Ovarian apoplexy is a hemorrhage of its cavity or rupture of an organ, which is accompanied by internal bleeding into the retroperitoneal space. This pathology occurs relatively rarely, accounting for about 15% of the total number of gynecological diseases. All women from 18 to 43 years of age are at risk of ovarian apoplexy.
Ovarian apoplexy
This pathology develops in the middle of the cycle during ovulation or after it, a few days before the onset of menstruation. According to the generally accepted classification of ovarian apoplexy, a code according to ICD 10 No. 83 “Non-inflammatory lesions of the ovary, oviduct and broad ligament of the uterus” is assigned. Due to a certain difference in the intensity of blood supply, apoplexy of the left ovary is observed less frequently than apoplexy of the right ovary.
Why can ovarian apoplexy occur?
Etiological factors of apoplexy can be divided into two groups:
- background conditions, or otherwise predisposing;
- and productive, that is, those that directly provoke a break.
Background states
Ovarian apoplexy can occur on any day of the menstrual cycle, but usually it coincides with the periovulatory period (ovulation and +/- 3 days), and also occurs during the stage of greatest activity of the corpus luteum. During a normal two-phase menstrual cycle, the follicle grows, matures and ruptures, followed by the release of the egg.
Ovulation provokes damage to the vessels of the parenchyma - ovarian tissue, and is accompanied by slight hemorrhage. Normally, the vessels spasm and the hemorrhage stops on its own without any significant clinical manifestations.
The likelihood of apoplexy increases if the ovarian tissue undergoes structural changes. This is predisposed to:
- frequent inflammation of the genitourinary organs;
- scleropolycystic ovarian disease;
- varicose veins of the small pelvis;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs (missing a pill, incorrect dosage regimen);
- spontaneous or artificial termination of pregnancy, including the use of emergency contraception.
The background is also the presence of ovarian cysts, stimulation of ovulation, and pathology of the blood hemostasis system.
Priority in the occurrence of the disease is given to dishormonal conditions. An imbalance of sex steroids and pituitary hormones predisposes to congestion of the pelvic vessels and congestion that impairs vascular permeability.
Immediate causes of emergency
The producing (provoking) trigger for spontaneous ovarian rupture is a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure.
The development of an emergency condition is caused by:
- physical effort (lifting weights, playing sports);
- abdominal injuries;
- sexual intercourse;
- bumpy ride;
- constipation
Against the background of increased intra-abdominal pressure, the walls of full-blooded vessels cannot withstand the tension and rupture, which entails bleeding.
According to statistics, apoplexy of the left ovary is recorded less frequently. This is due to the peculiarities of the anatomy, since the right ovary is supplied with blood by an artery originating directly from the abdominal aorta, and the left one receives nutrition from the ovarian branch of the left renal artery. Accordingly, the right ovary receives more intense blood supply and increased pressure in the vascular bed. This explains the fact that the right ovary ovulates more often, and functional cysts are more often right-sided.
Photo: https://pixabay.com/photos/sport-training-abdominals-sixpack-2250970/
Causes
One of the main causes of ovarian apoplexy is considered to be vascular pathology, which leads to disruption of the integrity of the blood vessels supplying the ovary and, as a consequence, to its rupture.
However, a number of other factors can cause this disease:
- changes in blood vessels in the pelvis: varicose veins, fibrosis, sclerosis, etc.;
- increased load on blood vessels during certain periods of the menstrual cycle;
- diseases that cause bleeding disorders (von Willebrand disease, thrombocytopenia, etc.);
- long-term use of anticoagulants - medications that thin the blood;
- hormonal disorders that cause excessive filling of the ovarian tissue with blood;
- the presence of an inflammatory process in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus or abdominal cavity;
- the presence of adhesions in the pelvic organs.
Risk factors contributing to the occurrence of apoplexy include:
- ovulation of the egg (mid-cycle) due to rupture of a mature follicle;
- the period of vascular growth in the corpus luteum is the 20-22nd day of the menstrual cycle;
- too violent sex;
- abdominal trauma;
- excessive physical activity or heavy lifting, etc.
However, medicine knows cases in which rupture of ovarian tissue occurred for no apparent reason in a state of absolute rest.
What forms of ovarian apoplexy exist?
Traditionally, it is customary to distinguish between the following forms of the disease.
- The painful form is clinically manifested by symptoms of an “acute abdomen”. Hemorrhage into the ovarian parenchyma is small, usually in the form of a hematoma or cystic cavity with hemorrhagic contents, but due to ischemia and stretching of the ovarian capsule, pain is pronounced.
- Hemorrhagic (anemic) form - characterized by severe intra-abdominal bleeding, up to hemorrhagic shock. The larger the caliber of the ruptured vessel, the greater the volume and time of blood loss. Due to the high pressure in the vascular bed, the vessel does not have time to thrombose and the bleeding does not stop.
- Mixed - combines the features of both variants of the course of apoplexy.
Symptoms
With apoplexy of the right ovary, symptoms are characterized by two main signs: pain and bleeding (both external and internal). The painful form can be moderate or intense, localized in the right lower abdomen.
Bleeding may resemble menstruation; with internal bleeding, the following symptoms are observed:
- pale skin;
- chills, tremors of extremities;
- increased body temperature;
- drop in blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- dizziness;
- cold sweat;
- general weakness.
With right-sided apoplexy, pain appears suddenly, usually in the second half of the cycle during or after ovulation. Often pain is felt not only in the ovary area, but also in the iliac region (right under the diaphragm), and can radiate to the buttocks, lower back, and sometimes to the leg. If the pain is intense, nausea or vomiting may be present.
If there is severe internal bleeding, there is a high risk of hemorrhagic shock.
Symptoms indicating ovarian rupture
The severity of symptoms depends on the prevalence of one or another form of the disease.
The symptom complex develops suddenly, usually after physical effort or sexual intercourse, and also has a connection with the day of the menstrual cycle. Two thirds of episodes of apoplexy occur on the 13-14th day from the onset of menstruation.
Local symptoms
Pain in the suprapubic and iliac region occurs suddenly , against the background of complete health, is localized on the affected side, and can spread to the lower back, leg, anus and tailbone. Changing position does not bring relief.
Vaginal examination during apoplexy is sharply painful. During the examination, it is possible to detect painful, pulsating appendages on one side. A typical symptom of free fluid or blood in the pelvis will be an overhang of the posterior vaginal vault and increased pain when palpating the cervix. Menstrually-like bleeding may occur.
Photo: https://www.pexels.com/
General symptoms of apoplexy
Common manifestations include symptoms of an “acute abdomen” and signs of intra-abdominal bleeding.
The pain begins acutely, concentrated in the right or left iliac region. Over time, painful sensations can spread to the entire abdomen, and peritoneal signs appear. Often, nausea, vomiting, and loose stools occur, but the temperature usually remains normal or increases slightly.
With continued bleeding, dizziness appears, weakness increases, blood pressure decreases, the pulse becomes weak and frequent, and loss of consciousness is possible. Clinical symptoms of bleeding become pronounced when blood loss exceeds 150 ml.
It is important to know that taking anticoagulant drugs (medicines that prevent blood clots) increases the rate and volume of blood lost, so you should seek help as soon as possible.
How to understand that an ovarian cyst has burst
Symptoms that an ovarian cyst has burst appear instantly. The intensity of the sensation depends on the type of rupture, the amount of hemorrhage and related factors. In some cases, there is no bleeding, but the contents of the burst sac, entering the abdominal area, can provoke many complications.
Painful sensations
The pain manifests itself acutely, on the left or right side of the lower abdomen, in the first seconds after apoplexy of the cyst. This often forces a woman to take a bent position, instinctively trying to reduce discomfort. Acute pain is short-lived - after a few minutes it becomes less intense, but loses its clear localization.
The rupture of the formation provokes the penetration of its contents into the abdominal cavity, which subsequently leads to pain throughout the abdomen. The patient is not able to clearly indicate the source of pain. Subsequently, it can spread to the buttocks, lower abdomen, and sides of the torso.
Sometimes pain appears a day or several hours before the onset of pathology. In this case, they are aching, pulling in nature, their intensity can increase over time. This is explained by the progressive thinning of the walls of the formation.
If you detect aching pain on the right or left side of the lower abdomen, you should immediately consult a doctor - if you follow his recommendations and timely medical intervention, cyst rupture can be avoided.
Changing the nature of discharge
With apoplexy, the amount of vaginal discharge increases.
However, they do not cause any discomfort; normally there should be no odor. They often contain streaks of blood, and the discharge itself can turn brownish or reddish. This indicates a violation of the integrity of the cyst tissue or possible bleeding.
The discharge contains the contents of the burst formation, so its consistency may be heterogeneous and contain foreign impurities. When a corpus luteum cyst or follicular ovarian cyst ruptures, there are no symptoms of this kind.
Intoxication of the body
This condition is caused by the contents of the formation and blood entering the peritoneum. In severe cases of intoxication, body temperature rises to 40 degrees, fever and chills are present. Most often, the signs of a ruptured ovarian cyst are less obvious - the patient feels weakness, general unsatisfactory condition, nausea, and vomiting. The mucous membranes of the mouth dry out, which causes constant thirst. The body temperature reaches 37-38 degrees.
Change in blood pressure
With apoplexy of a cyst of the right or left ovary with hemorrhage, blood pressure decreases and the pulse quickens. The skin becomes pale, rarely bluish. This is caused by a sharp drop in hemoglobin and severe pain in the affected area. With a significant drop in pressure, there is a risk of the woman losing consciousness and hallucinations.
What is needed to confirm ovarian apoplexy?
Diagnostics
An emergency condition can be suspected based on the patient’s examination and complaints. However, additional research is necessary to confirm the diagnosis. The first step is a gynecological examination. The classic symptom of this pathology is painful traction on the cervix (pulling and shifting from side to side) and a painful, overhanging posterior vaginal fornix.
Between the posterior wall of the uterus and the rectum there is an anatomical depression - the pouch of Douglas. When free fluid, including blood, forms in the abdominal cavity, it fills this pocket, causing a painful bulge through the posterior fornix. This symptom is known in the medical literature as the “Douglas cry.”
To confirm the presence of blood in the rectal uterine cavity, culdocentesis is performed - a puncture of the posterior vaginal vault. A hollow needle intended for this purpose is used to puncture the vagina behind the cervix. If there is blood or inflammatory fluid in the abdominal cavity, it will flow out of the needle.
All patients must undergo a general blood test. The level of red blood cells and hemoglobin can be used to judge the severity of blood loss, and the level of leukocytes makes it possible to distinguish apoplexy from inflammatory diseases that have a similar clinical picture.
Photo: https://pixabay.com/photos/laboratory-medical-lab-diagnostics-313864/
Differential diagnosis with conditions simulating acute abdomen
Difficulties often arise when verifying a diagnosis due to the fact that certain manifestations are typical for many emergency conditions. A similar clinical picture is given by acute appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, torsion of the cyst or appendages.
- Unlike apoplexy, acute appendicitis is accompanied by a rise in temperature and has markers of inflammation in the blood (an increase in leukocytes, mainly young forms of cells).
- An ectopic pregnancy has a mask of apoplexy. If a tubal rupture occurs, it is quite difficult to differentiate a tubal pregnancy from an ovarian rupture. In order to exclude pregnancy, a study of the level of hCG in the blood serum or urine is carried out using a pregnancy test.
- Torsion of the cyst or appendages occurs with similar symptoms. Ultrasound is of great importance in differential diagnosis. In a difficult situation, they resort to diagnostic laparoscopy. Thanks to this, it is possible not only to recognize surgical pathology, but also to take appropriate measures (to detect the source and stop the bleeding, remove a cyst, ectopic pregnancy, inflamed appendix, perform detorsion - unwinding of the appendages).
The fact of apoplexy does not exclude the possibility of another surgical pathology. Ovarian rupture can occur against the background of acute appendicitis, and pregnancy in the uterus is sometimes combined with tubal pregnancy.
Diagnosis of the disease
If characteristic pain in the ovarian area or other similar symptoms appears in the middle or second half of the cycle, you should immediately seek medical help to clarify the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of ovarian apoplexy includes:
1) Gynecological examination, during which pain is noted on the side of one of the affected ovaries, tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, displacement of the cervix, and the uterus itself, as a rule, is not enlarged, but it is dense, and its arches on the side of the rupture are painful. Sometimes there may be vaginal discharge mixed with blood (thus the uterine mucosa reacts to hormonal changes occurring in the woman’s body);
2) General blood test, the results of which indicate a reduced level of hemoglobin (usually with anemic or mixed form of ovarian apoplexy);
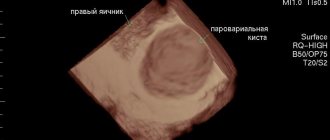
3) Ultrasound of the pelvic organs, showing signs of hemorrhage in the large yellow body of the affected ovary and/or in the peritoneum;
However, even with positive test results indicating a high probability of apoplexy, the final diagnosis can be made by a doctor only during surgery.
Treatment of ovarian rupture
Photo: https://www.pexels.com/photo/drink-girl-glass-hands-576831/
Ovarian rupture is an emergency condition, so treatment of the disease should be carried out only in a hospital. Tactics will be determined by the form of apoplexy and the degree of blood loss.
When the first symptoms of apoplexy appear, you should not resort to self-medication. Taking any medications before being examined by specialists makes it difficult to diagnose the disease and prevents timely action.
Conservative approach. Indications, contraindications, treatment methods
In the painful form of apoplexy, when there are no signs of ongoing bleeding and the amount of blood loss is small, a conservative approach to treatment is possible. Patients are prescribed rest, bed rest, a heating pad with ice on the lower abdomen, as well as antispasmodic and hemostatic drugs.
For hemostatic purposes, Tranexam and Etamzilat (Dicinone) are used. To relieve pain, Drotaverine, No-shpa, Papaverine are indicated.
Indications for surgical treatment of ovarian apoplexy and methods of surgical treatment
If clinical symptoms increase, it will not be possible to limit yourself to conservative therapy. If intra-abdominal bleeding is not stopped in time, the likelihood of hemorrhagic shock is high. Surgery will also be required in unclear cases, when it is not possible to fully determine the diagnosis.
As a rule, laparoscopic access is used for ovarian apoplexy. Through small punctures of the anterior abdominal wall, special video equipment and instruments are inserted into the cavity. This technique allows you to assess the condition of internal organs, detect pathology and take action. Bleeding vessels are cauterized, the abdominal cavity is cleared of blood and clots.
Laparoscopy has an undoubted advantage over open surgery: it reduces the time of rehabilitation and hospital stay, reduces the number of postoperative complications, and, last but not least, a better cosmetic effect.
To perform laparoscopy, air is pumped into the abdominal cavity. In some somatic diseases this is contraindicated, so surgeons have to use laparotomic access - that is, through an incision. Adhesive disease of the peritoneum significantly limits the possibilities for manipulating endoscopic instruments, so the only option is open access surgery.
Regardless of the surgical approach, the surgeon always tries to preserve the organ as much as possible. It is preferable to leave even a small amount of viable ovarian tissue than to resort to adnexectomy - complete removal of the ovary.
Photo: https://pixabay.com/photos/surgery-surgeons-operation-medical-688378/
Recovery in the postoperative period. Sex life and physical activity
For speedy rehabilitation in the postoperative period, physiotherapeutic procedures (magnet, electrophoresis with drugs that prevent the formation of adhesions, microwave) are useful.
Significant blood loss leads to the development of anemia, so in the postoperative period it is necessary to take iron supplements and vitamin complexes.
To avoid relapse of the disease, it is necessary to temporarily exclude ovulation through hormonal contraception. Combined oral contraceptives are prescribed for 3-6 months.
For 4 weeks from the date of surgery, you must refrain from sexual activity, sports, and heavy lifting. During the rehabilitation period, it is necessary to avoid hot baths, baths and saunas. If these recommendations are followed, the postoperative period usually proceeds without serious complications.
Treatment
Emergency care for right-sided ovarian apoplexy can be provided by an ambulance paramedic before arriving at a medical facility. Self-administration of any medications is strictly prohibited, as this is fraught with false improvement and erroneous diagnosis.
In the case of ordinary apoplexy or if an ovarian rupture occurs, hospitalization is mandatory.
Depending on the severity of the pathological process, treatment can be conservative, surgical, or a combination of both methods.
Conservative treatment includes bed rest, antispasmodics and muscle relaxants, as well as hemostatic drugs and anti-anemia drugs (high iron). Sometimes a cold heating pad is used on the right side of the abdomen.
Drug treatment is used in cases of mild forms of the disease, but is quite risky. Without surgical intervention, there is a high risk of relapse of the disease, the development of extensive adhesions (adhesions are formed from blood clots that have not been removed) and, as a result, infertility.
Therefore, in order to avoid these complications, it is recommended to restore the outer membranes of the damaged ovary and remove blood from the abdominal cavity. The tissue where the ovary ruptured is sutured (in the case of a cyst, its contents are removed) and then cauterized (coagulation method).
Usually, after the operation, the patient is in the hospital under the supervision of doctors for 5-7 days, then she is sent home. Further recovery at home includes physical rest, taking painkillers and other medications prescribed by the attending physician.
Possible complications of ovarian apoplexy
The expected complications of the disease can be roughly classified as early and late. As noted above, the most dangerous early complication is shock from sudden blood loss. If treatment measures are not started in time, massive blood loss can lead to tragic consequences.
The most common long-term complications of apoplexy are adhesive tubal obstruction and infertility . This usually happens as a result of conservative therapy, when blood clots remain in the abdominal cavity. Subsequently, they serve as a substrate for the formation of adhesions. Therefore, to preserve reproductive function, it is important to follow your doctor’s advice and not neglect visits to the gynecologist.
Symptoms
The signs of a burst ovarian cyst are not specific and resemble the symptoms of any acute processes in the pelvic area (“acute abdomen”). How can one understand that it is an ovarian tumor that has ruptured, when even experienced doctors are not immediately able to make an accurate diagnosis?
Do you use folk remedies?
Not really
Basic symptoms of ovarian cyst rupture in women:
- Before the development of the acute phase, nagging pain appears in the groin, lumbosacral area, and a feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen.
- Increasing acute pain, concentrated below - on the right or left, or involving the entire lower part of the peritoneum, radiating to the groin, thigh.
- Slow or rapid increase in temperature, which cannot be lowered with antipyretic drugs (an inflammatory process develops).
- Severe weakness, nausea, vomiting (signs of poisoning by decay products and bacterial poisons during suppuration), sometimes loose stools.
- Bleeding or bloody mucous discharge from the vaginal canal. If the membrane of a functional tumor is ruptured, blood loss usually does not exceed 100 ml. When an organic cyst ruptures, intra-abdominal bleeding can be significant, but this phenomenon is not always expressed in copious discharge of blood from the uterus.
- Pallor, dizziness due to acute blood loss.
- Flatulence, bloating, difficulty defecating - occur with extensive internal bleeding, which leads to increased pressure on the intestinal loops.
- A marked decrease in blood pressure, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, loss of consciousness are signs indicating life-threatening bleeding.
When can you plan a pregnancy after ovarian apoplexy?
Despite the overall good health at the end of treatment, pregnancy should be postponed. Trying to get pregnant is best delayed for 4-6 months. This time will be enough to correct disrupted hormonal levels and adapt the woman’s body.
After suffering apoplexy and surgery, the chances of ectopic pregnancy increase, so it is better to plan a future pregnancy with a gynecologist. During the rehabilitation period, the doctor will select hormonal contraception. Contrary to the fears of many patients, taking contraceptives does not reduce the chances of getting pregnant, but it allows the female body to cope with the stress it has suffered.
Photo: https://www.pexels.com/
Impact on current and future pregnancies
An ovarian rupture in itself does not deprive you of the opportunity to become pregnant, since during surgery, as a rule, only partial removal is performed. However, even with complete removal of the tissue of one of the ovaries, the egg is able to fully mature in the remaining healthy one.
Problems with conception may occur when adhesions form in the abdominal cavity.
To avoid this, you should:
- undergo a course of anti-inflammatory treatment (using antibiotics) and physiotherapy (laser therapy, electrophoresis, low-frequency ultrasound, etc.);
- protect against pregnancy during the first 4-6 months after surgery;
- use hormonal drugs (Yarina, Novinet, Logest, Regulon, etc.), which not only act as a prophylactic against the formation of adhesions, but also help restore hormonal levels.
In rare cases, apoplexy can also occur during an existing pregnancy. If this happens, for medical reasons, surgery is performed using laparotomy (incision). In this case, the pregnancy is maintained if possible, but it is worth noting that the risk of miscarriage still increases.
Is it true that coughing can cause vaginal prolapse? Find out what can cause this disease and be careful.
Read about the pathogenesis of the anovulatory cycle in the article dedicated to this problem.
The leakage of milk from the breast is a sign of galactorrhea, which signals serious disorders in the body, find out more
Recommendations for the prevention of ovarian apoplexy
There is currently no specific prevention of ovarian apoplexy. The most important thing to remember is that you should not neglect preventive examinations by a gynecologist, even if nothing bothers you. At a routine examination, the doctor will be able to recognize conditions that serve as a background to apoplexy and prescribe therapy. Timely and complete treatment of hormonal disorders and inflammatory diseases reduces the risk of developing apoplexy and unpleasant consequences.
You should not give up playing sports, the main thing is that the exercises are dosed within reasonable limits.
Methods of treating the disease
Previously, two methods were used to treat ovarian apoplexy: conservative and surgical. The use of the conservative method was possible in case of loss of a small volume of blood.
It includes antispasmodic and vascular strengthening therapy, as well as physiotherapy.
However, medical practice has shown that the lack of surgical intervention to cleanse the abdominal cavity of blood often becomes the cause of the development of the inflammatory process and its consequence – peritonitis.
In addition, the risk of complications is very high: in more than 80% of cases, the woman subsequently develops adhesive disease in the pelvis, and in 45% - infertility.
Therefore, today the priority method of treatment is surgical intervention, during which the damaged ovary is sutured, as well as cleansing of blood clots and treating the abdominal cavity with an antiseptic solution. Doctors always try to perform the operation in the most gentle way possible, however, if there is significant damage to the ovary, it still has to be removed.
Definition of pathology
With apoplexy, there is a sudden destruction of the integrity of the tissue of the ovaries, which implies internal hemorrhage. In addition to internal hemorrhage, rupture of an internal organ also has other symptoms - for example, severe pain.
Pathology is classified as follows:
By form:
- Painful - accompanied by a brightly intense pain syndrome, as well as a sharp and significant increase in temperature and nausea. Often the pain becomes so intense and acute that the woman easily loses consciousness. The pain syndrome is not accompanied by internal bleeding, therefore, when making a diagnosis, mistakes often occur - instead of apoplexy, a diagnosis of acute appendicitis is made at stages.
- Anemic - the main symptom is internal hemorrhage. Accompanying signs are pale skin, general weakness of the body, fainting, dizziness.
- mixed - the symptoms of the above forms are combined with each other.
By volume of blood lost:
- mild - the total volume of bleeding is 0.1 - 0.15 liters;
- average - the volume of leaked blood is 0.15 - 0.5 liters;
- severe - the total volume of hemorrhage exceeds 0.5 liters.
We also recommend viewing: Why do diffuse changes in the prostate gland occur?
At the location of the rupture:
- left-sided - in medical practice it is less common, since the blood artery of the left ovary does not connect to the aorta, but to the kidney artery, so it is less filled with blood;
- right-sided is the most common type of pathology, this is due to the fact that a significantly larger volume of circulating blood is observed in the right genital organ.
Therapy methods
Depending on the shape and severity of the ovarian cyst rupture, treatment can be conservative or surgical.
Conservative treatment is recommended only for mild disease severity. In such cases, the cyst is slightly damaged, and intense bleeding is prevented by a quickly formed blood clot. Therapy consists of taking antispasmodics, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and hemostatic agents. During the treatment period, the woman is recommended to undergo strict bed rest. The duration of the course is until the complaints disappear. To prevent the negative consequences that pathology may entail, the course is supplemented with physiotherapeutic treatment.
Surgical treatment is the main method of treatment for ruptured ovarian cysts.
Currently, gynecologists perform the following types of surgical interventions when a cyst ruptures:
- unilateral oophorectomy - removal of the affected ovary;
- ovarian resection - excision of a section of a damaged organ while preserving its function;
- tubovariectomy - removal of the uterine appendage.
Operations are performed laparoscopically or laparotomically. In the first case, all manipulations are performed through small punctures in the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall, using special instruments. The laparotomy method involves making a large incision in the lower abdomen, along the midline.
The main advantages of minimally invasive surgery include:
- minor injuries;
- less medication load;
- fast recovery.
Despite this, the final decision regarding the method of surgical treatment is made by the attending physician, taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient.
Initial consultation with a gynecologist
2,300 rub.
Hysteroscopy
RUB 22,550
Videocolposcopy
2,400 rub.
Classification
Taking into account the prevailing symptoms, the following forms of ovarian apoplexy are distinguished: anemic or hemorrhagic form with a predominance of symptoms of bleeding into the abdominal cavity; painful form, in which there is severe pain without signs of internal bleeding; mixed form, combining the symptoms of anemic and painful forms of ovarian apoplexy.
However, since in reality ovarian apoplexy is always accompanied by bleeding of varying severity, it is now customary to divide the pathology into degrees of severity. Taking into account the amount of bleeding, mild, moderate and severe degrees of ovarian apoplexy are distinguished.
Prognosis and possible complications
With significant blood loss accompanying ovarian apoplexy, hemorrhagic shock may develop, and if assistance is not provided in a timely manner, death.
Conservative management of ovarian apoplexy is fraught with the development of adhesions in the pelvis (85.7%), infertility (42.8%), and repeated ovarian rupture (about 50%). Timely recognition and active treatment of ovarian apoplexy is accompanied by a favorable prognosis in terms of preserving life and reproductive function.
Management of pregnancy in patients after ovarian apoplexy requires increased attention from an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Risk factors for apoplexy
In medical practice, there are a number of conditions under which the chance of apoplexy is higher:
- Inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs (uterus, fallopian tubes, bladder), which lead to hardening of ovarian tissue, fragility of blood vessels, increased blood circulation and varicose veins of the ovary.
- Pathological conditions that reduce the ability of blood to clot (thrombocytopenia, hemophilia).
- Long-term use of anticoagulants (drugs that reduce blood clotting) for thrombophlebitis and varicose veins of the lower extremities, atherosclerosis, hypercoagulation (increased coagulation), and so on.
Basic diagnostic methods
Ovarian apoplexy is an insidious disease that can masquerade as an ectopic pregnancy, which in many cases leads to misdiagnosis. Sometimes it happens that an accurate diagnosis of an illness occurs only on the operating table, during emergency care.
In order to differentiate ovarian apoplexy and ectopic pregnancy, the following differences must be taken into account:
| Ovarian apoplexy | Ectopic pregnancy |
| there is no delay in monthly discharge | delayed menstruation |
| normal or pale color of the vaginal and cervical mucosa | cyanosis of the vaginal and cervical mucosa |
| enlarged ovary with normal uterine size Recent Entries Is it possible to give a mirror: how to protect yourself from bad omens It became known about the influence of cell phone towers on human health Is it possible to eat bananas bought in Russia? | softening of the uterus and its increase in size |
| negative pregnancy test | positive pregnancy test |
In addition, with ovarian apoplexy, extreme pain is noted during vaginal two-handed examination.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following are usually used:
- a blood test showing a decrease in hemoglobin levels;
- an ultrasound examination to detect fluid accumulation;
- abdominal puncture, which is performed through the vagina.
It should be noted that if the patient has signs of abdominal bleeding, she will in any case need emergency surgery, regardless of what caused the bleeding. Here differential diagnosis is not of great importance.
Apoplexy of the right ovary can simulate an attack of appendicitis, however, with apoplexy, pain irradiates to the anus and right leg, while with appendicitis, pain is concentrated in the midline of the abdomen above the navel. For differential diagnosis, it is important to take into account the fact that with appendicitis, examinations through the rectum are especially painful for the patient, and with apoplexy, severe pain is caused by the impact on the uterus.
Ovarian apoplexy should also be differentiated from the following diseases:
- adnexitis (inflammation of the uterine appendage);
- torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst;
- intestinal obstruction;
- perforated stomach ulcer;
- an attack of pancreatitis and colic - hepatic and renal.
Etiology of the disease
The causes of ovarian rupture are quite varied, but most of them are associated with pathologies that arise in the structure of the organ. Among the most common reasons are:
- the presence of inflammation of the ovarian tissues, which may be caused by sexually transmitted infections, microflora disorders, severe hypothermia;
- varicose veins of the ovary - occurs as a result of heavy physical work, repeated pregnancy, endometriosis, increased estrogen levels, long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
- polycystic ovary syndrome - a pathology that disrupts the menstrual cycle and causes infertility;
- stimulation of egg maturation by medication - organ rupture occurs as a side effect of this procedure;
- abnormalities in the structure of neighboring organs, the presence of tumors that put pressure on the ovary;
- the presence of adhesions;
- disorders in the blood clotting system.
The disease is caused by a strong blood flow to the gonads, which provokes a rupture. More intensive blood supply to the right ovary leads to the fact that it ruptures more often than the left. The disease is usually acute and can be triggered by various external factors, such as:
- intense sexual intercourse;
- unreasonably heavy physical activity associated with lifting weights;
- horseback riding;
- bruises and abdominal injuries;
- long stay in a sauna or bath;
- rough gynecological examination.
In some cases, ovarian apoplexy can occur without the participation of provoking factors, when a woman is in a state of physical inactivity.
Why does apoplexy occur?
The above conditions create a background for external and internal factors, which leads to the development of apoplexy.
External factors include:
- Abdominal injury (impact, fall).
- Excessive physical stress.
- Violent or interrupted sexual intercourse.
- Horseback riding.
- Intensive rinsing of the vagina with solutions.
- Inaccurate gynecological examination.
Internal reasons may be:
- Incorrect position of the uterus due to congenital anomalies.
- Mechanical compression of the ovarian vessels by a tumor or cyst, which impairs blood circulation.
- Adhesions (fusion between tissues) in the pelvic area.
The decisive role in the occurrence of hemorrhage in the ovary is played by hormonal imbalance. The main cause of ovarian rupture is an excessive increase in the concentration and ratio of sex hormones of the pituitary gland, which leads to intense blood supply to the ovaries. Under stress, unfavorable living conditions and ecology, the nervous regulation of the release of these hormones is disrupted.
Ovarian apoplexy should be regarded as a complex of serious disorders not only in the reproductive system, which is limited to damage to the ovary. This is a disease of the whole organism with a disorder of nervous regulation against the background of chronic stress and a genetic predisposition to disorders of the body’s regulatory system.
What it is?
Ovarian apoplexy, or ovarian rupture, is an acute condition that occurs as a result of a sudden disruption of the integrity of ovarian tissue, accompanied by intra-abdominal bleeding and pain. It occurs in women of reproductive age, most often in the age group from 25 to 40 years.
Ovarian apoplexy on the right side occurs several times more often than on the left, which is associated with a stronger blood supply to the right ovarian artery due to anatomical features.
Statistics
At the age of 18-45, women's bodies and ovaries work in a very active way. Therefore, the incidence of ovarian apoplexy occurs precisely during the childbearing period. But women of other ages are included in the statistics of this diagnosis. In terms of numbers, among other common gynecological diseases, ovarian apoplexy occupies 2% of the total.
It is worth noting that if a woman has suffered such a disease once, the risk of recurrence increases to 70%. Apoplexy of the right ovary occurs 3 times more often than the left. This is a consequence of the fact that the largest number of blood vessels are located in the right ovary. In addition, the artery of the left ovary comes from the renal artery, and the right one comes directly from the aorta.
Prevention
In order to prevent the pathology of ovarian apoplexy, it is necessary to cure all existing gynecological diseases, such as adnexitis, PCOS, STDs, oophoritis, etc. It is also necessary to be observed by a gynecologist and exclude provocative factors.
All patients who have had ovarian apoplexy disease must take preventive measures to prevent recurrent hemorrhages, because the relapse rate for ovarian apoplexy is quite high. For prevention, complex treatment is carried out, which improves blood circulation and normalizes the menstrual cycle.
After surgery for ovarian apoplexy, the most important thing is to restore normal blood circulation and normalize hormonal levels. This is most important for the pelvis, where the disease manifests itself most. In the postoperative period, patients are recommended to take tranquilizers and nootropic drugs. To normalize hormonal levels and prevent ovulation, doctors prescribe multiphase oral contraceptives, which prevent the subsequent progression of the disease of ovarian apoplexy.
Throughout the recovery period, the patient must be registered with a doctor. Many women successfully carried a child after suffering from ovarian apoplexy. But it is better to wait until pregnancy - it is necessary for the female body to fully strengthen after surgery.
Diagnostics
Rupture of an ovarian cyst requires in-depth differential diagnosis to distinguish the pathology from other acute conditions and diseases. The task of the diagnostician is to exclude such abnormal conditions as suppuration of the appendix, ectopic pregnancy, perforation of purulent formations of the appendages, renal colic, torsion of the cystic pedicle, gastrointestinal bleeding during perforation of the ulcer, rupture of the fallopian tube, pelvioperitonitis.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will analyze the pathological sensations that the woman complains about. To clarify the characteristics of the pathological process, use:
- Gynecological examination, which reveals a focus of pain and enlarged gonads.
- Ultrasound is considered as the most reliable way to immediately determine that an ovarian cyst has burst, fix the location and assess the size of the abnormal lesion. Ultrasound also allows you to immediately find out about a possible early pregnancy and exclude ectopic pregnancy and other abnormal processes.
- Puncture (puncture) of the posterior wall of the vagina (necessary to ensure the accumulation of blood in the pelvic cavity).
- Blood and urine tests (protein indicates kidney damage, a decrease in hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells indicates increasing anemia due to bleeding, an increase in ESR and the number of leukocytes indicates inflammation).
Apoplexy and pregnancy
Ovarian rupture during pregnancy is quite rare.
If pathology occurs, gentle drug therapy is prescribed, but sometimes surgical intervention is necessary. In the latter case, all manipulations are carried out very carefully to prevent the development of possible complications in the fetus. Treatment is especially dangerous in the early stages of pregnancy - during this period there is a high probability of spontaneous abortion, which increases when taking medications or after surgery.
Planning pregnancy is possible after ovarian apoplexy with preservation of the organ or its subsequent removal.
In the latter case, the probability of conception is reduced, but fertilization is possible with normal functioning of the surviving appendage. Hormone therapy may be prescribed to increase the chance of pregnancy. In case of prolonged absence of conception, a fertilized egg is artificially implanted into the uterine cavity - this method in most cases gives a positive result. In the future, the absence or damage of the ovary will not affect the course of pregnancy.
How to behave after treatment
The main thing a woman needs to achieve is the restoration of reproductive function, and this requires measures to prevent the formation of adhesions and establish hormonal metabolism . Most likely, the patient will be offered a course of anti-inflammatory therapy, and to optimize hormonal balance and suppress the ovulation process, combined low-dose (Regulon, Femoden) or microdose contraceptives (Mersilon, Novinet) are usually prescribed, which must be taken for at least six months. The decision on the duration of their use is made by the attending physician on an individual basis.
For the most effective rehabilitation of the patient, physiotherapeutic methods can also be used - ultrasound, laser therapy, ultratonotherapy, electrophoresis.
Menstruation can be restored within a month or a month and a half after the operation, but pregnancy can be planned only after completion of rehabilitation measures, completion of hormonal medications, a detailed examination and consultation with a gynecologist. As for the resumption of sexual activity, a doctor’s consultation is also necessary here, since this depends on the severity of the cured illness, the form of treatment and the objective condition of the woman.