Gastritis is inflammation of the gastric mucosa, duodenitis is the part of the intestine below the stomach. The diseases have similar symptoms and treatments. In its acute form, it burns and stings in the upper abdomen in the middle or left, and can radiate to the back. Pain and discomfort go away without treatment. In the chronic form, the symptoms are less pronounced. In the case of the erosive type, the gastric mucosa is thinned; in the case of non-erosive gastritis, it is changed. If measures are not taken, the risk of developing stomach ulcers, neoplasms, and gastrointestinal pathologies is increased.
Symptoms
The acute and chronic course of the disease has some features of its manifestation. Acute, or acute atrophic gastritis is caused by exposure of the stomach to a strong irritating factor (chemicals, poor quality food, drugs) for a short period of time. Symptoms in adults include:
- sharp pain in the upper abdomen, aggravated by pressure;
- nausea;
- light gray or dirty yellow coating on the tongue;
- bowel dysfunction;
- vomiting, possibly repeatedly;
- weakness, pallor;
- dizziness;
- thirst;
- limb spasms.
If treatment is not started in time, it can lead to the disease becoming chronic, the symptoms of which may either temporarily subside or worsen again. Manifestations such as increased fatigue and flatulence can be attributed to intense exercise and poor nutrition, which will once again delay a visit to the doctor. Chronic gastritis can occur in conditions of increased or decreased acidity of the stomach and manifest itself with the following symptoms.
With increased acidity
- frequent belching;
- prolonged pain between meals in the solar plexus area;
- frequent diarrhea;
- heartburn from sour foods.
- With low acidity
- unpleasant sensations in the mouth, bad odor;
- heaviness after eating;
- constipation;
- frequent belching with the smell of rotten eggs;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- nausea in the morning
Lack of treatment for chronic gastritis can lead to erosion of the walls, which in turn will be the beginning of a peptic ulcer, and atrophy of the mucous membrane often ends with stomach cancer.
Types of disease
The variety of manifestations of the disease is expressed in their complex classification.
The considered pathological processes in the lining of the stomach can be primary and considered as a separate independent disease and secondary, which accompany other diseases or intoxications or are caused by them.
Depending on the duration and intensity of the damaging factors, the disease can be acute or chronic.
Acute gastritis occurs when poisoning with acids or alkalis, when taking large doses of certain medications, especially aspirin. After treatment, such a disease can develop into chronic gastritis, but more often the chronic form develops as an independent disease.
Acute gastritis can have the following types:
- catarrhal;
- fibrinous;
- phlegmonous;
- necrotic.
In this case, the catarrhal form of the disease is associated with mild food poisoning and poor nutrition. Necrotic and fibrinous gastritis develop as a result of poisoning with heavy metals, concentrated alkalis and acids. Phlegmonous gastritis is most often caused by traumatic damage to the walls.
Long-term exposure to acute diseases on the weakened body of the patient leads to the development of chronic gastritis. They are divided into the following types:
- microbial;
- alcoholic;
- NSAID-related;
- post-resection;
- caused by chemicals;
- unknown origin.
Depending on the secretory activity of the stomach, gastritis is distinguished:
- with high or normal acidity;
- with low or zero acidity.
It is quite possible to distinguish the symptoms of these conditions, but the final diagnosis is made on the basis of an analysis of gastric juice taken by intubation. In some cases, the pH of gastric juice is determined by indirect methods using urine tests.
Treatment
Treatment of acute gastritis is aimed primarily at eliminating the cause that caused it. Whether it is a chemical or biological irritant, interrupting contact with it is achieved by gastric lavage and, if necessary, an enema. Fractional drinking of special solutions helps to replenish the loss of fluids and salts. Another step is binding the incoming toxins. The simplest sorbent is activated carbon. If it is necessary to reduce pain, antispasmodics are used. And, of course, following a diet that excludes fried, spicy and fatty foods.
Treatment of chronic gastritis also largely depends on following a proper diet and diet. Gastric secretion plays an important role. If it is elevated, then drugs that reduce it, as well as antacids, are prescribed. Stimulation of gastric motility with prokinetics is also necessary. In case of decreased secretion, stimulants are used, as well as enzyme preparations.
Severe pain is relieved with antispasmodics, and the destruction of pathogenic bacteria, if present, is carried out with antibacterial drugs. Treatment usually lasts a week.
Gastritis is a very common disease, which is often the reason for decreased attention to it and refusal of treatment. This, in turn, can lead to serious complications such as stomach ulcers, often requiring surgery, and even cancer. Simple preventive measures will help not only prevent the occurrence of this disease, but also improve the quality of life:
- proper nutrition;
- lack of stress;
- refusal or, if possible, reduction in alcohol consumption and smoking;
- control of medication intake.
Our body is an integral system in which there are no accidents. By listening to it and responding to its signals, you can prevent the development of many diseases or avoid serious consequences. An important role in this is played by basic knowledge about the disease and its causes.
Patient examination plan
Before treating gastritis of the stomach, you need to be examined. For symptoms of the disease you will need:
- patient interview;
- visual inspection;
- physical examination;
- FEGDS;
- radiography;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- blood test for Helicobacter bacteria;
- pH-metry.
The attending physician (gastroenterologist) must determine the possible causes of gastritis. For this purpose, the nature of the sick person’s diet, the presence of bad habits, family history, occupational hazards and the presence of concomitant pathology are identified. It is necessary to establish what symptoms are bothering the patient and for how long.
It is necessary to know not only whether gastritis can be cured completely, but also what the diagnostic methods are. If pain is present, its nature is assessed (localization, connection with food intake, intensity, duration, time of onset). It is necessary not only to determine how the symptoms bother the person, but also to palpate the abdomen.
Treatment in adults and children begins after endoscopic examination.
The doctor inserts a thin probe with a camera into the stomach cavity and examines the mucous membrane.
This helps to exclude pathologies of the intestines, pancreas and gall bladder. During examination of the mucous membrane, hyperemia and swelling are revealed. FEGDS is often complemented by ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Gastritis is often caused by the bacterium Helicobacter. To identify these acid-fast microbes, the patient's blood is tested. If there is no evidence indicating the infectious nature of the disease, then antibiotics are not subsequently prescribed.
Diet for gastritis of the stomach
A diet for exacerbation of gastritis involves switching to gentle food. It will help quickly relieve inflammation, and the regeneration of the gastric mucosa will be much more effective. It is necessary to exclude hot, cold, spicy, fried, smoked, salty foods. Diet is a mandatory part of treatment; it ensures rapid remission and complete recovery.
During pregnancy, a strict diet is unacceptable. Nutrition should remain adequate, but the patient’s condition must be taken into account. For this reason, it is recommended not to boil most foods, but to steam them. This way they will retain maximum beneficial properties.
For concomitant inflammatory diseases of the pancreas, fasting is prescribed for a day or more, depending on the severity of the symptoms. If you do not adhere to the prescribed diet, gastritis will develop into an ulcer or become chronic. During an exacerbation, experts advise drinking as much liquid as possible: plain water (preferably mineral water without gas), a decoction of chamomile, St. John's wort, and rose hips. The volume of fluid consumed should be at least two liters per day.
After the end of the period of fasting or maximum food restriction, the patient is recommended to gradually introduce new foods into his diet. All food is cooked in a double boiler without adding salt or seasonings.
Cooking Tips
During the period of exacerbation of gastritis, the stomach is most vulnerable and sensitive. Therefore, all food cooked in a double boiler must also be chopped so that large pieces cannot damage the gastric mucosa.
Meals should be taken at least five times in small portions to avoid a feeling of fullness in the stomach.
The food consumed should not be hot or cold, since high and low temperatures greatly irritate the gastric mucosa.
Cook food exclusively in steamers or boil.
Fatty, difficult-to-digest foods are prohibited: seeds, all types of nuts, chocolate.
You need to take a glass of water in the morning on an empty stomach. This will help clear the gastrointestinal tract of mucus.
The duration of the diet depends on the severity of the patient’s condition and ranges from 7 to 14 days.
Tips for quickly relieving the inflammatory process in the stomach:
Drinking a glass of clean drinking water on an empty stomach in the morning helps remove mucus from the organ.
During the day, there should be at least five meals in small portions to avoid excessive production of gastric juice.
Introduce foods high in fiber into your diet. It works as a sorbent and quickly cleanses the stomach, accelerating the process of digesting food.
Causes of gastritis
If acute gastritis occurs as a result of ingestion of large quantities of ulcerogenic substances and their destructive effect on the gastric mucosa, then the causes of chronic disease are more diverse. It is interesting that in some people gastritis develops quite slowly, despite the presence of obvious causes. Apparently, the disease is most likely caused by many factors or certain combinations thereof.
Factors contributing to the development of this disease are divided into external and internal.
The main external causes of gastritis
For almost the entire last century, it was believed that chronic gastritis was caused by irregular diet, alcohol intake and stress. Australian doctors R. Warren and B. Marshall in 1981, having conducted an experiment on themselves, proved that the cause of the disease in most cases is a microbe called Helicobacter pylori. Approximately 80% of patients with gastritis contain acid-fast bacteria in their bodies, which have the ability to actively invade the wall of the stomach, secrete substances that irritate its lining, cause inflammation and a local change in pH. The most common of them are Helicobacter pylori. But it still remains unclear why they cause disease in some people and not in others.
Thus, the main causes of this pathology are now placed as follows:
- the effect of bacteria and fungi on the walls of the stomach;
- eating disorders;
- alcohol abuse;
- taking medications;
- the presence of helminthic infestations;
- chronic stress.
A common cause of gastritis is also malnutrition, overeating and other dietary disorders. When the initial stages of the disease occur, you need to exclude foods containing coarse fiber, canned food, marinades, and hot spices.
Alcohol abuse has been identified as a separate cause of gastritis. In small quantities, ethanol is a necessary component of biochemical processes, but too much of it causes an acid-base imbalance in the body. Regular consumption of alcohol has a negative effect on organs such as the liver, pancreas, kidneys, as well as on metabolic processes.
Many medicinal substances related to antiplatelet agents, painkillers, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have the ability to irritate the mucous membrane of the organ and cause gastritis. In this regard, they are recommended to be taken after meals, in small doses, with large quantities of water.
Internal causes of gastritis
Internal causes of the disease include:
- hereditary predisposition to gastrointestinal diseases;
- presence of duodenal reflux;
- violation of the protective properties of cells at the immune level;
- hormonal imbalances;
- reflex transmission of pathogenesis from neighboring organs.
Duodenal reflux is the phenomenon of pathological reflux of bile from the 12th intestine into the stomach. The bile that penetrates into it irritates the mucous membrane of the walls and also changes the pH of the gastric juice. Typically, the initial inflammation occurs in the antrum; later other parts may be involved.
If the protective properties of stomach cells are damaged at the immune level, they lose their original properties and normal functioning. As a result of this phenomenon, a whole cascade of small reactions is launched, affecting the pH of the juice and ultimately leading to irritation of the walls of the organ. Endogenous intoxication occurs, the resistance of the gastric mucosa to the aggressive environment of its own gastric juice is impaired.
List of allowed foods and what you can eat
Experts advise introducing into the diet of a patient with high acidity those foods that do not irritate the gastric mucosa, but promote its regeneration. Such products are usually classified as:
- dairy products: low-fat milk, cream, cottage cheese, sour cream;
- durum pasta;
- boiled meat (veal, turkey, rabbit) and fish;
- soft-boiled eggs;
- hard cheeses without hot spices;
- olive oil;
- mousses, jellies, puddings, ground in a blender;
- butter (50 g per day);
- omelette steamed from whites (yolks should be separated);
- oatmeal, fruit jelly;
- pureed vegetable puree;
- rosehip infusion, green tea.
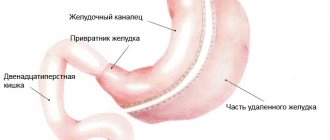
Structure of the stomach
This organ is delimited by four sections: the cardiac section - connecting to the esophagus, the gastric fundus - slightly raised above it and extending slightly to the left, the body and antrum - the lowest.
On the border line of the stomach and esophagus there is a ring-shaped muscle - the sphincter (valve) of the esophagus. The duodenum is separated from the stomach by the pyloric sphincter (valve).
The gastric walls contain blood vessels and nerve fiber connections, and the walls themselves have four layers:
- The gastric mucosa is covered with epithelial cells designed to produce mucus, which in turn protect the gastric lining from any harm. To produce digestive (stomach) juice containing hydrochloric acid, glands located deep in the mucous membrane are used.
- Submucosa is connective tissue arranged in a layer. Forms stomach folds.
- Muscularis – moves food to the small intestine.
- The serous membrane covers the outer surface of the stomach.
"Duties" of the stomach
The stomach is very important for the digestive process! Once in it, everything eaten is processed, then mixed with digestive juice in small parts, it moves into the first part of the small intestine - the duodenum. Hydrochloric acid, which is involved in the digestive process, can eliminate many microbes that enter the stomach from the outside.
Strictly prohibited:
- all types of sausages, frankfurters, sausages;
- sour and spicy foods;
- alcoholic drinks;
- coffee and strong tea;
- fatty meat - lard, brisket;
- carbonated drinks;
- chocolate;
- instant cereal;
- tomatoes, tomato juices and sauces;
- mushrooms;
- some cheeses (cheese products, processed cheese, sausage cheese).
With increased acidity in the stomach, foods rich in mucous substances provide maximum benefit. These include boiled porridge. Oatmeal is especially useful for such gastritis. It gently envelops the walls of the stomach, protecting them from destruction. Also, regular consumption of oatmeal for breakfast promotes rapid regeneration of the mucous membrane. It is also useful in cases where gastritis is accompanied by duodenitis, that is, inflammation of the duodenum. You can make dairy-free porridge, soup, and jelly from oatmeal.
After the acute period of gastritis with high acidity is over, it makes sense to enrich the diet with foods rich in vitamin C. These are fresh vegetables, fruits, and juices. But in the first month after diagnosis, these products are prohibited. Vegetables you can eat are cauliflower, steamed broccoli. Depending on tolerance, it is also possible to add green beans to the menu. Instead of juices, you can drink jelly; a week after acute gastritis is detected, gradual introduction of compotes is allowed. Coffee is strictly prohibited. It can be replaced with chicory, but you shouldn’t overuse it either. The tea should be weak, with a small amount of sugar.
How to prevent manifestations of the disease
You need to know not only what causes the stomach to become inflamed, but also how to prevent this pathology. There are no specific measures to prevent the disease. To prevent symptoms of inflammation of the gastric mucosa, you must:
- give up alcoholic drinks;
- give up fried and spicy foods;
- no smoking;
- do not drink sparkling water;
- eat from clean dishes;
- prevent acids and alkalis from entering the stomach;
- move more;
- treat pancreatitis and intestinal diseases;
- do not eat before bedtime;
- maintain equal intervals of time between meals.
Preventive measures should be carried out from childhood. Thus, everyone should know the symptoms of gastritis, the causes of the disease and methods of treating this pathology. Ignoring the problem and self-medicating can lead to dangerous complications.
A little more about the symptoms of gastritis with low acidity
- belching;
- bad breath;
- abdominal pain and bloating;
- increased gas formation;
- heartburn;
- heaviness and lump in the chest.
Products recommended for low stomach acidity:
- steam cutlets;
- durum wheat pasta;
- low-fat cottage cheese, milk;
- weak tea;
- dried white bread;
- fruits, greens.
The duration of the therapeutic diet in its strictest version is 30 days. At this time, the patient must systematically monitor his condition, record emerging symptoms, and write down foods that make him feel better.
The most important goal of a therapeutic diet is to reduce the inflammatory process in the stomach, along with restoring its proper functioning and adequate secretion of hydrochloric acid.
In this regard, gastroenterologists recommend expanding your diet with the following products:
- all types of broths (vegetable, fish, meat);
- pickled tomatoes and cucumbers;
- freshly squeezed carrot juice, diluted lemon juice.
- It is prohibited to use:
- milk;
- bakery products made from yeast dough;
- undried white bread;
- raisins, prunes, dates.
Possible consequences
With proper and timely treatment, gastritis can be cured or put into long-term remission. However, if the patient neglects the doctor’s recommendations or independently treats stomach inflammation, the risk of complications increases, including:
- internal bleeding;
- hypovitaminosis;
- stomach ulcer;
- peritonitis;
- dehydration of the body;
- anemia;
- anorexia;
- pancreatitis;
- stomach cancer.
Any complication of gastritis is fraught with consequences, therefore, in order to avoid their development, you need to know what gastritis is and how to treat it, consult a doctor on time, follow all recommendations, take prescribed medications, and follow a diet.
Recipes for exacerbation of gastritis
The sample menu includes dishes with the maximum content of vitamins and microelements. It is important to have mucous substances that have an enveloping effect on the stomach walls irritated by hydrochloric acid.
Rice soup with corn
Boil meat (turkey, beef) cut into small pieces and pre-washed rice in lightly salted water for no more than 20 minutes. Cut the peeled potatoes into slices and add to the water. When ready, transfer the potatoes to a container with rice and meat, add corn and finely chopped dill and parsley.
Pumpkin porridge
Boil or bake 500 grams of pumpkin. Boil about half a glass of rice. Grind the prepared pumpkin into puree and combine with the prepared rice, add 20-25 grams of butter and serve.
Carrot-curd casserole
Pour a glass of milk, 25 grams of butter, 3 tablespoons of honey into a small saucepan and add three medium-sized carrots, grated. Add semolina to the stewed carrots and cook for another five minutes with frequent stirring. Next, beat 500 grams of low-fat cottage cheese with 3 eggs, a pinch of salt, 1 tablespoon of potato starch and a small amount of sugar. It's possible without it. Carrots are added to the resulting mixture and cooked in the oven at a temperature of 200 degrees for 40-50 minutes.
Prevention
Prevention includes compliance with basic rules, including:
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- eating medium temperature food;
- regular increase in immunity;
- less stress and nervous tension;
- timely treatment of all concomitant diseases;
- periodic preventive examinations by a gastroenterologist for persons over 35 years of age;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- moderate physical activity.
Gastritis is a serious disease that negatively affects a person’s life, but if a person wants to cure gastritis forever, he needs to consult a doctor in time, undergo the necessary treatment, the prognosis for a successful recovery increases several times.
Diet menu No. 5 for seven days
To relieve exacerbation of gastritis, a therapeutic diet is used - table No. 5.
It is properly selected and balanced food that will help reduce the inflammatory load of the gastrointestinal tract. The patient will not have to waste time selecting a diet menu. The presented ready-made option will help the patient focus on recovery and mobilization of strength.
Menu in the attached photo (You can
)
What is gastritis?
The stomach is the most vulnerable organ of the digestive system, since it alone performs three important stages of digestion:
- mechanical mixing of food;
- its chemical breakdown;
- absorption of nutrients.
With the development of diseases, damage to the inner wall of the stomach is first noted, in which the production of two necessary components of digestion occurs - protective mucus and gastric juice.
The great wisdom of nature, which created the human body, was also manifested in the creation of this organ. The stomach of a healthy person not only does not digest its own tissues, but also the gastric juice produced by its different sections has different properties. For example, the pH of the esophagus is neutral, and the pH of the duodenum is already alkaline. Violation of the acid-base balance in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract and acid balance in different parts of the stomach is the root cause of gastritis. This is caused by rough influences on the digestive process of a very different nature. As a result, gastritis occurs - inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which causes dysfunction of this organ.
Treatment regimen for gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori
To eradicate the microorganism, active antibacterial therapy is carried out. A number of treatment regimens have been developed. Previously, a standard treatment regimen was used, which included exclusively two drugs: Clarithromycin and proton pump inhibitors. In recent years, Helicobacter has become resistant to antibiotics, and regimens of three or four drugs are more often prescribed.
First line drugs:
- Proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole and others) 20 mg 2 times a day, Amoxicillin 1000 mg 2 times a day, Clarithromycin 500 mg 2 times a day. Treatment is carried out for 2 weeks.
- Treatment with the second option is carried out with the addition of a fourth drug to the set of medications - bismuth (for example, De-nol). The medicine is prescribed 240 mg 2 times a day. Treatment is carried out for at least 10 days.
- Third option: Rabeprazole 10 mg 4 times a day, Amoxicillin 500 mg 4 times a day. As you can see, in the presented scheme, antibiotics are prescribed more often, which increases the effectiveness of eradication. The duration of taking these medications is 2 weeks. A probiotic is added to the treatment and taken for at least a month. A week after the start of treatment, it is necessary to add Clarithromycin 500 mg 2 times a day for a week.
- If you are allergic to Ampicillin, the disease is treated with a regimen of four other drugs: proton pump inhibitor, De-nol, Metronidazole 500 mg 3 times a day, Tetracycline 500 mg 4 times a day. Treatment is carried out for two weeks.
- If the patient is allergic to many antibiotics, only bismuth and a proton pump inhibitor are prescribed, although such treatment is considered less effective. Propolis preparations on an empty stomach, warm mineral waters without gas according to the scheme 30 minutes before meals, and probiotics are added to the treatment. Therapy is carried out for a month.
- For gastritis of the stomach with low acidity, proton pump inhibitors are not prescribed. Therapy is carried out with antibacterial drugs (Ampicillin and Clarithromycin according to the scheme), and a bismuth drug is prescribed.
If the first course did not help the patient, and Helicobacter pylori is detected again during the examination, a second course of antibiotics is prescribed. A preliminary study of the sensitivity of Helicobacter pylori to antibiotics will help to treat gastritis correctly.
Scheme:
- Drugs Metronidazole, Tetracycline, bismuth and reducing gastric secretion. The second course of treatment is prescribed for 2 weeks.
- A combination of two antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Nitrofuran), De-Nol and an antisecretory drug.
- The disease can be cured by using one of the antisecretory drugs, Amoxicillin and Levofloxacin.
If the second course did not help, you will need to re-examine the mucous membrane for Helicobacter, conduct an endoscopic examination to determine whether gastritis has been cured, determine sensitivity to antibiotics, and only then begin a third course of treatment. The medical history of patients in difficult cases contains several courses of antibacterial therapy.
Bismuth preparations and antisecretory agents are used for a long time, for a month. Antibiotics are not prescribed to pregnant women to avoid negative effects on the fetus. As an addition to treatment, antacids are prescribed to protect the gastric mucosa. Useful medicines for gastritis are probiotics. These are substances containing polysaccharides (FOS, lactiol).
Helicobacter pylori
If Helicobacter pylori is not detected, only proton pump inhibitors, bismuth preparations and antacids are prescribed for the treatment of gastritis.
Complications
Complications are more typical for the severe stage of stomach inflammation. They are expressed in direct destruction of the mucosa and involvement of neighboring organs:
- gastric bleeding (with erosive gastritis);
- hypovitaminosis, especially affecting the patient’s body, is a deficiency of vitamins B12 and folic acid, iron, and anemia develops;
- peritonitis is possible with phlegmonous gastritis;
- dehydration (dehydration) accompanies frequent vomiting;
- loss of appetite leads to metabolic disorders and exhaustion;
- transition to peptic ulcer and subsequent transformation of the epithelium into a malignant tumor;
- development of pancreatitis.
Acute form
An acute form of stomach disease is quite rare, the symptoms of which may manifest differently from those of a chronic disease. The acute form of inflammation is divided into 2 types:
- Catarrhal. In this case, gastritis occurs due to the effect of strong drugs on the human stomach. It could be antibiotics. Often the causative agent of this type of inflammation is aspirin. Medicines taken in large quantities or in a fasted state greatly damage the gastric mucosa. In addition, the catarrhal form of the disease can be caused by other severe diseases, for example, liver failure and even a severe form of pneumonia. Sometimes a certain type of disease can appear even due to stress suffered by the body.
- Phlegmonous. Perhaps this is the most severe form of the disease, in which the inflammation is purulent in nature, making this type of gastritis dangerous. The causes of this form are damage to the stomach or infection in it. This happens after swallowing glass, needles, and sometimes fish bones. In this case, treatment of gastritis of the stomach will be carried out using abdominal surgery.
The symptoms that indicate the presence of acute forms of the disease also vary. In the catarrhal form of the disease, the first signs occur 6-9 hours after the onset of the cause of the disease. It is accompanied by pain, nausea or vomiting with a metallic taste. Phlegmonous inflammation is accompanied by severe pain, as well as a shock state of the stomach, in which it inflates and its walls harden. This type of damage can be easily identified by palpation.
Why does gastritis occur in adults?
Experts believe that overeating is the main cause of inflammatory reactions in the stomach. The risk of developing pathology increases if a person eats low-quality foods. This includes not only food with a high content of chemical additives (industrial yoghurts, confectionery, sausages and frankfurters), but also products with an expiring date and signs of improper storage. Products with mold are especially dangerous, since the mixed nature of gastritis, combining bacterial and fungal flora, requires very long-term treatment with combined potent drugs with a broad spectrum of action.
Another possible cause of gastritis is long-term use of certain medications, the side effects of which are digestive disorders and disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. This group includes Aspirin, Acetylsalicylic acid, iodine and bromine preparations (Lugol, Iodomarin), as well as some herbal mixtures and tinctures, for example, infusion of adonis herb.
What is gastritis
Other negative factors contributing to the occurrence of acute gastritis include:
- smoking (especially for those who smoke for more than 3-5 years);
- alcohol abuse;
- work under constant emotional stress;
- stressful situation in the family;
- radiation exposure (especially common among residents living in settlements near cosmodromes, engineering plants, etc.);
- chronic kidney pathologies;
- history of myocardial infarction and stroke.
Infectious gastritis occurs after the bacteria Helicobacter pylori enters the gastric environment. Treatment of infectious inflammation of the gastric walls necessarily includes taking antibiotics.
Causes of gastritis
Important! Some types of damage to the skin and muscle layer (trauma, burns) can trigger the development of stress gastritis. Treatment of the pathology in this case begins with eliminating the provoking factor, and the doctor must include sedatives in the combined treatment regimen.
Diagnostic methods
Fibrogastroduodenoendoscopy
To determine gastritis, doctors most often use:
- fibrogastroduodenoendoscopy (FGS);
- FGDS;
- gastroscopy.
The doctor uses a probe to assess the condition of the stomach lining. To obtain a more accurate result, the doctor may take a piece of mucous membrane.
Blood analysis
To diagnose Helicobacteriosis, it is necessary to do a blood test, the results of which will show the level of antibodies to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Stool analysis
Chronic gastritis may be accompanied by bleeding, so to detect it, the patient is prescribed a stool examination.
How to treat gastritis with folk remedies
Gastroenterologists also recommend that patients use traditional methods of treatment, which involve the use of decoctions and infusions prepared on the basis of medicinal herbs.
- Milk. This product helps to quickly reduce stomach acidity at home. In addition, drinking a glass of warm milk quickly eliminates the symptoms of heartburn.
- Linen. For therapy, you can only take cold-pressed oil, which contains the required amount of beneficial substances. The duration of treatment with flaxseed product is 12 weeks. During this period, the patient’s digestion will significantly improve and the harmful effects on the mucous membrane will decrease. To obtain the necessary therapeutic result, you need to take a teaspoon of oil before breakfast and after dinner. In this case, be sure to drink the product with a small amount of warm water, which ensures better absorption.
- Aloe juice has anti-inflammatory and powerful regenerative properties. Egg white is able to envelop the gastric mucosa, protecting against the aggression of hydrochloric acid. Mix these two ingredients 1:1 and drink a large spoon three times a day before meals.
- Gastritis in adults can be treated with thyme tincture. Take two tablespoons of herb and pour 500 ml. white wine, stand in the refrigerator for a week, then the resulting mixture must be boiled and strained. Take two teaspoons daily before each meal. This tincture helps patients with chronic gastritis to completely get rid of the disease.
- Mumiyo is a healing remedy from Altai that helps with gastritis. Mix a quarter gram of mumiyo with honey and milk, use the folk remedy daily on an empty stomach and before going to bed. It will be best if you add homemade milk to this cocktail, it interacts better with the other ingredients.
What types of acute gastritis are detected on fibrogastroscopy?
A significant success in gastroenterology has been the widespread implementation of fibrogastroscopic examination for symptoms of gastric damage. This is the only way to visually examine the walls of the stomach and see how gastritis manifests itself. The differences in the picture made it possible to identify types of inflammation, treat them correctly and prevent the transition to the chronic phase.
Catarrhal (simple gastritis, banal) is the most common consequence of food poisoning, usually occurring together with enteritis. It also accompanies malnutrition due to overeating and prolonged hunger. The gastric mucosa is swollen due to a massive influx of leukocytes and tissue hyperemia, the folds are smoothed.
During biopsy, areas of dystrophic changes in epithelial cells are found
Fibrinous (diphtheritic) gastritis is named after the characteristic appearance of fibrin films covering the mucous membrane. Looks like diphtheria films in the throat. Formed during poisoning with sublimate, acids, and infectious diseases.
Corrosive (necrotic, toxic-chemical) gastritis - caused by concentrated alkalis and salts of heavy metals entering the stomach. Areas of necrosis are found on the mucosa.
Phlegmonous (purulent) gastritis - occurs against the background of a stomach ulcer, cancer, severe infections. Causes purulent melting of the wall, spreading throughout the inner layer. Clinically, signs of intoxication of the whole body are detected.
Classification
There are several classifications of chronic gastritis.
Types are classified according to their type:
- surface;
- atrophic – autoimmune, multifocal;
- special forms of chronic gastritis - granulomatous, lymphocytic, radiation, reactive, eosinophilic.
The most commonly used classification is:
- gastritis A, inflammation caused by decreased immunity, the production of antibodies to the lining cells of the stomach, often has a genetic predisposition;
- chronic gastritis type B, occurs without immune disorders. The main reason for the development of type B is infection by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- type C, occurs as a result of exposure to bile from duodeno-gastric reflux or drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
In addition, there is a type of chronic mixed gastritis - A and B or pangastritis.
Types of the disease according to the location of the lesion:
- chronic diffuse gastritis - the entire gastric mucosa is completely inflamed. The causes of the formation of the diffusion type are: the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, unhealthy diet, poisoning, stress.
- chronic focal gastritis is a local inflammation of the mucous membrane, affecting only one part of the stomach.
Chronic fundic gastritis is characterized by the fact that the inflammatory process in the mucous membrane covers the upper and middle region of the stomach. This is where the glands that produce acid are located.
Lesions of the mucous membrane are localized only in this part, and the antrum continues to function fully. Very rarely it may show signs of a superficial type.
By etiology:
- infectious – Helicobacter, fungi, parasites;
- non-infectious – bile reflux, exposure to medications, alcohol, chemical elements, unhealthy diet.
Stages of chronic gastritis, which characterize the degree of inflammation:
- exacerbation;
- remission.
Chronic gastritis remission is an inactive stage of inflammation, which, under irritating factors, can go into an exacerbation phase. In the remission stage it is characterized by complete or partial absence of symptoms. The patient can reduce the strict restrictions. However, he needs to systematically carry out prevention and be regularly monitored by a doctor to prevent exacerbation.
Chronic active gastritis is an exacerbation of the disease, which is characterized by swelling and congestion of blood vessels, significant infiltration, the appearance of a large number of leukocytes and their penetration into epithelial cells. This form is accompanied by chronic inflammation of the stomach, which most often affects the lower region of the organ.
Prolonged course of the disease can cause a pathological decrease in its functionality, and therefore requires mandatory therapeutic intervention. Manifestations of active chronic gastritis of the stomach often arise as a result of a decrease in the acidity of gastric juice.