What is alcoholic polyneuropathy
The long-term toxic effects of alcohol do not go unnoticed for an addicted person. All systems of the body are negatively affected. From the side of interconnected nervous structures, the reaction to systematic alcohol consumption is the emergence of a dangerous disease. Alcoholic polyneuropathy is a disease that is caused by chronic alcohol abuse, which leads to disruption and pathological changes in metabolic processes.
Alcoholic polyneuropathy code according to ICD 10
Decreased sensitivity of nerve endings is the result of prolonged consumption of alcoholic beverages. The toxic effect of alcohol provokes the development of pathological changes in the metabolic processes of nerve fibers. Since the disease is widespread throughout the world, and certain methods are used to treat it, according to international rules it has a certain labeling. The code for alcoholic polyneuropathy according to ICD 10 is G 62.1; behind these symbols is the name of the disease of the same name, which is characterized by dysfunction of the peripheral nerves.
Treatment of alcoholic neuropathy
There are several medical procedures, or rather medications, that can be used to treat the pain of alcoholic neuropathy. These include:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (analgin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, etc. )
. - Antidepressants : Although they are not approved for the treatment of alcoholic polyneuropathy, they are often prescribed for pain relief.
- Anticonvulsants . As with antidepressants, these drugs are not formally indicated for the treatment of alcoholic neuropathy, but they are sometimes prescribed for pain management.
- Vitamin supplements : Alcoholic neuropathy is partly to blame for nutritional deficiencies, so supplements with vitamin B12, folate (vitamin B9), vitamin E and thiamine may be recommended.
There are no medications that can help improve sensory loss, increase muscle weakness, or help with the coordination and balance problems caused by alcoholic polyneuropathy. However, some people notice improvement in symptoms a few months after stopping drinking.
Sometimes alcohol causes such serious harm to the body that a liver transplant . In this case, there may be some improvement in the symptoms of alcoholic neuropathy, however, often the neuropathy is so advanced that even after a liver transplant there may be little, if any, improvement.
Symptoms of polyneuropathy
Toxic neuropathy or atrophy of the muscles of the limbs makes itself felt gradually with slight numbness and a tingling sensation. The first symptoms of polyneuropathy do not cause much concern for some time, but if the development of the neurological disease is not stopped and the fight is not started, this will inevitably lead to paralysis of the legs and speech disorder. The main signs of toxic polyneuropathy are as follows:
- muscle tension, slight numbness of the limbs;
- weakness in the legs;
- convulsions;
- excessive sweating;
- cyanosis of hands and feet;
- speech disorder;
- dry skin, the appearance of ulcers;
- burning sensation;
- disorientation.
- Alcoholic encephalopathy of the brain - symptoms, degrees, treatment and prognosis
- Combilipen tablets: drug instructions
- Symptoms and treatment of alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver
Symptoms
The main signs of alcoholic polyneuropathy:
- a feeling of “crawling”, tingling or burning in the feet;
- soreness, cramps of the calf and thigh muscles;
- muscle weakness;
- numbness of the limbs;
- chilliness, cold extremities;
- decreased sensitivity of the “socks” and “gloves” type;
- change in gait;
- distortion of the perception of stimuli in the limbs;
- swelling and marbled pallor of the skin of the distal extremities;
- slurred speech;
- sweating of palms and feet.
A feeling of tingling, burning in the feet, numbness and decreased sensitivity are the main signs of alcoholic polyneuropathy
At the initial stage of the disease, patients present vaguely formulated complaints of transient muscle pain, numbness, and discomfort. Unpleasant sensations are localized in the distal parts of the extremities (feet, less often – hands). As these symptoms progress, they cover the entire limb, and signs of dysfunction of the internal organs appear. In severe cases, mental disorders are added; the oculomotor, optic, and vagus (less often) nerves are involved in the pathological process.
It has been established that daily consumption of 100 ml of anhydrous ethyl alcohol (corresponding to 200-300 ml of strong alcoholic drink) leads to the development of neuropathy within 3-10 years.
Causes of polyneuropathy
The appearance of such disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system can provoke other diseases. The clinical picture of the disease is similar, but it is caused by different causes of polyneuropathy. Overdose of drugs, diabetes mellitus, cancer, chemical poisoning, epilepsy - this is what can be a source of development of pathological changes. If it is alcoholic neuropathy, then the following factors contribute to the development of the neurological disease:
- metabolic disorders in nerve fibers;
- long-term toxic effects of ethyl alcohol;
- liver dysfunction;
- lack of B vitamins;
- prolonged squeezing in a monotonous position while intoxicated;
- the presence of a gene that affects the process of ethanol breakdown and the formation of enzymes that have a destructive effect on the entire nervous system of the body.
Causes of pathology
The main cause of alcoholic polyneuropathy is the toxic effect of ethanol on the nervous system. As a result, the patient develops conditions that are provoking factors for the development of the disease:
- Decreased immunity, in which the immune system cannot resist bacteria and viruses.
- Nutrient deficiency.
- Development of autoimmune reactions.
- Liver dysfunction.
- In many patients, doctors diagnose hereditary vulnerability of the nervous system to various factors, including the effects of alcohol.
Forms of alcoholic polyneuropathy
Pathological changes can be asymptomatic, and yet these are rare cases among patients with alcoholism. More often observed forms are chronic (more than a year) and acute (month), which serve not only as evidence of the presence of the disease, but also as confirmation of the progressive nature of the process. Based on the clinical picture of the disease, in medicine it is customary to distinguish between the following forms of alcoholic polyneuropathy:
- Motor. It is characterized by sensory disturbances (mild), peripheral paresis (various degrees), damage to the lower extremities, which accompanies impaired flexion of the fingers, rotation of the foot, and decreased Achilles reflex.
- Sensory. Reduced temperature, pain sensitivity of the extremities, numbness, convulsions, feeling of chilliness, marbling of the skin, vegetative changes - all these are characteristic signs that indicate sensory disturbances.
- Atactic. It is indicated by a lack of coordination of movements, numbness of the legs, a staggering gait, painful sensations when palpating the nerve trunks, and the absence of a tendon reflex.
- Mixed. It is a combination of motor and sensory disorders, and this manifests itself through numbness, pain, flaccid paresis, paralysis of the upper and lower extremities. This form may be accompanied by such signs as atrophy of the muscles of the forearm and hand, decreased deep reflexes, and hypotension.
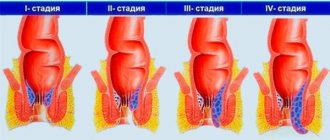
Forms and stages of the disease
In medicine, there are various classifications of alcoholic polyneuropathy. Depending on which nerves are affected, the following forms of pathology are distinguished:
- Sensory . The patient has loss of sensitivity in the limbs. The legs suffer the most. Temperature perception changes, limbs freeze in the warmth, and the skin turns pale. Tendon reflexes decrease, the patient feels numbness in the toes and palms.
- Motor . Characterized by impaired motor activity. The tibial and peroneal nerves are most often affected. The functions of flexion and rotation of the foot and fingers are impaired; the patient cannot walk on tiptoe. In the area of the feet, the muscles weaken and atrophy.
- Mixed . Combines sensory and motor types. It is characterized by flaccid paresis of the limbs, decreased reflexes, and loss of sensitivity along the main nerves.
- Atactic . The deep sensitivity of the lower extremities is impaired, so the patient’s coordination of movements is impaired, the lower legs do not feel anything, the gait changes, and there are no knee and Achilles reflexes.
- Vegetative . The autonomic nervous system is affected. The patient develops conditions similar to the manifestations of VSD: tachycardia, pressure surges, sudden sweating, fainting. The pupillary reflex worsens, visual acuity decreases.
- Autonomous . The most severe form, in which destruction affects the nerves responsible for the functioning of internal organs. An alcoholic's heart, kidneys, and bladder work poorly.
Another classification of the disease is based on the duration of the course and the severity of symptoms:
- Acute form. The pathology develops within a couple of weeks, the manifestations are pronounced.
- Chronic . It develops slowly over the course of a year. The most common form.
- Latent . It is asymptomatic, signs are detected during a detailed examination.
In its development, the disease goes through several stages:
- Subclinical . The patient does not feel any changes; signs are detected only during a neurological examination: decreased pain and temperature sensitivity.
- Clinical . First, the patient experiences pain in the affected nerves, then sensitivity worsens, and numbness of the fingers or parts of the body begins. Then the pain disappears, muscle weakness and difficulty moving appear.
- Stage of complications. Tissue atrophy occurs and ulcers form on the legs, usually painless. Most often, to save the patient’s life at this stage, a limb is amputated.
Diagnosis of alcoholic polyneuropathy
The main method of confirming the diagnosis is electroneuromyography (ENMG), which is used in the early stages. Diagnosis of alcoholic polyneuropathy in severe cases involves a biopsy of nerve fibers; in addition, this method is used when it is necessary to exclude other types of disease: is polyneuropathy toxic or diabetic? An examination using ENMG helps to determine the severity of the damage, how much the neuron, root, nerve, and muscles are affected, but first the neurologist must conduct an objective examination and collect an anamnesis.
Prevention
First of all, it is a healthy lifestyle and avoiding stressful situations. It is necessary to undergo annual preventive examinations in order to detect hidden pathology in time.
Patients with diabetes mellitus should be especially careful and attentive to themselves.
They need to protect their feet from injury, wash them daily, and inspect and feel them for damage or loss of sensation. If you notice symptoms of neuropathy, you should rush to see a doctor.
Sometimes a person does not even know that he has peripheral neuropathy and does not pay attention to its minor signs for a long time.
Peripheral neuropathy is a common disease, the symptoms and causes of which are quite varied. In most cases, this pathology can be successfully treated, but for this it must be detected in time. The sooner treatment is started, the greater the chances of getting rid of all unpleasant symptoms in a short time.
Treatment of polyneuropathy
A neurological disease can manifest itself either after a long period of heavy drinking, or against the background of gradual toxic effects over a long period of time. Taking these factors into account, treatment of polyneuropathy will proceed in different directions, but any therapy will involve a complete cessation of alcohol consumption and increased attention to nutrition. To improve microcirculation, neuromuscular conduction, and pain, the doctor may prescribe antihypoxants, analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antioxidants, and B vitamins.
- Lipoic acid
- Hypoxia - what it is, symptoms and signs, degrees and consequences
- Alcoholic coma - signs of deep or superficial, first aid to the patient and hospital treatment
Treatment of neuropathy of the lower extremities with drugs
It will be easier to achieve a full recovery if the disease is diagnosed in the early stages. Treatment of neuropathy of the lower extremities with drugs is aimed at restoring the functions of nerve fibers and improving blood circulation in the area of nerve endings. The subtlety of therapy lies in identifying the true causes of the disease, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body, for example, a predisposition to allergic reactions.
To improve the patient’s condition, when toxic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities is correctly diagnosed, the following types of therapy are used:
- medication with the prescription of a course of vasoactive drugs (Emoxipine, Vasonit, Nicotinic acid, Instenon);
- use of antidepressants (Mexidol, Actovegin, Sertraline, Berlition, Venlafaxine);
- a course of B vitamins, Benfotiamine, Thiamine to replenish the deficiency;
- taking painkillers non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nimesulide, Ketoprofen, Meloxicam);
- anticonvulsants (Gabapentin, Pregabalin);
- use ointments and creams for local anesthesia (Ketoprofen, Diclofenac, Finalgon, Capsicam, Capsaicin).
Non-drug methods
Treatment methods other than medications can also help speed up the healing process. Physiotherapeutic procedures have formed the basis of a non-drug method of treating toxic polyneuropathy; among them, electrical stimulation of nerve fibers, the spinal cord, and magnetic therapy have been successfully used. Research shows the effectiveness of massage in helping to restore muscle activity. The list of comprehensive measures should include physical therapy, mud therapy, and acupuncture.
Combining medicinal, non-medicinal, and traditional methods of treatment allows you to achieve excellent results and speed up recovery. The treatment will be helped by a freshly prepared cocktail of kefir (150 grams), parsley, sunflower seeds (2 tablespoons each), which is taken an hour before meals twice a day. A powerful natural antioxidant - cinnamon - goes perfectly with oregano and honey. To prepare a healthy decoction, you need to take all the ingredients in equal proportions, mix and take 1 teaspoon three times a day with a glass of warm water.
Forecast
With timely treatment, a reverse progression of the disease and an improvement in the patient’s quality of life are possible. A necessary condition for a favorable prognosis is a complete cessation of alcohol consumption.
According to the results of Western epidemiological studies, in the United States, alcoholic polyneuropathy is found in 25–66% of patients with chronic alcoholism.
In most cases, patients become disabled, acquiring one or another degree of disability, since early access to a specialist in this case is a rare occurrence. An important factor determining the unfavorable prognosis is the patient’s inability to give up alcohol and comply with a long-term medical and protective regime.
Prognosis of polyneuropathy
An advanced form of the disease or untimely initiation of treatment leads to disability, so it is necessary to start therapy and decide on a treatment regimen on time. A favorable prognosis for polyneuropathy with possible complete recovery is observed only in those patients who promptly consulted a doctor and underwent a course of therapy. It will not be possible to recover from a neurological disease in a short time; to achieve the desired goal, you will have to apply perseverance, adhere to proper nutrition, and avoid drinking any alcoholic beverages.
Treatment methods
The main goal of treating patients with NPC is to improve their quality of life: reducing psychological discomfort and improving physical well-being. This is achieved by restoring impaired motor skills, increasing sensitivity in the legs, and relieving pain.
With partial or complete loss of one or more types of sensitivity, these tasks are accompanied by the protection of the lower extremities from possible damage.
There are three principal approaches to NNC therapy:
- etiotropic;
- pathogenetic;
- symptomatic.
When the cause of the disease has been established, etiotropic therapy is most effective and can minimize or completely eliminate the manifestations of the disease. First of all, we are talking about eliminating the impact of the causative factor or reducing its pathogenic influence.
Depending on the type of NNK, this may be normalization of blood sugar levels (with diabetic neuropathy of the lower extremities), refusal to take alcohol-containing products (with alcoholic NNK), suppression of autoimmune reactions (neuropathy with systemic diseases) or exclusion of contact with toxic substances with toxic damage to peripheral nerves (lead, mercury, etc.).
Pathogenetic approaches to the treatment of NNC are the most universal, as they allow influencing the mechanism of development of the disease caused by any etiological factor, as well as in cases where the cause of neuropathy remains unknown.
The main directions of pathogenetic therapy for neuropathic syndrome are improving microcirculation in the lower extremities, increasing the rate of metabolic processes, vitamin therapy, as well as drugs with neurotrophic action.
In addition, drugs that have a complex effect on peripheral nerves, such as alpha-lipoic acid, are effectively used.
Symptomatic treatment is indicated to eliminate specific manifestations of NNC in a particular patient. Mainly, it is aimed at relieving neuropathic pain syndrome, eliminating the consequences of trophic disorders (ulcers, erosions), reducing the manifestations of restless legs syndrome, etc.
There are several methods for treating the disease, mainly determined by the etiology of NNK:
- surgical;
- medicinal;
- physiotherapy;
- orthopedic;
- spa treatment.
Surgical tactics are used for the traumatic nature of neuropathy resulting from compression of the nerve by tumors or hematomas, fractures of the lower extremities, dislocations of joints or wounds. When performing urgent (urgent) or planned surgery, the consequences of traumatic nerve damage are eliminated. In addition, the group of surgical methods includes therapeutic blockades with painkillers, glucocorticoids and neurotrophic agents.
An effective physiotherapeutic method for treating NNC is electrical myostimulation, used for atrophy and muscle weakness.
To restore atrophied muscle groups, massage courses are indicated.
Regular exercise therapy helps maintain muscle tone and also prevents the development of contractures.
The orthopedic method using special shoes and devices (orthoses) allows you to prevent ulcers and corns of the feet (for example, with diabetic foot), as well as normalize biomechanics and improve the quality of life of patients with muscle atrophy and limb deformities due to NNC.
Courses of treatment in specialized sanatoriums are necessary to restore lost functions, prevent relapses of the disease and its transition to a chronic form.
In chronic forms of NPC, patients in remission are subject to sanatorium-resort treatment.
Diagnostic methods
When diagnosing polyneuropathy, it is first necessary to exclude poisoning from poisons or drugs taken uncontrolled.
To do this, a number of tests are carried out in a medical institution:
- Blood tests of the patient can significantly reveal the clinical picture of the disease.
- Molecular genetic analysis can accurately identify the form of polyneuropathy.
- Needle electromyography provides information about the signs of the denervation-reinnervation process.
A doctor's examination is one of the most important examinations. The specialist will detect all signs of the disease.
Doctor's diagnosis:
- Testing the sensitivity of the limbs.
- Checking reflexes.
- Testing sensitivity to temperature changes.
- Testing muscle reflexes with a needle.
- Checking the reflexes of the knee joints.
Today there are the latest methods for diagnosing polyneuropathy. Using a computer, the exact sensitivity threshold is determined.
Briefly about the process of disease recognition
Diagnosis of polyneuropathy is carried out by a doctor by interviewing and examining the patient, considering the results of a venous blood test (laboratory tests can reveal the degree of liver damage by determining the level of transaminases). Vitamin deficiency is clarified by studying blood serum.
The dynamics of the disease is monitored by ENMG. Electroneuromyography allows us to identify the presence of a degenerative process in peripheral nerves and the degree of tissue damage to the latter.
The most important signs on the basis of which a diagnosis is made include:
- progressive muscle weakness;
- tendon areflexia;
- symmetry of violations.
An additional diagnostic method is to interview family members of the patient (if possible). Sometimes patients deny the fact of addiction to alcoholic beverages; It is a conversation with relatives that allows you to draw the correct conclusion and clarify the cause of pathological changes.
Polyneuropathy after chemotherapy
Toxic polyneuropathy after chemotherapy is classified as a separate group of diseases, since it can be a side effect of taking medications or result from the breakdown of tumor cells. It causes systemic inflammation and damages nerve cells and pathways. This phenomenon can be complicated by the presence of diabetes, alcoholism, liver and kidney dysfunction. This disease is expressed in impaired sensitivity and movement disorders, decreased tone of the muscles of the extremities. Polyneuropathy after chemotherapy, the symptoms of which are described above, can also cause motor dysfunction. Disorders of the autonomic and central nervous systems are less common.
Treatment of this type of disease is reduced to symptomatic therapy. The patient may be prescribed anti-inflammatory, painkillers, immunosuppressants, hormonal drugs, Neuromultivit and Thiamine vitamins.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of polyneuropathy completely depend on the degree of development of the disease. The more the nerve endings are affected, the more symptoms of the disease appear.
Polyneuropathy is a very serious disease, and if left untreated, the motor function of the limbs can be completely impaired.
General symptoms:
- Numbness of the legs.
- Pain in the limbs.
- Tingling sensations in the feet.
- Swelling and deformation of the fingers.
- weakness in the legs.
- Trophic ulcers.
- Cramps.
Impaired movement can significantly complicate life; a person cannot hold objects or care for himself. Walking also becomes difficult. The patient does not feel how his legs move and cannot perceive his own physical actions.
How does the disease progress?
The disease progresses slowly and is quite difficult to detect when it appears. The forms of the disease differ. A clear manifestation of what is present will appear only after a considerable dose of alcoholic beverages has been taken. Considering that the disease affects the nervous system, it is almost impossible to predict the speed and options for its development. This is the difficulty of further treatment.
If you have consumed a considerable amount of drinks containing ethanol, the most striking symptoms of the disease are guaranteed to appear a few days after their use. Its manifestation can be worsened or accelerated by a lack of vitamins and nutrients in the human body, problems with the liver, gastrointestinal tract, which very often manifests itself in people who abuse alcohol. It will be difficult for people who have problems with the cardiovascular system, people who are sick, who work in one position - leading a sedentary lifestyle.
All of the above factors complicate the manifestations of the disease. The main reason why polyneuropathy makes itself felt is the destruction of the barriers present in the nerve fibers. With a lack of vitamins, the situation worsens, causing the disease to develop even faster. The problem often occurs in people who have damaged genes. Their body cannot normally break down the ethyl alcohol they consume. As a result, total destruction of the cells of organs located in the body occurs.
The first manifestation of the deviation is noticeable by severe pain in the legs. The person cannot get up, walk normally, feels weak and burning. The condition does not stabilize when using ointment or compress.
The majority of clinic visitors are people who have been drinking alcohol for a considerable time. Most often, doctors observe advanced cases, since at the first symptoms the patient did not intend to visit the clinic in order to determine the causes of the disease.
With the more active development of the disease, you may notice a problem - numbness in the legs, cramps, accompanied by severe pain. After a certain amount of time, the problem spreads throughout the body, rises upward, and manifests itself in more severe forms.
Failure to pay attention to such a problem in a timely manner guarantees that in the near future there will be a loss of sensation in the legs, reflexes in the legs will be almost completely absent, and pathologies in the form of ulcers or paralysis will appear in the body.
A clear sign confirming the onset of the disease will be a change in the color of the skin on the legs. Besides:
- Hair falls out on the lower extremities.
- The temperature of the feet changes.
- Skin color changes.
- Pain appears when pressing on the muscles in the lower legs. All indicators directly indicate incipient paralysis; as a result, it is impossible to solve the problem associated with the extensor of the foot.
Drug-induced polyneuropathy
This type of neurological disorder is caused by taking the following medications:
- When treated with Perhexilen at a dosage of 200-400 mg per day, polyneuropathy occurs after a couple of weeks. It manifests itself in decreased sensitivity, ataxia, and paresis of the limbs. In these cases, the drug is stopped and the patient's condition improves.
- Isoniazid polyneuropathy develops when there is a deficiency of vitamin B6 in people with a genetic disorder of its metabolism. In this case, pyridoxine is prescribed orally.
- Excess Pyridoxine (50-300 mg/day) leads to the formation of sensory polyneutropathy, severe headache, fatigue and irritability.
- Long-term treatment with Hydrolazine can lead to dysmetabolic polyneutropathy and requires taking vitamin B6.
- Taking the drug "Teturam" at a dose of 1.0-1.5 g/day can result in paresis, loss of sensitivity, and optic neuritis.
- Treatment with Cordarone at a dosage of 400 mg/day for a period of more than a year can cause toxic polyneutropathy.
- With a lack of vitamins B6 and E, polyneutropathies also occur, as well as with their excess.
Drug-induced toxic polyneuropathy is designated by ICD 10 code G62.0.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the obtained research data , carried out in three stages:
Assessment of clinical manifestations - the doctor visually examines the patient for reflex activity, as well as muscle strength and sensitivity. A consultation with a neurologist is combined with a consultation with a therapist, after which a consultation with a narcologist may be required to establish the fact of alcohol dependence.
Laboratory testing - includes evaluation of urine, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid test results. Study of the latter is necessary to exclude diabetic and other forms of polyneuropathy that may develop in parallel.
Electroneuromyography - helps to evaluate the conduction of nerve impulses, which is important in the presence of paralysis.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - shows the general condition and performance of the abdominal organs.
Particular attention is paid to the liver, stomach and intestines.
Diagnostic methods
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to conduct the following studies:
- Studying the anamnesis - the doctor must analyze the patient’s complaints.
- Neurological examination - helps to identify abnormalities such as muscle weakness, loss of sensation, etc.
- Electroneuromyography is required to determine the degree of damage, inflammation and degenerative changes in nerve tissues. This technique allows you to control the dynamics of the disease.
- Biopsy of nerve tissue - in this case they are examined under a microscope.
When conducting diagnostic studies, it is important to differentiate alcoholic polyneuropathy from other diseases - the diabetic form of the disease, inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, genetic damage to nerve tissue, Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of the onset of the disease has not been fully studied to date. A number of scientists believe that autoimmune processes are at the heart of alcoholic polyneuropathy. The pathology is triggered by provoking agents (among them the Epstein-Barr virus, Campylobacter, cytomegalovirus).
Infectious diseases and other factors that increase energy expenditure exacerbate the lack of nicotinic and ascorbic acids, microelements, and B vitamins in body fluids.
The main target of the disease in its acute form is axons—the elongated processes of neurons.
Various types of alcoholic polyneuropathy have the ability to destroy the myelin sheath of the structural and functional units of the nervous system, as a result of which the speed of impulses slows down, and the necessary functions begin to be carried out in an altered form.
Arsenic polyneuropathy
Arsenic can enter the human body along with insecticides, medicines, and paints. This disease is occupational among smelters. If the exposure to the toxic substance was single, then vascular hypotension, nausea and vomiting develop. After 2-3 weeks, polyneuropathy appears, expressed in weakness of the leg muscles. If repeated arsenic poisoning occurs, then symmetrical distal sensorimotor manifestations of the disease occur. In the case of chronic intoxication with a toxic substance, hypersalivation, trophic and vascular disorders (skin hyperkeratosis on the soles and palms, rashes, stripes on the nails, pigmentation on the abdomen in the form of drops, peeling), and ataxia are observed. Arsenic polyneuropathy is diagnosed by analyzing the composition of urine, hair and nails. The patient’s recovery after an illness lasts months.
Treatment
Suppression of the development of alcoholic neuropathy occurs through the use of complex treatment regimens, including the use of medical products in combination with physical therapy, exercise therapy, massage and a number of other methods.
Medication
Symptoms of the disease are eliminated using various groups of drugs. The names of the main medications are shown in the table below.
| List of funds | Purpose of prescribing the medication |
| Vitamins (C, B1, B6, etc.), folic acid - injections and pills | Replenishment of the deficiency that develops in chronic alcoholism; ensuring the normal functioning of the structures of the nervous system. |
| Antihypoxants (Actovegin) | Increasing tissue resistance to oxygen deficiency. |
| Anticholinesterase drugs | Elimination of sensory and movement disorders. |
| Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Amitriptyline and Carbamazepine | Reducing the intensity of pain. |
| Anticonvulsants | Elimination of painful cramps. |
| Antidepressants | Improved emotional state. |
| Neuromidin | Acceleration of neuromuscular transmission. |
| Cytoflavin | Improving microcirculation, restoring metabolism. |
| Vinpocetine, Curantil | Facilitating venous outflow, strengthening blood vessels. |
| Hepaprotectors | Normalization of liver function. |
Autonomic disorders are corrected through the use of symptomatic therapy.
It is prohibited to use medications without a doctor’s prescription: the use of drugs unsupervised by a specialist can lead to the development of complications, deterioration of the patient’s condition, and death.
Non-drug treatment
As additional rehabilitation measures, acupuncture and magnetic therapy, and physiotherapeutic procedures (to stimulate the spinal cord and nerve fibers) are prescribed. To restore muscle tone, massage is used.