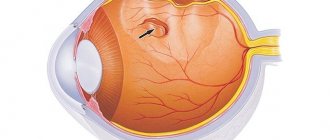
Ethmoiditis in adults is an acute or chronic inflammatory process that occurs in the mucous membrane of the ethmoid sinus. This sinus (labyrinth) is part of the ethmoid bone at the base of the nose. The disease is included in the broad category of sinusitis diseases. Taking into account the peculiarities of the localization of the pathological process, sometimes doctors make a diagnosis of ethmoid sinusitis. The pathology is viral in nature. The most characteristic sign of pathology is swelling of the upper eyelids and eyes. The pathological process develops as an independent pathology or is accompanied by sinusitis or rhinitis.
Classification of ethmoiditis
By the nature of development:
- acute;
- chronic.
According to the location of the pathological focus:
- unilateral - depending on the location of the pathological process, signs of the disease appear on the right and left sides.
- bilateral – the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves in two sinuses;
The nature and intensity of symptoms correspond to the nature of the disease.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the course of the disease, three forms of ethmoiditis are distinguished::
- catarrhal;
- polyposis;
- purulent.
Catarrhal ethmoiditis
The main causes of development are viruses. A distinctive feature of this form of pathology is lacrimation. Initial symptoms are headache, a feeling of weakness, dizziness, and nausea. The capillaries in the eyes burst, so the whites take on a red tint, the bridge of the nose swells, and the sense of smell is impaired.
Polypous ethmoiditis
This form of pathology is chronic and manifests itself against the background of a prolonged runny nose, which has not been treated. In this case, polyps form in the nasal sinuses, which cause swelling. Patients experience periods of remission when the symptoms of polyposis ethmoiditis completely disappear.
Purulent ethmoiditis
This form of pathology is called the most dangerous, it manifests itself with acute symptoms - fever up to +40 degrees, severe headache spreading to the forehead, bridge of the nose and eyes. Signs of severe intoxication appear:
- heat;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- nausea and diarrhea;
- fatigue;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
What is ethmoiditis?
What is it - ethmoiditis (ethmoidal sinusitis)? This is an inflammation of one of the paranasal sinuses, or rather, the cells of the ethmoid bone. It is often a secondary disease that develops against the background of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. It ranks 5th in terms of the prevalence of diseases that are treated with antibiotics.
The shape of the flow is:
- Acute – a bright and sudden manifestation. More often observed in children and adolescents.
- Chronic – a consequence of anatomical pathology or untreated acute ethmoiditis.
The following types of ethmoiditis are distinguished:
- Together with other departments:
- Maxillary ethmoiditis is inflammation of the ethmoid bone with the maxillary sinuses.
- Frontoethmoiditis is a lesion of the frontal sinus along with the ethmoid bone.
- Rhinoethmoiditis is inflammation of the ethmoid bone together with the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity.
- Sphenoethmoiditis is inflammation of the ethmoidal labyrinth with the sphenoid sinus.
- According to the nature of inflammation:
- Catarrhal.
- Polypous.
- Edema-catarrhal.
- Purulent.
- On the side of inflammation:
- Right-handed.
- Left-handed.
- Bilateral.
go to top
Causes of ethmoiditis
Most often, pathological processes develop after infection of the body with viruses of the cocci and fungi group. Sometimes laboratory tests reveal several causative agents of the disease.
The disease, as a rule, progresses against the background of pathologies of an infectious nature of the ENT organs. The infection process occurs hematogenously, that is, viruses enter the ethmoid sinus through the bloodstream. Contact infection occurs much less frequently.
Factors that predispose to the development of the disease:
- adenoids;
- anatomically incorrect structure of the nasopharynx;
- facial damage in the nose area;
- diseases of the nasopharynx of an allergic nature;
- infectious processes in the nasopharynx that occur in a chronic form.
It is important! Pathological processes in sinusitis without proper treatment spread to the bone and lead to its destruction. As a result, abscesses and empyema appear. If you do not consult a specialist in a timely manner, pus affects the area of the eye sockets and brain.
Symptoms and signs of ethmoiditis of the ethmoid bone cells
The following symptoms and signs of ethmoiditis of the ethmoid bone cells are distinguished:
- Pain. Localized in the bridge of the nose and fronto-orbital region. Accompanied by headaches, high fever, photophobia, and blurred vision. In the chronic form, insomnia, eye fatigue and swelling are observed.
- A feeling of fullness in the nasal cavity due to the occurrence of pus and swelling of the cells. Nasal congestion.
- Difficulty breathing through the nose due to swelling of the mucous membrane. Children may experience complete absence of nasal breathing.
- Nasal discharge, which characterizes exudate accumulated in inflamed cells. They can be mucous, purulent or bloody. At first they are scanty, and then they become abundant.
- Partial or complete absence of smell.
These symptoms are characteristic of both acute and chronic forms. The following signs appear clearly only in the acute form of ethmoiditis, and in the chronic form they are weak and unexpressed:
- Fever.
- Regurgitation (in children) and vomiting.
- Malaise.
- Loss of appetite.
- Neurotoxicosis.
- Weakness.
- Intestinal disorders: as with colitis or proctitis, stool disturbance is observed.
- Kidney failure.
- Tearing.
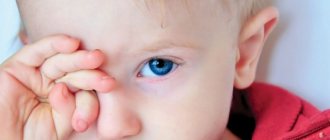
- Swollen eyelids that are slightly or completely closed. It occurs as a result of the destruction of part of the ethmoid bone and the penetration of exudate into the tissue of the orbit. Here there is deviation, protrusion of the eyeball, decreased vision and pain when moving the eye.
- Skin is hot and damp.
During remissions in chronic ethmoiditis, symptoms worsen only in intoxication (weakness, fever, decreased performance, headache).
go to top
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of acute ethmoiditis
Signs of acute ethmoiditis progress against the background of a common runny nose or flu. Inflammatory foci present in the adjacent sinuses provoke damage to the sinus (ethmoid labyrinth). Characteristic signs of the acute form:
- headache concentrated at the bridge of the nose;
- difficulty breathing and yellowish-green discharge;
- impaired sense of smell;
- heat;
- weakness, constant feeling of fatigue;
- The skin around the eyes becomes more sensitive.
Primary and secondary acute ethmoiditis manifest themselves differently. The primary form of the disease is more easily tolerated by the patient. The secondary form is more severe, symptoms appear quickly and progress. Complications develop already on the second day of illness.
It is important! If the attending physician does not promptly prescribe treatment for ethmoiditis occurring in the acute phase, multiple pathological foci will form, and osteomyelitis is possible.
Signs of chronic pathology
A chronic disease is a consequence of an acute pathology. Patients at risk are:
- with reduced immunity;
- those who have not completed treatment for the acute form of the pathology;
- with chronic inflammation located in the adjacent sinuses.
The symptoms of the disease are determined by the intensity of the inflammatory process.
During remission:
- Pain in the bridge of the nose rarely occurs;
- scanty nasal discharge;
- in the morning a small amount of discharge accumulates in the nose;
- During the examination, polypous growths are revealed.
During the period of exacerbation, the patient develops weakness, fatigue, and symptoms characteristic of acute ethmoiditis.
Important! This pathological form is dangerous due to degenerative processes. With a large accumulation of polyps, polyposis develops - formations fill the nasal cavity, which leads to deformation of the nasal septum.
General symptoms
- Headache.
- Swelling of the eyelids, worse in the morning.
- Runny nose lasting longer than ten days.
- Discharge of mucus from the nose.
- Heat.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Distortion of the sense of smell and taste.
It is important! Pathological processes in ethmoiditis occur near the eye sockets, so possible complications can affect vision, cause double vision, and redness of the eyelids.
Ethmoiditis in children
In newborns, the disease is much more severe than in other patients. The disease begins acutely, with a sudden increase in temperature to 40 degrees. The child looks restless, he refuses the breast and bottle, food is not absorbed by the body.
A characteristic feature of ethmoiditis in newborns is eye symptoms: red or bluish eyelids with severe swelling, tightly closed palpebral fissures, motionless and protruding eyeballs. If the disease is treated, the child will show signs of dehydration and neurotoxicosis. From the moment the pus breaks through, orbital and intracranial pathologies and sepsis develop.
The cells of the ethmoid bone are already formed at birth, and the frontal sinus begins to develop only after the fusion of the mucous membrane with the frontal bone. This usually occurs by the age of three, so ethmoiditis in children under three years of age occurs only in an isolated form, and then can spread to the frontal sinus.
Ethmoiditis in young children easily penetrates the bone tissue and periosteum, provoking the formation of abscesses and fistulas. The close proximity of the ethmoid bone to the orbit threatens the health of the eye, leading to intraorbital complications. In older children, the frontal and maxillary sinuses are formed, so they may end up in the affected area, which leads to mixed diseases such as maxillary ethmoiditis and frontoethmoiditis.
Diagnostics
Only an otolaryngologist can confirm or refute the diagnosis. The specialist examines the oral and nasal cavities, is interested in the symptoms of the disease and the course of respiratory pathologies. The final diagnosis is made only on the basis of laboratory tests and hardware diagnostics.
To confirm the diagnosis of ethmoiditis, the ENT doctor may prescribe some of the following procedures:
- A blood test is necessary to identify the inflammatory process and determine its intensity.
- Culture of mucus helps to identify the presence of pathogenic microflora and determine the degree of sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
- An endoscopic examination is aimed at examining the paranasal sinuses, identifying the presence of polyps and other formations.
- X-ray examination is carried out in several projections, which reflect the affected areas of the paranasal sinuses and inflammatory processes.
- A computed tomogram is usually performed on young children if other diagnostic methods are not informative.
Treatment of ethmoiditis is prescribed based on the results of the examination. If the patient’s condition is satisfactory, the specialist prescribes bed rest, certain changes in diet and outlines a drug therapy regimen. If the examination reveals a large amount of pus and widespread infection, treatment of ethmoiditis will most likely be carried out in a hospital setting.
Ethmoiditis: causes
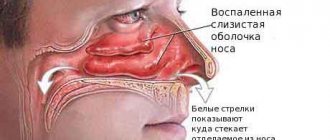
As we said above: the sinuses of the ethmoid sinus are lined from the inside with mucous membrane, and communicate with the nasal passages through small openings. This mucous membrane has a large number of glands that produce mucus, and its surface layer is covered with ciliated ciliated epithelium (the cilia of which move, thereby facilitating the removal of mucus from the sinuses into the nasal passages).
This active transport mechanism (plus ventilation of the sinuses through the openings) ensures healthy sinuses. If the removal of mucus from the sinuses is blocked, then it accumulates there, and this is what contributes to the development of infection and subsequent suppuration.
Factors that can cause sinus inflammation:
- Acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI and influenza) - the virus sharply increases the production of mucus in the sinuses and nasal passages, and also causes the development of swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose and sinuses.
Swelling of the mucous membranes leads to the closure of the holes through which mucus from the sinuses enters the nasal cavity. In addition, viral toxins block the motor activity of the ciliated epithelium of the mucous membrane, which also disrupts the removal of mucus from the sinuses. At the initial stage, inflammation in the sinuses is of a serous nature, i.e. no pus is found in the sinuses. But gradually, in the confined space of the sinuses (in the absence of ventilation and the presence of a large amount of mucus), a bacterial infection develops, which leads to the formation of pus in the sinuses. - Chronic inflammatory diseases of the nose (chronic rhinitis) - chronic inflammation of the nasal passages is usually of a bacterial nature.
Pathogenic bacteria and their toxins also contribute to swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose and sinuses, lead to nasal congestion, and increase mucus production in the nose and sinuses. All this leads to the formation of pus in the sinuses. Also, low-grade chronic inflammation can lead to the formation of polyps in the sinuses and nasal passages. - Allergic rhinitis – with allergic rhinitis there is also a sharp increase in mucus production and swelling of the mucous membranes. As a result, serous ethmoiditis may initially occur in the ethmoid sinuses, in which there are no signs of purulent infection. But over time (if the drainage of mucus from the sinuses is not established), a bacterial infection may develop, and ethmoiditis may turn purulent.
- Factors contributing to the development of ethmoiditis – → deviated nasal septum, → adenoids, polyps in the nasal passages, → active and passive smoking, → chronic inflammatory diseases of the nose, tonsils...
Treatment of ethmoiditis
Treatment of the pathology is complex and predominantly conservative. The following are prescribed as therapy:
- vasoconstrictor drugs;
- washing with medicinal solutions;
- physiotherapeutic measures;
- course of antibiotics.
In chronic and polypous forms of ethmoiditis, surgical intervention will most likely be required.
How to treat acute ethmoiditis - the use of vasoconstrictor drugs
Most often, conservative therapy is prescribed, however, such treatment is justified only in situations where there is no pus. The main goal of conservative treatment:
- restoration of nasal breathing;
- elimination of swelling and inflammation.
To treat acute pathology, medications are prescribed to ease breathing, anti-inflammatory drugs, where the active ingredient is ibuprofen. It is recommended to rinse your nose with medicinal solutions, and preferably sleep with your head elevated, using a high pillow.
The most traditional are vasoconstrictor drops, but they should be used for two to three days to eliminate the possibility of addiction.
- "Rinofluimucil" (280 rubles). The drug reduces the volume of discharge from the nasal cavity and eliminates swelling. The spray is usually prescribed in combination with Sinupret and Sinuforte drops (eliminate inflammation).
- "Nasonex" (500 rubles). The drug effectively eliminates congestion caused by allergic rhinitis. The advantage of the spray is that it can be used for several months without the body getting used to it; combine with drugs that activate the outflow of mucus.
Rinofluimucil
Medicines to stimulate mucus discharge:
- “Sinupret” (350 rubles) is presented in the form of dragees and drops. This is a herbal medicine created on the basis of medicinal herbs that eliminate swelling and activate the evacuation of mucus.
- “Sinuforte” (2,300 rubles) - nasal drops based on herbal ingredients that speed up the process of removing mucus and pus.
Nasonex
Washing - what solution to use?
Antiseptic solutions are used to rinse the nose. It is best to use a special device - a sinus catheter. During the procedure, the paranasal sinuses are cleaned and treated with medication. Rinsing is carried out until clear liquid begins to come out of the sinus.
An example of using the Yamik sinus catheter
Physiotherapeutic activities
Prescribed during the period of remission, when there are no signs of inflammation:
- electrophoresis using antibacterial drugs;
- phonophoresis;
- UHF.
Antibacterial therapy for ethmoiditis
Most often, antibiotics are prescribed for acute forms of pathology. Antibiotic treatment of chronic ethmoiditis makes sense when:
- a bacterial infection develops;
- pus appears.
If there are indications for antibiotic therapy, Amoxicillin is prescribed in combination with Clavulanic acid. Augmentin and Amoxiclav are also used. If there is an allergy to drugs of the penicillin group, medications of the fluoroquinol group or macrolides are prescribed.
The course of therapy is designed for two weeks, but after five days the doctor evaluates the effectiveness and feasibility of treatment. If there is no improvement, you need to choose another drug.
It is important! To reduce pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with the active substance paracetamol or ibuprofen are prescribed. Additionally, vitamin complexes are prescribed to strengthen the immune system.
How to treat ethmoiditis of an allergic nature
If the pathology is caused by an allergen, first of all, it is necessary to exclude the patient’s contact with the cause of the disease. The specialist prescribes therapy with antihistamines and nasal sprays with anti-allergenic effects. Therapy with corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory medications, is used. The active ingredient of such drugs is a synthetic analogue of the human hormone - cortisol. If necessary, calcium supplements are prescribed.
It is important! The most commonly prescribed treatment is Nasonex spray.
Surgical therapy for chronic form
There are certain indications for the operation:
- exophthalmos - pathological displacement of the eyeball, most often forward (bulging eyes), less often - to the side;
- decreased visual acuity;
- poor mobility of the eyeball;
- intracranial complications.
First, intensive therapy is prescribed; if it does not produce results, surgery is performed.
There are two types of surgical intervention:
- endoscopic technique - manipulations are carried out from inside the nose;
- The surgeon makes an external incision near the corner of the eye.
During the operation, the specialist opens the cells of the ethmoid sinus.
Treatment of chronic polypous ethmoiditis involves surgical removal of polyps.
It is important! With a timely visit to an otolaryngologist and well-chosen therapy, unilateral and bilateral ethmoiditis can be completely cured. As a rule, the prognosis for ethmoiditis is favorable.
Treatment
Treatment of ethmoiditis consists of undergoing medication and physiotherapeutic procedures. How to treat inflammation of the cells of the ethmoid area of the nose? The ENT doctor prescribes the following course of medications:
- Antibiotics and antiviral drugs.
- Immunostimulating drugs. Immunomodulators.
- Vasoconstrictor medications.
- Antipyretic medications.
- Antihistamines.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Painkillers.
- Galazolin.
- Xymelin.
- Oxymetazoline.
- Amoxicillin.
- Augmentin.
- Cefotaxime.
- Bioparox.
- Ceftriaxone.
- Rinofluimucil.
- Paracetamol.
- Aqua Maris.
- Sinuforte.
At home, the patient must adhere to the following rules:
- Increase immunity.
- Ventilate the room and humidify the air.
- Follow a diet:
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Consume vegetables, fruits, dairy products, nuts, meat, cereals, legumes.
- Avoid alcohol, fatty, fried and allergy-causing foods.
- Use decoctions of herbs, berries and fruits.
The following are used as physical procedures and surgical interventions:
- Sinus catheter "YAMIK" rinsing cells with antibiotics.
- Other types of washing.
- Electrophoresis with antibiotics.
- UHF.
- Phonophoresis with hydrocortisone.
- Helium-neon laser.
- Endoscopic removal of exudate.
- Septoplasty.
- Resection.
- Polypotomy.
go to top
Folk remedies
First of all, treatment with traditional recipes can only be started after consultation with an otolaryngologist. Many experts are against treating ethmoiditis at home, since the disease is dangerous due to its complications. If the doctor has approved the use of traditional methods, the treatment regimen is built on the principle of traditional treatment - the use of a vasoconstrictor, elimination of inflammation through rinsing, drops and inhalations.
Washing
- Soda, salt, tea tree oil. Dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of boiled water at room temperature. salt, a pinch of soda, a few drops of tea tree essential oil. The procedure is carried out three times a day using a syringe.
- Chamomile. Brew 1 tbsp in a glass of water for an hour. chamomile flowers. Strain the mixture and rinse your nose several times a day.
- Chlorophyllipt. A ready-made alcohol solution of chlorophyllipt can be purchased at a pharmacy. Dissolve a tablespoon of the product in two glasses of water. Wash your nose with the solution twice a day.
Inhalations
The procedure can be carried out in two ways: traditional (breathe healing vapors under a towel); using a nebulizer.
Traditional method of using steam inhalation
Recipes for decoctions for traditional inhalations.
- Pour 10 pieces of bay leaves with water, bring to a boil, reduce heat to low. Breathe in pairs for 5-10 minutes.
- Grind 3 cloves of garlic, add 100 ml of apple cider vinegar and a glass of boiling water. Carry out the procedure for a quarter of an hour three times a day;
- Pour 3 tbsp into two glasses of water. chamomile inflorescences, boil for 5-7 minutes, leave for 1.5-2 hours, bring to a boil again, add 5 drops of tea tree oil (can be replaced with eucalyptus oil). The duration of the procedure is 5-10 minutes, three times a day.
Steam inhalation using a nebulizer
Drops
- Drops from cyclamen juice. This remedy is the most effective in the list of folk recipes. To prepare, you will need to rinse the plant tuber, grate it, and squeeze out the liquid. The resulting juice is diluted with water - 1 part juice, 4 parts water. Place two drops of the prepared product into each nostril. The procedure is carried out before bedtime, since heavy discharge begins after instillation.
- Kalanchoe is another effective folk remedy against infections that get into the nose and prevent free breathing. You will need to cut three large leaves and put them in a cool place for three days. Then the plant needs to be crushed and the juice squeezed out. Strain the liquid and add water in equal proportions. The product is instilled 2-3 drops into each nostril several times a day.
- Black radish juice drops are a fairly effective folk remedy for ethmoiditis. To prepare, you will need to wash the radish, chop it, squeeze the juice out of the pulp, strain and bury it in your nose three times a day, 3-4 drops in each nostril.
After the procedure, the nose should be massaged especially actively in the area of the appendages. Then you need to lie on your back so that the drops spread evenly in the nasal cavity. After instillation, you need to blow your nose.
What kind of disease is this
Ethmoiditis is a disease that can be of bacterial or viral origin. It is classified into two main types - acute and chronic.
Acute ethmoiditis develops against the background of acute rhinitis or influenza. Most often, the inflammatory process occurring in other paranasal sinuses leads to repeated damage to the ethmoid labyrinth. If inflammation affects the maxillary and frontal sinuses, then damage may occur to the anterior cells of the ethmoid bone.
The photo shows what ethmoiditis looks like
Inflammation with ethmoiditis sharply attacks the deep layers of the mucosa. As a result, symptoms of ethmoiditis such as puffiness and diffuse swelling are observed. The opening between the cells of the ethmoid bone and their excretory tracts are reduced in size. All this leads to drainage.
Considering ethmoiditis, one cannot fail to note the main reasons for its formation. Viruses and bacteria that weaken the body’s defenses and nasal mucosa can affect the development of the disease.
Ethmoiditis can occur for the following reasons:
- rhinitis and colds, as well as all ailments of viral etiology;
- sinusitis of various types: fungal, viral and bacterial;
- septal defects of a congenital or acquired nature;
- rhinitis of allergic origin;
- weakened immunity, unable to fight pathogens;
- facial injuries.
Often the formation of ethmoiditis occurs against the background of influenza and scarlet fever. But still, most often the reason for the development of pathology lies in advanced frontal sinusitis or sinusitis. If the anterior parts of the ethmoid bone are introduced into the process, then the pathology is called frontoethmoiditis and maxillary ethmoiditis. The posterior areas of the bone are involved in the process when the disease is not treated properly and it is in an advanced form.
On video, detection of the disease ethmoiditis:
If the inflammatory process affects two sinuses at once, the disease is called pansinusitis or polysinusitis. It all depends on which cavities are involved in the inflammatory process.
Adenoid sinusitis is the result of growths in the nasal cavity. They prevent mucus from leaving the cells normally, resulting in excellent conditions for the formation of bacteria. There are certain situations when ethmoiditis itself becomes the cause of the formation of polyps. Then the pathology takes on a chronic form, and therapy comes down to surgery. There is no other way to cure the disease, since abnormal growths do not allow the nose to function normally.
adenoid sinusitis
Compared to a regular runny nose, ethmoiditis requires urgent treatment. This is due to multiple reasons. Firstly, an acute illness can develop into a chronic one, which is very difficult to treat. Secondly, ethmoiditis, in the absence of proper treatment, can provoke a number of complications that pose a danger to human life.
The most common complications include:
- violation of the integrity of the ethmoid labyrinth;
- decreased vision;
- spread of the inflammatory process to intracranial areas, which may result in complications such as brain abscess or purulent meningitis.
When traditional medicine is ineffective
Most often, doctors do not recommend treatment with folk remedies, since such therapy, as a rule, turns out to be ineffective and leads to loss of time. In this case, the acute phase very quickly transforms into chronic ethmoiditis, the symptoms of which are especially difficult for the patient to tolerate. That is why it is important not to waste precious time and promptly identify the symptoms of ethmoiditis and receive adequate treatment. It is not recommended to self-medicate during an exacerbation of a chronic form of pathology.
Kinds
Ethmoiditis can be classified according to the course, etiology and localization of inflammation
Acute course of the disease
The acute form of the disease has more vivid symptoms compared to the chronic form. But only the treatment of an acute illness is simpler. This is due to the fact that it is possible to recognize the symptoms of the pathology as early as possible and begin treatment at the initial stage.
The photo shows what acute ethmoiditis looks like
Acute ethmoiditis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe pain in the head, concentrated in the nose, forehead and corners of the eyes;
- difficulty breathing;
- impaired sense of smell or complete loss of it;
- temperature rise to 38 degrees.
In addition, in acute cases, the patient is bothered by a severe runny nose. But the discharge at the initial stage is serous, that is, there is no pus. Purulent discharge will be observed a little later, when the mucus is thick and green or yellow in color.
If ethmoiditis affects the patient for the first time, then if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, it can be cured quickly and without complications.
But with repeated damage, it is much more difficult to treat the disease, since it quickly becomes chronic. As a rule, complications can develop within two days.
But how to treat chronic tonsillitis during pregnancy, and what remedies should be used, is described in this article.
How to determine a deviated nasal septum, and how to restore the condition of the nasal structure. This information will help you understand.
Which ointment under the nose for colds for children is the best and most effective is indicated here:
You can understand which folk remedies for ear congestion during a cold are the most effective by clicking on the link.
Chronic
This form of the pathological process is characterized by an unpleasant clinical picture, as well as the presence of complications. The disease becomes chronic due to improper treatment of acute ethmoiditis or weak immunity. Chronic ethmoiditis cannot be completely cured, so it will become a constant companion. It can occur in two stages - remission and exacerbation.
In the photo - chronic ethmoiditis
Symptoms during exacerbation are similar to the clinic of the acute phase of ethmoiditis. In the relief stage, the disease occurs without severe symptoms.
But some patients complain of the following symptoms:
- discomfort in the root of the nose;
- constant headaches;
- purulent mucus coming out of the nose with a foul odor;
- concentration of discharge in the nasopharynx;
- nausea, which may lead to vomiting;
- impaired smell function.
Chronic ethmoiditis is very dangerous, because a person can live with it for more than one year, believing that he has a chronic runny nose. The only way to get rid of the chronic form forever is to have surgery.
In addition, ethmoitis may vary according to the location of the pathology:
- bilateral - damage is caused from both sides;
- right-sided - inflammation affects only cells from the right area;
- left-sided - inflammation affects cells from the left area.
The pathology may also vary according to the characteristics of its course:
- catarrhal;
- purulent;
- polyposis.
Catarrhal
In the photo - catarrhal ethmoiditis
The reason for the development of pathology lies in the penetration of the virus. A characteristic feature of catarrhal ethmoiditis is lacrimation. The patient complains of symptoms of intoxication - headache, dizziness, general weakness, nausea.
Redness of the whites of the eye is observed. Situations cannot be ruled out when burst blood vessels are observed in the inner corner of the eye. Swelling that affects the bridge of the nose can spread to the corners of the eyes. The catarrhal form is characterized by a lack of sense of smell.
Polyposis
This type of ethmoiditis develops in a chronic form of the pathology. The reason for the development is long-term rhinitis. Swelling affects the mucous membrane and does not go away for a long time, sometimes affecting the ethmoid bone.
In the photo this is what polypous ethmoiditis looks like
The inner part of the cells is affected by polyps. They block the lumens, as a result of which the mucous membrane is swollen all the time. Patients may go into remission during which they remain symptom-free. Nasal breathing is restored. Surgery is usually performed for nasal polyps.
Maybe
Nutrition and lifestyle
For the entire period of treatment, doctors recommend adhering to a gentle regimen - more rest, if possible limiting communication with people, and eliminating physical activity.
Nutrition requires certain adjustments - the diet should be balanced and complete, but should not overload the stomach and cause a feeling of heaviness. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe a vitamin complex.
It is important! If you follow all the recommendations and the prescribed treatment regimen, improvement occurs after three to four days, and you can count on a complete recovery in 7-10 days. If the disease was accompanied by complications, recovery will take 2 to 3 weeks.
Treatment of pathology
It is worth noting that treatment of ethmoiditis in a child should be started without delay. This is due to the fact that this disease poses a real danger to the lives of children, especially young children. It is not the inflammation of the ethmoidal labyrinth cells in itself that is dangerous, but the complications that arise from improper treatment. That is why it is extremely important to consult an otolaryngologist at the first symptoms of the disease. You should follow all the doctor’s recommendations, because improper treatment can worsen the course of the disease. The selection of medication is carried out taking into account the patient’s age, the severity of the pathology, concomitant diseases, and individual contraindications.
At the initial stage of therapy, it is important to rinse the child’s nasal cavity from accumulated pus and mucus. The doctor may prescribe antibiotics and painkillers. It is extremely important to complete the entire course of therapy. Under no circumstances should treatment be interrupted after the patient's condition has improved.
The mistake of many parents is that they think that antibiotics are very harmful to the baby, and therefore treatment should be stopped as early as possible. This is not entirely true: antibacterial drugs act in a special way, and for a complete recovery it is important to complete the full course of therapy. In case of early interruption of treatment, the likelihood of relapse increases.
After the patient’s condition improves, the doctor prescribes physiotherapeutic procedures:
- electrophoresis;
- phonophoresis;
- UHF.
Surgical treatment is used only in the event of life-threatening complications. In some cases, a flexible endoscope is used for such surgical interventions; it is inserted into the nasal cavity and the necessary manipulations are performed. After the procedure is completed, the nasal cavity is disinfected with a special antiseptic. The mucous membranes recover quite quickly after manipulations carried out using this method.
With a correct and timely diagnosis, the child’s disease is cured quickly enough and the baby makes a full recovery. The main task of parents at this stage is to fully comply with the specialist’s requirements. The use of medications is sometimes not enough; for a speedy recovery, a favorable psychological environment, proper rest (necessarily naps during the day), and proper nutrition are necessary.
Parents should not forget about the need to strengthen the baby’s immunity, especially in the autumn-winter period. After complete recovery, it is necessary to pay special attention to the child’s health. He shouldn't be overcooled. Parents should remember that ethmoiditis is a fairly serious disease that needs to be treated only under the supervision of a specialist. It is unacceptable to try traditional medicine recipes on a child.
Ethmoiditis is an inflammatory lesion of the mucous cells (special cells communicating with each other, as well as the nasal cavity) of the ethmoid bone. This disease occurs in isolation in children, since it is precisely these nasal sinuses (sinuses) that are sufficiently developed from birth. In adults, ethmoiditis does not occur separately due to its anatomical specificity; as a rule, we are usually talking about sinusroethmoiditis. Ethmoiditis in children is a very serious disease that requires hospitalization with intravenous antibiotics.
- General symptoms of the disease
- Treatment methods Drug therapy
- Surgical intervention
- Treatment at home
- Possible complications
- Drugs for the treatment of ethmoiditis and their cost
General symptoms of the disease
Ethmoiditis (inflammation of the ethmoid sinuses) in young children is a very severe independent pathology, while in adults it is observed with simultaneous damage to other sinuses.
The disease can be acute or chronic.
Signs of acute ethmoiditis:
- pain in the bridge of the nose, base of the nose, between the eyes;
- headache;
- swelling/swelling of soft tissues around the eyes;
- increased sensitivity of the wings of the nose to touch;
- nasal congestion;
- increased body temperature;
- partial loss of smell;
- profuse nasal discharge, changing in character from serous to serous-purulent/purulent.
In newborns, acute ethmoiditis is an extremely severe pathology , when serious complications develop in just a couple of hours. Also, in young children, the disease almost immediately takes on a purulent character.
With the primary nature of the disease, body temperature rises sharply, up to 40 degrees, toxic manifestations increase, possible: vomiting, regurgitation.
Along with nasal congestion, inflammation processes develop in the area near the upper jaw and in the periorbital tissue.
The eye on the affected side closes completely, the eyeball moves downward and to the side. Complications can arise already from the 3rd to 5th day of the disease as a result of a breakthrough of pus, and in the absence of adequate therapy, after a few days, intracranial or orbital complications or sepsis develop.
Secondary (against the background of an existing or after a previous illness, including: influenza, measles, etc.) ethmoiditis is characterized by a more pronounced severity of manifestations and their progression.
You can read about acute nasopharyngitis and treatment of the disease in the article after going to the page via the link.
You can read about the treatment methods for frontal sinusitis here with all the details.
Chronic ethmoiditis develops from an acute form of the disease, with characteristic; a feeling of pressure, pain in the projection of the sinuses, intensifying at night, nasal discharge, etc.
Treatment methods
Only a doctor can establish a diagnosis of “Ethmoiditis” based on the results of an examination and additional examination (CT, X-ray, etc.).
Drug therapy
Treatment of acute ethmoiditis in children is carried out in a hospital setting, and, first of all, is based on active antibacterial therapy (mainly drugs are administered intravenously), taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen.
To ensure free outflow of sinus contents, vasoconstrictors are prescribed. can be removed using an electric suction.
Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, etc. are used to reduce temperature.
In adults, treatment follows similar principles and includes:
- to facilitate outflow - vasoconstrictors (Oxymetazoline, Xylometazoline, etc.), combination drugs (Rinofluimucil), installation of cotton-gauze turundas soaked in an adrenaline solution into the nasal cavity on the affected side, antihistamines (Erius, etc.);
- taking antibiotics of the penicillin, cephalosporin series, macrolides (Augmentin, Zinnat, Sumamed, etc.);
- rinsing the nose with saline solutions;
- washing in a clinic (“cuckoo”);
- taking antipyretic and painkillers.
What to do if a runny nose does not go away during pregnancy, you can read in the article below the link.
But you can find out why women snore in their sleep here.
In the article on the page: it is written about nasal drops during pregnancy, recommended for use.
At the recovery stage, physiotherapy is prescribed to speed up the process (helium-neon laser, UHF, microwave, magnet, ultrasound, phonophoresis with hydrocortisone, electrophoresis with an antibiotic).
Surgical intervention
With the rapid development of a purulent process against the background of acute ethmoiditis, the cells of the ethmoid bone are opened through intranasal or external incisions to remove the infected tissue.
Also, surgical treatment through endoscopic surgery followed by antibiotic therapy is used in patients with a chronic form of the disease.
Treatment at home
Treatment of ethmoiditis at home is allowed only after consultation with a doctor and in strict accordance with his prescriptions!
Inhaling fir oil vapors can help relieve the condition.
If the condition worsens within a couple of days, hospitalization is indicated.
Possible complications
In children, ethmoiditis is often complicated by the development of:
- orbital phlegmon,
- eyelid abscess;
- retrobulbar phlegmon, etc.;
- sepsis;
- osteomyelitis of the upper jaw, etc.
Drugs for the treatment of ethmoiditis and their cost
Medicines for drug therapy of the disease can be purchased on Yandex.Market, in pharmacies, and online stores.
Cost of some drugs:
- Augmentin - 75 - 305 rubles;
- Zinnat - 170 - 313 rubles;
- Sumamed - 183 - 1246 rubles;
- AquaMaris - 105 - 249 rubles;
- Paracetamol – 2 – 280 rub.;
- Rinofluimucil - 195 - 312 rubles;
- Oxymetazoline – 50 – 380 rub.
The diagnosis of “Ethmoiditis” requires mandatory confirmation due to the high risk of complications. The seriousness of the disease determines its treatment in children in a hospital setting with intravenous administration of antibacterial agents.
You will learn how to help your body overcome illnesses associated with ethmoiditis, rhinitis, sinusitis and other diseases of the nasopharynx while watching the video.
Category: Nose You are in the section: Nose Section topics:
- Adenoids
- Sinusitis
- Snore
- Sinusitis
- Rhinitis
- Clinics
Recommended medical institutions
- Doctors
Full of doctors in your city
- Drugs
Drug treatment
Subscribe to the newsletter
Get the latest news on gastrointestinal treatment
Work on the site! We are looking for authors
- With honey education for writing articles
- Journalist on medical news
Ethmoiditis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the ethmoid bone cells, which is part of the structure of the anterior base of the skull and is adjacent to its important anatomical parts - the anterior cranial fossa, orbits and ethmoid arteries. The disease can be acute or chronic, and can occur as a separate disease or simultaneously with pathologies such as sinusitis, sinusitis and frontal sinusitis.
Did you like the article?
Complications
If treatment is not promptly done, the pus will spread to neighboring organs. This can cause complications that threaten the patient's life:
- complications related to vision and eyes;
- destruction of the latticed labyrinth;
- inflammation of intracranial areas, pia mater.
It is important! The chronic form of the pathology is dangerous due to the absence of symptoms; if signs of ethmoiditis appear, it is important to consult a doctor without wasting time. Inattention to inflammation will lead to irreversible pathological processes.
Catarrhal sinusitis - symptoms
Regardless of which sinuses are affected by sinusitis, it is characterized by general symptoms.
Acute sinusitis - symptoms:
- malaise caused by general intoxication;
- feeling of pressure in the sinus areas of the face;
- voice distortion - nasality;
- impaired sense of smell;
- lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids;
- bad breath;
- cough caused by mucus running down the back of the throat;
- nasal congestion, swelling of the mucous membrane;
- temperature increase;
- painful sensations in the forehead, back of the head, temples;
Acute maxillary sinusitis
When both maxillary sinuses become inflamed, bilateral catarrhal sinusitis occurs. This type of catarrhal sinusitis is characterized by nasal congestion - the patient is forced to breathe through the mouth, which causes dryness of the oral mucosa, cough, and infection with laryngeal viruses.
Catarrhal viral sinusitis of the maxillary sinuses – symptoms:
- complete nasal congestion;
- heat;
- feeling of fullness in the upper part of the nose;
- obsessive headache;
- swelling of the upper part of the face.
Acute frontal sinusitis
A type of sinusitis - catarrhal sinusitis - occurs when the frontal (frontal) sinuses become inflamed. An acute inflammatory process in the upper sinuses causes discomfort during the day and is especially severe at night.
Symptoms of catarrhal sinusitis:
- headache localized in the frontal region;
- feeling of fullness and heaviness in the forehead;
- photophobia;
- temperature increase;
- swelling of the face in the area of the nose and eyes.
Catarrhal ethmoiditis
Acute catarrhal sinusitis that develops in the ethmoid sinuses is called ethmoiditis. This form of sinusitis is very dangerous because the ethmoid sinuses are anatomically located very close to the brain, eye sockets, and arteries. Ethmoiditis can lead to serious complications affecting the brain and eyes. Catarrhal sinusitis of the ethmoid sinuses causes severe pulsating headaches, which are almost impossible to relieve with medications.
In addition, with pathology:
- severe malaise develops;
- the temperature rises.
Catarrhal sphenoiditis
Acute inflammation of the sphenoid sinus is called sphenoiditis. This disease is rare and is almost always combined with ethmoiditis. This pathology is characterized by severe headaches in the temporal and occipital parts, as well as in the area of the orbits.
The danger of sphenoiditis is due to the proximity of the brain, cartilage tissue and facial bones, which can be affected by pathogenic microflora.
Tips and tricks
Preventive measures consist of preventing the development of pathologies that can provoke ethmoiditis. Every disease must be treated promptly until complete recovery.
Doctors' recommendations:
- treat all infectious diseases completely;
- regularly strengthen the immune system;
- diversify the menu with vitamins and beneficial microelements;
- avoid hypothermia;
- move more, but the loads must be adequate;
- Carry out wet cleaning twice a week;
- regularly clean filters: household appliances (air conditioner, washing machine, etc.), hoods, water;
- If you have to work in a dirty room, use personal protective equipment.
Now you know what ethmoiditis is - symptoms and treatment in adults, and you also know how to resist the pathological process.
Consequences and complications
If you have symptoms of sinusitis, it is important to quickly identify the pathology and begin treatment. Instrumental and laboratory research methods include:
- X-ray examination of the paranasal sinuses. Allows you to identify areas of secretion accumulation. They look like a shadow. Requires 2 photographs in 2 projections.
- CT or MRI. They are carried out to identify the condition of the brain and in case of a complicated course of the disease.
- Ultrasound.
- Rhinoscopy.
- Examination of the pharynx and larynx.
- Physical examination. When the cells are inflamed, the pain syndrome is recorded during palpation. The area of the bridge of the nose and the root of the nose are often painful.
- General blood analysis.
- Analysis of nasal swab for microflora.
- Survey. The presence of a headache and runny nose will indicate the main risk factors.
After diagnosis, treatment of the skull in the facial area is carried out in a hospital (if complications develop) or on an outpatient basis. Treatment methods for catarrhal ethmoiditis are the use of antimicrobial agents (antibiotics, antifungal or antiviral drugs), vasoconstrictor drops or sprays (Galazolin, Rinonorma, Xylometazoline), rinsing the sinuses with saline solutions, physiotherapy and taking immunostimulants (for patients with reduced immunity).
Folk remedies in the form of herbal infusions and decoctions can be used as an addition to the main therapy. In the absence of treatment or incorrect therapy, the following consequences are possible:
- Psychoneurotic disorders. They occur in the chronic form of ethmoiditis due to sleep disturbances and decreased quality of life.
- Inflammation of other paranasal sinuses with the development of sinusitis, sinusitis or sphenoiditis.
- Loss of smell.
- Inflammation of bone structures.
- Empyema.
- Destruction of the ethmoid bone.
- Suppuration.
- A breakthrough of pus into the cranial cavity.
- Meningitis and meningoencephalitis (inflammation of the brain). They occur when the inflammatory process spreads to the posterior areas of the sinus.
- Abscess formation.
- Relapse. Possible after surgery (rhinoplasty, polypectomy and adenoid surgery) or drug therapy.
- Deterioration of vision.
- Inflammation of the eye socket.
The reasons for the development of complications include self-medication, late diagnosis and non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations.
Disease prevention. Recommendations
There is a small set of measures that must be taken to avoid the development of an acute form of ethmoiditis:
- It is necessary to promptly treat all diseases that may cause ethmoiditis.
- Eliminate bad habits.
- Monitor your immune system: eat right, enriching your diet with vegetables and fruits, engage in moderate physical activity, spend more time in the fresh air, and improve your sleep schedule. A healthy body will fight harmful microorganisms that penetrate it.
- Periodic consultation with an otolaryngologist, even if there are no clearly defined symptoms of the disease.
[ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1] to content ?
Treatment options
How to treat a child? Treatment of the disease is complex, combining methods of medication, physiotherapy (at the stage of remission), therapy, nasal lavage, and measures aimed at strengthening the child’s immunity.
In some cases, surgical treatment .
Medications
Depending on the cause of the disease, the child is prescribed antibacterial or antiviral drugs. In addition, symptomatic drug therapy is necessary, including the use of drugs from the following groups:
- antipyretics if body temperature exceeds 38 degrees, or if the child does not feel well at a lower temperature;
- anti-inflammatory to eliminate swelling and other signs of inflammation;
- vasoconstrictors to restore nasal breathing;
- antihistamines to eliminate the allergic reaction that provoked the development of the disease;
- immunomodulators to restore immunity.
Antibacterial therapy
Taking antibiotics is justified only if the cause of the disease is a bacterial infection.
In all other cases, antibiotics are not prescribed .
ethnoscience
Self-medication using traditional medicine is unacceptable.
Since the main cause of the development of pathology is considered to be viruses or bacteria, treatment should be carried out only with the use of medications prescribed by a doctor.
Traditional recipes can only be used as auxiliary therapeutic measures. Thus, rinsing the nose with herbal decoctions prepared on the basis of sage, chamomile, and fireweed will help speed up the healing process.
Other methods
AT the remission stage, a positive therapeutic effect , such as:
- phonophoresis and electrophoresis using medications (hydrocortisone, calcium hydrochloride);
- UHF ethmoid sinuses;
- laser treatment of affected areas.
Surgery
Surgery is indicated only if the source of inflammation spreads to the bone tissue located in the immediate vicinity of the ethmoid sinuses.
The operation is performed under anesthesia; during the procedure, an external opening of the cells of the ethmoid bone is performed, after which all inflamed areas of this area are removed.
Symptoms in newborns
The disease in newborns is severe and within a few hours passes into the purulent stage, leading to the following complications:
- osteomyelitis of the frontal process of the upper jaw, sepsis;
- inflammation quickly spreads to all cells of the ethmoidal labyrinth and sinuses of the upper jaw.
In newborns, acute ethmoiditis manifests itself in the first 5 days. The following symptoms are observed:
- constant anxiety: the child cannot sleep, eats poorly;
- a sharp increase in body temperature up to +40°C;
- frequent vomiting;
- swelling develops from the inner corner of the eye, then it spreads to the upper and lower eyelids;
- constant watery eyes and redness of the eyes;
- conjunctivitis;
- when feeling the orbit, the child is worried due to severe pain;
- motionless eyeball;
- nasal breathing disorder.
Before the age of one year, the disease occurs in a complicated form.
What is ethmoiditis - definition of the disease, ICD-10 code
Ethmoiditis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth. This labyrinth is one of the paranasal sinuses and is part of the ethmoid bone, which is located deep in the skull at the base of the nose.
Ethmoiditis can occur as an independent disease, but more often it accompanies other types of sinusitis: sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, sphenoiditis. It most often affects preschool children, but the disease can be diagnosed in everyone: from newborns to elderly patients.
Clinical manifestations
Depending on the form of the disease, its symptoms may be different:
| Acute form | Chronic form |
|
|
In newborn children, the clinical picture is more vivid and develops at a rapid pace; only a few hours can pass from the appearance of the first signs of rhinitis to a significant deterioration in the child’s condition.
Causes of the disease in adults and children
The main causative agents of ethmoiditis are ARVI viruses (influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus and rhinovirus infections), bacteria from the group of staphylococci and streptococci, as well as pathogenic fungi. In rare cases, several infectious agents are detected at once.
Ethmoiditis rarely develops independently. In children and adults, the disease is usually a complication of other infectious diseases of the ENT organs: rhinitis, sinusitis. In newborns, ethmoiditis can develop against the background of intrauterine, skin or umbilical sepsis.
Infection in the ethmoid sinus spreads more often hematogenously (through the bloodstream), less often through contact.
Factors predisposing to the development of ethmoiditis:
- Features of the structure of the nasopharynx (very narrow outlet openings of the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth, narrow middle nasal meatus);
- Adenoid growths;
- Facial injuries (for example, a broken nose or deviated septum);
- Allergic rhinitis, sinusitis;
- Chronic pharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis;
- Congenital and acquired immunodeficiencies.
Pathogens and provoking factors
In order to understand that this is ethmoiditis, and not another pathology with similar symptoms, it is necessary to turn to the anatomy of the ethmoid (ethmoid) bone.
The inside of the latter is covered with mucous membrane and has several chambers filled with air. This element consists of two plates through which blood vessels and the olfactory nerve pass. The top of the bone forms the nasal septum and is in contact with the other sinuses. Therefore, the disease in question occurs according to the type of rhinitis and other similar pathologies. In this case, ethmoiditis is characterized by inflammation of tissues related to the ethmoid bone. Staphylococcal or streptococcal infections can provoke pathology. Also, the tissues in the nasal cavities can become inflamed when the body is infected with influenza, adeno-, rhino- and coronoviruses. In addition, fungal microflora can lead to the appearance of disease. Infection with these viruses or bacteria does not always cause inflammation of the tissues of the nasal sinuses. The development of the disease occurs due to a decrease in immunity, which contributes to the active growth of pathogenic microflora. In addition, the causes of ethmoiditis are due to the following factors:
- diseases of the throat and nose;
- allergic rhinitis;
- congenital pathologies and nasal defects.
Due to the close location of the nasal
sinus ethmoiditis often develops as a complication of sinusitis, sinusitis. If adequate treatment is not carried out, and the inflammatory process spreads beyond the initial zone, then frontoethmoiditis or sinusitis occurs. When the pathology affects several sinuses, a bilateral form of the disease appears. In this case, they talk about the course of (pansinusitis). The risk group for developing ethmoiditis includes patients with adenoids or polyps. Such growths that form in the nasal cavity interfere with the normal outflow of mucus. As a result, optimal conditions arise in the sinuses for the growth and development of pathogenic microflora, which provokes inflammation of local tissues.
The main causative agents of sinusitis are the same viruses that provoke the occurrence of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, rhinovirus or adenovirus infections. The cause of the disease can be bacteria - staphylococci and streptococci, as well as pathogenic fungi. In medicine, there have been cases where sinusitis develops due to the so-called mixed infection. Several pathogens are detected in the material under study.
Ethmoidal sinusitis in rare cases develops primarily. As a rule, in preschool and school-age children and adults it appears as a complication from other infectious diseases: sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis. The infection enters the ethmoid sinus in two ways: hematogenous (most often) and contact. Sinusroethmoiditis can even affect newborn children. The cause is umbilical, intrauterine and skin sepsis.
Ethmoiditis is a non-contagious disease, that is, it is not possible for a healthy person to become infected from a sick person. The mechanism of development of the disease is as follows:
The ethmoid bone contains a large number of cells with air freely circulating in them;
- The sinuses are lined with mucous epithelium, which during the inflammatory process thickens and merges with the adjacent cavities;
- When pathogenic agents enter as a result of acute respiratory viral infection or other rhinovirus infection, microbes are located on epithelial cells, gradually penetrating into the deep layers;
- Microbes rapidly divide and fill the cells with purulent contents (the first clinical signs appear at this stage). The mucous membrane swells, hyperemia occurs;
- Impaired fluid metabolism leads to a complete inflammatory process in the sinuses.
As a result of all processes, air exchange is disrupted, and the accumulated pathogenic flora causes acute pain. If left untreated in children, the pathological process leads to complete or partial destruction of bone tissue.
The causative agents of the disease include:
- adenovirus;
- paravirus;
- fungi of the genus Candida;
- streptococcal infection;
- staphylococci;
- less often - Koch's wand.
Ethmoiditis is diagnosed as a consequence or complication of influenza, colds, ARVI or other types of sinusitis. Initially, it is extremely rare.
Note! The infection enters the ethmoid labyrinth through the bloodstream (hematogenous pathway); the infection is not transmitted through contact or household contact, but the pathogens that led to this disease are transmitted.
Prevention
The disease can occur for various reasons, therefore, to prevent ethmoiditis, you should:
- strengthen immunity;
- consume more fiber, perhaps take vitamin supplements;
- eat properly and rationally;
- play sports and do exercises;
- to harden;
- promptly treat all respiratory diseases;
- do not overcool;
- Do wet cleaning in the apartment twice a week;
- do not use medications without medical supervision;
- Supervise small children and remove all small objects that could get into the nose.
If you adhere to all the rules described above, you can protect yourself not only from ethmoiditis, but also other diseases.
Complications of ethmoiditis
Main reasons
Although acute ethmoiditis mainly develops in children as a complication after a viral respiratory disease, this is not the only cause that causes it. In newborns and infants, it can appear under the influence of an internal infection, against the background of existing sepsis, when the infection penetrates the ethmoid labyrinth through the bloodstream.
The most common causes of ethmoiditis in children are:
- regular colds and viral diseases weaken the immune system and create favorable conditions for infection to multiply;
- chronic diseases of the nasal sinuses (sinusitis, sinusitis) – inflammation in children easily passes from one sinus to another;
- a small foreign body getting stuck in the nose may not make breathing too difficult, but at the same time disrupt normal air circulation and interfere with the outflow of mucus;
- injuries to the nasal bones - because of them, the nasal passages narrow, or the nasal septum is bent;
- some medications - if used incorrectly or uncontrolled, can lead to swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- severe allergic reactions - swelling occurs and the natural passage into the lattice labyrinth is completely blocked;
- overgrowth of adenoids - compresses the mucous membranes, disrupting the flow of oxygen and normal air circulation.
Finding out the main cause of the disease is very important and this must be done as quickly as possible. Otherwise, treatment, even correct and high-quality treatment, will not produce results, and the disease will become chronic, which subsequently provokes serious complications.
Forecast
In acute ethmoiditis, early detection of the disease and qualified medical care make it possible to achieve complete clinical recovery. Relapses are usually not observed.
In chronic cases, the prognosis is somewhat less optimistic. It is virtually impossible to achieve recovery, despite all the achievements of modern medicine. Doctors can only achieve stable remission, which does not exclude periodic exacerbations.
Plisov Vladimir, doctor, medical observer
2, total, today
( 67 votes, average: 4.21 out of 5)
Rhinopharyngitis in children: treatment
Pharynx injuries: causes, symptoms, treatment
Related Posts
Diagnosis of the disease Ethmoiditis
The presence of ethmoiditis can be determined using an x-ray examination and analysis of clinical signs. A computer tomogram allows you to show with 100% accuracy the condition of the nasal concha, septum and diagnose sinus inflammation.
Ethmoiditis photo
On tomographic and x-ray photographs of the bones of the skull and nasal sinuses, darkness is recorded in the area of the cells of the ethmoid bone. To avoid serious complications, qualified treatment is necessary to identify the causes of inflammation.
When prescribing drugs, the individual characteristics of the patient should be taken into account. Diagnosing ethmoiditis becomes more difficult in the autumn-winter period, when local epidemics of acute viral diseases appear.
In this case, it is regarded as an acute respiratory viral infection, and its complications are stye, conjunctivitis, a reaction to an adenovirus, swelling of the eyelids due to allergies, or even insect bites. It is imperative to differentiate acute ethmoiditis from such ailments as osteomyelitis of the upper jaw, dental diseases, dacryocystitis and others.
to the content?
Prevention at home
Ethmoiditis is a disease caused by a wide variety of microorganisms, so there are no specific preventive measures. In order to prevent the development of ethmoiditis, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of diseases that can provoke it.
In addition, it is important to support the immune system by periodically taking vitamin-mineral complexes and immunomodulatory agents, especially in the autumn-winter period.
How to quickly treat a cold at home
Instructions for using Nimesil and when the drug is most effective are described here.
What can ear congestion without pain lead to //drlor.online/diagnostika-lechenie/zalozhennost-ushej/pri-prostude-kak-bystro-izbavitsya.html
Symptoms
Ethmoiditis can have an acute or chronic form. In the chronic course of the disease, the symptoms are mild, recovery and periods of illness differ little. In acute illness, against the background of reduced immunity, concomitant pathologies are activated.
Symptoms that may indicate the development of ethmoiditis:
- increasing headaches that are poorly relieved after taking painkillers;
- pain in the eye sockets and at the base of the nose;
- decreased or loss of sense of smell;
- increased fatigue;
- runny nose, purulent discharge from both nostrils;
- increase in body temperature up to +40°C;
- nasal congestion, difficulty breathing.
If these signs are present, you should immediately consult a doctor. Diagnostic methods:
- examination of the nasal passages;
- rhinoscopy;
- examination of the nasal cavity using an endoscope;
- X-ray of the paranasal sinuses;
- CT scan.