cholesterol, there are often non-drug treatment methods. It is suitable for the initial stage of the disease and is only being developed. Effectiveness assessment is carried out 1-3 months after the start.
- Laser therapy, when plaques are removed using a targeted method. Complications are possible due to the formation of microparticles and thromboembolism.
- Ultrasound cavitation method. Under the influence of high frequencies, cholesterol plaques are removed, stagnation is destroyed, passages in the vascular beds become freer. Tested on the lower extremities when the patient faces amputation.
The effect of such procedures brings results, but so far this has not been implemented everywhere, since lipid metabolism, its features, and the formation of cholesterol are all associated with other pathologies.
Drug treatment
The general practitioner prescribes statin drugs, which prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques and are mood stabilizers for lipid metabolism. Active ingredients: lavostatin, fluvastafin, simvastatin, pravastatin. The most effective for severe pathologies are:
- Choletar, Cardiostanitis (the main substance is lovastatin), reducing the levels to 6-4 mmol/l;
- Mertinil, Roxera, Crestor with rosuvastin;
- Lexol Forte based on fluvastatin, effectively affecting high values (from 9 mmol/l. and above);
- Owencor, Simvastol, Vasilip with fluvastine, allowing to achieve stable results with long-term use for more than 4 months.
Taking into account that increased cholesterol is associated with pathological processes of other diseases, therapy should be comprehensive, depending on the pathology.
When and why do you measure cholesterol levels?
Cholesterol is a substance belonging to the group of lipids, which is involved in fat metabolism, the synthesis of biologically active compounds, hormones, and the formation of cell membranes. The liver and intestines are responsible for the absorption and production of cholesterol. According to its structure, the lipid under study is an immobile molecule, therefore, in order to be transported to the desired part of the body, it binds to a carrier protein. In this form, cholesterol circulates in the blood in the form of high and low density lipoproteins (HDL and LDL) and triglycerides.
Depending on its density, cholesterol is conventionally divided into bad and good. “Good” are HDL molecules, “bad” are LDL molecules. Low-density cholesterol is involved in the formation of foci of atherosclerosis. It is prone to sticking, lingers on the walls of blood vessels, infiltrates it and causes local inflammation. When indicators increase, it is this fraction of lipoproteins that has a negative effect.
It is recommended to monitor blood lipid levels regularly, especially in adulthood, when background hormonal changes occur in the body. The first stages of pathological changes in fat metabolism are not clinically determined - they are characterized by an asymptomatic, subclinical course without pronounced signs. If this initial stage of laboratory changes is detected in time, it is possible to prescribe treatment in time and prevent a number of life-threatening diseases - atherosclerosis, strokes, heart attacks, transient ischemic attacks, gangrene, etc.
The lipid profile is monitored by a specialized specialist in the hospital department. In addition to the indicators of bad cholesterol, they also look at the numbers of triglycerides, the coefficient of atherogenicity, the presence of kidney disease and the hepatobiliary system.