Introduction
Dermatomycoses are diseases of the skin and nails caused by parasitic fungi..
Some types of this fungus only affect humans, while others can inhabit the body of a wider range of mammals.
However, some parasitic fungi are transmitted from animals to humans. Mycosis is an insidious disease that is difficult to treat and causes its carrier a lot of both physical and aesthetic inconvenience.
Why treatment doesn't always help
If, after several months of therapy, the patient still cannot forget what fungus looks like on the skin of the legs or another part of the body, treatment tactics should be adjusted and lifestyle should be reconsidered. Often, infected people themselves do not take their disease seriously, are in no hurry to seek help from doctors, or try to get rid of the fungus using untested folk remedies, following the advice of friends. You cannot experiment with treatment! Positive results can only be achieved with the help of specialists. Moreover, in no case should you stop the course of therapy after waiting for the first improvements. Getting rid of skin fungus will take a lot of time and patience.
How does the virus get onto human skin?
Anyone can become infected with a fungal infection. It is enough just to be at the wrong time in a place favored by pathogenic organisms and touch (eat, drink) an infected object or touch a living creature carrying mycosis spores. People, animals, common areas, household items and even food and drinks - the source of infection can lurk in the most unexpected place.
People with weakened immune systems are especially susceptible to the pathogenic flora of mycoses. At the same time, patients with diabetes mellitus, human immunodeficiency virus, AIDS carriers, as well as patients undergoing chemotherapy and taking steroid treatment are at increased risk. People suffering from:
- Nervous system disorders.
- Severe stress, including due to overwork.
- Increased sweating.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Hypovitaminosis or vitamin deficiency.
- Allergies.
- Worm infestation.
- Injuries to the skin and nails.
- Physical exhaustion, including as a result of prolonged fasting.
- Disturbed metabolism.
- Hereditary predisposition to fungal diseases.
In addition, young children, people taking antibiotics, as well as people living in difficult living conditions or in regions with poor environmental conditions are at risk.
Once on the skin, fungal spores quickly penetrate the epidermis and begin to rapidly multiply, using the body of the infected object as a nutrient medium.
The main signs of infection in this case, as a rule, are itching, accompanied by peeling and redness, as well as roughening and scaly layering of the skin.
If the disease was not noticed in the early stages, in the absence of proper therapy, the symptoms are often added to the discharge of ichor from the affected areas, leading to suppuration.
If a patient has onychomycosis (fungal infection of the nail plate), the nails turn yellow, lose their integrity and eventually (in the absence of proper treatment) move away from the bed.
Mycosis that has settled on the scalp is indicated by uncharacteristic dry hair, accompanied by the appearance of dandruff and itching.
Features of mycoses
Mycoses are the general name for skin lesions caused by pathogenic microflora that are aggressive towards the human body.
Mycosis of the skin can affect different parts of the body. This disease develops slowly and is characterized by many different symptoms. Mycoses are most often caused by aggressive fungi, but often the lesion develops in response to the action of opportunistic microflora, which is constantly present in the human body.
Among all dermatological diseases, mycosis of the skin is the most common. Moreover, statistics show that every second person encounters fungal infections of the epidermis or mucous membranes at least once in their life.
Features of mycoses:
- long incubation period;
- moderately severe symptoms;
- contagiousness;
- complex treatment.
Fungi that cause mycosis of the skin quickly develop resistance to the action of specific medications. This makes it difficult to treat diseases of this group. Recovery is complicated if a person tries to self-medicate by haphazardly using various antimycotics.
Skin mycosis is treated by a dermatologist. It is this specialist who should be contacted if symptoms of the disease are detected or if a fungal infection is suspected.
Symptoms depend on the location of the fungus
Forms of the disease
Depending on the type of strain that affects the body, dermatomycosis can have a wide variety of manifestations.
Erythematous-squamous form
Infection with this type of mycosis is especially dangerous in hot weather, since under the influence of high temperatures and sweat secreted by the skin, pathogenic organisms of the strain develop rapidly, becoming chronic and causing all sorts of complications.
Erythematous squamous fungus can affect any part of the skin of the body. The infection process is necessarily accompanied by severe itching.
At the same time, it is extremely difficult to establish which strain caused the symptoms that arose at an early stage of the pathology, since many dermatomycosis have a similar clinical picture.
As the disease progresses, pronounced lesions appear on the skin, arranged in arcs, rings, garlands and other single or grouped rounded patterns.
At later stages of infection, an intermittent pathological ridge begins to form, which is a characteristic external sign of the erythematous-squamous form of the fungus.
Follicular nodular form
It is characterized by a more rapid and pronounced course. The first foci of fungus appear in the areas of the lower leg, buttocks, forearms and feet. Infected areas resemble erythema nodosum and quickly spread, affecting healthy skin around them. The lack of timely diagnosis and treatment of this form of dermatomycosis threatens the development of serious pathologies.
Types of fungus in the body
Of the several hundred varieties of fungi, most are capable of causing various variants of mycotic infections of internal organs.
- Histoplasmosis begins as a disease of the oral cavity, nasopharynx, and ears. Further symptoms manifest themselves as an increase in the size of the spleen and liver, pathological changes occur in the intestines. An external sign of infection is high body temperature and abnormal blood composition. The disease is provoked by yeast fungi that appear in the body through contact from external carriers, through the respiratory system, or from dirty products.
- Blastomycosis. The first signs are external in nature and take the form of pustular lesions on the skin of the extremities, on the face and neck, and ulcers can form. With unprofessional treatment or its absence, the disease affects the central nervous system, as well as the kidneys, spleen, and possibly damage to the liver and lungs.
- Cryptococcosis is a chronic, deep type of infection. Localized in the tissues of the lungs, brain, and its membranes. It can affect other organs, manifesting as tumors or abscesses. When localized in the brain, pain in the head appears, frequent dizziness and loss of coordination are possible, increased muscle tone in the neck, decreased visual acuity, and the possibility of paralysis arises. If the fungi are localized in the lungs, a rise in temperature and cough are likely.
- Coccidioidosis initially manifests itself with flu-like symptoms. The patient may experience pain in the chest area, cough, and an increase in temperature. Rashes appear on the skin. Contact infection results in abscesses. Usually the infection ends on its own, but under certain conditions complications are possible. This affects the condition of internal organs: the brain, joints, and skeletal system suffer.
- Aspergillosis most often manifests itself as a superficial form of mycosis, which is caused by mold fungi. Symptoms appear on the skin; the type of infection is otomycosis (ear infection). In case of complications, it penetrates into the lungs and is accompanied by signs of tuberculosis.
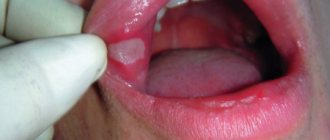
- Candidiasis, in its deep form, usually localizes to the genitals. It can parasitize in the tissues of the lungs or stomach. A variant of infection is penetration through the oral mucosa, manifesting itself on the palate, the surface of the tonsils and throat. The obvious sign is a pale creamy coating. The pulmonary variety is characterized by signs of pneumonia.
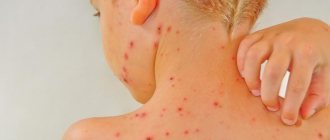
What do body spots, formations on the back, neck, abdomen look like (photo)?
Pityriasis versicolor or versicolor versicolor
A tendency to increased sweating, individual skin characteristics, hormonal and endocrine disorders, as well as individual characteristics of the chemical composition of sweat are the main factors that provoke the development of infection.
The infection is caused by yeast-like fungi and is more often diagnosed in people aged 16 to 25 years. It is at this time that active hormonal changes occur, caused by puberty. It has been noticed that the development of this fungal skin disease is often diagnosed against the background of diabetes mellitus, vegetative neurosis, accompanied by excessive sweating, and tuberculosis.
Symptoms
Yellow-brown and pink blurry spots on the body that increase significantly in size over time. Subsequently, the spots acquire a dark brown or beige color, covering increasingly larger areas of healthy skin.
The patient does not experience discomfort or pain. There is slight itching of the affected areas and peeling of the skin. That is why it is extremely difficult to diagnose infection in the early stages; patients simply do not attach importance to it and do not notice the infection.
Fungal infection of the body
Localization of spots - chest, upper back, neck, stomach, sides, outer surface of the shoulders. Sometimes there is damage to the scalp, but without damage to the follicles.
The course of the infection is sluggish and prolonged with frequent manifestations of relapses.
Signs and symptoms
The main signs of a fungal infection are itching and the appearance of rash-like or irritated patches of redness on the skin. Otherwise, the clinical picture of pathologies caused by skin fungi may vary depending on the specific strain.
Pityriasis versicolor
It is a superficial recurrent disease of the skin that is not inflammatory in nature. The causative agent is the yeast-like fungus Pityrosporum.
REFERENCE. People often call pityriasis versicolor “colored” for its ability to form rashes of a wide variety of shades on the affected areas of the skin. Other popular nicknames for this pathogen include “beach pityriasis” and “sun pityriasis.” These names are due to the most frequent occurrence of the disease during the hot season.
Men are more often affected by the pityriasis strain of mycosis than women . The main age group among patients with this diagnosis are people aged 15 to 40 years, while preschool children practically do not suffer from tinea versicolor.
An important feature of this type of pathogen is its low degree of contagiousness. In this case, an organism with a strong immune system can successfully fight the pathological strain.
The first stage of Pityrosporum reproduction occurs in the mouths of the sebaceous glands.
Further, the mouths of the hair follicles become infected, around which growing red spots form, merging with each other over time.
As a rule, these processes are observed on the chest, back, neck and scalp, but there are also cases of damage to other parts of the body.
As the disease progresses, the spots gradually change their shade from pink to red, then to burgundy and brown. In this case, there can be lesions of all shades on the body at the same time. The appearance of fused lesions is accompanied by intense peeling. Itching is practically absent.
Pityriasis versicolor can occur in 2 forms:
- Follicular (causes the formation of papules in the area of hair follicles).
- Inverted (progresses in skin folds).
If left untreated, the disease can progress for years, affecting more and more areas of healthy skin.
Damage to hair and nails
There are more than five thousand strains of fungus that can cause damage to nails and hair. All of them are extremely resistant to external influences, are difficult to treat and can remain viable for many years. The most common are the dermatomycetes Trichophyton, Epidermophyton and Microsporum.
Once on human skin, spores of Epidermophyton, Microsporum and Trichophyton usually affect only the nails and scalp.
Moreover, the chances of damage to these areas of the body rapidly increase in the presence of rubromycosis, trichophytosis and ringworm.
Athlete's nails are very contagious, can begin in people of any age and are expressed by yellowing of the nails, loss of the structure of the nail plate and its further falling away from the bed.
There are several most popular types of fungal hair diseases:
- Microsporia . With rare exceptions, it affects the hairy areas of the body and leads to focal or complete hair loss. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of red scaly inflammation on the skin, dryness and dandruff.
- Rubromycosis (rubrophytia) . An infectious fungal disease that can affect not only the scalp, but also the neck, face and torso.
- Trichophytosis . A fairly common type of lichen, caused by a parasitic fungus of the genus Trichophyton.
REFERENCE. The term lichen originated in the time of Hippocrates and refers to all fungal skin diseases accompanied by the appearance of a small scaly rash.
Mycosis of the feet
Caused by strains of Trichophyton interdigitale and Trichophyton rubrum. Often found among a wide range of age categories.
The cause of foot fungus is often simple neglect of hygiene rules , wearing uncomfortable shoes, as well as contact with the direct carrier of the strain or his personal items (shoes, socks, slippers, etc.).
Trichophyton interdigitale affects the skin on a person’s legs, while Trichophyton rubrum can cause inflammatory processes in any part of the body (including hair or nails).
Rubromycosis
Rubromycosis is a dermatomycosis that prefers smooth areas of skin for the propagation of its colonies. It is caused by the fungus Trichophyton rubrum and affects the tissues of the extremities, inguinal-femoral folds, as well as areas of the body with secondary hair growth.
Trichophyton rubrum spores can lie dormant for a long time after infection. After some time, the disease manifests itself. As a rule, the first rashes are found in the interdigital folds of the feet, moving to the sides of the feet, and then to the sole.
The course of rubromycosis is associated with the appearance of tiny scales (floury desquamation), as well as symptoms of dryness, hyperemia and hyperkeratosis.
Methods of infection
Mycosis of the skin develops as a result of fungal flora entering cracks and scratches in the skin. Insufficient treatment of wounds, abrasions and scratches, infection of the inflamed epidermis in chronic dermatological diseases are all potential ways of becoming infected with a fungus.
All mycoses are divided into two types - pathogenic and opportunistic. Pathogenic mycoses develop due to the action of foreign agents. Infection occurs with a fungus living in the soil or mold microflora.
The conditionally pathogenic causes of the development of the disease are an imbalance of a person’s own microflora. In this case, cutaneous candidiasis is diagnosed, caused by a fungus that is always present in the body.
Factors that increase the risk of contracting mycosis:
- decreased immunity;
- antibacterial therapy;
- taking glucocorticosteroids;
- the presence of chronic diseases of the epidermis;
- diabetes;
- HIV+;
- cancer treatment;
- autoimmune pathologies.
All these reasons lead to weakening of the body. As a result, he cannot resist the fungal infection and mycosis develops.
A separate group includes mycoses against the background of existing dermatological diseases. A fungal infection can develop with dermatitis, psoriasis, and eczema. The development of fungi in a child may be associated with the inferiority of the body’s own immune defense, but this is only true for infants whose bodies are not yet strong enough, so there is a risk of developing skin mycosis upon contact with various objects. In preschool children, mycoses are usually caused by poor hygiene and the habit of reaching out to various objects on the street. Any crack in the skin of the hands in this case becomes a gateway for infection to enter the body.
In patients with severe forms of psoriasis, mycoses develop due to a violation of the protective function of the skin and a decrease in local immunity. This occurs when the inflamed epidermis is damaged.
If the body's immunity is strong, the fungus will cause disease
Diagnostics
Most skin fungal diseases are characterized by rapid progression. That is why it is extremely important to notice the pathology in time, correctly identify the strain that caused it and prescribe effective treatment even before the onset of chronic complications.
It is necessary to understand that many types of dermatomycosis can occur not only on the external integument of the body, but also in the internal organs, causing difficult to correct consequences for the body.
You can anticipate the progression of the disease by promptly contacting a qualified dermatologist. The specialist will examine scrapings taken from the affected areas of the body and accurately determine the causative strain. Only after identifying the fungus will it be possible to prescribe effective therapy to completely get rid of not only the symptoms of the pathology, but also its causative agent.
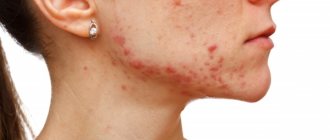
“Why is fungus on the face dangerous?”
Fungal infections of the skin of the face often coincide with mycoses of other parts of the body: legs, arms, and so on.
Mycoses on the face are doubly unpleasant: they bring a person significant discomfort and physical suffering:
- mycosis of the face affects a part of the body that is visible to others, the patient is embarrassed by his appearance and worries;
- a permanent cosmetic defect appears;
- the disease spreads to other parts of the body, covering large areas;
- chronic pathology of the skin occurs;
- the fungus can reach internal organs;
- infection often affects blood vessels;
- intoxication of the entire body occurs with waste products of the parasite;
- Complications are not uncommon: dermatomycide, secondary fungal infection of the skin;
- allergic reactions are possible;
- other infections are often associated.
Treatment of the disease
Most fungal diseases occur against the background of an immune decline in the body. This fact seriously complicates the treatment of dermatomycosis.
To successfully combat the fungus, it is customary to use medications that have a systemic effect.
In the most difficult cases, pathogenetic therapy comes to the rescue. Moreover, depending on the results of preliminary diagnosis, medical methods of combating the fungal strain may vary significantly.
The most effective results in the fight against dermatomycosis can be achieved by a set of measures, including:
- The use of antifungal agents, both local and systemic.
- Therapeutic treatment at the pathogenetic level.
- Thorough treatment of the patient’s home and personal belongings.
- Regular adherence to personal hygiene rules.
Local treatment
Getting rid of the external manifestations of dermatomycosis diseases is an easily accomplished task. For this purpose, dermatologists have an extensive list of effective topical remedies.
Among modern medicines for fungus there are ointments, sprays, drops, lotions, powders and other preparations convenient for self-application. All of them are effective, but can only relieve the patient from the external manifestations of the disease. Only longer and more complex therapy can destroy the strain of fungus that has settled in the body.
Depending on the diagnosed pathology, the fungus is treated with the following types of medications for topical use:
- Antimycotic drugs containing antibiotics, as well as corticosteroids (for example, Mikozolon, Lotriderm or Triderm). They are used in cases of significant damage to the skin and their swelling, as well as in the event of secondary infection.
- Azoles (for example, Clotrimazole, fluconazole, etc.) and drugs of the allylamine group (Lamisil, etc.).
Treatment with systemic antifungal drugs
If a moderate or severe stage of dermatomycosis is diagnosed, the patient is prescribed treatment with systemic drugs.
Typically, medications used in therapy are introduced into the body through pills or injections.
At the same time, throughout the treatment, it is extremely important for the patient to be regularly examined by the attending physician.
Modern dermatology uses two main groups of drugs to treat skin mycoses:
- Allylamines (for example, Intraconazole, Naftifine, etc.).
- Azoles (Fluconazole, Intraconazole).
The prescription of the drug, as well as its administration, must be carried out under the supervision of a qualified dermatologist.
Pathogenetic therapy
If a pathological course of a fungal disease is detected, the doctor prescribes drugs with pathogenetic effects. The main goal of such therapy is to restore the protective forces lost during the course of the disease, body functions, as well as normalize metabolism and immune reactivity.
Pathogenetic therapy allows you to minimize the risk of developing chronic forms of fungal disease and reduce the likelihood of side effects.
Reasons for treatment failure
During treatment for dermatomycosis, it is extremely important to strictly follow all recommendations given by your doctor. As a rule, the reason for the ineffectiveness of the therapy is the patient himself, who interrupted the course ahead of time or did not comply with the frequency of taking medications.
Another reason for re-infection is often self-medication (including traditional methods). An infected person cannot confidently determine the strain of the fungus, much less choose an effective and safe remedy to get rid of it. Therefore, the best way to end the infection once and for all is to visit a dermatologist.
Keratomycosis
This group includes lesions of the superficial parts of the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
This may be lichen versicolor, nodular trichosporia, erythrasma or axillary trichomycosis.
1.1 Tinea versicolor
The causative agent of pityriasis versicolor (pityriasis versicolor) is a fungus located at the mouth of the follicles or in the surface layer of the epidermis.
It may appear due to:
- individual characteristics of the skin;
- high sweating;
- disruption of the normal state of skin peeling.
Young men and women are most often affected by deprivation.
In rare cases it happens in children - it affects:
- the influence of a weakened body;
- diabetes mellitus;
- increased sweating.
The main symptoms of pityriasis versicolor include yellow-brown or pinkish spots, without inflammation, but prone to gradual growth and merging with each other.
Over time, the color of the rashes changes to dark brown or beige, and they may begin to peel off.
Most often, the rashes are located on the chest, neck, abdomen and back, sometimes on the head, but without affecting the hair.
The disease can last a very long time - from a couple of months to several years.
Treatment begins with:
- fungicidal (antifungal);
- keratolytic (exfoliating) agents.
These include salicylic alcohol, salicylic and sulfur ointment.
Exposure to ultraviolet rays is beneficial.
After completing the course of treatment, for prevention, continue to wipe the affected areas with salicylic alcohol.
1.2 Trichosporia nodosum
A hair disease that can be distinguished by the presence of white and black nodules on the hair.
The source is yeast-like pathogenic fungi.
Trichosporia can be caused by the use of unclean water, exposure to an unfavorable environment, or damage to the hair structure.
- Black nodules are most often located on the head;
- White - on the mustache, beard and eyebrows.
The symptoms are quite simple to recognize - irregularly shaped nodules appear on the surface of the hair, randomly located, representing large spores fused together.
They are hard to the touch, firmly attached to the hair in the form of a ring. If you get them wet, they will protrude above the surface of the hairline and swell a little.
ethnoscience
Folk remedies can effectively help get rid of the external manifestations of mycosis, but are ineffective in combating its root causes.
Thus, self-prepared medications can only support the therapy prescribed by the doctor, but cannot replace it.
Modern traditional medicine successfully uses the following remedies to treat skin and nail fungus:
- Garlic . Chopped garlic is mixed with butter in a 1 to 1 ratio and applied to infected areas of the body.
- Soda . For large-scale fungal infections, take a 20-minute bath a day with half a glass of baking soda.
- Mint . Lotions are made from mint and table salt and applied for 1 hour once a day until the external manifestations of mycosis are eliminated.
- Horsetail . 2 tablespoons of horsetail are brewed with a glass of boiling water. The infusion is used to wipe the affected areas.
- Onion . The juice of the rhizome of this plant is used in its pure form to wipe fungus-infected skin.
- Lilac . An alcoholic tincture from the flowers of this plant is used for medicinal rubdowns.
- Propolis . An alcohol solution of propolis is used to treat affected areas.
- Celandine . The juice of this plant is used to cauterize pathological formations on the skin caused by a fungus.
- Coffee . The freshly brewed grain drink is cooled and used to prepare baths and compresses.
- Kalanchoe . The juice of the leaves of the plant is used to make medicinal lotions.
Drug treatment of fungus on the face in adults
Treatment of fungus on the skin of the face and other parts of the body depends on the type of lichen. Diagnosis is of great importance: if treatment is incorrect, mycosis will remain with the patient until the doctor understands the situation and prescribes the correct medications.
The course of treatment contains the following drugs:
- immunomodulators (strengthen the immune system);
- vitamins;
- antifungal drugs for oral administration;
- local antimycotic drugs: ointments, creams, sprays;
- external agents that relieve itching and pain;
- physiotherapy (for some types of mycoses).
Stages of disease development
Once on the skin, fungal spores begin to develop, going through several main stages :
- Incubation period.
- Growth and reproduction of colonies.
- Infection subsides.
At the moment the pathological flora is introduced onto the human dermis, his immunity can work without failures, then the spores will remain in the incubation period. This stage can last weeks, months, and sometimes even years.
But as soon as the victim’s body’s defenses weaken, mycotic particles wake up and begin to rapidly infect healthy skin cells, using it as a nutrient medium.
REFERENCE. A person infected with spores of a parasitic fungus may not be aware of it for years, being a source of infection for everyone around him.
Thrush is also a fungus
The human body is not particularly resistant to yeast strains, so one of the most common fungal diseases is candidiasis. The causative agents of the disease are microorganisms that are normally present on the skin of each of us. When the composition of the microflora is disturbed, opportunistic microorganisms more often affect the mucous membranes, and sometimes the epidermis. For example, thrush on the skin occurs in the skin folds of infants and adults with excess weight and excessive sweating. Tissues affected by candida become inflamed, darken, and become red or brownish.
Prevention
Anyone can become infected with a fungus by picking up its spores from household items, surfaces in public places, animals, and even drinks or food. Where does this harmful fungus come from, and is it possible to predict in advance how it will get on the skin?
Fungus lives everywhere . That is why the best way to protect yourself from this insidious infection is to be sensitive to your own immunity and regularly follow all the rules of personal hygiene. It is also necessary to carefully monitor the living conditions in your own home, carrying out wet cleaning and sanitizing of personal use areas, and treating shoes.
Causes
A fungal infection can enter the body through skin damage - scratches, cracks. It is possible to be infected by pathogenic microflora when using other people's things or clothes. The causes of mycosis development are:
- contacts with sick animals and people;
- neglect of personal hygiene;
- taking antibiotics;
- weakened immunity;
- poor quality nutrition;
- deficiency of microelements, vitamins;
- hormonal imbalances;
- neuroendocrine pathologies;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- metabolic disease;
- unprotected sexual intercourse.
Therapeutic measures
Therapeutic actions are carried out individually in each case. There is no single scheme to cure mycosis of smooth skin. Treatment is selected by doctors based on the tests obtained. In addition, doctors take many factors into account when prescribing medications.
Therapy methods are prescribed taking into account the following factors:
- duration of the disease;
- type of fungus;
- size of skin lesions;
- whether the patient suffers from any chronic ailments;
- level of immunity;
- allergic reactions to medications;
- patient's age;
- physiological characteristics of the body.
Complex therapy is usually used. It allows you to effectively deal with extensive lesions. When taking medications, the body accumulates active substances. They enter the blood and are transferred to the skin, nails, and hair.
Who is affected?
According to doctors, there is no specific group of people who are susceptible to mycosis. It is diagnosed equally in both young children and adults. Weak immunity and the presence of the following factors can push the development of the disease:
- Presence of obesity;
- AIDS;
- Diabetes mellitus type 1 or 2;
- Problems with hormonal levels;
- Antibiotic abuse;
- Presence of vascular diseases;
- Oral (oral) administration of drugs from the category: cytostatics, immunosuppressants, glucocorticoids;
- Wearing shoes that are too tight or uncomfortable, such as those with narrow toes;
- Excessive sweating of the feet;
- Regular visits to public showers, baths or saunas;
- Heavy physical work;
- Active sports;
- The presence of infectious diseases in a chronic form, such as tuberculosis.
Damage to the nail plates
Fungal nail diseases occupy a leading position among foot infections. The disease manifests itself quite quickly, within three days after infection. Fungus is diagnosed on the feet twice as often as on the nail plates of the hands.
As the infection develops, deeper and deeper layers of the nail plate are affected, and when the root plate of the nail is destroyed, its growth stops completely. Fungal spores penetrate the edge of the nail, and the fungus gradually spreads to the skin surrounding the nail. Trimming infected edges regularly can help prevent the spread of the disease. That is why, with rapid nail growth, the disease quickly passes.
As the infection progresses, complete destruction of the nail is possible; in advanced forms, treatment of nail fungus can become a painful and lengthy process.
Symptoms
This type of infection is extremely contagious and is instantly transmitted through contact with objects used by a sick person. Most often, the infection can be acquired in swimming pools and on the beach, in baths or saunas, and also by simply trying on shoes. Nystatin ointment is used as prophylaxis.
When affected by the fungus, the nail plate thickens, and a change in color is observed along the edges and the entire surface of the nail (yellowish and brownish spots). The surface is cloudy, dull, the nail flakes.
Prevention and treatment of mycoses of the head
Modern treatment methods no longer require complete hair removal from damaged areas using a patch or laser hair removal. It is important that antifungal drugs are prescribed in combination - externally and internally; if necessary, additional pathogenetic therapy must be carried out.
Effective fungistatic drugs of general action, prescribed orally: ketoconazole, terbinafine, griseofulvin, itraconazole.
The dosage and duration of taking the drugs depends on the general condition of the patient, body weight, age, the presence of allergic reactions and chronic diseases.
The scalp is cleansed of visible dirt and exfoliated skin flakes and treated with fungicidal and symptomatic preparations:
- salicylic ointment and oil (two percent);
- Alibur liquid (lotions). The drug contains one percent copper sulfate and four percent zinc sulfate;
- resorcinol – one percent solution;
- ichthyol ointment (10 percent);
- fucorcin;
- solution of aniline dyes.
The choice of drug is based on test results; if the pathogen is not identified, then a broad-spectrum drug is prescribed.
For treatment to be effective and to prevent re-infection, the hair on the head must be shaved every ten days. Fungicidal preparations must be alternated during the treatment process.
In the presence of endocrine system disorders and chronic trichophytosis, it is advisable to prescribe corrective drugs and stimulating therapy.
The course of treatment is at least a month. Only after three examinations with a break of five days can we talk about complete recovery. A control final microbiological examination is prescribed one month after the end of taking the drugs.
Since the treatment is long-term and the active ingredients are toxic, such systemic therapy is prescribed individually for pregnant and lactating women, children and patients with kidney and liver diseases.
Prevention
Fungal diseases of the scalp are contagious and quickly spread from person to person, especially in large groups and confined spaces (schools, preschool institutions, factories). Therefore, it is important to quickly identify the source of infection.
All the patient’s belongings must be thoroughly disinfected, and family members must undergo preventive treatment.
In some cases, it is important to establish the correct diagnosis, since the development of a fungal infection may be associated with disruption of the endocrine system or sluggish chronic liver diseases. In this case, the dermatologist should prescribe medications based on the recommendations of the attending physician, strictly individually.
How can you get infected?
The main methods of infection with a fungus include:
- Contact with a person who is infected with a fungus;
- In a nail salon (through tools), if they have not been disinfected;
- Through towels, clothing, bed linen and other household items that come into close contact with the skin;
- Through indoor and outdoor shoes, shower slippers;
- Through microtrauma of the skin.
People with reduced immunity are most susceptible to mycosis.
Antifungal ointments for the intimate area
Not all ointments are suitable for use in the intimate area
The most delicate and sensitive skin on the human body is located in the intimate area. Many people are familiar with the feeling of itching and burning in the groin area - this is the main symptom of candidiasis. Pathogenic fungal microflora multiplies quickly in a warm, humid environment, so it is necessary to keep the area clean and dry. If the problem is already present, it must be dealt with immediately.
The best and most powerful remedy for candidiasis is Pimafucin. Nystatin ointment also works well. It is applied to the mucous membranes and kills yeast fungi. These are special antimycotic agents for the groin area. Treatment according to the standard lasts at least 10 days.
How to treat a child
Because a child's body continues to develop, the immune system is not yet fully developed, and the skin is especially susceptible to pathogens. Treatment should begin only after the doctor determines which fungus caused the disease. Below we describe the main lesions and methods of their treatment:
- If the skin of the feet or head is affected, the dermis should be lubricated with iodine, and then the surface should be treated with Miconazole ointment, which has an antifungal effect;
- If the infection is concentrated in the throat, then Fluconazole spray is suitable;
- For severe itching sensations that cause discomfort, Tavegil is prescribed, which must be taken according to the dosage specified in the instructions;
- As an additional therapy for infection of the legs (feet), you can take baths with chamomile decoction or soda in the evening;
- If there are a lot of lesions, then the doctor prescribes Nizoral, intended for oral administration.
Please note that before taking all these medications, you should carefully read the instructions and consult with your doctor. Independent selection of a drug may be erroneous, which will lead to the complication of the disease or its transition to a more severe form.
Popular drugs
The doctor prescribes tablets for oral administration (by mouth) in order to quickly cope with the infection. This applies to cases where the fungus has started or complications have begun to appear. The most effective in this case:
- Linex or Acipol, which will help normalize and restore intestinal microflora;
- Vitamin complexes to boost immunity;
- Viferon is an immunomodulator;
- Zyrtec or Diazolin will help relieve itching (antihistamines);
- Pimafucin or Natamycin are antimycotics that fight fungus;
- Fluconazole or Intraconazole is an antimycotic agent that kills fungal cells.
Popular ointments against fungus with antimycotic effect:
- Terbinafine is available as an ointment. It works well in the treatment of advanced forms of fungus and is effective against a large number of fungal infections.
- Clotrimazole is a fast-acting ointment that is aimed at combating several types of mycosis and a wide variety of fungi. The main advantage of this product is that it is safe for pregnant women.
- Griseofulvin belongs to the category of antifungal agents, is effective and quickly produces results, but accumulates in tissues.
Please note that all of the drugs listed have their own precautions for use and side effects. Before taking medications, you should definitely consult your doctor and make sure that you do not have an allergy to the components or other adverse reactions to the drug.
Fungus of feet and hands
The lesion is expressed by thickening of the stratum corneum, peeling and dryness. The surface of the foot is deformed, thickenings appear in the form of a roller. Cracks and peeling may appear in the heel area, the patient experiences burning and itching, and whitish hollow blisters are noticeable.
The disease is highly contagious, so all family members should be treated.
Lesions of the hands are less common, but have a clear clinical picture - damage to the back of the hand and the nail plate.
Products for external use
In case of a fungal infection on the surface of the skin or nails, patients are prescribed various ointments, creams, etc.
And in most cases this is enough for complete recovery. Among the most effective drugs it is worth noting:
- Terbizil (cream) is a broad-spectrum antifungal drug that relieves inflammation and flaking. It is used primarily to treat mycosis in the armpit area (as well as the feet and other parts of the body). The cream is recommended to be applied to clean and dry skin 1-2 times a day for 1-3 weeks. Price - 280 rubles (15 g).
- Exifin (cream) is an antimycotic agent that not only effectively fights the existing fungus, but also has an anti-inflammatory effect. Frequency of use: 2 times a day. Approximate course of therapy: 2-3 weeks. Price - 245 rubles (10 g).
- Ecodax (cream) is an antifungal drug with fungicidal and bactericidal effects that inhibits the growth and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms. It is recommended to apply 2 times a day (in a thin layer) to the affected areas. Course of treatment: 2-4 weeks. Price - 175 rubles (10 g).
- Clotrimazole (ointment) is an antimycotic, antiprotozoal, antibacterial agent that must be used 2-3 times a day for 1-3 weeks. Price - 40 rubles (15 g). Also available in the form of a cream and solution for external use.
- Exoderil (cream) is a fast-acting broad-spectrum antifungal drug. It is recommended to apply to affected areas of the skin once a day. Duration of therapy: 2-4 weeks. Price - 730 rubles (30 g).
- Zalain (cream) is an effective antimycotic agent that destroys all strains of fungi. Frequency of use: 2 times a day for 2-4 weeks. Price - 470 rubles (20 g).
Attention! The effectiveness of therapy depends on the correct choice of agent. To do this, it is necessary to undergo a preliminary diagnostic examination and identify the causative agent of the disease. Otherwise, it will be a “blind” treatment and will not bring the desired results.
Treatment of mycosis of the nail plate
The risk of spreading nail fungus in adults is much higher than in children. Since nail growth slows down in older people, damage to the plate occurs twice as often as with normal growth.
People suffering from varicose veins, diabetes mellitus and heart failure are also at risk. We must remember that even a cosmetic procedure - nail extensions - carries the risk of fungal infection.
The photo shows advanced mycosis of the nail plate
There are medical and surgical methods to eliminate the infection. Of course, radical surgery should be resorted to only when necessary, in particularly advanced cases of the disease.
Mycosis of toenails is treated with general and external drugs: griseofulvin (an inexpensive and effective means of combating mycosis of the nail), amorolfine, ciclopirox, bifonazole, itraconazole, terbinafine.
When prescribing treatment, the dermatologist is guided by the patient’s body weight, age, as well as the general clinical picture of the body’s condition. The modern pharmaceutical industry offers a large selection of antimycotic medicinal plasters and varnishes:
- fungicidal varnish is applied daily after a hot bath. Before application, you must carefully remove the remnants of the old polish and polish the nail plate. The course of treatment is from two to three months;
- fungicidal patch – contains phenol, lanolin, spermaceti ointment and lead. Application - once every four days, for a month.
It is important to remember that before each application of the medicine, the nail must be treated with medical alcohol.
There are folk remedies that will help cope with the infection - baths with soda solution, iodine applications at night, fresh walnut peel juice, celandine juice and ordinary laundry soap.
In case of advanced mycosis, it is advisable to remove the nail surgically, which guarantees a complete recovery.