Most women do not pay due attention when their breasts swell and hurt before menstrual bleeding. In the meantime, a long-term development of a rather serious disease - mastopathy - is possible.
Up to 90% of women suffer from this pathology of the mammary glands at a young or mature age. At the same time, some forms of the disease significantly increase the risk of developing breast cancer - the most common cancer pathology among women. The information provided about what breast mastopathy is, how to treat it and identify it in the early stages will help you avoid serious illnesses and maintain your own health.
Total information
Soreness of the mammary glands is one of the most common complaints in women of reproductive (childbearing) age. Almost all females experience such pain at least once in their lives. It was also revealed that every second woman experiences pain in the mammary glands on the eve of menstruation.
Mastodynia mainly affects patients aged 20 to 40 years, who have abnormalities in their gynecological history in the form of irregular sex life, gynecological pathologies, as well as those women who have not given birth or have given birth only once. If pain in the mammary glands appears after 40 years, it is often caused by organic diseases of the mammary glands.
Treatment of mastopathy with folk remedies
At home, using various recipes, it is also possible to engage in treatment; proven folk remedies are suitable for this. But first of all, you need to consult a doctor.
Burdock compress for the night
- You need to take a clean burdock leaf, rinse it well, lubricate it with honey and apply it to the affected areas of the chest every night. The procedure lasts 5-7 days, after which you need to take a break of 2-3 days.
- Take two tablespoons of chopped burdock root and pour 2 cups of boiling water over them. Then let it brew under the lid for 6-8 hours, strain and take 1 tbsp before meals. spoons, 3 times a day.
Linseed oil
You can use flax seeds and oil for breast mastopathy; this complements the entire treatment process well. Flax oil normalizes hormonal levels in women, improves appetite and strengthens the immune system. It can be added to salads, made into compresses, but it should not be subjected to heat treatment (the beneficial properties will be lost). The daily intake rate is 3 tbsp. spoons, also 1 tbsp. spoons can be taken as a preventative treatment. You can buy it at the pharmacy in capsule form.
Causes
Mastodynia can bother:
- during changes in the female body, which are considered a physiological norm;
- for various pathologies of the female genital organs, mammary glands and some other organs.
When assessing the patient’s pain, it is necessary to take into account her age - for example, in the puberty period (puberty), the described pain occurs during the maturation of the mammary glands, which occurs under the influence of estrogens.
It has been revealed that the majority of women of childbearing age who experience mastodynia do not have any pathological diseases of the mammary glands or gynecological area - pain occurs as a result of changes in hormonal levels.
Physiological mastodynia, which is not regarded as a pathology, can occur in conditions such as:
- ovulation – release of a mature egg from the ovary;
- taking oral contraceptives (birth control);
- large size of mammary glands.
During ovulation , the mammary gland undergoes periodic (cyclic) changes caused by the action of female sex hormones and aimed at preparing the mammary gland for future breastfeeding of the child (if conception, gestation and birth of a child take place). On the other hand, mastodynia in this case can act as a manifestation of premenstrual tension syndrome - psycho-emotional, vegetative-vascular and metabolic-endocrine changes that can occur 2-10 days before menstruation.
When taking oral contraceptives that regulate the menstrual cycle, mastodynia is one of the side effects. In this case, the same cyclic changes occur in the breast tissue as during ovulation. Usually, over the course of 2-3 months, the body adapts to the intake of oral contraceptives, due to which the pain weakens or disappears altogether.
If a woman has large mammary glands , pain occurs due to the influence of gravity (universal gravity), due to which the glands are “pulled” down, their tissues become tense, and a painful sensation occurs.
Mastodynia may occur due to a more prosaic reason - compression of the mammary glands by an uncomfortable bra, blouse, jacket or other item of clothing, but this is more of a social and everyday aspect than a medical one. Such wardrobe elements may be uncomfortable due to:
- improper tailoring;
- smaller than required for a bust.
Fashion often dictates the rules - in order to emphasize the aesthetics and sexuality of the mammary glands, they choose a bra to specifically compress and lift them, and this provokes pain. Such nuances need to be clarified before suspecting a woman of any disease that can provoke the development of mastodynia.
The described condition is formed as a pathology with shifts in:
- mammary gland;
- other organs.
The development of mastodynia due to breast pathology can be provoked by:
- hormonal disorders;
- injuries;
- inflammatory processes;
- tumor processes.
Mastodynia due to hormonal disorders can occur with diseases and pathological conditions such as:
- oophoritis - inflammatory lesion of the ovaries;
- ovarian cyst - formation in the form of a cavity with fluid;
- endometriosis is a pathology in which endometrial cells (the inner layer of the uterus) grow in other organs and tissues;
- ovarian cancer;
- pathology of the hypothalamic-pituitary region - a zone of the brain that performs regulatory functions.
Also, pain in the mammary glands can occur with endocrinopathies that do not affect the female genital area.
Mastodynia of a traumatic nature most often occurs with bruises of this organ.
note
Of the inflammatory processes, the most common cause of pain in the mammary gland is mastitis - an inflammatory lesion of its tissues.
Pain also acts as one of the symptoms of neoplastic processes in the mammary gland (proliferation of its tissues) - often these are:
- mastopathy – benign changes that occur due to hormonal imbalance;
- most benign tumors;
- Breast cancer is a malignant neoplasm of epithelial cells.
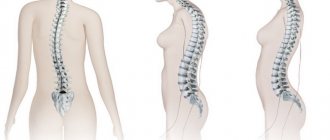
Of the diseases of other organs, the background for the formation of pain in the mammary glands most often becomes:
- osteochondrosis – dystrophic change in intervertebral discs;
- intercostal neuralgia – pain syndrome due to damage to the intercostal nerves;
- myalgia – muscle pain;
- Tietze's syndrome - inflammation at the attachment point of the ribs to the sternum;
- heart diseases;
- liver diseases;
- hysteria - a pronounced manifestation of emotions;
- hypochondria – a depressed state with elements of suspiciousness;
- depression is a depressed psychological state.
In the last three cases, mastodynia occurs in the absence of hormonal or organic changes in organs and tissues.
What is meant by mastodynia?
What is mastodynia? In accordance with ICD-10, this pathological condition is assigned code 64.4. It is characterized by unpleasant subjective discomfort in the breast, such as roughness, pain and increased sensitivity at the moment of touching the mammary glands.
Mastalgia (mastodynia) syndrome is most often diagnosed in women of childbearing age, but is also observed in elderly patients. Typically, pain occurs before the onset of menstruation, but can act as a sign of the following conditions:
- Pregnancy.
- Neurosis.
- Puberty in teenage girls.
- Various abnormalities of the body.
Almost every woman experiences mastodynia for one reason or another. According to medical statistics, 50% of the fair sex exhibit signs of it every month, which negatively affects their well-being.
Women complain of decreased performance, physical and psychological discomfort, tension in personal relationships with men, and so on.
Development mechanism
The pathogenesis of this anomalous phenomenon is as follows:
- Pain appears due to changes occurring in the breast tissues due to the vigorous influence of hormones on them, primarily progesterone.
- At the luteal stage of the ovarian cycle, there is an active proliferation of breast epithelial cells and prolonged fluid retention in the breast structure.
- The processes described above provoke breast enlargement. As a result, pinching of the nerve endings is observed, which is indicated by the occurrence of pain.
- If there are any other anomalies in the structure of the female breast, then the pain is a consequence of irritation of the nociceptive endings by metabolic substances, which are characteristic of necrosis and inflammation in the breast, or due to pressure on the tissue caused by an increase in the tumor present.
Regarding the difference between mastopathy and mastodynia, the latter can act as a symptom of the initial stage of diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy, which in turn is a precancerous phase of the oncological process.
Classification of forms
Medicine emphasizes that mastodynia in women has two types of manifestation:
| Types of mastalgia | Characteristics |
| Physiological | Puberty. Carrying a baby. Climax. |
| Pathological | Acts as a symptom of breast diseases. It is a sign of some other disease. |
In addition, mastodynia has characteristic differences in its occurrence, depending on the provoking cause.
| Forms | Peculiarities |
| Cyclic (true) | Appears in the second half of the menstrual cycle. Physiological ovulation. Premenstrual syndrome. Hormone-sensitive dysplastic reactions in the breast. Use of contraceptives. |
| Acyclic (symptomatic) | It is unsystematic in nature. Indicates injury to breast tissue (wounds, surgeries, illnesses, etc.). As a symptom, it is characteristic of the following breast diseases: - pathologies of adenosis of the sclerosing type; - adenoma; - fibroadenoma; — oncology; - Taitz syndrome. |
| False (reflected) | Develops as a result of impaired functionality of other organs or systems of the body (diseases of the cardiovascular system, spine and joints). |
Development of the condition
Pain in physiological mastodynia occurs due to changes in the tissue of the mammary gland, which develop due to the action of female sex hormones. In this case, progesterone has a particularly pronounced effect.
During the luteal phase of the ovarian cycle (this is the period of time from the moment of ovulation until the next physiological uterine bleeding), active proliferation of epithelial cells of the mammary glands occurs, and fluid is retained in the stroma (the connective tissue base on which the glandular tissue of the mammary gland rests). As a result of this, the following processes occur:
- the mammary glands swell;
- nerve endings are compressed;
- pain syndrome occurs.
In the case of non-physiological mastodynia, pain may occur due to the fact that the nerve endings are irritated by metabolic products (tissue metabolism), which are formed during various pathological processes in the mammary glands:
- inflammatory;
- necrotic;
- tumor
and so on.
When a tumor forms, pain occurs due to the fact that it puts pressure on surrounding tissues.
There are several variants of mastodynia:
- cyclic (also called functional or true);
- acyclic;
- false (its other names are reflected and irradiating).
The cyclic version of mastodynia occurs in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. It is characteristic of conditions such as:
- physiological ovulation;
- premenstrual syndrome;
- dysplastic (consisting in a failure of tissue development) processes in the mammary gland of a dishormonal nature. They develop in mastopathy;
- taking oral contraceptives.
The acyclic variant of mastodynia is formed in various pathologies of the mammary glands. In this case, pain occurs regardless of the menstrual cycle. Its appearance is observed in diseases and conditions such as:
- damage to breast tissue as a result of trauma (including during various medical procedures);
- inflammatory processes;
- tumor processes;
- sclerotic growths;
- developmental defects.
A false version of mastodynia is observed with disorders of other organs and systems. Most often this is:
- spinal lesions;
- joint diseases;
- heart pathologies;
- radicular syndrome (back pain due to compression of the spinal roots).
Treatment
Treatment of mastopathy in women may vary depending on the type of disease, number and type of formations. Hormonal and non-hormonal therapy, ointments, tablets and drops, as well as surgery are used.
Surgical intervention
Doctors are wary of surgical treatment. Indeed, the tumor can be excised. However, the causes of the disease are not eliminated and there is a high probability of new formations appearing.
Surgical intervention is recommended for nodular mastopathy, multiple microcalcifications, papillomas inside the ducts, epithelial proliferation, and also when there are cysts with hemorrhagic contents. Removal carries a risk of cancer.
The affected area is cut out. During the operation, a histological examination is performed. If malignant cells are found, the volume of the removed gland may be increased. When the gland has papillomas inside the duct, many cysts or nodes, extended resection is performed (the affected area and nearby tissues are cut out) or complete removal of the organ.
After surgery, observation at a dispensary and conservative therapy are recommended. If atypical cells are found during histology, chemotherapy is prescribed.
Pills
Tablets are the most popular and easiest form of medication use. They are convenient to drink and carry with you if necessary.
Mastodinon
The tablets are light cream in color. Packs of 3 or 6 blisters, each containing 20 tablets. Homeopathic remedy, which includes cohosh, violet, twig, tiger lily, cyclamen.
In mastopathy, the appearance of new formations is caused by prolactin. Mastodinone suppresses the production of prolactin. This helps fight the occurrence of tumors.
Cyclodinone
A preparation made from plant substances, the main one of which is an extract of the fruits of common twig. The component affects the neurons of the brain. The extract acts as a mediator that inhibits nerve chains. Due to this, the activity of certain areas of the brain decreases.
By reducing the amount of prolactin, the ratio between gestagens and estrogens is fully or partially restored. After some time, the symptoms of mastopathy weaken, new formations do not appear.
The drug acts slowly but effectively. The course of treatment can range from 3-4 weeks to several months.
Remens
Remens is a homeopathic remedy used for menstrual irregularities and menopause. It is prescribed, including for diseases of the genital organs that are caused by inflammation.
Ointments for mastopathy
All ointments for breast mastopathy act approximately the same and are aimed at:
- resorption of formations;
- struggle with feelings of pain and heaviness;
- elimination of edema;
- stopping tumor growth;
- preventing the emergence of new formations.
Apart from individual intolerance, non-hormonal ointments have no contraindications. Due to local effects, such means are sometimes more preferable.
Progestogel
The main substance is progesterone. It stops the creation of unnecessary estrogen and reduces the amount of prolactin. Thanks to the ointment, the feeling of “fullness” in the chest disappears, and the pain disappears.
Mastofit
A natural remedy based on fucus extract and indole-carbinol. It is not a medicine, it belongs to the category of biologically active additives. Used as part of combination treatment.
Matofit removes inflammation and swelling, reduces the likelihood of benign cells degenerating into malignant ones, and also normalizes hormonal levels.
Traumeel
Effectively fights pain and inflammation. It contains only natural ingredients, which, among other things, improve immunity and remove swelling of the gland. It is also used for fractures and arthrosis.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are prescribed for mastopathy in women only when there is inflammation in the body, as well as after purulent mastitis. Reception is carried out as prescribed and under the supervision of a doctor.
For the disease, 2 groups of drugs are used:
- Cephalosporins. A large group, based on 7-aminocephalosporic acid. They have a wide spectrum of action. Some of the safest. They inhibit the structural basis of the microbial network. Effective only during the period of reproduction and growth of microbes.
- Penicillins. Slightly toxic, successfully used against many microorganisms. Most often it is administered intramuscularly or into a vein. The course of treatment is at least 5 days.
Additional agents can be used in conjunction with antibiotics to enhance the effect. For example, Wobenzym is often taken.
Hormonal drugs
Prescribed only after a complete hormonal examination. The table below shows the groups of drugs and their effects.
| Group | Name of drugs | How to prescribe | Action |
| Contraceptives | Ovidon, Marvelon, Janine Regulon. | From six months to two years, girls of reproductive age. | Stabilizes hormone balance. |
| GnRH antagonists | Zoladex, Diferelin, Firmagon, Buserelin. | Treatment is carried out for 4-6 months or longer. | Reduce the production of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Because of this, the amount of sex hormones decreases and menopause occurs. |
| Prolactin blockers | Dostinex, Parlodel, Bromocriptine. | In tablet form once or twice a day. | Prescribed for hyperprolactinemia, they reduce the production of prolactin and act on dopamine receptors. |
| Thyroid hormones | Triiodothyronine, L-thyroxine, Thyrocomb. | They are prescribed by an endocrinologist, the dose is regulated by a doctor, and the duration of use is most often for life. | Reduce the synthesis of prolactin and thyroid-stimulating hormone. |
| Gestagens | Duphaston, Utrozhestan, Prozhestogel. | They are used in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, the first 2 orally, the third - externally. | Estrogen production decreases, sex hormones slow down in the pituitary gland. Prescribed for hyperestrogenism, when bleeding and fibroids are present, as well as for LH deficiency. |
| Antiestrogens | Toremifene, Tamoxifen. | In the form of injections or tablets for a long time. | The uptake of estrogen by cell receptors is blocked and is prescribed to women after menopause. |
The choice of funds is based on impairments and age. Most often, treatment is associated with a decrease in estrogen production.
Non-hormonal agents
They can be taken together with hormonal drugs as part of complex therapy. Such means include:
- Mamoklam. Reduces the risk of malignant tumors, helps resolve cysts, and contains iodine. The course of treatment is 3 months. Dosage – 1-2 tablets before meals 3 times a day. It has contraindications, which include diseases of the thyroid gland, liver and kidneys, as well as skin.
- Indinol is a natural remedy based on cruciferous plant extract. Blocks the growth of atypical cells. Take 2 capsules per day for six months.
- Mammoleptin. Tones, reduces pain. Drink for 2-3 months.
- Wobenzym. Has immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects. Duration of treatment is 2-8 weeks. It is not recommended for those on hemodialysis and girls with blood diseases.
- Mastiol. Reduces the number of tumors, eliminates the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. Taken 3 times a day, dissolved 5 granules at a time. You should not drink if you have malignant tumors.
As can be seen from the list, non-hormonal drugs help not only fight tumors, but also eliminate symptoms.
Use of contraceptives
Treatment with OCs (oral contraceptives) is not always possible. It depends on the type of mastopathy, the girl’s hormonal background, as well as the presence or absence of other diseases. In addition to combating unwanted pregnancy, oral contraceptives have a number of therapeutic effects:
- Reduce the number of appearances of new formations.
- Reduce estrogen levels.
- The organs of the reproductive system are treated, which has a positive effect on the condition of the mammary glands.
If you take oral contraceptives for a year, the risk of developing mastopathy will decrease by 60-70%.
Young girls are most often prescribed the following drugs: “Jess”, “Midiana”, “Belara”, “Lindinet 20”, “Dimia”. Before using OK, you should definitely consult a doctor and undergo a hormone test. Contraceptives can be used only as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision; self-administration of medications is unacceptable.
Symptoms of mastodynia
Manifestations of cyclic mastodynia are:
- pain in the mammary glands;
- feeling of discomfort;
- enlargement of the mammary glands;
- increasing their sensitivity.
The most common manifestations of cyclic mastodynia are pain and discomfort.
Characteristics of pain:
by localization - in the mammary glands;
- by distribution - cover the entire mammary gland;
- by nature - pulling, pressing, aching, but can also be sharp, stabbing;
- in terms of severity - tolerable, but intensifies when touching the mammary gland;
- by occurrence - they appear a few days before menstruation and disappear literally within one day after the first spotting appears.
note
A characteristic symptom is “tight underwear” - the mammary gland, swelling, increases in size, so the underwear may seem tight, it squeezes the gland.
Increased tactile (touch) sensitivity is observed from:
- pacifier;
- areolas;
- skin of the mammary glands.
Unpleasant sensations appear simultaneously in both mammary glands. It is characteristic that if there is an additional lobe of the mammary gland, then a feeling of discomfort and pain also appears in it.
Signs of acyclic mastodynia may be:
pain;
- the presence of a tumor formation in tissues;
- nipple discharge;
- changes in the usual shape of the mammary gland;
- changes in the color and structure of her skin;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness and lethargy.
The characteristics of pain will be somewhat different than with cyclic mastodynia - they are:
- periodic or constant;
- of different severity;
- most often occur in one mammary gland.
False mastodynia is characterized by symptoms of damage to other organs:
- strengthening the tone of the back muscles;
- pain along the intercostal spaces due to disorders of the spine;
- changes in blood pressure and heart rate in heart disease
and so on.
Symptomatic picture of the disease
Clinical signs of pathological manifestation depend on what form of mastalgia is present, since each of them is characterized by symptomatic individuality.
| Type of mastodynia | Symptoms |
| Cyclic | Pain occurs most often in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. |
| Soreness is provoked by increased synthesis of estrogen and lack of progesterone. | |
| The nature of the pain syndrome is squeezing, aching or pulling. There is an increase in volume and swelling of the breast tissue, excessive tactile sensitivity of the nipples and breast. Unpleasant discomfort when trying to touch the bust. Soreness occurs simultaneously in both breasts. | |
| The cyclic type of mastalgia occurs in nulliparous women aged 20-40 years or they have had one birth. | |
| Acyclic | Not related to menstrual cycles. |
| Features: Pain with clear localization. Periodic pain, either always mild or burning, usually manifests itself in one breast. The breasts do not swell, and there is no increased sensitivity. There is discharge from the nipple and its redness. | |
| It is mainly diagnosed in patients over 40 years of age. | |
| False | Increased tone of the muscle tissues of the back. |
| Pain is felt in the intercostal area. Blood pressure surges. Heart rhythm disturbances due to heart failure. | |
| The patient's medical history includes pathologies of other organs. |
Diagnostics
The main task is to find out whether pain in the mammary glands occurs due to mastodynia or organic disorders of the glands. Therefore, in addition to the patient’s complaints and medical history, a broad examination of the patient using a whole range of instrumental and laboratory methods is important.
The physical examination is as follows:
- upon examination, the shape, contours, size, symmetry of the mammary glands, the condition of the skin, the presence or absence of discharge are assessed;
- by palpation (palpation) - the soreness and skin sensitivity of the mammary gland, the consistency of the tissues, the presence or absence of formations are determined.
In the instrumental diagnosis of mastodynia, the leading one is mammography - a set of methods for examining the mammary gland. The following methods are used:
- x-ray mammography – an x-ray is taken in two or three projections;
- ultrasound mammography – it allows you to assess the condition of breast tissue and identify hyperplastic changes (growths) in them;
- tomosynthesis – allows you to create two-dimensional images of the mammary gland and evaluate its internal structure;
- magnetic resonance (MRI) mammography – a technique for obtaining a tomographic image of the breast;
- optical mammography is the study of the condition of the gland using optical equipment.
In addition, the following are performed:
- biopsy – collection of breast tissue followed by examination under a microscope;
- radiothermometry of the mammary gland - determination of the temperature of its skin and tissues;
- computed tomography (CT) – computer slices help to obtain detailed information about the condition of the breast tissue;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - the goals and capabilities are the same as CT;
- electrical impedance mammography – study of electrical conductivity of breast tissue;
- scintigraphy - the patient is injected with pharmaceuticals containing radioisotopes that accumulate in the breast tissue and, when scanned with a tomograph, create a color image, from which a conclusion is made about the condition of the tissue.
Laboratory tests that are informative are:
cytological examination of the biopsy - it is examined under a microscope for the presence of atypical cells;
- cytological examination of nipple discharge - they are studied for the same purpose;
- determination of tumor marker CA 15-3 - its presence indicates malignant degeneration of breast tissue;
- study of the hormonal profile - determination of the amount of hormones estradiol, progesterone, free and bound testosterone, follicle-stimulating and luteotropic hormones, thyroid hormones.
It is also important to consult related specialists - a neurologist, cardiologist, vertebrologist and others. To clarify the diagnosis of pathologies that could lead to pain in the mammary glands, they will prescribe the necessary instrumental and laboratory research methods.
Features of treatment of mastopathy at different ages
All doctors must take into account the woman’s age before prescribing treatment. For example:
- Age 25-35 years. If there is no hormonal imbalance, then mostly homeopathic remedies + herbal remedies are prescribed. If there is a hormonal disorder, the mammologist prescribes treatment individually.
- Age 35 -45 years. The priority is herbal homeopathic medicines and oral contraceptives.
- Age over 45 years. This category of patients often gets sick as a result of hormonal disorders (menopause, obesity, diabetes). They are prescribed complex treatment.
Regardless of age, all women are prescribed a complex of vitamins, hepatoprotectors, and sedatives.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of mastodynia is often carried out with such diseases and pathological conditions as:
- fibrocystic mastopathy;
- various tumors – benign and malignant;
- mastitis – inflammatory lesion of the mammary glands;
- involutive changes – age-related withering of the mammary glands;
- extramammary lesions (diseases of other organs).
Causes of mastopathy
There are many reasons for the occurrence of mastopathy, among them:
- nervous disorders and stress; - high level of physical activity; — harmful effects of the environment on the body; - inflammatory processes; — diseases of the endocrine system; - complications after childbirth and abortion.
Treatment of mastopathy is carried out both using therapy (hormonal and non-hormonal agents) and surgery.
Diffuse mastopathy - when small cysts form throughout the mammary gland - is not subject to surgical intervention. Whereas nodular mastopathy can be cured only with the help of surgery.
Complications
Complications of physiological mastodynia as such are not observed; due to the pain syndrome, the following are possible:
increased fatigue;
- tearfulness;
- depressed mood;
- anxiety;
- cancerophobia is an obsessive fear of contracting cancer (can develop in women with a hypochondriacal type of reaction).
More significant are the complications that arose due to untimely detection and inadequate treatment of organic pathologies, against the background of which pain in the mammary glands arose. Such complications depend on the type of pathology - for example, for cancer it can be:
- cancer intoxication – poisoning of the body by products of decay and vital activity of cancer cells;
- cancer cachexia - depletion of the body
and many others.
Additional treatments
The treatment of mastopathy includes medicines from the homeopathic group. They help relieve swelling from the mammary gland, narrow the ducts, and also reduce the formation of the connective tissue component. List of funds:
- Mastodinon;
- Remens;
- Cyclodinone.
It is worth noting that to eliminate the symptoms described above, the drug Mastodinon is more effective. It has a wide spectrum of action, thereby helping to quickly cope with mastopathy. This is a fairly new drug, which, in addition to its main spectrum, also has a dopaminergic effect.
Now you know the main medications for the treatment of mastopathy. For prevention, doctors recommend undergoing timely medical examinations. In addition, prevention of mastopathy includes:
- Timely birth of a child. Please note that women over 26 years of age are considered old-age.
- Have an active sex life with one sexual partner. When changing partners, take precautions.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- Selecting the right underwear, in particular a bra.
- Perform self-massage of the mammary glands.
If you follow these simple rules, you can prevent the development of mastopathy.
Treatment of mastodynia
If it is determined that mastodynia is physiological, prescriptions are made aimed at eliminating or reducing the discomfort in the mammary glands that occurs due to changes in hormonal levels. Based on the appointments:
- hormonal drugs;
herbal medicines;
- sedatives (calming);
- analgesics (painkillers);
- diuretics (diuretics);
- vitamins;
- minerals;
- physiotherapeutic methods of treatment.
Hormonal drugs are prescribed:
- combined oral contraceptives;
- gestagens;
- antiestrogens;
- gonadotropin-releasing factor agonists.
Herbal medicines are effective for dyshormonal disorders, since many plants have an estrogen-like effect - these are:
- evening primrose;
- sage;
- oregano
and others.
Derivatives of these plants are also included in homeopathic preparations.
note
Herbal medicines are prescribed if a woman refuses hormone therapy.
Sedatives are indicated if manifestations of mastodynia are:
- significant mood swings;
- tendency to anxious and hypochondriacal reactions.
If the manifestations of such signs are insignificant, they are limited to the prescription of herbs with sedative properties (valerian, motherwort, peony) and their preparations.
Analgesics are prescribed for severe pain. In this case, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used, which have an analgesic effect.
Diuretics are prescribed because pain occurs due to fluid retention in the breast tissue. In this case they use:
- potassium-sparing diuretics with antiandrogenic properties;
- herbal preparations.
Vitamins and minerals are used in the form of complexes.
Of the physiotherapeutic methods in the treatment of mastodynia, the following have proven themselves well:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- galvanization;
- balneotherapy.
With acyclic mastodynia, the underlying disease is treated, which provoked the occurrence of pain in the mammary glands.
Disorders of a nervous or psychogenic nature that lead to mastodynia are treated not only with medications, but also by creating a favorable psychological background. So, if a woman likes to travel, she should immediately buy a plane ticket - very often such actions are more effective than any medication or other prescriptions.
Types of disease
Currently, cyclic and non-cyclic mastalgia are distinguished. Clarifying the nature of a woman’s pain syndrome is the basis for differential diagnosis, selection of adequate therapy and assessment of the prognosis of the disease.
Cyclic mastalgia
It is caused by the endocrine activity of the ovaries, is associated with the ovarian-menstrual cycle and is part of the structure of the so-called premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Therefore, it is typical only for patients of puberty and reproductive age. The natural decline of sexual function is accompanied by the disappearance of cyclic mastalgia. Removal of the ovaries or suppression of their activity while taking chemotherapy or radiation therapy also leads to the patient’s relief from endocrine mastodynia. If a woman experiences mastalgia for the first time during menopause, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination to exclude a tumor process.
The fact is that the mammary glands are hormonal-dependent organs. Moreover, they are “targets” primarily for sex hormones, the action of each of which has its own characteristics. Other endocrine glands (pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands) have indirect effects, influencing the activity of the ovaries.
Estrogens (hormones of the first phase of the ovarian cycle) provoke proliferative processes. Hyperestogenia is a risk factor for pathological cyst-like proliferation of milk duct tissue and hypertrophy of the mammary gland stroma. But progesterone produced in the second phase of the cycle acts mainly on glandular tissue. It helps to increase the number and size of alveoli, increase the number of its own receptors in the thickness of the mammary glands and increase their sensitivity.
In addition, progesterone affects the general water-mineral metabolism, causing fluid retention in the body. It is these effects that cause the development of PMS, one of the manifestations of which is chest pain.
The severity of cyclic mastalgia may differ in different cycles. This depends on the level and balance of sex hormones, prolactin, the presence of hypovitaminosis and deficiency of fatty acids in food.
Noncyclic mastalgia
It may be associated with local edema or mechanical pushing apart of tissues by a tumor, pathological nerve impulses, excessive irritation of receptors, impaired microcirculation and other factors.
It does not depend on the level of sex hormones and does not change during the ovarian-menstrual cycle.
Prevention
To prevent the development of pain in the mammary glands that occurs due to cyclical fluctuations in hormone levels, the following are recommended:
normalization of work, sleep, rest, nutrition;
- regular sex life;
- reduction of workloads – regardless of their current intensity;
- diet correction - reducing the consumption of salt and foods that can retain water in the body (smoked and pickled foods, fried foods, alcohol);
- prevention of gynecological diseases accompanied by hormonal changes, and if they have already occurred, their timely detection and treatment.
To prevent pain arising from non-hormonal disorders, as well as due to diseases of other organs, such disorders and diseases should be prevented, promptly identified and treated. It is also important to choose the right clothes - they should match your bust size.
Non-hormonal drugs for mastopathy
A feature of non-hormonal drugs for mastopathy is their plant base. Due to this, a gentle effect is ensured; medicines of this type do not have a large number of contraindications.
Treatment with drugs of this group can be carried out either as monotherapy or used in complex therapy. List of representatives of non-hormonal drugs for mastopathy of the mammary glands:
- Mastodinon;
- Cyclodinone;
- Mammoleptin;
- Wobenzym;
- Klamin.
Mastodinon helps reduce prolactin levels and prevents the growth of cystic and fibrous areas. It is one of the most effective homeopathic remedies. It is prescribed as a tablet twice a day. Positive dynamics are observed after 2 months of treatment.
Cyclodinone corrects the balance of hormones, normalizes the cycle and eliminates tension and heaviness in the chest. Take a tablet every day. Therapeutic course - 3 months.
Mulimen is the newest non-steroidal drug. The medicine normalizes hormone levels, has an anti-inflammatory effect and an antispasmodic effect. Used for the prevention of cancer.
Mammoleptin tones, eliminates signs of a diffuse inflammatory process, and has analgesic and anti-edematous effects. Available in capsules, the duration of treatment is from 2 to 3 months. It is prescribed in a dosage of 5 capsules, which are used three times a day.
Wobenzym is an enzyme preparation with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. Klamin is a dietary supplement, available in capsules. Contains kelp, iodine, calcium, potassium, enterosorbent.
Forecast
The prognosis for mastodynia depends on its form. With cyclic mastodynia, the prognosis is favorable; with acyclic and false mastodynia, it depends on the disease or pathological condition that provoked the development of pain in the mammary glands.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
4, total, today
( 40 votes, average: 4.25 out of 5)
Inflammation of the nipple: causes, symptoms, treatment
Discharge from the mammary glands: causes and diagnosis
Related Posts
Antibiotics
Drugs of this group are recommended in those episodes when an inflammatory process is observed during mastopathy, and the presence of a malignant neoplasm is suspected. Women are often interested in how many days to take an antibiotic? You need to be treated with antibiotics for at least five days.
Maxipim
The antibiotic is produced in powder form for injection intravenously or intramuscularly. Price – from 164 rubles.
Dosage: prescribed individually 1-2 times/day.
Contraindications:
- Individual immunity.
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
- Pregnancy.
- Kidney failure.
Movisar
Quite an effective antibiotic. Dosage form – powder for injections. Cost – from 178 rubles.
Dosage: IV 2 g every 12 hours; intramuscularly – 0.5-1 g.
Contraindications:
- Individual intolerance.
- Pregnancy.
- Chronic pathologies.
Ceftriaxone
Has a wide spectrum of action against bacteria. Ceftriaxone is available in solutions for injection. Price – from 25 rubles for 1 bottle.
Dosage: intramuscularly – 0.5 g, intravenously – 0.5 g 2 times/day.
Contraindications:
- Pregnancy.
- Pathologies of the kidneys and liver.
- Ulcerative colitis.
Types of mastodynia
When determining the type of mastalgia, the cyclical occurrence of pain and the reasons that led to the development of the pathology are taken into account. The choice of diagnostic technique and course of treatment depends on determining the type of disorder.
The following types of pathology are distinguished:
- Cyclic pathology develops every time in the second part of the monthly cycle.
- Acyclic, which is not associated with cyclic changes. Does not depend on menstruation.
- False, not associated with gland pathologies at all. It is more often caused by diseases of other organs.
Cyclic mastalgia
This type of pathology is also called functional or true.
It is observed on the days of ovulation, premenstrual syndrome, during dysplastic-type processes, after the use of oral contraceptives.
Soreness manifests itself in the second part of the cycle and is the cause of a physiological change in the level of estrogens and progesterones in the body.
Excess hormones retain fluid in the gland cells, activate substances that irritate nerve cells and cause discomfort and pain.
Also the causes of this type of pathology are:
- Benign dysplasia within glandular tissues.
- Violation of water-mineral balance.
- Long-term use of combined contraceptives.
Acyclic pathology
This type of mastalgia is also called symptomatic. This type of mastalgia is associated with various abnormalities of the mammary glands. Soreness occurs without apparent dependence on cyclical monthly changes.
She talks about abnormalities in the mammary gland after injury or surgical treatment, inflammation, the presence of tumors and other anomalies that disrupt the functioning of the glands. With this form of the disease, changes in the color of the skin around the nipples, general lethargy and migraine attacks are observed.
False mastalgia
This pathology is also called reflected, irradiating. It is not caused by dysfunctional changes in the chest, but by dysfunction of other organs. Often the disease occurs due to disorders in the spine and joint tissues, heart pathologies, myalgia, etc.
Comprehensive prevention
To avoid mastalgia and other gynecological diseases, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle. It is worth giving up bad habits. Moderate physical activity is recommended for women. Physical inactivity often leads to pathologies. You should avoid stress and take a good rest from work. Sleep must be sound. It is important to normalize your diet. It is recommended to limit fats, smoked foods, and sweets. Dishes should be moderately salty. Include in your diet foods that are rich in vitamins and valuable microelements. If the body receives enough iodine, magnesium and zinc, the organs function better and the immune system becomes stronger.
It is worth fighting excess weight. Vegetables and fruits are recommended for women who suffer from this problem. It is prohibited to over-salt dishes. The fact is that salt slows down the metabolism, which is why the mammary glands swell. Your lifestyle should be adjusted. It is necessary to fight excess weight, as it predisposes to mastalgia. Adipose tissue accumulates estrogen. If there is a lot of this hormone in the body, the mammary glands swell and pain appears.
Physical education is recommended. Sports exercises help normalize blood flow. They improve well-being during mastalgia and reduce the severity of pain. You need to take care of your liver. The health of other internal organs depends on its condition. It is not recommended to wear tight underwear. Sports bras with padded straps are ideal.
The patient should not self-medicate. Before using medications, you should consult your doctor. It is important to establish the exact cause of mastalgia. If the patient follows preventive measures and undergoes a timely examination by a mammologist, she will be able to avoid breast disease.
Mastalgia has a favorable prognosis. However, the cyclic form requires urgent treatment, otherwise malignancy occurs (tumor cells become malignant). Signs of mastalgia are pain in the mammary glands, swelling and redness of the skin. Proper treatment will help eliminate pain and other manifestations of a purely female disease.
Types of pain with mastalgia
Chest pain has different origins.
- Cyclic. It is associated with menstruation. Cyclic pain is usually dull but intense. A woman feels discomfort in the middle of her chest. Sometimes the discomfort radiates to the armpit area. Cyclical pain is often associated with hormone use.
- Acyclic pain. In this case, the discomfort is not related to menstruation. Acyclic pain is diagnosed in patients who have crossed the forty-year mark. Discomfort appears in the center of the chest. It differs in type, i.e. it can be constant or variable. Acyclic pain is usually sharp and one-sided. The factor is the presence of fibroadenoma. In some patients, acyclic pain is associated with a cyst.
- Pain syndrome with mastitis. Discomfort is accompanied by weakness, malaise, and fever. Mastitis, like other gynecological pathologies, requires treatment, otherwise mastalgia with chronic pain syndrome occurs.
- Malignant breast tumor. To detect breast cancer, differential diagnosis should be carried out. Without a comprehensive examination, the tumor can be mistaken for mastalgia. A malignant formation is characterized by pain in the upper part of the gland. The patient should examine the breasts herself, then consult a doctor. If a lump is detected, you must visit a gynecologist.
Mastalgia - what is it?
Mastalgia or mastodynia is a collective concept and is characterized by the occurrence of pain or discomfort in the mammary gland, which may be a sign of functional changes in the body or a symptom of diseases of the mammary glands. Quite often, the appearance of mastalgia negatively affects women’s daily activity, sex life and family relationships, causing anxiety and fear.
Symptoms of mastodynia are more often observed at a young age or before the onset of menopause. At the same time, discomfort in the mammary glands is observed before or during menstruation, during stress and neurosis, during hormonal disruptions and imbalances. Signs of mastodynia can also be observed in postmenopausal women; they are caused by the natural involution of the ovaries and a persistent decrease in their hormonal activity.
Discomfort and pain intensify against the background of stress, physical and mental stress, endocrinopathies and other pathological changes in the body.
Typically, this condition is characterized as recurring (cyclical) pain in both mammary glands in the form of nagging, dull, bursting pain before the onset of menstruation. Every tenth woman experiences cyclic mastalgia for 5–7 days (before and during menstruation). The pain goes away on its own and does not require treatment.
Non-cyclic pain occurs regardless of the period of the menstrual cycle in women from 30 to 50 years of age and is characterized by the appearance of severe painful sensations in one mammary gland or in a certain area thereof. Such mastalgia has a burning, acute nature and significantly intensifies and lengthens against the background of stress. The appearance of symptoms of acyclic mastodynia requires urgent consultation with a specialist and clarification of the reasons for its occurrence.
Products for internal use
For mastopathy, it is very useful to treat with juices. To do this, you need to take them daily for 1 month. It is worth noting that this drug has antitumor and immunomodulating effects. In addition, juices help cleanse the body and rejuvenate.
You can get rid of mastopathy using milk with dill seeds. To do this, you need to boil them together for 1 minute, and then leave for 2 hours. Take daily. A decoction of chestnut flowers helps get rid of discomfort, as well as swelling. To prepare you need to pour 8 tbsp. l. dried chestnut flowers 1 liter of water, boil, leave overnight in a warm place. Then drink the prepared decoction throughout the day.
A decoction of the root or herb red brush helps well. You can purchase a ready-made infusion of this plant. This folk remedy helps normalize hormonal levels, increase immunity, and also helps treat erosion, fibroids, and ovarian cysts.
Walnuts infused with alcohol help to cope well with the problem of septum. You need to take 15-20 drops of the product diluted with water daily. The course of treatment is 2 months.
Aloe juice has an antitumor effect, and also eliminates inflammation and heals skin rashes. Preparations with the addition of this drug have a stimulating effect on the immune system, which helps to eliminate the disease more quickly. To prepare a healing elixir, you need to cut off the leaves of a plant that is 2-5 years old, wrap them in a bag with holes and put them in the refrigerator for 2 weeks. Then grind them in a blender and squeeze out the juice through cheesecloth. Mix it with honey in a 1:2 ratio. Take 1 tsp for a month.
Description of the disease
Breast mastalgia is a general name for a number of pathologies characterized by pain and discomfort in one or both breasts.
These pains are symptoms of organ dysfunction. In some cases, pain is felt constantly, in others periodically, and sometimes the sensations arise spontaneously. Pain is accompanied by engorgement of the nipples and breasts around them, swelling of the surrounding tissues.
Mastalgia often has a negative impact on a woman’s daily well-being, her sex life and family relationships. This disease is most often observed in young women, or on the eve of menopause.
Discomfort is felt before or during menstruation, as well as with neuroses, stress, and hormonal imbalances. This disease has another name - mastodynia. It is diagnosed as an independent disease only when there are no other reasons for its occurrence.
Classification of mastopathy
When deciding how to treat mastopathy in women, the doctor must first find out what particular form of this pathology is present in this particular case. The fact is that the concept of “mastopathy” unites more than 50 different forms of this disease. To simplify diagnosis, it is customary to distinguish two clinical signs. According to the first, these diseases are divided into mastopathy with proliferation (growth of cellular tissue) and atypia and without this process. In the first case, the prognosis will be more serious, since the presence of atypical cells, of course, does not mean an oncological process, but makes its development quite possible.
According to another clinical sign, mastopathy is also divided into two groups:
- nodal;
- diffuse.
In turn, nodular mastopathy (they are distinguished by the presence of only one lump in the mammary gland) are divided into:
- fibroadenomas;
- cysts;
- intraductal papillomas;
- leaf-shaped fibroadenoma;
- lipoma;
- hamartoma.
In order to make it more clear how to treat diffuse mastopathy (it is characterized by the presence of multiple diffuse compactions), it is also classified according to the following criteria:
- adenosis - mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component;
- fibroadenosis - the fibrous component predominates;
- fibrocystic — the cystic component predominates;
- sclerosing adenosis;
- mixed mastopathy.
Vitamin therapy
If the course of the disease does not require surgical intervention, then there is nothing left to do but treat mastopathy at home. Moreover, in addition to the use of hormones, treatment should be comprehensive and aimed at restoring and maintaining the woman’s health. Vitamin therapy plays an important role in this. It is known that vitamin A helps restore normal functioning of the ovaries and thyroid gland. Vitamin C lowers cholesterol levels, activates the adrenal glands and corpus luteum, and enhances the synthesis of corticosteroids. B vitamins help normalize the activity of the nervous system. Depending on the woman’s condition, various courses of taking vitamins can be formulated. As a rule, the duration of their use is at least 5 months. An allergic reaction may be a contraindication.
Conservative therapy
Non-hormonal agents
Diet
Products containing methylxanthines contribute to swelling and tenderness of the mammary glands in women with mastopathy.
Many clinical studies on the treatment of mastopathy point to the fact that there is a close relationship between the appearance of structural changes in breast tissue and the consumption of products containing methylxanthines (theophylline, caffeine and theobromine). That is why avoiding foods with high levels of methylxanthines (coffee, cocoa, chocolate, tea, cola) can significantly reduce swelling and soreness of the mammary glands. Many experts always recommend such a diet correction when treating any form of mastopathy.
Nutrition and this disease of the mammary glands have another relationship. Eating food that contributes to the development of chronic constipation and disruption of intestinal microflora also contributes to the development of mastopathy and breast cancer. It is likely that this relationship is dictated by the reabsorption in the intestine of estrogens already excreted in bile. That is why experts recommend that their patients introduce more foods containing fiber into their daily diet and drink enough water (up to 2 liters per day).
The condition of the liver is also important for the normal functioning of the mammary glands, since estrogen is utilized in this organ. That is why patients with mastopathy are advised to exclude from their diet any foods that adversely affect the functions of this organ. These include alcoholic beverages, fried and fatty foods, and hepatotoxic substances. And to improve liver function, women are recommended to additionally take B vitamins and dietary supplements based on them.
Products recommended for mastopathy:
- fish (preferably sea);
- vegetable oils (linseed, olive, pumpkin, nut);
- low-fat meats;
- dairy products: sour cream, cottage cheese, milk, cheeses, goat milk;
- cereals: buckwheat, wheat, oatmeal, etc.;
- mushrooms;
- legumes;
- spinach;
- bell pepper;
- carrot;
- cabbage;
- beet;
- eggplant;
- zucchini;
- seaweed;
- nuts;
- fruits and berries.
Products not recommended for mastopathy:
- fatty meats;
- flour products;
- semolina;
- salty dishes;
- smoked meats;
- margarine;
- conservation;
- coffee;
- tea;
- mayonnaise;
- ketchup;
- carbonated drinks;
- alcoholic drinks.
Choosing the right bra
Every representative of the fair sex should pay attention to the correct choice of bra, especially for patients with mastopathy. Wearing it is recommended for all women with this disease of the mammary glands.
Wearing a bra that doesn't fit properly or is shaped incorrectly can lead to breast deformation and compression. In addition, such a piece of clothing contributes to overload of the ligamentous apparatus. This point especially applies to women with large and drooping breasts.
Basic recommendations when choosing a bra:
- the product must fully correspond to the required size;
- preference should be given to natural or hygroscopic fabric;
- it is better to refuse to choose models with foam rubber seal;
- the fabric should not fade;
- wear strapless products as rarely as possible;
- choose models with wide straps (especially for large bust sizes);
- after purchase, adjust the length of the straps;
- do not sleep in a bra;
- do not wear a bra for more than 12 hours a day.
In some cases, choosing the right bra helps reduce or completely eliminate the symptoms of mastopathy.
Lifestyle change
Women suffering from mastopathy should stop smoking.
Women suffering from mastopathy should make lifestyle changes:
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- balanced diet;
- sufficient physical activity;
- refusal to visit baths and saunas;
- eliminating stress;
- refusal of natural and artificial tanning.
In addition, physiotherapeutic procedures and massage are contraindicated for them.
Vitamins
Taking vitamin supplements for mastopathy:
- helps normalize metabolism and hormonal levels;
- has an antioxidant effect;
- strengthens the immune system;
- stabilizes the activity of the central nervous system;
- normalizes the functions of the thyroid gland, liver, ovaries and adrenal glands;
- normalizes the reproduction and maturation of epithelial cells.
For mastopathy, women are recommended to take vitamins A, E, C and group B (especially B6). The drugs should be prescribed only by a doctor, since their overdose can lead to toxic effects.
Diuretics
The manifestations of cyclic mastopathy, which occurs during premenstrual syndrome and is accompanied by swelling of the feet and hands a few days before menstruation, can be reduced with the help of light diuretics. It is advisable to use diuretic medicinal herbs or preparations based on them for this purpose. In addition, during this period, a woman needs to limit the amount of salt consumed.
Means to improve blood circulation
Patients with mastopathy often experience local changes in blood circulation in the mammary glands. They usually occur due to impaired venous outflow. To normalize it, many experts recommend that their patients take foods containing vitamin P (black currants, citrus fruits, raspberries, cherries, rose hips, chokeberries) and preparations based on it (Ascorutin). Often, their use helps stabilize blood circulation, and repeated thermographic studies do not reveal such disorders.
Homeopathic medicines
To eliminate hyperprolactinemia, normalize the condition of the mammary gland ducts and eliminate pathological division of endometrial cells, women may be recommended to take medications based on various medicinal plants (twig, cyclamen, tiger lily, iris and chilibuha). The most popular homeopathic remedy prescribed for mastopathy is the drug Mastodinon. In addition to this, the following remedies may be recommended:
- Biocycline;
- Remens;
- Cyclodinone, etc.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
In some cases, to reduce cyclic mastalgia, specialists prescribe their patients to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs a few days before menstruation. For this the following can be used:
- Diclofenac;
- Nurofen;
- Nise et al.
However, such prescriptions cannot be long-term and permanent, and comprehensive treatment of mastopathy is recommended to eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Means for normalizing liver function
Hepatoprotectors can be used to eliminate liver dysfunctions that affect hormonal levels and stabilize its functioning. A woman may be prescribed:
- Essentiale;
- Legalon;
- Gepabene;
- Karsil and other drugs.
Adaptogens and iodine preparations
To normalize the functioning of the intestines, liver, thyroid gland and immune system in case of mastopathy, various iodine-containing drugs and adaptogens may be recommended:
- Klamin;
- Rhodiola extract;
- tincture of eleutherococcus;
- Iodomarin;
- Iodine-active, etc.
Sedatives
Chronic fatigue and stress at work contribute to increased chest pain with mastopathy.
In women, the condition of the mammary glands is often influenced by the psycho-emotional background. Troubles in the family and at work, chronic fatigue, frequent depression, dissatisfaction with oneself - all these factors can contribute to increased pain. To eliminate them, experts often recommend that their patients take sedatives. Typically, preference is given to prescribing mild medications based on medicinal herbs:
- tincture of valerian, motherwort, peony;
- Persen;
- Alvogen Relax;
- Novo-passit;
- Sedariston;
- Dormiplant;
- Nervoflux et al.
Only if they are ineffective can patients be recommended stronger sedatives:
- Afobazole;
- Adaptol;
- Tenoten et al.
dietary supplements
To stabilize the menstrual cycle and hormonal levels, normal functioning of the immune system, liver and intestines, various dietary supplements can be recommended:
- Indinol;
- Mastofit Evalar;
- Stella;
- Kelp;
- Diures;
- Garcisan;
- Lecithin Choline;
- Brest Care+;
- Biozyme;
- Indogrin;
- Citrus pectin, etc.
The choice of dietary supplements should be made only by a doctor, who is guided by data on the patient’s health status obtained during the examination.
Hormone therapy
The processes of development of mammary gland tissue, their differentiation, maturation and growth are completely coordinated by the interaction of the following hormones:
- estrogen;
- progesterone;
- prolactin;
- androgens;
- a growth hormone;
- thyroxine, etc.
Metabolism and the activity of the reticular formation and limbic system have a certain influence on these processes. Many facts indicate the significant influence of hormonal levels on the development of mastopathy:
- the tissues of both glands undergo changes;
- the severity of symptoms depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle;
- pain decreases after menopause;
- mastopathy is often combined with other hormone-dependent diseases (uterine fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome, infertility);
- Taking hormonal drugs affects the condition of the mammary glands.
Based on the above facts, the following hormonal agents can be used to treat mastopathy:
- antiestrogens;
- oral contraceptives;
- androgens;
- gestagens;
- prolactin inhibitors;
- LHRH (or gonadotropin-releasing factor analogues).
Hormonal drugs can only be prescribed by a doctor who is guided by the results of the patient’s examination.
Antiestrogens
Antiestrogens such as Tamoxifen and Fareston can be used to block estrogen receptors in breast tissue. With hyperestrogenism, these drugs do not allow estrogens to bind to receptors and reduce their effect on gland tissue.
Antiestrogens have been used to treat mastopathy since the 70s. First, Tamoxifen was used, which was effective in 65-75% of cases. 2-3 months after taking it, patients noted a decrease in mastalgia (in 97% of cases), stabilization of the menstrual cycle and a significant decrease in blood loss during menstruation.
Sometimes at the beginning of treatment, patients noted increased sensations of breast swelling and pain, but over time these adverse reactions decreased. In addition to these side effects, taking Tamoxifen can cause dizziness, nausea, increased sweating and hot flashes.
A number of publications have reported that this drug can have a carcinogenic effect on endometrial tissue and lead to the development of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. That is why another anti-estrogen drug was created - Fareston (ORION PHARMA INTERNATIONAL, Finland). According to many experts, its active component Toremifene is more effective and has fewer adverse reactions. The first therapeutic effects from taking this drug appear within a month after the start of use, and side effects are observed much less frequently.
Oral contraceptives
This group of hormonal drugs is usually prescribed to women under 35 years of age. In addition to protecting against unwanted pregnancy, oral contraceptives help normalize the menstrual cycle and reduce the manifestations of mastopathy in the first 8 weeks after starting use. When properly prescribed, the drugs suppress ovulation, steroidogenesis, the synthesis of ovarian androgens and the synthesis of endometrial estrogen receptors. In some cases, when choosing an oral contraceptive incorrectly, the signs of mastopathy in women increase; in such situations, it is necessary to select another drug.
The following drugs can be used for treatment:
- Femoden;
- Marvelon (or Mercilon);
- Silest;
- Janine et al.
When choosing an oral contraceptive, preference is given to means in which the content of estrogens is the lowest and the content of gestagens is higher. The drugs are prescribed for at least 3 months. For the treatment of mastopathy, it is not recommended to prescribe mini-pill oral contraceptives, since the dose of hormones in them is extremely low to affect the woman’s disturbed hormonal levels.
Gestagens
These drugs help suppress estrogen production and slow down the gonadotropic function of the pituitary gland. According to statistics, they are effective in the treatment of mastopathy in 80% of cases. The drugs are prescribed in courses with breaks, the duration of which is determined by the doctor individually for each woman.
Previously, gestagens - testosterone derivatives - Danazol, Linestrinol and Norgestrel were used more often. However, now preference is usually given to progesterone derivatives - medroxyprogesterone acetate. In addition, a progesterone-based topical preparation such as Progestogel (gel) can be used to treat mastopathy. When using it, a woman does not have to experience the side effects that are observed when taking hormones orally.
Androgens
These drugs are estrogen antagonists and suppress their activity. Danazol is usually prescribed for the treatment of mastopathy, which reduces the synthesis of gonadotropic hormone. As a rule, the therapeutic effect is observed in 2 out of 3 women - the structure of the mammary gland becomes homogeneous, and the risk of cysts decreases.
The following side effects may occur when taking Danazol:
- nervousness;
- weight gain;
- swelling;
- amenorrhea;
- sweating;
- vaginitis, etc.
The doctor must warn the patient about their possible appearance. In addition, the woman should be informed that the contraceptive effect of the drug is very low and an unwanted pregnancy may occur while taking it without additional methods of contraception.
Prolactin inhibitors
Drugs in this group can only be prescribed for laboratory-proven prolactinemia. To obtain more accurate test results, it is recommended to administer a thyroid-stimulating hormone releasing factor (TRP test) before drawing blood.
With proven prolactinemia, patients with mastopathy can be prescribed the following prolactin inhibitors:
- Bromocriptine;
- Parlodel.
After taking them, prolactin synthesis decreases, the balance between progesterone and estrogen is normalized, the menstrual cycle is stabilized, mastalgia and nodular formations in the glandular tissues are reduced.
Gonadotropin-releasing factor (or LHRH) analogues
Taking these drugs is usually recommended for severe mastopathy and the ineffectiveness of other hormonal drugs. These drugs help reduce estrogen and testosterone levels. However, LHRH drugs have a large number of side effects such as hot flashes, amenorrhea, dizziness and hypertension. That is why their prescription should always be balanced and focused on a specific clinical situation.
Causes of pathology
Mastodynia occurs during a period of changes in the body, as well as with various diseases of the reproductive organs and glands. In most women of reproductive age, the pathology is not associated with pathological changes, but refers to hormonal disorders. The appearance of mastalgia can lead to:
- Ovulation, which acts on the mammary gland through sex hormones and cyclic changes.
- Puberty, condition after abortion, miscarriage or childbirth.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland, liver or kidneys.
- The presence of fibroadenomas, cysts, and other neoplasms in the breast.
- Hormonal disorders, which are a sign of impaired hormone secretion due to ovarian disease or endocrinopathy.
- Taking oral contraceptives. In this case, it is a temporary side effect.
- Lack of essential acids in the body.
- Abuse of certain foods, such as chocolate, drinks containing coffee or tea.
- Mammary cancer.
Pain is possible with large glands, the use of uncomfortable underwear, and bruises. Pain can be a sign of inflammation and neoplastic pathology of the glands, for example, mastitis or other benign tumor growths, adenosis. Painful sensations radiate to the chest, radiating with osteochondrosis, neuralgia, myalgia, and other diseases.
Breast mastodynia: symptoms and treatment
Most women of childbearing age are familiar with the condition known as mastodynia of the mammary gland. Perhaps the condition itself is unknown, but every second woman has definitely experienced the sensation. Mastodynia is not a disease in the strict sense of the word; rather, it is a transient condition that appears in women who have a menstrual cycle. Although it is not a disease, the condition can be so unpleasant and painful that it causes serious harm to a woman's mental and physical health, affects her mood, performance and behavior, and contributes to the development of chronic stress.
Treatment tactics
In simple cases, in the absence of dangerous diseases, the following methods of combating cyclic pain can be used:
- vitamin therapy taking into account the cycle (taking B vitamins in phase 1, vitamins E and C in phase 2 of the menstrual cycle);
- fluid restriction a week before menstruation (elimination of tissue swelling).
Against the background of mastopathy, the following medical recommendations should be used:
- use of oral contraception (correction of dishormonal state);
- targeted therapy with transdermal gel (direct injection of the drug into the mammary gland);
- a course of taking plant-based tablets that can correct the balance of hormones.
According to indications, the doctor may refer you for a consultation with a neurologist, cardiologist, pulmonologist and therapist to exclude extramammary causes of mastalgia.
It is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of breast cancer due to pain. Mastodynia is extremely rarely the first symptom of a tumor, but even the detection of any form of mastopathy requires timely therapeutic and diagnostic measures. It is especially important to identify precancer – fibroadenomatosis of the mammary gland – in time. Mastalgia is a symptom that should prompt a woman to visit a doctor: early detected pathology can be cured without dangerous consequences for health and life.
Similar texts:
- BI-RADS scale: diagnosis of breast pathology
- Synchronous breast cancer - features of the disease
- Breast self-examination – breast cancer screening
- The first signs of breast cancer - 5 symptoms
Non-drug treatment
In addition to the listed drug interventions, in most cases it is necessary to prescribe drugs that stimulate the body's defenses. These can be various tinctures (ginseng, eleutherococcus). In addition, diet plays an important role in answering the question of how mastopathy is treated. It is better to exclude chocolate, coffee, cocoa from the diet, and reduce fat consumption. It is recommended to consume more vegetables and fruits, plant fiber, and bran. Another important link in the question of how to treat mastopathy at home is lifestyle. In order for the treatment to bear fruit, a woman needs to reconsider her habits in many ways. Despite the well-worn phrases about the need to lose excess weight, give up alcohol and smoking, and increase physical activity, all these factors play a huge role both in the development of mastopathy and in its treatment.
Diagnostic measures
The main goal of diagnostic measures in case of suspected mastalgia is to exclude organic causes of pain syndromes in the glands. In this case, a complete instrumental and laboratory examination is prescribed, which allows identifying abnormalities in the mammary glands. For examination use:
- Palpating the breast by a doctor and interviewing the patient. They are carried out during the initial visit to the doctor. The gynecologist must find out what other signs the patient feels that preceded the appearance of mastalgia. The size of the nipples, the boundaries of the site of inflammation are measured, the skin and its structure are examined.
- Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the structure of the glands, see tumor formations, clarify their parameters, and determine the condition of the lymph nodes.
- Mammography can detect even small tumor formations.
- Cytological examination of fluid secreted from the nipples, biopsy specimen. This study determines the level of the marker CA-15-3 for oncology.
- Puncture biopsy when tumor growths are detected.
- If there is discharge from the nipples, swabs are taken.
If appropriate equipment is available, microwave radiometry is used. Sometimes CT, MRI and other diagnostic methods are performed.
Products for external use
Treatment of mastopathy with folk remedies can be quite effective. Recipes are mainly intended for external use. Special compresses help well, using such means as:
- burdock and coltsfoot;
- beet;
- cabbage;
- iodine;
- propolis;
- salt;
- pumpkin;
- essential oils.
At night you need to apply burdock leaf and coltsfoot leaves. In the morning, wipe your chest and lubricate it with burdock oil. This folk remedy produces an antitumor effect and eliminates pain.
For mastopathy, you need to grate fresh beets on a fine grater and mix them with honey. Then place it on a cabbage leaf and apply it to the sore chest overnight. The course of therapy is 10-20 cycles. You can make compresses from the grated pulp at night. Literally after 3 days the swelling should decrease and the pain should go away.
A cabbage leaf compress for mastopathy is considered a good remedy, as this vegetable helps cope with swelling, eliminate pain and has an antitumor effect. To prepare a compress, you need to mix yogurt with finely chopped cabbage. For fixation, it is advisable to use natural fabric onto which the medicinal product is applied. You need to keep the compress overnight. Treatment procedures must be continued for 20 days.
Cabbage leaves are often used in their pure form. It needs to be washed thoroughly, large veins removed, then beaten a little with a wooden hammer. This remedy is considered the best folk recipe. You need to change the cabbage leaf as it dries out.
Treatment of mastopathy is carried out with the use of iodine, since the effectiveness of this remedy for fibrous and tumor formations has long been proven. It helps restore and regulate the function of the thyroid gland, which is responsible for the production of hormones. It is worth remembering that it can only be used with the permission of a doctor.
Salt compresses help quickly relieve pain and eliminate lumps in the mammary gland. To do this, you need to dissolve 3 tbsp in 1 liter of water. l. salt. Dampen the cloth, wring it out and apply the bandage overnight.
Propolis applications help quickly cure the disease, but they should only be used if you are not allergic to this product. To prepare the ointment, you need to mix 30 g of crushed propolis with 100 g of lard. Place the prepared product in a water bath for 2 hours and then strain. Apply in the morning after sleep.
How to make a diagnosis
If you experience chest pain, you should first analyze your condition. Remember physical activity, stress, medications and other factors that could change how you feel. Pregnancy should be excluded. To do this, you need to do a test or take a blood test for hCG. In order not to miss the onset of irreversible processes in the breast, it is recommended to conduct a monthly self-examination. It is difficult to establish the cause of mastodynia, but you can notice deviations from the norm in the shape and structure of the mammary glands, and detect tumor-like formations. In these cases, as well as if you have complaints of pain, you should consult a doctor.
Self-examination
Palpation should begin immediately after the end of menstruation or within 12 days after it. It is the first phase of the cycle that is most informative for diagnosing pathological processes in the breast. It is better to carry out the procedure in front of a mirror to check for:
- changes in the structure or color of the skin of the breast;
- the appearance of asymmetry;
- changes in the armpits (can be in a lying position).
You should mentally divide the mammary gland into four quadrants and examine each, separately - the periareolar region. Then place your right and left hands behind your head alternately and repeat the study. It is ideal to add examination in the supine position.
Analyzes and instrumental studies
If you have complaints regarding the mammary glands, you should consult a mammologist. He will collect anamnesis, clarify concomitant diseases and will be able to suggest the cause of the disorders. The doctor will conduct a careful examination and palpation of the breast. For an accurate diagnosis, the following studies are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the glands - for women under 45 years of age;
- mammography - for women during menopause;
- biopsy - if focal compactions are detected;
- blood test for CA-15.3 is a tumor marker and increases in malignant breast diseases;
- consultation with specialists - if you suspect other diseases with “mirror” chest pain, it is especially important to “be healthy” in the gynecological part, since inflammation of the pelvic organs often causes reactive chest pain.
There is no point in testing blood for sex hormones. It is important to examine the thyroid gland and, if necessary, correct its function. CT or MRI is rarely recommended. Depending on the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed or the issue of surgical intervention with subsequent therapy is decided.
How to make a diagnosis
You need to know that the diagnosis “mastalgia” or “mastodynia” is not in any medical reference book or in the ICD-10 classification. This ailment refers to specific conditions that can be associated with a number of different functional states of the female body or the development of diseases and disorders:
- menstrual cycle;
- taking medications;
- disorders in the endocrine system;
- gynecological diseases;
- mastopathy or mastitis;
- neoplasms of the mammary gland;
- congenital defects;
- postoperative complications and injuries.
Therefore, the diagnosis of mastalgia includes a complex of different methods that determine the true cause of pain in the mammary gland.
The main methods of examination for mastodynia include:
- Collection of complaints and medical history:
- duration, frequency, intensity of mastodynia;
- nature of pain;
- presence of additional symptoms.
- Examination and palpation of the mammary glands:
- sizing;
- changes in shape and nipple;
- changes in skin color and structure;
- the presence of pathological discharge from the nipple;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- determining the area of inflammation or mass formation in the breast.
- Consultations with specialized specialists (gynecologist, endocrinologist);
- Laboratory examinations (blood and urine tests, biochemical blood tests, hormone tests);
- Ultrasound examination of the mammary glands and axillary lymph nodes;
- Mammography, electrical impedance mammography;
- Ultrasound-guided puncture or fine-needle aspiration biopsy;
- Microwave radiothermometry;
- Core needle biopsy, histological and cytological examination of the biopsy specimen.