Inflammation of the liver is medically called hepatitis. The most dangerous thing about some types of hepatitis is the absence of symptoms. The patient may exhibit general signs of malaise, but they are often attributed to constant fatigue, a cold, or poisoning. If the disease is not detected in the initial stages, treatment is delayed for a long time, and the person feels the consequences of inflammation for several years. In some cases, the process becomes chronic. This can only be prevented by diagnosing the disease in a timely manner.
Where is the pain felt?
In order to recognize the first symptoms in time, it is necessary to have at least a rough idea of the location of the liver. Like other vital organs, it is located in the abdominal cavity, namely in its upper right corner, under the muscular septum of the diaphragm. In shape it is an obtuse triangle with rounded corners, consisting of two lobes. The first lobe attaches to the anterior abdominal wall in the area of the right hypochondrium, the second lobe tapers to the left costal arch. Painful symptoms appear with liver disease on the right side of the upper abdomen.
Sometimes signs of a diseased liver, if symptoms are not expressed, can be confused with pain in the gallbladder or stomach, since unpleasant sensations tend to radiate (spread) to nearby areas. To unambiguously determine the localization of the pathology, it is necessary to contact a therapist or hepatologist, who, by collecting an anamnesis and using palpation, will accurately determine which organ hurts.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
Inflammation is diagnosed with a general blood test. An increase in protein content is detected, as well as a high level of total plasma acidity. Detected abnormalities cause a biochemical blood test. Suspicions of liver inflammation arise if the following indicators change:
- Bilirubin. This is the main bile pigment contained in hepatocytes - liver cells.
- ALT and AST are enzymes produced by the liver. They are also released from the cells of an organ when it is damaged.
- Blood clotting factors. The amount decreases significantly as the weakened liver stops producing them.
To find out the cause of the disease, the doctor must collect anamnesis. If the patient took large quantities of medication, this would be a reason to suspect drug-induced hepatitis. With alcohol abuse, this form of inflammation is most often detected. Suspicion of viral hepatitis can be caused by travel to areas of unfavorable epidemiological conditions, where contact with patients with A and E forms could occur. For viral hepatitis, transmitted through blood and semen, the risk group includes drug addicts and those who have sex without a condom.
After a conversation with the patient, tests are prescribed for viral markers of hepatitis, which will confirm or rule out the infectious nature of the inflammation. Stool samples are also taken to look for parasites.
Additionally, ultrasound and computer diagnostics are prescribed. They identify the current state of the organ and determine the level of damage. The results of these studies influence the therapeutic regimen.
Types of pain
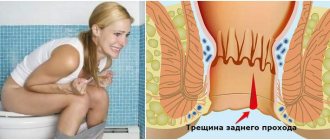
Any pathology begins with mild, dull or aching pain in the right hypochondrium. With the development of tumor formations, a feeling of heaviness may occur. The pain actively radiates to different areas of the abdomen. The development of the pathology is characterized by an increase in pain symptoms. Acute pain in this case indicates purulent or inflammatory processes. They are also accompanied by fever.
Indolent problems may not manifest themselves until liver failure or coma occurs. This is the most dangerous type of pathology, since not all patients respond to other external signs of the disease. It is important to pay attention to the condition of the skin, the color of stool, and general well-being, as this will help with early diagnosis of the disease.
Prevention and diet
In the course of life, many people often experience an increase in bilirubin; the liver is affected by toxic substances, excess weight and other factors. All this leads to organ disease. Baking damage is a real problem for those who work with toxic substances; these are the people who know most about preventative measures for any disease. These include:
If you have liver disease, you should avoid alcohol
- careful work with toxins;
- giving up alcohol;
- eating only fresh foods;
- control over the processing of instruments in the hospital, including in the dental department;
- isolation of patients with hepatitis A;
- using condoms during sexual intercourse;
- timely vaccination against hepatitis B;
- tracking the amount of medications taken;
- taking hepatoprotectors;
- regular visits to the doctor.
In case of liver damage, diet plays a special role. You will have to exclude from your regular diet:
- tea and coffee;
- grape and tomato juices, tomatoes themselves;
- soda;
- fatty foods;
- caviar, sushi;
- smoked meats;
- fermented baked milk, full-fat milk and any fatty dairy products;
- fresh baked goods;
- fresh fruits and berries;
- fatty fish;
- seasonings, vinegar, mustard.
Tea and coffee can be replaced with decoctions of chamomile, rosehip, sugar - a substitute. Vermicelli, pasta, and any non-fatty and non-spicy food are allowed. Honey, jam and marmalade can be consumed in small quantities. You can make salads from vegetables and fruits, seasoning them with refined oil. Food should be steamed or baked in the oven. The consumption of stewed and boiled foods is allowed.
Any liver disease is dangerous. Despite the fact that the organ recovers quickly, it is not worth risking your health. Impaired liver function provokes the formation of pathologies throughout the body.
Other unpleasant sensations accompanying liver disease
The manifestation of an unhealthy liver does not end with pain alone. Disruption of such an important organ is accompanied by digestive disorders, heartburn and a feeling of nausea. Patients are often tormented by a persistent feeling of hunger, and chills at night (which are later easily replaced by fever).
The first signs of liver disease, which may indirectly indicate the presence of problems in the functioning of the organ:
- Visual impairment (in particular, color perception; patients have decreased recognition of white and yellow).
- Constant thirst that does not go away even after drinking enough liquid.
- Itching. Particularly susceptible to this are areas of the body with thin, sensitive skin.
- General weakness, asthenia, constant feeling of fatigue.
- There is a bilious bitterness in the mouth.
- Decreased cognitive abilities and mental activity.
- Fever. This symptom may be more or less pronounced depending on the type of disease. For example, if you have opisthorchiasis, which was caused by a liver fluke (a parasitic organism), then the temperature will rise to 38 degrees.
The more acute the pathology, the stronger the internal symptoms. With their prolonged development, hepatic coma can occur, characterized by almost complete failure of the liver, impaired blood supply, respiratory function and leading to death without proper medical intervention.
Dangerous consequences
If you start inflammation in the gland, then the risk of cirrhosis and steatosis increases in the future. Once most of the liver cells die, liver failure occurs. This is a condition in which the liver cannot fulfill its role - to synthesize the necessary substances for digesting food, to filter the blood from toxins. A patient with liver failure gradually becomes exhausted. In the absence of help, this ends in death.
Another dangerous complication is the oncological process. Inflammation degenerates into a tumor. It develops in the liver, subsequently metastasizing to other organs.
Timely treatment can prevent complications and return the patient to a full life.
External manifestations of pathology
Not only subjective sensations will help identify the disease. External signs may also indicate pathology. Thus, a decrease in the detoxification function of the liver leads to a change in the color of stool, the smell of sweat becomes stronger, and urine acquires an unhealthy brown tint.
Other signs and indicators of poor liver function:
- Skin rash. It is often accompanied by itching.
- The skin and sclera of the eyes become an unpleasant yellowish tint.
- This is what the stomach looks like with ascites
Liquid stools, feces change in color to light yellow or green.
- Veins appear through the skin of the abdomen and pubis, and spider veins form.
- The abdomen itself has expanded and rounded (ascites) - signs of abdominal dropsy.
- Vessels regularly burst, bruises appear, and at an advanced stage, heavy bleeding develops.
- Swelling of the entire body due to overhydration (excess water). The legs suffer the most.
The patient looks extremely sick. The tongue becomes covered with cracks and a white coating, the person loses weight and suffers from headaches. Particular danger is posed by increased bleeding - one of the causes of possible death. Intestinal dysfunction also occurs, and tachycardia occurs in the cardiovascular system.
Causes
The liver recovers quickly and is not easily damaged due to its high degree of regeneration. A person is able to survive even with 70% damage to this organ. And yet, a diseased liver is not a factor that can be ignored. If a person’s liver is not in order, it is necessary to identify the cause of the pathology and begin treatment. The causes of most liver diseases are:
- Poisoning. Poisoning occurs when toxins and poisons enter the body. These include salts of heavy metals, lead, mercury, acids and other chemical compounds. Poisoning can occur instantly, provided that a large amount of poison enters the body at the same time. With prolonged exposure to toxins (working in conditions hazardous to health), an exacerbation of the disease does not occur immediately, but after weeks, months and even years. In this case, everything can end quite badly; after some time, liver necrosis is diagnosed, and in the absence of treatment, kidney failure.
- Drug abuse or long-term drug therapy. Many drugs contain substances that are dangerous to the body. By saving a person from one problem, they create many new ones. Medicine has not yet come up with an effective way to protect against such negative effects, while the liver plays the role of protector. Constant use of medications leads to depletion of the cells of this organ. Various hormones, antibiotics, antifungals and drugs used in chemotherapy are especially dangerous for it.
- Viral infections. An exacerbation of liver disease can be triggered by an infection that has entered the body. For example, an unhealthy lifestyle can lead to infection with hepatitis groups A, B or C. The gradual impact of hepatitis on the body leads to cirrhosis of the liver. The patient's health is seriously compromised.
- Diseases that are parasitic in nature. Damage caused to the body by parasites living in it (roundworms, echinococci, lamblia) can be not only mechanical. Being a living creature, the parasite releases its metabolic products into the blood, poisoning, among other things, the liver.
Diseases of such an important organ as the liver in women are diagnosed less frequently than in men. Problems are most often associated with vascular diseases, while men come with complaints of pain in the liver that they experienced after prolonged drinking. In some cases, liver dysfunction occurs due to:
- poor nutrition;
- genetic predisposition;
- injuries to the abdomen and nearby internal organs;
- exposure to radiation and ion radiation;
- improper lifestyle, including the above-mentioned drinking.
The liver is recovering well, but this does not mean that there is no need to worry about its condition.
Symptoms of individual diseases
Not all liver pathologies are characterized by the symptoms described above. Their intensity and degree of manifestation directly depends on the type of disease. Therefore, it is important to know about the most common diseases and their characteristic symptoms.
Spider veins on the skin
For example, cirrhosis of the liver is characterized by the following symptoms:
- proliferation of connective tissue replacing parenchymal tissue;
- increased pressure in the portal vein system;
- dysfunction of liver regeneration;
- sharp pain in the right hypochondrium;
- flatulence;
- weight loss;
- temperature from 37.1 to 38 degrees;
- splenomegaly - an increase in the size of the spleen.
The formation of spider veins (the same ones that are usually observed with varicose veins) on the pubis, a change in the color of the nails. Hormonal imbalance in men leads to gynecomastia. The body is subject to edema and venous collaterals (due to which bleeding often occurs).
Another common disease is liver cancer, which manifests itself with a gradual increase in symptoms. Among oncologies, it is in seventh place in terms of prevalence. It can be identified by increasing anorexia and a feeling of heaviness under the right hypochondrium (the tumor begins to burden the organ). I suffer from dull pain and bleeding due to varicose veins in the abdominal area.
List of liver diseases
- Hepatitis: acute or chronic inflammation of the liver - viral, drug-induced, toxic, due to lack of blood supply (ischemic).
- Cirrhosis: alcoholic, biliary, postnecrotic, with hemochromatosis, rare types (against the background of Wilson-Konovalov disease, cystic fibrosis, galactosemia).
- Liver neoplasms: hepatocellular carcinoma, liver metastases, cysts (echinococcosis, polycystic disease), abscess.
- Infiltrative liver lesions: amyloidosis, glycogenosis, fatty liver, lymphoma, granulomatosis (sarcoidosis, tuberculosis).
- Functional disorders with jaundice: Gilbert's syndrome, cholestasis of pregnancy, Crigler-Nayyar syndrome, Dubin-Johnson syndrome.
- Lesions of the intrahepatic bile ducts: blockage of the bile duct (stone, scar), inflammation of the bile duct (cholangitis).
- Vascular pathologies: congestive liver in heart failure and cardiac cirrhosis of the liver, thrombosis of the hepatic veins, arteriovenous fistulas.
Signs of parasites
If you have eaten a product contaminated with parasite eggs, symptoms will not appear immediately. The incubation stage of infection can last for years, although more often problems become apparent within a few weeks.
Characteristic symptoms of parasitic liver cysts:
- pressure inside the organ;
- heaviness under the ribs and in the sternum;
- urticaria on the skin (urticarial rashes);
- unstable stool;
- nausea and vomiting;
- heat.
Among the diseases that are caused by parasites (liver flukes) are clonorchiasis, opistrochiasis, and fascioliasis. Clonorchiasis is characterized by fever, rash, and respiratory problems. Opisthorchiasis – high fever, pain in muscle tissue, enlarged lymph nodes and diarrhea; patients are characterized by emotional instability and rapid heartbeat. Fascioliasis is a disease characterized by cough, rash and enlarged liver. The normal course of metabolic processes is disrupted.
Classification of liver inflammation
Liver inflammation, according to medical classification, can be classified into one of three forms. among which:
- steatosis;
- cirrhosis;
- hepatitis.
With steatosis, healthy hepatocytes are replaced by adipose tissue. As a result, cysts grow, the structure becomes heterogeneous, and metabolism becomes difficult. Steatosis often becomes a companion for men who abuse alcohol. The situation is complicated by poor nutrition and corresponding unfavorable heredity.
Cirrhosis is the destruction of liver tissue and its replacement with connective tissue elements. The liver in such patients looks wrinkled, its shape is deformed, and its color changes. This is caused by long-term intoxication as a result of abuse of alcohol, drugs, and poisons of various origins.
Cirrhosis often develops against the background of diseases such as tuberculosis, malaria, and malignant neoplasms.
Untreated cirrhosis is fatal in almost 100% of cases.
Hepatitis is actually inflammation of the liver. They can be infectious or non-infectious. According to epidemiological analysis, chronic forms of hepatitis are the most common among the population. Perhaps the reason for this is hidden forms of the acute process that were not detected in a timely manner. Such patients are sources of infection for the people around them, without knowing it.
What can the disease be confused with?
Non-acute diseases can often be confused with other, similar diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastritis can manifest itself as bitterness in the mouth, and a change in the color of urine may well accompany kidney disease. Therefore, you should remember that only a hepatologist or, at worst, a general practitioner can give you an accurate diagnosis. To make an accurate diagnosis, a liver profile is usually used through blood tests or ultrasound.
What diseases at an early stage resemble liver pathologies?
- Gastritis or ulcer.
- Intestinal colitis, irritable bowel syndrome.
- Gallbladder diseases.
- Pathologies of the pancreas.
- Kidney failure and others.
Pronounced liver symptoms occur already at an advanced stage of the disease. At the first signs, you should consult a doctor and differentiate the diagnosis, without waiting for the development of venous bleeding or acute colic.
Previous article: How coffee affects the liver: a modern view of the problem Next article: Blood test for liver tests: what is it, how to decipher and determine the norm?
Blood values that indicate disease
The liver performs a large number of vital functions. It will not be possible to find out what exactly happened to the organ by passing just one test.
The condition of the liver will help to recognize a biochemical blood test, which contains indicators of liver tests (AST and ALT enzymes, bilirubin, albumin, gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) and alkaline phosphatase). A blood test for markers of viral hepatitis and tumor markers is also necessary.
List of markers for hepatitis and their interpretation:
- Marker for viral hepatitis A (HAV) - Anti-HAV-IgM, IgM class antibodies to virus A. Positive result: anti-HAV IgM, anti-HAV IgG, HAV Ag, HAV RNA.
- Marker for hepatitis B virus (HBV) - Anti-HBs antibodies to the HBs antigen of virus B. Positive result: Pre-S1, Pre-S2, anti Pre-S2, HBsAg, HBeAg, anti-HBs, anti-HBc IgM, anti -HBc IgG, anti-HBe, HBV DNA, DNA polymerase.
- Marker for hepatitis C virus (HCV) - Anti-HCV-total antibodies to virus C antigens. Positive result: HCV Ag, anti HCV-IgM, anti HCV-IgG, HCV RNA.
The tumor marker AFP (Alpha Fetoprotein) is a marker for cancer. AFP and albumin are similar in composition. A result that exceeds 10 IU indicates the presence of pathology.
What examinations need to be completed
To obtain information about the condition of the body, all patients are sent for a general blood and urine test. If there are any pathologies in the body, the result will show deviations.
This is followed by a biochemical blood test of several types:
- Liver tests - give an idea of the presence and ratio of enzymes in the material being studied.
- For bilirubin - indicates an excess or deficiency of the main bile enzyme in the blood.
- Coagulogram - provides information about a person’s blood clotting and the presence of necessary enzymes.
To get a visual idea of the condition of the organ and any defects that have arisen, doctors prescribe:
- Ultrasound examinations. This is a scan with an ultrasound machine to obtain information about the size of the organ and the presence of formations in it. Doppler ultrasound, a type of ultrasound, is used to assess blood flow in an organ. Fiber scanning determines the presence and amount of scar tissue.
- X-ray and computer studies. Some liver problems can be seen using an X-ray machine; in addition, a computed tomography scan and magnetic resonance analysis will be required.
- Invasive procedures. During a biopsy, a small piece of gland is removed from a person for analysis.
- Laparoscopy involves inserting a probe using microsurgical devices to visually examine the liver.
When making a diagnosis, be sure to take into account the data from all examinations.
Variants of the inflammatory response in the liver
Inflammation in the liver is detected against the background of hepatitis of viral and infectious origin, fibrosis, cirrhosis and a number of other diseases.
Hepatitis of viral origin
There are several types of hepatitis in medicine - A, B, C, D, E, G. The incubation period varies from 14 to 180 days.
Virus A is transmitted through food, dirty hands, failure to comply with basic hygiene rules, and during sex. The remaining species are primarily transmitted through blood-to-blood contact during sexual intercourse. Hepatitis A has a favorable prognosis, no specific treatment is required, and complications are rare.
When infected with other types of viruses, there is a high probability of a chronic course. The most dangerous virus is considered to be variety C. Treatment with antiviral medications takes about 2 years. In approximately 20% of cases, the human immune system defeats the virus on its own.
Intoxication as a cause of inflammation
Intoxication develops due to the consumption of alcoholic beverages, medications, and the influence of toxic and poisonous substances. The most common diagnosis is alcohol toxic liver disease.
Alcohol gradually destroys hepatocytes; in the early stages, symptoms of the pathological process are not observed. An acute inflammatory reaction against the background of lack of treatment and continuation of the previous lifestyle leads to fibrosis, then to cirrhosis and primary cancer.
Intoxication due to medication leads to toxic hepatitis, after which cirrhosis develops. If complex treatment is started on time - diet, use of hepatoprotectors, the prognosis is favorable.
Inflammation in cardiovascular pathologies
The pathogenesis of inflammation in the liver is caused by heart failure and arrhythmia. These diseases provoke blood stagnation, gland hypoxia, and destructive processes in cells.
Against the background of an acute form of hepatitis in pathologies of the cardiovascular system, all the symptoms are revealed, and there are additional signs - jumps in blood pressure, pain in the sternum, dizziness, and a decrease in pulse rate.
Autoimmune form of hepatitis
The root causes of the disease have not yet been established. The disease develops like this - the immune system perceives liver cells as foreign objects and produces antibodies that attack hepatocytes. All this leads to a transformation of the structure of parenchymal tissues, and severe inflammation develops.
Drug treatment with immunosuppressive drugs gives only a temporary result and inhibits the process of destruction of hepatocytes. The therapy is long-term and requires the use of hormonal drugs, hepatoprotectors and other drugs.
Inflammation as a sign of cirrhosis
In the initial stages of the disease, there are no symptoms.
Inflammation is sluggish, leading to the death of hepatocytes and replacement with connective non-functional tissues. The patient exhibits hepatomegaly and the functionality of the organ decreases. Signs of cirrhosis are similar to the clinical picture of acute hepatitis. The enlarged organ is easily palpated, and patients exhibit yellowness of the skin. People complain of pain in the right side, increased gas formation, bloating, and digestive disorders.
Acute hepatitis
The clinic is bright and brings a lot of unpleasant sensations to the patient. Symptoms bother you for about a week, after which the condition returns to normal. And this means that the disease becomes chronic, which can worsen at any time. In case of acute inflammation of the liver in women, the symptoms are pronounced, treatment should be started immediately to prevent serious complications.
Choice of treatment
If you suspect liver disease, you should immediately seek medical help. Treatment of the inflammatory process cannot be delayed. Every minute, the liver passes and purifies up to 1.5 liters of blood, clearing it of toxins and breakdown products.
Important! The duration of the course of therapy depends on the cause and stage of the pathology. Medicines generally contain one or more active ingredients.
Glycyrrhizic acid
Active ingredient: licorice root. It has been used in medicine for a long time; according to scientific research, the acid protects the liver from external influences. The drug has an anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective effect. Medicine is prescribed for fatty degeneration to prevent cirrhosis of the liver.
Phospholipids
The active substance restores damaged cell membranes. Long-term use of phospholipids is recommended.
Milk thistle extract
A plant with a hepatoprotective effect accelerates the process of cell recovery.
Ornithine
The amino acid has been successfully used in the treatment of fatty degeneration and inflammation with toxic damage.
Thioctic acid
Widely used in the treatment of cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, and in the intoxication process.
Each drug must be prescribed by a specialist to avoid side effects.
Recommendations! Severe forms of the disease are treated in a hospital setting.
Anti-inflammatory drugs help restore necessary enzymes and successfully fight viruses.
Among them there is an antiviral group with a complex effect:
- destroys viruses;
- relieves inflammation;
- has an immunomodulatory effect.
Hepatoprotectors are effective in the fight against liver diseases.
Why does the liver hurt: the main factors
- alcohol abuse;
- exposure to aluminum (from food and packaging, polluted atmosphere, antiperspirants, fluoride from tap water);
- unhealthy foods (foods that have been heat-treated or contain a lot of sugar, artificial sweeteners, carbonated water, etc.);
- obesity;
- excess fat in the liver (fatty liver disease);
- excess iron and vitamin A in the body;
- use of medications (acetaminophen, antidepressants, statins, antibiotics, antacids);
- under the influence of chemicals (in agriculture, contained in household goods and hygiene products);
- smoking;
- liver diseases, such as hepatitis.
The liver is amazingly hardy and can withstand the roughest treatment. But she will tell you very subtly that you are overloading her.
Hormonal shifts
Changes in hormone synthesis are more noticeable in male patients (especially with alcoholism). Feminization is characteristic of patients with alcoholic (up to 80%) and viral (up to 15%) cirrhosis. It is believed that alcohol can cause testosterone and other androgens (male hormones) to transform into estrogens (female hormones), which explains the changes that occur:
- gynecomastia (breast enlargement);
- change in hair type;
- testicular atrophy;
- impotence;
- disappearance of libido.
Some liver diseases (primary biliary cirrhosis, etc.) lead to an increase in parathyroid hormone and its derivatives, which affect bone structures. These patients experience:
- bone pain;
- spontaneous fractures;
- bone deformities (usually flat bones).
In addition, chronic liver pathology (for example, hepatic steatosis) can cause diabetes.
Varieties
Inflammatory liver disease is caused by toxic damage, exposure to hepatitis viruses, as well as autoimmune pathologies.
All inflammatory processes in liver cells lead to the following consequences:
- Hepatitis. The main inflammatory process, which can be joined by other pathologies.
- Steatosis. Replacement of destroyed liver cells (hepatocytes) with adipose tissue. Alcohol damage most often leads to changes.
- Cirrhosis. In place of destroyed hepatocytes, connective tissue grows.
Viral provocateurs of inflammation
The causes of liver inflammation include primarily viruses.
There are 7 types of viral hepatitis. They all have a similar clinical picture, differing only in the modes of transmission, the risk of complications, and the likelihood of chronicity.
- Strains A and E are transmitted by the oral-fecal route. Virus A is more common and causes Botkin's disease. Its common name is jaundice. It is associated with a violation of the outflow of bile during illness, which causes yellowness of the skin. In A and E species there is no chronicity and complications in the form of fibrosis and steatosis.
- B, C, D, G species can be contracted through sexual contact with an infected person, as well as through the use of a non-sterile surgical instrument or transfusion of infected blood. The peculiarity of hepatitis B is that the liver destroys not the virus, but the cells of the immune system in an attempt to get to the causative agent of the disease. However, there is a vaccine for virus B that prevents infection. Strain D accompanies hepatitis B; if a person is not infected with this virus, then there is no risk of infection with delta hepatitis.
- Hepatitis C constantly mutates, most often is asymptomatic, and quickly becomes chronic. Different genotypes of this virus require different treatment regimens, and the invention of a vaccine is not possible.
- Hepatitis G is less common than C and has the same symptoms and clinical course. However, the G virus does not have such genetic diversity. The G virus is especially dangerous during pregnancy, as it leads to fetal death.
Additional factors
Other causes of inflammation of the liver tissue:
- Toxic lesions. Due to exposure to harmful substances and their accumulation in the liver, toxic hepatitis develops. It most often affects workers in hazardous industries. It can develop due to drug poisoning or alcohol abuse. In these cases, hepatitis is called alcoholic, drug-induced (drug-induced).
- Autoimmune reactions. Inflammation occurs due to a defect in the immune system, which mistakenly recognizes liver cells as hostile to the body. It occurs less frequently than other types of inflammation, but is also more difficult to treat. The problem of autoimmune hepatitis is the chronic course of the disease.
- Parasitic infestations. Sometimes inflammation develops due to the accumulation of lamblia and roundworms.
- Diseases of the digestive system. Inflammation in the liver tissue often occurs due to damage to the gallbladder, stomach or duodenum.
The cause of the disease is determined by the doctor based on medical history and laboratory diagnostics.
If the origin of the inflammation cannot be determined, hepatitis is called cryptogenic.
Diet
Diet during illness plays an important role, because it is necessary to reduce the load on the diseased organ.
A balanced menu, as an important addition to the main course of therapy, includes the following products:
- dairy products, especially cottage cheese;
- chicken fillet;
- turkey;
- rabbit meat;
- sea fish;
- porridge;
- low-fat vegetable soups;
- flour products dried for at least 1 day;
- fresh vegetables and herbs.
It is recommended to cook food only by steaming, in the oven, or boiling.
Important! For people with the chronic stage of hepatitis, the diet is prescribed for life.
Prohibited products include the following:
- alcohol;
- fried, salty, spicy foods;
- mushrooms;
- fresh baked goods;
- canned food;
- strong coffee and tea, cocoa.
The main principle of dietary nutrition remains unloading the liver, as well as the exclusion of foods that negatively affect its functioning.
Main functions of the organ
A healthy liver is able to cleanse the blood of harmful substances and is one of the important components of metabolism. Among the most common inflammatory processes are hepatitis, cirrhosis, fibrosis, liver failure, malignant processes, hepatosis or fatty degeneration, pathological changes in blood vessels, and vein thrombosis.
- The main purpose of the liver is to detoxify harmful substances. Special enzymes break down toxins and poisons in the blood.
- In addition to cleansing, metabolic processes occur, bile is produced, without which the digestive tract does not function. Bile consists of acids, cholesterol, which are necessary for digestion.
- The next function is the conversion of excess glucose into glycogen, an important compound; proteins are also broken down into essential amino acids for the body.