0
1793
Many people think of skin as a layer of cells covering the human body. But in fact, the dermis is a complex organ with its own difficult life, which is vital for each of us. Every day, human skin secretes on average 30 g of salt, 50 g of sebum and about a liter of water. By evaporating sweat, the body regulates body temperature, so sweating is a natural reaction for it. Sweat centers protect against overheating and other surprises from an unfavorable environment. Thermoregulation provides the body with a constant temperature in the range from 36.5 to 36.9 degrees, which is most optimal for the functioning of protein and other chemical compounds. An increase in temperature to 43 degrees, as well as a drop to 25, is fraught with death.
Any changes in the functioning of internal organs can disrupt the functions of the sweat glands, creating conditions for the development of anomalies of apocrine or eccrine centers. The latter are associated with hyperhidrosis, dyshidrosis, miliaria, anhidrosis, apocrine - with osmidrosis, acne inversus, bromhidrosis, hidradenitis, chromhidrosis.
You can consult a dermatologist or cosmetologist about diseases of the sweat centers, but the problem is radically solved, as a rule, by surgical methods.
The structure of the sweat gland
The sweat gland consists of tubular ducts running through the epithelium of the skin. Sweat accumulates in the secretory section of these ducts, which is subsequently released to the surface of the skin. These glands are located in different parts of the body: the armpits, groin area, palms and soles of the feet, and their number can also vary from person to person.
The structure of the sweat glands is as follows:
- The presence of a body in the form of a secretory tube having a spiral shape;
- For external removal of sweat, each gland is supplied with an excretory channel;
- The presence of pores in the skin through which sweat is released.
When examining the sweat gland under high magnification using a microscope, you can clearly identify openings on the skin, which are pores, as well as special cells located on the walls of the tubes and synthesizing sweat secretion. The tubules with ducts emerging from the sebaceous centers are connected to the roots belonging to the hair follicles. The secretory tangle is surrounded by a capillary network that provides blood supply; it is also here that the endings of the nerve receptors are located, with the help of which the work of the sweat gland, controlled by the nervous system, is regulated. In response to heat, hormonal releases, and being in stressful situations, the nerve receptors are irritated and, as a result of a signal from them, secretions are actively produced and released through the pores on the skin.
The number of sweat glands in different people can range from two to three million, most of which are located in strictly defined places. Sweating centers have different rates of sweat production, which depend on environmental influences.
Men sweat more intensely than women. The chemical composition of the secreted secretion is strictly individual and depends on the location of the sweat glands and the characteristic characteristics of the person.
How do sweat centers work?
Sweat glands on the skin are classified as exocrine glands. They have a simple, unbranched tubular shape. Tubular channels are located in the epithelial layer of the dermis. The tubules have a secretory compartment in the form of a spiral. It accumulates secretions, which are then released onto the skin. There are many sweat centers on the body: on the forehead and palms, in the armpits and feet, in the groin and on the neck. They are not found except on the external genitalia.
If you examine this important organ under a microscope, you can see pores and special cells in the channels for the production of sweat fluid. There are also sebaceous gland channels in the hair roots.
The anatomy of the human gland is:
- The body is a spiral-shaped tube with a secretory function;
- Excretory tubules;
- Pores.
Along the perimeter of the secretory glomerulus there is a network of capillaries that provide blood supply to the organ. Nerve receptors that regulate the functioning of the glandular centers are also located here. In addition to the central nervous system, the performance of the glands is controlled by hormones of the adrenal cortex.
The glands actively secrete secretions after influencing the network of nerve centers. Most often, such a reaction occurs to heat, serious hormonal surges, stressful situations and other moments dangerous to the body.
The number of sweat glands on the skin varies between two and three million. This means that for every centimeter of the palm there are 300-400 microvessels for sweat secretion.
The most active areas of sweating are localized in the armpits, on the forehead, and in the groin area. There are fewer such centers in other regions. Apart from the genitals, there are none on the lips. The main purpose of sweat glands is thermoregulation of the body. They work with varying intensities; this largely depends on environmental conditions - if you lie motionless in a cold room, most of the sweat glands will rest, unless, of course, a stress factor is involved. The male body produces more sweat than the female body. The chemical composition of the liquid is individual; it also changes depending on the location of the glandular center.
Sweat gland secretions
Sweating by apocrine glands plays a major role in the body; they create a certain odor of the human body. The secretions of these glands have properties that increase the elasticity of the skin and protect it from drying out. With their help, the body is cleansed of toxic accumulations, as well as other harmful substances that accumulate during the life of the body. In itself, the initial secretion of sweat does not have any odor, since most of it consists of water. Only one percent of its composition is occupied by metabolic products, menthol, acetone, which combine with bacteria existing on the human body and give sweat secretions a characteristic odor. Scientists have proven that this sweat contains special pheromones that attract a sexual partner.
Normally, the secretions of the sweat glands should be transparent, of normal consistency and without a strong odor. However, in the case of some diseases, sweat can change its character and become thick, sticky, with an uncharacteristic fetid odor. Any disturbances in the state of the endocrine system, especially in the endocrine glands, contribute to increased sweating - a disease called hyperhidrosis.
Conclusion
Sweat glands have very important functions for the human body. In addition to regulating body temperature, they remove harmful waste and toxins from the body, moisturize the skin and maintain its elasticity. However, there are many diseases that interfere with their work. If such occurs, the problem must be resolved as soon as possible.
Because in addition to discomfort, excessive sweating or its absence can lead to serious consequences. First of all, therapy consists of eliminating the root cause and using medications. And only as a last resort, if drug therapy is ineffective, doctors recommend resorting to such a radical method as removal of sweat glands.
Features of apocrine glands
There are significantly fewer apocrine glands in the human body than eccrine glands. They are located in the armpits, in the groin area, i.e. where hair growth is observed, since the ducts of these glands open into the hair follicles. The greatest activity of their functioning occurs during the puberty period, therefore, in children and the elderly, such glands do not function.
Currently reading: Devices for the treatment of hyperhidrosis – who is suitable for electrical treatment
Types and purpose of glands
There are 2 types of sweat glands, with their own specific functions that are indispensable for maintaining a comfortable body temperature.
- Superficial centers are eccrine sweat glands that function constantly;
- Apocrine glands are active from 14 to 60 years of age and have access to the hair roots.
It is worth considering the capabilities of each type in more detail.
Apocrine type
There are fewer glands of this type in the body than accrine glands. They can be seen in the armpits, in the groin area, and on the mammary glands. The ducts of the apocrine glands also exit into the root of the hair, so there are no apocrine glands on the palms, soles and other areas where there is no permanent hair. Until the end of puberty, they are inactive (their maximum activity is noted during puberty).
That is why neither children nor old people have hidradenitis, characterized by purulent secretion of the sweat glands, because none of these centers functions.
Apocrine glands provide each of us with our personal scent. Sweating centers have their own fluid composition, which is optimal for moisturizing, maintaining elasticity and preventing skin drying. These glands help rid the body of poisons. Therefore, when they are actively working, the body odor is not the most pleasant.
Mammals also attract individuals of the opposite sex with their apocrine glands. The synthesized liquid contains 98% water, the rest is sebum, acetone, methanol and other decomposition products. Initially, the discharge does not smell; after contact with the microflora of a particular organism, the skin receives a specific, characteristic aroma only for that organism.
Scientists claim that this type of glandular centers can produce “love pheromones” that attract the “other half” and enhance libido. A healthy body sweats moderately, the discharge is odorless and has a standard consistency. If there are problems, for example, with the thyroid gland, sweat can be thick, viscous, foul-smelling, cold and sticky to the touch.
Exocrine type
This variety is the most numerous. Exocrine glands are located throughout the body, but are most concentrated on the chest, back, armpits, hands and soles, as well as on the face. Purpose of eccrine glands:
- Thermoregulation - when sweating, secretions evaporate, cooling the dermis;
- Protection of internal organs and systems from heat stroke;
- Increased sweating as a reaction to stress factors;
- Elimination (removal) of waste metabolic products.
Features of the exocrine glands
Exocrine glands are more numerous, they are located over the entire surface of the body, more concentrated in the armpits, on certain areas of the facial skin, on the palms and soles. This type performs the following functions:
- Thermoregulation is carried out through the release of sweat and its evaporation;
- Organs are protected from the threat of overheating;
- Cleanses the body of accumulation of toxins;
- Increases sweat production when under stress.
These glands are highly active; they secrete sweat unnoticed, but constantly.
Carcinomas in cats
In representatives of the Persian and Himalayan breeds, tumor formations of the apocrine glands often appear on the eyelids. They are small in size - from 2 to 10 mm. As we have already mentioned, adenomas and carcenomas can be very similar in appearance, which in turn makes diagnosis and selection of the correct treatment difficult. However, keep in mind that carcinomas appear harder and more inflamed. In addition, they can be riddled with ulcers and suppurations.
Tumors are the same as in dogs, mostly solitary. Externally they resemble compacted subcutaneous balls of small size and bluish color. Carcinomas can be located anywhere on the animal's body. Adenomas can also appear in cats, but they are localized mostly in the head area.
Diseases
The sweating system is also susceptible to diseases, the nature of which is caused by excessive sweating - hyperhidrosis, or its insufficiency - hypohidrosis. There may also be a complete absence of sweat - anhidrosis. The sweat gland is subject to pathologies such as:
- Manifestation of chromhidrosis with symptoms manifested by colored sweat;
- Uridrosis with a characteristic high urea content, which is a symptom of kidney disease and weakening of their functions (the main signs can be considered the appearance of crystals in the armpits and on the hair);
- The development of steathidrosis, manifested by the appearance of oily sweat, caused by the connection of nearby sebaceous and sweat glands.
Some diseases that affect the sweat glands need to be discussed in more detail.
Gland pathologies
Every organ is capable of losing functionality, and sweat centers are no exception. Their pathologies are mainly characterized by increased sweating, the so-called hyperhidrosis, or its opposite, hypohidrosis - a decrease in sweating. There is also a complete absence of sweat secretion - anhidrosis. Other anomalies include:
- Chromhidrosis - secretion of colored sweat fluid;
- Uridrosis - a high content of urea salts in the secretion, occurs in renal failure, when the sweat glands take over the filtering functions (symptoms - sweat crystals on the head and in the armpits);
- Steathidrosis – fatty secretions if adjacent fat and sweat glands combine.
It is worth talking about some types of pathologies in more detail.
Hypohidrosis
With this disease, sweat production is extremely low. The reasons for this anomaly:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system;
- Blocking the channels through which sweat passes;
- Damage to sweat centers.
Hypohidrosis can also be a secondary pathology if it accompanies keratosis (skin disease), renal failure, or inflammation of nerve endings.
Anhidrosis
The disease develops in the complete absence of sweat. Its prerequisites will be chronic diseases - aplasia, hypoplasia. Of other causes, the most common is insufficiency of the sweat glands and deviation of their innervation.
Anhidrosis may also indicate cancer problems. If you have tumors on the lungs, it is not recommended to be in the heat, in stuffy rooms, or in the open sun. If internal organs overheat, it can cause severe heat stroke.
Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis refers to excessive sweating of the entire body or parts of it. There is a local type of the disease, when only some parts of the body suffer from excessive sweating, and an extensive type, in which uncontrolled sweating is observed throughout the body.
The causes of the pathology are considered to be:
- Neurodermatitis;
- Neurasthenia;
- Diabetes;
- Psoriasis;
- Tuberculosis.
The characteristic symptoms that are used for diagnosis are the characteristics of sweat: temperature, density, smell. Treatment must be comprehensive and long enough.
Hidradenitis
With this anomaly, the glands become inflamed with suppuration. Typical affected areas are the armpits, anal and groin areas. Usually occurs at 30-40 years of age in female patients. Provoke acute suppuration:
- Blocking the roots of the glands;
- Hormonal imbalance during pregnancy or menopause;
- Diaper rash (prickly heat);
- Mini-traumas with further infection (mainly by staphylococcal pathogens).
You can suspect the disease by a thickening nodule - it grows (up to 30 mm), becomes painful, and the color changes to purple-blue. Their numbers vary. Over time, the nodes stick together into a conglomerate protruding above the dermis.
Thanks to the specific shape of the cone with convex edges, it was popularly nicknamed “bitch udder” by analogy with the mammary glands of a dog. The nature of the disease is bacterial, because in a damp and warm environment pathogens multiply especially quickly. Therefore, the symptoms of pathology are loss of strength, fever. In the acute form of hidradenitis, blockage of blood vessels is treated with medication. If an infection occurs, the disease often becomes chronic.
In case of relapses, the problem is solved by surgical methods.
Osmidrosis
This pathology can be recognized by bad breath. The prerequisites for such a pronounced manifestation are ignorance of hygiene standards, endocrine pathologies, and menstrual cycle disorders. If the functioning of internal organs is disrupted, sweat centers can take control of the filtration of certain toxins. To radically solve the problem, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease and take the hygiene of problem areas more seriously.
Prickly heat
Characteristic signs of the disease are a small blistering rash with cloudy or clear liquid. The rashes are itchy, and when scratched, the affected areas become wet.
The prerequisites for the occurrence of prickly heat are deterioration of thermoregulation and a sharp increase in ambient temperature. If you dress inappropriately for the season, wrap your child up excessively and do not optimize your physical activity, diaper rash will appear due to insufficient or poor hygiene.
The first time people encounter heat rash is in childhood. This is facilitated by the child’s excess weight and skin diseases such as exudative diathesis. Miliaria can be recognized by characteristic rashes in the area where sweat glands accumulate. Sweat stains on clothes also remain in these places.
To cure diaper rash at the initial stage, lifestyle modifications, including a responsible attitude to hygiene procedures, are sufficient. Underwear should be made of natural hygroscopic fabric; avoid stuffy rooms and crowds of people in transport. At an advanced stage, with secondary infection, antibacterial treatment is necessary.
Chromydrosis
Pigmented sweat is a fairly rare occupational disease. It develops among specialists who have been in contact with compounds of iron, copper, cobalt and other metals for a long time. The main symptom is colored discharge from the sweat glands, often reddish in color. This occurs due to a chemical reaction between epithelial secretions and oxygen from the air. At the same time, sweat production increases. Treatment begins with eliminating provoking factors, normalizing the drinking regime, and increasing attention to personal hygiene issues.
Hypohidrosis
Hypohidrosis, a disease with abnormally reduced sweat secretion caused by the following:
- Experienced nervous conditions;
- There is a blockage of the sweat ducts, through which sweat is released;
- Pathological conditions in the gland itself.
This type of disturbance in the sweat glands can develop against the background of serious diseases in the form of extensive renal dysfunction. Inflammation affecting the nerve endings can also lead to the development of hypohidrosis. Often patients with skin pathology in the form of keratosis seek help from a doctor; after examination, they are also found to have a sweating disorder in the form of hypohidrosis.
Skin glands of cats
Cats have an excretory system very similar to dogs. They have sebaceous, sweat and mammary glands. The former help make the wool water-repellent. This may be why many cats don’t like water treatments.
As we have already mentioned, the glands that produce liquid sweat, like in humans, are found only on the pads of the paws in cats. The function of thermoregulation is performed by the mammary sweat glands. They secrete a liquid similar to milk. However, the cooling of the body is still small. The most important thing this liquid does is give off a smell. Animals use this to mark their territory. They simply rub against something, thereby leaving an odorous mark on the object.
Anhidrosis
A condition with a complete absence of sweating is defined as anhidrosis. The main factors in the development of the chronic form of this disease are chronic damage to sweat centers, such as aplasia and hypoplasia. Basically, the disease develops for the following reasons:
- State of insufficiency of sweat centers;
- Disturbances in their connection with the nervous system.
Often this condition is a symptom of the acute stage of lung cancer, so manifestations with a complete absence of sweating is a serious sign that requires a thorough examination.
Patients with this type of pathology are not recommended to spend long periods of time in the sun, in stuffy hot rooms or on the street during the hot season. Internal organs are not able to cool, which contributes not only to their overheating, but also to severe heat stroke, which can be fatal.
Diseases of the glands
These glands have their own diseases. For example, an apocrine cyst. This is a benign tumor-like pathology, which is a cavity filled with contents. Inflammation of the apocrine glands is expressed by adenomas and adenocarcinomas. They can affect the glands themselves or the cells that make them up.
Typically, these pathologies are not common among young cats and dogs. But they strike older animals with enviable frequency. For example, German shepherds and golden retrievers are most susceptible to apocrine tumors. Among cats, the greatest likelihood of carcinomas is observed in representatives of the Siamese breed.
Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is excessive sweating of the entire body or individual areas. The disease can manifest itself in the form of extensive sweating, when sweat covers the entire body, and this condition is not controlled and can occur for no apparent reason. When excessive sweating occurs locally, certain areas of the body suffer. A person is forced to use various methods of protection in order not to walk around in clothes with wet armpits. Such changes in the sweating system occur in the case of the following pathologies:
- Development of neurodermatitis and psoriasis;
- State of neurasthenia;
- Tuberculosis disease;
- Increased blood sugar in diabetes.
The main signs that are the reason for diagnosing the presence of these diseases are the distinctive features of sweat discharge. If there is a change in their smell, temperature, consistency or the appearance of other previously unusual differences from the norm, it is urgent to undergo a full examination.
What does a sebaceous gland blockage look like, photo
The blockage of the sebaceous gland forms a subcutaneous formation with a smooth and rounded shape, which has clear contours limiting it. It most often occurs on the face or neck, as well as on the head and back, but most cases of this pathology occur in the armpits. When palpating, one feels mobility and some pain in the resulting formation, especially in the case of secondary inflammation. The external features of sebaceous gland blockage depend on the stage of its development. The initial stage with the formation of a cyst forms a small elevation on the skin, which gradually changes its color, the skin above it is stretched and does not fold. Local swelling of the surrounding tissues is often observed, and patients feel pulsation, as is the case with abscesses, indicating the presence of contents with pus in the formation.
In the later stages of the disease, the cyst opens and an ulcer forms in its place. As a complication, an abscess may form in its place with the formation of an extensive abscess. Subsequently, a strong capsule forms around the inflamed sebaceous gland and cyst.
The main complication of blockage of the sebaceous gland is its suppuration, which occurs due to the penetration of microbes into it. This happens when hygiene is not observed, the cyst is constantly injured, or when they try to squeeze out its contents on their own. In such a situation, the skin over it is so stretched that its internal filling can be seen. Suppuration is always accompanied by severe painful symptoms that require medical attention.
You should not open the suppuration of the inflammation yourself, as this can lead to the penetration of pus into the blood, which threatens general intoxication of the body and sepsis.
Hidradenitis
The development of hidradenitis is characterized by damage to the apocrine centers, in the armpits, in the groin area and the area around the anus. This pathology is more common in women aged 25 to 40 years, and is a purulent acute inflammation in the sweat gland. The following conditions cause such disorders:
- Blockage of sweat glands;
- Disturbances in hormonal levels, often occurring during pregnancy or menopause;
- Diaper rash formation;
- Infliction of microdamages, on the basis of which subsequent infection of various types of bacteria occurs, most often staphylococcus.
Currently reading: Treatment of hyperhidrosis in St. Petersburg - treatment techniques and the best clinics
Pathology can be identified by the presence of a dense, painful nodule, surrounded by redness and with its constant growth. As the pathology develops, its color becomes bluish. The number of nodules formed, ranging in size from 5 to 30 millimeters, may vary. Gradually they unite together and begin to protrude above the skin, taking on the shape of a bump.
The disease develops as a result of an infectious process caused by the penetration of bacteria, usually accompanied by fever and poor health. Treatment involves complex therapy.
Classification
There are two types of sweat glands, each of which is responsible for its own functions:
- Eccrine. They belong to the young type of glands and are located in the upper layers of the epithelium (dermis or subcutaneous tissue).
- Apocrine. They begin to work around the age of 14 and fuse with the hair follicles.
Eccrine sweat glands have a large distribution area. They are located on almost all parts of the human body, but their greatest concentration is observed:
- in the sternum area;
- in the armpits;
- on the back, face and limbs.
It is the eccrine centers that are the main source of thermoregulation of the body. They begin to function from the moment a person is born. Similar centers are found mainly in higher primates. The functions of the eccrine glands include the following:
- secretion of sweat followed by its evaporation, due to which thermoregulation is carried out;
- ensuring protection of human organs from overheating;
- activation of sweating at the time of nervous overstrain;
- removal of various toxins and other harmful substances.
The eccrine centers secrete a watery secretion almost continuously, due to which, in particular, maximum traction of the soles of the feet with the ground is ensured.
Apocrine sweat glands are found in smaller numbers. Their tubes have a larger lumen than those of eccrine ones. In addition, unlike the previous ones, the first ones branch and form lateral outgrowths. In addition to the armpits and groin area, apocrine glands are located mainly in the areola of the mammary glands. Due to the fact that their ducts are connected to the hair follicles, these tubes are not found in places where there is no hair.
A feature of the apocrine glands is that they function only from 14 to 60 years of age. As a result, persons who do not fall into this category do not suffer from diseases such as hidradenitis, or purulent inflammation.
It is the apocrine glands that give a person its specific smell. Among the functions performed by such centers are also:
- increasing the elasticity of the skin;
- hydration;
- protection of the epidermis from the external environment;
- removal of toxins and other harmful substances.
It is worth noting that a person acquires its specific aroma due to the release of metabolic products, which constitute only 1% of the total volume of sweat secretion. In this case, the smell occurs only when these secretions come into contact with microorganisms living on the surface of the skin.
Apocrine and eccrine glands have tubes similar in structure. However, the secretion secreted first is more viscous and is released in certain portions, and not constantly. The fibers of the sympathetic nervous system are responsible for the innervation of the sweat glands.
Osmidrosis
With this disease, a characteristic foul odor of sweat is noted. The main reasons causing such conditions are:
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules for body care;
- Disorders occurring in the menstrual cycle;
- Changes in the organs of the endocrine system.
In diseases that result in the loss of the ability of organs to perform their functions, for example, in renal pathologies, the sweat centers take over their work, filtering and releasing toxins. To eliminate the problem, it is necessary to get rid of the underlying disease, and careful adherence to hygiene requirements is also required.
Traditional methods
Treatment of atheroma with folk remedies can be successful only as a complex treatment or at an early stage of the disease, and also in the absence of complications in the form of inflammation. In this case, ordinary garlic will be quite effective, which is crushed, mixed with any vegetable oil and applied to the cyst or rubbed into it. This treatment is continued until the formation is completely resolved.
To treat blockage of the sebaceous gland, a leaf of the coltsfoot plant is used, which is fixed to the lesion with a plaster. Usually a small cyst can be eliminated within a week of such treatment.
Leaves of aloe, plantain, and burdock, which are left on the skin until they dry completely, can cleanse the ducts of the gland. After this, the leaves are replaced with fresh ones. Two weeks of such daily treatment can pull the cyst to the surface of the skin.
A proven and long-used way to remove blockage of the sebaceous or sweat gland is to apply a baked onion. After baking, it is crushed, mixed with pre-grated laundry soap and applied to the damage. This composition must be changed every two days.
If inflammation develops at the site of blockage of the sebaceous gland, folk remedies are not used, and treatment is carried out by a dermatologist.
Prickly heat
Miliaria is a disease characterized by the formation of rashes consisting of numerous tiny blisters filled with clear liquid. The following conditions can be considered as additional signs by which the presence of this particular disease can be determined:
- The formation of annoying itching, especially at night or after sweating;
- Wet areas of the body where blisters form.
The cause of prickly heat is a violation of thermoregulation when the temperature of the living environment increases. This condition may occur due to the wrong choice of seasonal clothing. This can occur at any age, starting with the youngest, as parents tend to wrap their child up, causing him to overheat. The development of prickly heat can be provoked by the presence of excess weight and exudative diathesis.
The nature of the pathology is determined by visual examination, since the rash has a number of signs characteristic of this disease. Typically, rashes form in areas where sweat glands are most concentrated, as well as where large amounts of sweat are produced. Treatment options include medicinal baths and avoidance of synthetic clothing. Persons with this pathology should try to overheat less, if possible avoid being in hot rooms, and in case of secondary bacterial infection, they are prescribed antibiotics.
Why do acne occur?
Acne usually occurs in adolescents during puberty, but puberty is not always the main cause of acne. Pimples in the form of acne can occur in people of different ages, and they form not only on the face, but also on various parts of the body. The cause may be poor nutrition, hormonal imbalances, and problematic skin conditions.
The appearance of acne is caused by the sebaceous glands that produce sebum. With its increased production, the respiration of skin cells is impaired, as a result of which a large amount of dirt and microorganisms accumulates in them, causing inflammation.
Often the formation of acne occurs due to a long stay in a dirty room, due to household dust and insufficient cleansing of the face from applied decorative cosmetics. To cope with acne in this case, it is enough to pay more attention to more thorough cleansing of the face using various scrubs, cleansing creams or lotions. As a rule, such care is enough to make your skin clear.
One of the reasons for the appearance of acne may be poor ecology and environmental pollution from industrial waste.
An unhealthy diet with an excess of fatty and spicy foods, as well as a large amount of carbohydrates consumed, also often causes acne on the skin. Smoking and alcohol in large quantities are also a significant factor in skin disorders with the formation of acne.
In this case, getting rid of acne is not difficult; just review your diet, eliminating fatty and fried foods and eating more fruits and vegetables.
Often, when visiting a dermatologist about acne, a demodex mite is found in the skin. With a decrease in the body's defenses, this mite begins to multiply rapidly, and after its death causes the formation of inflamed pimples on the skin. For particularly extensive lesions caused by the vital activity of demodex, a cream that destroys it is used.
Chromydrosis
Chromidrosis, a condition where sweat becomes a different color. Such symptoms indicate professional local causes that contributed to the development of such changes in the sweat glands. It may occur in workers involved in chemical production and exposed to certain chemicals in the form of copper, cobalt, ferrous compounds, etc. The main sign by which diagnosis can be made is the appearance of color in sweat discharge, which often becomes red in color. The pathological condition is accompanied by more profuse sweating. The treatment process involves eliminating unsuitable conditions for existence, drinking plenty of water and observing hygiene rules.
Therapy methods
If atheroma is large in size or if it suppurates, mandatory surgical intervention is required; a small size of the formation does not require this. Usually in this case they resort to less traumatic methods using laser or radio waves.
Even if surgically removed, antibiotic treatment will be required in the postoperative period. With the help of drugs such as amoxicillin and penicillin, it is possible to speed up healing and prevent the inflammatory process from appearing again.
In case of residual effects in the form of a small compaction that occurs after removal of the atheroma, it is eliminated with local medications in the form of Vishnevsky ointment or ichthyol ointment. Dressings with these medicinal compositions are used daily until the seal is completely eliminated.
Inflammation of the sweat glands
Inflammation affecting the sweat glands - hidradenitis, is a pathology in which inflammation is localized in the armpit area, and can also occur in the perigenital area, but much less frequently. The main cause of development is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms that are constantly present on the human body through the smallest lesions on the skin. Once in the sweat gland, these infectious agents cause severe inflammation. The presence of a variety of diseases associated with weakened immunity can create favorable conditions for such processes, namely:
- Diseases of the endocrine organs, including diabetes mellitus;
- Presence of tuberculosis;
- HIV infection;
- Toxoplasmosis disease;
- Helminths;
- Long-term use of certain medications in the form of antibiotics;
- Rheumatism and lupus erythematosus;
- Failure to comply with the principles of proper nutrition;
- Obesity, which causes frequent profuse sweating;
- Advanced age;
- The period of bearing a child;
- State of anemia;
- Prolonged hypothermia.
Currently reading: Review of the anti-sweating drug Hydronex and honest reviews
Such conditions often cause inflammation of the sweat glands, and one patient may have several of them at once, and they are usually interconnected.
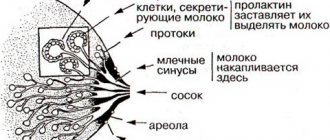
Apocrine metaplasia of the breast
Inflammatory diseases of the mammary glands are included in a separate class. Since it is in cats that they perform the important function of thermoregulation and limiting their territory, you need to be able to recognize the onset of the disease in time in order to avoid sad consequences. However, we should not forget that dogs are also susceptible to this pathology.
The reasons for the development of breast tumors may be the following factors:
- Age. In dogs, neoplasms most often appear between 7 and 10 years of age. The older the animal, the less likely it is for tumors to develop. In cats the situation is the opposite. In their case, the disease often develops in older animals.
- Castration and sterilization. The sooner these procedures are performed, the less likely tumors will occur. However, it should be borne in mind that previous pregnancies do not affect the frequency and risk of the disease. Moreover, veterinarians claim that periodic delivery and feeding the litter with milk is a kind of prevention of the development of mammary tumors in both dogs and cats.
- Suppression of estrus. The use of various hormonal drugs that contain progesterone increases the likelihood of mastopathy. Despite the fact that these tumors are benign, they are still classified as precancerous conditions and are best avoided.
- Gender. Typically, mammary cancer is predominantly a problem in female cats and dogs. However, males can also develop neoplasms. But they will be of a slightly different nature, since males do not have mammary glands, but have a mammary gland. It also has ducts in its structure that can be susceptible to tumor formation.
Symptoms of diseases
With the development of disorders in the condition of the sweat glands, especially in the case of acute hidradenitis, the following symptoms may occur, in the presence of which it is possible to easily diagnose and determine the nature of the disease. Usually the diseases are accompanied by the following:
- The appearance of a small node in the armpit is the initial sign of one of the diseases.
- In the absence of obvious signs of pathology, scant sweat production or its complete cessation may cause attention.
- A change in the nature of the secretion, the appearance of its viscosity and an increase in odor that was not there before.
- Formation of bubbles and filling them with liquid. In advanced cases, such rashes can be filled with purulent contents.
There are a number of symptoms that can help identify the presence of an inflammatory process in the sweat glands. First of all, they are the appearance of moisture in the hands and feet, sensations of itching, tingling, and dryness in the area where the sweat glands are located. Bubbles and cracks may be seen on the skin, where areas of peeling appear at the site of healing. Papules may form on the chin, cheeks, and lips, and sweat may be accompanied by an unpleasant odor when released.
Their functions and classification
Based on the method of formation and composition of the secretion, it is customary to distinguish two main types of sweat glands:
Apocrine
Apocrine glands are located in the hair follicles, and therefore are absent on the feet, palms and other areas of the skin where there is no hair. On the contrary, their increased concentration is located under the arms, in the groin, and on the external hearing aid. They begin to perform their functions after puberty, from about 13-15 years, and the peak of activity occurs in adolescence.
The main function of apocrine glands is to regulate humoral behavior. That is, the release of certain substances on a hormonal background. The released substances are called mediators; they are capable of influencing the receptors of another person, mainly an individual of the opposite sex. A secretion is formed due to the fusion of fat and cholesterol. Each individual organism has its own special smell that can excite a representative of the opposite sex. That is why the odor secreted by apocrine glands is often called sexual odor.
Also, this type of glandular centers regulates the normal microflora of the epidermis and prevents the development of inflammatory processes in the skin. At the same time, they are absolutely not involved in thermoregulation.
Eccrine
This class of sweat centers is directly responsible for regulating normal body temperature and removing toxins from the body. After all, sweat is a liquid consisting of 99% water, the remaining 1% being harmful substances. Also, thanks to their activity, a hydro-acid-lipid micro-film is formed on the skin, promoting hydration. It is thanks to this function that human skin has a fresh, elastic appearance and does not dry out.
The volume of secreted secretions is regulated by the same nervous system and depends on the activity of hormones, external factors, as well as the density of the sweat glands. Under normal conditions, they secrete between 300 and 800 ml of sweat per day. However, with any disorders affecting the nervous system or eccrine centers, sweating increases, which is medically called hyperhidrosis.
Doctors
If symptoms appear that indicate changes in the condition of the sweat glands in the form of rashes or blisters and increased sweating, you should consult with a specialist. A dermatologist, or, in the absence of such a specialist, a surgeon, must carry out a diagnosis and identify the true cause of the disorders that have arisen. They will be able to eliminate any problems that have arisen, and the help of a cosmetologist will help solve cosmetic problems and improve your appearance, if necessary.
Causes of atheroma
The main, but not the only reason for the formation of atheroma is blockage of the sebaceous glands, which occurs due to many internal and external factors. Typically, such changes in the condition of the skin occur under the influence of the following:
- Increased activity of sweat glands;
- Hormonal imbalance in women;
- The presence of seborrhea and acne;
- Accelerated proliferation of bacteria;
- Diseases that are chronic and accompanied by metabolic disorders.
Additional factors contributing to the development of atheroma are:
- Repeated microtraumas of the skin;
- Presence of dermatitis;
- Congenital disorders in the structure of the sebaceous gland;
- Insufficient skin care;
- Excessive use of various cosmetics;
- Congenital impaired synthesis of fats in the body.
Increased activity of the sebaceous gland, accompanied by insufficient patency of its excretory channel, leads to blockage of the pores. Due to the accumulation of contents in it, the gland swells and increases in size, which usually ends in an inflammatory process.
Tests and diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, which determines the direction of treatment, it is necessary to collect the following results:
- Visit a dermatologist and undergo a thorough examination;
- Collect the available medical history and provide it to the attending physician;
- Determine the rate at which the secretion is produced and determine its quantity.
The patient will be asked to undergo special tests and examinations using instrumental methods in the form of gravimetry, evapometry, iodine-starch analysis, the use of fingerprints, and ninhydrin analysis.
Methods for diagnosing sweat gland diseases
Those who like to diagnose themselves and receive treatment over the Internet should know that without identifying and eliminating the root cause, health experiments will be useless at best.
To clarify the diagnosis, a dermatologist:
- Inspects the patient's skin condition;
- Collects anamnesis;
- Analyzes the rate of secretion production, its volume and other parameters;
- Conducts testing and instrumental diagnostics: iodine-starch analysis, gravimetry, evapometry, fingerprint method, ninhydrin examination.
Treatment
When treating diseases occurring in the sweat glands, it is necessary to identify their root cause and eliminate it. Chronic types of disorders are treated with the use of ointments, which serve to soften and moisturize the skin. Such patients are prescribed vitamin complexes and Retinol, which accelerate metabolic processes in the skin and improve the regeneration of damage.
The following are effective means intended for the treatment of disorders in the condition of the sweat glands, as well as in the presence of inflammation in them:
- The drug Atropine, which is used in severe cases requiring suppression of secretion by the sweat glands;
- Malavit is a product containing silver that has an effective effect on the development of hyperhidrosis when used as a rub.
There are other treatment methods used for various pathological conditions in the sweat glands. Their choice depends on the nature of the lesion, the degree of changes that have occurred and the root cause that served as the onset of the disease.
Treatment options
Sweat glands and their anomalies are restored mainly through medication, but experts do not deny the benefits and methods of traditional medicine in improving symptoms. The doctor chooses a treatment regimen not only taking into account the patient’s health condition, but also depending on the cause of the dysfunction of the sweat centers. For congenital pathologies the following is prescribed:
- Ointments for local softening and moisturizing of the skin;
- Atropine – to suppress the production of sweat glands (in severe form);
- Malavit – for hypergyrosis, for treating problem areas;
- Retinol and multivitamin complex.
If an infection is associated with the disease, the course of therapy is supplemented with antibiotics. With anhidrosis, exposure to the open sun on hot days, as well as intense sports training, is contraindicated. Strengthen the effect with home remedies:
- Baths in a decoction of oak bark or soda solution - for mild forms of disease;
- Baths based on the rhizomes of valerian, lemon balm and mint - for disorders of the nervous system.
The possibilities of homeopathic remedies help reduce the activity of epithelial secretions and have a sedative effect.
Recommendations will be incomplete without lifestyle modifications and increased attention to personal hygiene.
- Shower as often as possible. The water temperature is warm (so as not to dry out the skin), the soap is antibacterial (including for prevention);
- Treat prepared (washed and dried) armpits and other areas where sweat glands accumulate daily with a natural-based antiperspirant (one-time use);
- Choose underwear and other clothing made from natural hygroscopic fabrics. Use synthetics as little as possible;
- Change your underwear and bed linen as often as possible (daily or when soiled);
- If it is impossible to avoid stressful situations, learn how to properly resolve conflicts
Surgical techniques
In some cases, surgical treatment of sweat gland diseases is also indicated. Operations are prescribed for:
- Adenocarcinoma of the sweat glands;
- Lack of expected results from drug therapy;
- Worsening of symptoms;
- Risk of developing serious complications.
Three options for such treatment have been developed.
- Endoscopic sympathectomy. A barely noticeable puncture is made on the back or chest to insert an endoscope with a camera. The surgeon cuts off the sympathetic trunk, which is responsible for hypergyrosis.
- Liposuction. A cannula (special needle) is inserted into the subcutaneous fat layer to suck out the contents of damaged sweat centers.
- Curettage. A small incision is made in the dermis to scrape out the problematic glands. Performed under local anesthesia.
Removing sweat ducts is a radical technique that requires high professionalism of the doctor, because with negligence, the innervation of the problem area can be disrupted with all the ensuing consequences. Therefore, surgery is chosen as a last resort. With a favorable outcome, relapses of the disease do not occur in this particular area, because the problem is solved radically.
The importance of the sweat excretory system can hardly be overestimated, because both human health and well-being depend on the performance of the sweat glands. Our body produces such an amount of heat per day that it would be possible to heat 33 liters of ice water with this energy. And 75% of this heat is released through the skin by sweat glands. A wet pillow during restless sleep, the smell of damp armpits after nervous or physical overload, and the awkward situation of having to take off your shoes outside the home are familiar to many. And there is no need to put up with such discomfort: medicine has accumulated sufficient experience in restoring thermoregulation mechanisms.
Reviews
Dear readers, your opinion is very important to us - therefore we will be glad to hear your feedback about sweat glands in the comments, this will also be useful to other users of the site.
Natalia:
I was lucky enough to experience inflammation of the sweat glands once. The condition was accompanied by severe pain and fever. I had to use antibiotics, and quite strong ones at that. I don’t understand why this condition arose, but I don’t want this anymore.
Nastya:
I think the cause of sweat gland diseases is poor hygiene. Many of my friends replace water procedures with strong antiperspirants. The armpits get dirty, and when sweat is released, it has to come out somewhere, so it accumulates and then becomes inflamed.
Clinical picture and possible complications
The cyst is located under the skin and has a round, smooth shape. It is usually not bothersome and may only be painful when you press on it. However, the very nature of such education, as it develops, can cause the following problematic situations:
- Open the cyst with the formation of a non-healing ulcer in its place;
- Lead to the formation of an abscess with the formation of a large abscess;
- It is rare, but possible, for a cyst to degenerate into a malignant formation.
A characteristic complication of blockage of the sebaceous gland is its suppuration, which causes a certain degree of danger, is accompanied by severe pain and requires medical attention. If this does not happen and suppuration does not occur, then after two to three weeks the formation may disappear on its own, leaving no trace. If, nevertheless, the pus from its contents comes out, then the infection may spread to the surrounding tissues, and at a fairly high speed. As a result, papules, after fusion, create formations with larger sizes, and can also form numerous ulcers, boils and abscesses that affect the deeper layers of the skin. Even after eliminating them, getting rid of unsightly marks and scars on the skin will only be possible with the help of cosmetic surgeries and salon procedures.
Varieties
This disease is dangerous due to the appearance of a life-threatening complication - sepsis.
Hidradenitis comes in the following varieties:
- Spicy. The root cause of the development of such a disorder is a simultaneously clogged sweat and sebaceous gland, which also becomes inflamed. The problem worries people who do not keep their groin area and armpits clean. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner and do not begin to treat the problem, the clogged gland begins to fester, and other life-threatening disorders will arise.
- Chronic. When the treatment of acute hidradenitis was carried out incorrectly, a recurrent type of pathology develops, in which a person is bothered by frequent relapses with copious discharge of pus. It is not easy to cure the pathology using conventional methods, so self-medication at home is contraindicated.
- Nodal. If you incorrectly shave excess hair on the skin under the arms or, for example, on the labia, microtraumas appear. Pathogenic microflora penetrates into the damaged areas, and if the correct therapy was not carried out in a timely manner, and the wound became clogged and inflamed, this type of pathology occurs.
Hidradenitis in the armpit, as in the groin, develops gradually, and characteristic symptoms appear over 1.5-2 weeks. The clogged glands, which are located in the armpits, become inflamed, then a bacterial infection occurs, and if you do not begin to treat and eliminate complications at the initial stage, the doctor will have to use surgical methods of therapy.
Development of hyperhidrosis due to disruption of the apocrine glands
Apocrine gland hyperhidrosis is characterized as a disease in which there is increased sweat production under the influence of various provoking factors. Local and extensive manifestations of pathology are distinguished.
Possible pathological causes:
- Development of neurodermatitis;
- Psoriasis;
- Tuberculosis;
- Diabetes;
- Neurasthenia.
Diagnosis of the above diseases is based on a detailed study of the secreted secretion (temperature, consistency, amber). Treatment is quite long-term using complex therapy.
Currently reading: Hydrogen peroxide as an effective remedy for sweat
Causes of prickly heat:
The main cause of prickly heat is insufficient ventilation of certain areas of the skin in the areas of natural folds: the axillary zone, groin, knee and elbow bends. In women, the area under the mammary glands is also affected. In children and adults with very thick hair, prickly heat appears behind the ears. Miliaria also appears in areas of the body that are constantly under thick clothing (bras, swimming trunks, diapers, bandages and bandages).
Contribute to the development of prickly heat:
- clothing made of thick, synthetic, non-breathable fabrics;
- high air temperature combined with high humidity;
- various injuries and abrasions of the skin;
- using various oily cosmetics that clog pores.
Prevention
Blockage of the sebaceous gland may not be a serious disease that causes fear for the lives of patients, however, it can lead to very unpleasant consequences. First of all, this affects the aesthetic side, since a growing formation on the face or on open areas of the body attracts unnecessary attention from others. To prevent such problems from occurring, it is best to listen to the recommendations of specialists on the prevention of atheroma formation and follow them. First of all you need to:
- Use mild cosmetics to wash your skin, since complete removal of the protective fat layer creates ideal conditions for the development of harmful microflora;
- Review your diet, more often use fermented milk products, fruits and vegetables, cottage cheese, and it is better to eat a little food, but of good quality;
- Good digestion and proper metabolism are promoted by sufficient consumption of plain drinking water;
- If possible, you need to reduce the consumption of foods that cause digestive problems, such as sugar, fats, starch, pickles, hot sauces, and smoked delicacies.
To prevent blockage of the sebaceous glands, it is important to cleanse the skin in a timely manner, which requires daily cleansing hygiene procedures.
Blockage of the sebaceous canals on the face can bring a lot of unpleasant moments. Even if they do not threaten inflammation, their appearance suffers significantly. Such a violation of the skin also affects the psycho-emotional state of a person, lowering his self-esteem. In this regard, you need constant care for your skin, and in the case of active development of pathology, do not delay contacting specialists.
What causes atheromas to form?
As is known, lipomas, which include atheroma, are formed when the sebaceous ducts are blocked by a viscous secretion or keratinized skin cells. The following factors contribute to the development of the pathological process:
Atheromas do not grow into surrounding tissues and do not compress them
- genetic diseases;
- hyperhidrosis;
- acne;
- inflammation of the epidermis;
- metabolic disorders leading to changes in the consistency of sebum;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- squeezing pimples;
- long-term use of cosmetics;
- damage to the sebaceous glands;
- hormonal imbalances;
- inflammation of the hair follicles.
Nails
Approximately half the surface of the rear of the terminal (distal) phalanges of the fingers and toes is covered with a dense transparent horny plate called the nail. The nail is located in the nail bed and is limited by skin folds. The nail has a free edge, the lateral and posterior edges cover the skin folds. The nail has a body - the main mass of the nail and a root, mostly hidden under the skin of the proximal ridge. The spinous layer of the root matrix contains onychoblast cells that form the horny plates of the nail.
Read also Hair masks with brewer's yeast
The nail mainly consists of the protein keratin, the specific density of which depends on the content of the amino acid cysteine in the body. Between the layers of keratin there are layers of water and fat, which give the nail shine and elasticity. Nails are able to absorb water molecules, so when they stay in water for a long time, they soften and thicken. The growth rate of nails on average is about 1 mm per week, while on the hands they grow almost twice as fast.
Complications
If treatment is not started on time, the sweat glands can become inflamed in the neck and chest area
Lack of timely treatment of hidradenitis leads to a number of negative consequences. Hidradenitis begins to spread to other parts of the body. Sweat glands can become inflamed in the groin, neck, and chest area. Other complications: abscesses, chronic lymphadenitis, cancer of the lymphatic system, sepsis.
Acute hidradenitis
The disease occurs when the sweat gland becomes blocked due to lack of regular hygiene. Symptoms are the formation of inflammation in the armpit, redness of the skin, pain. The patient develops a fever and develops a fever. The acute form of inflammation is considered dangerous. The infection quickly spreads throughout the body, affecting the lymph nodes. Immediate treatment is required.
Nodal form
Hidradenitis nodosum is a consequence of skin damage from inaccurate hair removal. Bacteria enter microcracks, causing inflammation. Signs: the formation of multiple small nodes. This form of inflammation can quickly progress to a purulent stage.
Chronic or recurrent hidradenitis
At the site of the inflammatory neoplasm, the gland emanating from it is affected by multiple purulent wounds. They take a long time to heal and are accompanied by a painful symptomatic picture. Frequent relapses alternate with short periods of remission.
The danger of the chronic form of hidradenitis is the spread of the pathological process to other glands of the axilla. Recurrent hidradenitis poses a threat to human health. Treatment is surgical.
How to get rid of the disease?
Treatment of the disease begins with taking medications. If no positive results are observed during therapy, it turns out to be ineffective. This indicates that the disease is at the last stage. In this case, surgical treatment is used.
Treatment with surgery is usually very quick. The inflamed abscess is opened. Its contents are completely removed. After surgical manipulations, a number of procedures are carried out, the purpose of which is to promote the healing of damaged tissue.
The patient is prohibited from opening the tumors on his own. He does not know all the intricacies of the procedure. In this case, there is a possibility of infection and further spread of the disease. The operation is performed only by a doctor using sterile instruments.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment of hidradenitis is carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist. From the first days, the patient must adhere to a strict diet, exclude spicy foods, sweets from the diet, and eliminate smoking and alcohol.
Treatment is accompanied by the use of antibiotics and sulfonamides. The patient should definitely use various types of immuno-strengthening agents and vitamins. Nitrofurans and autohemotherapy are also applicable. For local treatment, dry heat, UHF and ultraviolet irradiation are used.
Symptoms of blockage
- The appearance of a dense formation that can be easily felt by palpation of the skin. It can be small or reach the size of a large nut.
- Your temperature may rise.
- The skin around the blockage will turn red.
- Painful sensations occur.
- If the disease is advanced, the blockage becomes bluish in color.
- An unpleasant odor occurs if the cyst begins to fester.
The blockage looks like a small tumor. It is soft to the touch, its diameter is most often 5 cm. If inflammatory processes begin, the skin may acquire a light brown or red tint.
Most frequently asked questions
When faced with the appearance of a lump under the muscle cavity, it is natural to become worried and begin to look for methods to solve this problem. To avoid making the situation worse by doing the wrong thing, follow the following recommendations.
A lump has appeared under the muscle cavity and it hurts: what to do?
The only thing you can do at home is to treat the skin of your armpits with an antiseptic that is in your medicine cabinet: hydrogen peroxide, a solution of boric or salicylic acid, brilliant green. If you have severe pain and are unable to see a doctor, you can take a tablet of analgin, baralgin, or aspirin.
Important: carefully read the instructions for the drug you are going to take. If you suffer from any disease listed in the list of contraindications, this remedy is strictly prohibited for you. Also, you should not give any painkillers to children without first consulting a doctor: if your child complains of pain from a lump under the arm, go to the emergency room.
Applying warm, cold or alcohol compresses is unacceptable, as they can cause deterioration in health and complicate the course of the disease.
The “insidiousness” of compresses lies in their ability to quickly and effectively relieve pain, but this subjective sensation does not last long: heat and irritating action (as in the case of alcohol compresses) can cause the spread of purulent inflammation to nearby tissues, and cold can narrow the lumen of sweat or sebaceous tissue. duct, preventing the contents of the gland from being discharged out.
Lump under the arm: which doctor should I see?
If you have not previously encountered such a phenomenon as a lump under the armpit, contact a therapist who, after studying your medical history and listening to your complaints, will decide on further diagnostic procedures or consultation with a specialist.
If the lump under the muscle cavity is a chronic condition, and you know the reason for this (clogging of the sebaceous or sweat gland), if it recurs, make an appointment with a dermatologist.
In some cases, examination by an immunologist, hematologist, infectious disease specialist or oncologist may also be required if the attending physician sees the need for this.
It so happened that after unsuccessful hair removal, I had irritation under my armpit, and after a couple of days a painful lump the size of a cherry formed. All the surgeons shouted with one voice: “we need to make an incision.” The presumptive diagnosis was either hidradenitis or lymphadenitis. In general, I insisted on conservative treatment, or at least try. I was sent for an ultrasound to check whether there was fluid in the lump, or pus. Ultrasound 2 times showed that there was no fluid. And one of the surgeons at the local clinic in the Svyatoshinsky district of Kiev, Yuri Vasilyevich Antonyuk, began to treat me, for which I am immensely grateful to him. As a result, after 1.5-2 weeks the lump went away. Now you can barely feel a very slight lump with slight redness. I would like to share the stages of my treatment.
1). The first week I made a miracle compress that heals any abscesses and inflammation (I kept it almost all day): 1 tsp. dimexide 3 tsp. filtered water 1 ampoule of gentamicin sulfate solution 1 ampoule of hydrocortisone acetate solution 2.5% + drank the antibiotic Flemoklav 4 days (morning and evening) (drank kefir as a probiotic) + drank Nimesil 4 days (morning and evening after meals)
2). The second week I used a compress with iodicerine (I kept it only during the day, it was not convenient at night). How did you do it? I folded the bandage several times, glued it to the bump and generously applied iodicerin on top of it. After half an hour or an hour I checked, when it had dried, I applied it on top again. + drank Serrata. There was severe irritation from ioddicerin, I applied Pantestin to restore the skin faster.
Reasons for the formation of a lump under the armpit
All cases of lumps in the armpit can be divided into three categories, depending on the causes: blockage of the sebaceous gland, inflammation of the sweat ducts (hidradenitis) and inflammation of the lymph node.
Hidradenitis under the armpit
Hidradenitis occurs equally in both men and women and is caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms (most often staphylococci and streptococci) into the sweat gland.
But even the presence of pathogens is not enough for the development of a disease such as hidradenitis under the arm, which requires additional conditions:
- Failure to observe basic personal hygiene. Neglecting a shower or bath, especially in the warm season, leads to the formation of favorable conditions on the skin of the armpit for the growth and reproduction of microbes. Heat, moisture, microscopic particles of dead skin and sweat components create an ideal nutrient and climatic environment for bacteria or fungi and subsequent inflammation.
- Increased sweating. When excessive sweat is produced, the sweat ducts become dilated, allowing pathogens to easily enter the sweat gland.
- Incorrect or inappropriate use of cosmetics and hygiene products. The most obvious example of this is the use of antiperspirants before exercise. These products do not reduce the production of sweat, but only prevent its elimination, so the accumulation of sweat expands the ducts and leads to the development of stagnation in them, which makes the path easier for infections. Another “cosmetic” reason is the excessive use of deodorants, talcs and similar products, which provokes a decrease in local immunity and resistance to pathogens.
- Injuries. Abrasions, scratches, and skin cuts in the armpit become entry points for microbes that surround a person.
Lymph node enlargement
The cause of inflammation of the lymph nodes and their enlargement can be due to many circumstances:
- a previous or currently existing infectious disease (flu, sore throat, whooping cough, etc.);
- the presence of a constant infection in the body (tuberculosis, syphilis, etc.);
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- tumor diseases with metastases.
Depending on the reasons for the enlargement of the lymph nodes under the arms, they can be painful or painless, but they are always clearly visible to the touch (dense round formations directly under the skin, more or less mobile).
Treatment of a lump formed under the armpit, associated with enlarged lymph nodes, is carried out taking into account the disease that caused this condition. Treatment can be either conservative, using anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiseptic, immunostimulating, antitumor drugs, or surgical - with removal of the lymph node.
In each individual case, the decision is made by the attending physician, assessing the situation individually.
Eccrine glands
Eccrine sweat glands do not stop working around the clock. They are smaller in size and less deeply located in the dermal layer. Due to these sweat glands, body temperature is regulated by cooling it, removing toxins and participating in the formation of the protective shell of the upper layer of the epidermis.
Fact: The eccrine glands in the area of the feet and palms are somewhat less active, but react quite clearly to stress, and “cold sweat” appears.
The work of eccrine sweat glands directly depends on hormonal levels, i.e. completely regulated by the endocrine system.
Notes
- Kurosumi, Shibasaki, Ito, 1984, p. 254.
- ↑ 12
Histology, cytology and embryology, 2004, p. 662. - Kurosumi, Shibasaki, Ito, 1984, p. 255.
- Histology, cytology and embryology, 2004, p. 663.
- ↑ 1 2 3 Konstantinov V.M., Naumov S.P., Shatalova S.P.
Zoology of vertebrates. 7th ed. - M.: Publishing house. , 2012. - 448 p. — ISBN 978-5-7695-9293-5. — P. 315. - ↑ 1 2 Dzerzhinsky F. Ya., Vasiliev B. D., Malakhov V. V.
Zoology of vertebrates. 2nd ed. - M.: Publishing house. , 2019. - 464 p. — ISBN 978-5-4468-0459-7. — P. 375. - Histology, cytology and embryology, 2004, p. 665.
- Skin appendages
- Histology, cytology and embryology, 2004, p. 663-665.
Treatment of hidradenitis
In the first three days, hidradenitis under the arm looks like a painful subcutaneous node. If adequate treatment is prescribed during this period, the compaction may resolve.
1) Antibiotics are taken orally, and in case of complicated hidradenitis they are administered intramuscularly. The minimum duration of treatment is from 5 to 10 days, but if necessary, the doctor can extend the course to several weeks.
| Name of the drug and dosage regimen | Mechanism of therapeutic action |
| Tetracycline. 250 mg 4 times a day or 500 mg 3 times a day. | Tetracyclines penetrate the bacteria and inhibit the synthesis of protein necessary for the production of new microorganisms. Bacteria cannot multiply and the spread of infection stops. |
| Cephalexin. 0.5-2 grams 2 times a day every 12 hours. The course of therapy is 7-14 days. | Cephalosporins act on growing and developing bacteria, disrupting their cell membrane. |
| Erythromycin. 1-2 tablets every 6 hours (4 times a day). The course of treatment is 7-10 days. | Macrolides differ from other antibiotics in being well tolerated. They stop the proliferation of bacteria and protect healthy cells from infection. They penetrate well into the skin and reach high concentrations there. |
| Clindamycin in the form of lotions. 2% solution in the form of lotions. A gauze napkin of 4-6 layers is moistened in the solution and applied to the sore spot. As it dries, re-wet it every 20 minutes. | They stop the reproduction and cause the death of bacteria. Including streptococci, staphylococci, anaerobic microorganisms that cause chronic hidradenitis. |
At home, self-medication with antibiotics is unacceptable . Only an experienced specialist can prescribe a drug that will effectively act on the pathogen. In addition, it is necessary to take into account contraindications and individually adjust the dose of the antibiotic.
2) At the same time, other drugs are also included in the complex treatment of hidradenitis:
- Antihistamines relieve swelling and irritation of the skin (tavegil, cetrin) 1 tablet 2 times a day;
- Corticosteroid injections into the lesion reduce inflammation (prednisone). The dose is selected individually;
- Immunostimulating agents strengthen the general immune system (tincture of echinacea, eleutherococcus, ginseng) 15 drops 3 times a day;
- Specific immunotherapy is necessary for frequent relapses of hidradenitis (staphylococcal immunoglobulin, antifagin, toxoid, T-activin). Drugs are administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly only after consultation with a doctor;
- Isotretinoin capsules are taken in the early stages and in combination with surgical treatment. This drug reduces the activity of the skin glands and improves the healing of lesions. Take for a long time. The dose is calculated based on weight at 0.1 mg/kg per day.
Crystalline
Children are most susceptible to crystalline prickly heat. White or translucent small (up to 1 mm) bubbles form on the skin. These bubbles very often merge and form larger lesions. The blisters may burst and become easily infected. As with other forms of prickly heat, peeling and severe itching are observed. Swelling of the skin may occur, which can lead to false suspicions of measles, chickenpox and urticaria.
They occur throughout the body and, if a secondary infection occurs, can cause the formation of pustules (pyoderma) and diaper rash.
The basis for the treatment of prickly heat in both children and adults is the opening of air access to the skin and strict adherence to hygiene rules.
You should not wrap your child up tightly or wear tight clothes that increase sweating; you should also avoid wearing synthetic clothing in humid climates.
If there are rashes, drying measures are carried out: treatment with powders and a weak solution of manganese. Affected areas of the skin should be treated with antiseptics and non-greasy ointments with betamethmzone or preparations containing menthol can be applied topically to relieve itching.
If there is a bacterial infection, antimicrobial medications should be started.
When dealing with heat rash, do not use oils, creams and greasy lotions, as they can aggravate the situation.
You should also definitely consult a dermatologist and begin treatment for the primary manifestations of hyperhidrosis. Physical activity should be avoided and acclimatization to the hot climate should be slow.
Diagnosis of hidradenitis under the arm
The examination begins in the doctor’s office, he carefully palpates the formation and determines the reason why the sweat and sebaceous opening is clogged. For differential diagnosis, laboratory testing is mandatory, because hidradenitis is often mistaken for furunculosis or carbunculosis. In order for antibacterial treatment of hidradenitis under the arm to be effective, a bacterial culture is taken and the sensitivity of the pathogenic microflora to antibiotics is determined.
Why does blockage occur?
Blocked sweat glands can occur for a number of specific reasons, which are discussed in detail in the list below:
- Severe diaper rash of the skin;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- The appearance of abrasions;
- Favorable development of pathogenic microorganisms on the skin;
- Constant use of antiperspirants.
Ways to prevent pore clogging are based on following simple recommendations:
- Normalization of drinking regime;
- Strengthening immunity;
- Maintaining personal hygiene;
- Exclusions from the constant use of antiperspirants containing zinc and aluminum.
Eliminating acne during pregnancy
How to deal with the appearance of acne during pregnancy remains an open question. When prescribing any medications to a patient during pregnancy, those should be those that will not harm either the fetus or the woman herself. To be sure of this, it is necessary to test the drugs directly on a group of people with the same condition. However, pharmaceutical companies are reluctant to do this because they fear harmful consequences from the experiment.
Therefore, in relation to pregnant women, to eliminate acne, first of all, they use a more attentive attitude to the foods they eat. The diet includes those types of dishes that will not contribute to increased sebum secretion. In addition to dietary nutrition, the following measures can be applied to pregnant women to eliminate or prevent the appearance of acne:
- Thorough hygienic care for problem skin;
- Use of high-quality cosmetics for moisturizing;
- On the recommendation of a dermatologist and with the permission of a gynecologist, preparations with azelaic acid can be used.
In case of severe acne with extensive acne rashes all over the body, after the end of the 14th week of pregnancy, the drug josamycin can be used for treatment.
Local and systemic preparations of retinoic acid and tetracycline antibiotics are prohibited drugs for eliminating acne in women during periods of fetal development. These medications can negatively affect the intrauterine development of the child.
Diagnostics
Hidradenitis can be determined based on a blood test. Since the symptoms of the disease are similar to other skin diseases, inexperienced patients, trying to make a diagnosis on their own, confuse it, for example, with furunculosis. By examining blood tests, you can identify characteristic signs of inflammation: an increased number of white blood cells and a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Additionally, microflora from the inflamed area is examined. This helps the doctor choose the right antibiotics for further treatment of hidradenitis.
In chronic cases, doctors recommend an immunogram for the disease. It will tell you the state of the body’s protective functions. If there are corresponding violations, treatment will be prescribed by an immunologist. Basically, patients with inflammation of the apocrine glands require the help of a dermatologist or surgeon. Pregnant women should consult their gynecologist.
Places on the body where there is no sweating
In the human body there are also areas on the body in which apocrine glands are not located:
- Red border of the lips near the mouth;
- Inner surface of the penis;
- Female genital organs;
- Labia minora.
The lack of functioning of the apocrine glands leads to the formation of anhidrosis (decreased sweating). Excessive sweat production is called hyperhidrosis and most often indicates the development of parallel diseases in the body.
What does it represent?
The blockage of the sebaceous gland looks like a dense lump that is located under the armpits. At first it is motionless and does not cause pain. It has a regular round shape. It occurs as a result of improper functioning of the sebaceous ducts. They narrow and sebum cannot be removed properly.
At first, blockage of the sebaceous glands does not cause any inconvenience to a person. But if personal hygiene rules are not followed and under the influence of other factors, it can cause a deterioration in the quality of life. The lump enlarges and becomes painful. The situation worsens if the inflammatory process begins to develop.
The blockage is usually treated with surgery. After removal of the sebaceous gland, the patient must undergo a course of antibacterial therapy.