Protein or proteins?
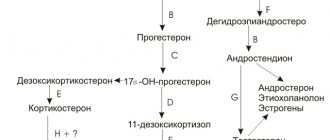
The concept of “total protein” includes not one criterion, but several. Each of its components or factions has its own function. Proteins are absolutely essential for the body and serve a number of purposes.
They are involved in the transport of nutrients, hormones, metabolic products and even drugs. Proteins are universal “transport” in human blood.
Another important function is neutralization. Many metabolic products are toxic to organs. But one of the fractions - albumin - binds to toxins and makes them safe. In this form, unnecessary substances are removed from the body.
Proteins do the same with harmful molecules that come from outside. Albumins are capable of neutralizing poisons.
The structure and purpose of blood protein.
The next major part is globulins. These are real protective squirrels. Globulins are represented by antibodies, so their other name is immunoglobulins. Antibodies are produced by our body to the invasion of any bacteria, viruses or fungi.
IMPORTANT! It is precisely because antibodies are represented by protein that immunity is significantly reduced in depleted people.
Among the proteins there are also those that are responsible for blood clotting - fibrinogen, prothrombin and other coagulation factors. These substances play a vital role in stopping bleeding. A lack of coagulation factors leads to increased bleeding - bruising and large blood loss when injured.
Total protein in the blood - what is it?
Total blood protein (TBP) is a collection of various protein compounds, each of which has its own functions and properties. Albumin is necessary to maintain the osmotic pressure of the blood, as well as for binding and transporting various compounds, globulins are responsible for immune processes, fibrinogen ensures normal blood clotting. The total protein norm is the total value of all protein components.
The main functions of blood plasma proteins:
- transport nutrients and medications to organs and tissues;
- provide osmotic blood pressure;
- maintain optimal pH levels in the blood;
- retain iron, copper, calcium in plasma;
- participate in the synthesis of hormones, enzymes, hemoglobin, antibodies;
The OBC level shows how correctly protein metabolism occurs in the body.
Important! There is not a single cell in the human body in which protein is completely absent; protein serves as a building material for all organs and tissues, therefore long-term protein-free diets negatively affect health.
SRB and RF – what is it?
Sometimes the doctor prescribes a rheumatic test. In this case, blood from a vein is analyzed for the content of certain proteins - rheumatoid factor and C-reactive protein.
Rheumatoid factor is immunoglobulins, antibodies that do not work correctly. They attack their own body. Therefore, the appearance of a large amount of RF in the body indicates the autoimmune nature of the disease.
Rheumatoid factor - autoantibodies that react as an autoantigen with their own immunoglobulins G, which have undergone changes under the influence of any agent (for example, a virus)
C-reactive protein is a universal criterion for inflammation. It increases if there is an active inflammatory process in the body. This is not always an infection; inflammation can be autoimmune.
Therefore, CRP and RF are calculated when an autoimmune nature of the disease, especially joint pathology, is suspected.
Consequences of Low Protein Levels
The consequences of a lack of protein in the body are very sad: children’s growth and development slows down, and adults suffer from liver failure, all kinds of hormonal disorders, vitamin deficiency, as well as anemia and disruption of the reproductive system.
With long-term protein deficiency, two types of protein deficiency can be observed:
- Marasmus is the highest degree of physical exhaustion, which is most often observed in babies in the first year of life who do not receive enough nutrition. With marasmus, the child’s body weight drops significantly, it is less than 60% of the proper weight, the skin becomes wrinkled and lethargic, the subcutaneous layer of fat disappears, and physical and neuropsychic development is disrupted. The child has a lack of appetite and interest in everything that happens.
- Kwashiorkor is a disease that affects adults and children over one year of age. The decrease in total body weight is about 20-40%, swelling is observed throughout the body, especially in the abdominal area. The skin becomes very rough and may develop rashes or scales. The psyche is greatly depressed, contact with the outside world is lost.
How much protein is good?
The range of protein blood test results varies depending on age and gender. What is normal for a newborn girl is not suitable for an older man. This is due to the characteristics of immunity, metabolism and liver function. In newborn children, many indicators change transiently - very quickly and for a short time. Therefore, any suspicious analysis at this age should be rechecked.
Normal blood protein levels are in table No. 1.
Table No. 1
| Age | Norms for women | Normal for men |
| Children up to 28 days | 40-60 | 41-60 |
| Children under 12 months | 45-80 | 45-70 |
| Children 12-48 months | 60-80 | 55-75 |
| Children from 5 to 7 years old | 50-80 | 55-80 |
| Children from 8 to 16 years old | 55-80 | 55-80 |
| 17-25 years old | 75-80 | 80-85 |
| 25-55 years | 70-80 | 75-80 |
| 56-75 years old | 70-75 | 70-75 |
| Over 75 years old | 65-75 | 70-75 |
Not every person needs to measure total protein. This criterion is always calculated not separately, but as a component in biochemical analysis.
Medical indications for calculating its amount are varied:
- Any infectious diseases
- Problems with the liver, gastrointestinal system,
- Hemoglobin is below normal,
- Metabolic disorders
- Before surgical interventions.
Deviations of an indicator from normal can be relative and absolute.
The relative decrease is due to the “dilution” of the blood . Transfusion of liquid solutions during intoxication causes an increase in the amount of liquid component of the blood. In this case, the protein content will be relatively low.
The absolute decrease is not due to blood dilution, it is a true decrease in protein content. It can be caused by either insufficient intake or excessive loss.
IMPORTANT! Protein loss in renal pathologies can be seen in a classic urine test.
The increase in protein can also be relative - with fluid loss through vomiting or diarrhea. An absolute increase in protein content may be a sign of systemic diseases, infections or neoplasms.
Changes in blood tests may be physiological . This means that protein is reduced or increased not due to illness, but due to the characteristics of the body. This is possible during pregnancy and while breastfeeding, due to prolonged bed rest or excessive physical activity - weightlifting, marathon.
Pathologies in which the amount of total protein changes in Table No. 2.
Table No. 2
| Low protein | High protein |
| Operations | Allergies |
| Tumors | Malignant neoplasms |
| Burns and burn disease | Scleroderma |
| Malabsorption and maldigestion syndrome | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| Fever | Myeloma |
| Liver pathologies | Blood loss, blood thickening |
| Gastrointestinal pathologies | Liver dysfunction |
| Thyrotoxicosis | Sepsis |
| Intoxication | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| Bleeding and anemia | Profuse diarrhea and vomiting |
| Massive infusion of solutions | |
| Exhaustion, fasting, strict vegetarianism |
Results
A decrease in total protein levels is an abnormal condition. The following physiological reasons can provoke the problem:
- poor nutrition;
- pregnancy;
- grueling physical activity.
A properly organized diet helps compensate for protein deficiency. It is necessary to increase the volume of foods high in plant and animal proteins in the daily menu. In the absence of the influence of physiological factors, low protein in the blood is a clinical diagnostic sign of dysfunction of the liver and kidneys, water intoxication of the body, and pathologies of the digestive tract.
Determination of the quantitative protein content is carried out using a biochemical blood test. For adults, indicators should fall within the range of 64–86 g/l. If the values decrease significantly, the patient should be prescribed an additional examination in order to identify the specific causes of the blood disorder.
What does high protein mean?
Doctors call high protein hyperproteinemia. All factions can increase at the same time, or each one separately.
The highest values are observed in myeloma, a type of blood tumor. The pathology is characterized by the fact that a large amount of protein is formed in the body, which has an abnormal structure.
It is too large and clogs the kidneys, and can be deposited in bone tissue.
IMPORTANT! Multiple myeloma is a malignant tumor of the blood system, so an increase in the amount of protein is a reason to visit a hematologist.
A lower level of protein fractions is observed in autoimmune diseases - systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis. This is due to the formation of a large number of antibodies to one’s own tissues - immunoglobulins.
Other, more rare pathologies in which hyperproteinemia occurs:
- Macroglobulinemia or Waldenström's disease is a pathology similar to myeloma, in which an abnormal protein is also synthesized,
- “Heavy chain diseases” are several pathologies of immunity in which incorrect immunoglobulins are formed in the body, which do not fulfill their protective function and are larger,
- Lymphogranulomatosis is a neoplasm of the blood system,
- Liver cirrhosis - usually causes hypo-, but in some cases hyperproteinemia occurs,
- Other pathologies with an autoimmune component - sarcoidosis, paraproteinemia,
- Acute and chronic infections with a pronounced immune response.
Protein analysis: indications, preparation
Kidney pathology may be an indication for analysis.
A protein level test is prescribed in the following cases:
- edema syndrome;
- liver diseases;
- kidney pathologies;
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- eating disorders;
- extensive injuries, burns;
- assessment of protein metabolism, liver functionality, nutritional status.
When preparing for analysis, you should consider the rules.
- The day before the test, limit physical and emotional stress, eliminate alcohol.
- The last meal should be completed 12 hours before blood collection.
- On the day of the test, do not drink coffee or tea; you can drink clean water in small quantities.
- Smoking should be avoided at least one hour before the test.
- The results of the analysis are affected by medications: immunosuppressants, barbiturates, glucocorticosteroids, oral contraceptives and many other drugs. If it is impossible to cancel their appointment, the entire list must be provided to the doctor.
What does low protein indicate?
Hypoproteinemia is the term doctors call low concentrations of protein in the blood serum.
Her reasons are:
- Insufficiency of liver cell function (occurs with hepatitis, cirrhosis, toxic damage to the liver, fatty degeneration of its tissue),
- Lack of protein products in food (fasting, fasting)
- Exhaustion due to fever and infections,
- Human immunodeficiency virus and congenital immunodeficiencies,
- Malignant neoplasms,
- Excess loss in urine when the kidneys are not functioning well
- Neoplasms of the blood system,
- Severe anemia
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal system, which are manifested by malabsorption and maldigestion syndromes (insufficient digestion and absorption),
- Pancreatic insufficiency,
- Diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy,
- Insufficiency of thyroid function.
General urine analysis: preparation and rules for collecting urine
Blood is made up of proteins which are known as serum proteins. Serum polypeptides make up 6-8% of all blood and perform many functions in the body. Deviation of concentration from normal values indicates the presence of diseases.
Promote the proper functioning of the immune system and regulate cell physiology. They are circulating transport molecules for other substances - lipids, hormones, vitamins, metals.
If total protein in the blood is elevated, you must seek medical help and take a biochemistry test. To measure protein levels, you must undergo a proteinogram study. Electrophoresis is also a valuable examination that evaluates the individual amount of proteins. Electrophoresis is a powerful diagnostic tool and is important for monitoring the effectiveness of therapy for disorders. As for proteins, blood contains 60% albumin, 30% globulins, 4% fibrinogen and 1% regulatory peptides (c-reactive protein).
DETAILS: Meteospasmil - instructions for use of capsules, price, reviews, analogues
Globulin
Proper preparation for a general urine test allows you to avoid erroneous test results. Before donating urine, the following rules must be observed:
- 24 hours before urine collection, exclude from the daily diet foods that can change the color of urine, for example, beets, sweets, smoked foods, marinades;
- 24 hours before urine collection, it is prohibited to drink alcohol and caffeine-containing drinks;
- 24 hours before taking a urine test, you should not take vitamins, diuretics or dietary supplements. In the case of systemic medication use, you must inform the doctor who gave the referral for a urine test;
- one day before taking a urine test, you should avoid hypothermia, overheating and excessive physical exertion, since these factors can cause functional proteinuria;
- during menstruation or infections that are accompanied by fever, it is recommended, if possible, to reschedule the urine test for analysis.
Urine collection rules:
- urine is collected in the morning after sleep;
- Before collecting urine, you must wash yourself or take a shower;
- To collect urine, use a sterile container, which can be purchased at a pharmacy. Children's urine is collected in urine bags, which are sold in pharmacies. Do not squeeze urine out of a diaper or diaper;
- for analysis you need to use urine collected from an average portion;
- Urine for analysis can be stored for no more than two hours (at a temperature of 4-18 ° C).
The test result is issued the next day, but in emergency cases – after 2 hours.
Interpretation of a general urine test:
- increased protein and leukocytes in the urine - almost always indicate pyelonephritis. In this case, women complain of lower back pain, high temperatures, general weakness, chills, nausea, and sometimes vomiting;
- increased protein and red blood cells in the urine - most often a sign of glomerulonephritis. But in the case when the red blood cells in the urine are fresh, then one can think about urolithiasis.
One of the most accurate and simple methods that allows you to determine daily proteinuria is a daily urine test for proteinuria.
Daily protein in urine is carried out to study the filtration function of the kidneys.
There are several ways to detect protein in daily urine. The simplest and most accessible method is chemical, when protein is detected using special chemical reagents. During the test, a chemical is added to a test tube containing urine, which reacts with the protein and denatures it, forming a white ring.
In modern laboratories, special electronic analyzers are used to determine daily proteinuria, which are more sensitive and more accurate than the method described above.
For the study, daily urine is used, which was collected during the day (24 hours).
Urine collection rules:
- urine is collected in a clean three-liter glass jar;
- The first portion of urine at six in the morning is not collected, but poured into the sewer;
- all subsequent portions of urine are collected until six in the morning the next day;
- the next day, all collected urine should be shaken slightly, then 10-150 ml should be poured into a sterile container and delivered to the laboratory, where daily proteinuria will be analyzed.
The analysis result is issued the next day.
Normally, no more than 140 mg of protein fractions should be detected in daily urine. Depending on the amount of protein, proteinuria is divided into three degrees.
Classification of daily proteinuria, table
| Amount of protein, mg | Proteinuria degree | Causes |
| 1000 or less | moderate | infectious diseases, early stages of cancer, long-term protein diet |
| 1001-2999 | average | severe infectious diseases, purulent processes in the body, glomerulonephritis |
| 3000 and more | pronounced | poisoning, glomerulonephritis |
Urinalysis is normal
Due to the fact that the body of a man and a woman is structured differently in some aspects, hence there will be differences in the normal protein content in the urine.
So, the following are considered normal indicators:
- In men, up to 0.3 grams per liter of urine. This figure was derived based on their body’s reaction to heavy physical activity, stress, and sometimes hypothermia. Anything above this indicator is considered a deviation
- In women, up to 0.1 grams per liter of urine. This indicator is also derived based on possible physical activity and stress.
- Children have 0.025 grams per liter of blood. Sometimes, especially in boys, one-time deviations in this indicator are observed. Especially if the age varies from 6 to 14 years (just corresponds to the period of maturation). Moreover, it usually appears in daytime urine, and is absent upon repeated testing.
After receiving the test results, the attending physician will focus on these indicators, and, based on this, will prescribe treatment or send for additional examinations.
Appointment for analysis
Most people turn to specialists only when they have some kind of health problem.
And it is at this moment that the doctor gives a referral for the two most standard and most reliable tests - a general analysis of urine and blood.
Also, indications for urine donation include:
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, before each appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, the expectant mother is forced to donate urine in order to observe how her kidneys cope with the new imposed load.
- Preventive examinations.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system, which require periodic testing for control.
Few people will purposefully go and donate urine just to get checked. But this is in vain, because periodic testing can make it possible to detect serious diseases in the early stages.
Useful video about urine analysis.
Some people think that urine collection is easy and end up with bad test results.
In order for the tests to be good and not have to be taken a second time, you need to do it as follows:
- Only morning and concentrated urine can be collected.
- Purchase a special sterile jar at a pharmacy kiosk.
- Before collecting material, wash thoroughly.
- There is no need to collect the first urine (that is, the first few drops, as they may contain secretions).
- After collecting the tests, they must be delivered to the clinic within a maximum of two hours. Otherwise, the results will be incorrect and false.
Every person has taken a urine test at least once in their life.
It is not recommended to draw conclusions yourself, since in some situations a small increase may be considered quite acceptable.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl Enter to let us know.
DETAILS: Laennec therapy in cosmetology: instructions for using placental therapy for rejuvenation
- Depending on the type of protein fraction:
- Standards for total protein by age:
| Total protein | Albumin | Fibrinogen | Globulins |
| 64-84 g/l | 35-55 g/l | 2-4 g/l | Determined only if necessary and only by fractions and types |
| Children of the first month of life | Children of the first year of life | Children under 5 years old | Teenagers | Adults |
| 48-73 g/l | 47-72 g/l | 61-75 g/ | 58-76 g/l | 65-85 g/l |
There are no special norms for total protein indicators for men and women due to the fairly wide range of upper and lower limits of standard values. But in women, total protein can be reduced by up to 10% compared to men of the same age group. This can be explained by the high needs of the female body for protein, which is spent on the synthesis of sex hormones. The synthetic properties of the liver in women are lower than in men;
In pregnant women, fluctuations in total protein are subject to even greater downward variation. A reduction of up to 30% compared to the generally accepted norm can be considered normal and quite natural.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JYmE-_5kULY
This may be a natural consequence:
- Increasing the circulating volume of plasma due to fluid retention in the vascular space;
- Increased needs of the pregnant woman’s body for plastic material for the synthesis of sex and other hormones of the endocrine glands;
- Requirements for plastic material for the growth and development of the fetus.
It may indicate:
- Dehydration of the body due to pathological loss of fluid or its redistribution between the vascular space and tissues during intoxication, infections and septic conditions;
- Enhanced synthesis of antibodies during the formation of immunity after vaccination or previous infectious diseases. As a rule, such an increase is not significant;
- Multiple myeloma. Such cases of hyperproteinemia are represented by a pronounced increase in protein levels due to pathological proteins (Bence-Jones protein);
- DIC syndrome with hypercoagulation against the background of intoxication and various critical conditions.
- Liver pathologies accompanied by hepatocellular failure: viral and toxic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis;
- Nutritional protein deficiency due to poor nutrition and depletion of the body in serious illnesses;
- Increased loss of protein in the urine with decompensated kidney pathology and severe proteinuria;
- Complications of diabetes mellitus;
- Chronic severe anemia and massive bleeding;
- Diseases of the stomach and intestines with impaired absorption of nutrients;
- Enzymatic and secretory pancreatic insufficiency in chronic pancreatitis;
- HIV infection and other immunodeficiencies;
- Endocrine pathology in the form of hypothyroidism;
- The progression of cancer and its metastasis.
Author of the article: Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich | Doctor of Medical Sciences general practitioner
Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I.M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational Diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”.
Other doctors
‹
9 Best Foods Before Bed
What to do if you have severe heartburn?
›
Ferritin. Blood test, what does it mean when it changes
To get the most reliable results, you need to properly prepare for the procedure. If you neglect these recommendations, then the likelihood of distorting data on the content of total protein in a biochemical blood test increases.
Preparation
It is recommended to donate blood fluid exclusively on an empty stomach in the morning.
8 hours before the procedure you should not eat food, sweets or alcoholic drinks.
It is allowed to drink purified water without gas.
Normal indicators will not be affected if the patient drinks unsweetened green tea a couple of hours before the test. This can be done if a person cannot fast for such a long period of time
If this is not possible, since the medicine contributes to the normal functioning of the patient’s body, then the doctor must be informed about this in advance.
In this case, the concentration of total protein will be determined in accordance with a special table.
Carrying out
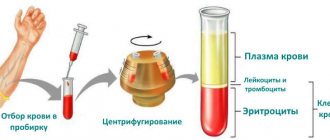
To study the protein, blood is taken from a vein. The procedure itself in terms of execution technique is the same as in standard analysis. After taking the blood fluid, it is necessary to obtain plasma from it, for which the centrifugation method is used. Next, using a special reagent, protein is isolated from the resulting whey.
Deciphering the results should be done exclusively by a specialist. Based on the data obtained, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment depending on the reason for which the deviation from normal values was detected.
This condition, in which total protein can be increased, is called hyperproteinemia in medicine. An increase in the concentration of an element indicates the development of some pathology in the human body.
Among the absolute reasons that can provoke deviations are:
- infection or inflammatory process (protein begins to enter the blood fluid from destroyed tissues);
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- lupus;
- oncological diseases;
- blood poisoning when protein synthesis and breakdown occur at different rates.
Physiological factors can also influence the level of total protein; when a specialist collected the material incorrectly, the patient suddenly changed the position of the body.
In addition, hyperproteinemia can begin to develop as a result of:
- cholera;
- vomiting and diarrhea, which contributes to dehydration;
- intestinal obstruction;
- acute bleeding.
If the test results show that total protein in the blood is reduced, this may indicate pathological conditions such as:
- exhaustion, which develops against the background of diseases of an infectious-purulent nature;
- complications of diabetes;
- oncopathology of blood fluid;
- severe anemia;
- chronic bleeding;
- kidney pathologies, as a result of which protein is rapidly excreted from the body along with urine;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- increased activity of the adrenal glands;
- malfunction of the thyroid gland;
- pregnancy complicated by pathological processes;
- HIV infections and other immunodeficiency conditions.
Poor diet, fasting and strict diets can also lead to protein deficiency. In this case, all therapy will consist only of changing the menu, which includes the inclusion of a large amount of protein foods.
How to prepare for biochemical tests?
Total protein regulates amino acid metabolism and reflects the concentration of protein molecules in the blood plasma. The protein metabolism rate characterizes the body's ability to self-heal. Blood plasma contains about 100 different types of proteins. The most famous are compounds of albumins and globulins:
- Globulins – regulate the reaction of the immune system to external irritation;
- Albumins – monitor the composition, viscosity of the blood, its circulation, balance the acid-base balance.
Other functions of protein fractions:
- Participate in blood clotting, create obstacles to the formation of blood clots;
- Control the transport of bilirubin, cholesterol, minerals to tissues;
- They combine with drug substances and ensure their delivery to organ cells;
- Monitor amino acid reserves;
- Participate in suppressing the inflammatory process;
- Regulate blood volume;
- They take part in the production of hemoglobin, antibodies, hormones, enzymes.
The OBC indicator is used to determine pathology in the body. To make a diagnosis, protein fractions, as well as non-protein components of the blood, are additionally determined.
The TBC level characterizes protein metabolism and allows one to judge the rationality of nutrition. When the level changes, the percentage of albumin and globulin in the blood is determined.
The OBC indicator is determined by:
- For liver and kidney diseases;
- For acute and chronic infections of various origins;
- For burns;
- For oncology;
- With impaired metabolism;
- For anemia;
- In case of severe poisoning;
- For injuries leading to blood loss;
- For diseases of the stomach, intestines, malnutrition, exhaustion;
- During a comprehensive health examination;
It is also important to know the level of protein fractions in the blood plasma before surgical operations, medical procedures, to control the quality of therapeutic measures when taking medications and for further prognosis of the disease.
| In men | Among women | |
| Young people 20-30 years old | 75-79 | 82-85 |
| In adults under 60 years of age | 79-83 | 76-80 |
| In adults 60-75 years old | 74-77 | 76-78 |
| More than 75 years | 69-77 | 73-78 |
Deviations from the above standards may be:
- Absolute – the rate of protein metabolism, its synthesis and breakdown changes;
- Relative - occurs when there is a change in blood volume, when it decreases in the case of increased sweating, diarrhea, bleeding, and when the volume increases, for example, with drip infusion;
- Physiological – deviations are not related to diseases, but are associated with various conditions of the body (pregnancy, feeding, prolonged bed rest, heavy physical activity).
Blood for analysis is taken from a vein, then delivered to the laboratory, where the main components of the plasma are determined. Spectrophotometry is used for this: when the solution is illuminated, its color and intensity changes at different protein levels.
Before donating blood for analysis, it is not recommended to eat food 12 hours before, so as not to distort the results. It is also worth giving up some medications that bind protein and promote its excretion.
In children, OBC is determined to study the functioning of all organs in order to identify the cause of the ailment, the presence of hidden diseases, and find out the lack of vitamins and minerals. The result of the analysis is compared with norms, taking into account the symptoms of the disease.
An increase in fractions in the blood of a child can occur with diarrhea, vomiting, intestinal obstruction, as well as with massive burns and infections. If the child's BBC decreases, malnutrition or oncology may be suspected.
| Age | Protein norm, grams/liter |
| In newborns | 46-70 g/l |
| At 1 month of age | 40-55 g/l |
| 2 months | 46-60 g/l |
| Up to 6 months | 55-68 g/l |
| 6 months – 1 year | 56-72 g/l |
| From 1 year to 4 years | 60-80 g/l |
| After 5 years | 62-82 g/l |
Immediately after birth, the level of OBC in children may fluctuate: in a premature baby, the level is slightly lower than in a child born at term. With age, the level of total protein in a child's blood increases.
An increase in the total amount of protein fractions in the body is called hyperproteinemia. If the level increases, it means that pathological processes are developing in the body. It is necessary to determine for what reasons this happened.
Timely consultation with a doctor will help to avoid irreversible changes and serious consequences.
Hyperproteinemia occurs in the following conditions:
- Frequent diarrhea and vomiting lead to dehydration;
- Intestinal obstruction – prevents fluid absorption;
- Cholera – blood density increases;
- Acute bleeding - protein increases due to a decrease in the volume of the liquid part of the blood.
These reasons are relative.
Protein may change upward for absolute reasons:
- Oncological diseases - metabolism is disrupted, a large amount of proteins is produced;
- Autoimmune processes – lupus, rheumatoid arthritis;
- Chronic inflammation and infections - protein from destroyed tissues enters the blood;
- Blood poisoning - protein is synthesized and broken down at different rates.
Sometimes OBC can increase for physiological reasons: improper collection of analysis (prolonged tugging of the forearm with a tourniquet), a sharp change from horizontal to vertical body position, or heavy load on the body.
In order not to pose a threat to the patient’s life, elevated protein levels must be reduced.
The patient can be warned by eliminating the cause of the increase. The doctor prescribes treatment, establishes the necessary diet and nutrition regimen.
The level of OBC changes downwards as a result of pathological changes in the human body, this is called hypoproteinemia. It can occur with a decrease in the synthesis of protein fractions, increased breakdown, impaired absorption of protein into the blood, or increased excretion in the urine. This situation may arise:
- With cirrhosis, hepatitis, tumors and metastases in the liver, protein synthesis is disrupted;
- In case of gastrointestinal diseases (pancreatitis, enterocolitis), protein absorption slows down;
- For diabetes mellitus;
- In case of chronic inflammatory processes in the kidneys, protein is utilized in the urine;
- For diseases of the thyroid gland;
- In case of burn or frostbite of tissues;
- For injuries, poisoning, bleeding;
- When fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity;
- After surgery.
Hypoproteinemia for physiological reasons can occur during pregnancy and lactation, when refusing meat products, during fasting and in young children, that is, with an increased need for protein or a lack of dietary intake.
It is necessary to raise the deficiency of protein fractions after identifying and eliminating the cause.
With effective treatment, a pathological decrease in OBC normalizes on its own. The physiological decrease in the amount of protein is regulated using a diet that is developed by a nutritionist.
An absolute decrease in the level of OBC is of greatest importance in diagnosis; the level decreases mainly due to a decrease in albumin. When albumin is normal in the blood, metabolism occurs correctly, this is an indicator of health.
A decrease in the indicator may mean reduced performance of the body. Loss, increased destruction, lack of synthesis occurs with various pathologies in the body.
An analysis of OBC allows one to judge the severity of the disease; this is the first step in making a diagnosis.
A blood test for protein concentration can also be done for monitoring during clinical observation, to assess the body's reserve. The analysis is prescribed at the time of initial treatment, in case of exhaustion, if a disease is suspected, before surgery or during a medical examination.
This article told you what the norm of protein in the blood should be for women and men, as well as why the protein in the blood is higher than normal or lower. You can learn more about increased protein levels here.
Total blood protein (TBP) is a collection of various protein compounds, each of which has its own functions and properties. Albumin is necessary to maintain the osmotic pressure of the blood, as well as for binding and transporting various compounds, globulins are responsible for immune processes, fibrinogen ensures normal blood clotting. The total protein norm is the total value of all protein components.
The main functions of blood plasma proteins:
- transport nutrients and medications to organs and tissues;
- provide osmotic blood pressure;
- maintain optimal pH levels in the blood;
- retain iron, copper, calcium in plasma;
- participate in the synthesis of hormones, enzymes, hemoglobin, antibodies;
The OBC level shows how correctly protein metabolism occurs in the body.
A biochemical blood test to determine this indicator is called a proteinogram. It is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis, identify the stage and duration of the pathological process, and determine the level of effectiveness of drug treatment.
When is a proteinogram prescribed:
- with anemia;
- patients with acute, chronic bleeding, women with heavy menstruation;
- with signs of severe dehydration, intoxication;
- for kidney and liver diseases;
- athletes;
- in the presence of malignant neoplasms.
To determine the level of BBC, blood is taken from a vein in the morning on an empty stomach; the last meal should be 8 hours before the examination. In the morning you can drink only still water, any other drinks are excluded. An hour before taking the material, you should not make sudden movements; any physical activity is contraindicated - changing body position can distort the values.
It is necessary to refrain from smoking and try not to be nervous. The day before the test, you should exclude fried, fatty, protein-rich foods, alcoholic beverages from your diet, and, if possible, do not take any medications.
The normal level of total protein in the blood in adults is 65–85 g/l; in children under 6 years of age, the lower limit of values is 56 g/l. Separately, biochemical tests are performed to determine the level of specific proteins - C-reactive protein (CRP) and rheumatoid factor. Rheumatoid factor (RF) indicates the presence of rheumatoid arthritis and other collagenoses.
- acute and chronic pathologies of an infectious-inflammatory nature;
- dehydration as a result of increased sweating, diarrhea, uncontrollable vomiting, extensive burns, fluid loss due to diabetes insipidus;
- peritonitis;
- jade;
- systemic autoimmune pathologies accompanied by damage to connective tissue;
- tropical diseases;
- leprosy;
- specific hypergammaglobulinemia;
- chronic polyarthritis;
- active phase of chronic hepatitis or cirrhotic liver damage;
- malignant neoplasms accompanied by increased synthesis of pathological protein. This picture can be observed in myeloma, macroglobulinemia, lymphogranulomatosis, and “heavy chain diseases.”
| category | Norma/women | Norma/ men |
| Newborns | 42-62 g/l | 41-63 g/l |
| Children under 1 year | 44-79 g/l | 47-70 g/l |
| Children from 1 year to 4 years | 60-75 g/l | 55-75 g/l |
| Children from 5 years to 7 years | 53-79 g/l | 52-79 g/l |
| Children from 8 years to 17 years | 58-77 g/l | 56-79 g/l |
| Adults 22-34 years old | 75 - 79 g/l | 82-85 g/l |
| Adults 35-59 years old | 79-83 g/l | 76-80 g/l |
| Adults 60-74 years old | 74-77 g/l | 76-78 g/l |
| Over 75 years old | 69-77 g/l | 73-78 g/l |
- Taking biochemical tests, including total protein, does not require special preparation, but you should remember that they are taken in the morning on an empty stomach. The previous meal should be no later than 8, and preferably 12, hours before the procedure.
- The day before the test, it is better not to eat a lot of protein foods.
- Don't drink too much liquid
- Avoid strenuous physical activity.
What does a decrease in the concentration of total protein in the blood serum indicate?
Reduced levels of total protein in the blood are called hypoproteinemia. This condition can be observed during pathological processes, for example, such as:
- parenchymal hepatitis
- chronic bleeding
- anemia
- loss of protein in urine in kidney disease
- diets, fasting, insufficient consumption of protein foods
- increased protein breakdown associated with metabolic disorders
- intoxications of various types
- fever.
Special mention should be made of physiological hypoproteinemia, i.e. conditions not associated with the course of pathological processes (disease). A decrease in total protein in the blood can be observed:
- in the last trimester of pregnancy
- during lactation
- during prolonged heavy loads, for example when preparing athletes for competitions
- with prolonged physical inactivity, for example, in bedridden patients
Indicator norm
Proteins are catalysts whose main role is to perform the immune defense of the body's system. Biochemistry determines the general indicator of a substance in a system and is performed as a mandatory procedure for diagnosis. If there is anemia in the body system, when nutrition is disturbed, as well as exhaustion in the body.
The total value increases if a system failure occurs. It is possible that a disease has developed, as a result of which the increase occurred. To lower the indicator, it is necessary to establish the cause. Protein levels in the blood: the reading of general indicators determines the assessment of a person’s condition and the functionality of the system, as well as the work that maintains proper protein metabolism and determines whether the diet is rational.
When a deviation from normal values occurs, the doctor prescribes further examinations to identify the exact cause of the disease. Deviation from the norm of the indicator occurs due to a failure in the system. If the total protein in the blood is elevated, then the help of a specialist is necessary to avoid unpleasant consequences. The relative deviation is due to the fact that there has been a change in the amount of fluid in the blood circulation. Blood test for total protein is normal: this occurs during infusion and when there is excessive sweating. The absolute deviation is caused by the fact that the rate of protein metabolism changes.
This often occurs due to a pathological process that affects the rate of synthesis, as well as the breakdown of protein compounds in the serum. Also due to the physiological process and during pregnancy. When the indicator is high, the physiological deviation from the norm of total proteins is not associated with the disease, and is also sometimes caused by protein intake or prolonged bed rest. The norm of total blood protein in serum: this indicator is determined differently in people. Elevated protein in the blood depends on age, weight and gender. To be in normal shape you need proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
Why is the protein level in the blood (serum) increased? The formation of such conditions, as a rule, begins to manifest itself when a pathological process occurs in the system. When there is a disease such as parenchymal hepatitis, chronic bleeding, anemia. When substance is lost due to kidney disease and diet, this happens. A deviation also occurs when there is fasting and a person does not consume enough foods containing this substance. Increased protein in the blood: When there is a strong breakdown of the substance’s indicator, due to the fact that the metabolic process is disrupted, and intoxication has also occurred in the body. This happens when a fever develops. And also when the overall indicator is significantly increased, this means that hyperproteninemia has formed.
Reasons for education
Increased protein: due to the increased need of the system in pregnant women, the need to supply plastic material, which is responsible for the synthesis of the reproductive system. It is also responsible for hormones. This is formed due to the need for the supply of plastic material in order for the fetus to grow and develop. An increase occurs due to the fact that the body is dehydrated. Due to pathological loss of water and during redistribution between vessels and tissue, when there is intoxication, infection, as well as a septic condition.
A biochemical blood test, total protein, is prescribed to accurately determine the diagnosis. This occurs as a pronounced increase in the indicator of a substance; due to a pathological protein, proteins can increase. Protein blood test for protein: When the level of general indicators in the circulatory system is reduced, this means that hypoteinemia is developing. If it has formed in the body, this means that a condition such as:
- pathological process in the liver;
- increased protein loss and loss of urine, when decompensated pathology has formed in the kidneys, as well as severe proteinuria;
- complication of diabetes mellitus;
- progression of cancer, as well as the process of metastasis.
Total protein in the blood is normal: there is no exact definition, but a laboratory test reveals a normal value. Elevated total protein: This occurs due to various factors that affect the body. Increasing total protein: synthesizing a substance from an amino acid that was formed in the body system and entered the circulatory system with food . In any case, when symptoms appear, medical attention is needed. After a thorough examination, the doctor will identify the cause of the deviation from the norm and also prescribe treatment to maintain the health of the body.
Total protein in a biochemical blood test is the most important indicator of metabolism in the human body. Using this analysis, you can evaluate the condition of the kidneys, liver, pancreas, etc. Also, a total protein analysis is carried out to assess lipid and carbohydrate metabolism and the presence of micronutrient deficiencies.
Deviations from the norm
The reason for the deviation of the test results for the TProt level from the norm may be:
- changes in the content of albumins and globulins with a constant volume of circulating blood;
- loss of fluid due to dehydration of the body or, conversely, an increase in the volume of circulating fluid.
If the test result increases due to dehydration of the body or decreases due to an increase in the total volume of fluid, as during pregnancy, then such values are called relative.
Relative analysis indicators do not reflect the actual amount of albumin and globulins. When assessing the results of a woman's blood protein during pregnancy, dehydration, or other conditions associated with changes in the volume of fluid in the body, the doctor must take into account the patient's condition.
The reasons for the relative change in TProt indicators are varied. An increase in the relative reading of total protein may be caused by fluid losses in the body caused by:
- repeated vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- loss of water through sweat;
- reduced daily water consumption;
- extensive burns.
A relative decrease in test results in the body is caused by an increase in circulating blood and lymph in diseases:
- kidney;
- hearts;
- thyroid gland.
Reasons for lower Total Protein results
Physicians are more likely to encounter a decrease in TProt values than an increase. The dangerous limit for total blood protein in women is considered to be 50 g/l.
Conditions in which the TProt result is less than 50 g/l are accompanied by the appearance of edema and are life-threatening.
The reason for the low relative protein level in a woman’s blood, as noted above, is pregnancy and lactation. A reduced total level of albumin and globulins is observed in hereditary disorders of protein synthesis.
The reasons for the absolute decrease in the amount of the total analysis indicator include:
- poor nutrition, fasting;
- malabsorption in the digestive tract - with infections, tumors, injuries, inflammation of the intestines, stomach;
- kidney disease and protein loss in urine;
- heart disease – myocarditis;
- protein breakdown caused by injury, high body temperature, poisoning, hyperthyroidism;
- bleeding, including uterine, internal, significant blood loss in women during menstruation.
Hypoproteinemia can be caused by long-term treatment with hormonal drugs, corticosteroids, or a protein-free or unbalanced diet in amino acid composition.
Causes of low protein in the blood include cancer, liver cirrhosis, and Wilson-Konovalov disease, which disrupts copper metabolism.
Reasons for the increase in indicators
The highest levels of Total Protein are found in malignant conditions of paraproteinemia, the reasons for which are:
- multiple myeloma;
- plasmacytomas;
- Waldenström's macroglobulinemia;
- non-Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- amyloidosis.
In these diseases, the protein content may exceed 120 g/l. These diseases, as statistics show, are quite rare.
Thus, the most common myeloma disease on this list is found in 1 person out of 100,000 people per year.
Much more often, deviations of Total Protein results from the norm towards high values are caused by less dangerous diseases that are successfully treated.
The level of total blood protein can be increased due to chronic infectious and inflammatory processes occurring in the body:
- inflammatory nature - nephritis;
- infectious – respiratory, intestinal, tuberculosis, AIDS;
- autoimmune – polyarthritis, scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis;
- blood diseases associated with the destruction of red blood cells - hemolytic anemia;
- pathologies of the adrenal glands;
- allergic reactions;
- hepatitis in the acute stage;
- diabetic acidosis;
- shock.
An increase in TProt levels occurs during acute infections and the associated increase in the production of immunoglobulins. A high TProt value is noted due to the development of certain skin diseases, for example, purulent pyoderma, psoriasis.
Based on the content of total blood protein, the doctor is able to objectively assess the state of protein metabolism, the efficiency of internal organs, and the balance of the diet.
Total protein by fractions
In addition to information about the usual values, it is necessary to have an idea of the presence of total protein by fraction.
This is especially important if surgical intervention or medical procedures are planned, as well as when there is a need to control the quality of the therapeutic measures being carried out, which involve treatment with drugs.
What the normal value for fractions is can be seen from the table below.
| Age | Protein fractions in grams per liter | ||||
| Albumen | Globulin | ||||
| Alpha 1 | Alpha 2 | Beta | Gamma | ||
| Until 1st week | 32.5-40.7 | 1.2-4.2 | 6.8-11.2 | 5.4-6.7 | 3.2-8.5 |
| From a week to a year | 33.6-42.0 | 1.24-4.3 | 7.1-11.5 | 4.6-6.9 | 3.3-8.8 |
| From one to five years | 33.6-43.0 | 2.0-4.2 | 7.0-13.0 | 4.8-8.5 | 5.2-10.2 |
| From five to eight years old | 37.0-47.1 | 2.0-42 | 8.0-11.1 | 5.3-8.1 | 5.3-11.8 |
| From eight to 11 years old | 40.6-45.6 | 2.2-5.3 | 7.5-10.3 | 4.9-7.1 | 6.0-12.2 |
| from 11 to 21 | 38.9-46.0 | 2.3-5.3 | 7.3-10.5 | 6.0-9.0 | 7.3-14.3 |
| After 21 years | 40.2-47.6 | 2.1-3.5 | 5.1-8.5 | 6.0-9.4 | 8.0-13.5 |
Prevention
To prevent deviations from the normal level of total protein in the blood, you must adhere to the following simple rules:
- eat a balanced diet;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- rest and do not subject the body to increased physical activity;
- regularly donate blood for biochemical analysis.
Total protein is important in the human body, which is directly involved in the functioning of many systems and organs. Its decrease or increase indicates the presence of deviations associated with ill health.
Only by seeking medical help in a timely manner can the cause of the pathology and measures for normalization be established, which will protect the body from adverse consequences.
Causes of hyperproteinemia
In the case when there are few plasma proteins, the reasons are more or less clear. The body “falls short” by synthesizing less proteins than needed. The liver may be affected, there may be a lack of immune strength in the body, and plasma cells begin to synthesize fewer antibodies. It is clear that there will be a lack of proteins during fasting. And under what conditions will there be an increase in protein in the body, the synthesis of fractions in excess quantities? When does increased protein content in the blood occur that goes beyond the reference values?
About absolute and relative values
First of all, hyperproteinemia, or increased total protein in plasma, can be either relative or absolute. What does it mean? Let us explain the concept of absolute and relative increase or decrease in the amount of something using a simple example. We have a bowl in which peas (protein) are floating in water (blood). If we add peas, then we can assume that the concentration of peas has increased (true hyperproteinemia). On the other hand, you can pour out the water, and as a result it turns out that the concentration of peas has increased again, since there are more peas in the same volume, as in the first case. But in fact, its quantity has not changed. In the first case we are talking about an absolute value, and in the second - about a relative value.
Blood protein norm
In adults, the norm of total protein in the blood is the same for men and women and ranges from 65 to 85 g/liter. In blood plasma, the protein content is slightly higher than in serum, since it also contains fibrinogen, which is involved in the process of blood clotting. Because of this, blood serum is predominantly used in the analysis.
Age affects total serum protein. By age category, the indicator (the designation g/l is used) changes as follows:
| first month after birth | from 46 to 68 g/l |
| up to 1 year | from 48 to 78 g/l |
| from 1 year to 16 years | from 60 to 80 g/l |
| after 16 years | from 65 to 85 g/l |
In some cases, deviations of 5 units may occur without the presence of pathological processes in the body. In such a situation, a blood test for total protein can be repeated, and if there is also an excess in the total protein mass, it is accepted as the norm for a particular person, which is noted in his medical record.
The protein norm in women during pregnancy deserves special attention. During the period when the fetus is formed, many substances from the mother’s body go to the development of the unborn child, and their level in the blood decreases significantly. So, for a pregnant woman, serum protein will be considered normal, even if its value is 30% less than the lower limit. However, this applies only to those cases when such low levels of protein in the blood in pregnant women do not cause unpleasant symptoms, in the presence of which it is necessary to consume protein to stabilize the condition. For the female body, protein deficiency (hypoproteinemia), if it is poorly tolerated, can become a big challenge.