Is it dangerous to health and how is effective treatment carried out?
Find the answer Are you having a problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
The site provides reference information. Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor. Any medications have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required, as well as detailed study of the instructions! Here you can make an appointment with a doctor.
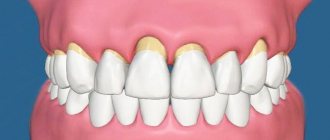
What is microsporia of smooth skin
Microsporia is an inflammation of certain areas of the skin, hair, and rarely nails, caused by a pathogenic fungus of the genus Microsporium (more than 20 of its varieties are known).
This lesion is often diagnosed in pediatric practice. Children get sick between the ages of 6 and 14 years.
Among adults, this pathology is registered in 9-25% of cases annually. Recently, there has been an increase in the number of reports of the identification of foci of infection in families affecting adults and the elderly.
Microsporia is a common disease; it ranks second among fungal diseases after mycosis of the feet.
In the last decade, there has been a trend towards a decrease in scalp microsporia and an increase in the number of smooth skin mycoses with additional inflammation of vellus hair - smooth skin microsporia.
Microsporia localization zones (photo)
Microsporia affects the smooth skin of the face, scalp and body. Fingernails and toenails, as a rule, do not suffer from this type of mycosis.
The causative agents of the disease and how long the incubation period lasts
The main causative agents of microsporia in humans are:
- The zoophilic fungus Microsporium canis - about 98% in the European part of Russia - is transmitted to humans from a sick animal;
- The anthropophilic fungus Microsporium ferrugineum - about 1% - is transmitted from person to person;
- In the territories of Siberia and the Far East, on the contrary, the pathogen Microsporium ferrugineum is more widespread.
The incubation period is the time from the first contact of the fungus with the skin until the onset of clinical manifestations of the disease.
The duration of this period for microsporia is: 7 days in the case of a zoonotic infection caused by Microsporium canis. In anthroponosis - the causative agent is Microsporium ferrugineum - longer, about 45 days.
Microsporia in humans: symptoms and signs
Once an infection enters the body, it usually appears after an incubation period. This is also typical for microsporia, the signs of which sometimes appear only a month and a half after infection.
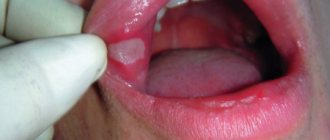
The main symptom of smooth skin microsporia is red spots with a clear contour and a swollen convex surface . The spots tend to grow and over time take on the appearance of intersecting or intersecting rings (up to three centimeters in diameter), the surface of which is covered with bubbles and crusts. The number of rings is limited - usually there are no more than five pieces.
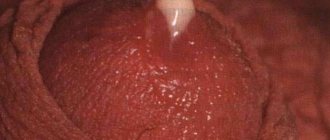
If a fungal infection occurs on the scalp , it first affects the follicle and then spreads to the entire hair , and fungal spores are deposited between the scales of the cuticle, causing damage. A striking symptom of microsporia is a “cover” of mecelium (mycelium) surrounding the hair shaft and filling the follicle. The lesions are usually one or two large spots with adjacent smaller formations. The skin in the affected area peels off (white, ring-shaped scales), and the hair easily breaks off, forming “stumps” up to six millimeters high, “powdered” with fungal spores.
The external manifestations of the fungus in children and women are similar - they are characterized by severe inflammation and moderate peeling. The most difficult thing to diagnose microsporia in a timely manner is in people suffering from atopic dermatitis , because the diseases have similar symptoms, but are treated completely differently: for atopic dermatitis, the use of hormonal ointments is indicated, which for microsporia are not only useless, but also dangerous, as they contribute to the further spread of the infection .
Attention! A late visit to the doctor is fraught with the development of a suppurative form of microsporia, the symptoms of which, namely: nodules that are soft to the touch, bluish skin color and a scattering of ulcers, significantly worsen the appearance of the skin and the patient’s well-being.
Quarantine for pathology
After identifying a sick person, you must:
- Isolate the patient from others (the child does not attend kindergarten or school);
- Disinfect clothing, work or study areas;
- Provide the patient with individual care products (soap, comb), bed linen for an infected person and thoroughly treat them daily (boiling water, washing, ironing, etc.);
- Examine relatives, employees, and classmates who were in contact with the patient;
- If you have pets, examine and treat them;
- Start antifungal treatment.
There are no clear standards for the duration of quarantine for microsporia.
- With a common form of microsporia (3 or more lesions on the skin, inflammation of vellus hair), after 1-2 smears that do not contain fungus, quarantine for the patient can be completed. This occurs approximately 2-4 weeks of treatment. The timing may be changed by the treating dermatologist.
- In mild cases of the disease - 1-2 small spots under clothes - you can limit yourself to exemption from physical education, visiting the pool, sports sections, provided that the necessary therapeutic and hygienic measures are carefully followed.
Routes of infection
The easiest way to get ringworm is through close contact with a sick person or animal. Street cats, which children love to play with, are especially dangerous in terms of infection with microsporia. After communicating with an unreliable four-legged friend, strange spots indicating illness appear in those places where the animal might have touched. It also happens that after playing with a cat or dog, a child does not wash his hands and touches his neck, stomach, face, scratches his arms or legs. Often infection occurs in a sandbox.
The second way of infection with microsporia is contact with things that were used by a person with mycosis (towel, clothing, household items). Thus, spores of the fungus Microsporum Canis can end up on any objects in a person’s environment. And as soon as he uses the contaminated item, the harmful strain will immediately spread to the skin.
Reasons for the spread of the disease
The reservoir of zoophilic microsporosis for humans is:
- Sick cats, especially kittens (70-80%);
- Dogs - much less often;
- In 4-5% of cases, small rodents (rabbits).
The main source of infection is mainly kittens, because, on the one hand, they are more susceptible to the disease due to their undeveloped immunity and developed undercoat, which is the basis for the proliferation of the fungus.
On the other hand, they are highly attractive to a child as a living toy.
Infection of children and adults with a fungus of the Microsporium canis type occurs:
- By direct contact with an affected animal;
- Or indirectly - through surfaces contaminated with its fur;
- Transmission of zoophilic fungus between people may occur rarely (2-10%).
At home, the cause of infection will be:
- Towels, bed linen;
- Hats, clothing;
- Toys;
- Carpets, upholstered furniture;
- Dust, sand of staircases;
- Animal rugs and care products.
The cause of infection in newborns can be a stroller left in the entrance at night, which is visited by cats.
In hairdressing salons:
- Towels, scissors;
- Haircut and shaving equipment;
- Peignoirs.
In kindergartens and schools:
- Towels;
- Toys;
- Clothing, hats;
- Books.
The level of infection by a fungus such as Microsporium canis varies throughout the year:
- The beginning of the increase in incidence is recorded in June.
- Growth occurs towards the end of summer and beginning of autumn.
- The maximum number of cases is often detected in October - November.
- Then there is a decline in the disease with a minimum in April.
The wavy curve is associated with the development cycle of the fungus in kittens and increased communication between children and animals in spring and summer - during the holidays (trips to dachas, villages, health and sports camps).
The increase in diseases in the autumn is explained by the return of children to the city from health camps, when they are carefully examined by their parents and routine medical examinations are carried out before visiting kindergartens and schools.
The source of anthropophilic microsporia is infected people. This microsporia is more contagious than zoophilic. Previously, when it was widespread, outbreaks of this disease were recorded in boarding schools, kindergartens, schools, orphanages, and summer camps.
Prevention
Prevention of microsporia comes down to three simple measures:
- Maintaining hygiene rules when caring for pets. Buy cats and dogs that have successfully passed a veterinary examination. Have pets living in the house periodically examined at a veterinary clinic so that a specialist can confirm the absence of diseases dangerous to the owner. Make sure that children do not kiss their pets or touch their litter box. Teach all family members to wash their hands after handling animals. Prohibit children from playing with homeless people.
- Timely diagnosis and isolation of the patient. Considering that children interact closely in kindergartens and other groups, it is important to prevent the transmission of microsporia between their visitors. Place a child sick with microsporia in home quarantine and, if possible, notify the parents of other children about the situation. Get yourself examined and ask other family members to visit a dermatologist.
- Disinfection of the patient's belongings. Any personal belongings of the patient must be disinfected. Clothes and bedding are washed with regular powder in water at a temperature of 60°C. Household items, if this does not spoil them, are boiled in a basin or pan for 15 minutes. If things cannot tolerate boiling water, they are treated with a special antifungal agent Terralin. Everything is subject to treatment - combs, dishes, towels, furniture and even shelves in the closet where the things of an adult or child with microsporia are stored.
Microsporia is a dangerous disease, and no one is immune from it. However, with timely access to the clinic and systematic treatment, doctors give a favorable prognosis for ringworm.
Strengthen your immune system and keep your body clean and your pets healthy. This will make the risk of microsporia infection minimal.
Clinical manifestations of damage to the head and other parts of the body
Conventionally, there are several types of “ringworm”:
- Damage to the scalp;
- Foci of inflammation on the skin of the limbs and torso;
- Mixed form.
In recent years, the number of atypical forms of this disease has increased, which complicate diagnosis and delay prevention and effective treatment.
Skin manifestations of microsporia:
- First, spots or papules (primary elements) appear on a piece of skin infected with a fungus.
- Then crusts appear (secondary elements of “lichen”).
More often, elements of inflammation occur at the site of contact with an infected animal:
- Face;
- Neck;
- Hands.
Much less often lesions appear on the skin:
- Shins;
- Stop;
- Sometimes on the genitals.
What does inflammation look like in zoonotic species?
Microsporium canis tends to produce many small lesions tending to merge. The dimensions of these zones are about 1-2 cm. Eyelashes and eyebrows are often involved in inflammation.
In 80-90%, vellus hair also shows signs of inflammation, which indicates the severity of the disease.
Periodically, with this form, microsporidae are detected - nodules that form with concomitant allergies. Sometimes the body temperature rises and the general condition of the person is disturbed.
Zoonotic microsporia is not characterized by a chronic course.
Description of foci of inflammation in anthropogenic microsporia
When affected by a fungus such as Microsporium ferrugineum, foci of inflammation are formed from a large number of small papules, which subsequently form a marginal border.
With a significant exudative component, papules alternate with vesicles - vesicles.
The exudate later organizes into crusts. The raised edge of the inflammatory focus consists of dried elements. In the center of the spot, inflammation can end as a result of the resorption of part of the fungus, and then begin again.
This is how the typical symptoms of this disease form - a ring in a ring. The spots on the skin are usually pale pink in color and moderately flaky.
They are often located in the form of a hyperemic border of inflammation at the junction of the scalp with the smooth skin of the neck and face. Due to the ability of neighboring elements to combine, these lesions are sometimes large and uneven in outline.
https://feedmed.ru/bolezni/kozhnye/mikrosporiya-gladkoj-kozhi.html
Unfused zones are often small in size and round in shape.
Inflammatory changes and peeling when affected by the fungus Microsporium ferrugineum are less pronounced than when affected by Microsporium canis.
Most infected vellus hairs in the area of inflammation do not have a sheath and do not break off.
This form is prone to chronicity.
Causes of microsporia
Microsporia is transmitted by contact through living and non-living objects that are contaminated with spores or infected with a fungus. The likelihood of infection increases if the skin has scratches, diaper rash, calluses and microtraumas , but for healthy skin the fungus is not dangerous, in addition, the virulence of microsporia is very low - it is impossible to get sick from it if you wash your hands with soap immediately after contact with an infected object.
Microsporia is often diagnosed in people who frequently come into contact with stray animals and land. In most cases, victims knew how the fungus was transmitted and tried to follow basic hygiene rules, but the individual characteristics of the chemical composition of human sweat and sebum .
Effective treatment for this disease
The main types of treatment for microsporia are:
- Local - the use of antifungal ointments and creams, removal of infected hair, many recipes for treatment with “traditional medicine”;
- Systemic - taking antifungal drugs orally;
- Sanitary and hygienic measures to limit the spread of infection.
Treatment of mild forms of the disease
The presence of single inflammatory areas on the skin (no more than 3 lesions) indicates a mild course. Treatment can only be external, in the form of antifungal ointments and hair removal.
External treatment:
- The locally infected area is lubricated with antifungal ointment daily for about 2 months;
- Epilation or shaving is carried out in areas of inflammation on the skin to mechanically remove the fungus, once every 5 days.
During therapy, scrapings from the lesion are performed once a week to monitor the quality of the therapy (the absence of fungus in 2-3 scrapings from the affected areas confirms a good effect of treatment).
Treatment of common forms of the disease
In the common form of “lichen,” more than 3 foci of inflammation and/or simultaneous inflammation of vellus hair at the site of the lesion are found on smooth skin. Such patients are prescribed combination therapy.
Its principle is to:
- Internal antifungal drugs;
- External treatment.
Any treatment is always carried out in conjunction with sanitary measures:
- Identification of the source of infection and its sanitation;
- Examination of those in contact with the sick person;
- Compliance with sanitary measures in the patient’s family (wet cleaning of the room, disinfection of the patient’s individual linen.).
Diagnostics
If there are strange spots on the body, a person should contact a dermatologist, infectious disease specialist or local physician. If signs of microsporia are suspected in a child, they go to the pediatrician. Due to the fact that red scaly spots are nonspecific symptoms, they are differentiated from atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, psoriasis, and lichen planus.
Experts diagnose microsporia in the following ways:
- Luminescent study.
- Analysis of biomaterial under a microscope.
- Cultural seeding.
Luminescence testing requires darkened conditions. Microsporia is identified by the bright green glow of hair whose follicles are affected by Microsporum fungi. The procedure is carried out with the help of Wood's Lama, having previously cleansed the skin of crusts and drug residues. On fresh lesions, the glow does not always occur, since the hair may not be sufficiently affected. In this case, all hair is removed from the suspected site of pathogen penetration, and then the glow is observed in the root part of the hair. When the microsporum dies, the glow remains.
Based on the results of the luminescent method, the causative agent of microsporia is determined, the effectiveness of therapeutic measures is assessed, and facts of infection and carriage of microbes in animals are revealed. Also, luminescent testing helps to monitor people who have had close contact with a patient with microsporia.
To examine the fungal nature of the disease, dermatologists conduct a microscopic examination of scales removed from the affected skin. If the fungus has affected the scalp, hair fragments are examined. When examining smooth skin flakes under a magnifying glass of a microscope, threads of mycelium are visible. When a laboratory technician examines the affected hair, a mass of small spores is found on its surface.
If microsporia is suspected, cultural diagnostics are carried out to identify the type of fungus. Knowing the exact strain, doctors can prescribe the correct treatment for microsporia and teach patients how to prevent the disease. Laboratory assistants place scales and hair in a nutrient medium and observe the growth of colonies.
The most reliable medications
The main antifungal agents for ringworm are:
- Griseofulvin, it can be used now, if it is available in the retail chain;
- Terbinofen;
- Intraconazole;
- Fluconazole.
Griseofulvin is synthesized by a number of fungi of the genus Penicillium.
Available in the following forms:
- Tablets of 500 and 125 mg (microionized and ultraionized to improve absorption);
- Suspension - 0.1 g in 1 ml of griseofulvin.
Children under 13 years of age are prescribed 22 mg/kg of griseofulvin per day, in 2-3 doses.
Take the medicine with food, adding a teaspoon of vegetable oil to improve the dissolution of the drug and increase its duration of action.
For young children - a suspension, 8 ml of which corresponds to 125 mg per tablet.
There are extended forms of this drug for a single dose.
The average duration of treatment is 8-12 weeks.
The next most commonly prescribed drug is terbinofen. Trade names: exifin, lamisil, terbizil.
Internally prescribed:
Children over 2 years old:
- Up to 20 kg - 62.5 mg;
- 20 - 40 kg - 125 mg;
- More than 40 kg - 250 mg.
Adults - 250 mg 1 time per day.
The duration of taking the drug is 8-12 weeks.
Intraconazole is a triazole derivative. Not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age.
Dosage regimen:
- 100 mg/day for children weighing up to 25 kg;
- 200 mg/day for children weighing over 25 kg in 2 divided doses.
The duration of treatment for “lichen” is about 6 weeks.
All antifungal drugs are toxic. Only a doctor should prescribe treatment.
Fluconazole is often prescribed topically (ointments, shampoos, creams, solutions).
Apply 1% exifin externally once a day for 2 months.
The use of local agents with an irritating effect (iodine, sulfur) to treat ringworm leads to an increase in residual cosmetic effects and is often not effective enough. Therefore, they can be prescribed only if the effect of more gentle methods (the use of local antifungal ointments) is poor.
Prevention of microsporia in children
To prevent ringworm, preventive measures are extremely important, since without compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules, the risk of rapid spread of the infection is high. Since there is no vaccination against this type of skin pathology, it is important to promptly detect lichen in a child and isolate him during treatment. Disease prevention should include:
- periodic examinations in children's groups;
- disinfection of household items, things on which fungal spores may live;
- raising a child, including an explanation of why stray animals should not be touched;
- Regular visits to the veterinarian for examination of pets.
Help from folk remedies
Microsporia is popularly called “ringworm.” There are many ways to treat this disease, which use juices and tinctures of vegetables, decoctions of herbs with antifungal properties, and healing ointments.
We list several recipes and substances used to treat “lichen” by non-medical methods.
Apply the juice squeezed from onions to the source of the disease.
Hungarian garlic vinegar recipe
- Peel 3 cloves of garlic and add apple cider vinegar (600 ml).
- They insist for 14 days.
- Treat the skin lesions with the prepared tincture.
Use compresses, baths and lotions from decoctions and tinctures of medicinal herbs:
- Wormwood;
- Celandine;
- Tansy.
Preparation of an effective ointment
Burnt sulfur ointment:
- Choose a base for the ointment: duck or goose fat, lanolin or petroleum jelly, or boric ointment.
- Powdered sulfur is combined with the selected base and brought to the state of thick sour cream.
The candied honey is combined with a small amount of fish oil, stirring until the mixture reaches a thick consistency.
Preparation of boric acid solution
- Dissolve a teaspoon of acid in half a glass of water.
- The solution is heated over a fire until the crystals completely disappear, then cooled.
- The prepared product is used to treat the affected areas.
Preparing propolis oil
- Grind 20 grams. Bee propolis.
- Combine with 50 gr. Vegetable oil.
- The components are combined and, stirring regularly, brought to a boil in a water bath.
- The mixture is brought to a boil again, the propolis dissolves, and the wax precipitates.
- The oil is carefully poured into a bowl.
- Lubricate areas of inflammation.
In folk medicine, birch tar, solid oil, and kerosene in pure form or in the form of ointments are widely used to treat ringworm.
Therapy only with folk remedies raises doubts about the possibility of achieving final recovery.
Causes
If a child develops lichen on smooth skin, the first step is to determine the etiology of the pathological process and the nature of the pathogenic agent. This will help prescribe external therapy as quickly as possible. The factors provoking the disease are presented below and predominate in patients of different age categories. This:
- weakened immune system;
- environmental factor;
- stay in the quarantine zone;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- use of contaminated objects;
- contact with an infected animal;
- violation of quarantine rules.
- Fungal diseases: symptoms and treatment
- Fungal skin infections in children and adults - causes, sources of infection, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
- Treatment of ringworm in humans
Risk group
As already mentioned, microsporia in humans most often develops in childhood. It is also worth highlighting a number of factors that increase the likelihood of infection:
- decreased immune defense in the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- the presence of any chronic disease in the body;
- living in a warm and humid room;
- excessive sweating;
- presence of microtraumas on the skin;
- non-compliance with sanitation standards within children's groups;
- lack of careful personal hygiene.
It is important to understand what microsporia looks like (photo can be seen below). This will help parents seek proper medical help when the first alarming symptoms appear. It is important to understand that self-medication can lead to aggravation of the disease and its progression.
Treatment of microsporia
Treatment of microsporia is carried out by a dermatologist. As a rule, local treatment of lesions is used with ointments, sprays, emulsions, which include antifungal agents. The frequency of application of these drugs and the total duration of therapy are determined by the doctor, taking into account the severity of the disease, the patient’s age, and his general condition.
In case of deep and multiple lesions, especially when the patient develops a suppurative form of microsporia, systemic treatment may be required, in which antifungal drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets or administered by injection.
In cases where microsporia is accompanied by a pronounced inflammatory reaction, combination drugs are used that include fungicides and corticosteroids, which have a powerful anti-inflammatory effect. In case of deep damage, a good effect is provided by the use of drugs based on dimethyl sulfoxide (dimexide).
Dimexide is effective for deep skin lesions
In the absence of skin lesions, the alternation method is used to treat microsporia, during which the lesions are treated with an iodine solution, then with ointment applications.
When a secondary infection occurs, local or systemic antibiotic therapy is performed.
After completing the course of treatment, the patient remains under the dispensary supervision of a dermatologist for 12 months. Deregistration is carried out only after receiving negative tests for fungi.
Recommendations for parents
During the quarantine period, children are sent home, where they must be kept subject to a number of restrictions. Quarantine should be taken calmly .
It is advisable to immediately explain its importance to the child and reassure him in order to avoid psychological problems. Parents need to accept three things:
- Quarantine is a measure necessary more for those around them than for the child himself. Therefore, even if parents are sure that a preschooler or schoolchild is healthy, they should not take him out into public places. During the incubation period, symptoms of the disease may not be noticeable, but the spores remain active and are transmitted to others.
- A child also poses a potential danger to household members, especially children, pets and weakened women. It is necessary to limit the contact of a potentially sick person with the listed groups.
- All instructions issued by a dermatologist or an employee of the sanitary-epidemiological station, including the requirements for ongoing disinfection, must be followed unquestioningly.
During the quarantine period, you need to provide the child with a separate place and separate things that will not come into contact with the things of other family members.
A separate sleeping place, cutlery and dishes, and toys are provided. Clothes are collected in a special bag and washed separately.
Important!
During the quarantine period, you cannot take documents from an educational institution and submit them to another. We must wait until the end of the dangerous period.
The causative agent of infection and methods of transmission
Fungi belonging to the genus Microsporum are very tenacious and can survive in the soil layer for up to 90 days. They easily get onto the surface of household objects and pet fur, from where they are carried onto human skin, provoking the appearance of characteristic symptoms of the development of an infectious disease.
According to modern medical concepts, the disease is a type of fungal infection that affects smooth skin, hair and nails, and at the same time this infection is considered a type of ringworm.
The genus Microsporum has about 20 species that provoke the appearance of pathology. Most often, the development of the disease occurs under the influence of such types of pathogens of the genus:
- distorum;
- rivalieri;
- angeronii;
- canis;
- nanum;
- persicolor;
- gypseum;
- cookii;
- Keratynomyces ajelloii.
About 90% of identified cases of infection are due to Microsporum canis and only 10% of cases of infection are due to all other species.
Infection with pathflora most often occurs through contact, when a healthy person comes into contact with a carrier.
Depending on the carrier, all representatives of the genus are divided into three large subgroups:
- Zoophilic - carriers are domestic animals. Most often, kittens act as carriers; less often, transmission of the pathogen occurs from puppies.
- Anthropophilic. The carrier is a person.
- Geophilic - their main habitat is the soil layer.
All three varieties of pathflora, when penetrating the skin, provoke the same disease - microsporia; they differ only in the routes of penetration and methods of infection.
Zoophilia is transmitted through contact with domestic animals. To become infected, it is enough to pet a pet that is infected with the fungus.
Anthropophiles are transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person through close contact between people and during the joint use of household items.
Geophiles are transmitted when the skin comes into contact with a soil layer contaminated with this type of fungus.
For the development of pathology in humans, only the transfer of spores to the surface of the skin is not enough. For the progression of the disease, the presence of certain factors contributing to this process is required.
Such factors allow pathogenic flora to penetrate the skin, these include:
- traumatic injuries of the body;
- maceration of the skin;
- presence of weak immunity.
For the progression of the disease, not only an infectious source with which contact is made is required, but also the presence of certain factors that allow the infection to spread and develop.
Preventive actions
Prevention of microsporia in children includes the following methods:
- maintaining distance from people infected with the disease;
- avoiding contact with stray animals;
- conducting routine examinations of family members and pets for microsporia.
If the baby is ill, all his personal belongings should be washed in water at a temperature of at least 60 degrees. It is also worth protecting the child if someone in the family becomes ill with this infectious disease.
By following simple rules of protection, you can protect yourself and your child from an unpleasant fungal disease. To maintain healthy skin and quickly get rid of the symptoms of pathology, it is important to immediately consult a doctor for a full examination when suspicious manifestations are detected.
Microsporia in children is a highly contagious pathology provoked by dermatophytes. It affects the skin, hair on the surface of the head and, in rare situations, the child’s nails.
p, blockquote 1,0,0,0,0 —>
The infection is caused by pathogenic flora belonging to Microsporum. The disease has a second, more common name - ringworm. The most common type of pathology is microsporia of the part of the head covered with hair.
p, blockquote 2,0,0,0,0 —>
Microsporia in humans is observed most often in childhood, which is associated with frequent contact of patients in this age group with pets and non-compliance with basic hygiene rules. Compared to adults, young patients suffer five times more often from this form of mycosis.
p, blockquote 3,0,0,0,0 —>
In addition to this reason, this difference in frequency of occurrence is also due to the fact that with age, the human body, starting from adolescence, is able to accumulate some organic compounds in the hair, which contribute to slower growth and the development of pathogenic flora.
p, blockquote 4,0,0,0,0 —>
What is this article about?
Characteristic symptoms of the disease
All types of microsporia are characterized both by a set of similar signs and symptoms, and by features of the clinical course that distinguish the types of the disease.
p, blockquote 24,0,0,0,0 —>
The earliest symptoms of a fungal infection are the formation of red spots in areas of infection. After a few days, the spots become pale and covered with whitish scales.
p, blockquote 25,0,0,0,0 —>
In case of infection of the skin in the scalp, hair breakage is observed, which creates the effect of a short haircut. Bald spots show skin covered with scales. Sometimes black dots form on bald spots.
p, blockquote 26,0,0,0,0 —>
Sometimes hair breakage is not observed, but instead a huge number of flakes are formed, which resembles severe dandruff. As microsporia progresses, the formation of a gray spot on the scalp may occur, from which intense hair loss occurs.
Treatment
Ringworm in children requires different treatment approaches depending on the location of the lesions. For microsporia of smooth skin, the use of external antifungal agents is sufficient; when the hair is involved, a combination of local and systemic therapy is necessary.
Local treatment
Lesions on the skin and scalp are treated with drugs with a pronounced antimycotic effect.
- Before using special antifungal drugs, it is recommended to treat the infected skin with an alcohol tincture of iodine, Dimexide or Fukortsin. It is better to carry out processing in the morning;
- After a couple of minutes, external antimycotics are applied: sulfur or sulfur-tar ointment, Clotrimazole, Iconazole, Terbinafine, available in the form of creams, ointments or sprays;
- Treatment of advanced forms of ringworm in children is carried out using combined agents containing antifungal and hormonal components (Mikozolin, Travocort). When the affected skin is infected with bacterial flora, use Triderm, which contains an antibiotic;
- For severe itching, antihistamine ointments and gels (Fenistil-gel, Suprastin) are prescribed. They block the production of the active substance of inflammation - histamine, helping to relieve inflammation, itching and swelling;
- If the hair is affected, before treatment it is necessary to cut off the lesions of ringworm in children. The hair should be washed twice a week with antifungal shampoos (Nizoral, Sebozol). After washing, the infected areas are treated with medicinal ointments.
Systemic therapy
Therapeutic measures for scalp lichen in children involve the use of external agents in combination with oral antimycotics.
The most effective and safe drug for the treatment of microsporia in children is Terbinafine. Its dosage is calculated based on the age and body weight of the child. A course of systemic therapy is carried out until the affected areas heal. Its duration is at least 4 weeks.
In case of severe itching, antihistamines for internal use are prescribed - Claritil, Suprastin, Tavegil, Fenkarol. They also reduce inflammation and redness of the skin in areas of ringworm.
Previously, the drugs Griseofulvin and Itraconazole were used in children. They eliminated the cause of ringworm quite well, but had many side effects. Currently, their use in children is prohibited.
Preventive measures
Due to the high contagiousness of ringworm, a sick child should use individual hygiene and household items. Toys, dishes, combs are treated with disinfectant solutions daily, and things are washed at temperatures above 60 degrees. To prevent an outbreak of microsporia epidemic in children's institutions, sick children are isolated.
To prevent infection, parents must conduct explanatory conversations with children about the dangers of communicating with stray animals. Timely identification of symptoms and immediate contact with a dermatologist will help cure ringworm quickly and without consequences.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
The basis for diagnosing an infectious process is an initial examination of the affected areas with the naked eye and subsequently using a fluorescent lamp.
p, blockquote 34,0,0,0,0 —>
After the initial examination, a microscopic examination is carried out to clarify the diagnosis and identify the exact type of representative of the pathflora.
p, blockquote 35,0,0,0,0 —>
The method of using a fluorescent lamp is very simple. To carry out diagnostic measures, the doctor examines the infected areas in a darkened room. Due to illumination with a special lamp, the skin and hair that have been subjected to pathological damage begin to flicker green. This phenomenon currently has no scientific explanation, but makes it easy to identify the presence of a fungal infection and diagnose microsporia.
p, blockquote 36,0,0,0,0 —>
Using a scalpel, the doctor carefully scrapes off a small amount of scale from the affected area for examination under a microscope.
p, blockquote 37,0,0,0,0 —>
Before carrying out the manipulation, the area where scraping is planned is treated with alcohol. After treatment, scales are scraped off from smooth skin, and hair fragments are also taken from the scalp.
p, blockquote 38,0,0,0,0 —>
The resulting biological material is placed on a glass slide and filled with a drop of 20% KOH solution, and after 30 minutes a microscopic examination is carried out.
p, blockquote 39,0,0,0,0 —>
When examining scales and hair, threads of the fungal mycelium are identified on which spores are attached, which makes the border of the hair unclear.
p, blockquote 40,0,0,0,0 —>
Cultural diagnostics are carried out to determine the type of fungal infection. In some cases, this method makes it possible to determine the most optimal method and tactics for carrying out therapeutic measures aimed at ridding the patient of the infectious process.
p, blockquote 41,0,0,0,0 —>
To make a reliable diagnosis, most often a visual examination and diagnosis under a Wood’s lamp, followed by microscopic examination of biological material obtained from the area affected by the infectious process is sufficient.
p, blockquote 42,0,0,0,0 —>
Skin microsporia: main symptoms of manifestation
What are the signs? What does microsporia look like? Its symptoms are quite characteristic. The incubation period in most cases lasts from five to seven days. First, a reddish spot appears on the surface of the skin where the pathogenic fungus has penetrated. It has fairly clear boundaries and increases in size as the disease progresses. Gradually, a roller forms along the edges of the spot, rising above the surface of the skin. The tissues inside turn pale, as a result of which the inflammation site takes on the appearance of a ring. The skin here begins to peel off. As for subjective sensations, patients in most cases complain of itching in the affected area, although it is not too severe.
The photo will tell you more about such a disease as microsporia. As a rule, a person develops 1-3 similar lesions. If left untreated, the spots can grow greatly and affect larger and larger areas of the skin. In women and children, the lesions often become severely inflamed. By the way, most often the fungus affects the skin of the neck, chest and shoulders.
How does infection occur?
The causative agent of the disease is two types of fungus: Microsporum ferrugineum and Microsporum canis. Both types of fungus parasitize humans, and the second also parasitizes animals. Very often, people become infected with microsporia through contact with an infected cat or dog. You can become infected not only through direct contact with an animal, but also indirectly. In addition, you can catch the disease through household items used by a sick person. Thus, combs, hats, dishes, etc. pose a potential danger.
You can become infected with microsporia in a kindergarten, at a hairdresser, and even while working in your own garden. Once in the soil, the mushroom retains its viability for another 2-3 months. Accordingly, it can pose a danger, for example, to a child playing in the sandbox. At increased risk are children and adolescents who have not yet reached puberty, as well as young women with light, sensitive skin.
Classification of the disease depending on the route of its transmission
During pregnancy
During this period, it is easier for a woman to get ringworm, since pregnancy affects hormonal levels, the state of the immune system, and makes her more vulnerable psychologically.
Early diagnosis will facilitate a quick cure, and the disease will not harm the fetus. The course of treatment is selected individually and depends on the stage of the disease and the timing of pregnancy. The main focus should be on immunity.
Underwear and bed linen should be changed twice a day, and after washing, be sure to iron both sides.
Traditional methods of treatment
Among the traditional methods that destroy microbes and fungi are:
- A mixture of onion and garlic for external use. A paste is prepared from equal proportions of onion and garlic. It is passed through a juicer and the mixture is applied several times a day to the affected areas.
- Tincture of calendula. The source of infection is wiped five times a day.
- Poplar bark tincture. Used for lubrication 4 times a day. The ratio of bark and water is 1:5.
- Birch buds. The solution is prepared from kidneys and medical alcohol. The mixture is infused for 2 weeks and applied externally. Apply to affected areas 5 times a day.
If the disease is advanced, then folk remedies are combined with traditional treatment methods.