The danger to humans is that ticks can carry pathogens of various diseases, for example, the tick-borne encephalitis virus. A person can encounter ticks everywhere (at the dacha, in the garden, in a park in the city, in the forest). Diseases transmitted by these organisms are called transmissible. Most often, arachnids bite humans in the spring and summer seasons. At this time their activity is highest.
What does a tick bite look like and what symptoms may appear when a person is infected with vector-borne diseases?
General information about ticks
Ticks are characterized by seasonality. The first cases of attacks are recorded in early spring, when the air temperature rises above 00 C, and the last cases - in the fall. Peak bites occur from April to July.
Bloodsuckers do not like bright sun and wind, so they lie in wait for their prey in damp, not too shady places, in thick grass and bushes. Most often found in ravines, on the edges of forests, along the edges of paths or in parks. Having sensed the victim, the tick raises its front legs and actively moves them, trying to catch on clothing. He does this very deftly, helped by suction cups and hooks located on the front limbs. During the bite, the parasites inject an anesthetic substance, like mosquitoes, so the suction goes unnoticed. Favorite places to bite are the neck, the area behind the ears, armpits, groin area, and elbow creases.
Attention. Not all ticks carry diseases. But even sterile parasites, and there are 85–90% of them, can cause allergic reactions.
Males of the bloodsucker need an hour to fully saturate, while females need several days. The parasites are not picky when choosing a hunting object; they bite everyone who gets in their way - birds, small and large animals, humans.
How a tick bites
The structure of the oral apparatus allows the tick to attach deeply and firmly to the skin without causing pain to the victim, so a person often discovers a parasite on his body only the next day or several days later, or even does not notice either the bite or the parasite at all.
Female mites can remain on the skin from several hours to a week, and males are able to attach for a short time, making small bites. Therefore, for example, if a person saw a tick not attached to his skin, but simply a crawling one, there is a high probability that the tick nevertheless inflicted a bite.
Tick attack and bite
The tick gnaws through the skin using a hypostome (oral apparatus) dotted with growths along the edges facing backwards. This structure of the organ helps the bloodsucker to remain firmly in the tissues of the host.
If the tick is a carrier of encephalitis, the pathogen is concentrated in the salivary glands of the bloodsucker and enters the victim’s body at the time of the bite. Therefore, even immediate removal of the attached parasite does not reduce the risk of infection. In the case of Lyme disease, the virus accumulates in the tick's gastrointestinal tract and enters the body when it begins to feed, that is, 5-6 hours after sucking. In this case, early removal of the parasite can prevent infection.
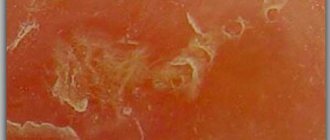
Redness of the skin at the site of the bite does not indicate infection. The color change may appear due to allergies or the presence of the parasite in the victim’s body for many hours. The body's reaction to a tick bite can be seen in the photo. If such symptoms appear, it is better to consult a doctor.
With borreliosis, a tick bite looks like focal erythema up to 20–50 cm in diameter. The shape of the inflammation is most often regular, with an outer border of bright red color. After a day, the center of the erythema turns pale and acquires a bluish tint, a crust appears and soon the bite site is scarred. After 10–14 days, no trace remains of the lesion.
Symptoms of borreliosis
If a tick carrier of borreliosis is bitten, the bite site takes on the appearance of specific erythema, which gradually increases to 10-20 cm, and sometimes up to 60 cm in diameter. The erythema patch may be round, oval, or irregular in shape. The victim may experience burning, itching and pain at the site of the bite, but more often the first signs are limited to erythema alone.
After some time, a border of rich red color forms along the contour of the spot, while the border itself looks slightly swollen. In the center, the erythema becomes pale white or bluish. After a few days, a crust and scar forms in the area of the bite, which disappear without a trace after about 2 weeks.
The incubation period before the first symptoms appear ranges from several days to 2 weeks. Then comes the first stage of the disease, which lasts from 3 to 30 days. During this period, the patient experiences muscle aches, headache, weakness, fatigue, sore throat, runny nose, stiff neck muscles, and nausea. Then, for some time, the disease can go into a latent form for up to several months, during which the heart and joints are affected.
Unfortunately, erythema is often mistaken for a local allergic reaction, without giving it much significance. And malaise during the first stage of the disease is attributed to a cold or overwork at work. The disease passes into a latent form, and openly declares itself after a few months, when serious damage to the body has already been done.
Signs of a tick bite
Most often, an attached parasite is not noticed immediately. Several hours pass before the victim begins to feel unwell and decides to examine himself. The first symptoms of a tick bite in a person are as follows:
- there is weakness, a desire to lie down;
- chills and fever occur, possibly an increase in temperature;
- photophobia appears.
The dynamics of the signs depends on the number of attached parasites and the characteristics of the victim’s body. The symptoms of a bite are especially pronounced in the elderly, children and those suffering from allergic reactions or immunodeficiency pathologies.
Attention. In people of this group, symptoms may be supplemented by low blood pressure, increased heart rate, itching, headache and enlargement of nearby lymph nodes.
In rare cases, difficulty breathing and hallucinations may occur.
Temperature after a bite as a symptom of the disease
An increase in body temperature in the first hours after a tick bite most often does not indicate anything serious. This is how an allergic reaction to the bloodsucker’s saliva manifests itself. You should be wary if fever appears a few days after the parasite has been ingested. This reaction of the body may indicate the onset of the disease.
Each infection caused by a bloodsucker bite has its own characteristics:
- With tick-borne encephalitis, relapsing fever appears. The first rise in temperature is recorded 2–3 days after the bite. After two days everything returns to normal. In some cases, a repeated increase in temperature is observed on days 9–10.
- Borreliosis is characterized by fever in the middle of the disease, which is accompanied by other symptoms of infection.
- With monocytic ehrlichiosis, the temperature rises 10-14 days after the tick bite and lasts about 3 weeks.
Almost all diseases transmitted by bloodsuckers are accompanied by fever.
What does a tick bite look like on a person?
A tick bite on a person (see photo) can often manifest itself in different ways. What does a tick bite look like in its usual manifestation? The most harmless manifestation is a slight redness around the place where the arthropod was found or a complete absence of marks on the skin, except for a small hole in the place where the proboscis was located.
The bite site may become slightly inflamed. An allergic reaction may also occur, provoked by saliva and existing microtrauma of the skin. A tick bite in a person can also lead to more dangerous skin reactions.
It is quite easy to recognize the location of a tick bite in a person infected with borreliosis. The area around the bite resembles erythema. The spot can increase in diameter to an average of 15-20 cm. Sometimes the red spot can reach 60 cm, covering not only the bite site, but also a significant part of the body. The spot in this case can have any shape. A characteristic sign of a tick bite that has suffered from borreliosis is the appearance of a distinct bloody border around the spot on the skin. In this case, the entire central part of the spot acquires a whitish or unhealthy, bluish color.
In addition to an allergic reaction, parasites can infect humans with dangerous illnesses. In most cases, the consequences of a tick bite are unpredictable. Not all parasites are carriers of dangerous pathologies. The sooner the bloodsucker is removed, the lower the risk of infection with various pathologies.
Rules of conduct when bitten by a tick
So, what to do if you are bitten by a tick? First of all, it is necessary to remove the bloodsucker as soon as possible. This should be done slowly and carefully so as not to damage it or cause infection. Do not use gasoline, nail polish or other chemicals. Vegetable oil or fat will not help either. It is better to use effective and practice-tested methods.
Removing a tick with a thread
The method is simple, but requires a lot of dexterity and patience. It will be useful when extracting large specimens. For the procedure to be successful, it is recommended to perform the following steps:
- Take a long and strong thread
- Tie a loop at the border between the skin and the body of the parasite and carefully tighten it.
- Using rotating, rocking and pulling movements counterclockwise, slowly remove the tick.
Removing the tick with a thread
The removed bloodsucker must be placed in a glass container with a tight lid and taken to the laboratory for research.
Removing a tick using tweezers
Another simple way to get rid of a tick. Using tweezers you can remove a bloodsucker of any size. The basic manipulations are similar to the thread pulling option. It is better to use tweezers with flat edges, grabbing the parasite at the very base. Then, using careful rotational movements, remove the tick and disinfect the wound.
Proper tick removal with tweezers
Attention. When removing the bloodsucker, tweezers must be held strictly parallel or perpendicular to the skin.
Tick twisters
Not long ago, the pharmaceutical industry began producing special devices for removing the parasite. The kit includes two tools - a large one and a small one for pliers of different sizes. Using a twister, you can quickly and effectively remove the parasite without damaging it.
Tick removers are very effective
The kit includes a test tube into which it is recommended to place a live parasite and store it in the refrigerator for further research.
Other ways to remove ticks
If there are no devices nearby when a tick bites you, you can try to pull the parasite out with your hands. The method is risky, but if you do everything correctly, the result will be good. In this case, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Wrap your fingers in a handkerchief or gauze to make it easier to hold the tick.
- Grab it at the very border with the skin and pull it out with smooth twisting movements.
- Disinfect the wound or rinse with water.
If for some reason the tick cannot be preserved for analysis, it should be destroyed by pouring boiling water over it or burning it over a fire.
You can often hear advice from “experienced” people on how to remove a bloodsucker using oil. Despite its apparent simplicity, the method is not only useless, but rather harmful. The parasite, sensing a threat to life, will relax its proboscis and regurgitate the contents of the stomach along with the pathogens back. At the same time, the risk of infection will increase sharply.
Attention. If you cannot remove the bloodsucker yourself, you must go to the nearest emergency room.
Medical workers will provide first aid in case of a tick bite: they will professionally remove it and send it for examination, they will disinfect the wound and tell you what to do next. The doctor will definitely inform you what symptoms you should pay attention to in the next month.
What should I do if bitten by a tick?
Since the likelihood of contracting dangerous infections increases significantly with prolonged contact of the human body with a tick, the main thing that needs to be done is to remove the arthropod. But the removal procedure should be carried out correctly so as not to crush or damage the tick, since this can further contribute to infection. In addition, the tick can and even should be examined in the laboratory for the fact of infectiousness, and for this it must remain intact.
Therefore, if you do not have the skills to remove ticks, but there is a possibility, it is better to contact the nearest medical institution, where they will expertly remove the arthropod and give recommendations on further actions. In addition, you can ask all your questions regarding tactics of behavior in the presence of a tick on the body by calling 103 (by calling an ambulance).
What to do after removing a tick?
In people predisposed to allergies, a tick bite can cause a strong response in the body. Facial swelling often develops, difficulty breathing and muscle pain appear. In this case it is necessary:
- give the victim an antihistamine: Suprastin, Claritin, Zyrtec;
- provide access to fresh air, unbutton clothes;
- Call an ambulance.
All other diagnostic and treatment measures are carried out only in a hospital setting.
It is recommended that ticks be tested for diseases as soon as possible.
Advice. A live parasite can be stored in the refrigerator for no longer than a day, and moved at normal air temperature. If crushed during removal, it is better to put it in ice.
You can submit a tick for analysis to the SES, the Rospotrebnadzor center or a serological laboratory at a medical institution. You can find out the addresses and telephone numbers of parasite collection points at the reception of the city clinic. Analyzes are carried out for a fee, the price of research depends on the region.
If the tick could not be kept alive, for early diagnosis of the disease it is recommended to donate blood to detect immunoglobulins for infections. The analysis is carried out quickly, the result is usually ready within 5-6 hours. If you have been vaccinated, you must indicate the date when donating blood. The presence of vaccine antibodies may confuse health care providers.
What to do?
What should I do if bitten by a tick? It must be removed as quickly as possible. The longer he sucks blood, the greater the likelihood of infection.
It is best to remove the parasite in the emergency room and then send it to the laboratory for testing to prevent the development of dangerous consequences.
If you notice a parasite on the body that has not yet attached itself, then carefully remove it with tweezers or fingers, do not crush it on the body.
How to delete?
You can remove a tick yourself only if you have an antiseptic on hand to treat the bite site.
Under no circumstances should you crush the blood-sucking animal, otherwise infection will get into the wound.
First aid for a tick bite can be of several types:
- Removal using conventional tweezers, fork-shaped tweezers or surgical forceps. The individual must be clamped between the teeth in the area of the proboscis and gently twisted, but not pulled. If you jerk sharply, the head will remain in the skin, in which case the risk of infection increases.
- With a thread. It is necessary to grab the tick in a loop closer to the proboscis and slowly pull it perpendicular to the skin.
If there are no special tools or other available means, you can remove the tick with your fingers. It is necessary to grasp the body firmly and gradually twist it.
The parasite is removed in a counterclockwise direction.
How to treat a wound and what to take?
Antiseptic treatment is a mandatory preventive measure against infection. Suitable antiseptics:
- 5% iodine;
- alcohol;
- brilliant green;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- antibacterial solution (crush an antibiotic tablet and dissolve in boiled water);
- antibacterial ointment, for example, Tetracycline or Erythromycin.
If these products are not available, even perfume or cologne will do. You need to treat the bite site itself and the skin around it.
After removing the tick, to prevent infection, your hands should be washed with soap and then treated with antiseptic.
On average, a wound after a tick bite takes 1-2 weeks to heal. To quickly heal the wound, you can use Fenistil or Diclofenac.
Within 2-3 hours after a tick bite, allergy sufferers may develop a severe allergic reaction, so you need to take an antihistamine, for example, Suprastin.
To prevent infection, you can use Anaferon. It is approved for use in children from 1 month of age. Treatment 21 days.
Where can I submit a tick for analysis?
After removing the tick, place it in a damp cloth and place it in a glass jar. It must be delivered to any independent laboratory as quickly as possible (no later than 48 hours).
One in 10 individuals is a carrier of dangerous diseases, in particular tick-borne encephalitis.
Information about such laboratories is on the official website of Rospotrebnadzor. You can call the emergency room first, they will tell you where to check for ticks. Analysis is paid.
Which doctor should I contact for help?
To remove the parasite, you need to go to the emergency room or the surgeon on duty. Next, the person may be referred to an infectious disease specialist.
The consequences of a tick bite on a person are dangerous not only to health, but also to life, especially if the parasite has bitten a child. To prevent infection, immunoglobulin is administered for 96 hours.
What not to do?
What not to do at home after a tick bite:
- remove the tick using kerosene, melted wax or sunflower tick oil, it will die and remain in the body;
- pull on the abdomen or sharply pull out;
- crush;
- unscrew clockwise;
- remove without antiseptic treatment.
If a child is bitten, the baby must be shown to a doctor.
Diseases caused by tick bites
So, why is a tick bite dangerous for humans? Infections carried by bloodsuckers can be microbial, viral, rickettsial or protozoal in nature. All of them cause serious illnesses, often resulting in disability and, in rare cases, death. The cause of irreparable disorders in the body is late detection of the parasite and untimely therapy.
Encephalitis and borreliosis are the most common diseases caused by a tick bite
For Russia, the most significant diseases from tick bites are tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme borreliosis and zoonotic infections. Let's look at them in a little more detail.
Tick-borne encephalitis
The main carrier of this disease is the ixodid tick. In the wild, the pathogen circulates between bloodsuckers and small animals, usually rodents and birds. In areas developed by humans, livestock—cows and goats—become an additional reservoir. The causative agent of tick-borne encephalitis persists in parasites for a long time and passes to the offspring through eggs.
Attention. The virus is transmitted through a tick bite. Transmission of the pathogen through the alimentary route is often recorded - through infected cow's or goat's milk that has not been boiled.
Asymptomatic disease is very common and can reach 85–90% in some areas. Prolonged blood sucking significantly increases the risk of developing pronounced forms of pathology. The virus tolerates low temperatures well, but dies fairly quickly when heated to 80 °C.
Infection with tick-borne encephalitis is seasonal. The first peak of the disease occurs in May-June, the second is recorded in August - early September.
During a bite, the pathogen immediately enters the human blood through the salivary glands of the tick, where it is found in the greatest concentration. After a few hours, the virus penetrates the victim’s central nervous system, and after 2 days it can be detected in brain tissue. The incubation period for encephalitis from a tick bite is 14–21 days, and when infected through milk - no more than a week.
Symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis
The majority of victims have an asymptomatic form of infection, and only 5% have a pronounced form of infection. Tick-borne encephalitis most often begins suddenly with the following symptoms:
- increased body temperature to 39-40 °C;
- Strong headache;
- sleep disturbance;
- nausea leading to vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- redness of the skin of the face and upper body;
- weakness, decreased performance.
Such symptoms are characteristic of the febrile form of the disease, which disappears after 5 days. There is no damage to the central nervous system in this case.
Symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis - this is what a person who gets sick after a tick bite looks like
Meningeal and meningoencephalitic forms of pathology are much more severe. The patient complains of lethargy, apathy and drowsiness. Hallucinations, delirium, impaired consciousness, and convulsions similar to epileptic seizures appear. The meningoencephalitic form can be fatal, which is very rare in recent years.
Periodic muscle twitching indicates damage to the peripheral nerves. A polyradiculoneuritic form of encephalitis develops, in which general sensitivity is impaired. With the polioencephalomyelitis form of the disease, paresis of the arms and legs is observed.
Lyme disease (Lyme borreliosis)
Borreliosis is common in the northern regions of Russia. The pathogen enters the human bloodstream when bitten by ixodid ticks and can persist in the body for years. The first symptoms of the disease include:
- headache;
- temperature rise to 38-39 °C;
- fatigue, weakness and apathy.
1–3 weeks after a tick bite, a thickening and ring erythema appear at the site of suction, which can reach 20–50 cm in diameter.
Circular erythema is the main symptom of borreliosis
Attention. Despite the fact that a few weeks after the bite the red spot disappears without a trace, it is necessary to test for the presence of the causative agent of Lyme borreliosis, since the disease has serious complications and can be transmitted from a pregnant woman to a child.
Often the central nervous system, heart, muscles and ligaments, joints and organs of vision are involved in the pathological process. Late diagnosis and untimely therapy can lead to chronic borreliosis, which often ends in disability.
Ehrlichiosis
The disease is also transmitted by ixodid ticks. Deer are considered the main reservoir of Ehrlichia, with dogs and horses serving as intermediate reservoirs.
The virus enters the human body during a bite through the parasite's saliva. The incubation period can be up to 3 weeks, and the acute form of the disease lasts 14–21 days. In some cases, the pronounced phase drags on for up to 6–8 weeks.
Ehrlichiosis can be asymptomatic or clinically pronounced, even fatal. Common signs of the disease include:
- fever;
- increased sweating;
- weakness, drowsiness;
- nausea to the point of vomiting;
- rigor.
In the acute phase of ehrlichiosis, anemia and a decrease in the level of platelets and leukocytes in the blood are observed.
Relapsing tick-borne typhus
The infection is usually recorded in southern Russia, Armenia, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Georgia and Kyrgyzstan. The disease always occurs suddenly and begins with a vesicle at the site of the tick bite. Then other symptoms are added to the skin manifestations:
- fever;
- increased body temperature;
- aching joints;
- nausea and vomiting;
- headache.
Gradually, the bubble becomes bright red, a pronounced rash appears on the patient’s body, the liver enlarges, the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow.
Tick-borne typhus rash
The disease is wavy in nature. The acute phase usually lasts from 3 to 5 days, then the victim’s condition returns to normal and the temperature drops. A few days later everything repeats again. There can be many such attacks. Each subsequent one occurs with less severity.
Coxiellosis
It is one of the most common zoonotic infections in the world. The disease can be transmitted by both farm and wild animals. One of the distributors of the pathogen is the tick, most often the ixodid tick. It is capable of maintaining rickettsiae in the body for a long time and transmitting them to offspring. The first symptoms appear 5–30 days after the tick bite:
- increased sweating;
- elevated temperature;
- dry, exhausting cough;
- loss of appetite;
- redness of the face and upper body;
- migraines, weakness and drowsiness.
KU fever is often accompanied by pneumonia, pain in the lower back and muscles. The temperature in the first days of the disease can change several times during the day. This disease can only be treated in a hospital setting; it responds well to therapy and recovery occurs quickly. Complications are rare, and the outcome of the disease is most often favorable. A person who has recovered from coxiellosis develops a strong immune system.
Types of parasites
The subcutaneous mite is a parasitic organism that settles under human skin. The parasite is not visually detectable and can only be seen using an optical device. People come to a dermatologist asking for help to get rid of a rash, but they have no idea about the cause of their illness.
Dermatologists who study the types of subcutaneous mites distinguish them by size and habitat. The first type, feeding on sebum, is localized on the skin of the face, shoulders, and neck. The second type of mite attacks the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelash follicles. Having analyzed and determined what type of parasite it belongs to, the doctor begins treatment.
Remember! Many factors can lead to the rapid spread of subcutaneous mites. Having seen the first signs of the disease, you need to immediately contact a dermatologist; delay can result in intensive reproduction of the parasite, which will entail many problems with well-being.
Treatment of victims of tick bites
If a tick has bitten and the test results reveal an infection, the patient is given immunotherapy based on doctor’s prescriptions. Further treatment depends on the type of pathogen that has entered the body.
Treatment of patients with tick-borne encephalitis
There are currently no specific treatments for tick-borne encephalitis. If signs of central nervous system damage appear, the victim must be hospitalized to provide medical care. The treatment regimen includes:
- Bed rest during the entire duration of the fever and a week after it ends.
- In the first days of the disease, administration of immunoglobulin is indicated. To achieve the best result, it is necessary to apply the product as early as possible, preferably in the first three days after the tick bite.
- In general cases, the patient is prescribed corticosteroid drugs and blood substitutes.
- For meningitis, increased doses of vitamins B and C are administered.
- If respiratory functions deteriorate, the victim is advised to receive artificial ventilation.
During the recovery period, the patient is prescribed nootropics, tranquilizers and testosterone simulators.
As an addition to the main treatment, antibiotics may be prescribed to the bite victim. Antimicrobial drugs are used to suppress pathogenic microflora that can cause various complications.
Therapy for patients with borreliosis
Treatment for Lyme borreliosis involves taking antibiotics. They are used to suppress spirochetes, the causative agents of the disease. The most commonly used drugs are penicillins and cephalosporins. To relieve erythema, antimicrobial agents of the tetracycline group are prescribed.
Antibiotics are used to treat borreliosis
If neurological disorders appear, the victim is hospitalized. In the hospital, complex therapy is carried out, including:
- blood substitutes;
- corticosteroids;
- testosterone mimics;
- nootropic drugs to improve cerebral circulation;
- vitamin complexes.
The outcome of borreliosis depends on the timely detection of a tick bite, correct diagnosis and early initiation of therapy. Incompetent treatment often leads to the chronic phase of Lyme disease, which is difficult to treat and can result in disability or death of the victim.
Attention. To treat protozoal infections, medications are used that prevent further growth and development of protozoa.
Causes of the disease and conditions of reproduction
The parasite is activated for various reasons, sometimes leading to catastrophic consequences:
- with functional pathologies of the human thyroid gland, as a result of which the degree of sebum secretion increases, the pores expand, thereby creating fertile soil conditions for the flourishing of subcutaneous mites and similar parasitic microorganisms;
- Disruptions in the hormonal system lead to an imbalance in the chemical composition of the skin. Increased production of sebum begins - an excellent nourishment for the parasite. Women whose hormonal balance constantly changes due to menstrual cycles, pregnancy and the onset of menopause are especially susceptible to such phenomena;
- a weakened immune system is one of the main reasons for the spread of skin-destroying arthropods. During prolonged depression or nervous shock, the body's resistance decreases, which contributes to the emergence and development of subcutaneous mites that attack the human protective membrane;
- consumption of sweets, fatty, spicy foods, abuse of alcoholic beverages, strong coffee has a bad effect on the skin, spoils the complexion and its structure. The correct approach to nutrition will help normalize the functioning of the sebaceous glands and get rid of parasites.
- excessive makeup, the use of aggressive products while washing, and exposure to ultraviolet rays leads to an imbalance in the chemical processes occurring on the skin, providing excellent conditions for the aggression of subcutaneous mites on the face and body. The skin suffers from solarium exposure, leading to disruption of its protective functions, which, under the influence of artificial radiation, open the way for harmful organisms.
- Other factors contributing to the development of the disease include respiratory infections, hypothermia, and unfavorable ecology. The subcutaneous tick easily navigates, finds weak points in the human body and attacks them, causing physical and mental suffering.
Demodex mites often attack teenagers who do not value their health, do not pay due attention to hygiene, and do not take good care of their skin. At this age, restructuring processes occur in the body. The appearance of the disease is often observed in expectant mothers and elderly people. Treating a rash that appears on the face or other areas of the body on its own is useless and sometimes dangerous. It is necessary to consult a doctor so that, after making an in-depth analysis of all aspects, he makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Complications after a tick bite
Summarizing all of the above, we can draw a very disappointing conclusion about the consequences of a tick bite. As you can see, infections affect the most important systems of the body:
- lungs - with the development of symptoms of pneumonia and pulmonary hemorrhages;
- liver - indigestion, problems with stool (diarrhea);
- CNS - with frequent headaches, hallucinations, paresis and paralysis;
- cardiovascular system - arrhythmia and blood pressure surges appear;
- joints - arthritis and arthralgia are formed.
The consequences of a tick bite can develop in two ways. With a favorable outcome, loss of performance, weakness and lethargy continue for 2–3 months, then all body functions return to normal.
For moderate illness, recovery lasts up to six months or longer. A serious form of the disease requires a rehabilitation period of up to 2–3 years, provided that the disease proceeded without paralysis or paresis.
If the outcome is unfavorable, there is a persistent and long-term (or permanent) decrease in the quality of life of the victim of a tick bite. Manifests itself as a violation of motor function. The clinical picture worsens significantly under the influence of nervous and physical fatigue, pregnancy, and regular alcohol intake.
Persistent disorders in the form of epileptic manifestations and spontaneous convulsions lead to the patient's incapacity.
Disability as a consequence of a tick bite
As you know, there are 3 groups of disabilities. The degree of damage to the body after a tick bite is determined by a special medical commission:
- Group III disability - mild paresis of the arms and legs, rare epileptic seizures, inability to perform highly skilled work that requires precision and attention.
- Disability of group II - severe paresis of the limbs, partial paresis of muscles, severe epilepsy with mental changes, asthenic syndrome, loss of the ability to self-care.
- Group I disability - acquired dementia, severe motor dysfunction, persistent and complete epilepsy, widespread muscle paresis, loss of self-control and inability to move independently.
In especially severe cases, with inadequate treatment of infections caused by a tick bite or complete lack of therapy, death is possible.
Diagnostics
A visual examination is not enough to make a diagnosis; symptoms occur differently in representatives of the opposite sex and age. Medical professionals will suggest doing a series of tests to thoroughly study the picture of the disease. Under laboratory conditions, the secretions of the sebaceous glands, acne, and mucous membranes of the eyes will be analyzed. To make the picture clear, eyelashes and hair follicles attacked by parasites will be analyzed.
At the same time, the doctor completely studies the patient’s condition, taking into account his chronic diseases, checks for the presence of pathologies and disturbances in the functioning of all vital systems. It is not difficult to identify the culprit of the disease; it is important to determine the reason for the appearance of the subcutaneous mite. Having received the results of all tests, the dermatologist will determine the cause of the patient’s condition and select the appropriate course of treatment.
Remember! In order for the test results to be objective and reliable, you should not use cosmetics, pharmaceutical ointments, or creams before collecting the test material. Then the picture will be clear.
Prevention of tick bites
The main and main measure to prevent diseases transmitted by bloodsuckers is vaccination. The event significantly reduces the risk of infection after tick bites. Vaccination is necessary for people living in epidemiologically dangerous areas or people whose work is related to forestry.
Vaccination is the main measure to prevent diseases caused by tick bites.
Advice. Despite the limited risk group, it is better for everyone to get vaccinated. After all, it is not known where you will be “lucky” to encounter a tick.
Primary vaccination is allowed from an early age. Adults can use domestic and imported drugs, children - only imported ones. You should not buy the vaccine yourself and bring it to the vaccination office. They won't drive her anyway. The drug requires very strict storage rules, adherence to certain temperature and light conditions, which is impossible to do at home. Therefore, there is no point in purchasing an expensive drug and storing it in the refrigerator.
There are two vaccination options:
- Preventive vaccination. Helps protect against tick bites for a year, and after additional vaccination - for at least 3 years. Revaccinations are carried out every three years.
- Emergency vaccination. Allows you to protect yourself from tick bites for a short period of time. For example, such a procedure will be necessary for an urgent trip to regions with high tick-borne activity. While staying in epidemiologically dangerous areas, it is recommended to take iodantipyrine.
The vaccine is administered only after a detailed interview, visual inspection and temperature measurement. Persons with inflammatory diseases are not vaccinated until complete recovery.
How to protect yourself from a tick bite?
When going to an unfavorable area, you should choose clothes in light colors:
- a shirt or jacket with cuffs and a tight-fitting collar, trousers tucked into boots;
- anti-encephalitis suit;
- a thick hood with ties that protects the ears and neck from ticks;
- It is advisable to treat clothes with insecticidal agents.
When hiking, it is recommended to avoid ravines and tall grass; it is better to walk in the middle of the path. When leaving the forest, you need to carefully examine yourself for ticks. In this case, it becomes possible to detect and remove the parasite before the bite.
The best way not to “meet” a tick is to strictly follow all preventive measures
To repel ticks, special insecticidal products based on DEET are produced, but repellents are not effective enough and require application every 2 hours. They can be used on exposed areas of the body and clothing.
Acaricides are more effective. The drugs are used for contact destruction of ticks. They can only be used on outerwear worn over underwear.
Attention. Acaricides for application to the skin are often found on sale. However, they should be used very carefully. A severe allergic reaction and poisoning is possible.
Common bite sites and what they look like
Ticks only choose soft places on the body. They are the most delicious for them. Once on the skin, the parasite never penetrates immediately; it searches for the most delicate skin.
If a person is dressed in such a way that all parts of the body are covered, then it may take the tick several hours to find an open area. He doesn't bite through fabric.
Favorite places:
- neck, behind the ears, head;
- armpits;
- stomach;
- groin area;
- inner side of the leg;
- under the knees.
If it is impossible to get to these areas, they can bite in any part of the body. How does a bite occur? The tick's head is its mouthparts and contains the salivary glands. It consists of a base, proboscis and pedipalps. The proboscis resembles a sting; it is attached motionlessly. There are hooks on it that are bent backwards. They are used to cut the skin. The chelicerae at the base of the proboscis also cut the skin like a blade.
The process of a tick bite looks like this:
- The proboscis and chelicerae cut through the skin within 15-20 minutes. During the process, saliva is actively released, and along with it an anesthetic substance. The bitten person does not feel pain.
- The proboscis gradually sinks into the tissue until the oral apparatus is completely in the human body.
- The pedipalps move apart and are parallel to the skin.
The whole process takes 30-40 minutes.
Tick-borne encephalitis insurance
Recently, insurance for expenses associated with possible encephalitis after an “encounter” with a tick has become widespread. This measure is often used as an addition to vaccination or as an independent measure.
Insurance for the costs associated with the treatment of a tick bite will not hurt anyone
Insurance will help pay for expensive treatment for tick-borne encephalitis and other infections carried by bloodsuckers.
The irreparable consequences of a tick bite can be prevented if you seek medical help in time and begin treatment. Remember, an attached parasite does not immediately transmit the infection. The longer it stays on the body, the greater the risk of contracting tick-borne encephalitis or Lyme borreliosis.
Attention. The article is for reference only. Competent diagnosis and treatment of diseases is possible only under the supervision of a specialist.
Signs of the development of tick-borne encephalitis
The incubation period of tick-borne encephalitis can last from 4 to 14 days. During this period, the infected person does not experience any external health problems. Then the temperature rises sharply to 38-39 °C, the patient has a fever, loss of appetite, pain in the muscles and eyes, nausea or vomiting, and severe headache.
Then remission occurs, during which the patient feels some relief. This is the second phase of the disease, during which the nervous system is affected. Subsequently, meningitis, encephalitis, and paralysis may develop. If left untreated, death is likely.
The problem is that the signs of the disease in the initial stage are often confused with the flu and acute respiratory infections, so they do not consult a doctor, but self-medicate. If a high temperature appears after a detected or suspected tick bite, you should not waste time - a blood test and treatment in a hospital are necessary.
Prevention
You can avoid the disease by taking preventive measures. It is necessary to strengthen the immune system, avoid stressful situations, follow hygienic requirements, promptly treat colds, undergo regular examinations, and prevent failures of the body’s vital systems.
If a subcutaneous mite has attacked you, a dermatologist will help you get rid of the parasite if you contact him immediately. After a comprehensive examination, he will prescribe complex therapy. By following all his instructions, you will regain your former attractiveness and self-confidence.
First aid
In order not to increase the risk of developing diseases after a tick bite, you need to properly remove it. It is strictly forbidden to kill, crush or inadvertently pull it out. The result will be a significant increase in the likelihood of infection entering the blood. It is also prohibited to use repellents, as they will definitely not give the desired result.
Before removing a tick, be sure to wear rubber gloves. You need to pull it out using tweezers or tweezers. You should act with the utmost care. To do this, just grab the tick near the proboscis or by the neck and, with slow movements, twisting along the axis, pull it out of the damaged skin. You can also use a loop of regular thread to remove it. If the tick's head comes off and remains under the skin, it should be removed using a disinfected needle in the same way as splinters are removed.
Further actions:
- Place the tick in a jar with soaked cotton wool.
- Wash the bite area with warm water and soap and let it dry.
- Treat the damaged area of skin with alcohol or iodine.
- Send the tick for infection analysis.
- Visit a doctor and carry out the necessary tests.
It is recommended to do everything quickly, as delay can complicate the situation. You need to undergo all tests not only on the first day after the bite, but also later in order to accurately confirm the absence of infections.
Possible consequences
The consequences of a bite directly depend on whether the tick was infected. If it is absent, the patient may experience itching for some time. Sometimes a local allergic reaction occurs, which is manifested by redness of the skin and fever. All symptoms go away quite quickly.
If the tick is infected, serious illness can develop after the bite. As a result, most systems and organs can be affected. The most serious consequences are caused by infection with encephalitis. With the most favorable outcome, it will be possible to completely get rid of the disease only after 2 months. The average stage lasts for 6 months. Signs of severe infection will disappear after 2 years. If events develop unfavorably as a result of an encephalitis tick bite, a person’s quality of life may deteriorate on an ongoing basis. Possible deterioration of motor functions and the occurrence of epilepsy. In the most severe cases, death can occur.
Appearance of a tick
Ticks are, in fact, not large spiders, the dimensions of which reach 0.4 mm, with females being 1 mm larger. Males are different in that after saturation they disappear on their own, but with females there is a real problem. They dig into the human skin and can leave the proboscis, and often the head, in it. When saturated with blood, the mites noticeably increase in volume. After 20 minutes, when the effect of the anesthetic substance produced by the tick ends, the person begins to feel the effect of the bite.
Symptoms of encephalitis
The symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis in children are, in principle, the same as in adults. True, in childhood, symptoms are often accompanied by allergies and high fever. It is important to know and understand the sequence in which emergency care is performed for allergic reactions to the bites of these parasites and vectors of infection. It must be said that in childhood allergies are not as difficult as in adults. If it does appear, care should be taken to reduce discomfort as much as possible. The area of skin with allergies should be treated with an antiseptic solution (peroxide or any alcohol-based solution). To relieve itching or swelling, you can take antihistamines after first obtaining permission from an allergist. You should definitely call an emergency team.
Tick-borne encephalitis is a serious infectious disease that causes gradual destruction of the nervous system. A person infected with encephalitis due to a tick often suffers from inflammatory processes in the membranes of the brain. The infection enters the body immediately after the tick pierces the skin. Toxic components enter the skin along with the saliva of the parasitic insect. The incubation period for encephalitis is approximately 1-2 weeks. For those readers who do not know what the incubation period is, we will explain that this is the time when the virus is already present in the body, but there are no obvious symptoms of its presence yet. That is, if a person is infected with encephalitis, the first symptoms will appear only after a couple of weeks. It must be said that this disease begins very abruptly, and the main signs of the disease are:
- Painful sensations are felt in the joints, muscles of the body and eyeballs.
- Vomit.
- Body temperature rises to 38-40 ºC.
- Cramps.
- Increased sleepiness.
If the disease is acute, then in the absence of medical intervention, death occurs within a week.
Another common tick-borne disease is borreliosis. Its characteristic features are
- Gradual damage to joints;
- The presence of an incubation period, sometimes reaching 30 days, but generally lasting from 5 to 11 days;
- The appearance of a ring-shaped redness in the area of the bite, which in the central part has a more saturated color;
- Presence of itching and pain;
- Headaches, pain in joints and muscles;
- Weakness, high temperature (39-40 ºC).
In the advanced stage of borreliosis, the symptoms expand with the following symptoms:
- Acute conjunctivitis;
- Bronchitis or sore throat;
- Impaired liver and kidney function;
- Heart pain and rapid heartbeat.
Danger of ticks
Science now knows more than 50 thousand species of ticks. Not all of them pose a threat to humans. Many species feed on organic waste and only harm the harvested crop. But there are other species - ixodidae. These are individuals that parasitize warm-blooded individuals. Their food is blood. But that's not even scary.
Their blood contains poison that is transmitted to humans. This poison is the causative agent of fatal diseases. Not all individuals tolerate it. There are also healthy ones. The number of infected people is only 20%. But it's still a huge number.
Treatment methods
It is not easy to overcome subcutaneous mites; it is necessary to apply complex treatment. The first thing to do is to find the causes and eliminate them step by step. First, they treat chronic diseases, normalize hormonal levels, strengthen the immune system, and remove them from a depressive state. After getting rid of all diseases, measures are taken to eliminate signs of damage to the epidermis by a microscopic parasite.
Pharmaceuticals
Ointments that contain components that destroy mites and help regulate the metabolic processes of sebum are suitable for drug treatment. These means normalize the condition of the epidermis.
The following drugs are particularly effective:
- Ichthyol ointment is a strong antiseptic, a sulfur-containing compound of ichthammol and medical petroleum jelly. The first component is the basis of the ointment, which has a healing effect, the second nourishes the skin. In tandem, they successfully cope with subcutaneous mites, dry and eliminate damage that appears on the skin, and relieve inflammation. Price - 90 rubles;
- Permethrin ointment has insecticidal properties. It paralyzes the tick by entering its nerve cells. You can buy the drug for 200 rubles;
- Sulfuric ointment. From time immemorial, the well-known drug has been used in official and folk medicine. It has a detrimental effect on the tick, paralyzing it. The effect of the medicine is not limited to the destruction of parasites, it relieves inflammation and promotes wound healing. The average price of sulfur ointment is 45 rubles.
- benzyl benzoate. An antiparasitic ointment that is extremely effective in defeating parasites, having a toxic effect on them and disrupting their vital functions. Medicines in the form of an ointment can be purchased for 20 rubles, a suspension will cost more.
- Yam ointment is a bactericidal preparation with a concentrated creolin odor. The product successfully fights mites, softens and heals pustular lesions and restores the structure of the skin. The cost of the drug is no more than 80 rubles, and the effect is significant.
How to use the tools:
- Wash yourself with tar soap, wipe yourself dry with a sterile cloth, now start applying the ointment to your face;
- Place a thin layer of the drug on the problem area, carefully distribute it over the entire surface of the inflamed area, covering a couple of centimeters around the area of infection;
- Leave the applied layer until it is absorbed. Repeat the procedure daily in the morning and evening until complete recovery.
An effective remedy is talker. Following the doctor's recommendations, you can make it at home. To do this, you will need the following components: salicylic alcohol in the amount of one hundred grams and chloramphenicol and trichopolum tablets, four of each drug. The preparation is simple. Medicinal components need to be crushed into powder, combined with alcohol, and placed in a convenient jar. Treat the affected part of the face daily with a swab soaked in the solution. After the procedure, apply a moisturizer to avoid drying out the skin.
Treatment with nutrition and folk remedies
Nutrition should be rational and balanced. Your table should contain foods that include proteins, fats and carbohydrates in reasonable proportions. Avoid sweets, smoked meats, pickles, hot spices, consume less fat, and avoid strong drinks. They negatively affect intestinal function, body functions, and skin. They are dangerous because they create favorable conditions for the activity of subcutaneous mites.
Products containing fiber, vitamins, and beneficial microelements will help overcome the disease. The leading place on the podium of your diet should be occupied by fruits and fish, milk and cottage cheese, products made from cereals and white meat.
You cannot experiment with the skin; you need to treat your face, body and hair with gentle means: herbal decoctions, light tinctures. A mixture of one liter of herbal decoction with 15 grams of tar soap gives a good effect.
Main symptoms of a bite
The first sign of a bite is redness. Moderate pain and itching of the skin appears after some time. The affected area becomes inflamed and a slight swelling is visible. The bite site looks like a round or oval spot with a diameter of 10 to 20 mm. Sometimes a scar forms on the skin.
After a few hours, a person’s temperature may rise to 37 degrees or higher, which indicates a possible infection. Antipyretic medications will not help here; they will only relieve symptoms for a short time.
A few days after the bite, the following may appear:
- aches in joints and muscles;
- nausea;
- headache;
- vomit;
- chills;
- drowsiness;
- hardening of the lymph nodes.
Treatment
After the initial treatment of the bite site with alcohol, you will need to proceed to the main stage of treatment. The doctor prescribes an exact list of necessary medications in each case individually, taking into account the circumstances and condition of the victim. If a severe infection is detected, therapy will be adjusted accordingly. A prerequisite for recovery in any case is bed rest, combined with limited physical activity and drinking plenty of clean water.
Main categories of drugs:
- antiviral;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antibiotics;
- antihistamines;
- corticosteroids;
- painkillers;
- antipyretics;
- vitamin B;
- immunostimulants.
The prognosis for victims of a tick bite is most often favorable. An exception may be protracted cases when an infection has developed, causing severe complications. In some cases, the patient may become disabled. Therefore, it is extremely important to visit a doctor in a timely manner to undergo the necessary examinations.
A person who is bitten by a tick is under medical supervision for two years. Adults can stay at home, but children are recommended to be hospitalized for two weeks.
Description of the pest
Represents the arachnid family. For this reason, the insect will move in a similar way. This is one of the hallmarks of ticks. However, if you are not aware of other signs, it can be mistaken for a spider. Pest habitats: undergrowth, small bushes, grass. They don't live in trees. If a tick bites you on the neck or head, it means that it independently climbed to the desired area. These insects do not fall from the tree.
External signs
You need to understand exactly what a tick is and what it looks like. The insect is characterized by its small size (on average 3-4 mm), however, small individuals (less than 1 mm) are also found. Number of paws – 4 pairs. The body is large, and the head, on the contrary, is small in size relative to the abdomen. Color black or brown. Having found a tick on the body, you need to take into account that initially (in a hungry state) it will be round and flattened. Having fed on blood, the insect increases in size. The abdomen becomes spherical.
The tick is in a “hungry” state; small arachnid with a flattened body, reddish-brown in color
Why is it dangerous?
When a tick bites, the risk of contracting infections and pathogens increases. The most dangerous diseases: encephalitis, borreliosis. Not every pest is a carrier of these diseases, however, the probability is sufficient to be wary of these insects. In addition, ticks can bury their head so deeply under the skin when they bite that removing it on their own increases the risk of its separation from the abdomen. This is fraught with an inflammatory process.
Who are ticks and what diseases do they carry?
Ticks belong to one of the oldest groups of arthropod insects that feed mainly on plant waste, small arthropods and soil fungi. Among them, the most famous are Ixodidae. The diseases carried by ticks are serious and complex.
Ticks are characterized by a wide variety of varieties, but only a couple of types have epidemiological significance:
- Taiga tick;
- European tick.
The parasitism of these two varieties, as well as their impact on human health, will be discussed in the article.
Features of vaccination against encephalitis
Protect yourself from tick-borne diseases by getting vaccinated. Only healthy people who have previously been examined by a therapist are allowed to see it. He will inform the patient where exactly he can get vaccinated against tick-borne infections.
Vaccination
Preventive vaccines against encephalitis are represented by the following types of drugs:
- EnceVir;
- Encepur for adults;
- Children's Encepur;
- Cultured viral vaccine, presented in the form of purified dry inactivated concentrate.
Where can you pick up a tick?
Any person can detect a tick upon careful inspection. These parasites prefer to bite on the following areas of the body:
- Armpits;
- Elbow bends;
- The area on the skin behind the ears;
- Neck;
- Groin areas;
- Areas of skin with close proximity of blood vessels.
Possible tick bite sites
People are looking for a solution to a problem if they are bitten by a tick. But the occurrence of a bite can be completely prevented if you know where the tick is picked up and protect the body from parasites.
Most ticks live in wooded areas, often in coniferous or deciduous forests. The greatest activity of parasites is observed in the spring and summer, mainly in May and the first half of June. At this time of year, hungry female ticks awaken from hibernation. Parasites prefer to attack in the early morning. In hot or rainy seasons, their activity decreases significantly. Fans of outdoor activities will be interested to know what symptoms after a tick bite indicate the presence of a parasite on the body . At the time of the bite, it is extremely difficult to notice the parasite. And the insect bites through the skin silently, without causing pain. It all starts much later. Understanding how to spot a tick is not difficult. Inflammation forms at the site of parasitism after a tick bite. In its central part a darkish dot is visible, which is the body of the insect. After some time, the tick will be well saturated with blood, which is why its body will increase in size, becoming more noticeable.