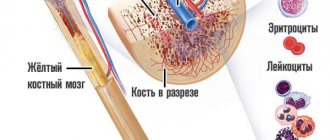
A biochemical blood test is one of the most informative studies in diagnosing diseases.
ALT blood test, what is it?
ALT or ALT (Alanine aminotransferase or alanine transaminase) is one of the indicators of the analysis and is a vital enzyme, indispensable in the metabolic processes of amino acids, which is localized in the tissues of internal organs.
In addition, ALT regulates the process of alanine conversion in cells, which in turn helps strengthen the immune system and saturate nerve cells, and also participates in the metabolic processes of various substances.
Various concentrations of alanine transaminase are present in:
- Liver (most pronounced presence).
- Pancreas;
- Muscles;
- Heart;
- Lungs;
- Kidneys.
Only a small amount of alanine aminotransferase is present in the blood of a healthy person, so significant increases in the level of this substance in the blood indicate the formation of a pathological process that causes rapid destruction of body cells.
What do ALT readings tell you?
Alanine aminotransferase is an enzyme that is a diagnostic indicator of the development of a significant number of pathologies. Analysis of the performance indicators of the human body is sometimes carried out in the ratio of ALT and AST (aspartate aminotransferase). A detailed examination allows you to get the most accurate picture of the state of the body.
Using this analysis, it is possible to detect the development of hepatitis at an early stage, when the disease does not yet make itself felt by any symptoms. The same applies to the diagnosis of cardiovascular pathologies. When diagnosing myocardial infarction, great attention is paid to the ALT indicator.
Alanine aminotransferase is synthesized inside cells, and only a small amount of it can enter the blood. In hepatitis, cirrhosis and other forms of liver damage, this substance is detected using routine diagnostic measures. A decrease in enzyme activity indicates that the body is in danger and urgently needs help.
Monitoring ALT levels is necessary because the liver performs the most important functions in the body:
- neutralizes allergens, poisons;
- synthesizes cholesterol, bile acids, bilirubin, lipids and phospholipids;
- stores and replenishes energy reserves, provides the body with glucose;
- provides synthesis of some vitamins.
A decrease in ALT activity means that these life-support functions of the body are at risk.
Enzyme indicator standards
The presence of small amounts of aminotransferases in the blood is considered normal. The coefficient may differ for adults and children, men and women. Indicators during pregnancy are slightly elevated.
Table “Normal ALT and AST”
| Patient category | Normal values, U/l | |
| ALT | AST | |
| Among women | Up to 31 | Up to 31 |
| In men | Up to 45 | Up to 47 |
| In infants from the first day to 6 days of life | Up to 49 | Up to 105 |
| For a child up to 6 months | Up to 60 | Up to 83 |
| In children from 6 months to 1 year | Up to 55 | Up to 59 |
| 1-3 years | Up to 34 | Up to 38 |
| 3-6 years | 29-32 | |
| From 6 to 15 years | Up to 39 | |
| During pregnancy | Up to 32 | Up to 30 |
A slight deviation in values with normal bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase and albumin is acceptable and is not a pathology.
What is alanine aminotransferase used for?
This enzyme is found in the kidneys, myocardium, liver, and muscles. It is necessary for normal amino acid metabolism. The substance is indispensable for the synthesis of pyruvic acid and glutamic acid. Alanine can be converted into glucose, a source of energy for the central nervous system and, in particular, the brain. This amino acid helps strengthen the immune system and produce lymphocytes.
Alanine aminotransferase exhibits maximum activity in the serum of representatives of the stronger sex. Biochemical processes in women with the participation of this enzyme are somewhat weaker.
Preparation and standards of ALT in blood tests
The material is collected according to generally accepted rules. Blood sampling is carried out in the morning, and the period of overnight fasting should be from 8 to 14 hours. You can drink water without restrictions, and if it is impossible to donate blood in the morning, daytime blood donation for transaminases is allowed, which is preceded by a 4-hour period of fasting. Before the study, you must lead a normal lifestyle the day before. Be sure to exclude alcohol, physical activity with severe muscle fatigue, and sports training.
In a healthy adult over 17 years of age, the amount of ALT in the blood plasma should not exceed 41 units per liter (U/L) in men, and 31 U/L in women. In childhood and in adolescents, boys and girls from 12 to 17 years old, these indicators correspond to 27 and 24 U/l.
As for childhood, there is an inverse proportionality between age and the concentration of enzymes in the blood plasma. So, in a baby at 2-3 months the enzyme concentration should be less than 56 units, at 3 years - 29, at 10 years - 39 units. This is due to the optimization of biochemical processes in the liver, which require less amount of enzyme as the body grows, and the improvement of metabolic mechanisms.
Changes in ALT levels with age
Human alanine transaminase concentrations decline slowly after reaching 70 years of age. Recent medical research suggests that ALT has value as a marker of the aging process. A prolonged decrease in this enzyme below 14–17 IU after 70 years of age indicates a high risk of death. Its onset is associated with a decrease in the activity of some vital liver functions, incl. gluconeogenesis.
What are ALT and similar enzymes?
ALT is a feminine word, since it stands for alanine aminotransferase, with the ending characteristic of this gender. Transferases are a class of enzymes, or enzymes, that significantly accelerate the process of transferring one chemically active group within a molecule to another substrate (cleaving it from one molecule and attaching it to another).
In this case, the enzyme ALT, alanine aminotransferase, or, in other words, AlAt in the blood, significantly accelerates the transfer of the NH2 group, or amino group. This enzyme breaks it down from the amino acid alanine and attaches it to another molecule, which is ketoglutaric acid. As a result, glutamic and pyruvic acids are formed from the original compounds. This reaction is called transamination, and vitamin B6 is required for it to fully occur.
An example of another enzyme that is similar in function to ALT is aspartate aminotransferase, or AST. The task of this enzyme is to transform oxaloacetate into aspartate. AST also belongs to transaminases, and performs transamination reactions, but is found in slightly different concentrations in organs and tissues, and performs slightly different tasks.
If ALT plays a key role in providing the body with energy by participating in the Krebs cycle, then AST is mainly involved in the release of ammonia and is involved in the production of urea, which is the end product of the breakdown of protein compounds. This cycle is called the ornithine cycle and takes place in the liver.
When a specialist prescribes a biochemical blood test for liver damage, the concentration of ALT in the blood is determined. Usually, a blood test is immediately taken for ALT and AST, and the values of these enzymes are compared.
Mainly, this enzyme exists inside the cells of specialized parenchymal organs. ALT functions most actively in the liver tissue, in the kidney. It is found in slightly lower concentrations in the myocardium, skeletal striated muscles, pancreatic tissue, spleen, lungs and red blood cells - erythrocytes. Due to the fact that men have better developed muscle tissue, they also normally have a slightly higher concentration of ALT than women.
Of great clinical importance is the fact that both of these enzymes are located inside cells under normal conditions, and they enter the bloodstream only when the corresponding cellular structures are destroyed. If the laboratory had the opportunity to take ALT and AST tests directly inside the cells, then their concentration would be much higher. But it is physically impossible to do this, and it is not required, since it is much more important for doctors to indirectly assess the degree of damage to a parenchymal organ by analyzing ALT in the blood. Almost all of ALT in humans is contained in hepatocytes - liver cells, and in other organs it is much less.
Therefore, an increase in the number of enzyme molecules in the ALT analysis, first of all, indicates that liver enzymes have left the destroyed cells and rushed into the peripheral bloodstream. But we must remember that these enzymes do not have organ specificity, and damage to any organs can only be judged indirectly by the results of an increase in ALT and AST.
ALT norm
Normal ALT values for men over 17 years of age are 41 U/l, for women - 31 U. The ALT norm in newborns is 17 units, then it gradually increases by six months of age to 56 units, slowly decreasing in old age.
Often, ALT results are compared with AST results. In this case, the so-called de Ritis coefficient is used. Normally, it varies from 0.91 to 1.75. Exceeding the coefficient above 2 indicates damage to the heart muscle and the likelihood of developing myocardial infarction. A decrease in this indicator indicates liver damage, and the lower the coefficient, the more serious the problem.
Alanine aminotransferase is increased during pregnancy
- In the absence of pathologies, the concentration of alanine aminotransferase in a woman’s blood should be no more than 34 units/l.
- During pregnancy, the level of ALT and AST rarely goes beyond normal values, but minor deviations are not always due to the presence of pathologies. For example, in the first trimester, a slight increase in alanine aminotransferase concentration is considered normal.
- Mild and moderate degrees of gestosis in pregnant women can affect the change in ALT values towards an increase. In this case, there is an increase in blood pressure, fatigue, nausea, and dizziness.
- Proportional to the severity of gestosis, the level of ALT increases, which is explained by the increased load on the liver.
Symptoms of low ALT
Quite often, the amount of alanine aminotransferase is reduced due to vitamin B6 deficiency. With this hypovitaminosis the following symptoms develop:
- increased irritability;
- lethargy;
- disturbance of night sleep;
- polyneuritis of the hands and feet;
- loss of appetite (up to anorexia);
- dyspeptic disorders;
- stomatitis;
- glossitis;
- seborrheic facial dermatitis.
The symptoms of cancer depend primarily on the stage of its development and the affected organ. You should be wary of causeless weight loss, loss of appetite, abnormal stool, the appearance of atypical discharge, etc.
With pathologies of the pancreas, the following signs are observed:
- pain of varying intensity;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increased gas formation and bloating.
The role of ALT in the body
ALT (AlAT, Alt), or the enzyme alanine aminotransferase, is found in all cellular structures of the body, but most of it is concentrated in the liver, kidneys and heart. It is found in much smaller quantities in the pancreas, spleen and lung tissues.
Formed inside cells, this substance takes an active part in the formation of a significant part of various amino acids. Without it, energy and nitrogen metabolism could not be fully carried out. At the same time, ALT is present in minimal concentration in the blood of a healthy person.
Reference! An increase in ALT in the blood may indicate destruction of the cellular structures of various organs, but initially it indicates a pathology developing in the liver.
Diagnostics is primarily indicated for patients who complain of nausea, weakness, pain in the right hypochondrium, loss of appetite, changes in the skin and changes in the color of stool. This study is also done for people who have recently had hepatitis, are overweight and have a predisposition to liver diseases.
In addition, the procedure is prescribed for people taking alcohol and various medications that can have a negative effect on the liver. ALT testing is used to detect diseases of the liver, pancreas, heart, skeletal muscles and bile ducts. This test is considered mandatory for blood donors.
Determining the bioactivity of this enzyme is very important for diagnosing hepatitis in the initial stages. ALT is often observed above normal even at the pre-icteric (first) stage of the disease, which can last 10-350 days, and directly depends on the type and form of the pathology. If there is a suspicion of the development of serious disorders of the liver tissue, the patient will definitely be prescribed an ALT test in conjunction with other diagnostics - AsAt (aspartate aminotransferase, Ast), bilirubin and others.
ALT and AST are important for the diagnosis of liver and cardiac pathologies, but their quantitative indicator relative to each other is of particular importance. This ratio is called the de Ritis coefficient (norm 0.91-1.745), and its calculation is advisable only when one of the parameters goes beyond the reference values.
A coefficient below one indicates damage to hepatocytes (liver cells), and above 2 indicates the presence of cardiovascular pathology, for example, myocardial infarction. In this case, muscle injuries in the patient are accompanied by increased values of both enzymes to an equal extent. Since an increased level of ALT can be a sign of various diseases, when deciphering the obtained analysis materials, it is necessary to take into account its specific content.
Characteristics of ALT and AST
For example, with fatty liver degeneration its concentration increases by 2-3 times, with liver cirrhosis by 4-5 times, with alcoholic hepatitis by approximately 6 times, while with carcinoma by 5-10 times. With viral hepatitis, the concentration of the enzyme increases in direct proportion to the destruction of cells, and its level can exceed the norm by 50-100 times.
Dietary supplements of a certain series can also increase ALT levels. The use of these drugs often causes reversible damage to liver cells. The same thing is observed among fast food followers, but when the diet is normalized, the enzyme level returns to normal.
Symptoms of liver cell necrosis
A reduced amount of ALT in the body may indicate necrosis of liver cells. The earliest signs of the disease are pain and slight enlargement of the largest gland in the human body. The patient is concerned about dyspeptic symptoms - nausea, turning into vomiting. As ALT levels further decrease and necrosis increases, hepatic encephalopathy develops. Its signs:
- drowsiness;
- memory loss;
- trembling of hands and feet;
- aggressive behavior and a tendency to commit inappropriate acts;
- disorientation in time and space, i.e. a person cannot explain where he is and what is happening to him;
- increased muscle tone.
Biochemical blood test decoding, norm and deviation from it
In order to obtain accurate results of biochemical analysis for enzyme content, decoding must be carried out exclusively by an experienced, highly qualified specialist. The amount of each enzyme contained in the blood corresponds to its specific concentration. The blood level of ALT ranges from 31 units/l to 41 units/l, depending on the gender of the patient. The norm for women corresponds to an ALT content in an amount lower than that of men. To obtain accurate results, the ratio of the degree of activity of each enzyme is determined. An increase in the coefficient may indicate the emergence and development in the patient’s body of prerequisites for myocardial infarction, and if this indicator decreases, the development of infectious hepatitis in the body.
Since aminotransferases have different tissue specializations (each of these enzymes is concentrated in a certain type of tissue), a deviation from the norm in the content of one or another enzyme almost instantly signals the presence of diseases associated with certain organs in which the maximum localization of ALT and AST is observed. The interpretation of the analysis can be used as a factor in diagnosing the condition of the heart muscle (myocardium) and abnormalities in the functioning of the liver tissue. In cases where the level of enzyme content is increased, there is a suspicion of the presence of any problems in the functioning of certain organs in the body.
In the process of death and destruction of tissue cells that make up the organ, enzymes are released into the bloodstream. The concentration of substances increases, which is determined by the blood test and subsequent interpretation of the results. An AST enzyme level exceeded by 2 or more times can reliably confirm the presence in the patient’s body of prerequisites for the occurrence of a myocardial infarction attack.
In cases where ALT in the blood is elevated, the body usually experiences the development of infectious hepatitis during its incubation period.
If the normal levels of AST and ALT are reduced, a deficiency of B vitamin (hyridoxine) can be stated. However, it is worth remembering that a lack of hyridoxine can be caused not only by pathological changes in the body, but also by the process of a woman bearing a child.
What is the reason for the deviation from the norm of ALT and AST?
The activity of ALT in the blood is directly dependent on the degree and severity of viral hepatitis. The more complex the situation in the body with the development of the disease, the higher the level of ALT activity in the blood. In particularly severe cases, a blood test may show ALT activity that is 5 or more times higher than normal. The use of a biochemical blood test will help identify the disease at the very initial stage of development in the patient’s body, i.e. at the moment when the course of the disease passes without clearly defined symptoms. A blood test of AST and ALT makes it possible to accurately determine the patient’s condition and the complexity of the course of a particular disease.
An increased level of ALT and AST in the blood during analysis may occur in the case of diseases such as:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- liver cancer;
- various forms of hepatitis,
- damage to the liver tissue as a result of toxic and drug poisoning.
In addition, deviations from the norm can cause diseases such as:
- pancreatitis;
- heart failure or myocardial infarction;
- getting burns over large areas of the body;
- necrosis of skeletal tissue;
- shock states of various nature.
A decrease in ALT below normal is observed when there is a deficiency of vitamin B6 in the patient’s body, as well as when liver tissue is damaged as a result of extensive necrosis. As a rule, a decrease in ALT is observed due to the death and destruction of the cells that make up the liver tissue and produce ALT.
How to prepare for a blood test
In order for the examination results to be as accurate as possible, you need to prepare for it. The general rules for preparing for biochemical analysis are standard:
- do not eat for 8-12 hours before blood sampling;
- do not take aspirin or valerian tablets the day before the test;
- do not drink alcoholic beverages several days before the examination;
- immediately before the examination, do not smoke, avoid heavy physical work and emotional overload.
Blood for this analysis is taken from a vein in the morning. The blood collection procedure is standard. For examination, a kinetic method is used, characterized by a high degree of sensitivity. The period for receiving results is no more than 2 days.
The survey results are influenced by the following factors:
- poor adherence to the rules of preparation for analysis;
- unhealthy diet leading to excess weight;
- use of drugs that affect liver function;
- severe compression of the vein;
- following a vegetarian diet;
- insufficient physical activity.
Rules for donating blood for analysis of ALT and AST
- The day before the test, you should refrain from playing sports and drinking alcohol, and also try to avoid excessive anxiety.
- The day before you can have dinner by eating some light dish. Blood is donated in the morning from a vein on an empty stomach. The interval between the last meal and testing must be at least 14 hours.
- Water is allowed as a drink.
- If tests must be taken during the daytime, then before taking blood you must refrain from eating for at least 4 hours.
When is a blood test for ALT prescribed?
The maximum amount of the enzyme is found in liver tissue. Therefore, a blood test for ALT is used to diagnose diseases of the largest gland in the body that do not manifest external symptoms. With the help of ALT analysis, even the most minor deviations in the functioning of the body can be detected.
You should be tested for ALT levels in your blood if the following symptoms appear:
- increased weakness and fatigue;
- significant decrease in appetite;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- abdominal pain and bloating;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- itchy skin.
All these symptoms indicate possible liver damage. An examination is also necessary if there is a risk of diseases of this organ:
- previous hepatitis;
- contact with the hepatitis virus;
- alcohol abuse;
- unfavorable genetic predisposition;
- use of drugs with hepatotoxic effect;
- overweight;
- diabetes
ALT analysis is also done to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Every person needs to take a blood test for ALT and other liver enzymes once a year. This is necessary to monitor the normal functioning of the human body.
Why are ALT and AST levels higher than normal?
To identify the specific cause of the increase in markers in blood biochemistry, it is important to determine the extent of the isolated increase in ALT or AST transferases.
- A slight increase (several times higher than normal) occurs with viral hepatitis, fatty liver disease, and steatohepatosis. Other markers of blood biochemistry also change - bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase increase.
- Moderate increase (from 5 to 20 times) – inflammation in the liver tissues of a chronic or acute nature, viral, alcoholic hepatitis, development of cirrhosis.
- A pronounced degree of increase in aminotransferases (more than 20 times) - severe drug or toxic liver destruction, acute hepatitis, pancreatitis or atrophy of liver tissue, myocarditis, ischemia. Not only transaminases increase, but also cholesterol and bilirubin.
- Critical indicators (exceeding 2000–3000 U/l) are evidence of the death of the muscular parts of the heart (extensive myocardial infarction), cancer cells in the liver tissue, and overdose of certain drugs (acute intoxication).
A strong increase in aminotransferases indicates the development of acute hepatitis
During destructive processes in the liver, ALT goes off scale and AST increases slightly. A high concentration of aspartic transaminase is observed in acute necrosis of the heart muscle (infarction) and other severe pathologies of the heart, when organ tissue is destroyed and a huge amount of a specific enzyme is released into the blood.
Important!
If the level of ALT and AST is slightly increased during pregnancy, this is an acceptable phenomenon, the cause of which is a surge in hormones during changes in a woman’s hormonal background. Significantly increased transaminase levels may indicate malfunctions of the liver, pancreas and pathology in the cardiovascular system. Here you need a full examination and observation by a doctor.
How to increase ALT levels in the blood
To normalize the content of this enzyme in the blood, it is necessary to follow these recommendations.
- Conduct a complete diagnosis of the entire body to detect dangerous pathologies.
- As prescribed by your doctor, take medications that improve liver function and protect it (hepatoprotectors).
- If you have vitamin deficiency, take vitamin supplements.
- Follow the principles of proper nutrition.
The following should be completely excluded from the diet:
- spicy, fatty, rich foods;
- marinades and smoking;
- alcoholic drinks;
- all products made from white flour;
- hot seasonings, spices.
Dishes must be boiled or cooked in a steam bath.
Useful:
- nuts, especially pine and walnuts;
- grenades;
- fish;
- Sweet pepper;
- liver.
Why does ALT increase in men?
Men more often violate all the rules of proper nutrition and experience stress and nervous strain much more actively, which they try to overcome with the help of bad habits.
This will cause liver diseases and will naturally increase ALT levels. Elevated ALT in the blood of men is detected when:
- Taking certain medications;
- Abuse of fast food, which is sold in any eatery;
- Muscle injuries;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Violation of blood sampling rules;
- Stress and nervous overload;
- Physical activity associated with sports or hard work;
- Testing after any surgical intervention;
- A large accumulation of fat cells in the liver area or simple obesity;
- Malignant tumors;
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy;
- Lead poisoning;
- Taking drugs;
- Psychological shock.
Table ALT norm by age:
Treatment of hypovitaminosis B6
If the decrease in the amount of this vitamin is caused by fasting, then the patient is indicated for diet therapy. A diet is prepared for him that would include a large amount of meat and dairy products. It is useful to eat legumes, grains, fresh vegetables and fruits.
If diseases are discovered that lead to decreased absorption in the intestine, they are treated. In severe cases, intramuscular administration of this vitamin is indicated.
This type of hypovitaminosis responds well to correction and treatment. Vitamin deficiency and decreased activity of liver transaminases can be eliminated within a few months.
What blood tests should be taken for elevated ALT to prescribe treatment?
As the pathological process develops, damage to the integrity of the cellular structure of organs and leakage of enzymes occurs.
The diagnostic significance of the increase in the activity of ALT and AST in human peripheral blood was clarified back in the 50s of the last century. Amino transferases are responsible for transporting molecules from one group of amino acids to another
, which is why these enzymes are called transaminases.
- The largest amount of ALT (alanine transaminase) is contained in the liver and kidneys, and less in the heart muscle, pancreas and skeletal muscles.
- AST (aspartic transaminase) is distributed in all tissues of the human body, the highest levels of its content are observed in the liver, muscle mass, red blood cells and heart.
When the cell walls of organs are damaged, enzymes “leak” into the circulating blood, causing an increase in concentration.
Due to the high content of transaminases in hepatocytes (liver cells), changes in their levels in the patient’s blood are most often associated by medical specialists with dysfunction of the liver and biliary tract.
Additional examination to clarify the diagnosis includes ultrasound, sometimes a biopsy (to identify the cause and assess the extent of tissue damage), as well as biochemical analysis (liver tests). Blood biochemistry contains several indicators that characterize the condition and functioning of the liver and biliary tract.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) – ALP levels are significantly elevated in bile duct obstruction, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and bone diseases.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is highly elevated in acute hepatitis, may increase in chronic hepatitis, bile duct dysfunction, cirrhosis, cancer, after heart attacks, muscle damage.
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) - comparison of the blood levels of GGT and alanine aminotransferase makes it possible to differentiate liver and bone diseases. If both indicators increase, problems are associated with the liver or bile ducts.
To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to monitor the levels of bilirubin, albumin, total protein, prothrombin time, iron (to exclude hemochromatosis), and determine antibodies to chronic hepatitis viruses (B, C, D).
Treatment of patients with ALT deviations from normal values is prescribed depending on the reason that caused the increase in the level of this enzyme in the blood.
Albumin is normal or increased
The level of this protein increases in chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, rheumatism and a number of other disorders of the internal organs.
Platelet abnormalities
The normal platelet count changes with age. There are other reasons for an increase in platelets: iron deficiency anemia, exposure to drugs, diseases of connective tissue, liver, pancreas, etc.
Reduced platelets are observed in cases of anemia, infections with bone marrow damage, taking medications, and other conditions. The treatment regimen for deviations in analysis parameters depends on the cause of these deviations. Treatment is aimed at eliminating it.
Danger of low ALT
In most cases, reduced (almost zero) ALT activity does not pose a danger to humans, because often results from a lack of pyridoxine (vitamin B6). This pathology is easily corrected with diet and drug injections.
Severe liver conditions accompanied by a decrease in the number of hepatocytes are much more dangerous. And if ALT is low in the presence of pathologies of this organ, this indicates a danger to life. Timely diagnosis of these diseases and their treatment with low enzymes significantly increases the patient’s chances of recovery.
Decoding analysis responses
ALT levels may vary depending on age, gender, and individual characteristics. Therefore, only a doctor should decipher the result. It's best to see a therapist. In the future, he can write out a referral to a doctor of another specialization.
Alanine aminotransferase may be increased or decreased. Doctors will find out the reason by how much the indicator changes. Detailed information is shown in the table.
| Changing the ALT value | Cause |
| Up to 2 times | Neglect of preparatory measures, severe stress, test retake required |
| 2 – 3 times | Drinking alcohol, vigorous physical activity |
| 3 – 5 times |
|
| 5 – 10 times | Inflammatory process in organs as a result of an infectious lesion |
| 10 – 20 times | Chronic liver diseases |
| 20 or more times | Serious liver pathologies, malignant tumor, cirrhosis |
In what diseases is alanine aminotransferase elevated?
If the analysis shows an increase in ALT, this indicates the presence of inflammation, which can occur in certain pathologies.
Hepatitis
- The disease can be expressed in different forms. The chronic and infectious form increases the enzyme level slightly.
- In alcoholic hepatitis, a significant increase in alanine aminotransferase is observed.
Oncological diseases of the liver
- The occurrence of cancerous tumors is common in people suffering from hepatitis.
- If the enzyme level significantly exceeds normal levels, surgery may be prohibited, as complications are possible.
Pancreatitis
- The diagnosis obliges the patient to regularly check the level of ALT in order to prevent attacks of pathology and monitor the course of the disease.
Myocarditis
- The disease is characterized by disruption of the heart muscle.
- Its main symptoms are shortness of breath, weakness, fatigue, increased levels of ALT and AST.
Cirrhosis
- This disease is especially dangerous due to the absence of pronounced symptoms of its development. Pathology can be detected at earlier stages using ALT testing.
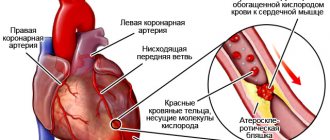
Myocardial infarction
- Occurs when blood circulation is impaired, which results in tissue death.
- If the pathology proceeds without complications, the enzyme level increases slightly, however, it can be used to determine the causes of the attack.
Other causes of elevated alanine aminotransferase
- taking barbiturates and antibiotics;
- excessive consumption of fast food immediately before blood sampling;
- injuries resulting in damage to muscle tissue;
- drinking alcohol less than 7 days before the test;
- failure to comply with the hygienic requirements of the study;
- intense physical and emotional stress;
- steatosis;
- chemotherapy;
- drug use;
- intoxication with salts of heavy metals.
In what cases is analysis prescribed?
A biochemical blood test determines the level of these enzymes.
- Usually one type of research is used if there is no need for additional ones. Such a study is an analysis for alanine aminotransferase, since ALT has selective tissue localization.
Analysis indicators warn of disturbances in liver function even before the appearance of the main symptom - jaundice, therefore studies that determine the content of these enzymes are prescribed mainly for liver diagnostics:
- after long-term use of medications,
- interactions with toxic substances,
- when diagnosing hepatitis.
A blood test for ALT and AST is prescribed for:
- fatigue;
- nausea;
- chronic fatigue;
- pain in the abdomen;
- general weakness.
To identify additional information about liver problems, it is necessary to determine the de Ritis coefficient. This name means the ratio of enzymes.
- The normal ratio of aspartate aminotransferase to alanine aminotransferase (ALT to AST) should be no less than 0.91 and not exceed 1.75.
- When the value exceeds 2, pathology of the heart muscle occurs, which is accompanied by the destruction of cardiomyocytes. Myocardial infarction may occur.
- When the coefficient is less than 1, liver disease is diagnosed. The lower this indicator, the more likely a negative outcome.
The analysis in question can be used both as a diagnostic method and directly during therapy to monitor the course of the disease and the dynamics of recovery.
The analysis is indicated in the presence of factors that negatively affect the condition of the liver. Among them: alcoholism and the use of drugs that destroy the organ.
Alanine aminotransferase analysis is also done in the following cases:
- contact with a person suffering from hepatitis;
- recent history of hepatitis;
- excess body weight;
- diabetes;
- predisposition to liver disorders.
To conduct the study, either capillary or venous blood is required. The reliability of the result depends on compliance with two conditions:
- 12 hours before blood sampling, refrain from eating;
- 7 days before the test, avoid alcohol.
Immediately before the analysis (30 minutes) you cannot
- smoke;
- withstand increased physical or emotional stress.
The result of an ALT test in the blood can be found out the very next day after the test.
Examples of diagnostics for elevated ALT and other biochemical parameters: AST, GGT
Excess of ALT and AST is only a symptom of the disease that needs to be treated. The doctor prescribes a set of additional examinations and may write a referral to a specialist, for example, a cardiologist or gastroenterologist.
The liver treatment regimen includes hepatoprotectors:
- Gepabene - restores liver cells and accelerates the flow of bile.
- Karsil.
- Essentiale forte N.
In addition to the main treatment, it is important for the patient to adhere to the rules of a balanced diet:
- In summer and autumn, eat plenty of vegetables and fruits. Vitamin deficiency has a detrimental effect on immunity, mood and the body’s ability to take on physical and mental stress.
- Don't give up protein foods. Today it has become fashionable to be a vegetarian. But reasonable people don’t just exclude protein from their lives, but replace meat products with others that are no less rich in protein. If you don’t want to face difficulties in choosing vitamin nutrition, eat meat, eggs, fish and dairy dishes every day.
- Small meals are just what the doctor ordered. 5 times a day is the optimal number.
- Drink water, it also gives you energy. Sometimes we confuse hunger with dehydration, but fluid is simply necessary for the digestive process.
- For breakfast, eat oatmeal, adding dried fruits is acceptable. For lunch, cook porridge, consume cottage cheese and meat. Dinner should be as light as possible and consist of vegetables or dairy dishes.
An increase in ALT and AST in the blood is caused by various reasons, including a lack of vitamin B6. A person needs 2-3 mg of vitamin B6 per day. It is found in abundance in the following foods:
- Walnut;
- meat;
- fish;
- avocado;
- soy;
- banana;
- spinach;
- liver.
There are other, not related to diseases, reasons for increased concentrations of ALT and AST in the blood serum:
- alcohol intoxication, drinking alcohol-containing drinks less than a week before the test;
- taking sleeping pills (barbiturates), antibiotics, statins;
- excessive physical activity;
- significant stressful conditions;
- heat stroke and burns;
- violation of blood sampling rules, especially sterility;
- drug poisoning.
Reasons such as lead poisoning and chemotherapy can also lead to increased rates. Moreover, in the latter case, the level of enzymes remains elevated for several months after the end of the course.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the reasons for the increase in transaminases in the blood in pregnant women.
It is necessary to monitor the status of ALT and AST levels so that both the baby and mother remain healthy.
During the first trimester of pregnancy, a slight upward deviation of ALT from the norm is acceptable, while the AST content should remain within normal values. Further, the concentration of both enzymes should gradually reach normal levels.
During pregnancy, the causes of increased transaminases can also be liver pathologies, for the diagnosis of which an analysis of the content of liver enzymes is also used. This is, first of all, cholestatic hepatosis of pregnant women.
After conducting a blood test to determine the amount of transaminases in the blood and identifying the reasons for their increase, you should know how to lower ALT and AST in the blood in order to eliminate the disease and prevent it in the future.
Often, deviation of alanine aminotransferase from the norm is accompanied by changes in other liver test parameters. The nature of the changes allows us to suggest a possible diagnosis and conduct additional examination to clarify the cause of the changes.
Alanine aminotransferase is significantly higher than normal
A sharp rise in ALT levels (up to 300-1,000 U/l) occurs with acute damage to liver cells. This effect can be caused by infections, toxins or drugs. Prothrombin time (PT) and albumin are usually normal; alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin may be elevated. AST remains lower than ALT. It may take up to 6 months for the indicator to return to normal.
ALT increased 2-3 times
The level of ALT in the blood is increased to 2-3 norms during inflammatory processes of various etiologies in the liver and biliary tract. In chronic hepatitis, albumin and PV remain normal, bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) may be normal or beyond the upper limit. ALT is higher than AST.
With autoimmune hepatitis, in addition to elevated transaminases (ALT higher than AST), bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase levels may be increased. PT remains normal, albumin is usually low.
Elevated ALT and AST may be due to alcoholic hepatitis. When the liver is damaged by alcohol, the level of AST in the blood can be several times higher than the level of alanine aminotransferase. Albumin and PT are usually normal;
bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase remain within the reference values or are moderately increased. Similar changes in blood biochemistry are caused by non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (fatty degeneration), which is detected in diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, chronic hepatitis, when taking glucocorticoids, tetracycline, and other drugs.
DETAILS: B12 deficiency anemia blood test causes treatment
Liver cirrhosis is also a cause of elevated ALT and AST. In cirrhosis, AST exceeds ALT, but not as much as in alcoholic hepatitis. Bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase are usually normal or higher, albumin is normal or low. Prothrombin time is increased. Hepatocellular carcinoma has a similar picture.
With cholestasis and obstruction of the biliary tract, transaminases exceed the norm, bilirubin is normal or increased, alkaline phosphatase is significantly increased, albumin and PV are normal (albumin may decrease with chronic stagnation).
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor analyzes not only the test results, but also the manifestations of the disease, the patient’s complaints and medical history, the results of ultrasound and other types of diagnostics. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based only on the results of one analysis.
Important!
What to do if ALT is elevated?
What can an increase and decrease in ALT levels in the blood indicate?
The level of ALT in the blood is very low, but extremely rarely it can drop to values significantly below existing standards. This may indicate very severe liver conditions:
- cirrhosis and organ necrosis;
very low ALT levels may indicate liver cirrhosis (pictured right)
- mechanical damage to the liver as a result of injury;
- significant deficiency of B vitamins.
Much more often in medical practice one has to deal with elevated levels of the ALT enzyme in the blood. The reasons for this are usually:
- viral hepatitis, both acute and chronic;
Viral hepatitis affects the liver. which causes an increase in ALT levels in the blood
- biliary dyskinesia;
- tumor processes;
- ischemic pathologies;
- mononucleosis.
In addition, the concentration of ALT in the blood also increases in acute pancreatitis (damage to the pancreas).
What factors can influence enzyme performance?
The above reasons are pathological, as evidenced by the increased level of ALT. However, levels of the enzyme in the blood that differ from the norm can occur even in the absence of painful conditions. Physiological reasons for increasing the level of this substance in human blood include:
- intense physical activity;
- severe physical tension, constant stress;
- taking certain groups of medications (immunosuppressants, steroids, oral contraceptives);
- improper, unbalanced diet;
- excess weight.
Analysis transcript
An analysis for the activity of liver transaminases is taken, as is a biochemical analysis of blood from a vein. The doctor bandages the patient’s arm with a tourniquet so that the vein is better visible and removes blood. For the tests to be reliable, you need to donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. The day before the test, it is better to avoid drinking alcohol and certain medications. Before the procedure itself, you should not smoke or drink juices. You can obtain a detailed list of prohibited medications from your doctor. If you are being treated for concomitant diseases, be sure to tell us what medications you have used over the past three days.
The norm of alat in the blood is different for men and women. Alt in the blood of men is normally about 45 U/l. (0.5 - 2 µmol), alt in the blood of women is considered normal up to 34 U/l. (0.5 – 1.5 µmol). There are several degrees of increased transaminase in the blood:
- light – 1.5-5 times;
- average – 6-10 times;
- high – 10 times or higher.
ALT higher than normal may be due to myocardial infarction, the presence of a viral form of hepatitis, toxic liver damage, as well as malignant tumors or liver metastases. Alanine aminotransferase may be elevated if the person was previously treated with drugs such as Aspirin, Warfarin, Paracetamol or oral contraceptives.
The reasons for the increase in alt may also be associated with increased human activity before blood sampling and subcutaneous injections, which were carried out several days in advance. When alt is elevated, the doctor can tell you what this means, but in most cases, if 5 times more than the norm of the enzyme enters the blood, then this is a pre-infarction condition or a heart attack; if the alt norm in the blood increases 10 times, this indicates a deterioration patient after a heart attack.
An 8-fold increase in alate may indicate muscular dystrophy, and a 3-fold increase in transaminase may indicate acute pancreatitis. Increased alt in the blood by 20-50 times is a clear sign of hepatitis.
An increase in an enzyme such as alanine aminotransferase, the rate of which is fixed, indicates a pathology in the body such as liver cancer - biochemistry in this case is necessary to diagnose the condition of the organ, as well as to decide on the advisability of surgery; if ALT increases significantly, then surgery is not recommended carried out because there is a risk of complications. If the ALT indicator has low values, then the person does not have enough vitamin B6.
What does an ALT test show?
- The highest level of transferase content is observed in liver cells. The analysis is used to identify pathologies of this organ that are asymptomatic. The amount of ALT is determined by a biochemical blood test. He diagnoses even the early stages of diseases. Sometimes this requires comparing alanine aminotransferase with the content of other blood components, which makes it possible to determine the presence of diseases.
- Another enzyme often used is aspartate aminotransferase (AST). It is also synthesized inside cells; its increased amount in the blood can also reveal pathologies.
- To get an accurate picture of the disease, you need to know the content of ALT and AST.
- If ALT exceeds the amount of AST, this indicates liver pathologies:
- An increase in indicators indicates an advanced stage of the disease, for example, cirrhosis.
- When the content of aspartate aminotransferase is higher than the amount of alanine aminotransferase, disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle can be suspected.
The ratio of ALT and AST is an important indicator when diagnosing various types of pathologies. Analysis for these enzymes can confirm the disease and determine the direction of its development and the stage of organ damage.
Methods for reducing enzymes in the blood
Treatment of elevated levels of ALT and AST in the blood after diagnosis and identification of the causes can be presented in two options. You can reduce ALT and AST in the blood using folk remedies, or you can use the appropriate medications directly. In both cases, you should consult your doctor.
The main direction of treatment for high levels of transaminases is to eliminate the cause of excessive release of enzymes into the blood.
In case of liver problems, both hepatoprotectors and drugs aimed at a specific damaging factor are prescribed. For example, in the case of infectious hepatitis, a treatment method such as powerful antiviral or antibacterial therapy is used.
To reduce the toxic effect during attacks of the disease, you can give droppers, intramuscular injections, the decision on the prescription of which is made by the attending physician. For long-term use, drugs are used in tablet form.
If we are talking about pathology of the heart muscle, then all efforts should be aimed at stabilizing the patient’s condition and normalizing the activity of the heart. When the damaging effect is eliminated, the AST level will gradually return to normal.
It should be noted that a correct lifestyle plays an important role in maintaining the health of the body.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle not only helps reduce transaminase levels, but also improves overall well-being.
Basic rules for a healthy lifestyle:
- eat right - limit the consumption of fried, fatty, carbohydrates, which are quickly absorbed. It is important to increase the consumption of vegetables and fruits, especially those containing large amounts of vitamins D, A, B and C, which are very important for the health of the liver and the body as a whole;
- reduce the consumption of salt and products based on its substitutes, for example, bouillon cubes;
- limit as much as possible, or better yet, completely abstain from drinking alcohol;
- Give your body regular moderate physical activity. This will improve heart function, blood circulation and organ nutrition, as well as remove more toxins through the skin.
If you lead a healthy lifestyle from a young age, the risk of developing conditions that lead to elevated transferases is significantly reduced. This method of treatment does not require material costs and is quite effective. Next, we will consider the treatment of increased ALT and AST using folk remedies.
In addition to possible myocardial infarction and cirrhosis of the liver, a patient with elevated ALT and AST levels in the blood may experience injury to muscles and bones. Pregnant women need to be especially careful, because testing determines the fact that the liver cannot cope with the load placed on it. In most cases, it is enough to switch to a diet, and the problem goes away on its own.
ALT also increases if you take certain medications. Drugs with a long list of side effects include Aspirin, Paracetamol, Warfarin, hormonal contraception, tinctures based on echinacea and valerian.
ALT in the blood and its role in metabolic mechanisms
ALT, or alanine aminotransferase, is an enzyme that is produced in greatest quantities in the liver and in smaller quantities in the kidneys, pancreas, myocardium and skeletal muscles. When these organs are damaged, an increase in ALT levels is observed in the blood. In a healthy body, the enzyme is contained in plasma in small quantities.
Analysis of ALT (ALT, GPT) content helps in diagnosing diseases of the liver, pancreas and bile ducts, diseases of the heart muscle and skeletal muscles. The doctor can also give a referral to donate blood for an ALT test if he wants to find out the degree of liver damage due to hepatitis, the effect of medications or other toxic substances on the condition of this gland. This test is mandatory for blood donors.
You should pay special attention to your health and ask your doctor whether you need to get tested if you experience the following symptoms:
- general weakness;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea or vomiting;
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- darkening of urine;
- light-colored stool;
- bloating and abdominal pain.
Often, together with an ALT test, a test for AST (aspartate aminotransferase) is prescribed. Both of these enzymes help in diagnosing liver and heart diseases, but their relative amounts to each other are of particular importance. This ratio is called the de Ritis coefficient. Its normal value is 0.91–1.75. Calculation of the coefficient is advisable only when AlAt and/or AsAt go beyond the reference values. A coefficient below 1 indicates damage to liver cells (hepatocytes), and above 2 indicates cardiovascular disease, possibly myocardial infarction. The procedure for donating blood for AlAt and AsAt is the same.
In order to obtain a reliable analysis result, you need to properly prepare for it. Blood is donated in the morning, on an empty stomach. At least 8 hours must pass after the last meal. Biomaterial is taken from a vein. Vacutainer tubes (vacuum systems for blood collection) are used, usually with a gel phase (preservative) without an anticoagulant. The material for the study is blood serum. The Enzyme Commission of the International Biochemical Union proposed using “U/L” to designate the unit of measurement for indicators.
Norma AlAt
As mentioned above, the level of alanine aminotransferase in a healthy body is quite low. Throughout life, the rate of enzyme production changes. Thus, in newborns, an overestimated indicator is considered normal, which is explained by the presence of physiological postpartum jaundice. It occurs due to the fact that during the birth process a large amount of hemoglobin is “released” into the baby’s bloodstream. Within 3–4 weeks, hemoglobin in the baby’s body actively breaks down, resulting in the formation of bilirubin. And it is its high concentration that causes icteric manifestations.
In the first 5 days of a child’s life, it reaches 49 U/l, from five days to six months – from 56 to 60 U/l. Further, the level of the indicator decreases: from 6 to 12 months - to 54 U/l, from one year to 3 years - to 33 U/l. From 3 to 6 years, the norm is considered to be up to 29 U/l. From 6 to 12 years, the indicator increases again - to 38–39 U/l, and from 12 to 17 depends on the gender of the child (for girls - up to 24 U/l, for boys - up to 27 U/l). The norm for an adult male is up to 41 U/l. The norm for women is up to 31 U/l. Note that women in the first trimester of pregnancy may experience a slight increase in ALT, which is normal. However, in late pregnancy, an increase in the enzyme level may indicate gestosis (complications expressed in a feeling of weakness and increased blood pressure). The greater the deviation of ALT from the norm, the more severe the gestosis.
Deviations from normal values indicate an inflammatory process occurring in the body.
Reasons for increasing AlAt
It is believed that the level of ALT in the blood serum is elevated if it exceeds the normal value by tens or even hundreds of times. Thus, the indicator increases more than 20 times with the development of acute forms of hepatitis A, B and C. The concentration of ALT increases approximately 6 times in alcoholic hepatitis. If a disease such as fatty liver occurs, the ALT level exceeds the norm by 2-3 times. But with tumor lesions of the liver, the “jump” of the enzyme can be quite insignificant, but even this a specialist should pay close attention to.
The indicator may also be increased in the following cases:
- acute stage of pancreatitis;
- burns of a large area of the body;
- state of shock;
- pathologies of the hematopoietic system;
- mononucleosis;
- muscular dystrophy;
- viral infections;
- strong physical activity;
- uncontrolled intake of dietary supplements;
- poor nutrition.
How to reduce enzyme concentration?
The surest way to lower the level of ALT in the blood is to diagnose and treat the pathology that caused the changes. When treating liver diseases, which most often cause an increase in ALT, medications are taken that improve digestion, hepatoprotectors and choleretic agents. All of them have a number of contraindications, so they should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
If the increase in the amount of ALT is caused by taking any medications, then you should stop using them if possible. Let's assume the selection of alternative therapy. In addition, in order to reduce the concentration of the enzyme, it is recommended to diversify your diet with foods containing vitamin D (fish, green vegetables, soy milk, dairy products and eggs). Carrots, zucchini, nuts, whole grains and lean meats will also be beneficial. Do not abuse fatty and salty foods. Following a healthy lifestyle will help in recovery.
During the course of treatment, the biochemical composition of the blood is periodically examined to find out how effective the prescribed therapy is.
Why might AlAt be lowered?
A decrease in the concentration of ALT in the blood indicates liver rupture and the occurrence of serious diseases such as cirrhosis and necrosis. Another reason for the decrease lies in the lack of vitamin B6 in the body and in taking certain medications containing aspirin, interferon, and phenothiazine.
Alanine aminotransferase is present in almost all cells of the human body, but in different proportions. And when its content in the bloodstream changes, it affects the state of many systems. In order to avoid the serious consequences of possible diseases, diagnostic procedures, in particular blood donation, should not be neglected.
Results
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) is an endogenous enzyme that accelerates the chemical reaction of the amino acid alanine. The main part of ALT is contained in the liver, the rest is localized in the pancreas, myocardium and muscles. In a healthy man, the amount of enzyme in the blood is no more than 45 U/l, in a woman – 34 U/l.
If the levels are significantly elevated, it means that the tissues and cells are pathologically altered and have serious damage, through which alanine aminotransferase enters the bloodstream. ALT levels are determined as part of a biochemical blood test.
In most cases, with an increased enzyme value, liver diseases (hepatitis, hepatosis, cirrhosis, etc.), chronic or acute pancreatitis, and cardiac dysfunction (myocarditis, heart attack) are diagnosed. The diagnosis must be confirmed by a detailed examination, including a number of laboratory tests and hardware diagnostic procedures.
The quantitative content of ALT in the blood is an important indicator of many diseases of the liver, the largest gland in the human body. It can also report diseases of other internal organs. Which blood test results indicate an increased or decreased ALT content, and which indicate normal? What can a deviation from the normal ALT content lead to? Let's find out in this article.
AST growth levels
There are three levels of increase in AST in plasma:
- minor – with fatty deposits in the liver, taking certain medications (antibiotics, statins, aspirin, antitumor drugs, barbiturates, etc.);
- medium – for heart attack, heart failure, liver cirrhosis, some types of cancer, alcoholism, autoimmune diseases with muscle damage, taking high doses of vitamin A, lung and kidney damage, muscular dystrophy, mononucleosis;
- high – with multiple liver damage due to viral hepatitis, reactions to drugs and medications, with necrosis of a large tumor.
AST in the blood has diagnostic value in myocardial infarction
The highest level of AST is observed at the onset of the disease with significant tissue destruction. A decrease in the enzyme in the blood means the beginning of liver restoration and recovery. A slight increase in AST is not yet a sign of tissue destruction. An AST level that is more than twice the normal level has diagnostic value.
Decoding the results
ALT and AST readings for cirrhosis should be assessed by a specialist, preferably in conjunction with other examination results and clinical symptoms. A sign indicating an early stage of liver cirrhosis when interpreting the results is an increase in ALT, prevailing over an increase in AST and a decrease in the de Ritis coefficient.
For differential diagnosis between cirrhosis and hepatitis, one should take into account the fact that the level of aminotransferase activity in hepatitis is much higher than their activity in cirrhosis. You should not ignore instrumental methods that allow you to determine the affected area.
It should be noted that ALT and AST indicators for liver cirrhosis are not included in the parameters of the International Childe-Pugh Calculator and similar ones, which allow assessing the degree of compensation, the risk of perioperative complications, and survival time.
Indications for analysis
A biochemical blood test, during which the AST level is determined, is prescribed for a number of diseases, including:
We also recommend reading: Treatment of elevated bilirubin in the blood
- All liver pathologies.
- Diseases of the circulatory system.
- Chronic and acute heart diseases.
- Kidney failure.
- Infections.
- Intoxication.
- All types of jaundice and bilirubin metabolism disorders.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Purulent-septic pathologies.
- Encephalopathy of unknown etiology.
- Bile outflow disorders, cholelithiasis.
- Chronic pancreatitis.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Malignant tumors.
- Allergic skin diseases.
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics, chemotherapy and various toxic drugs.
- Injuries to the abdomen and chest.
- Preparation for a complex surgical operation.
- Evaluation of treatment of liver and cardiac pathologies.
Reasons for increased AST in adults
An increase in AST concentration is a marker of diseases of the cardiac and vascular systems, liver, and pancreas.
Qualified specialists distinguish several pathological processes in which the level of aspartic enzyme in the patient’s blood significantly exceeds the permissible norms:
- Myocardial infarction is the main cause of increased levels. Compared to the concentration of ALT, which increases slightly, AST levels increase tens of times.
- Biliary cirrhosis is a special type of pathology that develops with long-term damage to the biliary tract and cholestasis.
- Pancreatitis (acute or chronic) causes a sharp increase in the concentration of the enzyme.
- Serious damage to muscle mass (burns, injuries).
- Alcohol poisoning.
- Malignant liver disease.
Why are ALT and AST elevated in the blood of children?
An increase in the concentration of enzymes in a child’s body is associated with increased permeability of hepatocyte membranes when exposed to damaging factors on the liver.
Most often this is due to:
- congenital anomalies of the bile ducts;
- hereditary liver pathologies (hematochromatosis, autoimmune hepatitis);
- acute viral or chronic hepatitis;
- drug-induced liver damage;
- infectious mononucleosis, causing diffuse changes in the cells of the spleen and liver;
- cardiological pathologies - myocardial dystrophy (metabolic disorder in the cells of the heart muscle) or myocarditis;
- endocrine diseases - dysfunction of the pituitary gland or diabetes mellitus;
- hemorrhagic vasculitis - inflammation of the vascular walls;
- oncological pathology.
Parents should take the following symptoms very seriously and seek immediate medical attention:
- increased enzymatic activity in the child’s blood;
- the baby has complaints of weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- nausea;
- the appearance of yellowness of the skin and sclera;
- darkening of urine and lightening of stool.
ALT is elevated in the blood
The amount of alanine aminotransferase in the blood is considered elevated if it exceeds the established norm, especially tens, and in some cases hundreds of times. Depending on this, the presence of the disease is determined. When the ALT level increases by 5 times, myocardial infarction can be diagnosed; if it reaches 10-15 times, we can talk about the deterioration of the patient’s condition after the attack. The value of the de Ritis coefficient also changes upward.
Hepatitis provokes an increase in ALT in the blood by 20-50 times, muscular dystrophy and dermatomyositis - by 8. Gangrene and acute pancreatitis are indicated by exceeding the upper limit of the indicator by 3-5 times.
It is possible not only to increase the content of alanine aminotransferase in the blood. Its too low amount is associated with a lack of vitamin B6, which is part of this enzyme, or with complex inflammatory processes in the liver.
What does an increase in ALT indicate?
An increase in ALT indicates the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the body. They can be caused by the following diseases:
Hepatitis. This inflammatory liver disease can come in several forms. For chronic or viral hepatitis, the excess level of alanine aminotransferase in the blood is insignificant. For hepatitis A, ALT analysis makes it possible to detect infection in advance. The amount of enzyme in the blood increases a week before the first external manifestations of the disease appear in the form of jaundice. Viral or alcoholic hepatitis is accompanied by a pronounced increase in ALT levels.
Liver cancer. This malignant tumor often forms in patients with hepatitis. ALT analysis in this case is necessary both for diagnosing the disease and for making operational decisions. When alanine aminotransferase levels are significantly higher than normal, surgery may not be possible, as there is a high risk of various complications.
Pancreatitis. The presence of this disease is also indicated by the level of ALT. Its increased amount indicates an exacerbation of pancreatitis. Patients with this diagnosis will have to undergo ALT testing periodically throughout their lives. This will help avoid attacks of the disease and monitor the progress of treatment.
Myocarditis. It manifests itself in lesions of the heart muscle. Its main symptoms are shortness of breath, rapid fatigue of the patient and increased ALT levels in the blood. To diagnose this disease, the AST level is determined, and then the de Ritis coefficient is calculated.
Cirrhosis. This disease is dangerous because it may not have pronounced symptoms for a long time. Patients quickly get tired and feel tired. Pain in the liver area occurs less frequently. In this case, cirrhosis can be determined by the increased level of ALT in the blood. The amount of enzyme in the blood can exceed the norm by 5 times.
Myocardial infarction. This disease is a consequence of impaired blood flow, resulting in necrosis of cardiac muscle tissue. In the case of an uncomplicated heart attack, the level of ALT increases slightly compared to AST, however, it can be used to determine the attack.
Reasons for increased ALT
Taking a number of medicinal or herbal preparations – barbiturates, statins, antibiotics;
frequent consumption of fast food before taking an ALT test;
drinking alcohol less than a week before blood sampling;
non-compliance with the basic rules for taking the test, including the sterility of the procedure;
increased emotional or physical stress;
Carrying out cardiac catheterization or other surgical intervention shortly before analysis;
steatosis - a disease manifested in the accumulation of fat cells in the liver area, most often found in overweight people;
necrosis of a malignant tumor;
taking narcotic substances;
lead poisoning of the body;
mononucleosis is an infectious disease that manifests itself in changes in blood composition, damage to the liver and spleen;
ALT is elevated during pregnancy
In women, the amount of alanine aminotransferase is limited to 31 U/l. However, in the first trimester of pregnancy, a slight excess of this value is possible. This is not considered a deviation and does not indicate the development of any disease. In general, ALT and AST levels should be stable throughout pregnancy.
A slight increase in the number of enzymes of this group is observed during gestosis. In this case, they are mild or moderate in severity. Preeclampsia is a complication that occurs in late pregnancy. Women experience weakness, dizziness and nausea. Their blood pressure rises. The greater the deviation of ALT from the norm, the more severe the gestosis. This is the result of too much stress on the liver that it cannot handle.
What is alanine aminotransferase (ALT, AlAT)
Alanine aminotransferase is essentially a marker for determining various pathologies of the body in laboratory studies. The substance alanine itself plays an extremely important function in human biochemistry. It is involved in the synthesis of various amino acids, sugar metabolism, and the functioning of the immune system, promoting the production of leukocytes. Alanine is present in almost all tissues and organs of the human body, synthesized in ALT, but a particularly large amount is found in the liver. The substance is also present in the blood, but in small quantities.
However, when tissue is damaged, ALT is released from cells and enters the blood. Thus, an excess of the enzyme level indicates a pathology that has arisen in the body, and primarily about problems with the liver, where its content is highest.
When liver cells (hepatocytes) are damaged, alanine aminotransferase is released and enters the blood
Why might AST be elevated?
An increase in AST has its own gradation, since the enzyme can be slightly exceeded, or it can be moderately or strongly increased. Prescriptions, examinations and treatment will also vary.
AST can be exceeded in case of alcohol intoxication and poisoning with plant products - mushrooms or jam.
Increased AST
A stable, slight increase in the level in the blood indicates the presence of fatty deposits on the liver or frequent use of certain drugs - protumor drugs, barbiturates, antibiotics or statins. It is registered as an increase in the AST index by 5-6 times from normal values. You may not know this, but even taking aspirin shortly before the test can show an excess reading.
Average elevated AST levels usually indicate a heart attack or heart failure, mononucleosis or autoimmune diseases in which muscles have been damaged. This also includes donating blood after long-term constant intake of high doses of vitamin A. Exceeding the AST level of moderate severity may indicate the presence of cirrhosis of the liver or some types of cancer tumors. The results look like AST exceeding the norm by 7-10 times.
A high level of increase in AST plasma indicates a large tumor and its necrosis, a large number of liver lesions of different sizes, viral hepatitis, positive reactions to drugs and long-term use of serious medications. The highest AST levels are usually observed at the beginning of the active phase of the disease. It is during this period that the destruction is most significant and is accompanied by the release of toxins into the blood. It is detected when AST increases more than 10 times higher than normal.
Attention! A significant decrease in the indicator does not indicate complete restoration of the function and integrity of the liver and heart. Most often, this indicates its rupture, severe cirrhosis and a significant deficiency of vitamin B6.
Increased AST for no reason
Exceeding the normal threshold
In medical research, the upper limit of normal ALT is important. The limit for adult men is 45 units/l, for women 34 units/l. An increase in ALT in a blood test indicates an inflammatory process in the body. Below are the diseases that cause this pathology.
- Pancreatitis. Severe damage to the pancreas. Occurs due to the appearance of a tumor blocking the enzyme ducts. As a result, the accumulated digestive enzymes begin to digest the pancreas itself. Possible death;
- Hepatitis. Liver disease. Characterized by inflammation of organ tissue. It is divided into several types. Hepatitis C is considered the most dangerous. The latter often becomes chronic and can cause cirrhosis of the liver. Common causes of hepatitis are: toxic damage to liver cells (for example, alcohol), viral infection;
- Myocardial infarction. The most severe heart disease. It is characterized by the death of some parts of the heart muscle due to a critical decrease in blood circulation. The pathology has many causes. The main ones: smoking, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, sedentary lifestyle.
There are reasons for exceeding the ALT norm in a blood test that are not related to the diseases listed:
- Chemotherapy;
- Injuries accompanied by damage to the muscles of the body;
- Taking potent drugs;
- Physical and emotional stress;
- Eating fatty fried foods
- Taking drugs.
Important! The main recommendations aimed at reducing the likelihood of the occurrence of these diseases will be: proper nutrition, avoidance of drug use (including alcohol, nicotine), moderate physical activity, and reduction of stressful situations in life.
Expert opinion
Cardiologist Grigory Viktorovich
If the pressure is above 130/90, the blood vessels need to be cleaned. The easiest way: drink a decoction of
How the research is carried out
Detection of ALT and AST in the blood of men is performed using a biochemical analysis. For this examination, blood is taken from the cubital vein, the volume of fluid obtained is about 5-10 ml. Blood collection is carried out by a qualified doctor in a medical hospital, and the rules of asepsis and antiseptics, which are necessary to exclude the possibility of human infection, must be observed. Blood is drawn into a clean tube, where it will remain for a specific period of time, which will be required to create a clot and separate the serum. The taken material is examined in the laboratory. As a rule, a special biochemical apparatus is used to detect the activity of the ALT and AST enzymes.
To obtain the correct indicator during the study, a person must perform some preparatory measures:
- You will need to donate blood on an empty stomach, so the collection is scheduled for early in the morning. For breakfast, you can only drink non-carbonated mineral water or tea without sugar.
- The last meal is allowed 12 hours before the test, so people only eat dinner the evening before the test.
- 2-3 days before donating blood for ALT and AST levels, you must avoid fatty, fried foods, as well as alcoholic beverages. The listed components significantly increase the load on various organs, in particular the liver.
- On the day of biochemistry, it is recommended to avoid increased emotional and physical stress; you should not smoke a couple of hours before the test.
If a person takes into account simple recommendations, then when checking the activity of the enzymes ALT and AST in the blood, it will be possible to obtain reliable results of the study. Already from them it will be possible to clearly understand whether there are health problems or whether everything is in order with the body.