Ureaplasma in men is intracellular microorganisms that do not have their own membrane, which affect the organs of the genitourinary system and lead to the development of ureaplasmosis. Women are more susceptible to this disease. Ureaplasmosis in men in most cases is asymptomatic, so many of them do not even suspect that they are carriers of the bacterium. The infection is considered conditionally pathogenic, as it can occur in completely healthy people. But, as soon as a person’s immunity decreases, microorganisms begin to actively multiply, leading to the development of the disease.
The effect of ureaplasma on an infected organism
Ureaplasma belongs to the opportunistic flora. This means that it is also found in healthy people. It can be present in the human microflora for a long time and not cause any discomfort. The occurrence of ureaplasma in the body does not always cause inflammation, that is, a disease as such. The active reproduction of ureaplasma is prevented by normal microflora. However, as soon as the balance is disrupted due to decreased immunity, for example, with cystitis, prostatitis, colpitis and other inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system of men and women, ureaplasma is activated and pathogenic processes begin to occur. Therefore, such an infectious disease as “ureaplasmosis” does not appear officially in medical documents at the moment; however, inflammatory diseases may be named, indicating their location and clarifying that they are caused by a specific type of ureaplasma. According to the latest (2006) classification of sexually transmitted infections according to the World Health Organization, Ureaplasma urealyticum is also included among the causative agents of sexually transmitted infections. We will conditionally call all pathogenic processes occurring as a result of the activity of ureaplasma, collectively, ureaplasmosis.
Routes of infection and causes
The activity of transient microflora is defined as an infection, since the main route of transmission of ureaplasmosis is infection through unprotected intimate contact. Household transmission is excluded; spices are anaerobes that are not capable of existing in an oxygen environment. Ureaplasma urealiticum is highly contagious (infectious), but with strong immune protection, the symptoms of its penetration into the body can be suppressed. In this case, the disease will occur in a latent form. The progression of infection is provoked by certain triggers:
- weakened immunity and anemia (anemia);
- distress (constant neuropsychological tension);
- long course of antibacterial therapy for other diseases;
- treatment with hormone-containing medications;
- presence of other STIs (sexually transmitted infections);
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system.
The incubation period of ureaplasma in men and women varies from 10 to 60 days.
During the incubation period, a man is a carrier of the disease without knowing it, which significantly increases the risk of infection of his sexual partner.
Immunoglobulins (antibodies) to bacteria are not produced in the body, so the possibility of re-infection cannot be ruled out.
Types of ureaplasma bacteria
The genus Ureaplasma is divided into 7 species. Of these 7 species, only 2 cause ureaplasmosis. It is for the presence of these two species that laboratory tests are usually taken:
- Ureaplasma urealyticum,
- Ureaplasma parvum.
When microorganisms of both types are found in a smear, they are conventionally classified as Ureaplasma spp.
Determining the type of microbes is primarily necessary to prescribe effective therapy. As for the symptoms of infection, they differ little, and there is still debate about the specific pathogenicity of both microbes. But in general, researchers are inclined to believe that there is no particular difference in the approach to treating diseases caused by these two microorganisms. And the treatment regimen in all cases of ureaplasmosis will be the same (antibiotics + local treatment + immunostimulating therapy).
Causes
The disease is provoked by ureaplasma. Habitat in the human body: mucous membranes of the genital organs, urinary tract. Microorganisms can remain in this environment for years without causing pathologies in their hosts.
Health problems begin not after ureaplasma penetrates the body (sexually transmitted), but from the moment of active growth in their numbers.
Factors that provoke their reproduction in the male body:
- HIV infection and other STDs;
- refusal to use condoms (they should be used even if a woman uses birth control pills or has an IUD installed);
- therapy with potent medications (antibiotics, hormones, anti-cancer drugs);
- long-term intake of sports nutrition in large doses (foods that affect a man’s hormonal system are especially dangerous);
- surgeries on the pelvic organs;
- disturbance of the psycho-emotional background, mental stress.
A growth spurt can be caused by the penetration of other viruses and pathogens. The cause of ureaplasmosis is also sought in lifestyle. Moreover, sometimes the disease is provoked by events that, in isolation from the situation, can be described as positive. For example, a decision to lose weight.
For the body, weight correction is a strong stress, accompanied by instability of the hormonal system. This background is ideal for activating microorganisms in the genitourinary tract. If strict diets and fasting are added to the process, then the likelihood of activation of the pathological process increases many times over. Lack of nutrients, vitamin deficiency are prerequisites and common causes of ureaplasmosis.
Important! The microorganisms in question occupy an intermediate position between viruses and bacteria. They are considered opportunistic pathogens. This means that a positive test result does not always lead to therapy.
Causes of ureaplasmosis in men
In the vast majority of cases, ureplasma infection enters the body through sexual contact. Intrauterine transmission of infection from a sick mother to a child or infection during childbirth is also possible. A number of experiments have proven that it is possible to spread the virus through household means. Thus, it is able to remain viable on a damp surface for 2 days. Ureaplasma was detected in samples taken from public toilet seats. However, the possibility of this method of infection has not been proven.
Just because a pathogen has entered your body does not mean that you will get sick. Therefore, the causes of ureaplasmosis can also be called:
- general decrease in immunity,
- the presence of other diseases of the genitourinary system,
- insufficient hygiene,
- long-term use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs,
- general exhaustion, stress, etc.
For the same reason, the infection can be contracted not only from a sick person, but also from someone who is a carrier but does not have any symptoms of the disease.
Causes of the disease and factors predisposing to it
Ureaplasma is transmitted from a sick partner (carrier) through unprotected sex. Infection of children is possible in utero or at the time of birth - passing through the mother’s birth canal, the newborn can become a carrier of infection if the microorganism is present in the epithelium.
In the first weeks, the microbe does not have a negative effect on the baby’s body, but as the protective forces decrease, it becomes more active, which may be indicated by urination problems and discharge from the genital tract in girls.
Very often, ureaplasmosis in children causes combined infections, since the microbe settles not only on the genital tract, but also in the respiratory tract.
The likelihood of infection with Ureaplasma urealyticum in adults is increased in several cases:
- With promiscuous sexual intercourse and frequent changes of partners;
- If sexual activity begins early. In adolescents, the development of the body continues, the immune system does not work at full strength, that is, it does not fully protect the body from dangerous pathogens;
- Under the age of 30. It is during this period that sexual life is most active, so the risk of any sexually transmitted infections is greatly increased;
- During treatment with antibiotics and hormonal medications. These medications disrupt the natural microflora of the genital organs, as a result of which the development of pathogenic microorganisms is activated;
- During immunosuppressive therapy and chemotherapy;
- With emotional stress, frequent stress;
- If the most basic rules of intimate hygiene are not followed.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Hydronephrosis of the kidney, what is the danger, how to treat the disease
The main symptoms of ureaplasmosis in men
It is important to remember that ureaplasmosis in men often occurs latently, without causing clear symptoms. The incubation period, that is, the period between infection and the appearance of the first symptoms, is approximately a month. All this time, ureaplasmosis does not manifest itself in any way, but a person can already infect a sexual partner. After incubation time, ureaplasma in men causes symptoms such as: pain, itching, burning in the urethra, especially disturbing during urination. There is also cloudy mucous discharge from the canal in the morning.
The penetration of ureaplasma into epithelial cells can manifest itself as a sore throat if the infection occurs orally. The problem is that the severity of symptoms can be mild, it depends on the general condition of the body. In addition, after a few days the symptoms completely disappear. And if at this time the patient does not consult a doctor and begin treatment, the disease progresses. The microorganism moves through the mucous membrane of the urethra into the seminal vesicles, testicles, and prostate gland. The virus does not reveal itself in any way until the immunity decreases. Then signs of inflammation will appear again.
Forecast
The prognosis for life is favorable.
In the absence of treatment, ureaplasmosis in men can become chronic. Under the influence of stress, colds, hypothermia or drinking alcoholic beverages, the disease periodically worsens, and then goes into remission again - such a protracted course of the disease reduces the quality of life and can lead to infertility.
Treatment of ureaplasmosis in men is carried out using broad-spectrum antibiotics, which leads to an imbalance of the normal microflora of the patient’s body. As a result, they may develop secondary fungal infections that require appropriate therapy.
Possible complications with ureaplasmosis
An inflammatory process in the genitourinary system, provoked by ureaplasma, especially if it occurs repeatedly against the background of any decrease in immunity, as a consequence of hypothermia or stress, or any other disease, can lead to serious complications:
- Urethritis (inflammation of the urethra). The most common complication in men. Its manifestations are the same as during the initial manifestation of infection. In the acute course of the disease, the symptoms are absolutely similar to those of gonorrhea: the external opening of the urethra becomes swollen and inflamed, purulent discharge is noticeable. Urine may be cloudy only in the morning when you first urinate or constantly, depending on what part of the canal is affected by the inflammatory process.
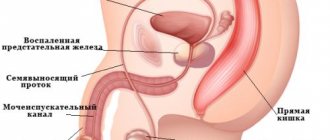
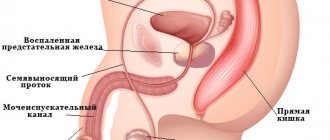
- Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland). With prostatitis, there is pain in the perineum, discomfort, frequent urge to urinate, which is very difficult and causes pain. The consequences of prostatitis are erectile dysfunction and infertility.
- Epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis) Occurs much less frequently than urethritis and prostatitis. It has a single subjective symptom: compaction, swelling in the scrotum area. It is usually painless.
Ureaplasma can parasitize sperm, attaching to their cell membrane. This significantly reduces their mobility. In addition, ureaplasma in the process of life produces enzymes that disrupt spermatogenesis. All this together causes male infertility.
The infection can also affect other organs, leading to pyelonephritis, urolithiasis, and rheumatic diseases.
Symptoms of infection
Women always have pronounced manifestations of the disease, but men do not have characteristic signs pointing specifically to ureaplasmosis. The symptoms caused by the infection are similar to other STIs. Bacterial damage to the genitourinary system occurs in waves. Latent periods are replaced by exacerbation, during which the following appear:
- pain in the genitals during intimacy;
- burning sensation when emptying the bladder;
- slight discharge through the external opening of the urethra (urethra).
Severe infection is accompanied by low-grade body temperature (37-38℃).
If you suspect an infection, you should seek medical help. A doctor who treats ureaplasma in men and women is called a dermatovenerologist. In parallel, a man needs to consult a urologist or andrologist (specialists in male diseases).
Diagnosis of ureaplasmosis
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is based on the detection of antibodies to ureaplasma proteins in the blood. This method allows you to determine the type of ureaplasma (urealyticum or parvum), as well as the titer, that is, the number of microorganisms. Currently, it is considered a not very accurate method and difficult to interpret, since stable immunity to ureaplasma is not developed, in addition, patients infected with ureaplasma do not always have an inflammatory process.
- Direct and indirect immunofluorescence (RNIF and RPIF). The most accessible diagnostic method, but, unfortunately, also approximate (accuracy 50 - 70%).
- Bacteriological seeding (cultural method). Longer and more expensive method. But it allows you to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to drugs and prescribe the most adequate therapy. It is based on sowing flora on an artificial nutrient medium, growing microbes and treating them with antibacterial drugs.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) The most accurate and effective diagnostic method. Detects even a single bacterium long before the clinical picture of the disease appears. Its disadvantage is its high cost.
Diagnosis and tests used
In order to make a correct diagnosis, the doctor prescribes several tests for the patient to detect ureaplasma. Urine, blood, a smear from the walls of the vagina or urethra, and scraping are used as biomaterial for research.
The doctor decides what kind of analysis the patient needs based on the symptoms and course of the disease, and concomitant pathologies.
Analysis methods:
- CULTURAL METHOD. Or in other words, bacteriological culture. A smear from the cervix or from the walls of the urethra is placed in a nutrient medium; in the presence of ureaplasmas, the process of their active reproduction begins, which is recorded by a laboratory assistant. At the same time, bacterial culture is used to determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to antibiotics (helps to select the most effective medicine). Cultural analysis is one of the most accurate, but it takes on average 3-7 days;
- PCR – POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION. The accuracy of the diagnostic method is about 98%, and the results are ready in a few hours. The biomaterial used is vaginal secretion, urine. PCR detects sections of ureaplasma RNA in the human body, even if the microbe is contained in the smallest amount in the sample. But PCR also has its drawbacks - during the analysis it is impossible to obtain information about the degree of activity of the infectious agent, the result can be false positive (if the biomaterial is collected incorrectly) or false negative. In the latter case, ureaplasma is often not detected if the subject took antibiotics less than 4 weeks before sampling;
- ELISA – ENZYME IMMUNO ASSAY. It involves placing the patient’s blood on a strip containing antigens with the suspected causative agent of the disease. ELISA does not detect the pathogenic microorganism itself, but the antibodies produced by the immune system. With each infection, certain complexes are produced, so enzyme immunoassay is also considered accurate. The main disadvantage of the ELISA method is that antibodies are not always produced in the body, so ureaplasma may not be identified.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Can polycystic kidney disease be cured? Prognosis and lifestyle of the patient
Serological analysis can also be used, but compared to the above, it is less accurate.
Where is material donated for ureaplasmosis?
It is currently possible to submit biomaterial for detection of ureaplasma in almost any municipal and private clinic.
The accuracy of diagnosis depends not only on the research method, but also on the equipment used in the selected laboratory.
Therefore, it is better to carry out diagnostics in modern medical centers that specialize specifically in laboratory diagnostics.
Rules for collecting biomaterial
The accuracy of laboratory methods for detecting ureaplasmosis depends on how correctly the biomaterial is taken:
- Blood tests are taken in the morning on an empty stomach;
- When collecting urine, it is advisable not to urinate for at least 5 hours, so a morning portion of urine is required;
- When taking scrapings from the urethra, men should not urinate for at least 2 hours;
- For women, vaginal smears and scrapings are not taken on menstrual days; it is preferable to take biomaterial in the middle of the cycle;
- Sexual contact should be avoided 2-3 days before collecting biomaterial from the urethra and genitals;
- Before taking a scraping and smear, intimate hygiene is carried out the evening before the test; this cannot be done in the morning;
- A few days before collecting biomaterial, women should stop using local contraceptives in the form of ointments, suppositories, vaginal tablets, and should not douche or wash themselves with hot water.
False negative results may occur if the patient has taken antiviral or antibacterial agents for less than a month. Therefore, the doctor should be warned about such treatment.
Interpretation of analyzes
Decryption is carried out by a specialist. Each research method has its own norm. When examined using the ELISA method, the form indicates the amount of antibodies (titer) and the normal values are next to it.
Different laboratories use their own equipment, so the normal titer may vary.
When performing PCR and culture methods, the norm is considered to be 104 CFU per 1 ml of sample; exceeding this value indicates pathology. But in any case, the tests must be deciphered by the attending physician and, based on them, a treatment regimen must be selected.
Which doctor treats ureaplasmosis in men
When the first symptoms appear that may indicate ureaplasmosis, you should consult a urologist. A urologist will conduct an initial examination, collect anamnesis, and prescribe the necessary tests. If ureaplasma is detected, treatment will be prescribed. If the case is quite ordinary and there are no other concomitant infections, then a urologist will handle the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. If the case turns out to be more advanced or complex, the urologist will refer the patient to a venereologist who directly specializes in sexually transmitted diseases. You can also immediately contact a venereologist. Especially if the presence of ureaplasmosis has already been confirmed.
Diagnostic measures
Ureaplamoz in men is rarely asymptomatic, so when the first signs appear, you should seek qualified medical help from a urologist . At the initial appointment with the doctor, the man will be given directions for laboratory tests, the doctor will interview the patient to find out the possible route of infection and the form of the disease.
Laboratory tests for ureaplasmosis in men include:
- spermogram;
- bacteriological culture of microflora discharged from the patient’s urethra;
- linked immunosorbent assay;
- microbiological examination of ejaculate.
Any examination of a man is prescribed on an individual basis - the doctor, for example, may prescribe specific diagnostics to identify concomitant infections of the genitourinary and other systems.
Treatment of ureaplasmosis in men
Treatment of ureaplasma in men is carried out in the same way as treatment in women. However, the specifics of treatment may be determined by concomitant diseases and the specific localization of the inflammatory process. Treatment of ureaplasma in men includes drugs such as antibiotics, immunostimulants and local agents, the regimen for which should be drawn up by a doctor.
The following drugs are used to treat ureaplasma in men:
- The basis of treatment is tetracycline antibiotics, macrolides or fluoroquinolones. The most common choice for primary disease is Doxycycline (Unidox Solutab) or Azithromycin (Sumamed). Doxycycline is prescribed in a dosage of 100 mg 2 times a day. Duration of treatment is 7 – 14 days. Begin by taking the drug in a double dose (200 mg), then continue treatment according to the usual regimen.
- Azithromycin has more regimens for use. 500 mg on the first day and 250 mg for another 4 days. Or 250 mg for 7 days.
It is possible to prescribe other antibiotics, since the resistance of strains to certain groups of drugs changes and, unfortunately, tends to increase. Judging by the reviews of some doctors on medical forums, many of them are already inclined to consider Doxycycline ineffective and prescribe only macrolide or quinolone antibiotics (for mixed infections). A widely used method of treating STDs with a single dose of Azithromycin (Sumamed) at a dosage of 1 g is ineffective against ureaplasma. A longer dosage regimen is required.
Recently, when prescribing treatment for ureaplasmosis, doctors are attaching increasing importance to immunomodulatory drugs. Because without restoring the good state of the immune system, no antibacterial drugs can completely cure a ureaplasma infection, much less prevent its relapses. Drugs such as Immunal, Amiksin, Likopid, Methyluracil, Pantocrim may be prescribed. Another thing is that the very effect of pharmacological drugs on the state of the immune system still causes controversy in the scientific community. Some doctors prescribe immunomodulatory drugs, others prefer to make do with multivitamins and recommendations on non-drug ways to increase immunity, which come down to a healthy lifestyle.
Local preparations, such as suppositories, are most often used as additional means, for example, to prevent the development of a fungal infection, which often accompanies ureaplasmosis, and in addition, can develop while taking antibiotics. Quite often, both men and women are prescribed suppositories with immunomodulatory and immunostimulating effects (Genferon, Viferon). Wound healing agents are also used for local treatment in cases of severe swelling and damage to the skin.
To alleviate the manifestations of inflammation, folk remedies are also suitable: baths or compresses with decoctions of herbs that have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects, such as chamomile, string, plantain. Such procedures will relieve the condition associated with itching and swelling, in parallel with antibiotic treatment or before prescribing therapy by the attending physician, while awaiting test results.
After completing a course of antibiotic treatment, it is necessary to restore the intestinal microflora by taking probiotics or prebiotics (Linex, Bifiform, Hilak Forte, etc.), since healthy microflora is an important condition for the well-being of the immune system. And also support the body by taking multivitamins.
During the period of treatment, it is necessary to exclude sexual activity; in extreme cases, be sure to use condoms, even with a regular partner who is also undergoing treatment. During the treatment period, you need to follow a diet: it is important to exclude spicy, fatty foods, sweets, and alcohol. Prefer boiled and stewed dishes to fried ones. Eat enough vegetables and fruits. The diet is aimed both at reducing unpleasant symptoms and at maintaining the body engaged in fighting infection.
Treatment
Treatment of Ureaplasmosis is based on test results and the presence of concomitant diseases. As a rule, therapeutic therapy consists of the following drugs:
- antibacterial agents;
- antifungal drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- immunomodulators;
- vitamin complex.
Quite often, the medicine is administered locally, that is, directly into the urethra. Physiotherapeutic procedures may also be prescribed. It is important to carry out therapeutic therapy for concomitant diseases. Treatment measures may be required to relieve urinary stagnation. A person who has been diagnosed with Ureaplasmosis must understand that he could infect his sexual partner, which means both should undergo treatment. Such measures are very important, because if this is not done, the infection will occur again. And if the disease becomes chronic, it can lead to complications.
Relapse or reinfection in men
If symptoms return, you should definitely contact a specialist again.
Important: Under no circumstances should you independently prescribe a second course of treatment with the same drugs that were prescribed by your doctor for the first time!
As a rule, ureaplasma that is not completely cured becomes resistant to the drug. Such actions can provoke the transition of the infection into a chronic, difficult-to-treat form. In addition, the symptoms of ureaplasmosis are almost identical to the symptoms that occur when infected with other microorganisms, for example, gardnerella. If you contact a paid specialist who is not familiar with your medical history, be sure to report the previous episode and what medications and regimen were used. Whether the course of treatment was completed completely and whether control tests were taken.
What happens if ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis are not cured?
In large numbers, microorganisms that cause these diseases, in addition to inflammatory processes, also provoke the following pathological manifestations:
- respiratory diseases (with the accumulation of other infections);
- problems with hematopoiesis;
- vascular damage;
- some types of arthritis;
- disruption of the process of seminal fluid formation;
- decreased sperm motility.
On a note! In approximately 40% of patients with complete or partial infertility, mycoplasma and ureaplasma were found in biomaterials.
Prevention of ureaplasmosis in men
The most important rule for preventing any STDs is to have sex with a reliable partner and avoid casual sexual contact. If they do occur, it is necessary to use barrier contraception - condoms. They do not provide 100% protection against ureaplasmosis, however, they reduce the risk of infection many times over. It must be remembered that infection can also occur through oral contact. If unprotected contact occurs, you need to treat the genitals as quickly as possible with an antiseptic: miramistin, chlorhexidine.
If unprotected contacts sometimes occur, you need to be regularly tested for hidden infections. Remember that ureaplasmosis is very often asymptomatic.
Any genitourinary disease must be treated promptly and thoroughly.
Maintain genital hygiene. Ureaplasma infection is especially dangerous for people with reduced immunity, so a healthy lifestyle is of particular importance.
Prevention
To prevent ureaplasmosis, as with other sexually transmitted infections, it is important to avoid unprotected sex with casual partners. Using a condom is also necessary during anal sex.
Antiseptics Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, etc. are suitable for local use; they are recommended to treat the mucous membranes of the genital organs, but no later than 2 hours after sexual intercourse. However, it is worth remembering that using them too often can lead to burns or provoke an allergic reaction.
Miramistin is a drug that has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and local immunoadjuvant effects. The average price in Russian pharmacies is 300 rubles.
Having noticed any signs of ureaplasmosis, a man should consult a doctor. This will help identify the infection at the initial stage of its development, when the disease responds well to treatment. Only a doctor should choose therapy, since uncontrolled use of medications can only aggravate the situation and cause a number of complications.
Due to the fact that ureaplasma can remain silent for a long time, every man should undergo a preventive examination with a urologist at least once a year. It is also important to strengthen your immune system and lead an active and healthy lifestyle.
Types of disease
The clinical characteristics of ureaplasmosis are judged by the characteristics of its course and the severity of symptoms:
- Carriers of ureaplasma . The overwhelming majority of women who carry these bacteria in their bodies have no signs of inflammation at all.
- Acute pathology . It is rare and has severe symptoms of intoxication and pathology of the genitourinary organs. In this case, the most difficult course of treatment for ureaplasmosis is in men.
- Chronic pathology . There are no indicators of acute inflammation. Or they make themselves felt periodically - in case of provocation. There may be problems with reproductive function and inflammation in the urogenital tract.
One type of pathology can easily transform into another; it is enough to trigger the disease.
Which specialist should I contact with a delicate problem?
At the slightest suspicion of the development of ureaplasmosis or if there is discomfort when urinating or having sexual intercourse, it is recommended to visit the offices of a urologist and venereologist.
The initial appointment allows the doctor to collect the patient’s medical history and perform a genital examination. After the first visit, the patient is sent for tests. Only after receiving the results, the attending physician prescribes a treatment regimen for the disease.
Diet
During the treatment of ureaplasmosis with drugs of the tetracycline group, you should not consume kefir, smoked meats, cottage cheese, and milk. Dairy products, as well as spinach, cabbage, nuts, eggs and cranberries are not eaten during the treatment of pelvic inflammatory diseases with Biseptol.
All groups of antibiotics are incompatible with alcohol. Against the background of simultaneous use, persistent gastrointestinal disorders, shortness of breath, and tachycardia develop.
It is not recommended to consume foods that have an aggressive effect on the intestines:
- canned food (primarily meat, fish, vegetables);
- yoghurts;
- sweet fruits;
- kidneys, liver, heart;
- condensed milk;
- semi-finished products;
- ready-made dishes with the addition of tomato paste;
- pasta made from soft flour;
- sweets;
- legumes;
- carbonated drinks;
- refractory fats of animal origin.
Eating these foods entails an increased likelihood of developing intestinal dysbiosis due to the use of antibiotics. To prevent events from developing in a negative way, a man should include the following foods in his diet:
- porridge from buckwheat, corn, rye, millet, wheat;
- Jerusalem artichoke;
- non-canned juices;
- zucchini, pumpkin;
- banana;
- carrot.
On a note! Berries are generally useful and necessary, but they are not compatible with some medications. You should definitely ask the attending physician who prescribed drug therapy about the advisability of using these food products.
Symptoms
The duration of the latent period of ureaplasmosis ranges from several days to several months. When signs of pathology have not yet made themselves felt, but microorganisms are already present, the person is simply considered a carrier.
Quite often, bacterial damage is subtle and does not appear at all. Carriers may not be aware of the pathology even after being infected with bacteria for several years.
In men
Ureaplasmosis in men manifests itself as follows:
- Urethritis - inflammation of the urinary canal traditionally appears first. A man feels a burning sensation in the urethra, which increases with urination. Having sex with ureaplasmosis is also painful, especially during ejaculation.
- Discharge from the urinary tract is quite scanty and in the form of liquid mucus.
- Inflammation of the appendages - observed with severe pathology. In the testicles there is heaviness and pain of a bursting nature, especially when palpated.
- Prostatitis - appears a short period after the symptoms of the pathology are detected. Talks about the development and progression of bacteria. A man feels pain in the perineal area, which often increases in a sitting position and when palpating. Libido and erection duration often decrease. During sexual intercourse, discomfort can sometimes occur.
- Infertility - occurs in cases of advanced prostatitis and testicular pathology.
In general, ureaplasmosis in men is a rarer occurrence than in women. Quite often, symptoms do not appear.
Among women
Ureaplasmosis in women has the following symptoms:
- Urethritis is a burning sensation in the area of the urethra, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the outer urethral part. Discharge from the urethra and vagina, scanty and in the form of mucus.
- Pain during sexual intercourse - appears due to mechanical impact on the mucous membrane, which is inflamed.
- Vaginal discharge is more abundant than usual, but colorless and odorless, and may be bloody after intimate contact. With ureaplasmosis, they appear due to inflammation of the mucous membrane and increased sensitivity of the vagina.
- Pain just above the pubis - similar symptoms of ureaplasmosis in women appear due to the movement of bacteria through the genital tract and infection of the uterine mucosa and tubes. May lead to andexitis and endometritis.
- Infertility is a consequence of inflammation of the genital tract and infection of the uterine endometrium. Causes miscarriages in the early stages of pregnancy or complete infertility.
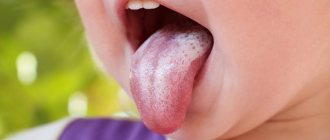
In the oral cavity, these bacteria cause a sore throat, manifested by the following specific symptoms:
- Enlarged tonsils and lymph nodes;
- Pain when swallowing;
- Weakness and ailments.
The symptoms of ureaplasmosis are mild and subside fairly quickly, but the bacteria have not left the body.
Under the slightest favorable conditions for bacteria, such as a weakened immune system or stress, the infection will manifest itself again and the symptoms will return with greater force.
Distinctive features
Ureaplasmosis is classified as a disease transmitted during sexual intercourse. The causative agent is an intracellular parasite, which in medicine is called Ureaplasma urealyticum.
The disease affects the genitourinary system. Symptoms are localized in the urethra and on the surface of the genital organs. Ureaplasma occurs in chronic or acute form.
The incubation period lasts 2 weeks. At this time, the carrier of the infection is unaware of its presence. Bacteria can affect the prostate area. This provokes the development of orchitis, pyelonephritis and prostatitis. Complications of the disease include infertility.
Ureaplasma can be transmitted from mother to child during labor. Doctors recommend getting rid of the infection before planning a pregnancy.
Causes
The infection is transmitted during intimacy. There is a claim that you can get sick with ureaplasma by contacting the patient’s personal belongings. But such cases are rare. The disease actively develops when the body is weakened.
The reasons for the appearance of pathology are as follows:
- damage to the mucous surface of the genital epithelium;
- suppression of immunity;
- increased titer of the disease.
The risk of getting sick is present in men with a low quality of life. This list includes people with pathologies of the immune system, addicted to bad habits and men who have multiple sexual relationships. Exacerbation of ureaplasmosis occurs after therapy with antibiotics or hormones.
Treatment at home
In addition to drug treatment, you can use some folk remedies, but it is worth remembering that self-medication and turning to traditional medicine may not only not help, but also aggravate the situation.
For this reason, before drinking decoctions and tinctures made according to traditional recipes, it is worth consulting with doctors: in many cases, doctors not only do not reject alternative medicine, but even encourage it.
Collections of medicinal herbs
In the same ratio you need to mix yarrow, birch buds, thyme leaves, the root of the Leuzea plant, wild rosemary, string and burnet grass. Everything is crushed and mixed, after which a glass (200 ml) of boiling water is taken per tablespoon of this ready-made mixture, in which the product is infused for nine hours.
The collection is taken twice a day, half a glass, strictly before meals.
An alternative remedy is a herbal mixture, which includes:
- lungwort;
- violet;
- dill fruits;
- primrose roots;
- nettle and birch leaves.
All herbs are crushed, two parts of meadowsweet and plantain flowers and a little more (three parts) of raspberry leaves, string grass and rose hips are added to the mixture (all this needs to be ground and chopped).
The product is also infused for eight to nine hours and in the same quantities (a tablespoon per glass of boiling water), but you need to drink the product by dividing the contents of the glass into three equal parts three times a day before breakfast, lunch and dinner.
goldenrod
This plant is used not only for treating ureaplasmosis at home, but also perfectly helps with some other common diseases of the genitourinary system (in particular, cystitis and urethritis).
In the case of ureaplasmosis, goldenrod is used as follows: the grass is crushed and two tablespoons are added to a glass of boiling water, in which it is infused for half an hour.
The product must be taken four times a day at regular intervals. The course lasts three weeks.
Garlic
This is the simplest, cheapest and safest of all folk remedies. To speed up the treatment of ureaplasmosis, it is enough to eat four cloves of garlic daily - this is enough to stop the proliferation of pathogenic microflora in the body.
But garlic is not a full-fledged remedy for treatment, the use of which could neglect other methods.
Yes, and other folk methods and treatment at home are only auxiliary, but the main course should be prescribed by a doctor.
Routes of transmission and main risk factors
Ureaplasma urealiticui and parvum can enter a man’s body in several ways:
- The main method of transmission of infection is considered to be sexual. This occurs during sexual intercourse in which a condom is not used.
- In some cases, microorganisms can be transmitted through blood or saliva.
- Experts note cases of infection during medical procedures with poorly sterilized instruments.
The appearance of ureaplasmosis in men is due to the influence of certain negative factors. These include: a decrease in the body’s protective functions, the presence of concomitant or previously suffered urological diseases, prolonged stay in a state of stress, disruption of the hormonal system, insufficient duration of proper rest, addiction to smoking or drinking alcohol.
If you have a healthy immune system, bacteria that enter the body quickly die and do no harm. Therefore, a correct lifestyle, a sufficient amount of vitamins consumed, physical activity and proper rest will help protect against many diseases.
The main danger is promiscuity. Therefore, when having sexual intercourse with an untested partner, it is imperative to use a condom.
Treatment methods
If the disease is chronic, then immunostimulating agents are used in treatment. Local treatment and antibiotic treatment are carried out. If necessary, antibiotics are administered by intravenous infusion, which significantly improves their bioavailability and makes it possible to avoid many side effects associated with the passage of the antibiotic through the liver when taking tablets.
Doctor Sergei Lenkin talks about methods of treating ureaplasmosis in men in this video:
Antibiotics
Therapy for ureaplasmosis is based on taking antibiotics. Most often it is Josamycin or Doxycycline. They are the most effective. However, the following antibacterial drugs are also used:
- Tetracycline;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Erythromycin;
- Ofloxacin;
- Midecamycin;
- Azithromycin;
- Levofloxacin.
In some special cases, lincosamines and aminoglycosides are used.
Treatment regimens with the main drugs - Doxycycline and Josamycin - are as follows:
- Doxycycline – 100 mg twice a day for 10 days. The cost of a course of treatment is from 50 rubles.
- Josamycin - 500 mg three times a day for 10 days. The cost of a course of treatment is up to 400 rubles.
Antifungal agents
For the purpose of prevention, it is recommended to use antifungal drugs, as well as anti-inflammatory drugs. For example, Diflucan is an antifungal drug, and Vitaferon is an anti-inflammatory drug. These drugs relieve the main symptoms of the disease and also partially help normalize the microflora.
Immunomodulators and vitamins
To treat ureaplasmosis, immunomodulators are used to strengthen the immune system and increase the patient’s own defenses. After all, the causative agent of the disease may not manifest itself in any way when it enters the human body for a long time.
Popular immunomodulators:
- Immunoglobulins are drugs made from human plasma. For example, Ureaplasma Immun is intended for intramuscular administration. The peculiarity of this drug is that it is synthesized from human blood, and then processed and concentrated using a special method.
- Interferons are most often used in the treatment of ureaplasma in men. The use of interferons can significantly reduce treatment and enhance the effect of antibacterial drugs (Cycloferon, Neovir).
- Stimulators of the formation of endogenous interferon - plant or synthetic origin. The main role is to activate the body's own defenses. These include Cycloferon, Levamisole and Cyanocobalamin.
- Stimulators of cellular immunity - designed to increase the level of T-lymphocytes. The most popular are Thymogen, Myelopid, Timalin.
- At the end of the course of treatment, the attending physician prescribes vitamins B and C.
Nutrition when infected with ureaplasma
There are no special dietary requirements during treatment of ureaplasma. It is worth adhering to the principles of rational nutrition and a healthy lifestyle. The diet aims to increase the body's defenses and must contain the required amount of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, beneficial vitamins and microelements.
Permitted products include:
- seafood;
- porridge;
- lean meat;
- dairy products;
- pasta;
- vegetables;
- fruits and berries.
Folk remedies
Ureaplasmosis is also treated using traditional methods, among which decoctions and infusions are considered the most effective. You can take note of the following recipes:
- Mix flax seeds, coltsfoot flowers and olive leaves in equal proportions. Mix everything, take 1 tbsp. l. the resulting collection, pour half a liter of boiling water over it and let it brew for 2 hours. The decoction is taken 3 times a day, 100 ml.
- Goldenrod decoction. 4 tbsp. l. pour 1 liter of boiling water over the herbs and let it brew overnight. In the morning, strain the broth and take half a glass 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 3 weeks. The herb is known for its anti-inflammatory properties. It helps restore intestinal microflora.
- Take 1 tbsp. l. clover, calamus root, dill seeds and St. John's wort. Then add another 1 tsp. wormwood and violet flowers, as well as 2 tbsp. l. dried plantain leaves. Mix and grind in a coffee grinder. Take 1 tbsp. l. powder, pour half a liter of boiling water and leave for 10 hours, after which the broth is filtered and taken 1/3 cup three times a day 15 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 3 months.
- Alcohol tincture. 25 g of juniper berries and 50 g of celandine, poplar buds and bird cherry bark are mixed, placed in a glass jar and filled with 350 ml of medical alcohol. After this, the jar is closed and left to infuse in a dark place for 2 weeks, shaking it periodically. When the tincture is ready, it is taken 45 minutes before meals. The first 10 days, 20 drops each, then 10 days, 30 drops each, and 10 days again, 20 drops each. The course is repeated after 2 months.
Homemade ointment is also used to treat men. You need 100 g of walnuts, grind and mix with 250 g of melted pork fat. The resulting mixture is ground through cheesecloth and sent to the refrigerator. Apply to the genitals every day before bed for a month.
Is treatment required for the partner?
Ureaplasma is an infection that is sexually transmitted. Therefore, treatment will be effective only when both sexual partners undergo it.
As in men, in women the main drugs are antibiotics (macrolides and tetracyclines). The main goals of treatment for women are:
- reduction in the amount of ureaplasma;
- elimination of clinical signs of inflammation;
- elimination of laboratory signs of inflammation;
- increasing immunity.
The main therapy is supplemented with local treatment, physiotherapeutic procedures, and immunomodulation.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is prescribed after a course of antibiotics. When selecting methods, they rely on concomitant diseases. For prostatitis and inflammatory processes that have developed in a man against the background of ureaplasmosis, the following is prescribed:
- electrical stimulation of the prostate (during stimulation with current, electrodes are both placed on the external parts of the body and inserted into the anus);
- laser physiotherapy (indicated for pronounced inflammatory processes, helps relieve symptoms and normalize hematopoietic and metabolic processes);
- electrophoresis (performed after prostate massage, helps consolidate the results of drug treatment);
- magnetic therapy (improves the permeability of medications, relieves the symptoms of the underlying and concomitant diseases, often used in parallel with the previous technique).